Distribution of horizontal permeability coefficient of the cover layer of HBS at Site W18/19 of Shenhu area
-
摘要:
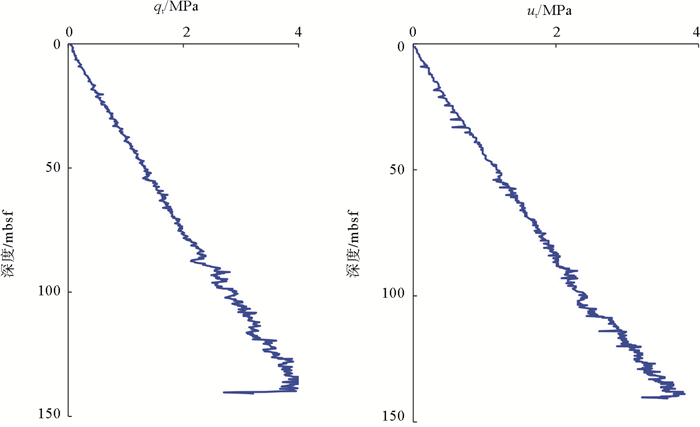
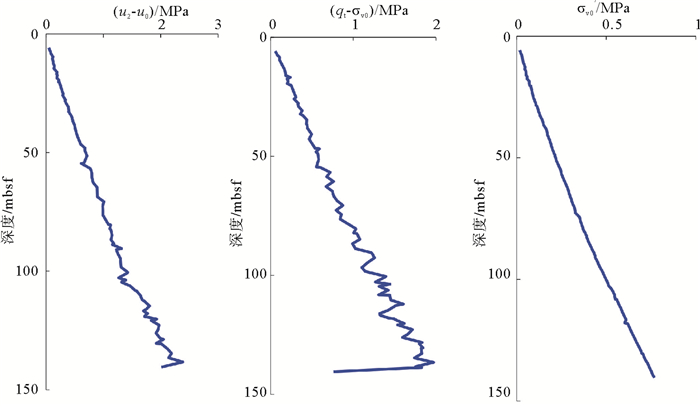
水合物储层上覆地层水平渗透系数是水合物试采工程设计的关键参数之一。以我国南海北部神狐海域W18/19区块水合物上覆钙质黏土层孔压静力触探数据为依托,在剖析基于位错理论的地层水平渗透系数预测模型基本原理的基础上,进行W18/19区块水合物层上覆钙质黏土层水平渗透系数纵向分布规律预测。结果表明,Elsworth方法不适用于W18/19区块水合物层上覆钙质黏土层水平渗透系数评价; W18/19区块水合物层上覆钙质黏土层水平渗透系数为0.1×10-8 ~4×10-8m/s,且随着深度的增大而减小; 30mbsf以浅地层预测结果受扰动较大,30mbsf以深地层的水平渗透率系数为0.1×10-8 ~0.6×10-8m/s,且不同模型预测结果间的差异较小; 孔压扩散模型和初始孔压分布函数的差异是导致不同模型预测结果差异的根本因素。
Abstract:Horizontal permeability coefficient (HPC) of the cover layer of hydrate bearing sediment(HBS) is one of the crucial factors that affect engineering design for marine hydrate production test. Based on the piezocone penetration test (CPTU) data obtained from the calcareous cover layer of hydrate formation at site W18/19 of the Shenhu area, different HPC estimation models based on the dislocation theory were analyzed, together with their corresponding adaptability to calcareous cover clay in the Shenhu area of northern South China Sea. Finally, the vertical distribution of HPC value for the calcareous cover clay of HBS at the site of W18/19 was predicted and analyzed using the above prediction models. The research results show that the Elsworth (2005) method is not adapt for HPC evaluation at site W18/19. Totally, HPC value at site W18/19 ranges from 0.1×10-8~4×10-8m/s and increase gradually with depth. In the interval shallower than 30mbsf, HPC values are vastly fluctuated because of some disturbance. In the interval below 30mbsf, of which the HPC values range from 0.1×10-8~0.6×10-8m/s, however, the gaps from different prediction models come closer. Prediction results indicate that pore-pressure diffusion model and diffusion function are two basic factors that lead to the gaps among HPC values obtained from different models.
-

-
表 1 基于位错理论的地层水平渗透系数计算方法对比
Table 1. Horizontal permeability coefficient calculation methods based on CPTU dislocation theory
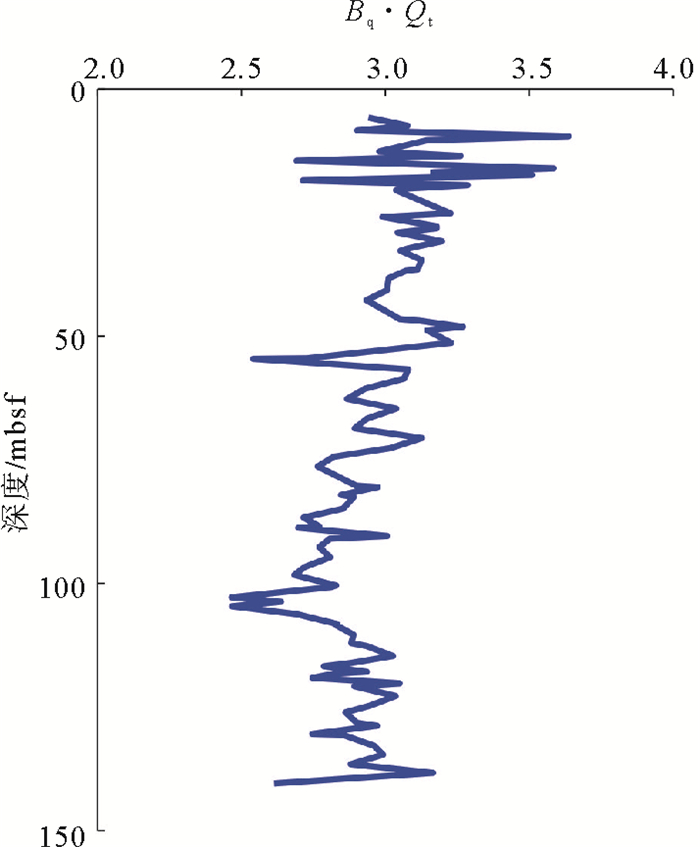
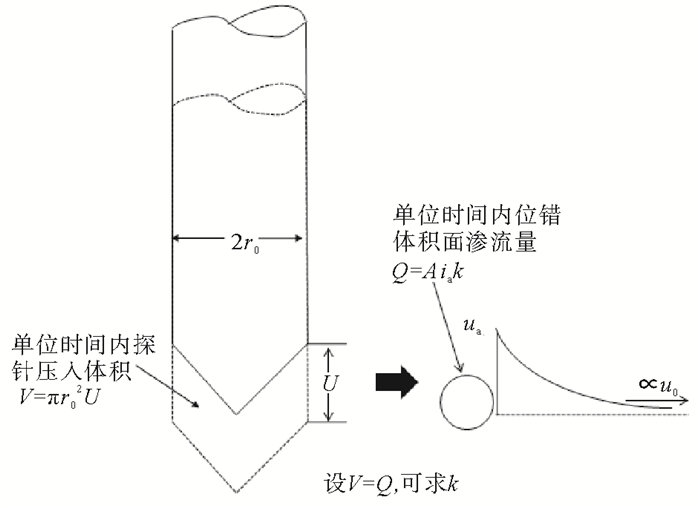
求解模型 孔压扩散模型 初始孔压分布函数 KD ξ 建议适用条件 Elsworth方法[17, 18] 球面流 幂函数分布 ${K_D} = \frac{{0.62}}{{{{\left( {{B_q}{Q_t}} \right)}^{1.6}}}}$ 0.25 BqQt<1.2, 不排水地层 Chai方法[12] 半球面流 幂函数分布 $\left\{ \begin{gathered} {K_D} = \frac{1}{{{B_q}{Q_t}}}, {B_q}{Q_t} < 0.45 \hfill \\ {K_D} = \frac{{0.044}}{{{{\left( {{B_q}{Q_t}} \right)}^{4.91}}}}, {B_q}{Q_t} \geqslant 0.45 \hfill \\ \end{gathered} \right.$ 0.5 正常固结或轻微超固结的黏性土和松散的无黏性土 王君鹏方法[19, 20] 任意锥角球面流 负指数分布 $\frac{{{{\sin }^2}\frac{\alpha }{2}}}{{0.3{{\text{e}}^{-0.3}}\left( {\frac{1}{{\sin \alpha }}-1} \right)}}$ 邹海峰方法[15] 柱面径向流 幂函数分布 $\left\{ \begin{gathered} {K_D} = \frac{1}{{{B_q}{Q_t}}}, {B_q}{Q_t} < 0.35 \hfill \\ {K_D} = \frac{{0.017}}{{{{\left( {{B_q}{Q_t}} \right)}^{4.64}}}}, {B_q}{Q_t} \geqslant 0.35 \hfill \\ \end{gathered} \right.$ $\frac{{{r_0}}}{{2h}}$ 李镜培方法(2016)[21] 柱面径向流 负指数分布 $\left\{ \begin{gathered} {K_D} = \frac{{0.1}}{{{B_q}{Q_t}}}, {B_q}{Q_t} < 0.45 \hfill \\ {K_D} = \frac{{0.0044}}{{{{\left( {{B_q}{Q_t}} \right)}^{4.91}}}}, {B_q}{Q_t} \geqslant 0.45 \hfill \\ \end{gathered} \right.$ $\frac{{{r_0}}}{{0.6h}}$ -
[1] Wu Nengyou, Zhang Haiqi, Yang Shengxiong, et al. Gas hydrate system of Shenhu area, northern South China Sea: Geochemical results [J]. Journal of Geological Research, 2011, 10: 1687-8833.
[2] 龚跃华, 张光学, 郭依群, 等.南海北部神狐西南海域天然气水合物成矿远景[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2013, 33(2): 97-104. http://hydz.chinajournal.net.cn/WKD/WebPublication/paperDigest.aspx?paperID=b58780ab-1d0d-4a82-9c9c-29518bb203d0
GONG Yuehua, ZHANG Guangxue, GUO Yiqun, et al. Prospect of gas hydrate resource in the area to southwest Shenhu of northern South China Sea [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2013, 33(2): 97-104. http://hydz.chinajournal.net.cn/WKD/WebPublication/paperDigest.aspx?paperID=b58780ab-1d0d-4a82-9c9c-29518bb203d0
[3] Li J F, Ye J L, Qin X W, et al. The first offshore natural gas hydrate production test in South China Sea[J]. China Geology, 2018, 1: 5-16. doi: 10.31035/cg2018003
[4] http://china.cnr.cn/xwwgf/20170518/t20170518_523762235.shtml, 2017-05-18.
[5] 苏明, 沙志彬, 乔少华, 等.南海北部神狐海域天然气水合物钻探区第四纪以来的沉积演化特征[J].地球物理学报, 2015, 58(8):2975-2985. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dqwlxb201508030
SU Ming, SHA Zhibin, QIAO Shaohua, et al. Sedimentary evolution since Quaternary in the Shenhu hydrate drilling area, northern South China Sea [J]. Chinses Journal of Geophysics, 2015, 58(8):2975-2985. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dqwlxb201508030
[6] 陈芳, 周洋, 苏新, 等.南海神狐海域含水合物层底栖有孔虫群落结构与同位素组成[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2010, 30(2): 1-8. http://hydz.chinajournal.net.cn/WKD/WebPublication/paperDigest.aspx?paperID=1b656c0f-3b6c-4f07-acd5-b8ec0b6ae4a3
CHEN Fang, ZHOU Yang, SU Xin, et al. Benthic foraminifera and stable isotopic composition of gas hydrate-bearing sediments from Shenhu area in the northern South China Sea[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2010, 30(2): 1-8. http://hydz.chinajournal.net.cn/WKD/WebPublication/paperDigest.aspx?paperID=1b656c0f-3b6c-4f07-acd5-b8ec0b6ae4a3
[7] 高红艳, 钟广法, 梁金强, 等.应用改进的Biot-Gassmann模型估算天然气水合物的饱和度[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2012, 32(4): 83-89. http://hydz.chinajournal.net.cn/WKD/WebPublication/paperDigest.aspx?paperID=40c7b358-da8c-429a-aa12-c4e520124394
GAO Hongyan, ZHONG Guangfa, LIANG Jinqiang, et al. Estimation of gas hydrate saturation with modified Biot-Gassmann theory: A case from northern South China Sea [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2012, 32(4): 83-89. http://hydz.chinajournal.net.cn/WKD/WebPublication/paperDigest.aspx?paperID=40c7b358-da8c-429a-aa12-c4e520124394
[8] Bergado D T, Asakami H, Alfaro M C, et al. Smear effects of vertical drains on soft Bangkok clay[J]. Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 1991, 117(10):1509-1530. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9410(1991)117:10(1509)
[9] Takai A, Inui T, Katsumi T. Evaluating the hydraulic barrier performance of soil-bentonite cutoff walls using the piezocone penetration test[J]. Soils & Foundations, 2016, 56(2):277-290. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=2b22be8b80ac212c7813eedc060d4404
[10] Indraratna B, Rujikiatkamjorn C, Sathananthan I. Radial consolidation of clay using compressibility indices and varying. [J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal, 2005, 42(5): 1330-1341. doi: 10.1139/t05-052
[11] Robertson P K. Estimating in-situ soil permeability from CPT & CPTU[C]// Proceedings of the 2nd International Symposium on Cone Penetration Testing (CPT′10). Huntington Beach, California, May, 2010: 535-542.
[12] Chai J C, Agung P M A, Hino T, et al. Estimating hydraulic conductivity from piezocone soundings [J]. Géotechnique, 2011, 61(8): 699-708 doi: 10.1680/geot.10.P.009
[13] Ansari Y, Merifield R, Sheng D. A piezocone dissipation test interpretation method for hydraulic conductivity of soft clays[J]. Soils & Foundations, 2014, 54(6):1104-1116. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=b566c9ab7ed26230c5799651c8a531ad
[14] Elsworth. Analysis of piezocone data using dislocation based methods[J]. Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 1993, 119(10): 1601-1623. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9410(1993)119:10(1601)
[15] 邹海峰, 蔡国军, 刘松玉.基于位错理论的饱和土渗流特性CPTU评价研究[J].岩土工程学报, 2014, 36(3):519-528. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ytgcxb201403015
ZOU Haifeng, CAI Guojun, LIU Songyu. Evaluation of coefficient of permeability of saturated soils based on CPTU dislocation theory [J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2014, 36(3):519-528. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ytgcxb201403015
[16] Shen S L, Wang J P, Wu H N, et al. Evaluation of hydraulic conductivity for both marine and deltaic deposits based on piezocone testing[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2015, 110:174-182. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2015.10.011
[17] Elsworth D, LeeD S.Permeability determination from on-the fly piezocone sounding [J]. Journal of Geotechnical and Geo-environmental Engineering, 2005, 131 (5): 643-653. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)1090-0241(2005)131:5(643)
[18] Elsworth D, Lee D S. Limits in determining permeability from on-the-fly UCPT Sounding [J]. Géotechnique, 2007, 57(8): 769-685. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=f8fdb8a0280082c9429bb9e6962eea3a
[19] 王君鹏, 沈水龙.基于孔压静力触探确定土体的渗透系数[J].岩土力学, 2013, 34(11): 3335-3339. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ytlx201311045
WANG Junpeng, SHEN Shuilong. Determination of permeability coefficient of soil based on CPTU [J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2013, 34(11): 3335-3339. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ytlx201311045
[20] Wang J P, XU Y S, Ma L, et al. An approach to evaluate hydraulic conductivity of soil based on CPTU test [J].Marine Georesources and Geotechnology, 2013, 31(3): 242-253. doi: 10.1080/1064119X.2012.676154
[21] 李镜培, 李险峰, 张亚国. CPTU确定饱和土体水平渗透系数的改进方法[J].哈尔滨工业大学学报, 2016, 48(8):185-188. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hebgydxxb201608031
LI Jingpei, LI Xianfeng, ZHANG Yaguo. A modified approach to determine horizontal permeability coefficient of saturated soils based on CPTU [J]. Journal of Harbin Institute of Technology, 2016, 48(8):185-188 http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hebgydxxb201608031
[22] Elsworth LEE D S. Limits in determining permeability from on-the-fly uCPT Sounding [J].Géotechnique, 2007, 57(8): 769-685. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=f8fdb8a0280082c9429bb9e6962eea3a
[23] 马淑芝, 汤艳春, 孟高头, 等.孔压静力触探测试机理、方法及工程应用[M].武汉:中国地质大学出版社, 2007.
MA Shuzhi, TANG Yanchun, MENG Gaotou, et al. Theory, Method and Application of Piezocone Penetration Test [M]. Wuhan: Press of China University of Geoscience, 2007.
[24] Koizumi Y, Ito K. Field tests with regard to pile driving and bearing capacity of piled foundations [J]. Soils and Foundations, 1967, 7(3): 30-53. doi: 10.3208/sandf1960.7.3_30
-



 下载:
下载: