Sedimentary stratigraphic framework and palaeoenvironmental evolution of the northern outer shelf of East China Sea since MIS 6
-
摘要:
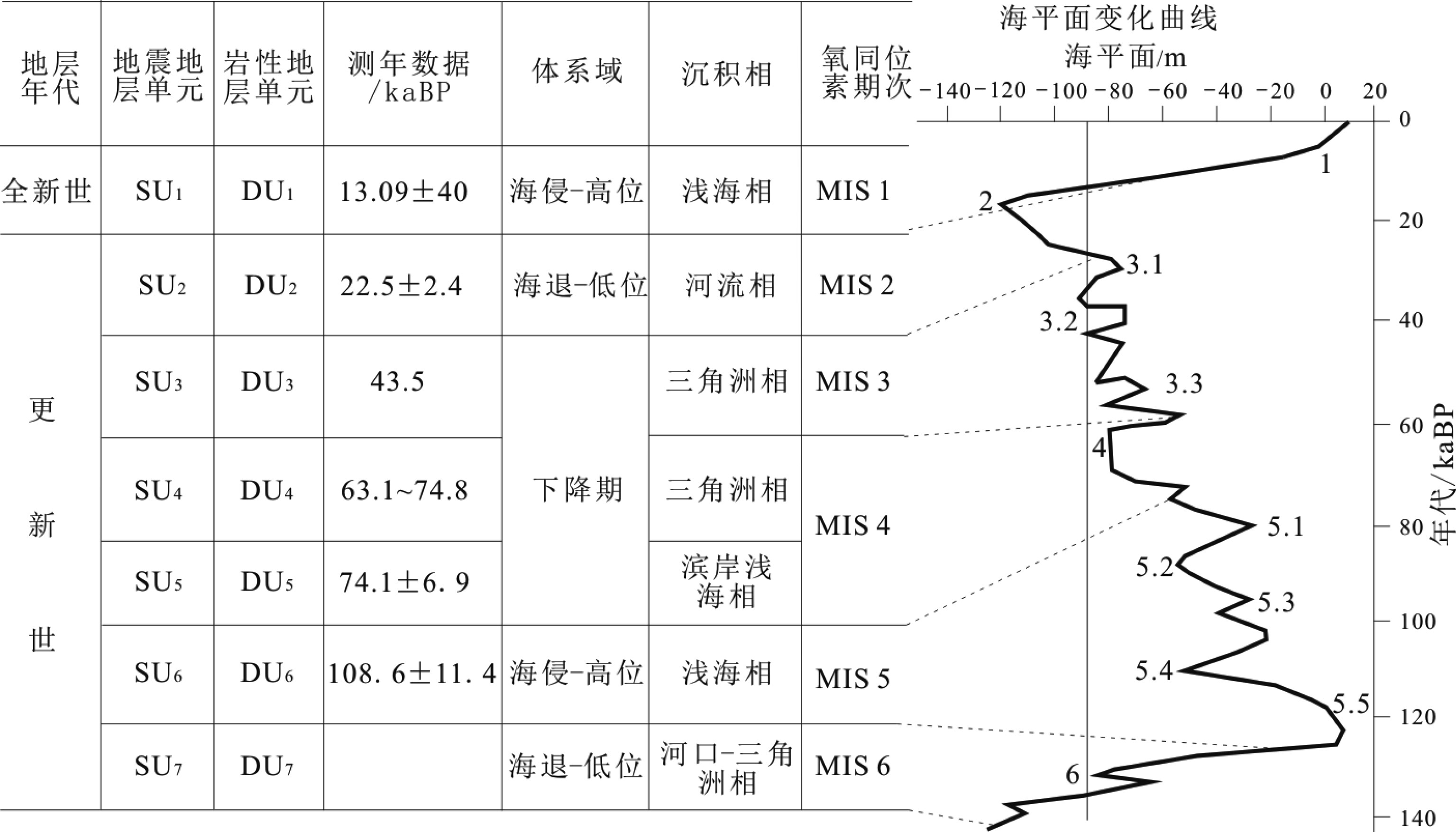
利用最新采集的高分辨率浅地层剖面资料,结合SHD-1钻孔岩心资料,对东海北部外陆架MIS 6以来的地层结构进行了分析,建立了MIS 6以来的沉积地层格架,并对地层的地质年代进行了厘定。根据Octavian Catuneanu(2005)的层序地层学理论,研究区地层划分出海侵和高位体系域、下降期体系域、海退和低位体系域。研究表明,过孔的浅地层剖面与钻孔岩心的沉积地层有很好的对应关系。东海北部外陆架MIS 6以来可划分出7个不整合界面(D7—D1)和7个地震单元(SU7—SU1)。东海外陆架的海进层序与海退层序有规律地交替发育,它们与海平面变化曲线也有很好的对应关系。其中,地震单元SU1、SU5分别为MIS 1、MIS 5形成的海侵沉积,主要发育浅海沉积层,100 m以浅的位置发育潮流沙脊;地震单元SU2、SU4、SU6分别对应 MIS 2、MIS 4和MIS 6低海平面时期形成的河流/河口—三角洲沉积;地震单元SU3、SU4为下降期体系域,这两个亚单元分别对应MIS 3和MIS 4晚期。MIS 4—MIS 3发育厚层且分布广泛的水下三角洲,但MIS 4发育的水下三角洲的规模不及MIS 3大。总之,对MIS 6以来沉积地层格架的建立和古环境研究可为东海外陆架晚第四纪地层的海平面变化、古环境演化等相关研究提供参考。
Abstract:Based on the newly collected high-resolution shallow seismic and lithological data of the Borehole SHD-1, the stratigraphic framework of the outer shelf of the northern East China Sea since MIS 6 was established with ages. Using the method of sequence stratigraphy newly proposed by Octavian Catuneanu (2005), it is observed that the strata since MIS 6 in the study area may be subdivided into transgressive, highstand, falling, regressive and lowstand system tracts. The shallow seismic profile data fit well with the stratigraphic pattern disclosed by drilling cores, upon which 7 reflective interfaces (D7—D1) were recognized and 7 seismic units (SU7—SU1) subdivided for the strata since late Pleistocene. The transgression and regression system tracts are observed in a rather regular pattern, corresponding well to sea level fluctuation. Both the seismic units SU1 and SU5 were transgressive deposits corresponding to MIS 1, MIS5, when neritic facies prevailed, and the places less than 100 m in water depth were dominated by tidal ridge deposits. Seismic unit SU2, SU4 and SU6 correspond to MIS 2, MIS 4 and MIS 6 stage, respectively. They were deposited in regressive periods and dominated fluvial and deltaic facies sediments. The seismic unit SU3 and SU4 were the system tracts formed during the sea level falling periods, corresponding to late MIS 3 and MIS 4 respectively. MIS 4—MIS 3 are dominated by thick and widely distributed underwater deltaic deposits, but the size of the underwater deltas in MIS 4 was smaller than those in MIS 3. In conclusion, the study of sedimentary stratigraphy framework and sedimentary environment since MIS 6 may provide a good reference for sea level changes and palaeoenvironmental evolution of the East China Sea continental shelf in Late Quaternary.
-

-
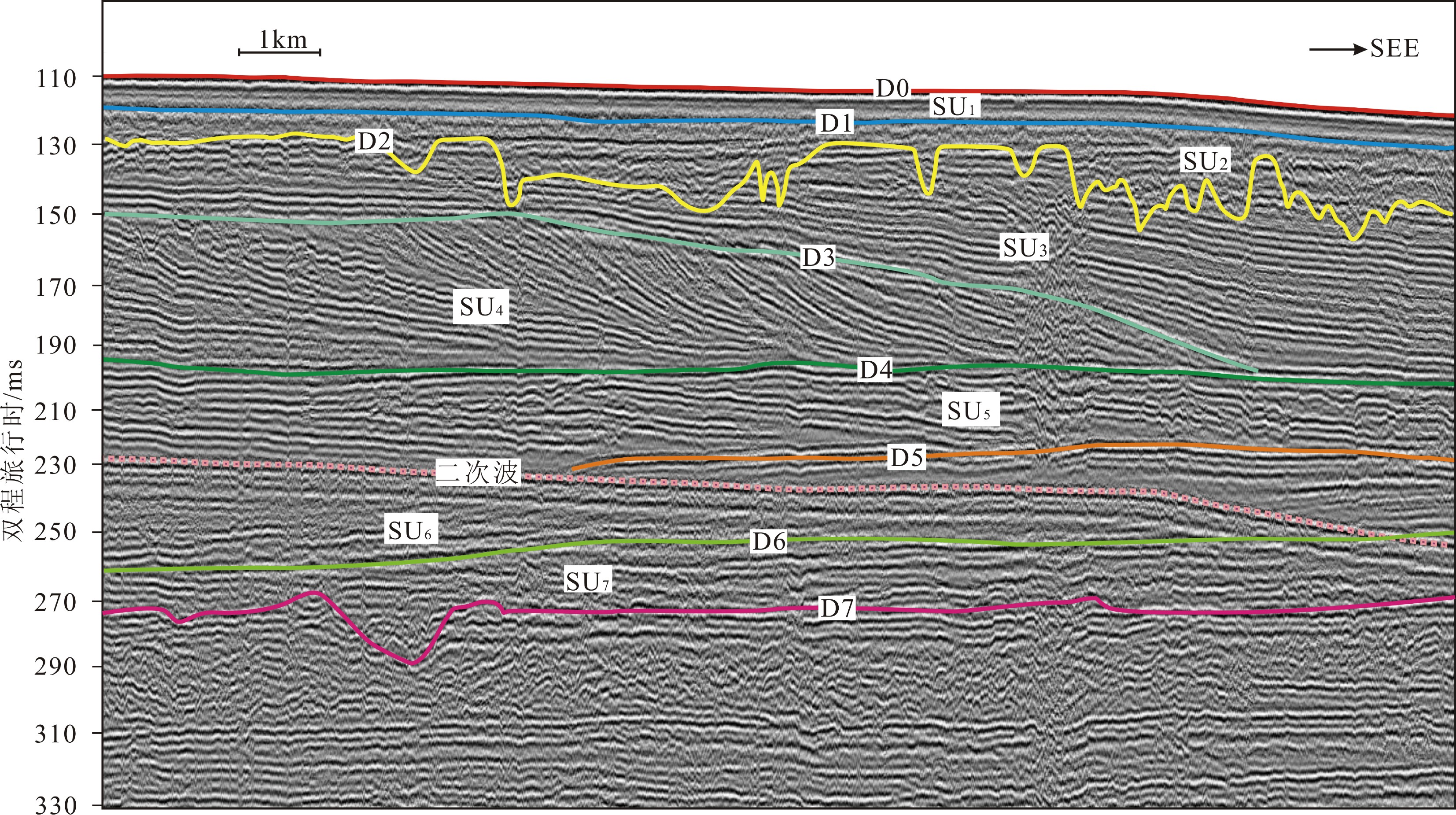
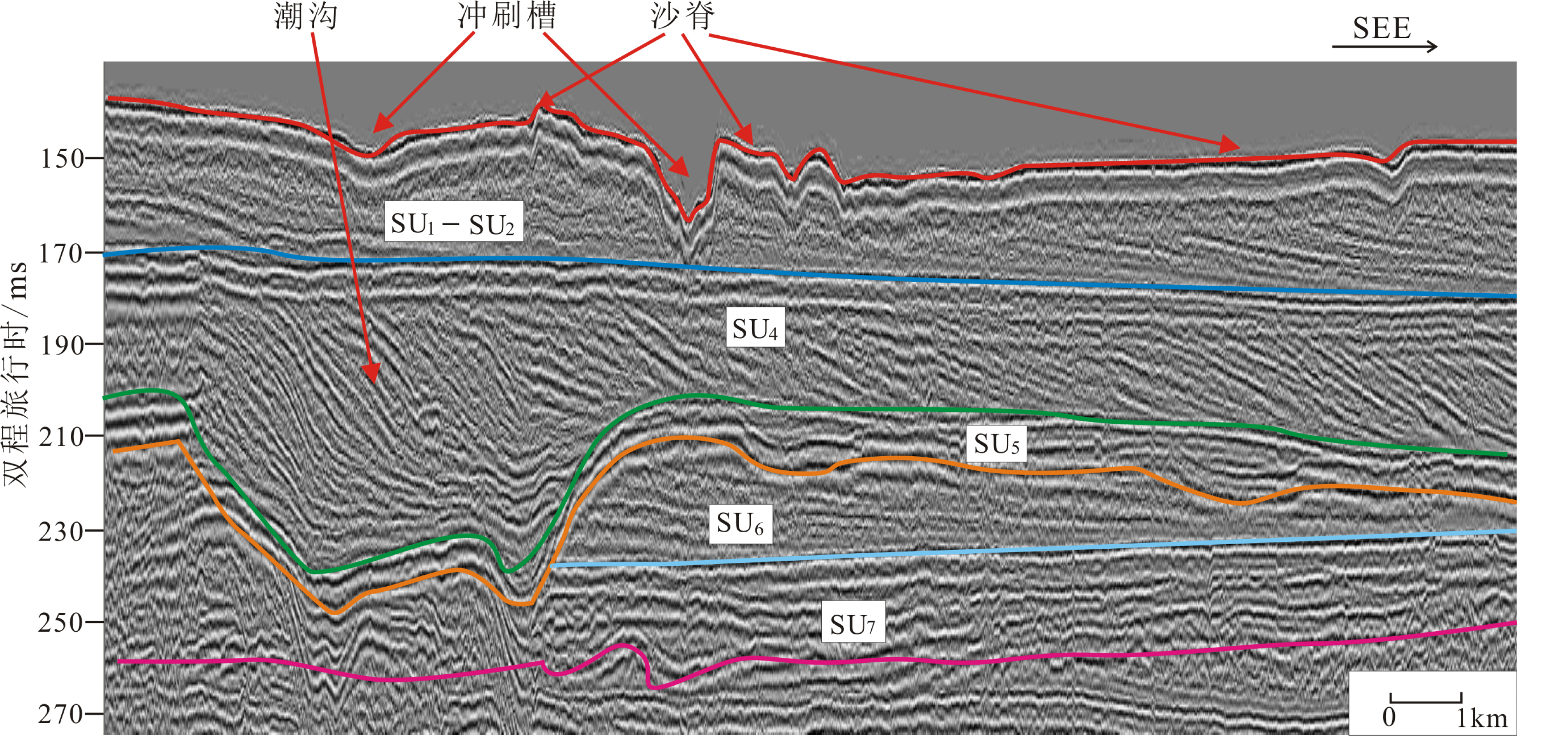
图 2 研究区SU1—SU7地震单元结构(剖面位置见图1,a-a’)
Figure 2.
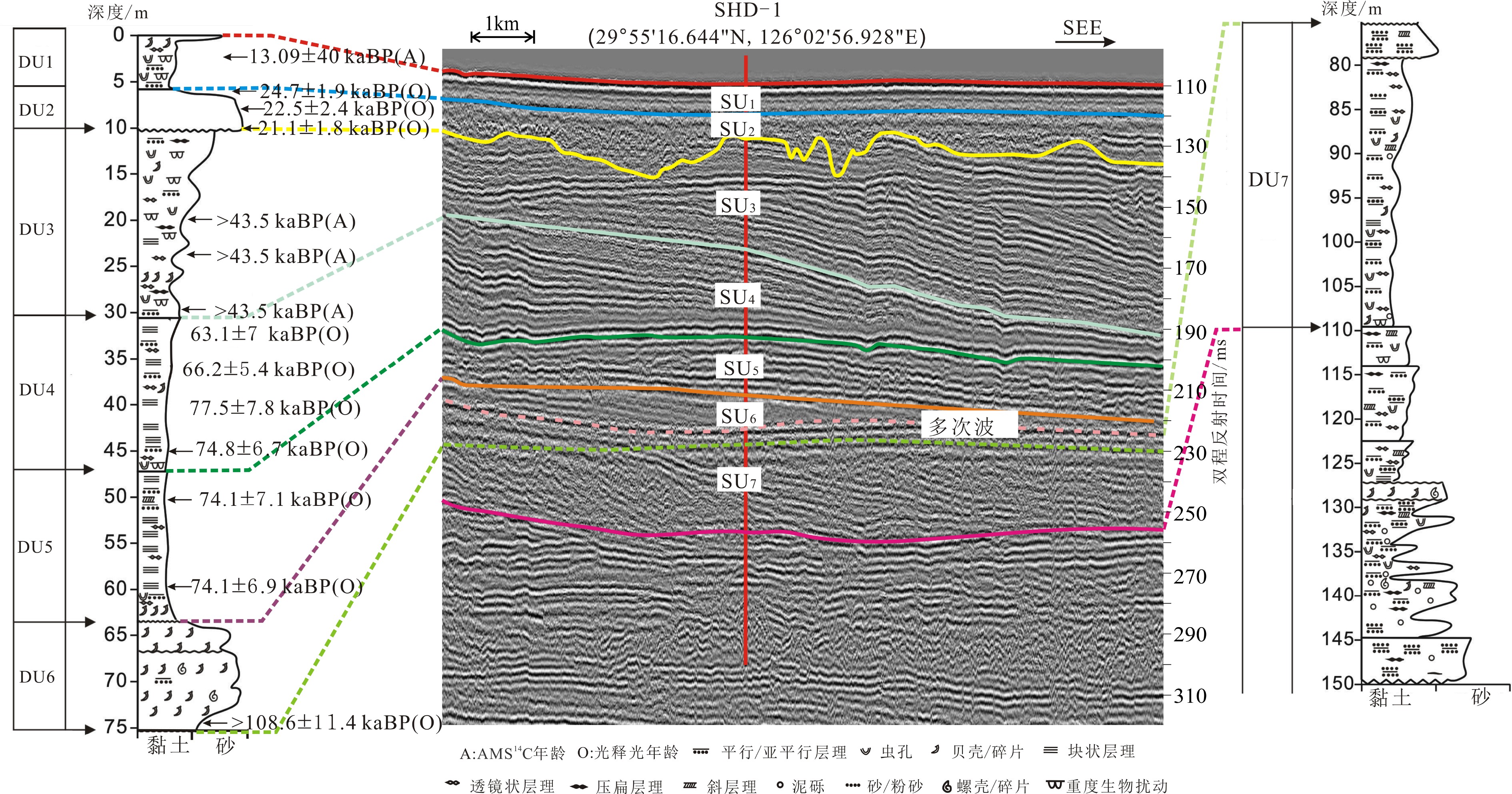
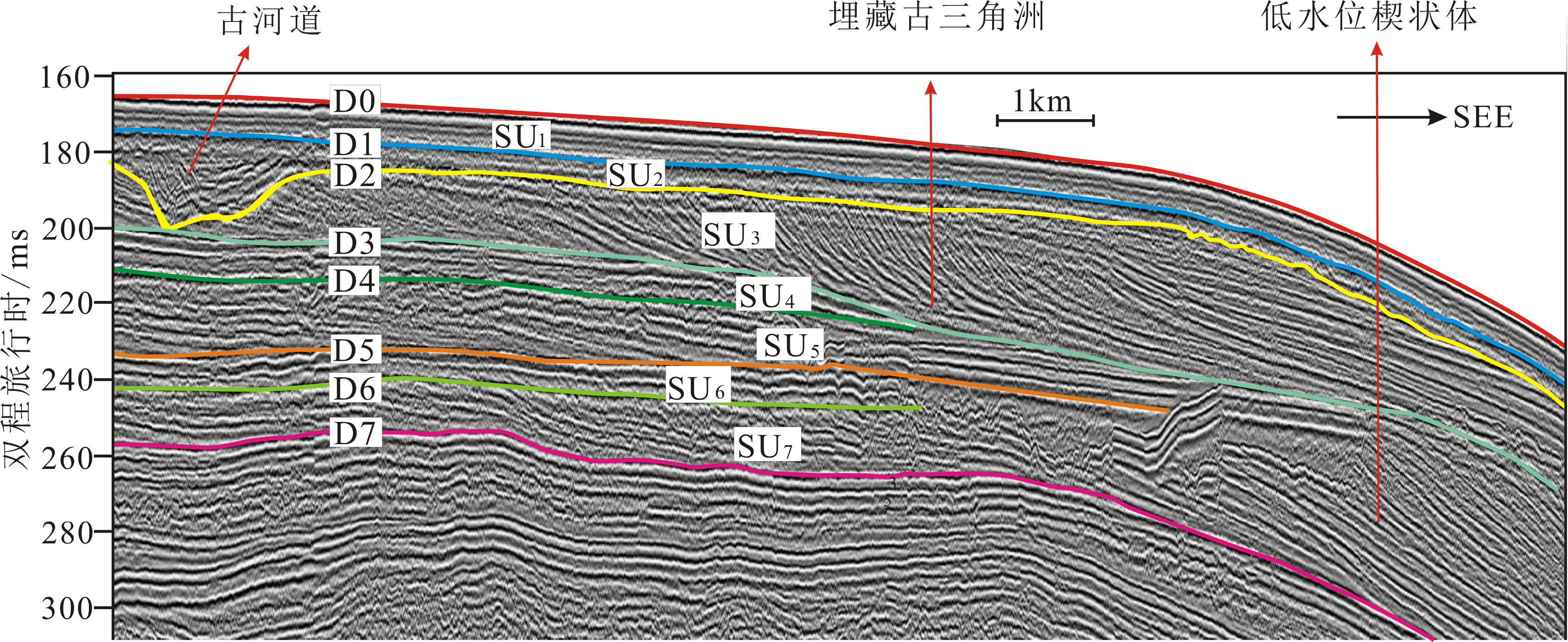
图 5 钻孔SHD-1与过孔浅地层剖面对比图(剖面位置见图1,b-b’)
Figure 5.
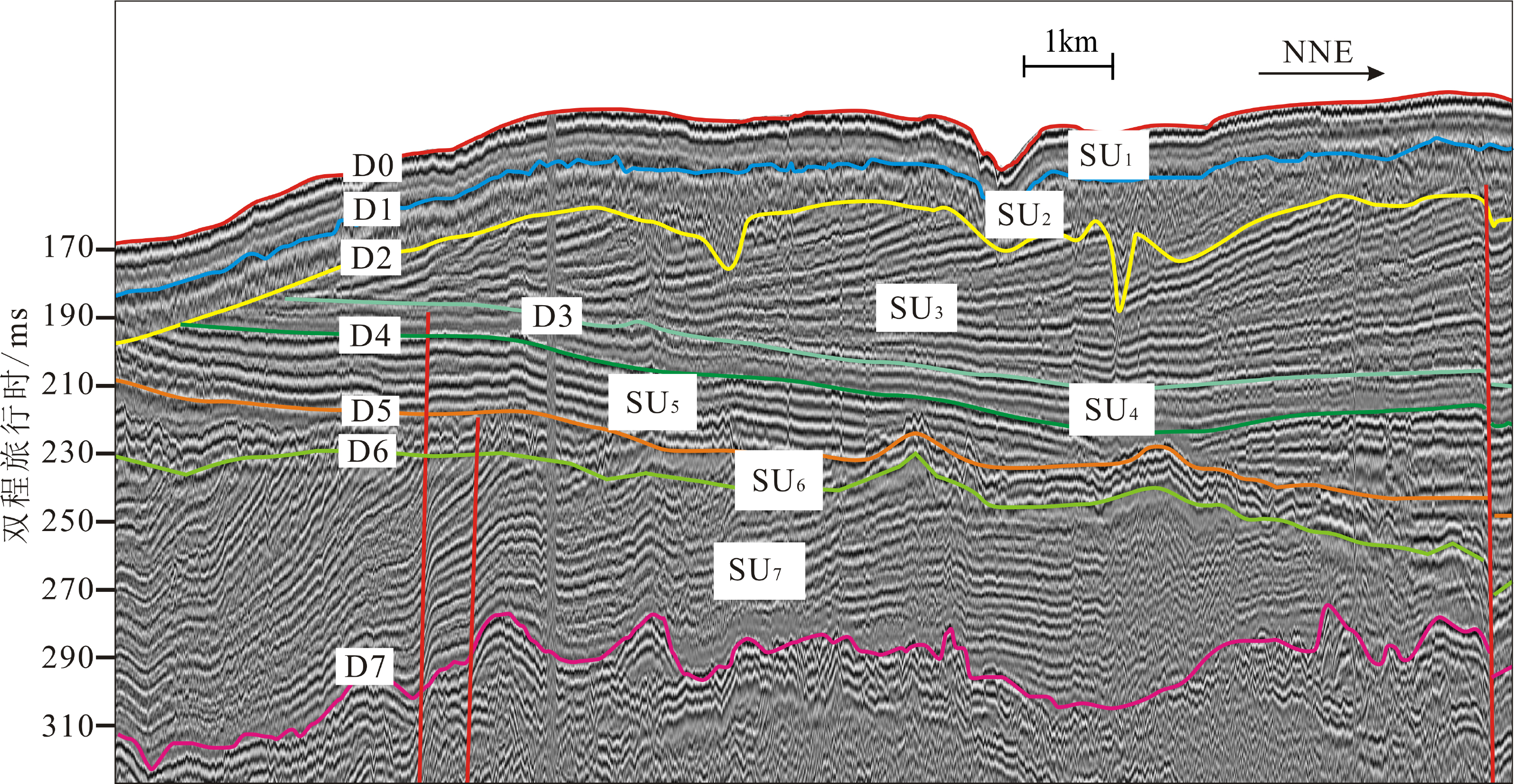
图 7 研究区典型的浅地层剖面(剖面位置见图1,d-d’)
Figure 7.
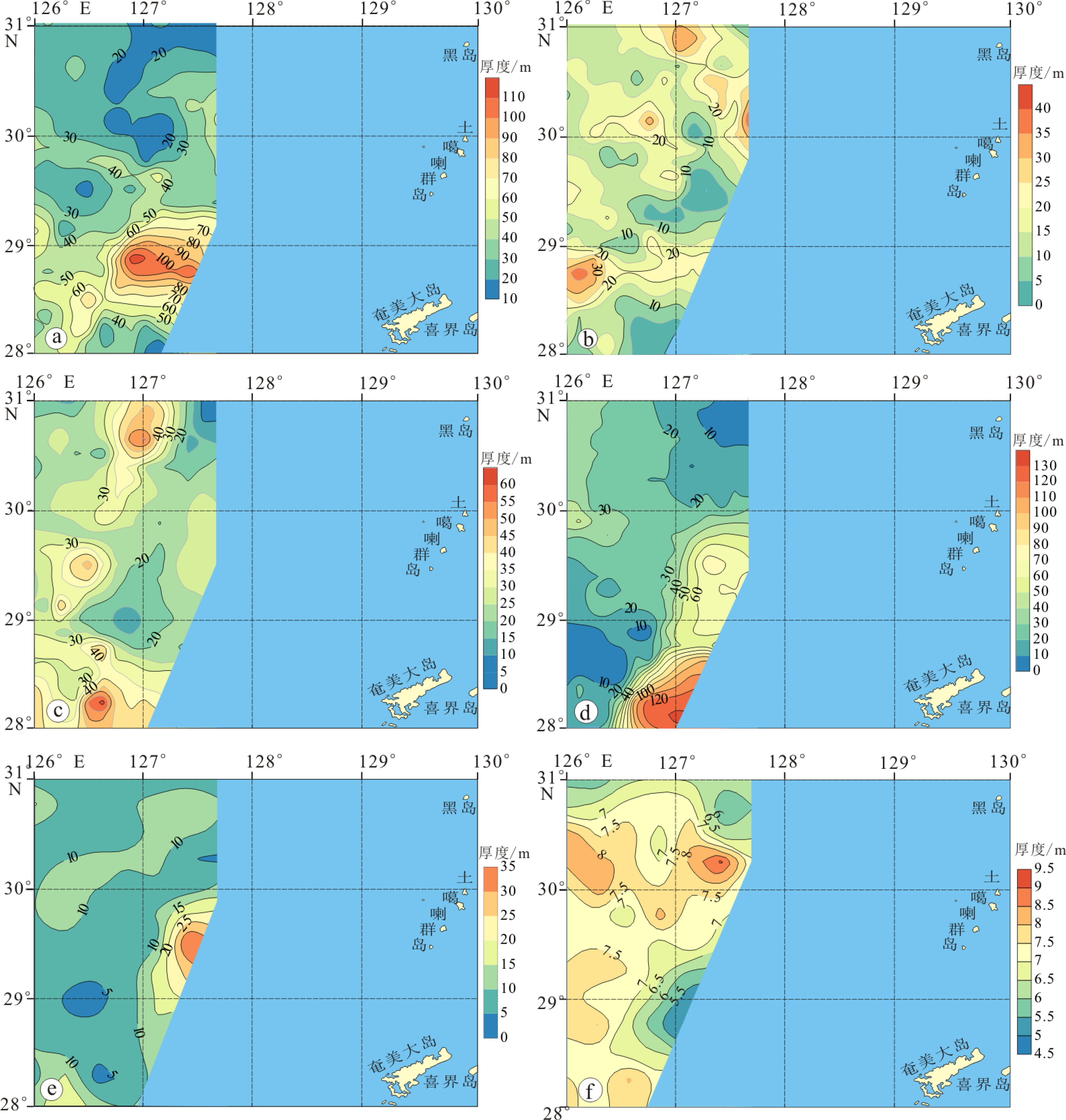
图 8 东海外陆架上的潮流沙脊(剖面位置见图1,c-c’)
Figure 8.
图 9 研究区典型的浅地层剖面(剖面位置见图1,e-e’)
Figure 9.
图 10 研究区典型的浅地层剖面(剖面位置见图1,f-f’)
Figure 10.
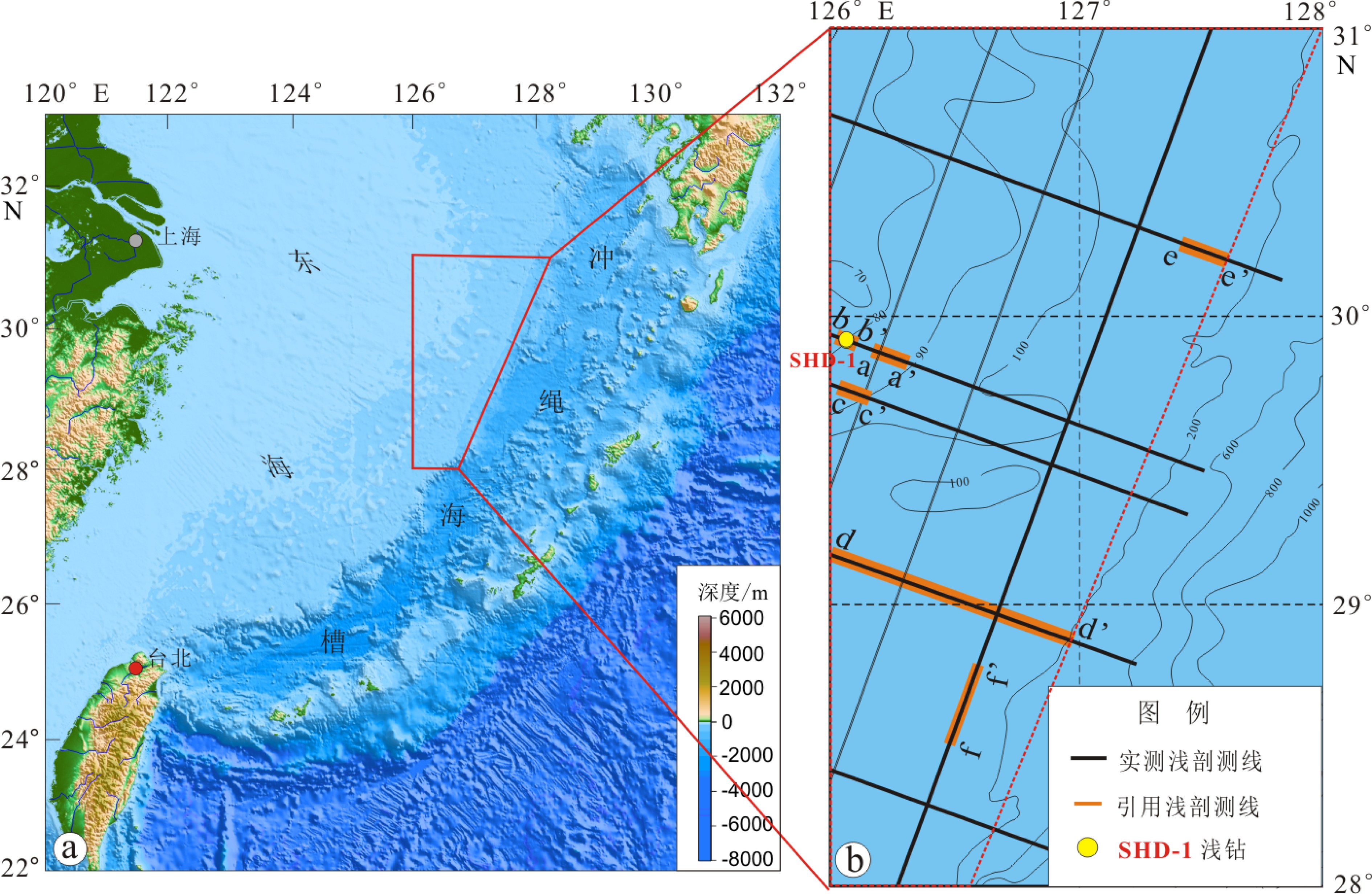
表 1 浅地层剖面施工采集参数
Table 1. Working parameters for shallow seismic data acquisition
震源类型 电火花 震源沉放深度/m 1 ±0.5 震源总能量/J 750、1 000 震源频谱宽度/Hz 100~2 000 放炮间隔/s 1.22 采样率/ms 0.2 记录长度/s 0.8~2.0 -
[1] Chen Z Y, Stanley D J. Quaternary subsidence and river channel migration in the Yangtze Delta Plain, eastern China [J]. Journal of Coastal Research, 1995, 11(3): 927-945.
[2] 王中波, 杨守业, 张志珣, 等. 东海外陆架晚第四纪若干沉积学问题的研究现状与展望[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2012, 32(3):1-10
WANG Zhongbo, YANG Shouye, ZHANG Zhixun, et al. A review of the Late Quaternary Sedimentological studies on the outer shelf of the East China Sea [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2012, 32(3): 1-10.
[3] 刘振夏, 印萍, Berné S, et al. 第四纪东海的海进层序和海退层序[J]. 科学通报, 2001, 46(S1):74-79
LIU Zhenxia, YIN Ping, Berné S, et al. The quaternary transgression and regression of the East China Sea [J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2001, 46(S1): 74-79.
[4] 刘振夏, Berné S, L’ATALANTE科学考察组. 中更新世以来东海陆架的古环境[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 1999, 19(2):1-10
LIU Zhenxia, Berné S, L'ATALANTE Scientific Party. Paleo-environment in the continental shelf of the East China Sea since the Mid-Pleistocene [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 1999, 19(2): 1-10.
[5] Xu T Y, Wang G Q, Shi X F, et al. Sequence stratigraphy of the subaqueous Changjiang (Yangtze River) delta since the Last Glacial Maximum [J]. Sedimentary Geology, 2016, 331: 132-147. doi: 10.1016/j.sedgeo.2015.10.014
[6] Wang Z H, Xu H, Zhan Q, et al. Lithological and palynological evidence of late Quaternary depositional environments in the subaqueous Yangtze delta, China [J]. Quaternary Research, 2010, 73(3): 550-562. doi: 10.1016/j.yqres.2009.11.001
[7] Chen Z Y, Song B P, Wang Z H, et al. Late quaternary evolution of the sub-aqueous Yangtze Delta, China: sedimentation, stratigraphy, palynology, and deformation [J]. Marine Geology, 2000, 162(2-4): 423-441. doi: 10.1016/S0025-3227(99)00064-X
[8] Li C X, Wang P, Sun H P, et al. Late quaternary Incised-valley fill of the Yangtze Delta (China): its stratigraphic framework and evolution [J]. Sedimentary Geology, 2002, 152(1-2): 133-158. doi: 10.1016/S0037-0738(02)00066-0
[9] Hori K, Saito Y, Zhao Q H, et al. Architecture and evolution of the tide-dominated Changjiang (Yangtze) River delta, China [J]. Sedimentary Geology, 2002, 146(3-4): 249-264. doi: 10.1016/S0037-0738(01)00122-1
[10] Wang Z H, Saito Y, Hori K, et al. Yangtze Offshore, China: highly laminated sediments from the transition zone between Subaqueous Delta and the Continental Shelf [J]. Coastal and Shelf Science, 2005, 62(1-2): 161-168. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2004.08.012
[11] 肖尚斌, 李安春, 陈木宏, 等. 近8ka东亚冬季风变化的东海内陆架泥质沉积记录[J]. 地球科学—中国地质大学学报, 2005, 30(5):573-581
XIAO Shangbin, Li Anchun, CHEN Muhong, et al. Recent 8 ka Mud Records of the East Asian winter monsoon from the inner shelf of the East China Sea [J]. Earth Science-Journal of China University of Geosciences, 2005, 30(5): 573-581.
[12] Liu J P, Xu K H, Li A C, et al. Flux and fate of Yangtze River sediment delivered to the East China Sea [J]. Geomorphology, 2007, 85(3-4): 208-224. doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2006.03.023
[13] Zhao B C, Wang Z H, Chen J, et al. Marine sediment records and relative sea level change during Late Pleistocene in the Changjiang delta area and adjacent continental shelf [J]. Quaternary International, 2008, 186(1): 164-172. doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2007.08.006
[14] 王张华, 赵宝成, 陈静, 等. 长江三角洲地区晚第四纪年代地层框架及两次海侵问题的初步探讨[J]. 古地理学报, 2008, 10(1):99-110 doi: 10.7605/gdlxb.2008.01.011
WANG Zhanghua, ZHAO Baocheng, CHEN Jing, et al. Chronostratigraphy and two transgressions during the Late Quaternary in Changjiang delta area [J]. Journal of Palaeogeography, 2008, 10(1): 99-110. doi: 10.7605/gdlxb.2008.01.011
[15] 徐方建, 李安春, 肖尚斌, 等. 末次冰消期以来东海内陆架古环境演化[J]. 沉积学报, 2009, 27(1):118-127
XU Fangjian, LI Anchun, XIAO Shangbin, et al. Paleoenvironmental evolution in the inner shelf of the East China Sea since the Last Deglaciation [J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2009, 27(1): 118-127.
[16] Yang C S. Active, moribund and buried tidal sand ridges in the East China Sea and the southern Yellow Sea [J]. Marine Geology, 1989, 88(1-2): 97-116. doi: 10.1016/0025-3227(89)90007-8
[17] 石斯器, 杨长恕. 东海陆架浅地层地震地层学的初步研究[M]//杨子赓, 林和茂. 中国近海及沿海地区第四纪进程与事件. 北京: 海洋出版社, 1989: 62-67.
SHI Siqi, YANG Changshu. The seismic stratigraphy preliminary study of the shelf of the East China Sea[M]//YANG Zigeng, LIN Hemao. Quaternary Processes and Incidents of the Marginal Sea and Its Coastal Areas. Beijing: China Ocean Press, 1989: 62-67.
[18] 唐保根. 东海陆架第四纪地层[M]//杨子赓, 林和茂. 中国第四纪地层与国际对比. 北京: 地质出版社, 1996: 56-75.
TANG Baogen. The Quaternary stratigraphy of the East China Sea Shelf[M]//YANG Zigeng, LIN Hemao. Quaternary Stratigraphy in China and Its International Correlation. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1996: 56-75.
[19] Saito Y, Katayama H, Ikehara K, et al. Transgressive and Highstand systems tracts and post-glacial transgression, the East China Sea [J]. Sedimentary Geology, 1998, 122(1-4): 217-232. doi: 10.1016/S0037-0738(98)00107-9
[20] Liu Z X, Berne S, Saito Y, et al. Quaternary seismic stratigraphy and paleoenvironments on the continental shelf of the East China Sea [J]. Journal of Asian Earth Science, 2000, 18(4): 441-452. doi: 10.1016/S1367-9120(99)00077-2
[21] Berné S, Vagner P, Guichard F, et al. Pleistocene forced regressions and tidal sand ridges in the East China Sea [J]. Marine Geology, 2002, 188(3-4): 293-315. doi: 10.1016/S0025-3227(02)00446-2
[22] Yoo D G, Lee C W, Kim S P, et al. Late Quaternary transgressive and highstand systems tracts in the northern East China Sea Mid-shelf [J]. Marine Geology, 2002, 187(3-4): 313-328. doi: 10.1016/S0025-3227(02)00384-5
[23] 吴自银, 金翔龙, 李家彪. 中更新世以来长江口至冲绳海槽高分辨率地震地层学研究[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2002, 22(2):9-20
WU Ziyin, JIN Xianglong, LI Jiabiao. Seismic stratigraphic interpretation of High-Resolution seismic profiles between Yangtze Estuary and Okinawa Trough [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2002, 22(2): 9-20.
[24] 杨文达. 东海海底沙脊的结构及沉积环境[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2002, 22(1):9-16
YANG Wenda. Structure and sedimentary environment for submarine dune ridges in the East China Sea [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2002, 22(1): 9-16.
[25] Wellner R W, Bartek L R. The effect of sea level, climate, and shelf physiography on the development of incised-valley complexes: a modern example from the East China Sea [J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 2003, 73(6): 926-940. doi: 10.1306/041603730926
[26] 印萍. 东海陆架冰后期潮流沙脊地貌与内部结构特征[J]. 海洋科学进展, 2003, 21(2):182-187
YIN Ping. Geomorphology and internal structure of postglacial tidal sand ridges on the East China Sea Shelf [J]. Advances in Marine Science, 2003, 21(2): 182-187.
[27] Liu Z X, Berné S, Saito Y, et al. Internal architecture and mobility of tidal sand ridges in the East China Sea [J]. Continental Shelf Research, 2007, 27(13): 1820-1834. doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2007.03.002
[28] Wu Z Y, Jin X L, Li J B, et al. Linear sand ridges on the outer shelf of the East China Sea [J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2005, 50(21): 2517-2528. doi: 10.1007/BF03183643
[29] 张军强, 唐璐璐, 邹昊. 晚更新世以来古气候与海平面变化在东海地区的响应[J]. 海洋湖沼通报, 2008(1):25-31 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6482.2008.01.004
ZHANG Junqiang, TANG Lulu, ZOU Hao. The response to the variety of paleoclimate and sea level in the East China Sea after the Late Pleistocence [J]. Transactions of Oceanology and Limnology, 2008(1): 25-31. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6482.2008.01.004
[30] 唐保根. 东海陆架第四纪地层层序的初步研究[J]. 上海地质, 1996(2):22-30
TANG Baogen. Preliminary study on the Quaternary stratigraphic sequence in the continental shelf of the East China Sea [J]. Shanghai Geology, 1996(2): 22-30.
[31] 李绍全, 李双林, 陈正新, 等. 东海外陆架EA01孔末次冰期最盛期的三角洲沉积[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2002, 22(3):19-26
LI Shaoquan, LI Shuanglin, CHEN Zhengxin, et al. Deltaic sedimentary sequences developed during Last Glacial Maximum in the EA01 core on the outer shelf of the East China Sea [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2002, 22(3): 19-26.
[32] 余华, 刘振夏, 熊应乾, 等. 末次盛冰期以来东海陆架南部EA05岩心地层划分及其古环境意义[J]. 中国海洋大学学报, 2006, 36(4):545-550
YU Hua, LIU Zhenxia, XIONG Yingqian, et al. Stratigraphy of core EA05 from southern East China Sea continental shelf since the Last Glacial Maximum and its Paleo-environment implication [J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 2006, 36(4): 545-550.
[33] Uehara K, Saito Y. Late Quaternary evolution of the Yellow/East China Sea tidal regime and its impacts on sediments dispersal and seafloor morphology [J]. Sedimentary Geology, 2003, 162(1-2): 25-38. doi: 10.1016/S0037-0738(03)00234-3
[34] 夏东兴, 刘振夏. 末次冰期盛期长江入海流路探讨[J]. 海洋学报, 2001, 23(5):87-94
XIA Dongxing, LIU Zhenxia. Tracing the Changjiang River's flowing route entering the sea during the Last Ice Age maximum [J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2001, 23(5): 87-94.
[35] 刘振夏, Berné S, L'ATALANTE科学考察组. 东海陆架的古河道和古三角洲[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2000, 20(1):9-14
LIU Zhenxia, Berné S, L'ATALANTE Scientific Party. Paleochannels and Paleodeltas in the continental shelf of the East China Sea [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2000, 20(1): 9-14.
[36] Liu Z X, Yin P, Xiong Y Q, et al. Quaternary transgressive and regressive depositional sequences in the East China Sea [J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2003, 48(S1): 81-87. doi: 10.1007/BF02900944
[37] 李从先, 范代读, 杨守业, 等. 中国河口三角洲地区晚第四纪下切河谷层序特征和形成[J]. 古地理学报, 2008, 10(1):87-97 doi: 10.7605/gdlxb.2008.01.010
LI Congxian, FAN Daidu, YANG Shouye, et al. Characteristics and formation of the late Quaternary Incised-valley sequences in estuary and Delta areas in China [J]. Journal of Palaeogeography, 2008, 10(1): 87-97. doi: 10.7605/gdlxb.2008.01.010
[38] Li G X, Liu Y, Yang Z G, et al. Ancient Changjiang channel system in the East China Sea continental shelf during the Last Glaciation [J]. Science in China Series D: Earth Sciences, 2005, 48(11): 1972-1978. doi: 10.1360/04yd0053
[39] 刘奎, 庄振业, 刘冬雁, 等. 长江口外陆架区埋藏古河道研究[J]. 海洋学报, 2009, 31(5):80-88
LIU Kui, ZHUANG Zhenye, LIU Dongyan, et al. Study of the buried ancient channels in the continental shelf area out of the mouth of the Changjiang River in China [J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2009, 31(5): 80-88.
[40] Liu Z X, Xia D X, Berné S, et al. Tidal deposition systems of China's continental shelf, with special reference to the eastern Bohai Sea [J]. Marine Geology, 1998, 145(3-4): 225-253. doi: 10.1016/S0025-3227(97)00116-3
[41] 李广雪, 刘勇, 杨子赓. 中国东部陆架沉积环境对末次冰盛期以来海面阶段性上升的响应[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2009, 29(4):13-19
LI Guangxue, LIU Yong, YANG Zigeng. Sea-level rise and sedimentary environment response in the East China Continental Shelf since the Last Glacial Maximum [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2009, 29(4): 13-19.
[42] Li G X, Li P, Liu Y, et al. Sedimentary system response to the global sea level change in the East China Sea since the last glacial maximum [J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2014, 139: 390-405. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2014.09.007
[43] Wang Z B, Yang S Y, Zhang Z X, et al. Paleo-fluvial sedimentation on the outer shelf of the East China Sea during the Last Glacial Maximum [J]. Chinese Journal of Oceanology and Limnology, 2013, 31(4): 886-894. doi: 10.1007/s00343-013-2253-5
[44] 李双林, 李绍全, 杨文达, 等. 东海陆架HY126EA1孔有孔虫壳体的氧、碳同位素记录[J]. 海洋学报, 2002, 24(3):81-87
LI Shuanglin, LI Shaoquan, YANG Wenda, et al. Oxygen and carbon isotopic record of foraminiferal crusts from HY126EA1 hole in the continental shelf of the East China Sea [J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2002, 24(3): 81-87.
[45] 金秉福, 林晓彤, 季福武, 等. 东海钓鱼岛北侧Q43柱状样上更新统的沉积[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2005, 25(1):25-31
JIN Bingfu, LIN Xiaotong, JI Fuwu, et al. Sediments of upper pleistocene in core Q43 North of Diaoyu Island in the East China Sea [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2005, 25(1): 25-31.
[46] 秦蕴珊, 赵一阳, 陈丽蓉, 等. 东海地质[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1987.
QIN Yunshan, ZHAO Yiyang, CHEN Lirong, et al. Geology of the East China Sea[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1987.
[47] Xu T Y, Shi X F, Liu S F, et al. Late Quaternary sedimentary evolution of the outer shelf of the East China Sea [J]. Quaternary International, 2018, 493: 59-69. doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2018.06.043
[48] 窦衍光, 陈晓辉, 李军, 等. 东海外陆架-陆坡-冲绳海槽不同沉积单元底质沉积物成因及物源分析[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2018, 38(4):21-31
DOU yanguang, CHEN xiaohui, Li jun, et al. Origin and provenance of the surficial sediments in the subenvironments of the East China Sea [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2018, 38(4): 21-31.
[49] 朱永其, 李承伊, 曾成开, 等. 关于东海大陆架晚更新世最低海面[J]. 科学通报, 1979(7):317-320
ZHU Yongqi, LI Chengyi, ZENG Chengkai, et al. The lowest sea surface of the East China Sea on the continental Shelf during Late Pleistocene [J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 1979(7): 317-320.
[50] Catuneanu O. Principles of Sequence Stratigraphy[M]. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2006.
[51] Wu Z Y, Jin X L, Zhou J Q, et al. Comparison of buried sand ridges and regressive sand ridges on the outer shelf of the East China Sea [J]. Marine Geophysical Research, 2017, 38(1-2): 187-198. doi: 10.1007/s11001-016-9278-z
[52] 吴自银, 金翔龙, 曹振轶, 等. 东海陆架两期沙脊的时空对比[J]. 海洋学报, 2009, 31(5):69-79
WU Ziyin, JIN Xianglong, CAO Zhenyi, et al. Space-time contrast of two stages sand ridges on the East China Sea Shelf [J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2009, 31(5): 69-79.
[53] 吴自银, 金翔龙, 曹振轶, 等. 东海陆架沙脊分布及其形成演化[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2010, 53(3):822-828
WU Ziyin, JIN Xianglong, CAO Zhenyi, et al. Distribution, formation and evolution of sand ridges on the East China Sea shelf [J]. Science China Technological Sciences, 2010, 53(3): 822-828.
[54] 杜文博, 叶银灿, 庄振业. 东海Zk23孔的古沙脊沉积环境[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2007, 27(2):11-16
DU Wenbo, YE Yincan, ZHUANG Zhenye. Sedimentary environment analysis of ancient sand ridges from Zk23 hole in the East China Sea [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2007, 27(2): 11-16.
[55] 刘振夏, 余华, 熊应乾, 等. 东海和凯尔特海潮流沙脊的对比研究[J]. 海洋科学进展, 2005, 23(1):35-42 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2005.01.005
LIU Zhenxia, YU Hua, XIONG Yingqian, et al. A comparative study on tidal sand ridges in the East China Sea and Celtic Sea [J]. Advances in Marine Science, 2005, 23(1): 35-42. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2005.01.005
[56] 刘振夏, 夏东兴. 中国近海潮流沉积沙体[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 2004.
LIU Zhenxia, XIA Dongxing. Tidal Sands in China Seas[M]. Beijing: Ocean Press, 2004.
[57] Emery K O. Relict sediments on continental shelves of World [J]. The American Association of Petroleum Geologists Bulletin, 1968, 52(3): 445-464.
[58] 王张华, 过仲阳, 陈中原. 东海陆架平北地区残留沉积特征及古环境意义[J]. 华东师范大学学报: 自然科学版, 2002(1):81-86
WANG Zhanghua, GUO Zhongyang, CHEN Zhongyuan. Relict sediment and its environmental implication in Pingbei area, East China Sea continental shelf [J]. Journal of East China Normal University: Natural Science, 2002(1): 81-86.
[59] Vail P R. Seismic stratigraphy interpretation using sequence stratigraphy: part 1: seismic stratigraphy interpretation procedure[M]//Bally A W. Atlas of Seismic Stratigraphy. AAPG Studies in Geology, 1987: 1-10.
[60] Galloway W E. Genetic stratigraphic sequences in basin analysis I: architecture and genesis of flooding-surface bounded depositional units [J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1989, 73(2): 125-142.
[61] Posamentier H W, Kolla V. Seismic geomorphology and stratigraphy of depositional elements in deep-water settings [J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 2003, 73(3): 367-388. doi: 10.1306/111302730367
-



 下载:
下载: