Stability analysis of geosynthetic-reinforced soil bridge abutments under extreme rainfall conditions
-
摘要:
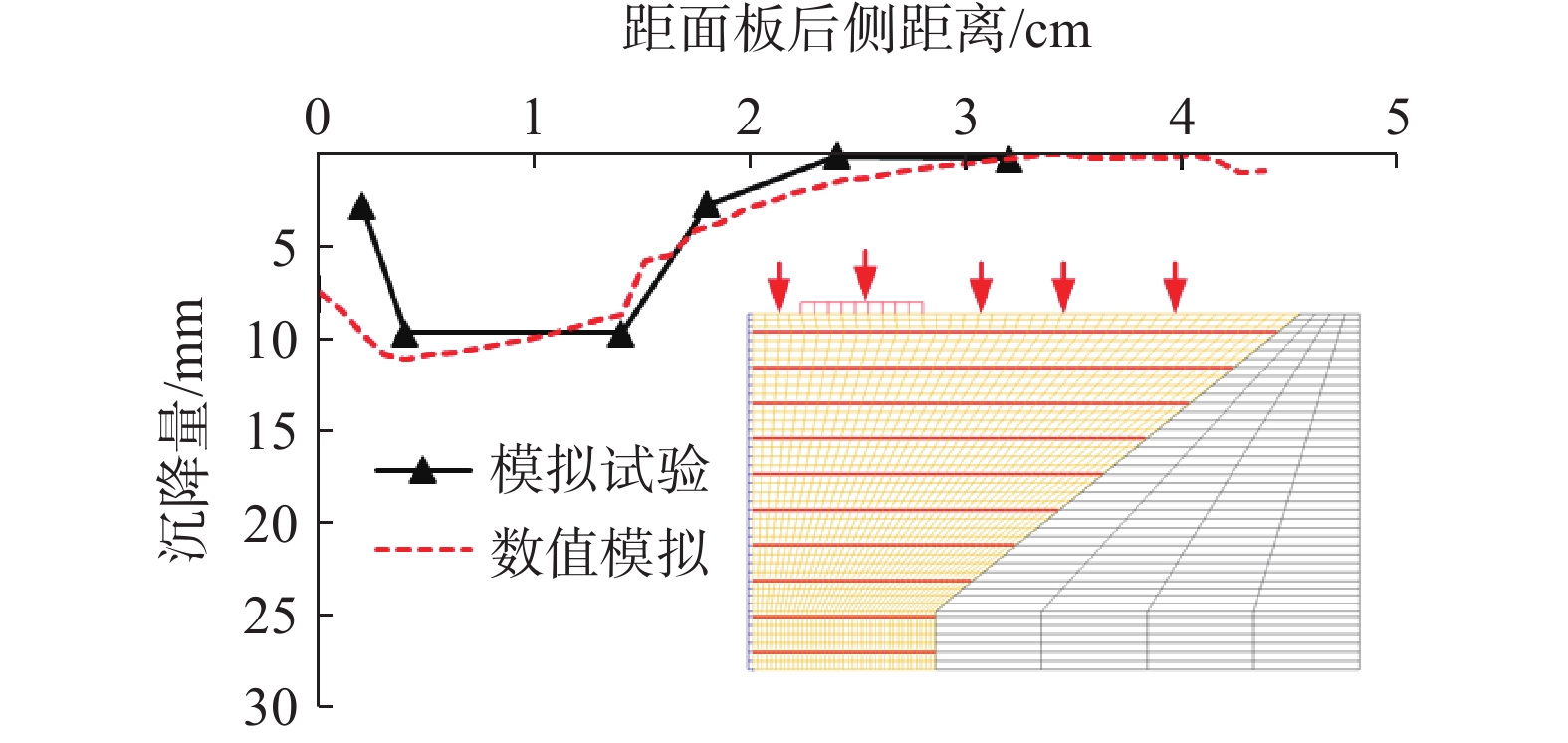
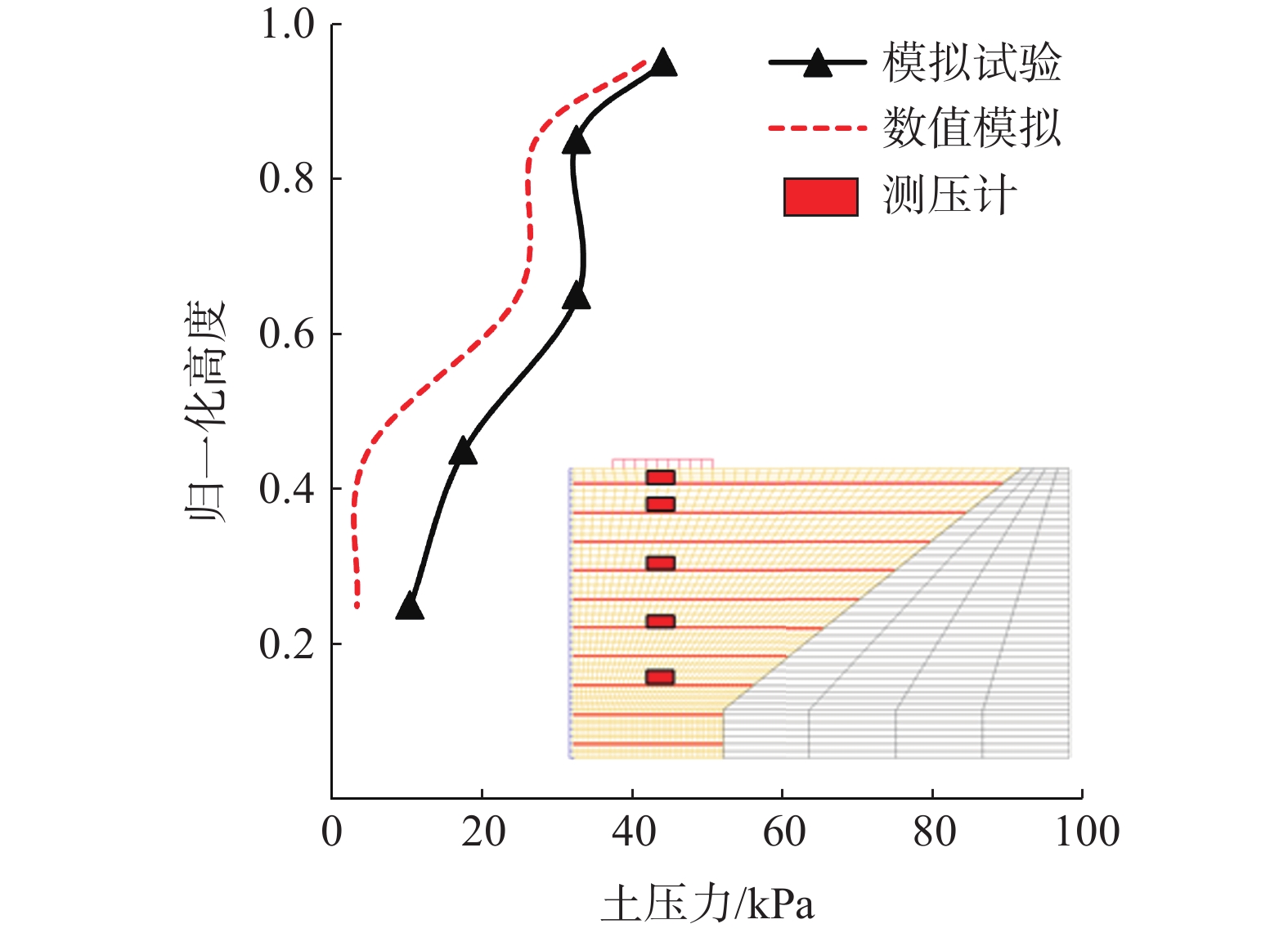
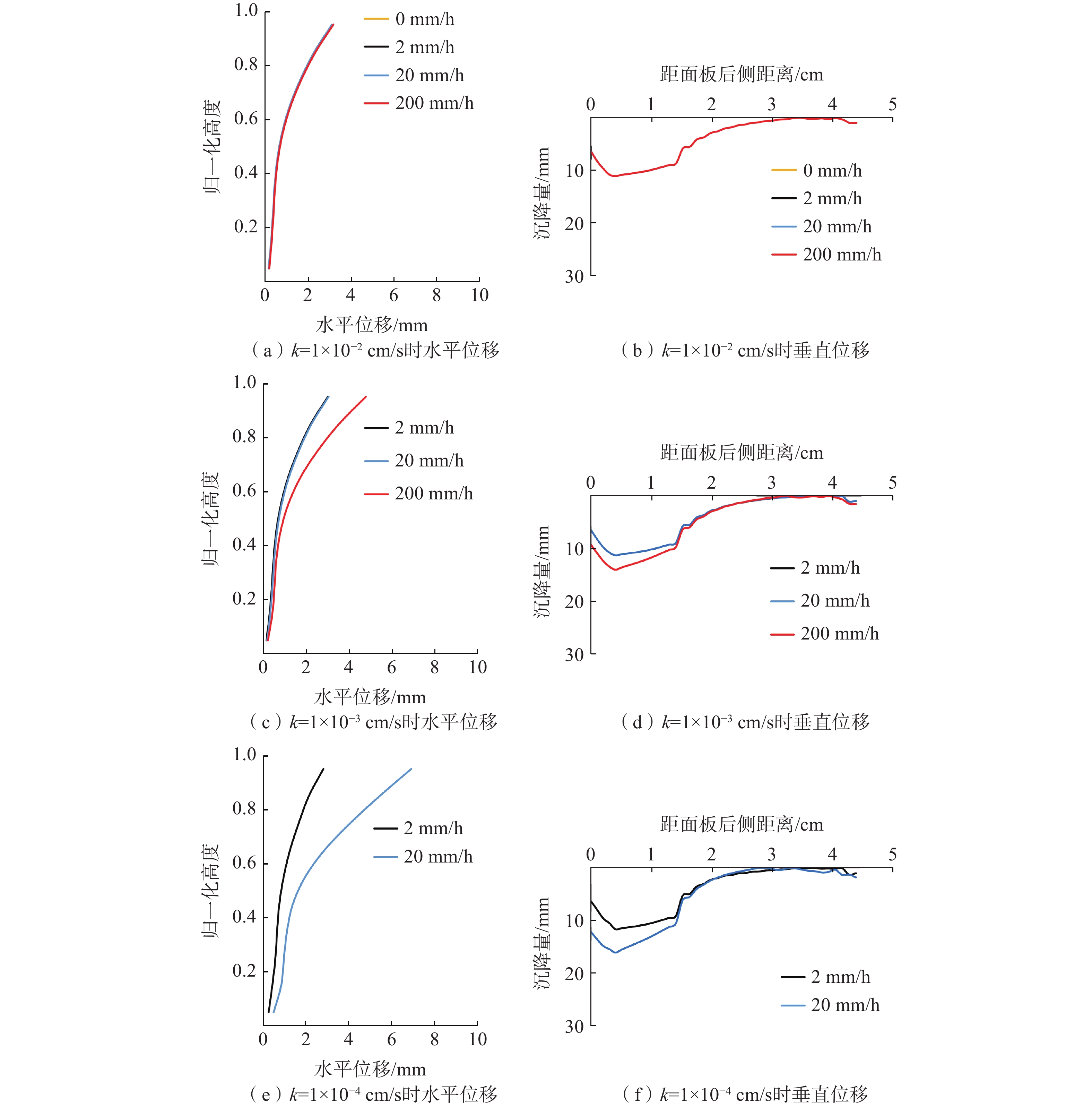
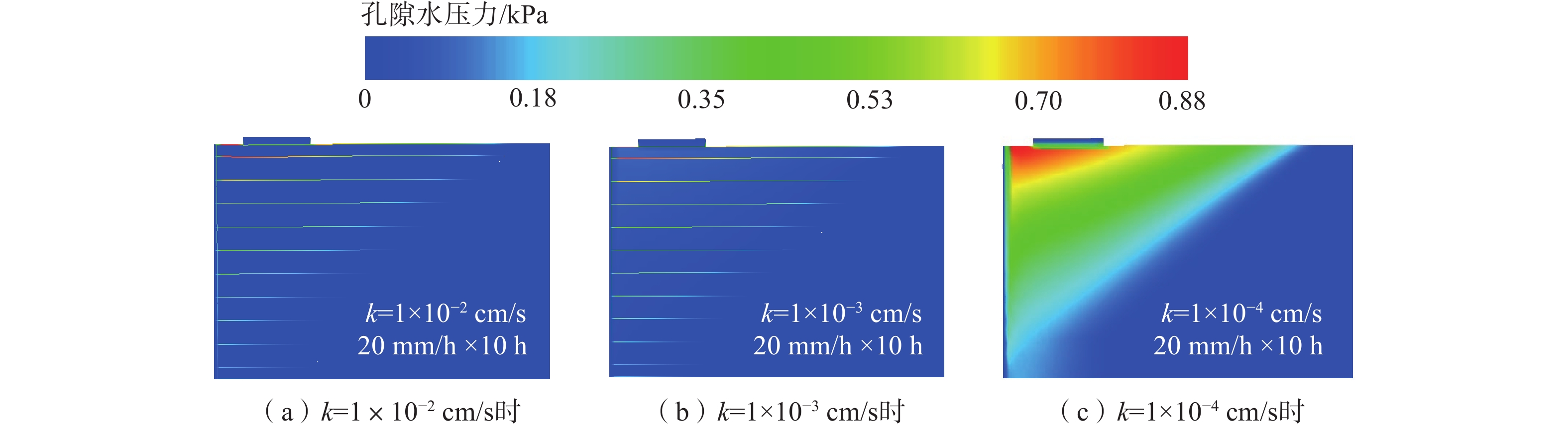
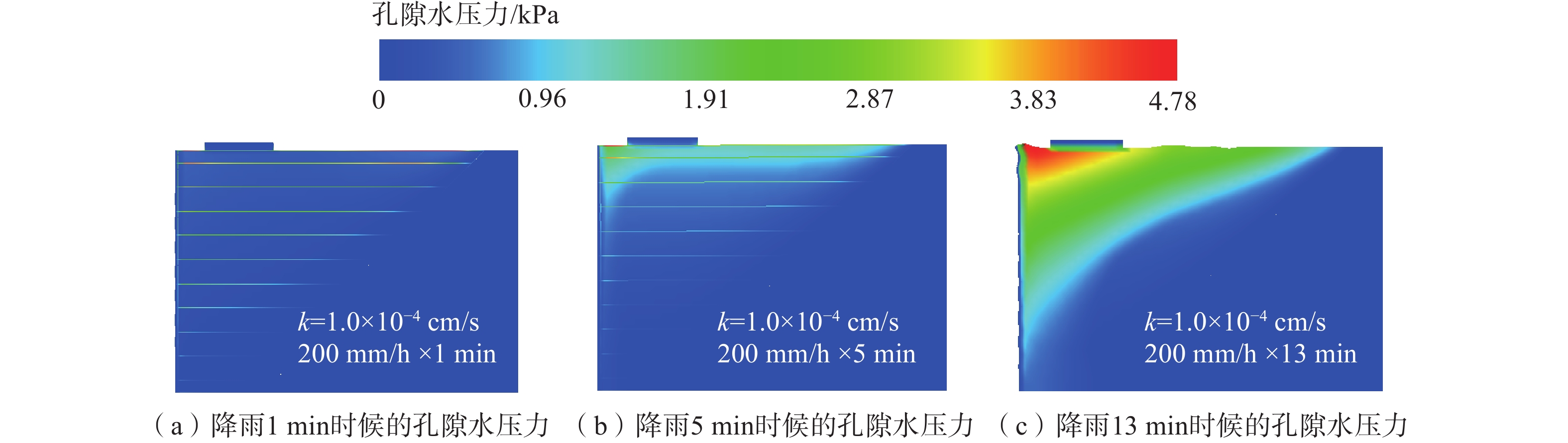
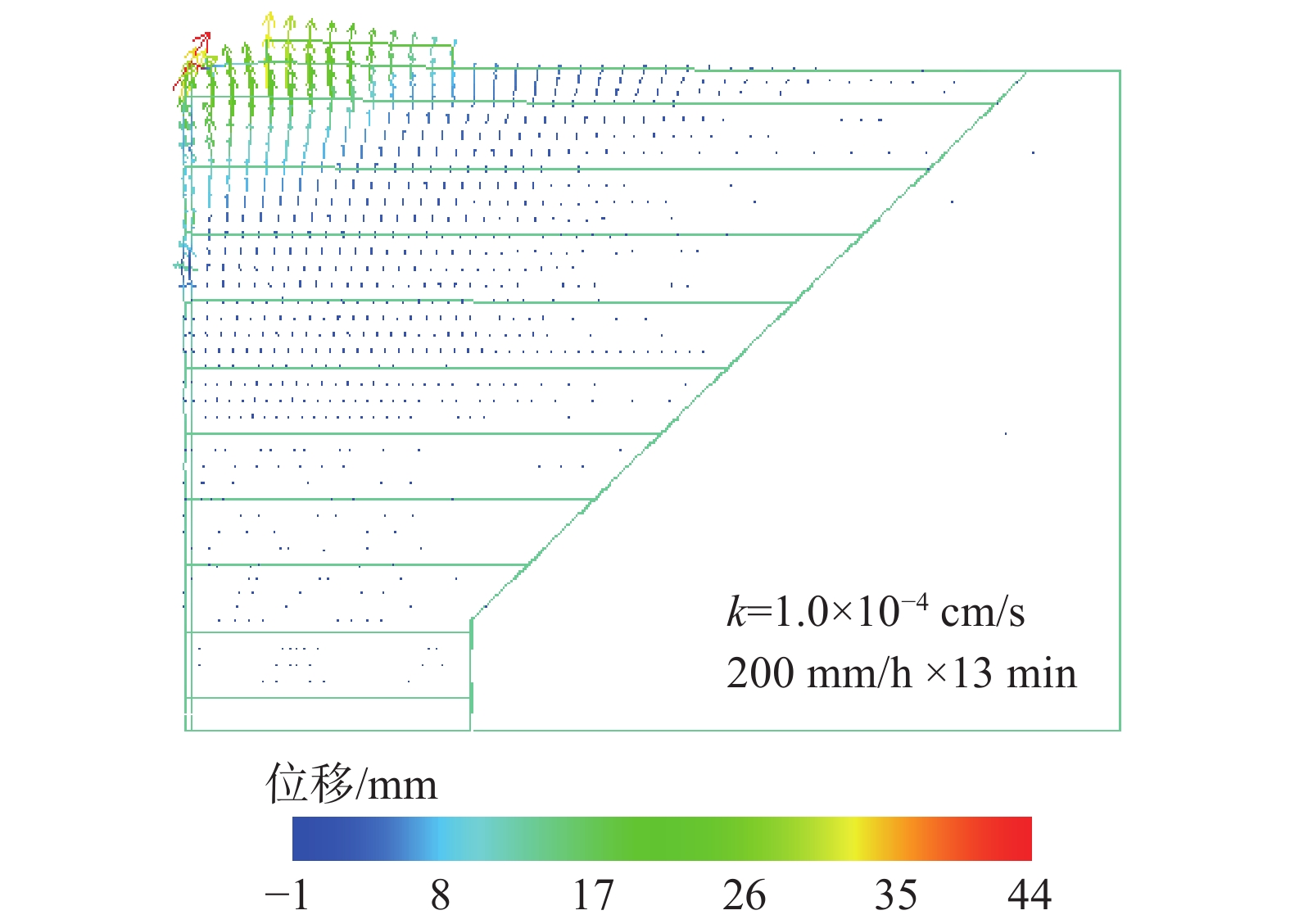
土工合成材料加筋土桥台因其造价低廉、施工便捷和绿色低碳的特点,在道路交通工程中具有广泛的应用潜力。然而,近年来极端降雨事件频发,对桥台的变形与稳定性造成了显著影响。采用模型试验与数值模拟相结合的方法,系统分析了极端降雨条件下桥台在交通荷载作用下的力学行为。研究表明,基于DBLEAVES-X建立的数值计算模型能够准确模拟降雨入渗条件下桥台的力学响应,验证了其在非饱和土力学分析中的可靠性。参数分析结果显示,降雨强度和填料渗透系数对桥台的稳定性具有显著影响。采用渗透系数为1.0×10−2 cm/s的高渗透性填料可以显著增强桥台的抗降雨稳定性,即使在200 mm/h的极端降雨条件下,桥台的稳定性仍接近未降雨工况。当填料渗透系数为1.0×10−3 cm/s或1.0×10−4 cm/s时,降雨可能导致孔隙水压力迅速积累,引发土体膨胀变形,显著加剧桥台的变形和失稳风险。因此,在实际工程设计中,应优先选用渗透性能良好的填料,优化排水系统设计,并采取针对性防护措施,以提高桥台在复杂环境条件下的长期稳定性和安全性。
-
关键词:
- 土工合成材料加筋土桥台 /
- 极端降雨 /
- 交通荷载 /
- 渗透系数 /
- 稳定性分析
Abstract:Geosynthetic-reinforced soil (GRS) abutments have demonstrated significant potential in road and transportation engineering due to their cost-effectiveness, ease of construction, and eco-friendly characteristics. However, the increasing frequency of extreme rainfall events in recent years has significantly impacted on the deformation and stability of these structures. This study systematically evaluated the performance of GRS abutments under traffic loads and extreme rainfall conditions through model tests and numerical analysis. The findings indicate that the numerical model developed with the DBLEAVES-X program can accurately simulates the mechanical response of GRS abutments under conditions of rainfall infiltration, confirming its reliability in the analysis of unsaturated soil mechanics. Parameter analysis reveals that rainfall intensity and the permeability coefficient of the backfill significantly influence the abutment’s resistance to rainfall. Using high-permeability backfill with a permeability coefficient of 1.0×10−2 cm/s can significantly enhance the abutment’s resistance to rainfall, maintaining stability even under extreme rainfall conditions of 200 mm/h. In contrast, a permeability coefficient of 1.0×10−3 cm/s or 1.0×10−4 cm/s may lead to rapid accumulation of pore water pressure, causing soil swelling deformation and substantially increasing the risk of deformation and instability of the abutment. Therefore, it is advisable in practical engineering design to prioritize high-permeability backfill materials, optimize drainage system designs, and implement specific protective measures to enhance the long-term stability and safety of the GRS abutments under complex environmental conditions.
-
Key words:
- GRS abutments /
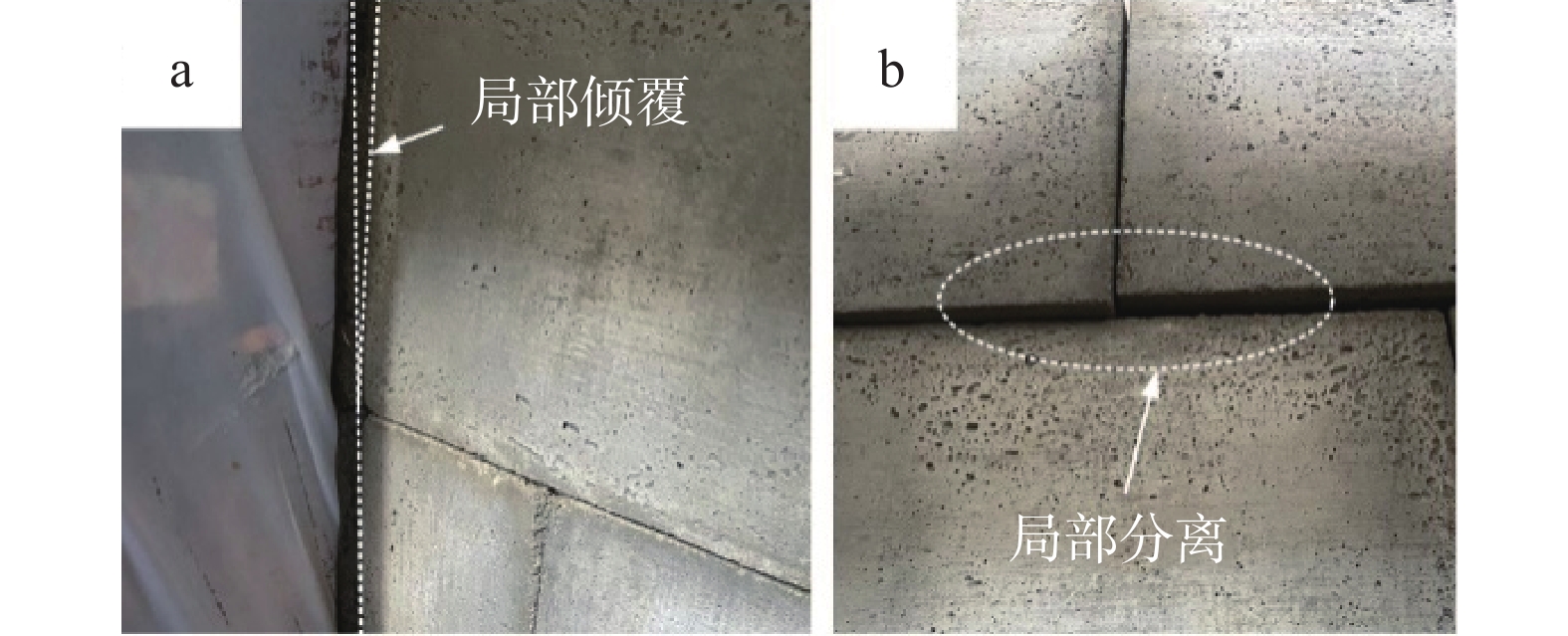
- extreme rainfall /
- traffic load /
- permeability coefficient /
- stability analysis
-

-
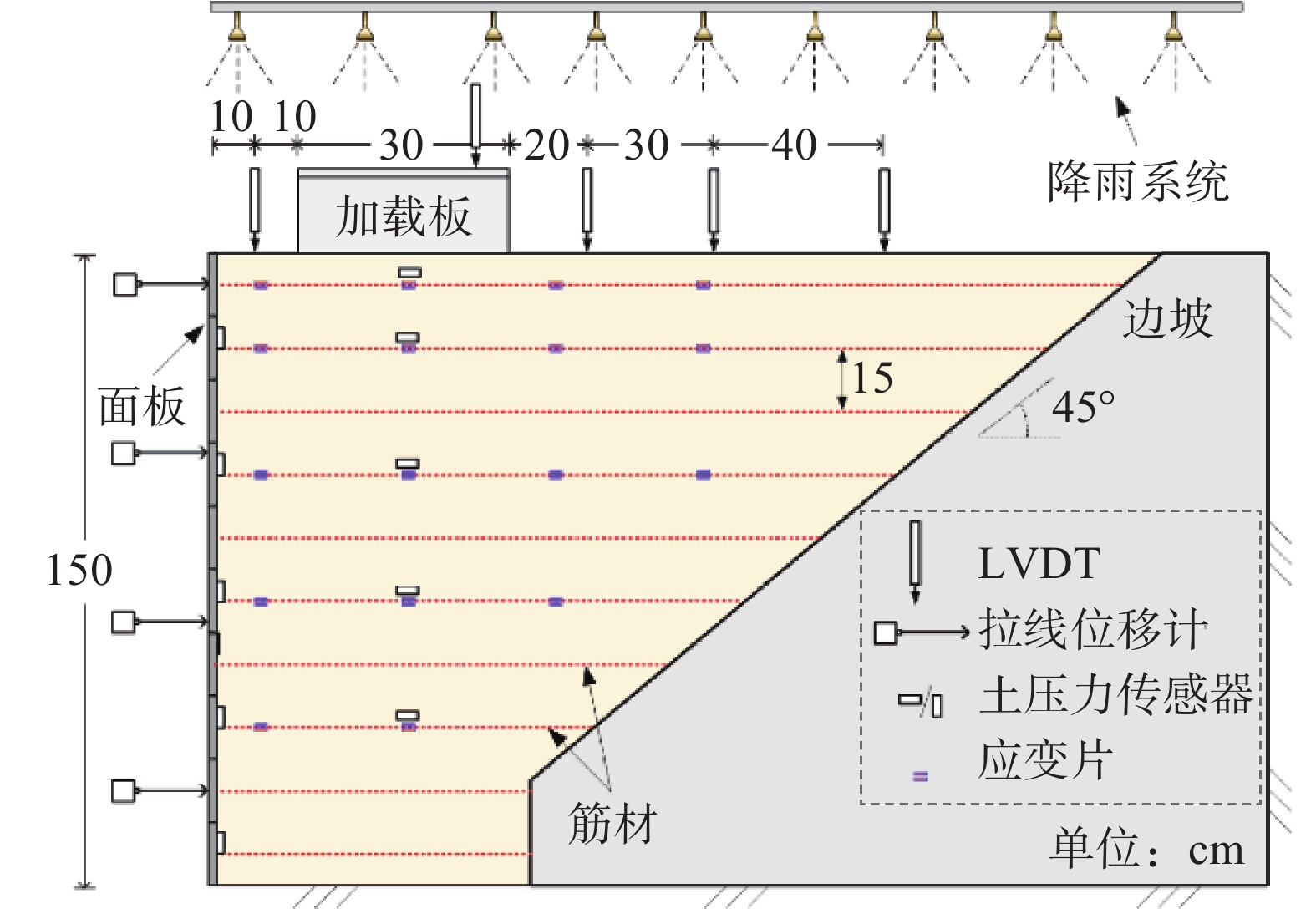
表 1 填料物理力学试验参数
Table 1. Physical mechanical test parameters of backfill
最大干密度
/(g·cm−3)最小干密度
/(g·cm−3)比重 黏聚力
/kPa内摩擦角
/(°)渗透系数
/(cm·s−1)1.768 1.373 2.64 0 45 1.0×10−2 表 2 数值计算中各材料力学参数
Table 2. Mechanical parameters of materials used in numerical analysis
材料 参数 取值 填料 压缩指数 0.01 回弹指数 0.001 泊松比 0.3 临界应力比 5.2 正常固结线上的参考孔隙比 0.628 超固结性参数 0.1 结构性参数 1.5 各向异性参数 1 面板 弹性模量 /(kN·m−1) 2.0×102 泊松比 0.3 边坡 弹性模量 /(kN·m−1) 1.6×105 泊松比 0.3 加载板 弹性模量/(kN·m−1) 9.9×109 泊松比 0.3 筋材 弹性模量/(kN·m−1) 500 表 3 不同渗透系数与降雨强度组合的数值模拟工况设置
Table 3. Numerical simulation settings for different combinations of permeability coefficients and rainfall intensities
工况 渗透系数
/(cm·s−1)降雨强度 /(mm·h-1) 降雨时间
/h降雨总量
/mm工况1 1.0×10−2 0 — — 工况2 2 100 200 工况3 20 10 200 工况4 200 1 200 工况5 1.0×10−3 2 100 200 工况6 20 10 200 工况7 200 1 200 工况8 1.0×10−4 2 100 200 工况9 20 10 200 工况10 200 1 200 -
[1] ABU-HEJLEH N,ZORNBERG J G,WANG T,et al. Monitored displacements of unique geosynthetic-reinforced soil bridge abutments[J]. Geosynthetics International,2002,9(1):71 − 95. doi: 10.1680/gein.9.0211
[2] ADAMS M T,SCHLATTER W,STABILE T. Geosynthetic reinforced soil integrated abutments at the bowman road bridge in defiance county,Ohio[C]//Geosynthetics in Reinforcement and Hydraulic Applications. Denver,Colorado,USA. American Society of Civil Engineers,2007:1-10.
[3] ADAMS M,NICKS J,STABILE T,et al. Geosynthetic reinforced soil integrated bridge system[C]// EuroGeo4 Paper 2011(271).
[4] 任非凡,何江洋. 加筋土结构动力特性研究现状综述[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2016,27(4):120 − 129. [REN Feifan,HE Jiangyang. Research status review on dynamic properties of reinforced earth structure[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2016,27(4):120 − 129. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
REN Feifan, HE Jiangyang. Research status review on dynamic properties of reinforced earth structure[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2016, 27(4): 120 − 129. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] 徐超,金宇,杨阳,等. 路面荷载下包裹式加筋土桥台变形的试验研究[J]. 岩土力学,2023,44(增刊1):410 − 418. [XU Chao,JIN Yu,YANG Yang,et al. Experimental study of deformation of mixed reinforced soil abutment under pavement load[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2023,44(Sup 1):410− 418. (in Chinese)]
XU Chao, JIN Yu, YANG Yang, et al. Experimental study of deformation of mixed reinforced soil abutment under pavement load[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2023, 44(Sup 1): 410− 418. (in Chinese)
[6] GEBREMARIAM F,TANYU B F,CHRISTOPHER B,et al. Evaluation of vertical stress distribution in field monitored GRS-IBS structure[J]. Geosynthetics International,2020,27(4):414 − 431. doi: 10.1680/jgein.20.00004
[7] ZHAO Chongxi,XU Chao,WANG Qingming. Centrifuge model studies on the load-bearing characteristics of geosynthetic-reinforced soil abutment[C]// Engineering Geology for a Habitable Earth:IAEG XIV Congress 2023 Proceedings,Chengdu,China. Singapore:Springer Nature Singapore,2024:875 − 883.
[8] 王裘申,徐超,张振,等. 交通荷载下加筋土桥台工作性能试验研究[J]. 岩土力学,2022,43(12):3416 − 3425. [WANG Qiushen,XU Chao,ZHANG Zhen,et al. Experimental study on service performance of reinforced soil abutment subjected to traffic loads[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2022,43(12):3416 − 3425. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
WANG Qiushen, XU Chao, ZHANG Zhen, et al. Experimental study on service performance of reinforced soil abutment subjected to traffic loads[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2022, 43(12): 3416 − 3425. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] XU Chao,LUO Minmin,SHEN Panpan,et al. Seismic performance of a whole Geosynthetic Reinforced Soil–Integrated Bridge System (GRS-IBS) in shaking table test[J]. Geotextiles and Geomembranes,2020,48(3):315 − 330. doi: 10.1016/j.geotexmem.2019.12.004
[10] JIA Yafei,ZHANG Jun,TONG Lihong,et al. Cumulative deformation behavior of GRS bridge abutments under cyclic traffic loading[J]. Geosynthetics International,2025,32(1):94 − 108. doi: 10.1680/jgein.23.00144
[11] 孟亚,徐超,赵崇熙,等. 分离式加筋土桥台性能及气候因素的影响研究[J]. 华中科技大学学报(自然科学版),2024,52(9):118 − 126. [MENG Ya,XU Chao,ZHAO Chongxi,et al. Research on the performance of disconnect-type reinforced soil abutment and the influence of climatic factors on the abutment[J]. Journal of Huazhong University of Science and Technology (Natural Science Edition),2024,52(9):118 − 126. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
MENG Ya, XU Chao, ZHAO Chongxi, et al. Research on the performance of disconnect-type reinforced soil abutment and the influence of climatic factors on the abutment[J]. Journal of Huazhong University of Science and Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2024, 52(9): 118 − 126. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] REN Feifan,HUANG Qiangqiang,WANG Guan. Shaking table tests on reinforced soil retaining walls subjected to the combined effects of rainfall and earthquakes[J]. Engineering Geology,2020,267:105475. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2020.105475
[13] REN Feifan,HUANG Qiangqiang,GENG Xueyu,et al. Influence of groundwater level changes on the seismic response of geosynthetic-reinforced soil retaining walls[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University:Science A,2022,23(11):850 − 862. doi: 10.1631/jzus.A2200188
[14] ADAMS M,NICKS J. Design and construction guidelines for geosynthetic reinforced soil abutments and integrated bridge systems[R]. United States:Federal Highway Administration,2018.
[15] 廖碧海,王国鼎. 巫山(新县城)超高加筋土挡土墙质量事故及原因分析[J]. 中南公路工程,2001,26(2):58 − 59. [LIAO Bihai,WANG Guoding. Quality accident and causes analysis of retaining wall with bar-soil at the superelevation section in Wushan[J]. Central South Highway Engineering,2001,26(2):58 − 59. (in Chinese)]
LIAO Bihai, WANG Guoding. Quality accident and causes analysis of retaining wall with bar-soil at the superelevation section in Wushan[J]. Central South Highway Engineering, 2001, 26(2): 58 − 59. (in Chinese)
[16] ABDULLAH N H H,NG K S,JAIS I B M,et al. Use of geosynthetic reinforced soil-integrated bridge system to alleviate settlement problems at bridge approach:A review[J]. Physics and Chemistry of the Earth,Parts A/B/C,2023,129:103304. doi: 10.1016/j.pce.2022.103304
[17] HATAMI K,BOUTIN J. Influence of backfill type on the load-bearing performance of GRS bridge abutments[J]. Geosynthetics International,2022,29(5):506 − 519. doi: 10.1680/jgein.21.00052
[18] 刘海洋,王录仓,常跟应. 郑州“7•20” 特大暴雨灾害对中国铁路运网的冲击过程和机制[J]. 地理学报,2024,79(3):617 − 634. [LIU Haiyang,WANG Lucang,CHANG Genying. The impact process and mechanism of the superheavy rainfall event in Zhengzhou on July 20,2021 on the China’s railway transport network[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica,2024,79(3):617 − 634. (in Chinese with English abstract)] doi: 10.11821/dlxb202403005
LIU Haiyang, WANG Lucang, CHANG Genying. The impact process and mechanism of the superheavy rainfall event in Zhengzhou on July 20, 2021 on the China’s railway transport network[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2024, 79(3): 617 − 634. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.11821/dlxb202403005
[19] NICKS J E,ESMAILI D,ADAMS M T. Deformations of geosynthetic reinforced soil under bridge service loads[J]. Geotextiles and Geomembranes,2016,44(4):641 − 653. doi: 10.1016/j.geotexmem.2016.03.005
[20] 上海市政工程设计研究总院,北京市市政工程设计研究总院,天津市市政工程设计研究院,兰州市城市建设设计院. 城市桥梁设计规范:CJJ11-2011[S]. 行业标准-城建,2019. [Shanghai Municipal Engineering Design Institute,Beijing Municipal Engineering Design Research Institute,Tianjin Municipal Engineering Design Institute,Lanzhou Urban Construction Design Institute. Design code for urban bridges:CJJ11-2011[S]. Industry Standard - Urban Construction,2019. (in Chinese)]
Shanghai Municipal Engineering Design Institute, Beijing Municipal Engineering Design Research Institute, Tianjin Municipal Engineering Design Institute, Lanzhou Urban Construction Design Institute. Design code for urban bridges: CJJ11-2011[S]. Industry Standard - Urban Construction, 2019. (in Chinese)
[21] XIONG Yonglin,BAO Xiaohua,YE Bin,et al. Soil–water–air fully coupling finite element analysis of slope failure in unsaturated ground[J]. Soils and Foundations,2014,54(3):377 − 395. doi: 10.1016/j.sandf.2014.04.007
[22] 谢轶,朱文轩,熊勇林,等. 非饱和路堑和路堤边坡地震响应的数值分析[J/OL]. 上海交通大学学报,2024:1 − 24. (2024-07-12)[2024-12-16]. [XIE Yi, ZHU Wenxuan, XIONGYonglin, et al. Numerical analysis of seismic response of unsaturated cutting and embankment slope[J/OL]. China Industrial Economics, 2024: 1 − 24. (2024-07-12)[2024-12-16]. https://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=SHJT20240708001&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
XIE Yi, ZHU Wenxuan, XIONGYonglin, et al. Numerical analysis of seismic response of unsaturated cutting and embankment slope[J/OL]. China Industrial Economics, 2024: 1 − 24. (2024-07-12)[2024-12-16]. https://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=SHJT20240708001&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[23] REN Feifan,HUANG Qiangqiang,CHEN Jianfeng. Centrifuge modeling of geosynthetic-reinforced soil retaining walls subjected to the combined effect of earthquakes and rainfall[J]. Geotextiles and Geomembranes,2022,50(3):470 − 479. doi: 10.1016/j.geotexmem.2022.01.005
[24] 周洪福,冯治国,石胜伟, 等. 川藏铁路某特大桥成都侧岸坡工程地质特征及稳定性评价[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2021,48(5):112 − 119. [ZHOU Hongfu,FENG Zhiguo,SHI Shengwei,et al. Slope engineering geology characteristics and stability evaluation of a grand bridge to Chengdu bank on the Sichuan-Tibet Railway[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2021,48(5):112 − 119. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
ZHOU Hongfu, FENG Zhiguo, SHI Shengwei, et al. Slope engineering geology characteristics and stability evaluation of a grand bridge to Chengdu bank on the Sichuan-Tibet Railway[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2021, 48(5): 112 − 119. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[25] 杨豪,魏玉峰,张御阳,等. 基于离心试验的反倾层状岩质边坡内非贯通性裂缝变形特性分析[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2022,49(6):152 − 161. [YANG Hao,WEI Yufeng,ZHANG Yuyang,et al. An analysis of non-penetration cracks in anti-dip rock slope based on centrifugal test[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2022,49(6):152 − 161. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
YANG Hao, WEI Yufeng, ZHANG Yuyang, et al. An analysis of non-penetration cracks in anti-dip rock slope based on centrifugal test[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2022, 49(6): 152 − 161. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[26] 郭延辉,杨溢,杨志全,等. 国产GB-InSAR在特大型水库滑坡变形监测中的应用[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2021,32(2):66 − 72. [GUO Yanhui,YANG Yi,YANG Zhiquan,et al. Application of GB-InSAR in deformation monitoring of huge landslide in reservoir area[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2021,32(2):66 − 72. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
GUO Yanhui, YANG Yi, YANG Zhiquan, et al. Application of GB-InSAR in deformation monitoring of huge landslide in reservoir area[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2021, 32(2): 66 − 72. (in Chinese with English abstract)
-



 下载:
下载: