Sediment source-to-sink processes of small mountainous rivers under the impacts of natural environmental changes and human activities
-
摘要:
山地小河在地球环境变迁和大陆边缘物质循环过程中具有重要作用,且受人类活动干预影响越来越明显。相比世界大河而言,中小河流多具有瞬时大通量、快速物质转换、易受极端事件和人类活动影响,且对环境变化响应敏感等特点,但学术界对它们的研究很薄弱。目前迫切需要以地球系统科学的思路来重新审视中小河流在圈层相互作用中的角色,加强中小河流地学的系统研究,尤其是通过系统的野外观测与采样分析,积累较长期的实时连续现场水文泥沙等多参数观测资料;同时利用多学科交叉和多方法集成的研究手段,重点研究在全球变化与人类活动影响的双重因素驱动下,世界主要大陆和岛屿地区代表性的中小河流入海物质的通量与组成,向边缘海和全球大洋的物质输运、埋藏与循环过程,以及对不同尺度的全球气候变化和海陆物质循环的响应和影响;重点揭示不同纬度、地带性气候和人类活动影响下的中小河流代表的源汇体系特征,及与世界大河源汇体系的差异,深入理解地球表生过程和全球海陆相互作用的机制。
Abstract:Small mountainous river systems (SMRS) play a key role in the global environmental changes and material cycle on the continental margin, and are subject to increasing human perturbation. Compared to large river systems, the SMRS are characterized by rapid and huge discharges, fast sediment transfer, and being easily influenced by extreme events and human activities, which make them more sensitive to global environmental changes. However, they have received less research attention relative to large rivers. Currently, the role of SMRS that play in the interactions among earth's spheres deserves more in-depth researches, as the concept of earth system science is put under consideration. In particular, the combination of real time and long term hydrographic observations in the fields with multi-disciplinary analytical approaches is urgently needed for better understanding the role of these rivers played on earth surface processes. The major research directions include the discharges and compositions of dissolved and particulate materials by the SMRS from continents and islands into the global oceans, under the impacts of natural environmental changes and human activities, and the difference in sediment source-to-sink processes between the SMRS and large rivers. The comprehensive understanding of SMRS will definitely increase our recognition on earth surface processes and global sea-land interactions.
-
Key words:
- small mountainous rivers /
- source to sink /
- sediment /
- natural environmental change /
- human activities
-

-
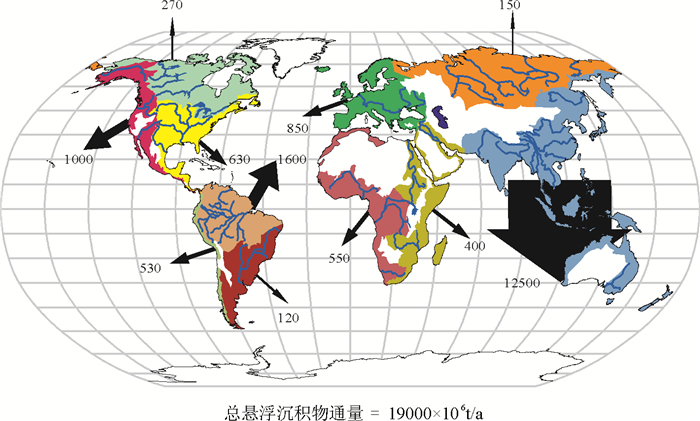
图 1 全球河流入海悬浮沉积物通量示意[2]
Figure 1.
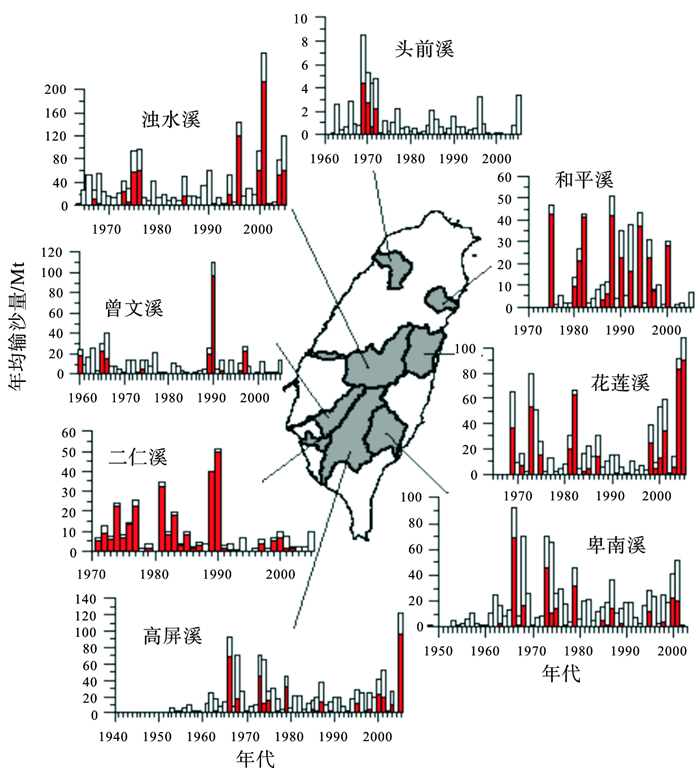
图 3 台湾入海河流悬浮泥沙受台风事件影响显著[42]
Figure 3.
表 1 东海周边(浙闽沿岸及台湾)中小河流基本参数
Table 1. Basic information of medium and small rivers around the East China Sea (Along Zhejiang and Fujian coasts and in Taiwan)
省份 名称 长度/km 流域面积/103km2 注入 年径流量/(m3/s) 径流总量/108m3 输沙量/万t 浙江省 钱塘江 688 55.6 杭州湾 1400 442, 342[50] 440[ 50], 608, 668 瓯江 388 18.0 温州湾 457, 615 144, 202 232, 273 飞云江 176, 185 3.73 东海 144 40 42 灵江 198 6.61 台州湾 122 51.7 112 甬江 121 5.03 杭州湾 136 43 172 椒江 202 6.75 东海 212 67[ 50] 840[ 50] 鳌江 82, 124 2.54 东海 96.4 17.5 43 福建省 闽江 577 61.0 东海 1779 616[ 50], 624[ 51] 824,716[ 52], 770[ 50] 九龙江 258 14.7 泉州湾 391, 147[ 50] 147[50], 82[53] 330, 212, 310[50] 晋江 182 5.63 泉州湾 184 49 254 木兰溪 168 1.73 兴化湾 31 10 47 台湾西部[49, 54] 浊水溪 186 3.1 台湾海峡 117 37 6555, 3000~6000 头前溪 63 0.5 台湾海峡 21 6.6 100~200 八掌溪 81 0.6 台湾海峡 20 6.4 200 曾文溪 138 1.2 台湾海峡 33 10.4 900~1600 乌溪 119 2 台湾海峡 114 36 400~1000 大安溪 96 0.63 台湾海峡 30 9.5 300~500 淡水河 159 2.73 台湾海峡 180 57 100~300 -
[1] Smith S V, Swaney D P, Talaue-Mcmanus L, et al. Humans, hydrology, and the distribution of inorganic nutrient loading to the ocean[J]. BioScience, 2003, 53(3): 235-245. doi: 10.1641/0006-3568(2003)053[0235:HHATDO]2.0.CO;2
[2] Milliman J D, Farnsworth K L. River Discharge to the Coastal Ocean:A Global Synthesis[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2011.
[3] Bi L, Yang S Y, Li C, et al. Geochemistry of river‐borne clays entering the East China Sea indicates two contrasting types of weathering and sediment transport processes[J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2015, 16(9): 3034-3052. doi: 10.1002/2015GC005867
[4] Li C, Yang S Y, Zhao J X, et al. The time scale of river sediment source-to-sink processes in East Asia[J]. Chemical Geology, 2016, 446: 138-146. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2016.06.012
[5] Wheatcroft R A, Goñ i M A, Hatten J A, et al. The role of effective discharge in the ocean delivery of particulate organic carbon by small, mountainous river systems[J]. Limnology and Oceanography, 2010, 55(1): 161-171. doi: 10.4319/lo.2010.55.1.0161
[6] Salomons W. European catchments: catchment changes and their impact on the coast[J]. Biochemical & Biophysical Research Communications, 2004, 228(3): 852-858.
[7] Kremer H H. River catchment-coastal sea interaction and human dimensions[J]. Regional Environmental Change, 2004, 4(1): 1-4. doi: 10.1007/s10113-003-0066-3
[8] 高抒.美国《洋陆边缘科学计划2004》述评[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2005, 25(1):119-123. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hydzydsjdz200501018
GAO Shu. Comments on the "NSF margins program science plans 2004"[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2005, 25(1): 119-123. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hydzydsjdz200501018
[9] 张经.关于陆-海相互作用的若干问题[J].科学通报, 2011, 56(24): 1956-1966. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=kxtb201124002
ZHANG Jing.On the critical issues of land-ocean interactions in coastal zones[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2011, 56(24): 1956-1966.] http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=kxtb201124002
[10] Walsh J P, Wiberg P L, Aalto R, et al. Source-to-sink research: economy of the Earth's surface and its strata[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2016, 153: 1-6. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2015.11.010
[11] Milliman J D, Syvitski J P M. Geomorphic/tectonic control of sediment discharge to the ocean: the importance of small mountainous rivers[J]. The Journal of Geology, 1992, 100(5): 525-544. doi: 10.1086/629606
[12] Syvitski J P M, Peckham S D, Hilberman R, et al. Predicting the terrestrial flux of sediment to the global ocean: a planetary perspective[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 2003, 162(1-2): 5-24. doi: 10.1016/S0037-0738(03)00232-X
[13] Milliman J D. Sediment discharge to the ocean from small mountainous rivers: the New Guinea example[J]. Geo-Marine Letters, 1995, 15(3-4): 127-133. doi: 10.1007/BF01204453
[14] Milliman J D, Farnsworth K L, Albertin C S. Flux and fate of fluvial sediments leaving large islands in the East Indies[J]. Journal of Sea Research, 1999, 41(1-2): 97-107. doi: 10.1016/S1385-1101(98)00040-9
[15] Farnsworth K L, Milliman J D. Effects of climatic and anthropogenic change on small mountainous rivers: the Salinas River example[J]. Global and Planetary Change, 2003, 39(1-2): 53-64. doi: 10.1016/S0921-8181(03)00017-1
[16] Syvitski J P M, Vörösmarty C J, Kettner A J, et al. Impact of humans on the flux of terrestrial sediment to the global coastal ocean[J]. Science, 2005, 308(5720): 376-380. doi: 10.1126/science.1109454
[17] Vörösmarty C J, Meybeck M, Fekete B, et al. Anthropogenic sediment retention: major global impact from registered river impoundments[J]. Global and Planetary Change, 2003, 39(1-2): 169-190. doi: 10.1016/S0921-8181(03)00023-7
[18] Kuehl S A, Nittrouer C A. Exploring the transfer of Earth surface materials from source to sink[J]. EOS, Transactions American Geophysical Union, 2011, 92(22): 188. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=10.1029/2011EO220007
[19] Romans B W, Castelltort S, Covault J A, et al. Environmental signal propagation in sedimentary systems across timescales[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2016, 153: 7-29. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2015.07.012
[20] Berner R A. Burial of organic carbon and pyrite sulfur in the modern ocean: its geochemical and environmental significance[J]. American Journal of Science, 1982, 282(4): 451-473. doi: 10.2475/ajs.282.4.451
[21] Ludwig W, Amiotte-Suchet P, Munhoven G, et al. Atmospheric CO2 consumption by continental erosion: present-day controls and implications for the last glacial maximum[J]. Global and Planetary Change, 1998, 16-17: 107-120. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0921818198000162
[22] Hedges J I, Keil R G. Sedimentary organic matter preservation: an assessment and speculative synthesis[J]. Marine Chemistry, 1995, 49(2-3): 81-115. doi: 10.1016/0304-4203(95)00008-F
[23] Lyons W B, Nezat C A, Carey A E, et al. Organic carbon fluxes to the ocean from high-standing islands[J]. Geology, 2002, 30(5): 443-446. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(2002)030<0443:OCFTTO>2.0.CO;2
[24] Gomez B, Trustrum N A, Hicks D M, et al. Production, storage, and output of particulate organic carbon: Waipaoa River basin, New Zealand[J]. Water Resources Research, 2003, 39(6): 1161. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/248808588_Production_Storage_and_Output_of_Particulate_Organic_Carbon_Waipaoa_River_Basin_New_Zealand
[25] Carey A E, Gardner C B, Goldsmith S T, et al. Organic carbon yields from small, mountainous rivers, New Zealand[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2005, 32(15): L15404. doi: 10.1029/2005GL023159
[26] Coynel A, Etcheber H, Abril G, et al. Contribution of small mountainous rivers to particulate organic carbon input in the Bay of Biscay[J]. Biogeochemistry, 2005, 74(2): 151-171. doi: 10.1007/s10533-004-3362-1
[27] Hilton R G, Galy A, Hovius N, et al. Efficient transport of fossil organic carbon to the ocean by steep mountain rivers: An orogenic carbon sequestration mechanism[J]. Geology, 2011, 39(1): 71-74. doi: 10.1130/G31352.1
[28] Hilton R G, Galy A, Hovius N, et al. The isotopic composition of particulate organic carbon in mountain rivers of Taiwan[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2010, 74(11): 3164-3181. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2010.03.004
[29] Schlünz B, Schneider R R. Transport of terrestrial organic carbon to the oceans by rivers: re-estimating flux-and burial rates[J]. International Journal of Earth Sciences, 2000, 88(4): 599-606. doi: 10.1007/s005310050290
[30] Galy V, Beyssac O, France-Lanord C, et al. Recycling of graphite during Himalayan erosion: a geological stabilization of carbon in the crust[J]. Science, 2008, 322(5903): 943-945. doi: 10.1126/science.1161408
[31] Bouchez J, Beyssac O, Galy V, et al. Oxidation of petrogenic organic carbon in the Amazon floodplain as a source of atmospheric CO2[J]. Geology, 2010, 38(3): 255-258. doi: 10.1130/G30608.1
[32] Mckee B. The transport, transformation, and fate of carbon in riverdominated ocean margins[C].2003.
[33] Keil R G, Mayer L M, Quay P D, et al. Loss of organic matter from riverine particles in deltas[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1997, 61(7): 1507-1511. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(97)00044-6
[34] Aller R C, Heilbrun C, Panzeca C, et al. Coupling between sedimentary dynamics, early diagenetic processes, and biogeochemical cycling in the Amazon-Guianas mobile mud belt: coastal French Guiana[J]. Marine Geology, 2004, 208(2-4): 331-360. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2004.04.027
[35] Leithold E L, Blair N E. Watershed control on the carbon loading of marine sedimentary particles[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2001, 65(14): 2231-2240. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(01)00593-2
[36] Goñi M A, Yunker M B, Macdonald R W, et al.The supply and preservation of ancient and modern components of organic carbon in the Canadian Beaufort Shelf of the Arctic Ocean[J]. Marine Chemistry, 2005, 93(1): 53-73. doi: 10.1016/j.marchem.2004.08.001
[37] Leithold E L, Blair N E, Wegmann K W. Source-to-sink sedimentary systems and global carbon burial: a river runs through it[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2016, 153: 30-42. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2015.10.011
[38] Yang S Y, Bi L, Li C, et al. Major sinks of the Changjiang (Yangtze River)-derived sediments in the East China Sea during the late Quaternary[J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 2016, 429(1): 137-152. doi: 10.1144/SP429.6
[39] Raymo M E, Ruddiman W F. Tectonic forcing of late Cenozoic climate[J]. Nature, 1992, 359(6391): 117-122. doi: 10.1038/359117a0
[40] Wang P. Cenozoic deformation and the history of Sea‐land interactions in Asia[C]//Clift P, KuhntW, Wang P, et al, Eds. Continent-Ocean Interactions Within East Asian Marginal Seas. Washington, DC: The American Geophysical Union, 2004: 1-22.
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/242531708_Cenozoic_Deformation_and_History_of_Sea-Land_Interaction_in_Asia [41] Liu J T, Hsu R T, Hung J J, et al. From the highest to the deepest: the Gaoping river-Gaoping submarine canyon dispersal system[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2016, 153: 274-300. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2015.10.012
[42] Kao S J, Milliman J D. Water and sediment discharge from small mountainous rivers, Taiwan: the roles of lithology, episodic events, and human activities[J]. The Journal of Geology, 2008, 116(5): 431-448. doi: 10.1086/590921
[43] Dadson S J, Hovius N, Chen H, et al. Links between erosion, runoff variability and seismicity in the Taiwan orogen[J]. Nature, 2003, 426(6967): 648-651. doi: 10.1038/nature02150
[44] Goldsmith S T, Carey A E, Lyons W B, et al. Extreme storm events, landscape denudation, and carbon sequestration: Typhoon Mindulle, Choshui River, Taiwan[J]. Geology, 2008, 36(6): 483-486. doi: 10.1130/G24624A.1
[45] Xu K H, Milliman J D, Li A C, et al. Yangtze-and Taiwan-derived sediments on the inner shelf of East China Sea[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 2009, 29(18): 2240-2256. doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2009.08.017
[46] Li C S, Shi X F, Kao S J, et al. Rare earth elements in fine-grained sediments of major rivers from the high-standing island of Taiwan[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2013, 69: 39-47. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2013.03.001
[47] Liu J T, Kao S J, Huh C A, et al. Gravity flows associated with flood events and carbon burial: Taiwan as instructional source area[J]. Annual Review of Marine Science, 2013, 5(1): 47-68. doi: 10.1146/annurev-marine-121211-172307
[48] Milliman J D, Lee T Y, Huang J C, et al. Impact of catastrophic events on small mountainous rivers: Temporal and spatial variations in suspended-and dissolved-solid fluxes along the Choshui River, central western Taiwan, during typhoon Mindulle, July 2-6, 2004[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2017, 205: 272-294. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2017.02.015
[49] Liu J P, Liu C S, Xu K H, et al. Flux and fate of small mountainous rivers derived sediments into the Taiwan Strait[J]. Marine Geology, 2008, 256(1-4): 65-76. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2008.09.007
[50] Zhang J, Liu C L. Riverine composition and estuarine geochemistry of particulate metals in China—weathering features, anthropogenic impact and chemical fluxes[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2002, 54(6): 1051-1070. doi: 10.1006/ecss.2001.0879
[51] 徐茂泉.闽江口表层沉积物中碎屑矿物的研究[J].厦门大学学报:自然科学版, 1995, 34(3): 466-469. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-XDZK405.021.htm
XU Maoquan.Studies on fragmentary minerals in surface sediments of the MinjiangEstuary[J]. Journal of Xiamen University: Natural Science, 1995, 34(3): 466-469.] http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-XDZK405.021.htm
[52] 刘苍字, 贾海林, 陈祥锋.闽江河口沉积结构与沉积作用[J].海洋与湖沼, 2001, 32(2): 177-184. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.2001.02.009
LIU Cangzi, JIA Hailin, CHEN Xiangfeng.Sedimentary texture and sedimentation in the MinjiangRiver[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinia, 2001, 32(2): 177-184.] doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.2001.02.009
[53] 徐茂泉.九龙江口表层沉积中碎屑矿物的研究[J].厦门大学学报:自然科学版, 1994, 33(5): 675-680. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199400507045
XU Maoquan.Studies on fragmentary minerals of surface sediments in Jiulong River Estuary[J]. Journal of Xiamen University: Natural Science, 1994, 33(5): 675-680.] http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199400507045
[54] Milliman J D, Kao S J. Hyperpycnal discharge of fluvial sediment to the ocean: impact of Super-Typhoon Herb (1996) on Taiwanese rivers[J]. The Journal of Geology, 2005, 113(5): 503-516. doi: 10.1086/431906
[55] Chen J S, Wang F Y. Chemical composition of river particulates in eastern China[J]. GeoJournal, 1996, 40(1): 31-37.
[56] 李伯根, 谢钦春, 夏小明, 等.椒江河口最大浑浊带悬沙粒径分布及其对潮动力的响应[J].泥沙研究, 1999(1): 18-26. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0468-155X.1999.01.004
LI Bogen, XIE Qinchun, XIA Xiaoming, et al. Size distribution of suspended sediment in maximum turbidity zone and its response to tidal dynamics in Jiaojiang River Estuary[J]. Journal of Sediment Research, 1999(1): 18-26.] doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0468-155X.1999.01.004
[57] Chen J S, Wang F Y, Li X D, et al. Geographical variations of trace elements in sediments of the major rivers in eastern China[J]. Environmental Geology, 2000, 39(12): 1334-1340. doi: 10.1007/s002540000224
[58] 蔡锋, 苏贤泽, 陈锋, 等.彩沙示踪研究九龙江河口湾北侧湾口海区底沙运动[J].海洋环境科学, 2000, 19(4): 36-40. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-6336.2000.04.009
CAI Feng, SU Xianze, CHEN Feng, et al. Bedload movement in north mouth of Jiulongjiang Estuary using colored sand tracing[J]. Marine Environmental Science, 2000, 19(4): 36-40.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-6336.2000.04.009
[59] 高建华, 高抒, 董礼先, 等.鸭绿江河口地区沉积物特征及悬沙输送[J].海洋通报, 2003, 22(5): 26-33. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6392.2003.05.005
GAO Jianhua, GAO Shu, DONG Lixian, et al. Sediment distribution and suspended sediment transport in Yalu River Estuary[J]. Marine Science Bulletin, 2003, 22(5): 26-33.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6392.2003.05.005
[60] 高建华, 李军, 汪亚平, 等.鸭绿江河口及近岸海域沉积物中重矿物组成、分布及其沉积动力学意义[J].海洋学报, 2009, 31(3): 84-94. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-4193.2009.03.010
GAO Jianhua, LI Jun, WANG Yaping, et al. Heavy mineral distributions and their implications for sediment dynamics in the Yalu Estuary and its adjacent sea area[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2009, 31(3): 84-94.] doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-4193.2009.03.010
[61] 李东义, 陈坚, 王爱军, 等.闽江河口洪季悬浮泥沙特征及输运过程[J].海洋工程, 2009, 27(2): 70-80. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9865.2009.02.012
LI Dongyi, CHEN Jian, WANG Aijun, et al. Suspended sediment characteristics and transport in the Minjiang estuary during flood seasons[J]. The Ocean Engineering, 2009, 27(2): 70-80.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9865.2009.02.012
[62] Chen C H, Lu H Y, Lin W, et al. Thermal event records in SE China coastal areas: constraints from monazite ages of beach sands from two sides of the Taiwan Strait[J]. Chemical Geology, 2006, 231(1-2): 118-134. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2006.01.023
[63] 徐勇航, 陈坚.台湾海峡西岸闽江口和九龙江口沉积物中碎屑锆石铀-铅定年及物源意义[J].海洋学报, 2010, 32(4): 110-117. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hyxb201004011
XU Yonghang, CHEN Jian. Uranium-lead dating of detrial zircons from the Minjiang and Jiulong Estuaries in the western coast of the Taiwan Strait: implication for itsprovenance[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2010, 32(4): 110-117.] http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hyxb201004011
[64] Deng K, Yang S Y, Li C, et al. Detrital zircon geochronology of river sands from Taiwan: Implications for sedimentary provenance of Taiwan and its source link with the east China mainland[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2017, 164: 31-47. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2016.10.015
[65] Simpson G, Castelltort S. Model shows that rivers transmit high-frequency climate cycles to the sedimentary record[J]. Geology, 2012, 40(12): 1131-1134. doi: 10.1130/G33451.1
-



 下载:
下载: