Ocean drilling and marine geology in China
-
摘要:
中国的大洋钻探开始于20年前南海的ODP184航次。20年来,中国在国际大洋发现计划(IODP)中的作用大幅度提升,最近5年里在南海实现了三个半IODP航次以探索其裂谷与扩张过程。积极参加国际大洋钻探合作为中国的海洋地质学科带来了深刻的变化,不但将研究区域从近岸扩大到深海,而且壮大了中国深海科学研究队伍。边缘海构造和气候变化低纬驱动两方面的研究进展,就是成功的例子。现在中国为了增强在大洋钻探国际合作的作用,制定了三步走的方针。作为第二步,中国将提供执行钻探航次的钻井平台,从而进入大洋钻探的核心层。与此同时,中国提出在2020年主办国际学术大会,准备制定2023年以后的国际大洋钻探科学计划。对于中国深海科学界来说,这些新任务都将是空前的挑战,是否能够成功将取决于我们在科学上的准备程度。
Abstract:In China, ocean drilling started twenty years ago with the ODP (Ocean Drilling Program) Leg 184 to the South China Sea.Over the twenty years, China has significantly enhanced its contributions to the IODP (International Ocean discovery Program), and 3 ½ IODP expeditions were implemented in the recent 5 years to explore the rifting and drifting processes of the South China Sea. Active participation in the international ocean drilling cooperation has led to profound changes in the marine geology science in China. It has not only geographically extended the research area from costal sea to deep ocean, but promoted the growth of a deep-sea scientific community in the country. Remarkable research progress has been made, for example, in the tectonics of marginal basin and the climate forcing by low-latitude processes. Now China has adopted a three step development strategy to further upgrade its role in the international cooperation. As for the 2nd step, Chins is ready to enter the core group of IODP by providing drilling facilities to implement the IODP expeditions. Meanwhile, China intends to host the next international conference in 2020 to prepare the new ocean drilling science plan beyond 2023. All these new targets present an unprecedented challenge to the Chinese deep-sea community, and the success will depend on its scientific preparation.
-
Key words:
- ocean drilling /
- deep-sea research /
- marine geology /
- South China Sea
-

-
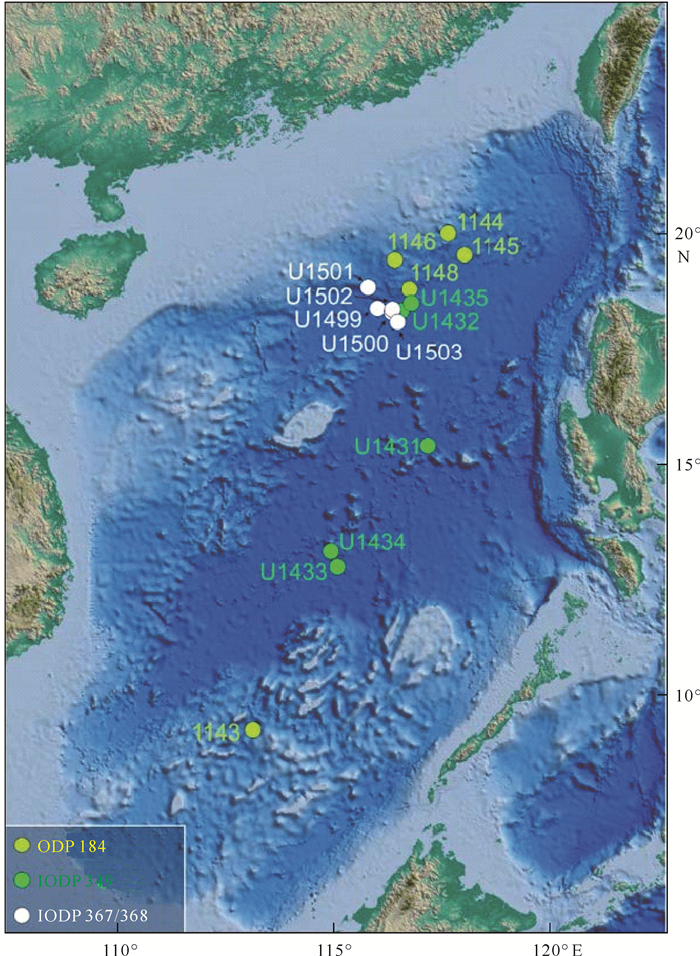
表 1 南海大洋钻探钻井统计
Table 1. Scientific ocean drilling sites and expeditions to the South China Sea
-
[1] 丁仲礼.中国大洋钻探二十年[J].科学通报, 2018, 63(36):3866-3867.
DING Zhongli. Twenty years of ocean drilling in China[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2018, 63(36):3866-3867.
[2] 汪品先.大洋钻探五十年:回顾与前瞻[J].科学通报, 2018, 63(36):3868-3876. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqkxjz201902012
WANG Pinxian. Fifty years of scientific ocean drilling: Review and prospect [J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2018, 63(36):3868-3876. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqkxjz201902012
[3] 翦知湣.进军深海科学前沿——我国参与大洋钻探的进展[J].科学通报, 2018, 63(36):3877-3882.
JIAN Zhimin. Towards the scientific frontier of deep-sea research——progress of China's participation in ocean drilling[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2018, 63(36):3877-3882.
[4] 中国大洋发现计划办公室、海洋地质国家重点实验室(同济大学)编.大洋钻探五十年[M].同济大学出版社, 2018.
IODP-China Office and State Key Laboratory of Marine Geology (Tongji University). Fifty Years of Ocean Drilling [M]. Tongji University Press, 2018.
[5] Wang Pinxian, Prell W, Blum P, et al. Proceeding, Ocean Drilling Program, Initial Reports 184[R]. ODP, Texas A & M, College Station, USA, 2000.
[6] Li Chunfeng, Lin Jian, Kulhanek D K, and the Expedition 349 Scientists. Proceedings of the International Ocean Discovery Program, 349, South China Sea Tectonics[R]. IODP, College Station, Texas, 2015.
[7] Sun Zhen, Stock J, Klaus A, and the Expedition 367 Scientists. International Ocean Discovery Program Preliminary Report, 367, South China Sea Rifted Margin[R]. IODP, College Station, Texas, 2018.
[8] Jian Zhimin, Larsen H C, Alvarez Zarikian C, and the Expedition 368 Scientists. International Ocean Discovery Program Preliminary Report, 368, South China Sea Rifted Margin[R]. IODP, College Station, Texas, 2018.
[9] Wang Luejiang, Wang Pinxian. Late Quaternary paleoceano-graphy of the South China Sea: glacial-interglacial contrasts in an enclosed basin[J]. Paleoceanography, 1990, 5(1): 77-90. doi: 10.1029/PA005i001p00077
[10] Zhang G L, Chen L H, Jackson M G, et al. Evolution of carbonated melt to alkali basalt in the South China Sea[J]. Nat Geosci, 2017, 10: 229-235. doi: 10.1038/ngeo2877
[11] Tapponnier P, Peltzer G, Armijo R. On the mechanism of collision between India and Asia[C]//In: Coward M P, Ries A C (eds). Collision Tectonics. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 1986, 19: 11-157.
[12] Hall R, Breitfeld H T. Nature and demise of the Proto-South China Sea[J]. Bulletin of the Geological Society of Malaysia, 2017, 63:61-76. doi: 10.7186/bgsm63201703
[13] Wang Pinxian, Li Qianyu, Tian Jun, et al. Monsoon influence on planktic δ18O records from the South China Sea[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2016, 142: 26-39. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2016.04.009
[14] 汪品先, 李前裕, 田军, 等.从南海看第四纪大洋碳储库的长周期循环[J].第四纪研究, 2015, 35(6):1297-1319. doi: 10.1093/nsr/nwt028
WANG Pinxian, LI Qianyu, TIAN Jun, et al. Long-term cycles in the carbon reservoir of the Quaternary ocean: a perspective from the South China Sea [J]. National Science Review, 2014, 1: 119-143, doi: 10.1093/nsr/nwt028.
[15] IODP科学规划委员会译.地球、海洋与生命. IODP初始科学计划(2003-2013)[M].上海: 同济大学出版社, 2003.
Integrated Ocean Drilling Program (IODP) Planning Sub-Committee (IPSC). Earth, Ocean and Life. IODP Initial Science Plan: 2003-2013 [M]. Washington D C, International working Group Support Office, 2001.
[16] 国际大洋发现计划2013-2023科学计划书: 照亮地球—过去、现在与未来[M].中国综合大洋钻探计划办公室译.上海: 同济大学出版社, 2011.
IODP. Illustrating Earth's Past, Present and Future: The Science Plan for the International Ocean Discovery Program 2013-2023 [M]. Washington DC: Intergrated Ocean Drilling Program, 2011.
[17] Kopf A, Camerlenghi A, Canals M, et al. The Deep Sea and Sub-Seafloor Frontier[R]. Germany: European Commission, 2012: 1-57.
-



 下载:
下载: