Assemblage and distribution of planktonic foraminifera in the upper water layer of southern South China Sea
-
摘要:
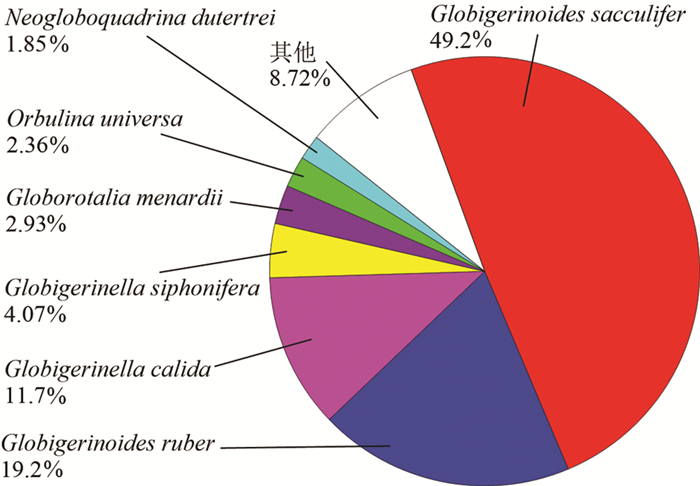
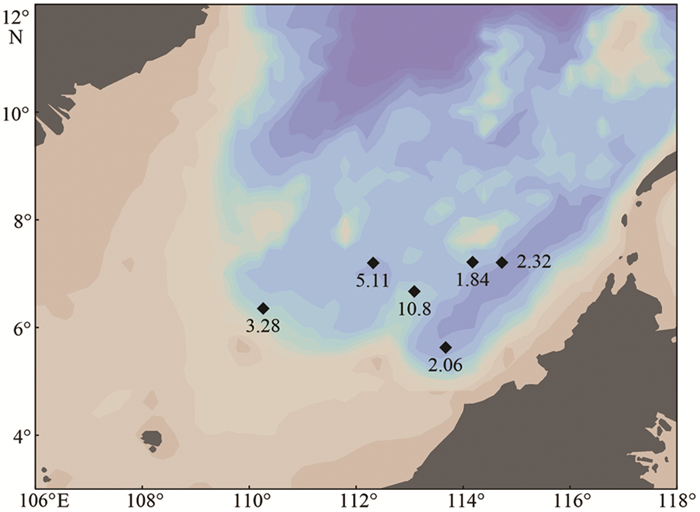
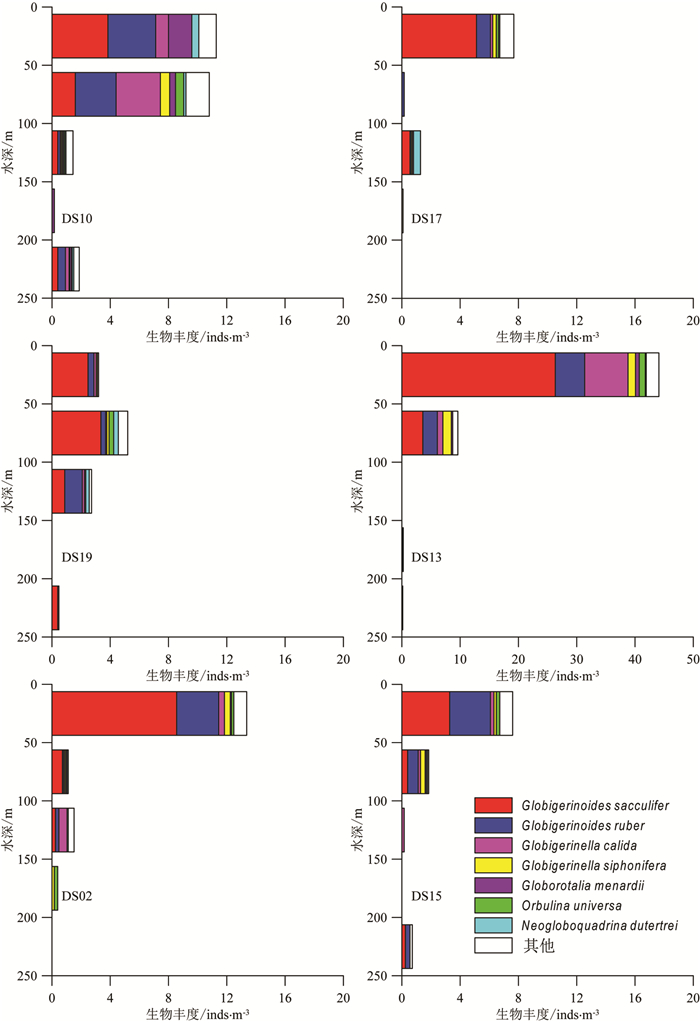
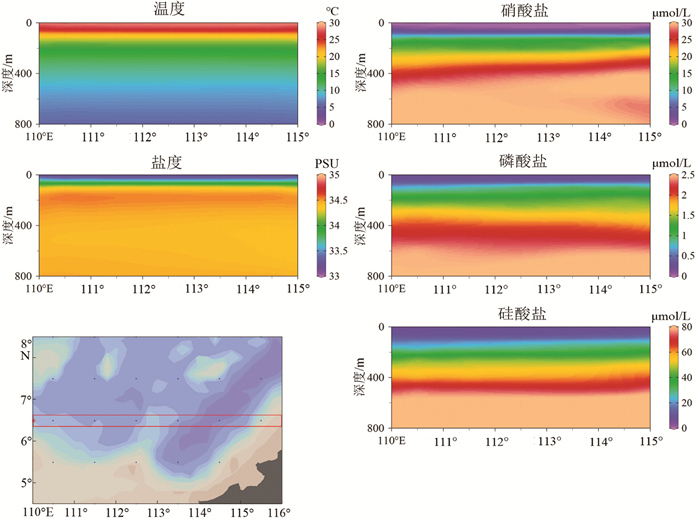
通过分析2012年4月在南海南部获取的浮游生物拖网样品,对水体中浮游有孔虫的区域分布特征及其影响因素进行了初步探讨。南海南部上层水体中共鉴定出现代浮游有孔虫19种,其中优势种为Globigerinoides sacculifer、Globigerinoides ruber、Globigerinella calida、Globigerinella siphonifera、Globorotalia menardii、Orbulina universa、Neogloboquadrina dutertrei。浮游有孔虫种属组成整体上呈现为热带-亚热带群落特征,浮游有孔虫生物丰度与西太平洋北赤道流区域的生物丰度相当。南海南部春季上层水体中浮游有孔虫整体表现为西高东低的区域分布特征,在垂直分布上浮游有孔虫集中分布在上部0~50m水层中,50m以深水体中浮游有孔虫生物丰度迅速降低。认为浮游有孔虫的分布受到温度、水体层化、初级生产力等多方面环境因子的综合作用。个别深水种(如Globorotalia menardii)出现了主要分布在0~50 m水深的特殊现象。
Abstract:Modern planktonic foraminifera are quantitatively analyzed for 30 stratified towing samples collected from 6 sites in the southern South China Sea (SCS) in April, 2012. 19 planktonic foraminifera species ae identified from the upper 250m of water column, and most of them are tropical and subtropical warm water species. The faunal assemblage is dominated by Globigerinoides sacculifer, Globigerinoides ruber, Globigerinella calida, Globigerinella siphonifera , Globorotalia menardii , Orbulina universa, Neogloboquadrina dutertrei. The foraminiferal abundance is higher in the west part of area than that in the east region. High abundance value occurs in the upper 0~50 m of water column, and then quickly decrease with water depth. Some subsurface dwellers, such as Globorotalia menardii, are also found in high abundance in the upper 0~50 m water column. This distribution pattern is believed to be influenced by various factors, such as temperature, water stratification and primary production.
-
Key words:
- plankton tow /
- planktonic foraminifera /
- vertical distribution /
- southern South China Sea
-

-
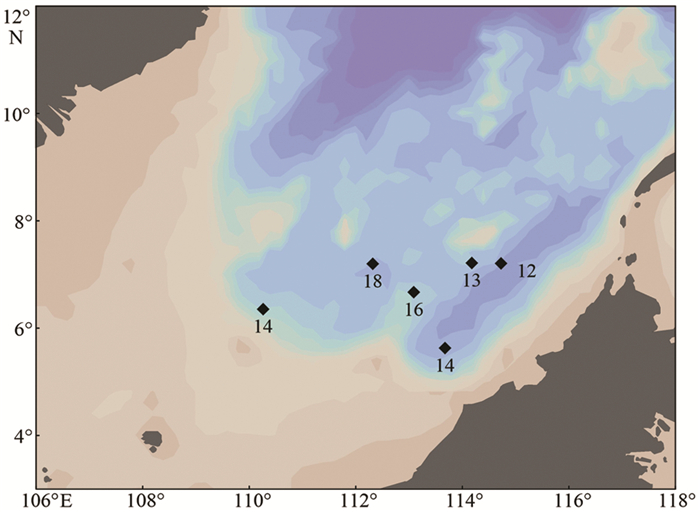
表 1 南海南部各站位采样信息
Table 1. Samplinginformation in the Southern South China Sea
站位 取样位置 取样日期和时间 DS10 7.2°N,112.3°E 2012-05-08-21:01 DS17 7.2°N,114.2°E 2012-04-20-16:16 DS19 7.2°N,114.7°E 2012-04-21-10:39 DS13 6.7°N,113.1°E 2012-05-04-17:14 DS02 6.4°N,110.3°E 2012-05-03-01:17 DS15 5.6°N,113.7°E 2012-04-25-13:30 -
[1] Schiebel R.Plankticforaminiferal sedimentation and the marine calcite budget[J]. Glob.Biogeochem. Cycle, 2002, 16: 1-21. doi: 10.1029/2001GB001398
[2] Kuroyanagi A, Kawahata H. Vertical distribution of living planktonic foraminifera in the seas around Japan[J]. Marine Micropaleontology, 2004, 53: 173-196. doi: 10.1016/j.marmicro.2004.06.001
[3] Manno C, Pavlov A. Living planktonic foraminifera in the Fram Strait (Arctic): absence of diel vertical migration during the midnight sun[J].Hydrobiologia, 2014, 721: 285-295. doi: 10.1007/s10750-013-1669-4
[4] Kucera M. Planktonic foraminifera as tracers of past oceanic environments[J]. Developments in Marine Geology, 2007, 1: 213-262. doi: 10.1016/S1572-5480(07)01011-1
[5] Pflaumann U, Jian Z, Modern distribution patterns of planktonic foraminifera in the South China Sea and western Pacific: A new transfer technique to estimate regional sea-surface temperatures[J]. Marine Geology, 1999, 156: 41-83. doi: 10.1016/S0025-3227(98)00173-X
[6] Darling K F, Kucera M, Pudsey C J, et al. Molecular evidence links cryptic diversification in polar planktonic protists to Quaternary climate dynamics[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2004, 101: 7657-7662. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0402401101
[7] Chen M T, Wang C H, Huang C Y, et al. A late Quaternary planktonic foraminifer faunal record of rapid climatic changes from the South China Sea[J]. Marine Geology, 1999, 156: 85-108. doi: 10.1016/S0025-3227(98)00174-1
[8] Xiang R, Chen M, Li Q, et al. Planktonic foraminiferal records of East Asia monsoon changes in the southern South China Sea during the last 40000 years[J]. Marine Micropaleontology, 2009, 73: 1-13. doi: 10.1016/j.marmicro.2009.06.004
[9] Katz M E, Cramer B S, Franzese A, et al. Traditional and emerging geochemical proxies in foraminifera[J]. Journal of Foraminiferal Research, 2010, 40: 165-192. doi: 10.2113/gsjfr.40.2.165
[10] Mix A C, Morey A E, Pisias N G, et al. Foraminiferal faunal estimates of paleotemperature: Circumventing the no-analog problem yields cool ice age tropics[J]. Paleoceanography, 1999, 14: 350-359. doi: 10.1029/1999PA900012
[11] Barker S, Elderfield H, Foraminiferal calcification response to glacial-interglacial changes in atmospheric CO2[J]. Science, 2002, 297: 833-836. doi: 10.1126/science.1072815
[12] Bijma J, Spero H, Lea D. Reassessing foraminiferal stable isotope geochemistry: Impact of the oceanic carbonate system (experimental results) [C]// Fischer G, Wefer G, eds.Use of proxies in paleoceanography-Examples from the South Atlantic. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, 1999: 489-512.
[13] Foster G. Seawater pH, pCO2 and [CO32-] variations in the Caribbean Sea over the last 130 kyr: a boron isotope and B/Ca study of plankticforaminifera[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2008, 271: 254-266. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2008.04.015
[14] Hall J M, Chan L H. Ba/Ca in Neogloboquadrina pachyderma as an indicator of deglacial meltwater discharge into the western Arctic Ocean[J]. Paleoceanography, 2004, 19(1), doi:10.1029/2003PA000910.
[15] Moy A D, Howard W R, Bray S G, et al. Reduced calcification in modern Southern Ocean planktonic foraminifera[J]. Nature Geoscience, 2009, 2: 276-280. doi: 10.1038/ngeo460
[16] Russell A D, Hönisch B, Spero H J, et al. Effects of seawater carbonate ion concentration and temperature on shell U, Mg, and Sr in cultured planktonic foraminifera[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2004, 68: 4347-4361. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2004.03.013
[17] Weinkauf M F G, Kunze J G, Waniek J J, et al. Seasonal variation in shell calcification of planktonic foraminifera in the NE Atlantic reveals species-specific response to temperature, product ivity, and optimum growth conditions[J]. Plos One, 2016, 11: e0148363. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0148363
[18] Weldeab S, Lea D W, Schneider R R, et al. 155000 years of West African monsoon and ocean thermal evolution[J]. Science, 2007, 316: 1303-1307. doi: 10.1126/science.1140461
[19] Yu J, Elderfield H. Benthic foraminiferal B/Ca ratios reflect deep water carbonate saturation state[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2007, 258: 73-86. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2007.03.025
[20] Bé A W H. An ecological, zoogeographic and taxonomic review of recent planktonic foraminifera[M]// Ramsay A T S. Oceanic Micropaleontology. London: Academic Press, 1977.
[21] 崔喜江, 向荣, 郑范, 等.南海南部活体浮游有孔虫分布特征及其影响因素初探[J].热带海洋学报, 2006, 25:25-30. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5470.2006.04.005
CUI Xijiang, XIANG Rong, ZHENG Fan, et al. A preliminary study of living planktonic foraminifera distribution and its affecting factors in southern South China Sea[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography.2006, 25: 25-30. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5470.2006.04.005
[22] 向荣, 陈木宏, 张兰兰, 等.南海北部秋季活体浮游有孔虫的组成与分布[J].地球科学:中国地质大学学报, 2010(1):10. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqkx201001001
XIANG Rong, CHEN Muhong, ZHANG Lanlan, et al. Compositions and distribution of living planktonic foraminifera in Autumn waters of the Northern South China Sea [J]. Earth Science-Journal of China University of Geosciences, 2010(1):10. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqkx201001001
[23] 罗琼一, 金海燕, 翦知湣, 等.南海现代浮游有孔虫的垂直分布及其古海洋学意义[J].第四纪研究, 2015, 35: 1342-1353. doi: 10.11928/j.issn.1001-7410.2015.06.04
LUO Qiongyi, JIN Haiyan, JIAN Zhimin, et al. Vertical distribution of living planktonic foraminifera in the northern South China Sea and its paleoceanographic implications [J]. Quarternary Sciences, 2015, 35: 1342-1353. doi: 10.11928/j.issn.1001-7410.2015.06.04
[24] 方文东, 黄企洲, 邱章, 等.春夏季季风转换期南海南部的异常表层水[J].热带海洋学报, 2001, 20: 77-81. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5470.2001.01.010
FANG Wendong, HUANG Qizhou, QIU Zhang, et al. Anomalous sea surface water in southern South China Sea during spring to summer monsoon transition[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2001, 20: 77-81. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5470.2001.01.010
[25] Garcia H, Locarnini R, Boyer T, et al. Nutrients (Phosphate, Nitrate, Silicate) [M]//World Ocean Atlas. US Gov. Printing Office, Washington, DC, 2010: 71.
[26] 万随, 翦知湣, 成鑫荣, 等.南沙海区浮游有孔虫通量及其壳体化学性质的季节变化[J].中国科学:地球科学, 2010, 40: 881-892. http://cpfd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CPFDTOTAL-ZUGS200910001326.htm
WAN Sui, JIAN Zhimin, CHENG Xinrong, et al. Seasonal variations in planktonic foraminiferal flux and the chemical properties of their shells in the southern South China Sea[J]. Science China:Earth Science, 2010, 40: 881-892. http://cpfd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CPFDTOTAL-ZUGS200910001326.htm
[27] Lin H L, Hsieh H Y. Seasonal variations of modern planktonic foraminifera in the South China Sea[J]. Deep Sea Research Part Ⅱ: Topical Studies in Oceanography, 2007, 54: 1634-1644. doi: 10.1016/j.dsr2.2007.05.007
[28] 张凯南, 王珍岩, 王保铎. 2012年春季南海南部不同水团上层海水中悬浮体分布特征及其物源分析[J].海洋科学, 2014, 38(3):26-36. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hykx201403005
ZHANG Kainan, WANG Zhenyan, WANG Baoduo.Distribution characteristic and provenance of suspended matter in upper water of the southern South China Sea during the spring of 2012[J]. Marine Sciences, 2014, 38(3): 26-36. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hykx201403005
[29] 柯志新, 黄良民, 李刚, 等.春末夏初巽他陆架表层水体的叶绿素粒级结构及其和营养盐的关系[J].海洋学报, 2012, 34: 190-196. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hyxb201203024
KE Zhixin, HUANG Liangmin, LI Gang, et al. Size structure of chlorophyll a in relation to environmental factors in surface waters of Sunda shelf during late spring and early summer[J]. Acta Oceanological Sinica, 2012, 34: 190-196. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hyxb201203024
[30] 赵辉, 齐义泉, 王东晓, 等.南海叶绿素浓度季节变化及空间分布特征研究[J].海洋学报, 2005, 27(4):45-52. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-4193.2005.04.006
ZHAO Hui, QI Yiquan, WANG Dongxiao, et al. Study on the features of chlorophyll-a derived from SeaWiFS in the South China Sea[J]. Acta Oceanological Sinica, 2005, 27(4):45-52. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-4193.2005.04.006
[31] 朱根海, 宁修仁, 蔡昱明, 等.南海浮游植物种类组成和丰度分布的研究[J].海洋学报, 2003, 25:8-23. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10384-1014227619.htm
ZHU Genhai, NING Xiuren, CAI Yuming, et al. Studies on species composition and abundance distribution of phytoplankton in the South China Sea[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2003, 25: 8-23. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10384-1014227619.htm
[32] 张兰兰, 陈木宏, 陆钧, 等.南海南部上层水体中多孔放射虫的组成与分布特征[J].热带海洋学报, 2005, 24: 55-64. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5470.2005.03.008
ZHANG Lanlan, CHEN Muhong, LU Jun, et al. Living polycystine radiolarian fauna in upper water column of southern South China Sea and its distribution[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2005, 24: 55-64. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5470.2005.03.008
[33] Li B H, Jian Z M, Wang P X.Pulleniatinaobliquiloculata as a paleoceanographic indicator in the southern Okinawa Trough during the last 20000 years[J]. Marine Micropaleontology, 1997, 32(1-2): 59-69. doi: 10.1016/S0377-8398(97)00013-3
[34] Xu J, Wang P X, Huang B Q, et al. Response of planktonic foraminifera to glacial cycles: Mid-Pleistocene change in the Southern South China Sea[J]. Marine Micropaleontology, 2005, 54(1-2): 89-105. doi: 10.1016/j.marmicro.2004.09.005
[35] An B, Li T, Liu J, et al. Spatial distribution and controlling factors of planktonic foraminifera in the modern western Pacific[J]. Quaternary International, 2018, 468: 14-23. doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2018.01.003
[36] 万随, 翦知湣, 成鑫荣.赤道西太平洋冬季浮游有孔虫分布与壳体同位素特征[J].第四纪研究, 2011, 31:284-291. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7410.2011.02.10
WAN Sui, JIAN Zhimin, CHENG Xinrong. Distribution of winter living planktonic foraminifers and characteristics to their shell's stable isotopic in the western equatorial Pacific[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2011, 31: 284-291. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7410.2011.02.10
-




 下载:
下载: