Calculation of the return period for shallow landslides triggered by extreme rainfall
-
摘要:
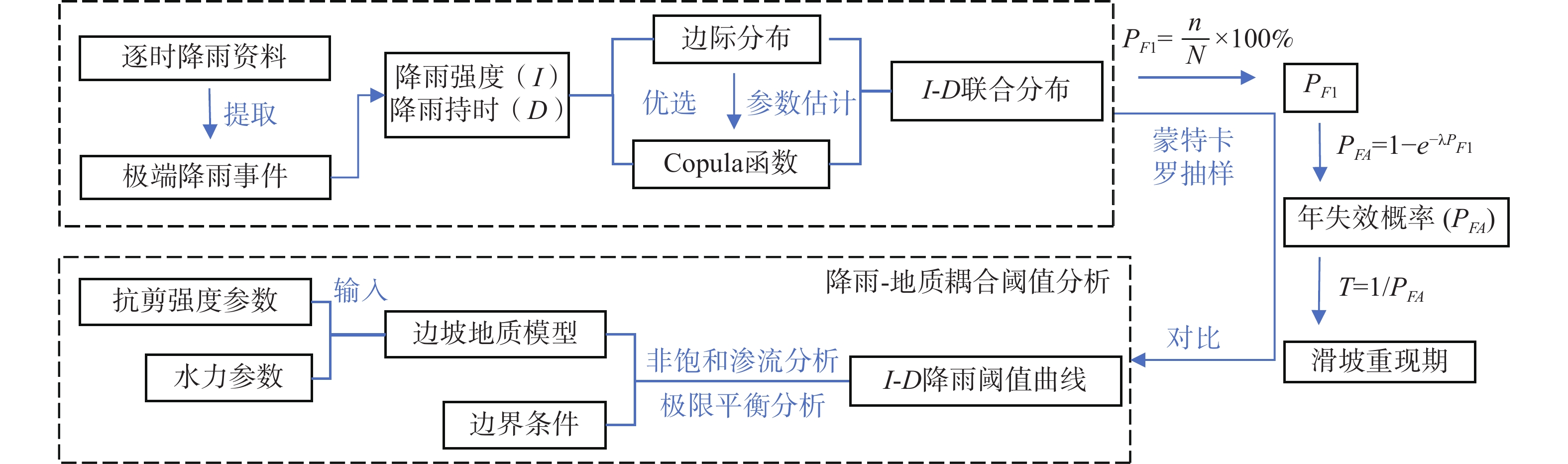
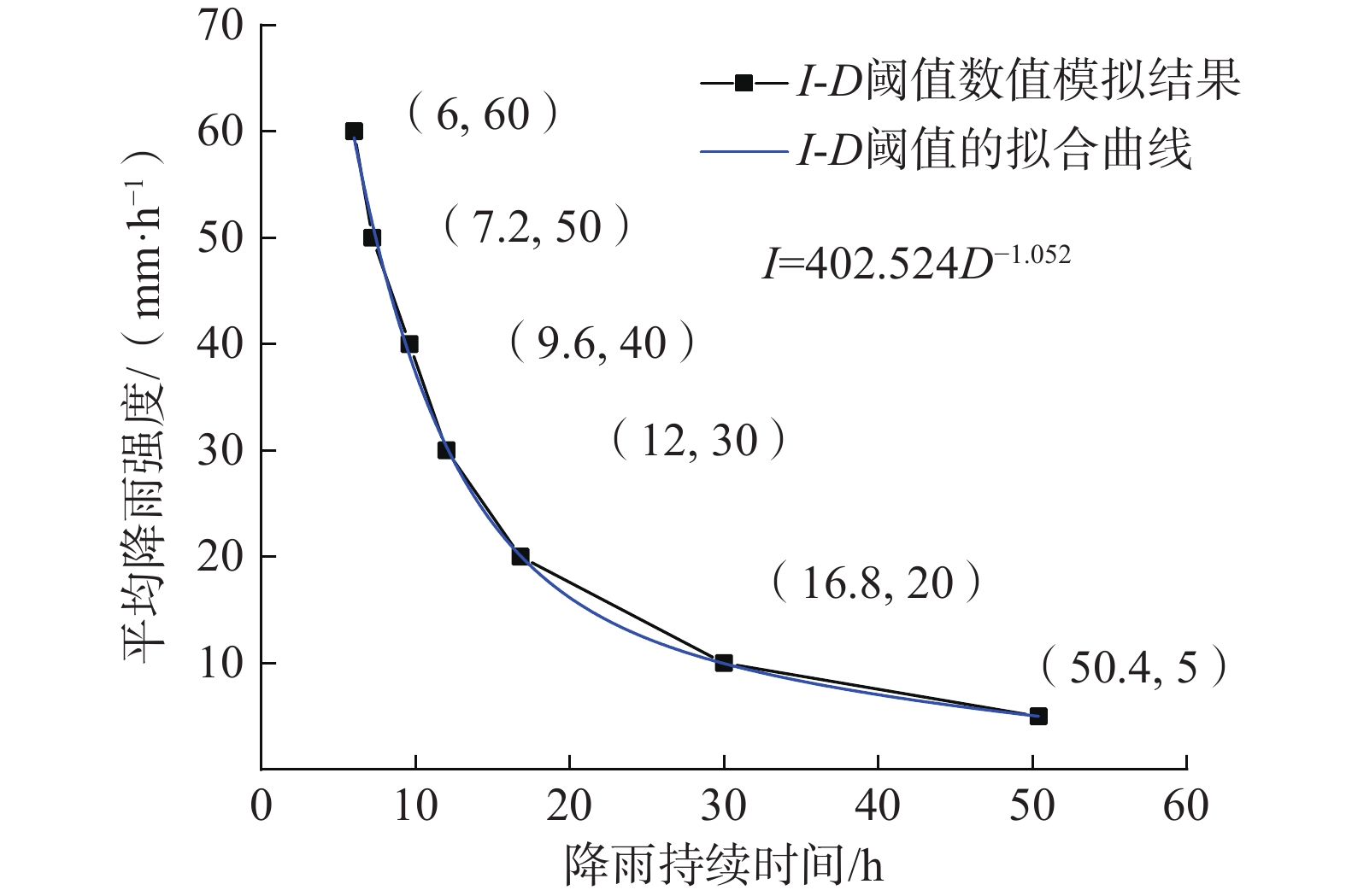
为了在长时间尺度下定量评估极端降雨诱发浅层滑坡灾害的动态危险性,为东南地区地质灾害风险防治工作提供参考,文章提出了一种考虑降雨不确定性的浅层滑坡重现期计算方法。具体计算框架为:(1)基于Copula函数构建极端降雨平均强度-持续时间(I-D)联合分布;(2)基于地质条件与水文要素计算滑坡I-D阈值;(3)采用蒙特卡罗法模拟极端降雨事件I-D联合分布超过I-D阈值的概率,作为单次降雨条件下的边坡失效概率$ P_{F 1} $,进一步计算滑坡重现期。以浙江省马剑镇某滑坡隐患点为例验证该方法的可行性,得到其滑坡重现期的预测值为17 a。建议采取相关防治措施以降低灾害可能造成的损失。
Abstract:To quantitatively assess the dynamic risk of rainfall-induced shallow landslides over extended periods and provide references for geological disaster risk prevention and mitigation in southeast China , this study proposes a method for calculating the return period of shallow landslides considering rainfall uncertainty. The specific calculation framework includes: (1) Constructing the joint distribution of extreme rainfall intensity-duration (I-D) based on the Copula function; (2) Determining the I-D threshold for landslides based on geological conditions and hydrological factors; (3) Using the Monte Carlo method to simulate the probability that the joint I-D distribution of extreme rainfall events exceeds the I-D threshold, representing the probability of slope failure, and further calculating the landslide return period. The feasibility of this method was validated at a potential landslide site in Majian Town, Zhejiang Province. The predicted return period for the landslide is 17 years. It is recommended that relevant preventive and mitigation measures be implemented to reduce potential disaster losses.
-
Key words:
- return period of landslide /
- extreme rainfall /
- Copula function /
- I-D threshold /
- Monte Carlo Method
-

-
表 1 马剑站边际分布拟合优度检验结果
Table 1. Results of the goodness-of-fit test for the marginal distribution of the Majian station
降雨强度(I) Lognormal GEV GPD Exponential Gumbel AIC 834.9 832.4 850.5 856.5 920.2 统计量(D) 0.0678 0.0673 0.0961 0.1239 0.1517 P-value 0.4239 0.4322 0.0921 0.0122 0.0010 降雨持续时间(D) Lognormal GEV GPD Exponential Gumbel AIC 1231.4 1233.9 1244.9 1250.3 1234.6 统计量(D) 0.0538 0.0544 0.1253 0.1562 0.0583 P-value 0.7117 0.7001 0.0109 0.0006 0.6163 表 2 边际分布与Copula函数参数值
Table 2. Marginal distribution and Copula function parameter values
I(GEV) D(Lognormal) Copula函数单参数( $ \theta $ )$ c $ −0.52 $s $ 0.54 − 7.8903 $ \mu $ 3.34 $ {loc} $ −4.57 $ \sigma $ 2.01 $ { scale } $ 19.32 表 3 斜坡土体参数表
Table 3. Soil parameters of the investigated slope
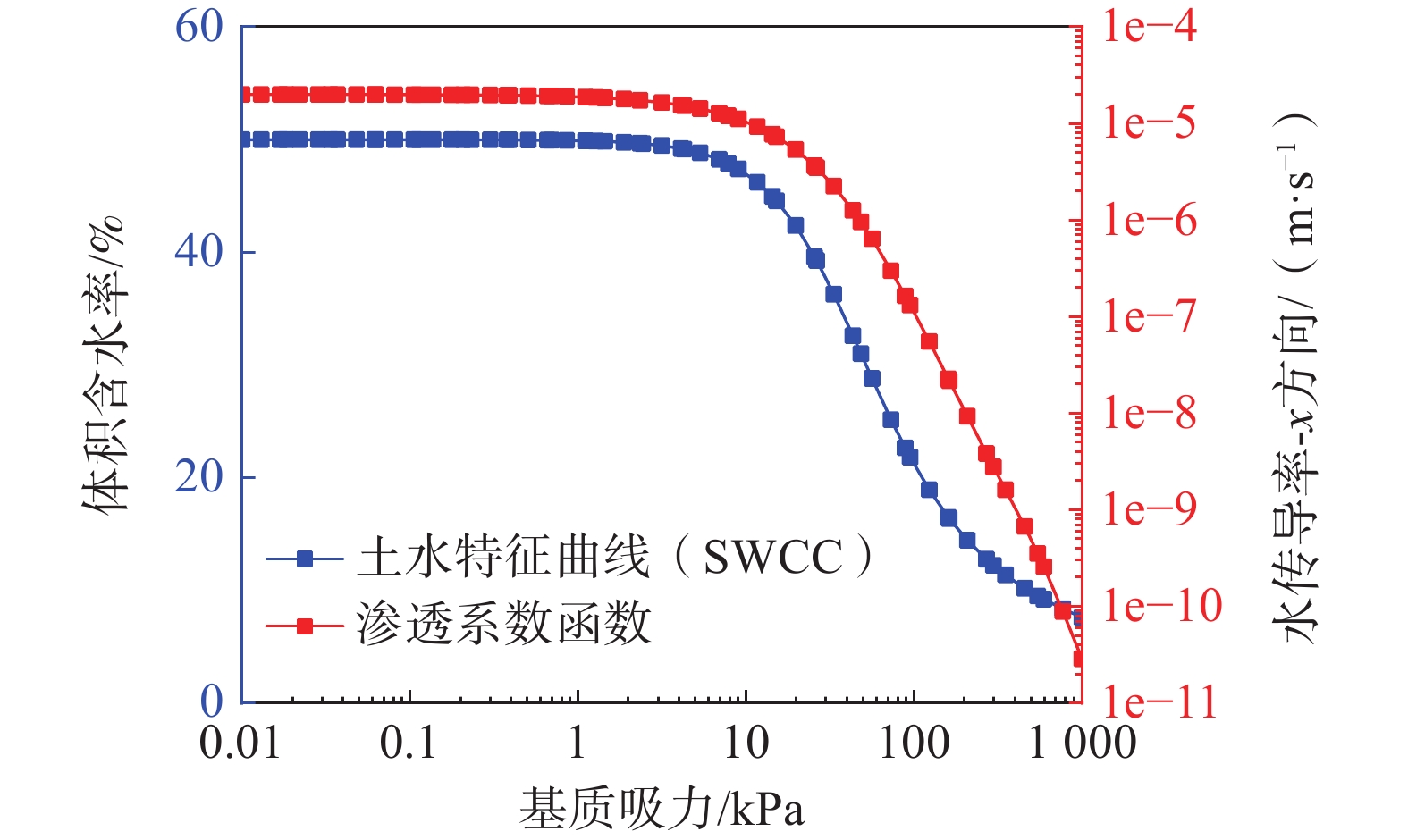
岩土体水力参数 岩土体抗剪强度参数 饱和体积含水率/% 50 饱和重度/(kN·m−3) 21 残余体积含水率/% 5 有效黏聚力/kPa 13 饱和渗透系数/ (m·s−1) 2×10−5 有效内摩擦角/(°) 18 -
[1] 周创兵,李典庆. 暴雨诱发滑坡致灾机理与减灾方法研究进展[J]. 地球科学进展,2009,24(5):477 − 487. [ZHOU Chuangbing,LI Dianqing. Advances in rainfall-induced landslides mechanism and risk mitigation[J]. Advances in Earth Science,2009,24(5):477 − 487. (in Chinese with English abstract)] doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.2009.05.003
ZHOU Chuangbing, LI Dianqing. Advances in rainfall-induced landslides mechanism and risk mitigation[J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2009, 24(5): 477 − 487. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.2009.05.003
[2] 王芳,殷坤龙,桂蕾,等. 不同日降雨工况下万州区滑坡灾害危险性分析[J]. 地质科技情报,2018,37(1):190 − 195. [WANG Fang,YIN Kunlong,GUI Lei,et al. Landslide hazard analysis under different daily rainfall conditions in Wanzhou District[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information,2018,37(1):190 − 195. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
WANG Fang, YIN Kunlong, GUI Lei, et al. Landslide hazard analysis under different daily rainfall conditions in Wanzhou District[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2018, 37(1): 190 − 195. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] LU Meng,ZHANG Jie,ZHENG Jianguo,et al. Assessing annual probability of rainfall-induced slope failure through a mechanics-based model[J]. Acta Geotechnica,2022,17(3):949 − 964. doi: 10.1007/s11440-021-01278-7
[4] HE Zhengying, AKIYAMA M, ALHAMID A K, et al. Probabilistic life-cycle landslide assessment subjected to nonstationary rainfall based on alternating stochastic renewal process[J]. Engineering Geology,2024,338:107543.
[5] PERES D J,CANCELLIERE A. Estimating return period of landslide triggering by Monte Carlo simulation[J]. Journal of Hydrology,2016,541:256 − 271. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2016.03.036
[6] LIU Xin,WANG Yu. Analytical solutions for annual probability of slope failure induced by rainfall at a specific slope using bivariate distribution of rainfall intensity and duration[J]. Engineering Geology,2023,313:106969. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2022.106969
[7] LIU Xin,WANG Yu. Probabilistic hazard analysis of rainfall-induced landslides at a specific slope considering rainfall uncertainty and soil spatial variability[J]. Computers and Geotechnics,2023,162:105706. doi: 10.1016/j.compgeo.2023.105706
[8] ZHANG J,ZHANG L M,TANG W H. Slope reliability analysis considering site-specific performance information[J]. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering,2011,137(3):227 − 238. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)GT.1943-5606.0000422
[9] LIU Xin, WANG Yu. Reliability analysis of an existing slope at a specific site considering rainfall triggering mechanism and its past performance records[J]. Engineering Geology,2021,288:106144. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2021.106144
[10] 孔锋,史培军,方建,等. 全球变化背景下极端降水时空格局变化及其影响因素研究进展和展望[J]. 灾害学,2017,32(2):165 − 174. [KONG Feng,SHI Peijun,FANG Jian,et al. Research progress and prospect of spatiotemporal pattern change of extreme precipitation and its influencing factors in the context of global change[J]. Journal of Catastrophology,2017,32(2):165 − 174.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-811X.2017.02.029
KONG Feng, SHI Peijun, FANG Jian, et al. Research progress and prospect of spatiotemporal pattern change of extreme precipitation and its influencing factors in the context of global change[J]. Journal of Catastrophology, 2017, 32(2): 165 − 174. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-811X.2017.02.029
[11] VINNARASI R,DHANYA C T. Bringing realism into a dynamic copula-based non-stationary intensity-duration model[J]. Advances in Water Resources,2019,130:325 − 338. doi: 10.1016/j.advwatres.2019.06.009
[12] KWON H H,LALL U. A copula-based nonstationary frequency analysis for the 2012–2015 drought in California[J]. Water Resources Research,2016,52(7):5662 − 5675. doi: 10.1002/2016WR018959
[13] SARHADI A,BURN D H,AUSÍN M C,et al. Time-varying nonstationary multivariate risk analysis using a dynamic Bayesian copula[J]. Water Resources Research,2016,52(3):2327 − 2349. doi: 10.1002/2015WR018525
[14] 雷德鑫,易武,柳青,等. 三峡库区卧沙溪滑坡稳定性的可靠度及敏感性分析[J]. 安全与环境工程,2018,25(1):23 − 28. [LEI Dexin,YI Wu,LIU Qing,et al. Reliability and sensitivity analysis of woshaxi landslide stability in Three Gorges Reservoir area[J]. Safety and Environmental Engineering,2018,25(1):23 − 28. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
LEI Dexin, YI Wu, LIU Qing, et al. Reliability and sensitivity analysis of woshaxi landslide stability in Three Gorges Reservoir area[J]. Safety and Environmental Engineering, 2018, 25(1): 23 − 28. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] LU Meng,ZHENG Jianguo,ZHANG Jie,et al. On assessing the probability of rainfall-induced slope failure during a given exposure time[J]. Acta Geotechnica,2023,18(3):1255 − 1267. doi: 10.1007/s11440-022-01655-w
-




 下载:
下载: