Characteristics and transport mechanism of suspended particles in offshore area of Zhoushan Islands
-
摘要:
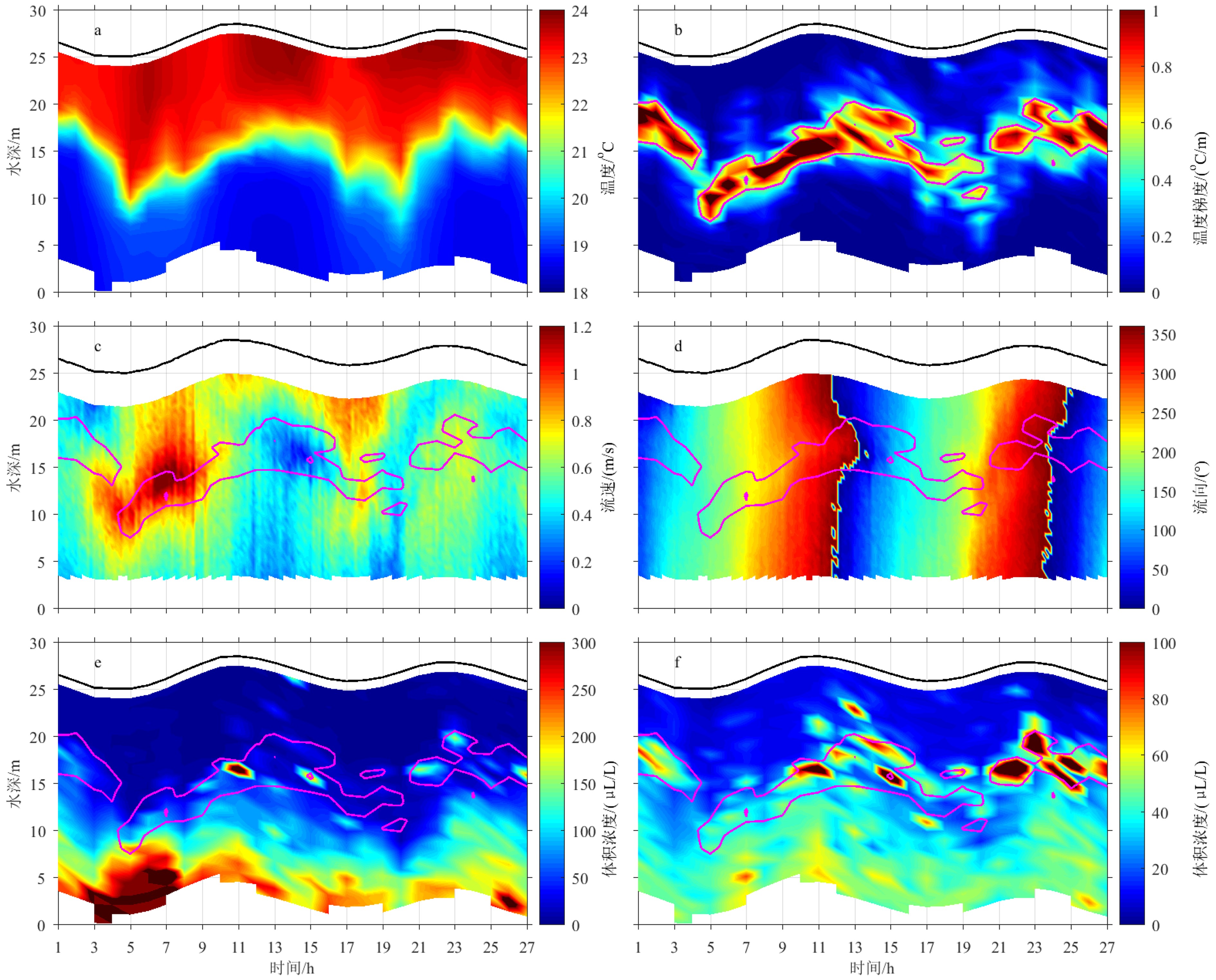
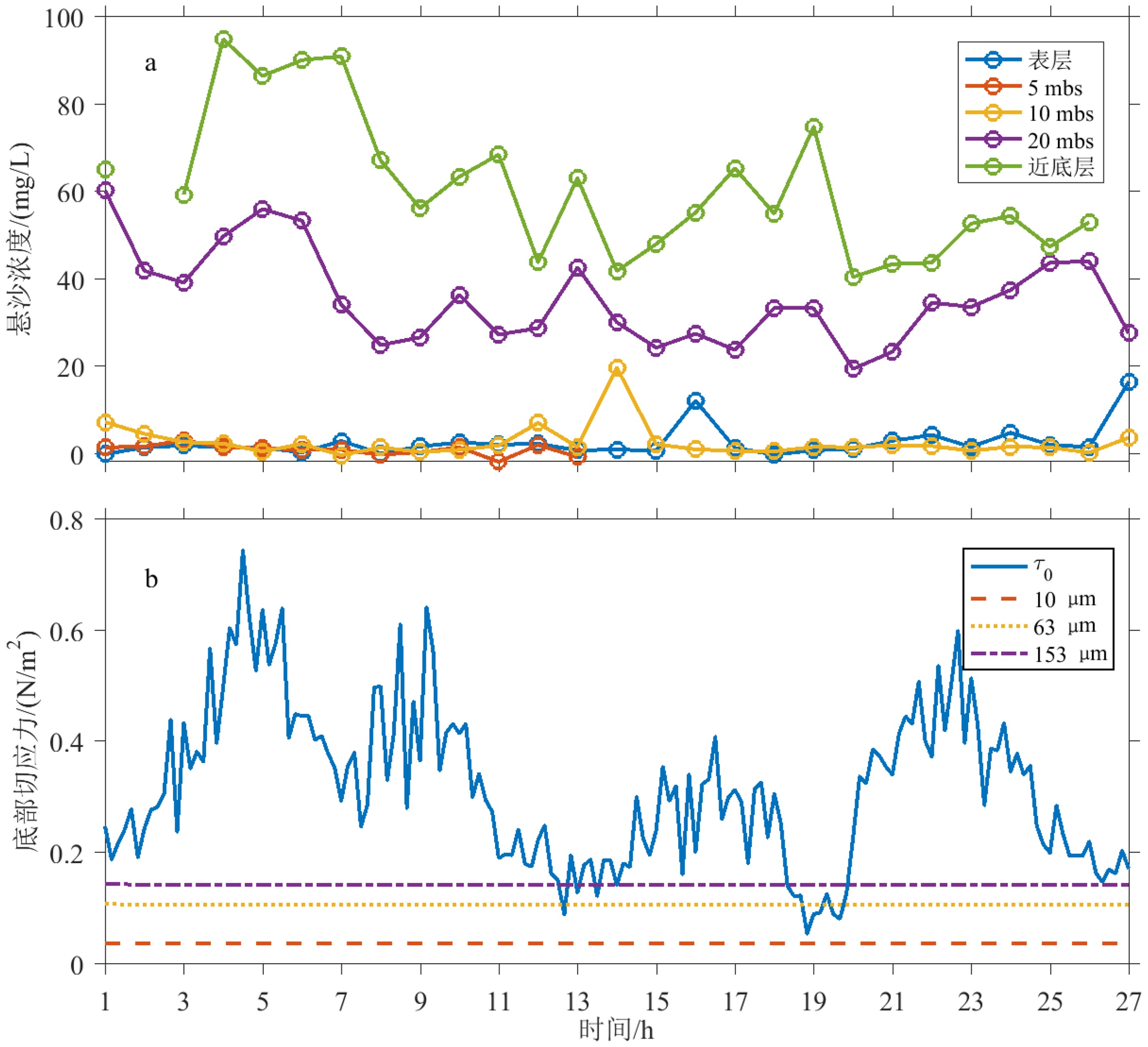
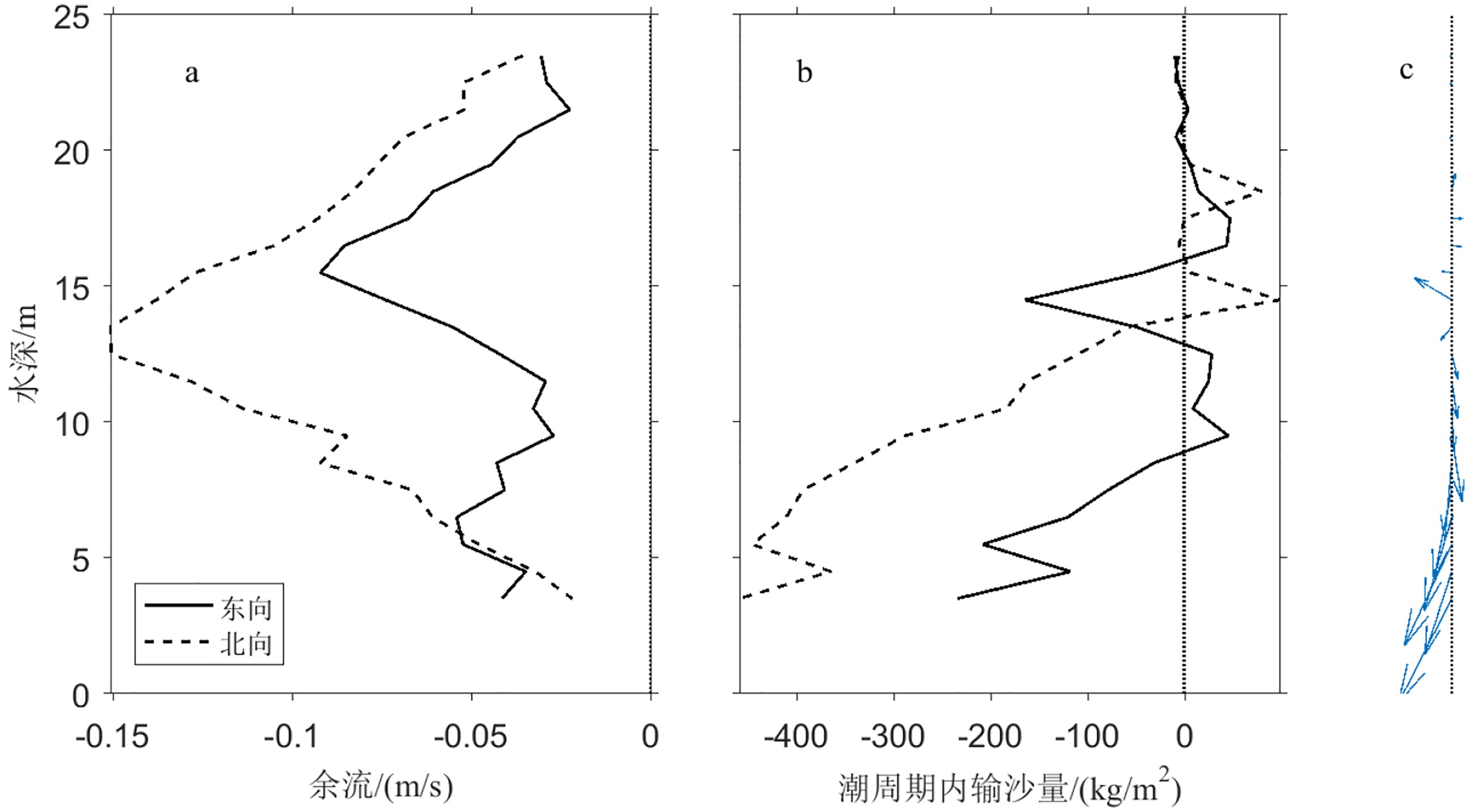
为了明确舟山群岛海域悬浮体的特征和输运机制,本研究于2018年夏季大潮期间进行了现场观测,包括温盐深、水动力和悬浮体的剖面观测,以及海水和海底表层沉积物的采集等。结果发现,悬浮体在垂向上可分为3种类型:跃层以上有效密度较高的颗粒絮凝程度低;跃层以下的颗粒絮凝程度较高;跃层附近的悬浮体主要为生物颗粒,有效密度最低。一个全日潮周期内,超过3 000 kg·m−1的悬浮体向南输运,受控于夏季陆架环流和潮汐捕捉以及垂向净环流输运的共同作用。因此,浙闽沿岸流和潮汐的不对称性导致的南向悬浮体输运对浙闽泥质区的演化起积极作用;而流速和悬浮体的垂向分布不均导致的北向输运,在一定程度上抑制了这一作用。
Abstract:The transportation and dispersal of suspended particles play a key role in the deposition and evolution of offshore muddy deposits. In order to reveal the characteristics and transport mechanism of suspended particles in the offshore of Zhoushan Islands, field survey had been carried out during the spring tides in the summer of 2018, which include the observations of temperature, salinity, hydrodynamics, contents of suspended particles, and samples of sea water and seafloor surface sediment, etc. The results show that the suspended particles could be divided into three types: micro-flocs above thermocline with higher effective density formed by low-degree flocculation; larger flocs with lower effective density below thermocline aggregated by high degree of flocculation; and larger biological particles around the thermocline with the lowest effective density. During one diurnal tidal cycle, more than 3 000 kg·m−1 suspended matters were transported southwards, controlled by Stokes drift, tidal pumping and gravitational circulation. In conclusion, the southward transport of suspended particles by continental circulation and tidal asymmetry played a positive role in the evolution of Zhejiang-Fujian muddy system. Nevertheless, the northward transport caused by uneven vertical distribution of velocity and suspended particle weakened the process to certain extent.
-

-
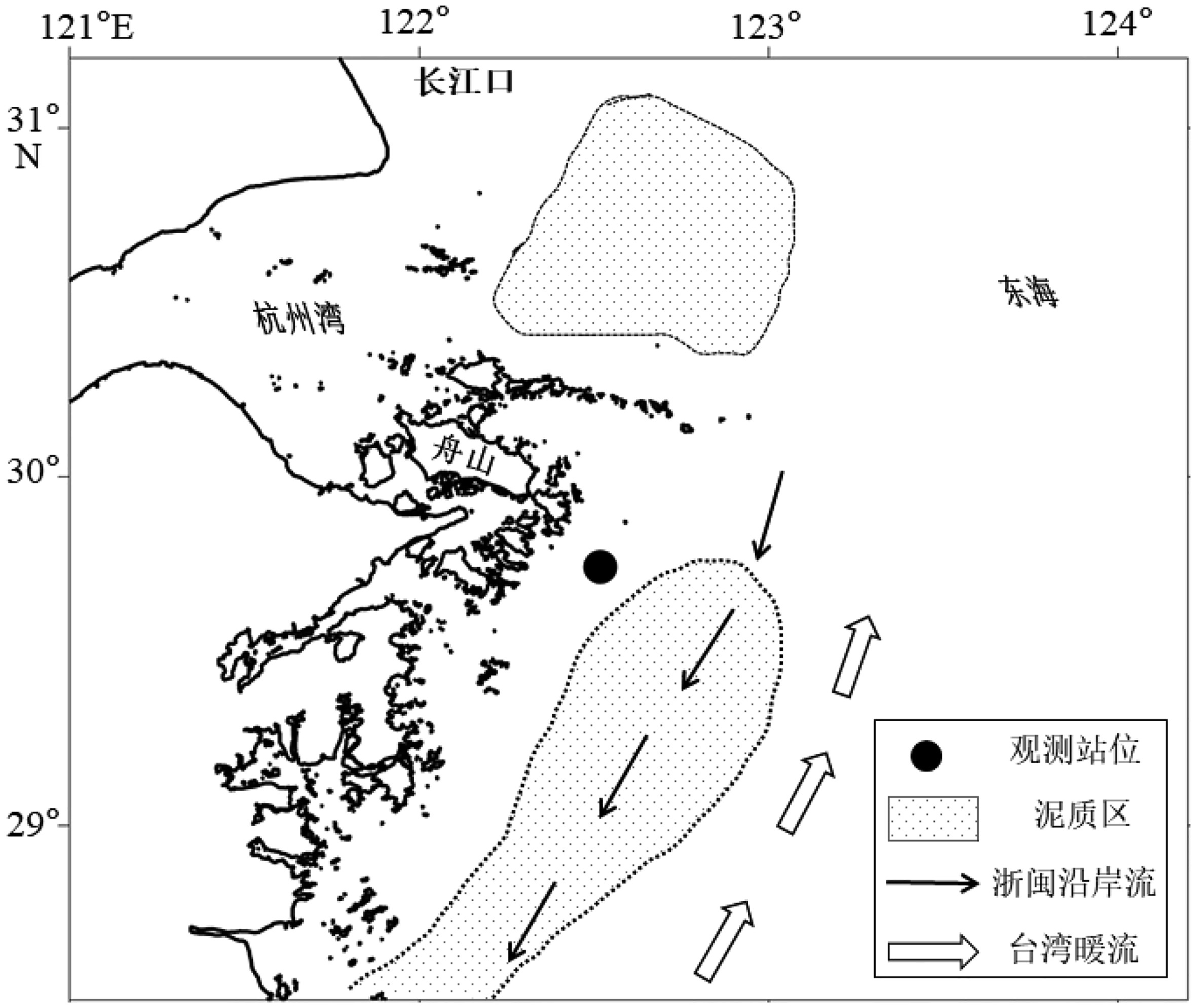
图 1 研究区域和观测站位图(据胡日军[12]绘制)
Figure 1.
表 1 悬浮体质量浓度的特征值
Table 1. The characteristic values of mass concentration of suspended particles
平均质量浓度/
(mg·L−1)质量浓度的标准差/
(mg·L−1)质量浓度梯度/
(mg·L−1)表层 2.88 3.62 − 5 mbs 1.55 0.69 −0.26 10 mbs 2.83 3.82 0.26 20 mbs 35.52 10.45 3.27 近底层 61.02 15.73 5.10 表 2 单位宽度悬浮体通量各分量及方向(正北方向为0°)
Table 2. Tidal-averaged suspended particle flux per width and direction
F1 F2 F3 F4 F5 F6 F7 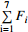
东向通量 −0.020 1 −0.003 5 0.000 1 0.014 9 0.000 0 −0.000 3 0.000 7 −0.008 2 北向通量 −0.041 8 0.007 1 0.000 2 −0.016 0 0.000 8 0.013 3 −0.000 7 −0.037 2 通量/(kg·m−1·s−1) 0.046 4 0.007 9 0.000 2 0.021 9 0.000 8 0.013 3 0.001 0 0.038 1 输运方向/(°) 206 334 26 137 359 359 135 -
[1] 秦蕴珊, 李凡, 徐善民, 等. 南黄海海水中悬浮体的研究[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 1989, 20(2):101-112
QIN Yunshan, LI Fan, XU Shanmin, et al. Suspended matter in the South Yellow Sea [J]. Oceanologia Et Limnologia Sinica, 1989, 20(2): 101-112.
[2] 高抒. 浅海细颗粒沉积物通量与循环过程[J]. 世界科技研究与发展, 2000, 22(5):73-77 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6055.2000.05.016
GAO Shu. Fine-grained sediment fluxes and cycling on continental shelves [J]. World Sci-Tech R & D, 2000, 22(5): 73-77. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6055.2000.05.016
[3] 石学法, 胡利民, 乔淑卿, 等. 中国东部陆架海沉积有机碳研究进展: 来源、输运与埋藏[J]. 海洋科学进展, 2016, 34(3):313-327
SHI Xuefa, HU Limin, QIAO Shuqing, et al. Progress in research of sedimentary organic carbon in the East China Sea: sources, dispersal and sequestration [J]. Advances in Marine Science, 2016, 34(3): 313-327.
[4] 李云海, 陈坚, 黄财宾, 等. 浙闽沿岸南部泥质沉积中心表层沉积物粒度特征及其季节性差异[J]. 沉积学报, 2010, 28(1):150-157
LI Yunhai, CHEN Jian, HUANG Caibin, et al. Grain-size characteristics of the surface sediments and their seasonal variability in the mud depocenter off the southern Zhejiang-Fujian coast [J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2010, 28(1): 150-157.
[5] 肖尚斌, 李安春, 刘卫国, 等. 闽浙沿岸泥质沉积的物源分析[J]. 自然科学进展, 2009, 19(2):185-191 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-008X.2009.02.009
XIAO Shangbin, LI Anchun, LIU Weiguo, et al. Provenance analysis of mud along the Zhe-Min coast [J]. Progress in Natural Science, 2009, 19(2): 185-191. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-008X.2009.02.009
[6] 黄惠明, 王义刚, 王乐乐, 等. 群岛阻滞效应影响舟山群岛水流挟沙力空间变化研究[J]. 泥沙研究, 2010(6):60-67
HUANG Huiming, WANG Yigang, WANG Lele, et al. Spacial distribution of sediment carrying capacity caused by retarding effect of Zhoushan Archipelago [J]. Journal of Sediment Research, 2010(6): 60-67.
[7] 于谦, 王韫玮, 高抒. 潮汐与陆架环流作用下的悬沙输运: 江苏新洋港海岸冬季观测结果[J]. 南京大学学报: 自然科学版, 2014(5):626-635
YU Qian, WANG Yunwei, GAO Shu. Tide and continental shelf circulation induced suspended sediment transport on the Jiangsu Coast: winter observations out of Xinyanggang [J]. Journal of Nanjing University: Natural Sciences, 2014(5): 626-635.
[8] Liu J P, Xu K H, Li A C, et al. Flux and fate of Yangtze River sediment delivered to the East China Sea [J]. Geomorphology, 2007, 85(3-4): 208-224. doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2006.03.023
[9] 闵建雄, 丁咚, 李广雪, 等. 利用Landsat卫星影像研究浙闽地区表层悬浮体的分布和迁移[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2017, 37(2):44-55
MIN Jianxiong, DING Dong, LI Guangxue, et al. Distribution and migration pattern of surficial suspended matter in Zhejiang and Fujian mud area detected by Landsat satellite images [J]. Marine Geology and Quaternary Geology, 2017, 37(2): 44-55.
[10] 刘世东, 乔璐璐, 李广雪, 等. 东海内陆架悬浮体输运、通量及季节变化[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2018, 49(1):24-39
LIU Shidong, QIAO Lulu, LI Guangxue, et al. Transport and flux of suspended sediment and its seasonal variation over the inner shelf of the East China Sea [J]. Oceanologia Et Limnologia Sinica, 2018, 49(1): 24-39.
[11] 周连成, 李军, 高建华, 等. 长江口与舟山海域柱状沉积物粒度特征对比及其物源指示意义[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2009, 29(5):21-27
ZHOU Liancheng, LI Jun, GAO Jianhua, et al. Comparison of core sediment grain-size characteristics between Yangtze River Estuary and Zhoushan islands and its significance to sediment source analysis [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2009, 29(5): 21-27.
[12] 胡日军. 舟山群岛海域泥沙运移及动力机制分析[D]. 中国海洋大学博士学位论文, 2009.
HU Rijun. Sediment transport and dynamic mechanism in the Zhoushan Archipelago sea area[D]. Doctor Dissertation of Ocean University of China, 2009.
[13] 寿玮玮. 舟山群岛附近海域水动力特征及其对物质输运的影响分析[D]. 中国海洋大学硕士学位论文, 2009.
SHOU Weiwei. Hydrodynamic characteristics and its impact on mass transport in the Zhoushan Archipelago sea area[D]. Master Dissertation of Ocean University of China, 2009.
[14] Dyer K R. The salt balance in stratified estuaries [J]. Estuarine and Coastal Marine Science, 1974, 2(3): 273-281. doi: 10.1016/0302-3524(74)90017-6
[15] 吴华林, 沈焕庭, 朱建荣. 河口泥沙通量研究综述[J]. 泥沙研究, 2001(5):73-79 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0468-155X.2001.05.013
WU Hualin, SHEN Huanting, ZHU Jianrong. Estuarine sediment fluxes: an overview [J]. Journal of Sediment Research, 2001(5): 73-79. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0468-155X.2001.05.013
[16] Hansen D V. Currents and mixing in the Columbia River Estuary[C]//Ocean Science and Ocean Engineering. Washington D. C.: Marine Technology Society and American Society of Limnology and Oceanography, 1965: 943-955.
[17] Fischer H B. Mixing and dispersion in estuaries [J]. Annual Review of Fluid Mechanics, 1976, 8(1): 107-133. doi: 10.1146/annurev.fl.08.010176.000543
[18] Uncles R J, Elliott R C A, Weston S A. Dispersion of salt and suspended sediment in a partly mixed estuary [J]. Estuaries, 1985, 8(3): 256-269. doi: 10.2307/1351486
[19] Dyer K R. Estuarine: A Physical Introduction[M]. 2nd ed. New York: John Wiley & Sons, 1997.
[20] 吴祥柏, 汪亚平, 潘少明. 长江河口悬沙与盐分输运机制分析[J]. 海洋学研究, 2008, 26(4):8-19 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-909X.2008.04.002
WU Xiangbai, WANG Yaping, PAN Shaoming. Analysis of the transportation mechanism of suspended sediment and salt in the Changjiang River Estuary [J]. Journal of Marine Sciences, 2008, 26(4): 8-19. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-909X.2008.04.002
[21] 宋永港, 卢永金, 刘新成. 黄浦江河口水沙输运机制研究[J]. 华东师范大学学报: 自然科学版, 2016(3):136-145
SONG Yonggang, LU Yongjin, LIU Xincheng. Water and sediment transport mechanism in the Huangpu River Estuary, Shanghai [J]. Journal of East China Normal University: Natural Science, 2016(3): 136-145.
[22] 吴德安, 张忍顺, 严以新, 等. 辐射沙洲东大港潮流水道悬沙输移机制分析[J]. 河海大学学报: 自然科学版, 2006, 34(2):216-222
WU De'an, ZHANG Renshun, YAN Yixin, et al. Mechanism of suspended sediment transport in Dongdagang tidal channel of radial sand ridges [J]. Journal of Hohai University: Natural Sciences, 2006, 34(2): 216-222.
[23] 刘运令, 汪亚平, 吴祥柏, 等. 南黄海苏北近岸西洋水道水沙输运机制分析[J]. 海洋科学, 2011, 35(11):120-127
LIU Yunling, WANG Yaping, WU Xiangbai, et al. Mechanism of water and suspended sediment transport in the Xiyang Channel along the southwestern Yellow Sea coast [J]. Marine Sciences, 2011, 35(11): 120-127.
[24] Yu Q, Wang Y P, Flemming B, et al. Tide-induced suspended sediment transport: Depth-averaged concentrations and horizontal residual fluxes [J]. Continental Shelf Research, 2012, 34: 53-63. doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2011.11.015
[25] 徐粲, 高建华, 杨旸, 等. 南黄海辐射沙脊群潮汐水道的悬沙输运特征[J]. 海洋学报, 2014, 36(11):150-162
XU Can, GAO Jianhua, YANG Yang, et al. Suspended sediment transport patterns in the tidal channels in the southwestern Yellow Sea [J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2014, 36(11): 150-162.
[26] 宋立松, 余祈文. 杭州湾悬沙净输移机制探讨[J]. 泥沙研究, 2003(3):48-52 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0468-155X.2003.03.011
SONG Lisong, YU Qiwen. Preliminary study on suspended sediment transport in the Hangzhou Bay [J]. Journal of Sediment Research, 2003(3): 48-52. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0468-155X.2003.03.011
[27] Hu R J, Wu J Z, Zhu L H, et al. Suspended sediment transport and deposition in the Zhoushan Archipelago sea area [J]. Journal of Ocean University of China, 2009, 8(4): 343-351. doi: 10.1007/s11802-009-0343-y
[28] Turner A, Millward G E. Suspended particles: their role in estuarine biogeochemical cycles [J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2002, 55(6): 857-883. doi: 10.1006/ecss.2002.1033
[29] van Rijn L C. Principles of Sediment Transport in Rivers, Estuaries and Coastal Seas[M]. Amsterdam: Aqua Publications, 1993.
[30] Mikkelsen O A, Pejrup M. In situ particle size spectra and density of particle aggregates in a dredging plume [J]. Marine Geology, 2000, 170(3-4): 443-459. doi: 10.1016/S0025-3227(00)00105-5
[31] Soulsby R L. Dynamics of Marine Sands: a Manual for Practical Applications[M]. London: Telford, 1997.
[32] Lee J, Liu J T, Hung C C, et al. River plume induced variability of suspended particle characteristics [J]. Marine Geology, 2016, 380: 219-230. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2016.04.014
[33] Liu J T, Hsu R T, Yang R J, et al. A comprehensive sediment dynamics study of a major mud belt system on the inner shelf along an energetic coast [J]. Scientific Reports, 2018, 8(1): 4229. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-22696-w
[34] Gibbs R J, Matthews M D, Link D A. The relationship between sphere size and settling velocity [J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 1971, 41(1): 7-18.
[35] Gibbs R J. Estuarine flocs: their size, settling velocity and density [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1985, 90(C2): 3249-3251. doi: 10.1029/JC090iC02p03249
[36] Geyer W R, Hill P S, Kineke G C. The transport, transformation and dispersal of sediment by buoyant coastal flows [J]. Continental Shelf Research, 2004, 24(7-8): 927-949. doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2004.02.006
[37] Wang Y P, Voulgaris G, Li Y, et al. Sediment resuspension, flocculation, and settling in a macrotidal estuary [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 2013, 118(10): 5591-5608. doi: 10.1002/jgrc.20340
[38] Krone C A, Burrows D G, Brown D W, et al. Nitrogen-containing aromatic compounds in sediments from a polluted harbor in Puget Sound [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 1986, 20(11): 1144-1150.
[39] Droppo I G. Rethinking what constitutes suspended sediment [J]. Hydrological Processes, 2001, 15(9): 1551-1564. doi: 10.1002/hyp.228
[40] Derenbach J B, Astheimer H, Hansen H P, et al. Vertical microscale distribution of phytoplankton in relation to the thermocline [J]. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 1979, 1: 187-193. doi: 10.3354/meps001187
[41] Dekshenieks M M, Donaghay P L, Sullivan J M, et al. Temporal and spatial occurrence of thin phytoplankton layers in relation to physical processes [J]. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 2001, 223: 61-71. doi: 10.3354/meps223061
[42] Ferland J, Gosselin M, Starr M. Environmental control of summer primary production in the Hudson Bay system: The role of stratification [J]. Journal of Marine Systems, 2011, 88(3): 385-400. doi: 10.1016/j.jmarsys.2011.03.015
[43] Du X Q, Liu J T. Particle dynamics of the surface, intermediate, and benthic nepheloid layers under contrasting conditions of summer monsoon and typhoon winds on the boundary between the Taiwan Strait and East China Sea [J]. Progress in Oceanography, 2017, 156: 130-144. doi: 10.1016/j.pocean.2017.06.009
[44] 李占海, 高抒, 沈焕庭. 金塘水道的悬沙输运和再悬浮作用特征[J]. 泥沙研究, 2006(3):55-62 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0468-155X.2006.03.010
LI Zhanhai, GAO Shu, SHEN Huanting. Processes of suspended sediment transport and resuspension in Jintang Channel [J]. Journal of Sediment Research, 2006(3): 55-62. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0468-155X.2006.03.010
[45] 宋泽坤, 张俊彪, 施伟勇, 等. 杭州湾口门中部水沙输运机制初探——以岱衢洋为例[J]. 海洋通报, 2015, 34(3):267-274 doi: 10.11840/j.issn.1001-6392.2015.03.005
SONG Zekun, ZHANG Junbiao, SHI Weiyong, et al. Mechanism of water and suspended sediment transport in the middle outlet of the Hangzhou Bay: a case study of Daiquyang Sea [J]. Marine Science Bulletin, 2015, 34(3): 267-274. doi: 10.11840/j.issn.1001-6392.2015.03.005
[46] 董超, 陈俊兵, 谢永清, 等. 舟山沈家门海域悬沙输运特征研究[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2018, 38(1):78-86
DONG Chao, CHEN Junbing, XIE Yongqing, et al. Transportation of suspended sediment in Shenjiamen offshore area of Zhoushan [J]. Marine Geology and Quaternary Geology, 2018, 38(1): 78-86.
[47] 刘升发, 石学法, 刘焱光, 等. 东海内陆架泥质区表层沉积物常量元素地球化学及其地质意义[J]. 海洋科学进展, 2010, 28(1):80-86 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2010.01.011
LIU Shengfa, SHI Xuefa, LIU Yanguang, et al. Geochemical characteristics and geological significance of major elements in the surface sediments from the inner shelf mud area of the East China Sea [J]. Advances in Marine Science, 2010, 28(1): 80-86. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2010.01.011
-



 下载:
下载: