“Multi–factor control of sandboies distribution”in the Pinghu Formation, Pingbei region of Baochu slop, the Xihu Sag
-
摘要:
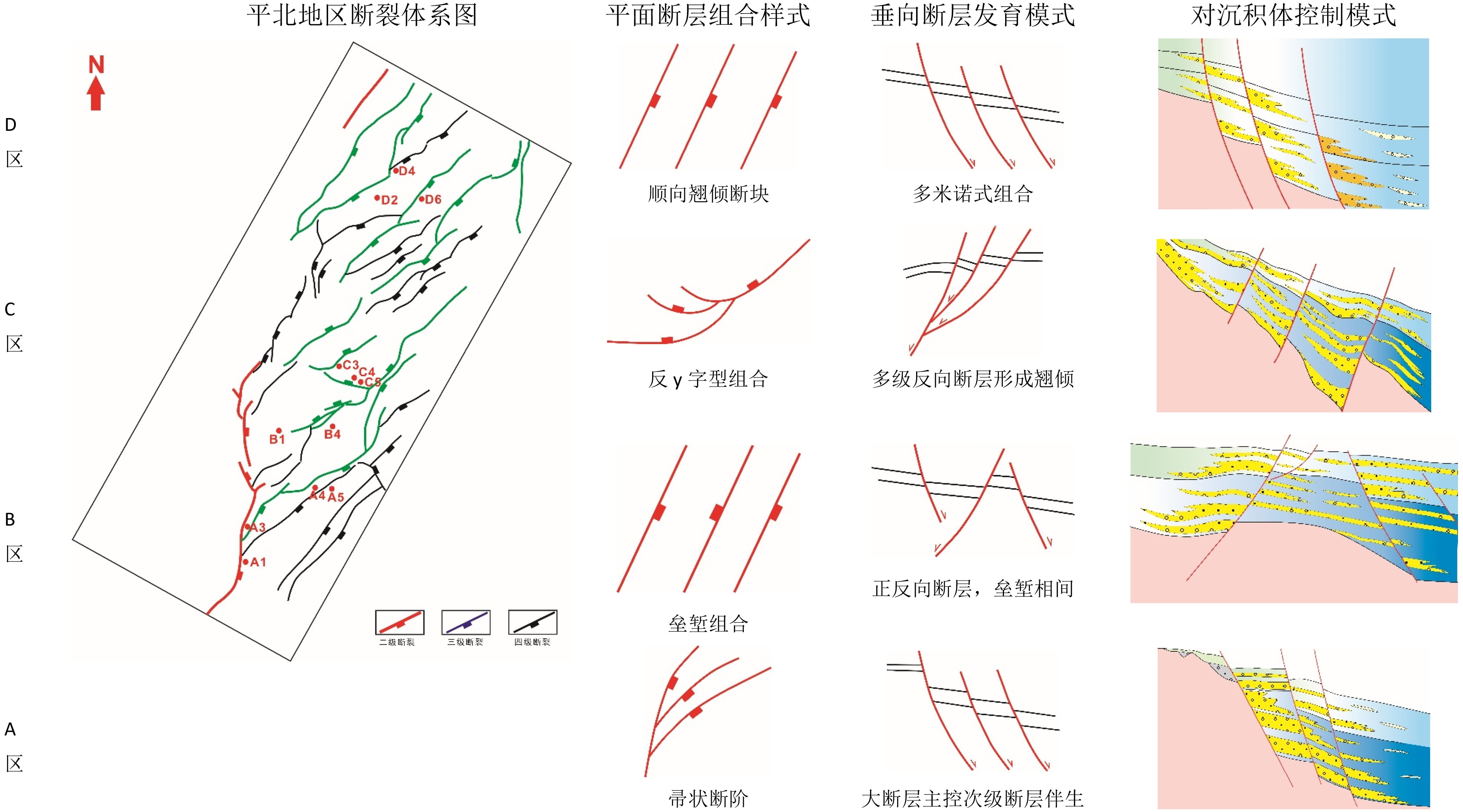
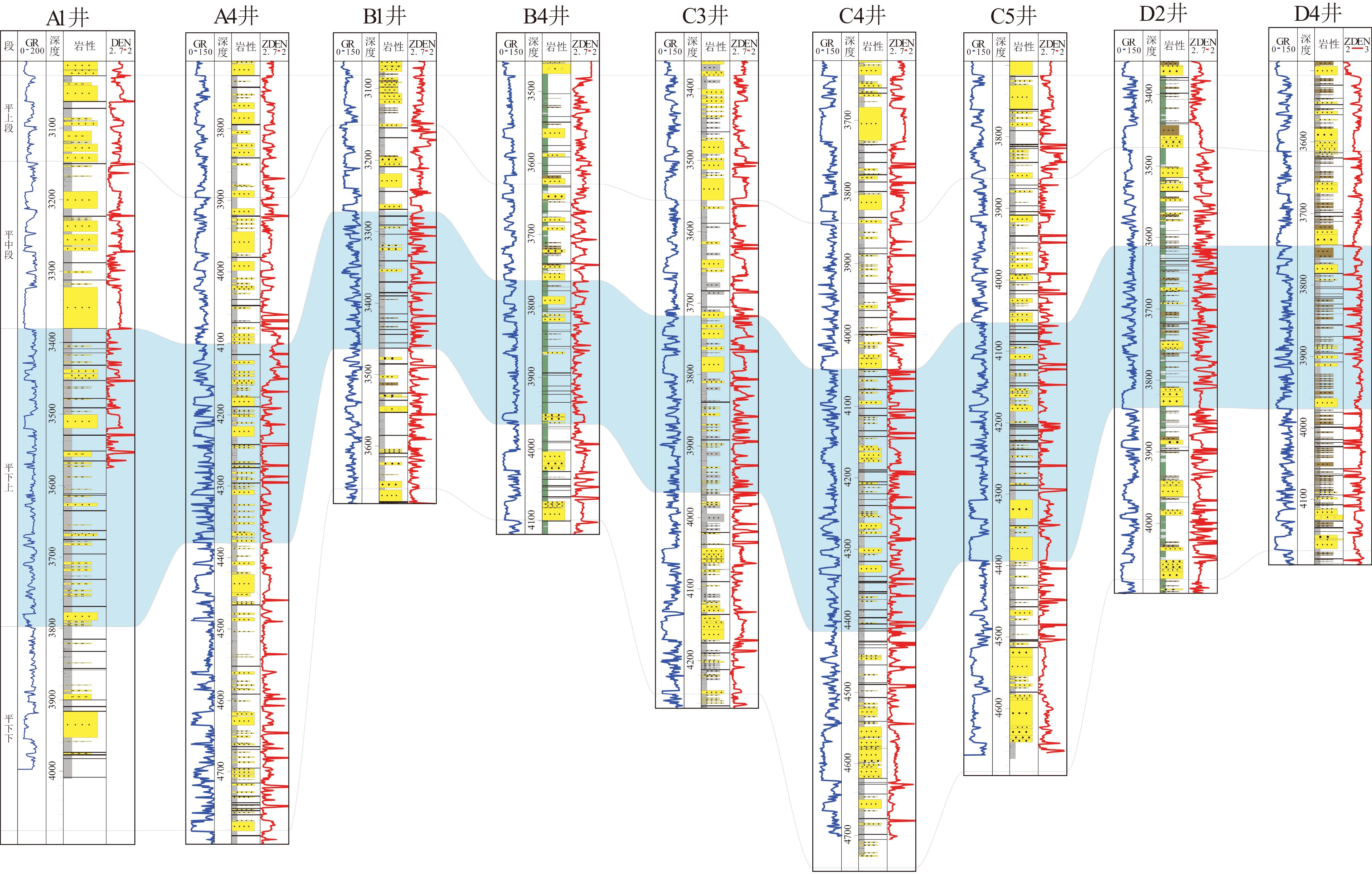
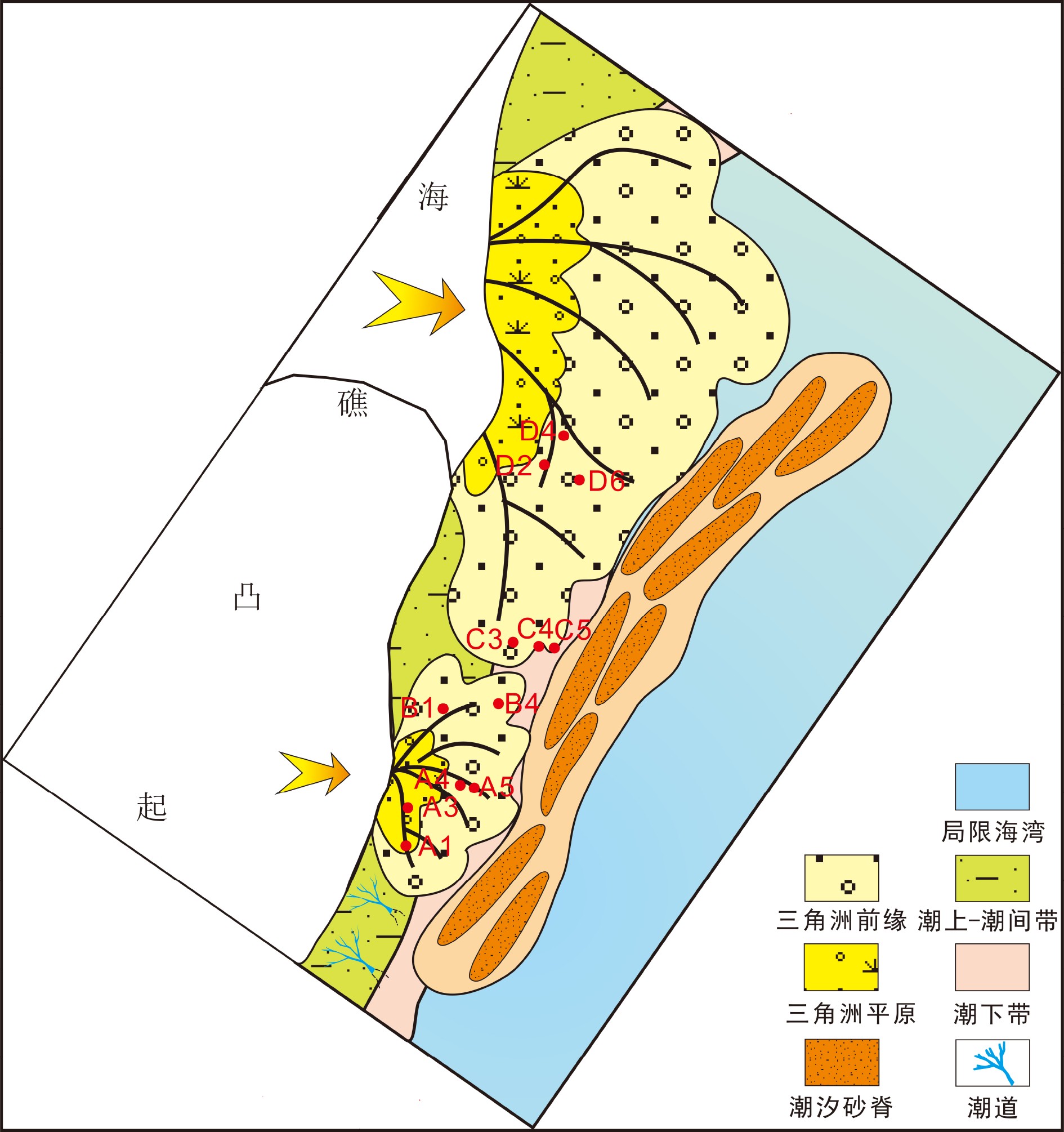
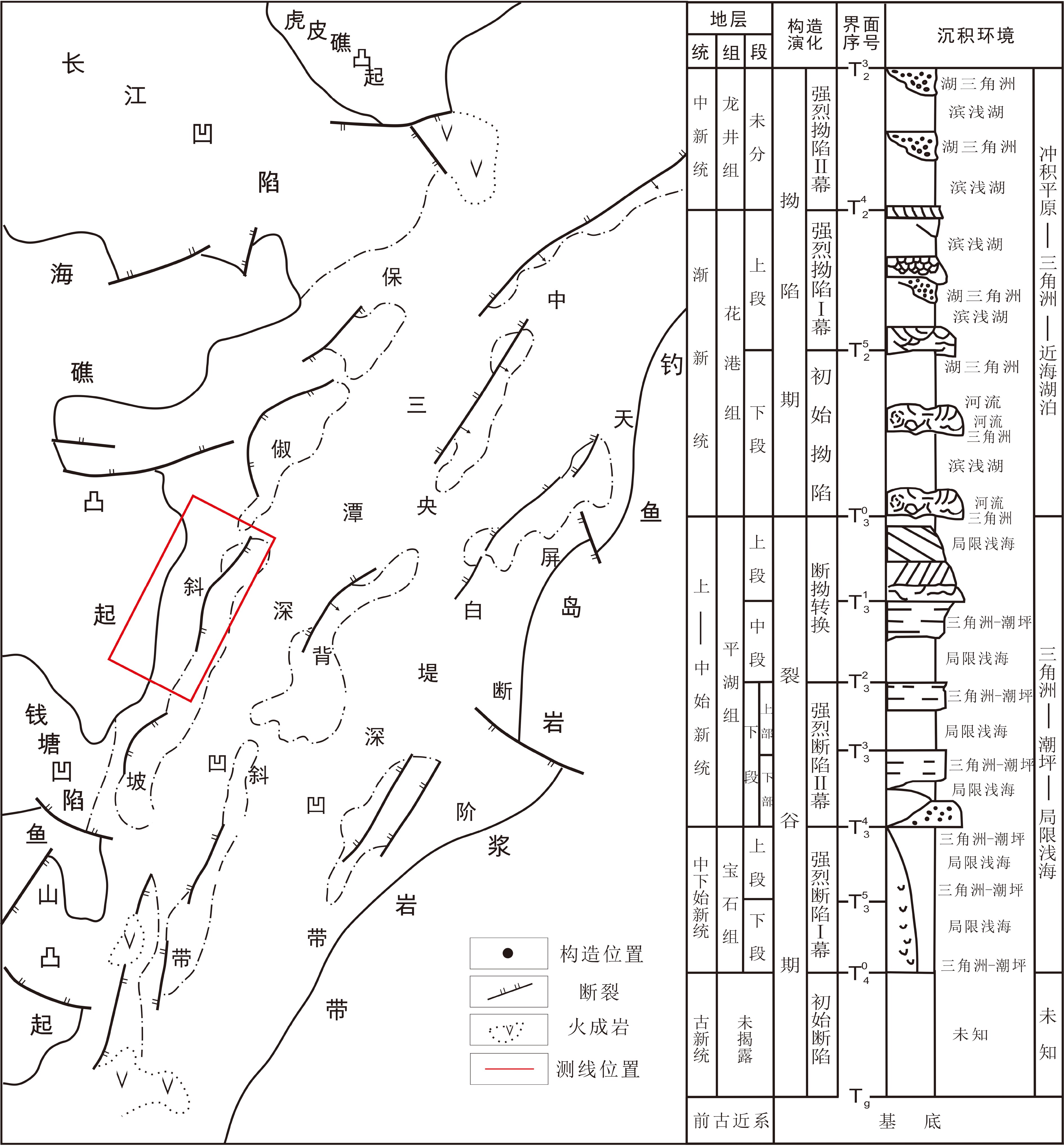
随着勘探开发程度的不断升高,西湖凹陷保俶斜坡带平北地区中上始新统平湖组构造―岩性复合油气藏显示出较大的勘探潜力。然而,该区构造―岩性复合油气藏勘探基础薄弱,加之构造、沉积条件复杂,砂体展布规律不清,阻碍了该区的勘探进程。本文基于三维地震及钻井等资料,从构造、层序及沉积3个方面对砂体分布的控制因素进行分析,认为构造古地貌及可容纳空间控制地层厚度及沉积体规模;同沉积断裂坡折带控制砂体的展布;体系域类型控制砂体的时空配置,沉积微相类型控制砂体的储集物性。综合分析控砂因素认为:断陷期的平下下段和平下上段是构造―岩性圈闭发育的主要层段,勘探方向为低位体系域控沉积断层下降盘的地势低洼汇砂区,而平中上段有利的岩性圈闭勘探区为三角洲前缘砂地比低或三角洲前端发育的潮汐砂脊带。
Abstract:With the progress of hydrocarbon exploration and development, structural-lithologic reservoirs have become more and more significant. However, the exploration of the structural-lithologic reservoirs is not so successful owing to the complexity of the tectonic evolution of the region and the changes in related sedimentary conditions. The sand bodies’distribution boundaries and patterns are difficult to define and have always become the difficult problems to exploration. Based on the newly acquired 3D seismic and drilling data, this article analyzed the controlling factors on sand bodies from the viewpoints of structure, stratigraphic sequence and sedimentation. It is found that there are four factors to be considered: The paleotectonics, paleogeomorphology and accommodation spaces, which control the thickness of the strata and the spatial distribution of sand bodies; the syn-depositional faulting slope break belt which restricted the lateral extension of sand bodies; the sequence patterns and system tracts, which control the spatial and temporal framework of sand bodies; and the types of sedimentary microfacies which determines the reservoir physical properties. The Lower Pinghu Formation was deposited in an intensive faulting period, in which there developed plenty of structural - lithologic traps, which are always been found in the low-lying areas of the downthrow block of syn-depositional fault. However the favorable structural-lithologic traps in the upper-middle Pinghu Formation may occur in the delta front deposits and tidal ridge sandbodies.
-

-
表 1 平北地区不同类型砂体特征
Table 1. The characteristics of different sandbodies in Pingbei region
砂体类型 平下段 平中-上段 水道 河口湾砂坝 水下分流河道 单砂厚 20~70m 10~30m 10~40m 颜色 浅灰、灰白 浅灰、灰白 浅灰、灰白 岩性 砂岩 砂岩 砂岩 粒度 中-粗砂,含砾 细-粗砂,偶含砾 细砂-砾岩 岩电特征 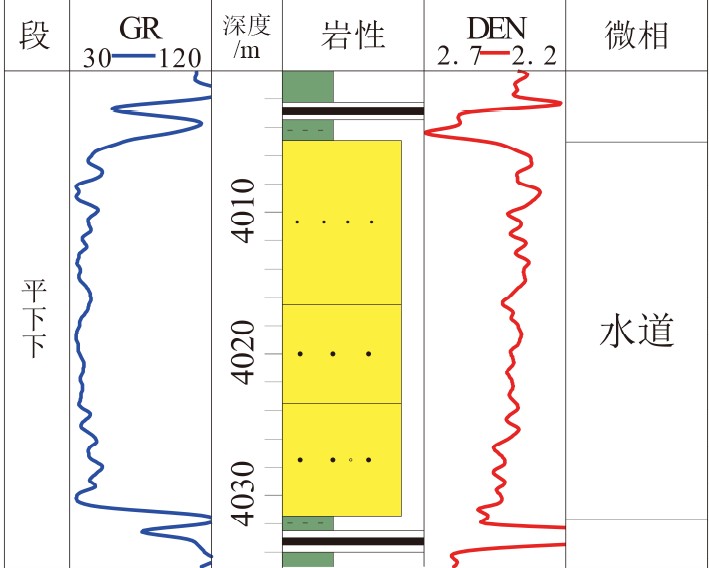
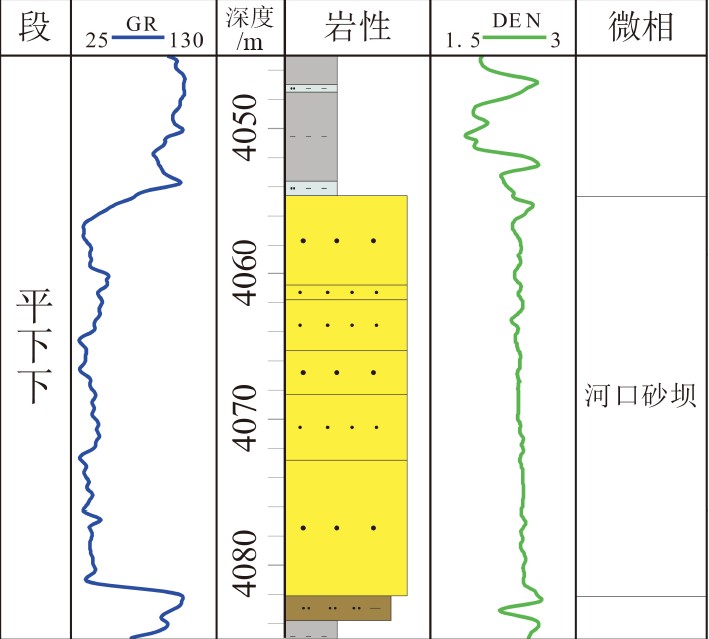
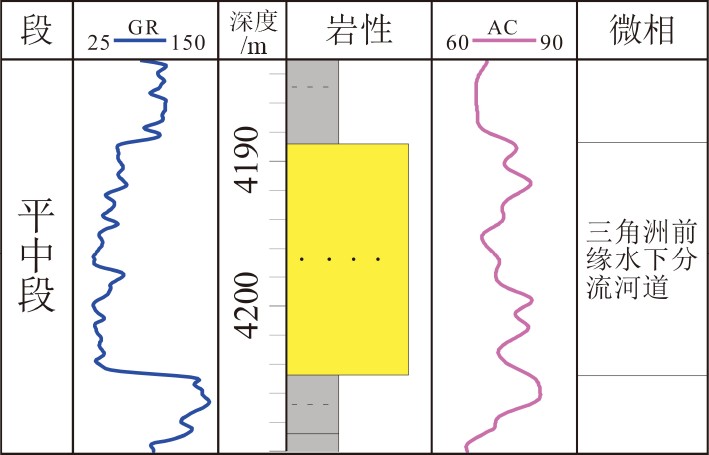
沉积构造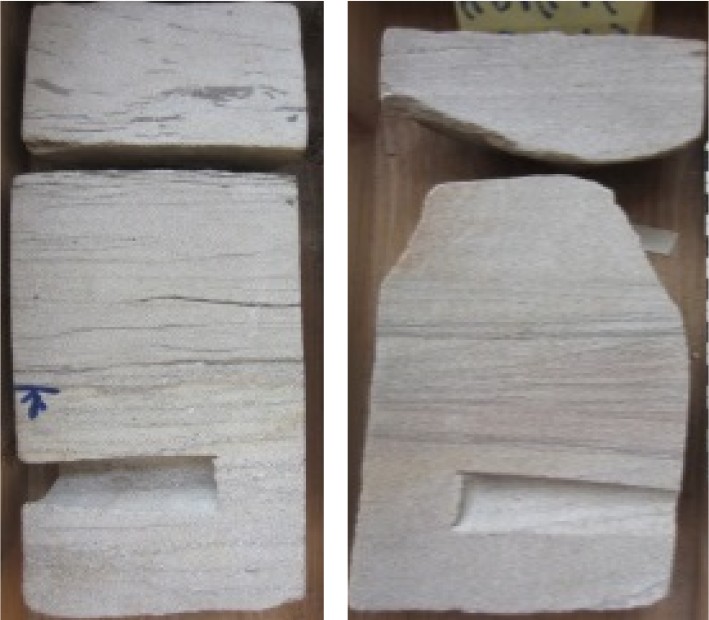 
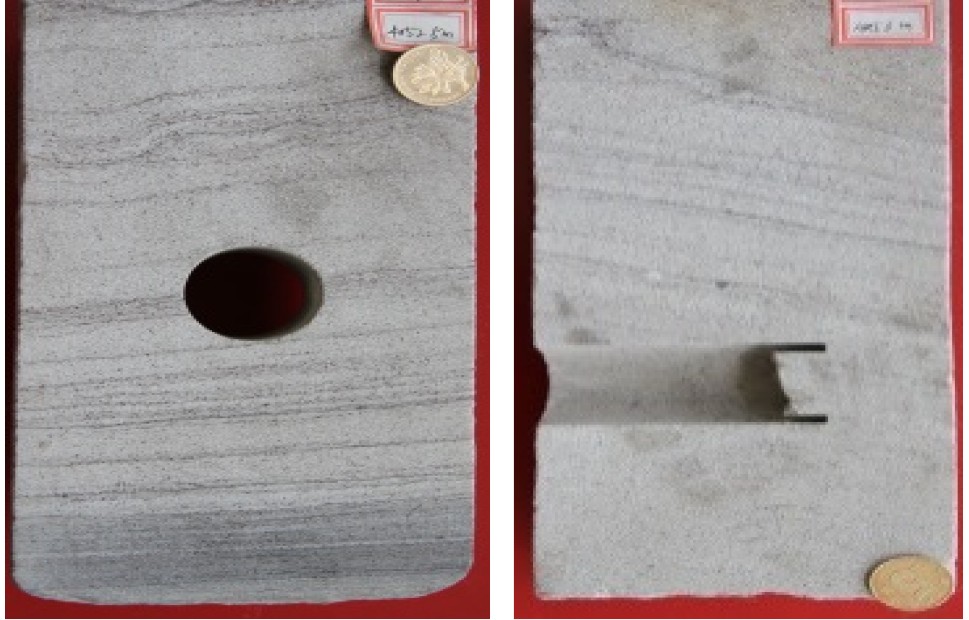
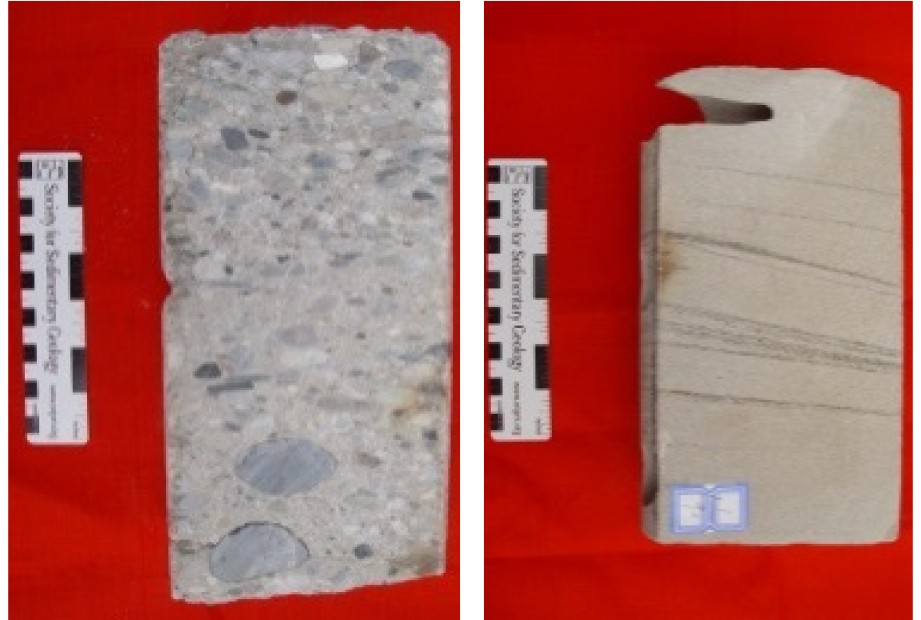


孔隙度(%) 9.9~15(12.5) 9~19.56(13.77) 8~22.23(13.12) 渗透率(mD) 0.5~31.6(5.1) 0.49~145(21.88) 1~227(35.98) -
[1] 贾承造, 池英柳. 中国岩性地层油气藏资源潜力与勘探技术: 隐蔽油气藏形成机理与勘探实践[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2004: 15-25.
JIA Chengzao, CHI Yingliu. Resource Potential and Exploration Techniques of Stratigraphic and subtle Reservoirs in China: Formation Mechanism and Exploration Practice of Subtle Pool[M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 2004: 15-25.
[2] 贾承造, 赵文智, 邹才能, 等. 岩性地层油气藏形成条件与分布规律[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2004: 100-109.
JIA Chengzao, ZHAO Wenzhi, ZOU Caineng, et al. Formation Conditions and Distribution of Lithogic Stratigraphic Reservoirs[M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 2004: 100-109.
[3] 李丕龙, 庞雄奇. 陆相断陷盆地隐蔽油气藏形成-以济阳坳陷为例[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2004.
LI Pilong, PANG Xiongqi. The Formation of Subtle Reservoirs in Continental Fault-Depression Basins-Take Jiyang Depression as an Example[M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 2004.
[4] 赵贤正, 金凤鸣, 刘震, 等. 二连盆地地层岩性油藏“多元控砂-四元成藏-主元富集”与勘探实践(Ⅰ)-“多元控砂”机理[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2007, 6(2):9-15 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8926.2007.02.002
ZHAO Xianzheng, JIN Fengming, LIU Zhen, et al. “Multi-factor controlling, four-factor entrapping and key-factor enrichment” of stratigraphic-lithologic reservoirs and exploration practice in Erlian basin(Ⅰ)-“Multi-factor controlling” mechanism [J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2007, 6(2): 9-15. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8926.2007.02.002
[5] 赵贤正, 蒲秀刚, 王家豪, 等. 断陷盆地缓坡区控砂控藏机制与勘探发现-以歧口凹陷歧北缓坡带为例[J]. 石油学报, 2017, 38(7):729-739 doi: 10.7623/syxb201707001
ZHAO Xianzheng, PU Xiugang, WANG Jiahao, et al. Sand and reservoir controlling mechanism and exploration discovery in the gentle slope of fault basin: a case study of Qibei slope in Qikou Sag [J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2017, 38(7): 729-739. doi: 10.7623/syxb201707001
[6] 韩春元, 赵贤正, 金凤鸣, 等. 二连盆地地层岩性油藏“多元控砂-四元成藏-主元富集”与勘探实践(Ⅳ)-勘探实践[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2008, 20(1):15-20 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8926.2008.01.003
HAN Chunyuan, ZHAO Xianzheng, JIN Fengming, et al. Multi-factor controlling, four-factor entrapping and key-factor enrichment of stratigraphic-lithologic reservoirs and exploration practice in Erlian basin(Ⅳ)-Exploration practice [J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2008, 20(1): 15-20. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8926.2008.01.003
[7] 李磊, 王小刚, 陈玲玲, 等. 东海西湖凹陷始新统复合潮汐水道三维地震表征[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2015, 26(2):352-359
LI Lei, WANG Xiaogang, CHEN Lingling, et al. 3-D seismic characterization of the Eocene complex tidal channels in Xihu Sag, East China Sea [J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2015, 26(2): 352-359.
[8] 林畅松, 潘元林, 肖建新, 等. “构造坡折带”-断陷盆地层序分析和油气预测的重要概念[J]. 地球科学-中国地质大学学报, 2000, 25(3):260-266 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-2383.2000.03.008
LIN Changsong, PAN Yuanlin, XIAO Jianxin, et al. Structural slope-break zone: key concept for stratigraphic sequence analysis and petroleum forecasting in fault subsidence basins [J]. Earth Science-Journal of China University of Geoscience, 2000, 25(3): 260-266. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-2383.2000.03.008
[9] 王英民, 金武弟, 刘书会, 等. 断陷湖盆多级坡折带的成因类型、展布及其勘探意义[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2003, 24(3):199-203, 214 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9985.2003.03.002
WANG Yingmin, JIN Wudi, LIU Shuhui, et al. Genetic types, distribution and exploration significance of multistage slope breaks in rift lacustrine basin [J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2003, 24(3): 199-203, 214. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9985.2003.03.002
[10] 肖焕钦, 王宝言, 陈宝宁, 等. 济阳坳陷陡坡带断裂控砂模式[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2002, 9(5):20-23 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-9603.2002.05.007
XIAO Huanqin, WANG Baoyan, CHEN Baoning, et al. Fracture sand control pattern in actic region of Jiyang Depression [J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2002, 9(5): 20-23. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-9603.2002.05.007
[11] 赵贤正, 卢学军, 崔周旗, 等. 断陷盆地斜坡带精细层序地层研究与勘探成效[J]. 地学前缘, 2012, 19(1):10-19
ZHAO Xianzheng, LU Xuejun, CUI Zhouqi, et al. Detailed research of fine sequence stratigraphy and exploration results in the slope zone of faulted basin [J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2012, 19(1): 10-19.
[12] 陈贤良, 樊太亮, 王宏语, 等. 松辽盆地梨树断陷层序结构特征及岩性地层圈闭[J]. 地层学杂志, 2016, 40(3):308-317
CHEN Xianliang, FAN Tailiang, WANG Hongyu, et al. Sequence structures and lithologic-stratigraphic traps in the Lishu rift, Songliao Basin [J]. Journal of Stratigraphy, 2016, 40(3): 308-317.
[13] 邹才能, 陶士振, 古志东. 陆相坳陷盆地层序地层格架下岩性地层圈闭/油藏类型与分布规律-以松辽盆地白垩系泉头组-嫩江组为例[J]. 地质科学, 2006, 41(4):711-719 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0563-5020.2006.04.014
ZOU Caineng, TAO Shizhen, GU Zhidong. Types and distributions of litho-stratigraphic traps/reservoirs in sequence stratigraphic framework in continental depressional basin: an example from the Cretaceous in the Songliao basin [J]. Chinese Journal of Geology, 2006, 41(4): 711-719. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0563-5020.2006.04.014
[14] 曹颖辉, 迟柳英, 薛良清, 等. 沉积基准面在层序划分对比及地层岩性油气藏预测中的应用[J]. 石油实验地质, 2002, 24(1):36-47 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6112.2002.01.006
CAO Yinghui, CHI Liuying, XUE Liangqing, et al. Application of depositional base-level concept in sequence stratigraphic division, correlation and litho-stratigraphic traps prediction [J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2002, 24(1): 36-47. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6112.2002.01.006
[15] 郭少斌. 陆相断陷盆地层序类型及隐蔽圈闭预测[J]. 地质科技情报, 2006, 25(5):15-20 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7849.2006.05.003
GUO Shaobin. Sequence types and subtle reservoirs exploration in continental rift-subsidence basin [J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2006, 25(5): 15-20. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7849.2006.05.003
[16] Abbas A, Zhu H T, Zeng Z W, et al. Sedimentary facies analysis using sequence stratigraphy and seismic sedimentology in the Paleogene Pinghu Formation, Xihu Depression, East China Sea Shelf Basin [J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2018, 93: 287-297. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2018.03.017
-



 下载:
下载: