GEOCHEMICAL HETEROGENEITY OF OCEANIC MANTLE: A REVIEW
-
摘要:
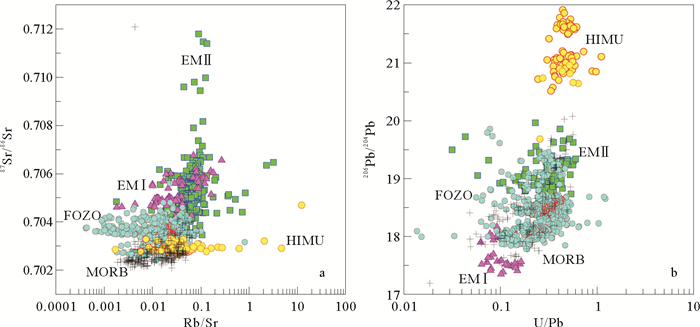
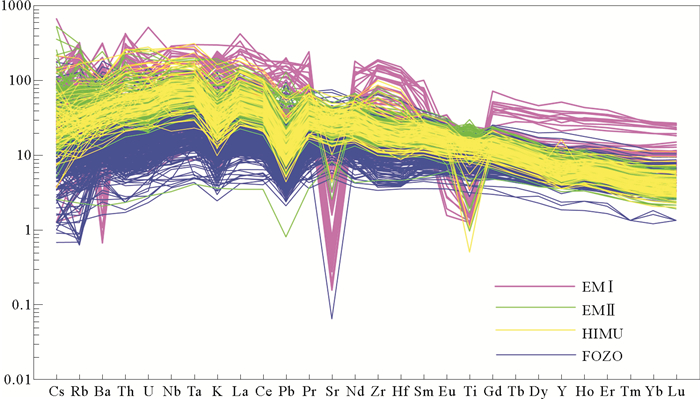
认识地幔组成不均一性及其成因对于揭示固体地球的演化规律具有重要意义。简要论述了全球典型大洋玄武岩(洋岛/海山玄武岩(OIB)、洋中脊玄武岩(MORB))源区组成不均一性的化学特征及成因,并分析了国内外对地幔组成不均一性的认识不足之处和原因。30多年以来,玄武岩地球化学研究主要围绕地幔组成端元成分差异性及其成因,包括HIMU(‘μ’=238U/204Pb)、EMI和EMII及FOZO(同位素组成介于HIMU和MORB之间)富集端元,以及DMM亏损地幔端元(包括印度洋型(Indian-type MORB)和太平洋型(Pacific-type MORB)。富集地幔端元通常被认为与板块构造导致的地球化学循环有关,然而,这些端元的成因存在多解性。尽管过去常将亏损地幔作为一个地幔端元,但全球主要地幔库的亏损端元之间的同位素差别也是长期演化的结果,地幔亏损端元组成差异的研究也是至关重要的。地幔端元成因的多解性主要是由于对板块构造导致物质循环的关键环节了解不够,以及对地球早期熔融导致的上地幔亏损过程的认识不足。在总结研究现状和科学问题的基础上,本文指出地幔不均一性成因研究的潜力方向和方法:(1)深化对玄武质洋壳深部地幔压力下的物理化学相变研究,认识再循环洋壳重返浅部地幔的基本理论前提;(2)利用年轻的大陆裂张海盆玄武岩,有效检验大陆富集物质是否拆离进入地幔软流圈;(3)碳酸岩熔体来源及其对碱性玄武岩富集端元组成的贡献;(4)板块俯冲进入地幔过程中化学分异过程。
Abstract:It is crucial to study the nature and origin of the mantle heterogeneity for understanding the solid Earth evolution. In this study we evaluated the mantle heterogeneity through oceanic basalts, e.g., ocean island basalts (OIBs) and mid-ocean ridge basalts (MORBs), and discussed the reason for insufficient understandings of the mantle heterogeneity. Studies in the past three decades show that the enriched mantle end-members include HIMU (('μ'=238U/204Pb) (low 87Sr/86Sr and high 206Pb/204Pb)), EMI (medium 87Sr/86Sr, low 206Pb/204Pb), EMII (high 87Sr/86Sr, medium 206Pb/204Pb), FOZO, and depleted mantle end-member of DMM (including Indian-type and Pacific-type). Origins of enriched mantle end-members are supposed to be related to plate tectonics, such as oceanic plate subduction, continent rifting and detachment. However, the origin of compositional differences between the end-members remains highly controversial. We consider that studies on depleted mantle end-members are also important for understanding the diversity of the compositions of mantle end-members. Debates on the origin of mantle end-members are mainly caused by lack of knowledge on the role of plate subduction in driving geochemical cycling and the mantle depletion in the early stage of melting of the Earth. We, therefore, suggest the following study aspects: Firstly, phase transition and the fate of subducted oceanic plate in the lower mantle; Secondly, test if detached continental crust can be mixed into the upper mantle due to continent rifting; Thirdly, the role of carbonate in the genesis of alkali basalts; Fourthly, the geochemical fractionation of subducting oceanic plate in the mantle.
-

-
[1] Valley J W. A cool early Earth[J]. Geology, 2002, 293, 4: 58-65. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/OAPaper/oai_arXiv.org_1005.2923
[2] Vervoort J, Patchett P, Gehrels G, et al. Constraints on early Earth differentiation from hafnium and neodymium isotopes[J]. Nature, 1996, 379 (6566): 624-627. doi: 10.1038/379624a0
[3] Blichert-Toft J, Albarède F. The Lu-Hf isotope geochemistry of chondrites and the evolution of the mantle-crust system[J]. Earth & Planetary Science Letters, 1997, 148, 1: 243-258. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/NSTLQK/10.1016-S0012-821X(97)00040-X/
[4] Lee D. Nature of the earth's earliest crust from hafnium isotopes in single detrital zircons[J]. Nature, 1999, 399: 252-255. doi: 10.1038/20426
[5] Zindler A, Hart S. Chemical geodynamics[J]. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 1986, 14(1): 493-571. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ea.14.050186.002425
[6] Bach W, Hegner E, Erzinger J, et al. Chemical and isotopic variations along the superfast spreading East Pacific Rise from 6°S to 30°S[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1994, 116: 365-380. doi: 10.1007/BF00310905
[7] Goss A R, Perfit M R, Ridley W I, et al. Geochemistry of lavas from the 2005—2006 eruption at the East Pacific Rise, 9°46′~9°56′N: Implications for ridge crest plumbing and decadal changes in magma chamber compositions[J]. Geochemistry Geophysics Geosystems 2010, 11(5), doi: 10.1029/2009GC002977.
[8] Regelous M, Niu Y, Wendt J I, et al. Variations in the geochemistry of magmatism on the East Pacific Rise at 10 degrees 30' N since 800 ka[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1999, 168: 45-63. doi: 10.1016/S0012-821X(99)00048-5
[9] Zhang G L, Zong C L, Yin X B, et al. Geochemical constraints on a mixed pyroxenite-peridotite source for the East Pacific Rise basalts[J]. Chemical Geology, 2012, 330-331: 176-187. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2012.08.033
[10] Zhang G L, Chen L H, Li S Z. Mantle Dynamics and Generation of a geochemical mantle boundary along the East Pacific Rise-Pacific/Antarctic ridge[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2013, 383: 153-163. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2013.09.045
[11] Dasgupta R, Hirschmann M M, Smith N D. Water follows carbon: CO2 incites deep silicate melting and dehydration beneath mid-ocean ridges[J]. Geology, 2007, 35(2): 135-138. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/NSTLQK/NSTL_QKJJ029557710/
[12] Hofmann A W. Mantle geochemistry: the message from oceanic volcanism[J]. Nature, 1997, 385: 219-229. doi: 10.1038/385219a0
[13] Silver P G, Carlson R W, Olson P. Deep slabs, geochemical heterogeneity, and the large-scale structure of mantle convection: Investigation of an enduring paradox[J]. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 1988, 16(2): 477-541. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ea.16.050188.002401
[14] Van der Hilst R D. Compositional heterogeneity in the bottom 1 000 kilometers of Earth's mantle: toward a hybrid convection model[J]. Science, 1999, 283: 1885-1888. doi: 10.1126/science.283.5409.1885
[15] Sobolev A V, Hofmann A W, Sobolev S V, et al. An olivine-free mantle source of Hawaiian shield basalts[J]. Nature, 2005, 434: 590-597. doi: 10.1038/nature03411
[16] Zhang G L, Zeng Z G, Beier C, et al. Generation and evolution of magma beneath the East Pacific Rise: Constraints from U-series disequilibrium and plagioclase-hosted melt inclusions[J]. Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, 2010, 193 (1): 1-17. doi: 10.1016/j.jvolgeores.2010.03.002
[17] Jackson M G, Hart S R, Koppers A A P, et al. The return of subducted continental crust in Samoan lavas[J]. Nature, 2007, 448 (7154): 684-687. doi: 10.1038/nature06048
[18] Halliday A N, Lee D C, Tommasini S, et al. Incompatible trace elements in OIB and MORB and source enrichment in the sub-oceanic mantle[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1995, 133 (3): 379-395. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/NSTLQK/10.1016-0012-821X(95)00097-V/
[19] Niu Y, O'Hara M J. Origin of ocean island basalts: A new perspective from petrology, geochemistry, and mineral physics considerations[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 2003, (1978-2012), 108(B4).
[20] Gao S, Rudnick R L, Xu W, et al. Recycling deep cratonic lithosphere and generation of intraplate magmatism in the north China craton[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2008, 270 (1-2): 41-53. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2008.03.008
[21] Lustrino, M. How the delamination and detachment of lower crust can influence basaltic magmatism[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2005, 72: 21-38. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2005.03.004
[22] Anderson D L. Speculations on the nature and cause of mantle heterogeneity[J]. Tectonophysics, 2006, 416 (1-4): 7-22. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2005.07.011
[23] Willbold M, Stracke A. Trace element composition of mantle end-members: Implications for recycling of oceanic and upper and lower continental crust[J]. Geochemistry Geophysics Geosystems, 2006, 7(4): 170-176. doi: 10.1029/2005gc001005
[24] Van der Hilst R D, Widiyantoro S, Engdahl E R. Evidence for deep mantle circulation from global tomography[J]. Nature, 1997, 386: 578-584. doi: 10.1038/386578a0
[25] Hirose K, Fei Y W, Ma Y Z, et al. The fate of subducted basaltic crust in the Earth's lower mantle[J]. Nature, 1999, 397: 53-56. doi: 10.1038/16225
[26] Plank T, Langmuir C H. The chemical composition of subducting sediment and its consequences for the crust and mantle[J]. Chemical Geology, 1998, 145(3): 325-394. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/NSTLQK/10.1016-S0009-2541(97)00150-2/
[27] Cohen R S, O'Nions R K. The lead, neodymium and strontium isotopic structure of ocean ridge basalts[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1982, 23: 299-324. doi: 10.1093/petrology/23.3.299
[28] Zindler A, Staudigel H, Batiza R. Isotope and trace element geochemistry of young Pacific seamounts: implications for the scale of upper mantle heterogeneity[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1984, 70(2): 175-195. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(84)90004-9
[29] Hamelin C, Dosso L, Hanan B B, et al. Sr-Nd-Hf isotopes along the Pacific Antarctic Ridge from 41° to 53°S[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2010, 37 (10): L10303. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/NSTLQK/10.1029-2010GL042979/
[30] White W M, Hofmann A W. Sr and Nd isotope geochemistry of oceanic basalts and mantle evolution[J]. Nature, 1982, 296: 821-825. doi: 10.1038/296821a0
[31] Hofmann A W, Jochum K P, Seufert H M, et al. Nb and Pb in oceanic basalts: New constraints on mantle evolution[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1986, 79: 33-45. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(86)90038-5
[32] White W M, Mcbirney A R, Duncan R A. Petrology and geochemistry of the galapagos islands: portrait of a pathological mantle plume[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1993, B98: 19533-19563. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/NSTLQK/10.1029-93JB02018/
[33] Brousse R, Barsczus H G, Bellon H, et al. The Marquesas, French Polynesia: volcanology, geochronology, and discussion of a hot spot model[J]. Bull. Soc. Geol. France Ser., 1990, 86: 933-949.
[34] Mahoney J J, Jones W B, Frey F A, et al. Geochemical characteristics of lavas from Broken Ridge, the Naturaliste plateau and southernmost Kerguelen plateau: Creataceous plateau volcanism in the southeast Indian ocean[J]. Chemical Geology, 1995, 120: 315-345. doi: 10.1016/0009-2541(94)00144-W
[35] Teasdale R, Geist D J, Kurz M D, et al. Eruption of volcan Cerro Azul, Galapagos islands: 1. Syn-eruptive petrogenesis[J]. Bulletin of Volcanology, 1998, 67: 170-185.
[36] Ielsch G, Caroff M, Barsczus H G, et al. Geochemistry of U Huka island basalts (Marquesas Islands): Partial melting variations and mantle source heterogeneity[J]. Compt. Rend. Acad. Sci. Paris Ser., 1998, 2, 326: 413-420.
[37] Blichert-Toft J, White W M. Hf isotope geochemistry of the Galapagos Islands[J]. Geochemistry Geophysics Geosystems, 2001, doi: 10.1029/2000GC000138.
[38] Neal C R, Mahoney J J, Chazey W J. Mantle sources and the highly variable role of continental lithosphere in basalt petrogenesis of the Kerguelen plateau and Broken Ridge lip: Results from ODP Leg 183[J]. Journal of Petrology, 2002, 43: 1177-1205. doi: 10.1093/petrology/43.7.1177
[39] Stracke A, Hofmann A W, Hart S R. FOZO, HIMU, and the rest of the mantle zoo[J]. Geochemistry Geophysics Geosystems, 2005, 6(5), doi: 10.1029/2004GC000824.
[40] Weaver B L. The origin of oceanic island basalt endmember compositions: Trace element and isotopic constraints[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1991, 104: 381-397. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(91)90217-6
[41] Chauvel C W, McDonough G, Guille R, Contrasting old and young volcanism in Rurutu Island, Austral chain[J]. Chemical Geology, 1997, 139: 125-143. doi: 10.1016/S0009-2541(97)00029-6
[42] Haase K M. Geochemical constraints on magma sources and mixing processes in Easter Microplate MORB (SE Pacific): a case study of plume-ridge interaction[J]. Chemical Geology, 2002, 182: 335-355. doi: 10.1016/S0009-2541(01)00327-8
[43] Kempton P D, Pearce J A, Barry T L, et al. Sr-Nd-Pb-Hf isotope results from ODP Leg 187: evidence for mantle dynamics of the Australian-Antarctic discordance and origin of the Indian MORB source[J]. Geochemistry Geophysics Geosystem, 2002, 3(12), 1074, doi:10.1029/2002GC000320.
[44] Mühe R, Bohrmann H, Garbe-Schönberg D, et al. E-MORB glasses from the gakkel ridge (Arctic ocean) at 87°N: evidence for the earth's most northerly volcanic activity[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1997, 152: 1-9. doi: 10.1016/S0012-821X(97)00152-0
[45] Fontignie D, Schilling J. Mantle heterogeneities beneath the South Atlantic: a Nd-Sr-Pb isotope study along the Mid-Atlantic Ridge (3°S-46°S) [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1996, 142(1-2): 209-221. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(96)00079-9
[46] Salters V J M, Mallick S, Hart S R, et al. Domains of depleted mantle: New evidence from hafnium and neodymium isotopes[J]. Geochemistry Geophysics Geosystem, 2011, 12, Q08001, doi:10.1029/2011GC003617.
[47] Allégre C, Turcotte D L. Implications of a two-component marble-cake mantle[J]. Nature, 1986, 323: 123-127. doi: 10.1038/323123a0
[48] Stracke A, Bourdon B. The importance of melt extraction for tracing mantle heterogeneity[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2009, 73: 218-238. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2008.10.015
[49] Bebout G E. Metamorphic chemical geodynamics of subduction zones[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2007, 260 (3-4): 373-393. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2007.05.050
[50] Alt J C, Honnorez J, Laverne C, et al. Hydrothermal alteration of a 1 km section through the upper oceanic crust, deep sea drilling project hole 504B: mineralogy, chemistry and evolution of seawater-basalt interactions[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research Solid Earth, 1986, 91, B10: 10309-10335. doi: 10.1029/JB091iB10p10309
[51] Zhang G L, Smith-Duque C. Seafloor basalt alteration and chemical change in the ultra thinly sedimented South Pacific[J]. Geochemistry Geophysics Geosystems, 2014, 5 (7): 3066-3080. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=10.1002/2013GC005141
[52] Alt J C, Muehlenbachs K, Honnorez J. An oxygen isotopic profile through the upper kilometer of the oceanic crust, DSDP Hole 504B[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1986, 80(3-4): 217-229. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(86)90106-8
[53] McDonough W F. Partial melting of subducted oceanic crust and isolation of its residual eclogitic lithology[J]. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. London, Ser. A, 1991, 335: 407-418. doi: 10.1098/rsta.1991.0055
[54] Ishikawa T, Nakamura E. Origin of the slab component in arc lavas from across-arc variation of B and Pb isotopes[J]. Nature, 1994, 370 (6486): 205-208. doi: 10.1038/370205a0
[55] Sobolev A V, Hofmann A W, Kuzmin D V, et al. The amount of recycled crust in sources of mantle-derived melts[J]. Science, 2007, 316: 412-417. doi: 10.1126/science.1138113
[56] Pilet S, Hernandez J, Sylvester P, et al. The metasomatic alternative for ocean island basalt chemical heterogeneity[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2005, 236: 148-166. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2005.05.004
[57] Kogiso T, Hirschmann M M, Frost D J. High-pressure partial melting of garnet pyroxenite: possible mafic lithologies in the source of ocean island basalts[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2003, 216 (4): 603-617(15). doi: 10.1016/S0012-821X(03)00538-7
[58] Morris J D, Leeman W P, Tera F. The subducted component in island arc lavas: Constraints from Be isotopes and B-Be systematics[J]. Nature, 1990, 344: 31-36. doi: 10.1038/344031a0
[59] Hirose K. Post perovskite phase transition and its geophysical implications[J]. Reviews of Geophysics, 2006, 44(3):75-83. doi: 10.1029/2005RG000186
[60] Class C, Goldstein S L. Plume-lithosphere interactions in the ocean basins: constraints from the source mineralogy[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1997, 150(3): 245-260. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/NSTLQK/10.1016-S0012-821X(97)00089-7/
[61] Class C, Goldstein S L, Altherr R, Bachèlery P. The process of plume-lithosphere interactions in the ocean basins—the case of Grande Comore[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1998, 39(5): 881-903. doi: 10.1093/petroj/39.5.881
[62] Bizimis M, Sen G, Salters V J M. Hf-Nd isotope decoupling in the oceanic lithosphere: constraints from spinel peridotites from Oahu, Hawaii[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2004, 217: 43-58. doi: 10.1016/S0012-821X(03)00598-3
[63] Delpech G, Grégoire M, O'Reilly S Y, et al. Feldspar from carbonate-rich silicate metasomatism in the shallow oceanic mantle under kerguelen islands (south Indian ocean) [J]. Lithos, 2004, 75: 209-237. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2003.12.018
[64] Rychert C A, Fischer K M, Rondenay S. A sharp lithosphere-asthenosphere boundary imaged beneath eastern North America[J]. Nature, 2005, 436 (7050): 542-545. doi: 10.1038/nature03904
[65] Kawakatsu H, Kumar P, Takei Y, et al. Seismic evidence for sharp lithosphere-asthenosphere boundaries of oceanic plates[J]. Science, 2009, 324 (5926): 499-502. doi: 10.1126/science.1169499
[66] Naif S, Key K, Constable S, et al. Melt-rich channel observed at the lithosphere-asthenosphere boundary[J]. Nature, 2013, 495 (7441): 356-359. doi: 10.1038/nature11939
[67] Escrig S, Capmas F, Dupré B, et al. Osmium isotopic constraints on the nature of the DUPAL anomaly from Indian mid-ocean-ridge basalts[J]. Nature, 2004, 431 (7004): 59-63. doi: 10.1038/nature02904
[68] von Huene R, Ranero C R, Vannucchi P. Generic model of subduction erosion[J]. Geology, 2004, 32: 913-916. doi: 10.1130/G20563.1
[69] Kesson S E, Gerald J F, Shelley J M G, et al. Mineral chemistry and density of subducted basaltic crust at lower-mantle pressures[J]. Nature, 1994, 372(6508): 767-769. doi: 10.1038/372767a0
[70] Ono S, Ito E, Katsura T. Mineralogy of subducted basaltic crust (MORB) from 25 to 37 GPa, and chemical heterogeneity of the lower mantle[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2001, 190(1):57-63. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=1af1183b0ddcc52b4349817383259244
[71] Poli S, Schmidt M W. Petrology of subducted slabs[J]. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 2002, 30(1): 207-235. doi: 10.1146/annurev.earth.30.091201.140550
[72] Ohta K, Hirose K, Lay T, et al. Phase transitions in pyrolite and MORB at lowermost mantle conditions: implications for a MORB-rich pile above the core-mantle boundary[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2008, 267(1): 107-117. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2007.11.037
[73] Tschauner O, Ma C, Beckett J R, et al. Discovery of bridgmanite, the most abundant mineral in Earth, in a shocked meteorite[J]. Science, 2014, 346(6213): 1100-1102. doi: 10.1126/science.1259369
[74] Hoernle K, Hauff F, Werner R, et al. Origin of Indian Ocean Seamount Province by shallow recycling of continental lithosphere[J]. Nature Geoscience, 2011, 4(12): 883-887. doi: 10.1038/ngeo1331
[75] Goldstein S L, Soffer G, Langmuir C H, et al. Origin of a 'Southern Hemisphere'geochemical signature in the Arctic upper mantle[J]. Nature, 2008, 453(7191): 89-93. doi: 10.1038/nature06919
[76] Kaliwoda M, Altherr R, Meyer H. Composition and thermal evolution of the lithospheric mantle beneath the Harrat Uwayrid, eastern flank of the Red Sea rift (Saudi Arabia) [J]. Lithos, 2007, 99: 105-120. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2007.06.013
[77] Dasgupta R, Hirschmann M M. Melting in the Earth's deep upper mantle caused by carbon dioxide[J]. Nature, 2006, 440(7084): 659-662. doi: 10.1038/nature04612
[78] Neumann E -R, Wulff-Pedersen E, Pearson N J. et al. Mantle xenoliths from Tenerife (Canary Islands): Evidence for reactions between mantle peridotites and silicic carbonatitie melts inducing Ca metasomatism[J]. Journal of Petrology, 2002, 43 (5): 825-857. doi: 10.1093/petrology/43.5.825
[79] Hudgins T R, Mukasa S B, Simon A C, et al. Melt inclusion evidence for CO2rich melts beneath the western branch of the East African Rift: implications for longterm storage of volatiles in the deep lithospheric mantle[J]. Contribution to Mineralogy and Petrology, 2015, 169 (5): 1-18.
[80] Hoernle K, Tilton G, Le Bas M J, et al. Geochemistry of oceanic carbonatites compared with continental carbonatites: mantle recycling of oceanic crustal carbonate[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 2002, 142: 520-542. doi: 10.1007/s004100100308
[81] Pearce J A, Baker P E, Harvey P K, et al. Geochemical evidence for subduction fluxes, mantle melting and fractional crystallization beneath the south sandwich island arc[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1995, 36 (4): 1073-1109. doi: 10.1093/petrology/36.4.1073
[82] Spandler C, Pirard C. Element recycling from subducting slabs to arc crust: A review[J]. Lithos, 2013, 170: 208-223. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2013.02.016
[83] Yaxley G M, Green D H. Experimental demonstration of refractory carbonate-bearing eclogite and siliceous melt in the subduction regime[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1994, 128(3-4): 313-325. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(94)90153-8
-




 下载:
下载: