Sedimentary facies and environmental evolution of the Yangtze shoal, eastern China Sea shelf since Late Pleistocene: Evidence from core YZ05
-
摘要:
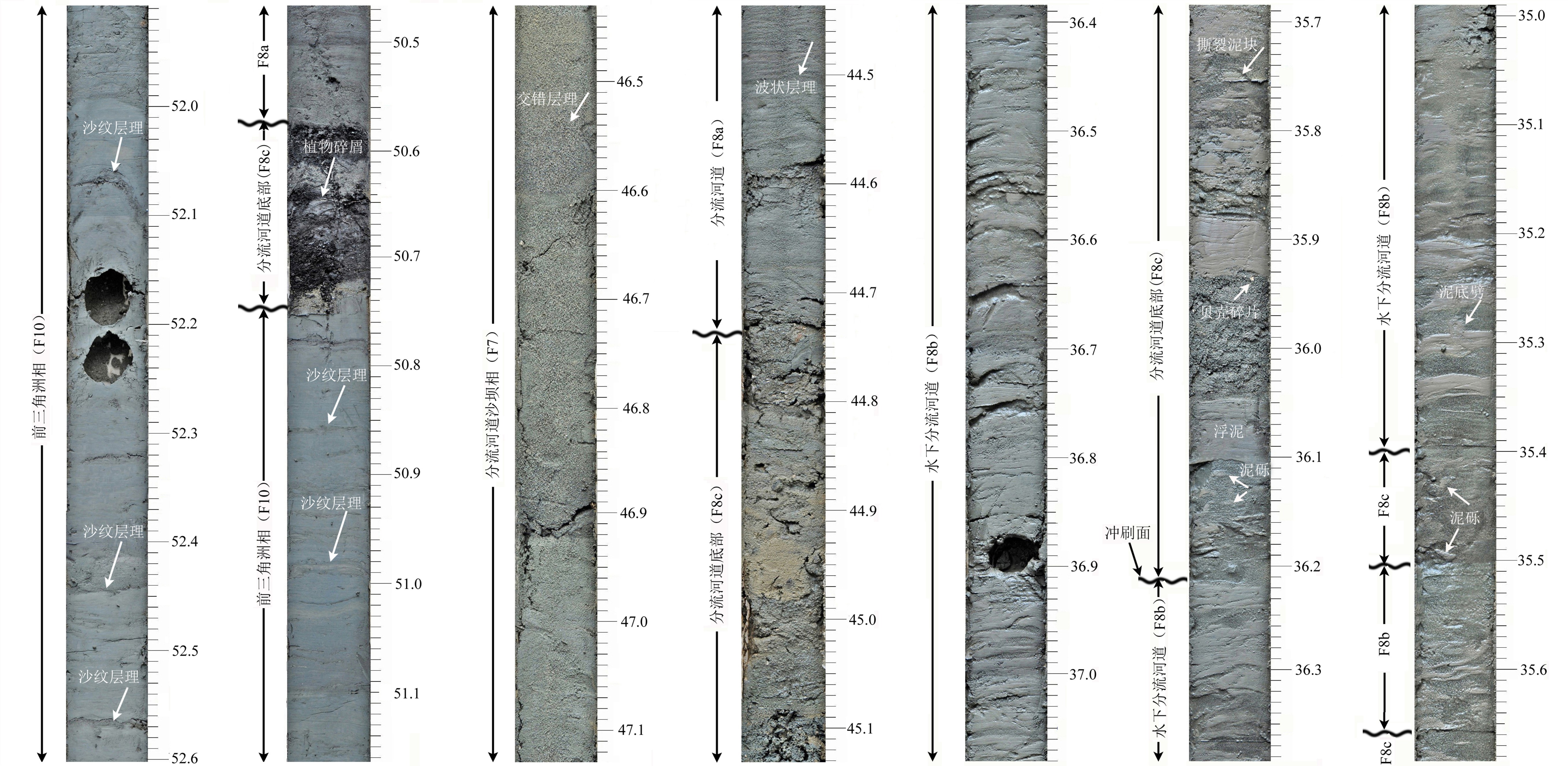
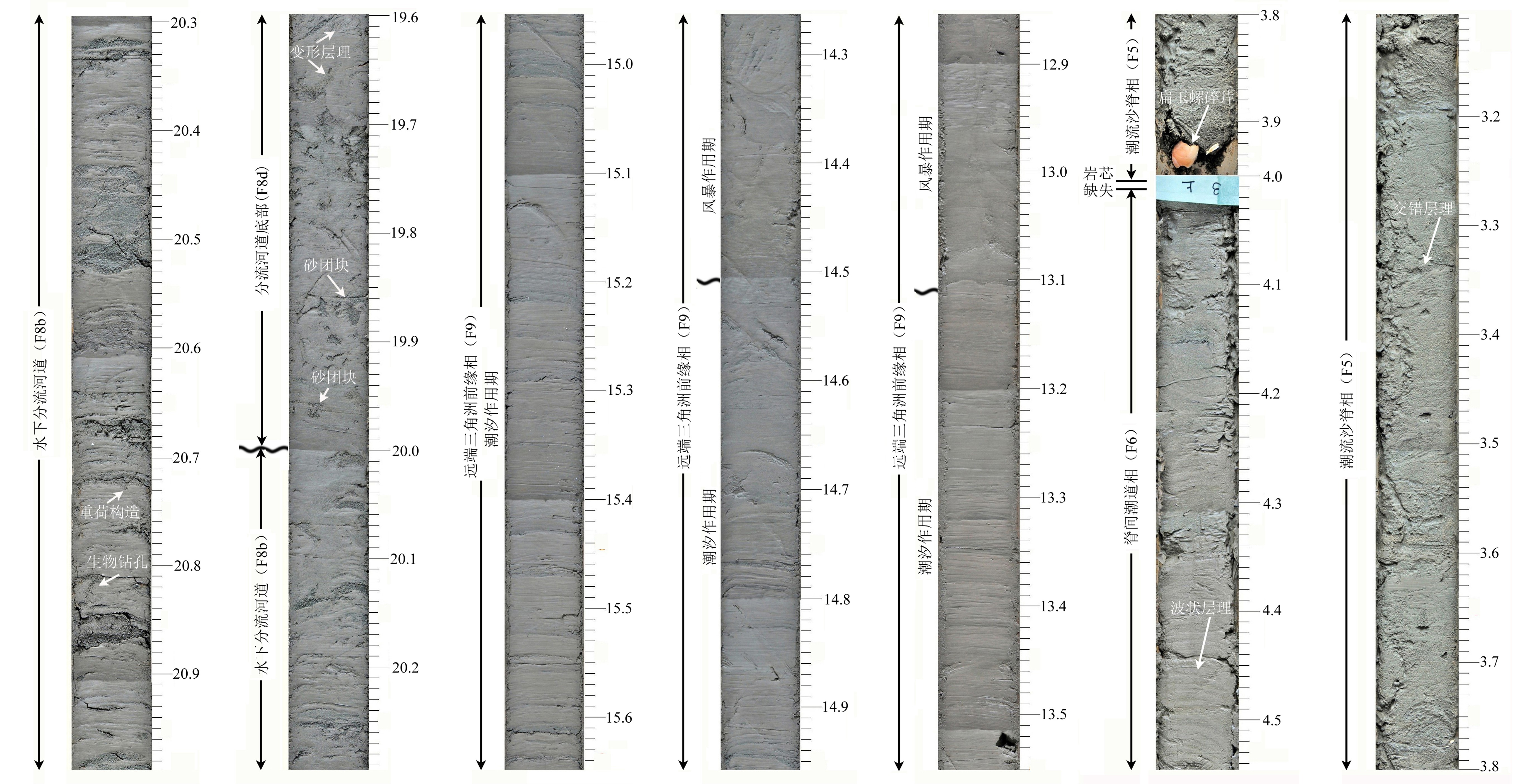
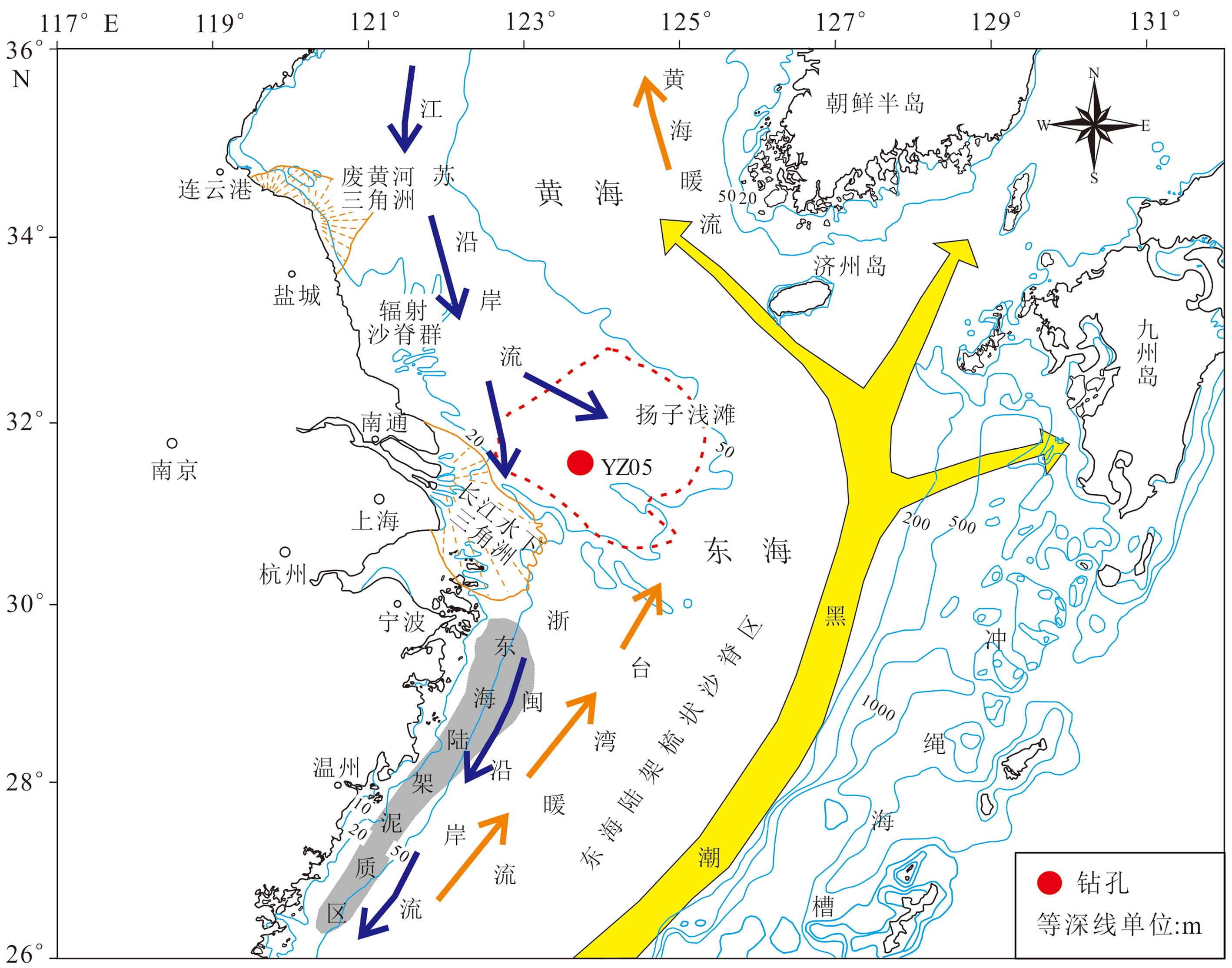
2014年在东海陆架扬子浅滩水深41.5 m处钻获进尺80 m的YZ05孔,该孔沉积相方面的研究成果虽然已经发表过,但略显简单,结合新获得的有孔虫鉴定结果和指示海陆环境变化的Sr/Ba比值,仍有必要对沉积相进行更为精细的研究。根据沉积物颜色、粒度、沉积结构和构造、接触关系和所含化石,共识别出河道-边滩相(F1)、河漫滩相(F2)、泥质潮滩相(F3)、河口湾前缘相(F4)、潮流沙脊相(F5)、脊间潮道相(F6)、分流河道沙坝相(F7)、分流河道相(F8)、远端三角洲前缘相(F9)以及前三角洲相(F10)十种类型。通过相组合与相序列分析,并辅以选择性提取方法获得的可交换态Sr/Ba比值,识别出退积型的河口湾序列和进积型的三角洲序列,它们与冰后期长江三角洲具有相似的沉积层序。AMS14C测年和光释光测年数据指示YZ05孔属于晚更新世以来的沉积。扬子浅滩的物质基础是晚更新世的三角洲堆积体,在全新世早期海面快速上升背景下,堆积成潮流沙脊,改造后形成潮流沙席。
Abstract:A 80 m long core, i.e. the Core YZ05, taking from the Yangtze shoal at the inner shelf of Eastern China Sea, is carefully studied by this paper. Although some preliminary results have been published before, it is still necessary to reexamine the interpretation concerning sedimentary facies and the previous models with the newly acquired information. Based on color, grain size, sedimentary texture and structure, contact relationship and fossils, the Late Pleistocene and Holocene succession of the core YZ05 can be classified into ten environmentally significant facies, which include fluvial channel-point bar (F1), overbank (F2), muddy tidal flat (F3), estuary front (F4), tidal sandy ridge (F5), inter-ridge channel(F6), distributary channel bar (F7), distributary channel (F8), distal delta front (F9) and prodelta (F10). Through the analysis of facies association and facies sequences, with the support of Sr/Ba ratios, a retrogradational estuary sequence and a progradational detaic sequence are recognized, which are similar to the post glacial sequences in the Yangtze River delta. AMS14C and OSL dating suggest that the deposits penetrated by Hole YZ05 are younger than Late Pleistocene. Then the Yangtze Shoal is sourced from the Late Pleistocene deltaic deposits reworked by tidal current.
-
Key words:
- sedimentary facies /
- ancient delta /
- ancient estuary /
- Sr/Ba ratio /
- the Yangtze shoal
-

-
表 1 YZ05钻孔AMS 14C 测年数据[17]
Table 1. Accelerator Mass Spectrometry(AMS)ages of organic sediments and shell samples from the core YZ05
Beta实验室编号 采样深度/m AMS14C惯常年龄/aBP 日历年龄/cal.aBP 测年材料 内插年龄 2σ年龄 416391 0.14 6980±30 7475 7425~7540 贝壳 423299 2.35 7700±30 8165 8115~8210 贝壳 59493 6.0 27377 29315 29167~29462 泥质沉积物 416392 7.17 7420±30 7905 7825~7940 贝壳 59494 12.09 30035±253 32140 31918~32361 泥质沉积物 59495 18.08 34210±420 36810 36328~37292 泥质沉积物 59582 24.08 34474±482 37066 36546~37585 泥质沉积物 59496 30.11 30364±264 32407 32169~32644 泥质沉积物 416393 35.86 >43500 — — 贝壳 416394 41.15 >43500 — — 贝壳 59230 50.36 >47000 — — 丽蚌碎片 表 2 YZ05钻孔不同沉积相单元中的Sr/Ba比值
Table 2. Sr/Ba ratio of sedimentary facies from core YZ05
沉积环境 沉积相单元 深度范围/m 样品数 平均 最大 最小 潮控陆架 潮流沙脊与脊间潮道 0~12.5 41 6.29 11.63 1.61 古三角洲I期 远端三角洲前缘 12.5~19.4 13 8.68 10.24 5.55 古三角洲II期 水下分流河道 19.4~39.0 27 7.62 12.64 3.13 远端三角洲前缘 39.0~40.5 60 8.86 10.10 5.77 古三角洲III期 水上分流河道 40.5~51.9 6 3.66 9.04 0.80 前三角洲 51.9~57.8 53 8.24 12.82 5.84 古河口湾 河口湾前缘 57.8~60.8 9 6.01 9.80 4.90 泥质潮滩 60.8~62.4 8 5.28 6.00 4.03 古河流 河漫滩 62.4~72.3 9 3.79 5.63 2.02 河道-边滩 72.3~80.2 34 1.69 3.22 0.73 -
[1] 龙海燕, 庄振业, 刘升发, 等. 扬子浅滩沙波底形活动性评估[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2007, 27(6):17-24
LONG Haiyan, ZHUANG Zhenye, LIU Shengfa, et al. Activity magnitude of the small-medium subaqueous dunes in the Yangtze Shoal [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2007, 27(6): 17-24.
[2] 叶银灿, 庄振业, 来向华, 等. 东海扬子浅滩砂质底形研究[J]. 中国海洋大学学报, 2004, 34(6):1057-1062
YE Yincan, ZHUANG Zhenye, LAI Xianghua, et al. A study of sandy bedforms on the Yangtze Shoal in the East China Sea [J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 2004, 34(6): 1057-1062.
[3] 朱永其, 曾成开, 金长茂. 东海陆架地貌的初步研究[C]//东海研究文集, 北京: 海洋出版社, 1984: 82-93.
ZHU Yongqi, ZENG Chengkai, JIN Changmao. Primary study on the physiognomy in East China Sea continental shelf[C]//Study Collection on the East China Sea. Beijing: China Ocean Press, 1984: 82-93.
[4] 陈中原, 周长振, 杨文达, 等. 长江口外现代水下地貌与沉积[J]. 东海海洋, 1986, 4(2):32-41
CHEN Zhongyuan, ZHOU Changzhen, YANG Wenda, et al. The Yangtze River estuary of modern underwater landform and sediment [J]. Donghai Marine Science, 1986, 4(2): 32-41.
[5] 秦蕴珊. 东海地质[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1987: 188-192.
QIN Yunshan. Geology of East China Sea[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1987: 188-192.
[6] 金翔龙. 东海海洋地质[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 1992.
JIN Xianglong. Marine Geology of the East China Sea[M]. Beijing: Ocean Press, 1992.
[7] 海洋图集编委会. 渤海 黄海 东海 海洋图集 地质 地球物理图集[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 1990.
Editorial Board for Marine Atlas. Marine Atlas of Bohai Sea Yellow Sea East China Sea Geology and Geophysics[M]. Beijing: China Ocean Press, 1990.
[8] 刘锡清. 中国陆架的残留沉积[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 1987, 7(1):3-16
LIU Xiqing. Relict sediments in China continental shelf [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 1987, 7(1): 3-16.
[9] 刘振夏. 对东海扬子浅滩成因的再认识[J]. 海洋学报, 1996, 18(2):85-92
LIU Zhenxia. Re-recognition of the cause of the Yangtze shoal in the East China Sea [J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 1996, 18(2): 85-92.
[10] Dalrymple R W, Baker E K, Harris P T, et al. Sedimentology and stratigraphy of a tide-dominated, foreland-basin delta (Fly River, Papua New Guinea)[M]//Sidi F H, Nummedal D, Imbert P, et al. Tropical Deltas of Southeast Asia: Sedimentology, Stratigraphy, and Petroleum Geology. SEPM, 2003: 147-173.
[11] Hori K, Saito Y, Zhao Q H, et al. Sedimentary facies of the tide-dominated paleo-Changjiang (Yangtze) estuary during the last transgression [J]. Marine Geology, 2001, 177(3-4): 331-351. doi: 10.1016/S0025-3227(01)00165-7
[12] Hori K, Saito Y, Zhao Q H, et al. Sedimentary facies and Holocene progradation rates of the Changjiang (Yangtze) delta, China [J]. Geomorphology, 2001, 41(2-3): 233-248. doi: 10.1016/S0169-555X(01)00119-2
[13] Zhang X, Lin C M, Dalrymple R W, et al. Facies architecture and depositional model of a macrotidal incised-valley succession (Qiantang River estuary, eastern China), and differences from other macrotidal systems [J]. GSA Bulletin, 2014, 126(3-4): 499-522. doi: 10.1130/B30835.1
[14] 侯志民. 扬子浅滩成因探讨[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学, 2010.
HOU Zhimin. Discussion on the Genesis of the Yangtze Shoal[D]. Qingdao: Ocean University of China, 2010.
[15] 金秉福, 林振宏, 季福武. 海洋沉积环境和物源的元素地球化学记录释读[J]. 海洋科学进展, 2003, 21(1):99-106 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2003.01.013
JIN Bingfu, LIN Zhenhong, JI Fuwu. Interpretation of element geochemical records of marine sedimentary environment and provenance [J]. Advances in Marine Science, 2003, 21(1): 99-106. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2003.01.013
[16] 王爱华. 不同形态锶钡比的沉积环境判别效果比较[J]. 沉积学报, 1996, 14(4):168-173
WANG Aihua. Discriminant effect of sedimentary environment by the Sr/Ba ratio of different existing forms [J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 1996, 14(4): 168-173.
[17] 林文荣, 殷勇, 于革, 等. 扬子浅滩MIS6阶段以来沉积地层及环境演变[J]. 南京大学学报: 自然科学版, 2017, 53(5):912-925
LIN Wenrong, YIN Yong, YU Ge, et al. Characteristics of sedimentary strata and environmental evolution of the Yangtze Shoal since Marine Isotope Stage 6 [J]. Journal of Nanjing University: Natural Sciences, 2017, 53(5): 912-925.
[18] 李家彪. 东海区域地质[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 2008: 27-71.
LI Jiabiao. Regional Geology of East China Sea[M]. Beijing: China Ocean Press, 2008: 27-71.
[19] 杨文达, 崔征科, 张异彪. 东海地质与矿产[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 2010: 65-72.
YANG Wenda, CUI Zhengke, ZHANG Yibiao. East China Sea Geology and Mineral Resources[M]. Beijing: China Ocean Press, 2010: 65-72.
[20] 邵和宾. 长江口及其邻近海域秋季悬浮体组成、分布及其影响因素研究[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学, 2012.
SHAO Hebin. Research on composition, distribution and influencing factors of suspended matters in the Yangtze River estuary in fall[D]. Qingdao: Ocean University of China, 2012.
[21] Liu Z X. Yangtze Shoal: a modern tidal sand sheet in the northwestern part of the East China Sea [J]. Marine Geology, 1997, 137(3-4): 321-330. doi: 10.1016/S0025-3227(96)00026-6
[22] 刘振夏, 夏东兴, 王揆洋. 中国陆架潮流沉积体系和模式[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 1998, 29(2):141-147 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.1998.02.006
LIU Zhenxia, XIA Dongxing, WANG Kuiyang. Tidal depositional systems and patterns of China’s continental shelf [J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 1998, 29(2): 141-147. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.1998.02.006
[23] Liu J P, Xu K H, Li A C, et al. Flux and fate of Yangtze River sediment delivered to the East China Sea [J]. Geomorphology, 2007, 85(3-4): 208-224. doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2006.03.023
[24] Droser M L, Bottjer D J. Ichnofabric of sandstones deposited in high-energy nearshore environments: measurement and utilization [J]. Palaios, 1989, 4(6): 598-604.
[25] Wang A H, Liu J K, Zhang F, et al. Selective extraction of sedimentogenic Strontium and Barium in terrigenous clastic sediments: US, 10151018B2[P]. 2018-12-11.
[26] Pemberton S G, MacEachern J A, Frey R W. Trace fossil facies models: environmental and allostratigraphic significance[M]//Walker R G, James N P. Facies Models, Response to Sea Level Change. St. John’s, Newfoundland: Geological Association of Canada, 1992: 47-72.
[27] Zhang X, Dalrymple R W, Lin C M. Facies and stratigraphic architecture of the late Pleistocene to early Holocene tide-dominated paleo-Changjiang (Yangtze River) delta [J]. GSA Bulletin, 2018, 130(3-4): 455-483. doi: 10.1130/B31663.1
[28] Allen G P, Posamentier H W. Facies and stratal patterns in incised valley complexes: examples from the Recent Gironde Estuary (France) and the Cretaceous Viking Formation (Canada) (abstract)[C]//American Association of Petroleum Geologists Annual Convention, Dallas, Texas, 7-10 April, Abstracts with Programs, 1991: 70.
[29] Hori K, Saito Y, Zhao Q H, et al. Evolution of the coastal depositional systems of the Changjiang (Yangtze) River in response to late Pleistocene-Holocene sea-level changes [J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 2002, 72(6): 884-897. doi: 10.1306/052002720884
[30] Hori K, Saito Y, Zhao Q H, et al. Architecture and evolution of the tide-dominated Changjiang (Yangtze) River delta, China [J]. Sedimentary Geology, 2002, 146(3-4): 249-264. doi: 10.1016/S0037-0738(01)00122-1
[31] Hori K, Saito Y, Zhao Q, et al. Control of incised-valley fill stacking patterns by accelerated and decelerated sea-level rise: the Changjiang example during the last deglaciation [J]. Geo-Marine Letters, 2002, 22(3): 127-132. doi: 10.1007/s00367-002-0105-y
[32] Wang Z H, Saito Y, Hori K, et al. Yangtze offshore, China: highly laminated sediments from the transition zone between subaqueous delta and the continental shelf [J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2005, 62(1-2): 161-168. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2004.08.012
[33] Li G X, Li P, Liu Y, et al. Sedimentary system response to the global sea level change in the East China Seas since the last glacial maximum [J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2014, 139: 390-405. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2014.09.007
[34] 刘宝君. 沉积岩石学[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1980.
LIU Baojun. Sedimentary Petrology[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1980.
[35] 刘英俊. 元素地球化学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1984.
LIU Yingjun. Element Geochemistry[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1984.
[36] Ichaso A A, Dalrymple R W. Eustatic, tectonic and climatic controls on an early syn-rift mixed-energy delta, Tilje Formation (Early Jurassic, Smørbukk Field, offshore mid-Norway)[M]//Martinius A W, Ravnås R, Howell J A, et al. From Depositional Systems to Sedimentary Successions on the Norwegian Continental Margin. Chichester: Wiley Blackwell, 2014, 46: 339-388.
[37] Ichaso A A, Dalrymple R W, Martinius A W. Basin analysis and sequence stratigraphy of the synrift Tilje Formation (Lower Jurassic), Halten terrace giant oil and gas fields, offshore mid-Norway [J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2016, 100(8): 1329-1375. doi: 10.1306/02251614081
[38] Wells J T. Tide-dominated estuaries and tidal rivers [J]. Developments in Sedimentology, 1995, 53: 179-205. doi: 10.1016/S0070-4571(05)80026-3
[39] Sternberg R W, Cacchione D A, Paulso B, et al. Observations of sediment transport on the Amazon subaqueous delta [J]. Continental Shelf Research, 1996, 16(5-6): 697-715. doi: 10.1016/0278-4343(95)00045-3
[40] Dalrymple R W, Choi K. Morphologic and facies trends through the fluvial–marine transition in tide-dominated depositional systems: a schematic framework for environmental and sequence-stratigraphic interpretation [J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2007, 81(3-4): 135-174. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2006.10.002
[41] Feldman H, Demko T. Recognition and prediction of petroleum reservoirs in the fluvial/tidal transition [J]. Developments in Sedimentology, 2015, 68(14): 483-528.
[42] Uehara K, Saito Y, Hori K. Paleotidal regime in the Changjiang (Yangtze) Estuary, the East China Sea, and the Yellow Sea at 6 ka and 10 ka estimated from a numerical model [J]. Marine Geology, 2002, 183(1-4): 179-192. doi: 10.1016/S0025-3227(01)00255-9
-



 下载:
下载: