Subduction dynamics of the New-Guinea-Solomon arc system: Constraints from the subduction initiation of the plate
-
摘要:
新几内亚-所罗门弧(PN-SL)位于印度-澳大利亚板块与太平洋板块汇聚边界、新特提斯构造域东端。晚白垩世以来,逐渐演化形成复杂的沟-弧-盆-台、俯冲时序完整的俯冲构造体系。受多期次、多类型板块俯冲起始作用的制约,PN-SL俯冲体系深部结构呈现出明显的空间差异性:板块俯冲深度由>500 km减小至不足100 km,板块俯冲角度则由>70°减小至30°。俯冲体系东侧毗邻的翁通爪哇海台作为世界上最大的海台,其显著的“凸起”构造以及低密度结构,重新塑造了PN-SL俯冲体系的构造格局,但不同于低密度结构俯冲诱发海沟位置后移、俯冲极性反转二元经典模式,弧后所罗门海盆发生反向俯冲的同时,中新世以来呈现出NW向、NE向和SW向的多向俯冲过程。这意味着翁通爪哇海台与PN-SL俯冲体系汇聚形变过程并非仅依据板块密度变化来简单解释,需要考虑其复杂的构造环境和诸多的构造要素。特别是作为岩石圈强度的重要影响因子—俯冲体系流体活动,导致岩石圈强度减弱、熔点降低的同时,伴随板块俯冲向地球深部运移,促使板片脱水并与地幔楔发生水化交代作用,进而改变壳幔物质组成及流变学性质,诱发地幔楔部分熔融和岛弧岩浆活动,是理解板块俯冲构造动力的关键切入点。
Abstract:A complicated subduction system, the New-Guinea-Solomon arc (PN-SL), exists in the convergent boundary between the Indo-Australian and Pacific plates at the eastern end of the Neo-Tethyan tectonic domain. Since late Cretaceous, the PN-SL system has gradually become a complex trench-arc-basin-oceanic plateau system suffered various stages of subduction. Constrained by the multi-stages and multi-types of plate subduction initiation, the deep structure of the PN-SL subduction system varies dramatically in space. Among the subduction zones within the PN-SL subduction system, the extension depth of the subducting plate changes from over 500 km to nearly 100 km and the dip angle of the plate decreases from over 70° to 30°. The Ontong Java Plateau, the largest oceanic plateau in the world, is located in the east of the PN-SL subduction system. Owing to the large crustal bulge and associated low-density structure, the tectonic framework of the PN-SL subduction system is reconstructed. Driven by the subduction of the Ontong Java Plateau, the Solomon Sea back-arc basin has subducted beneath the Pacific ocean towards northwest, northeast and southwest directions since Miocene, sharply contrasted with the classical binary model of the subduction polarity reversal and transference or trench jump induced by the subduction of the buoyant lithosphere. This indicates that the convergent deformation process between the Ontong Java Plateau and the PN-SL subduction system cannot just be interpreted as the change in plate density. Complex tectonic environment and various tectonic elements must be considered in the studies on the subduction and convergent deformation of the oceanic plateau. In particular, as an important influence factor of the strength of the lithosphere, the fluid activity of the subduction system, which may induce the strength weakening and decrease in the melting point of the lithosphere, must be carefully considered. Moreover, the fluid may be transported into the deep part of the Earth together with the subduction of plate and make contributions to the dehydration of plate and the hydro-metasomatism within the mantle wedge, which changes the composition and rheological properties of the crust and mantle and induces partial melting of the mantle wedge and island magmatism. Therefore, it is concluded that fluid plays an important role in the subduction initiation and evolution as a key entry point for understanding the subduction tectonic dynamics of the plate.
-
Key words:
- New-Guinea-Solomon arc /
- Ontong Java Plateau /
- subduction tectonic dynamics /
- density /
- fluid
-

-
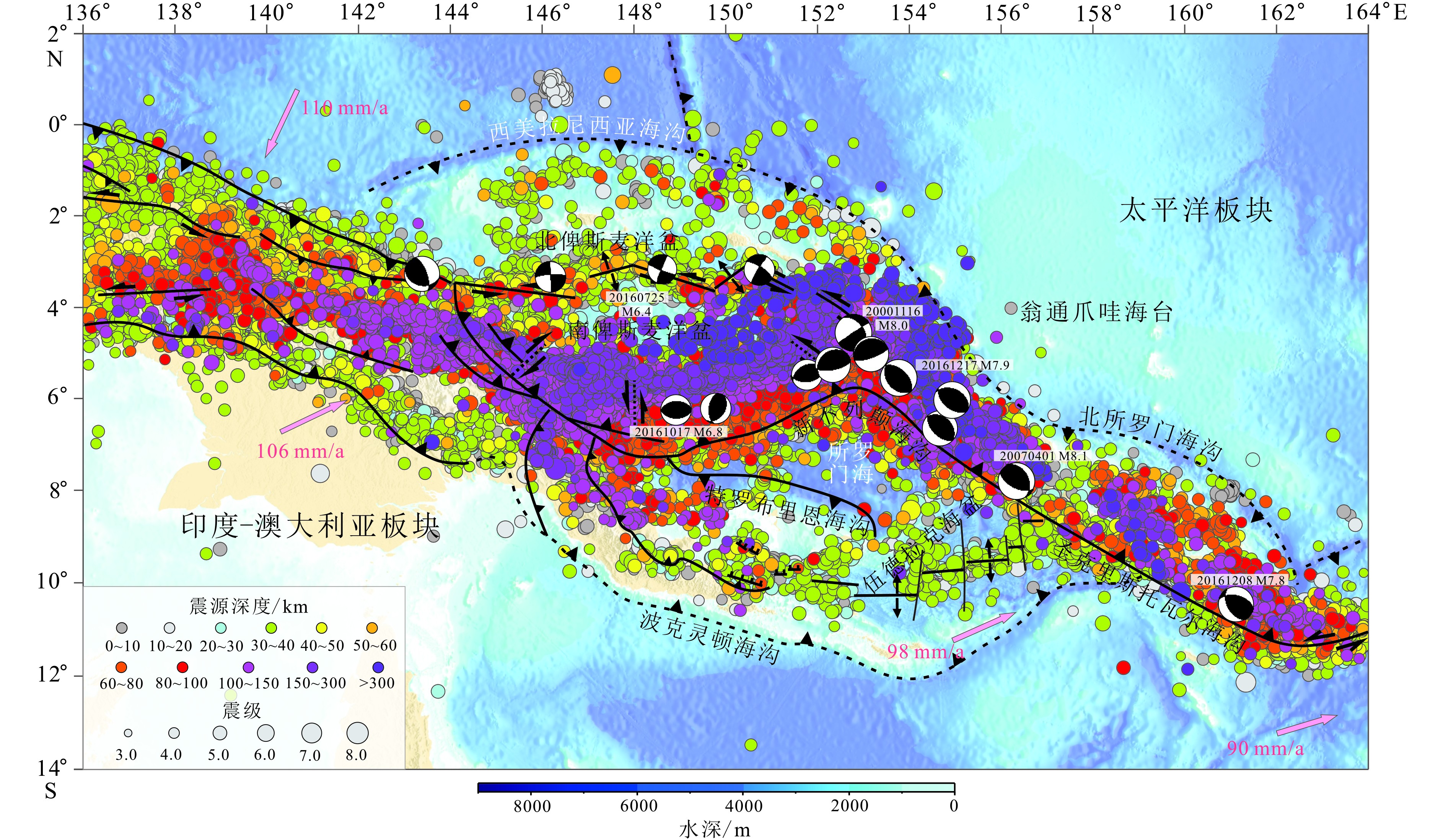
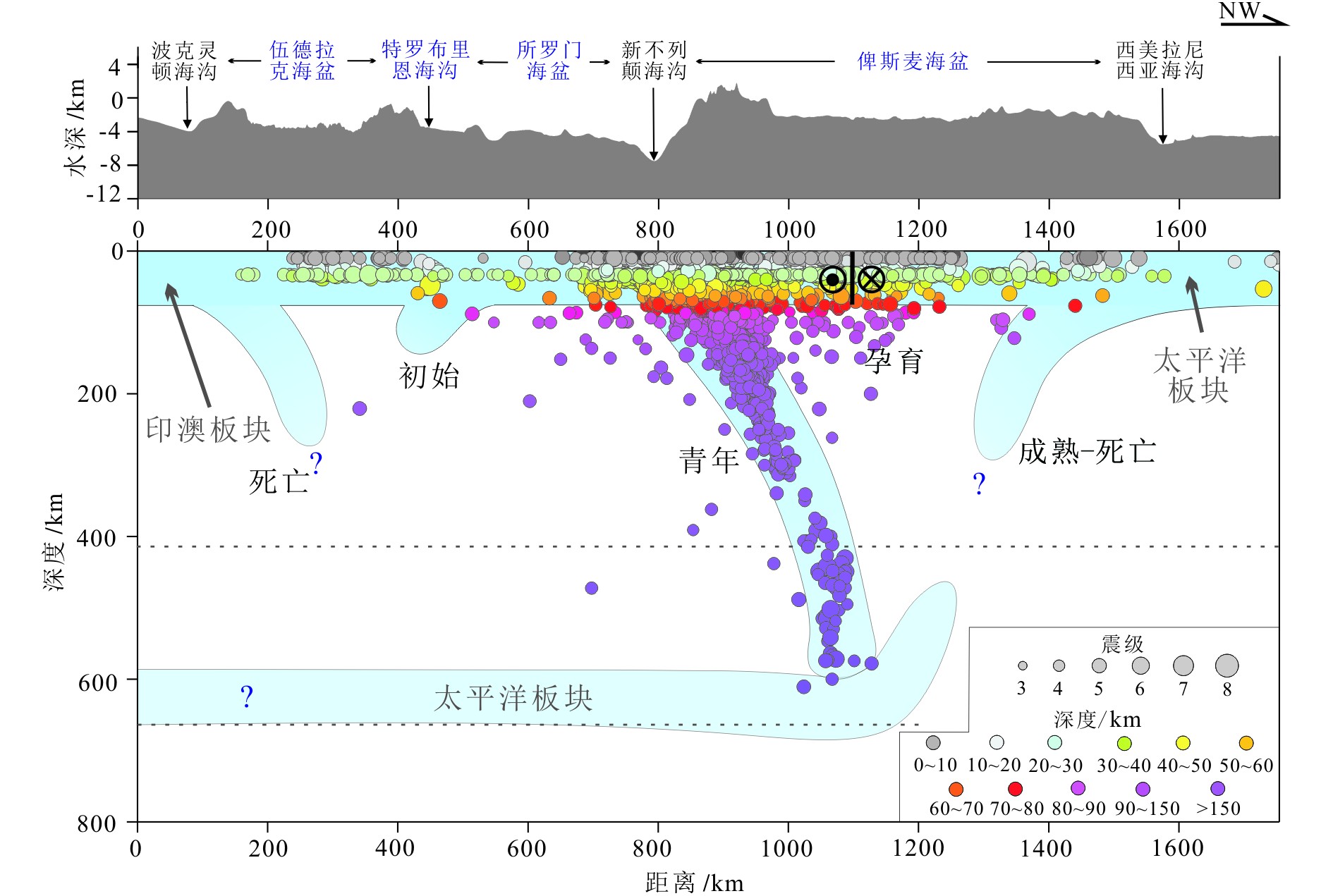
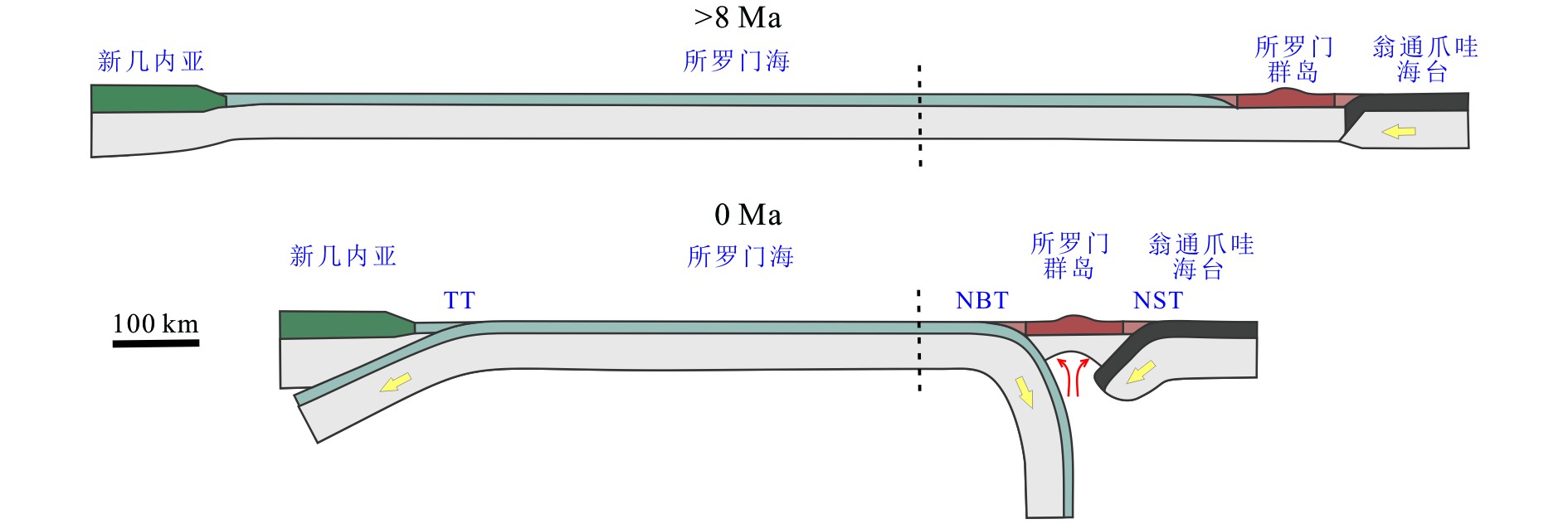
图 3 测线L地形及PN-SL俯冲体系深部结构示意图(测线L位置见图1所示)
Figure 3.
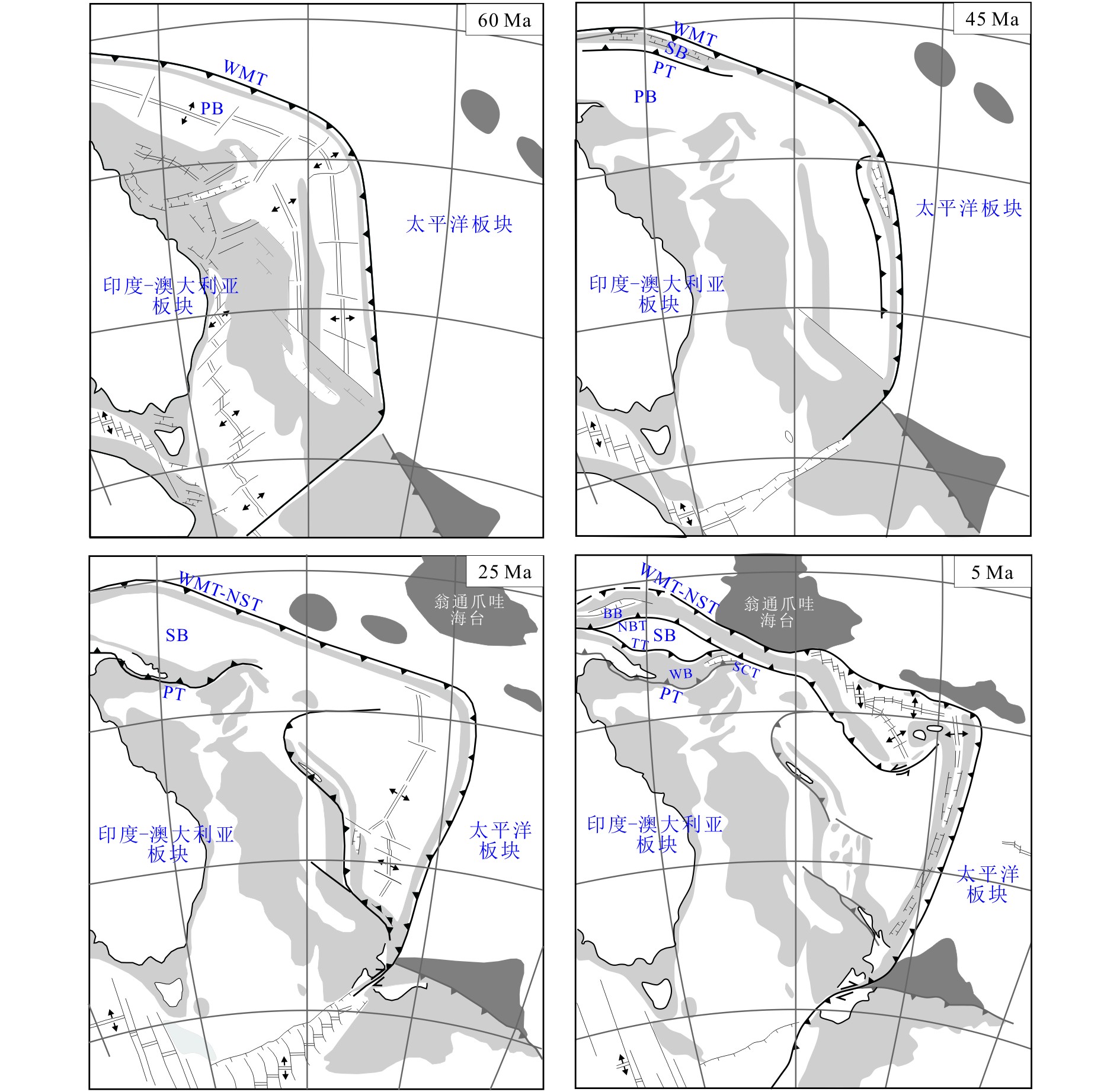
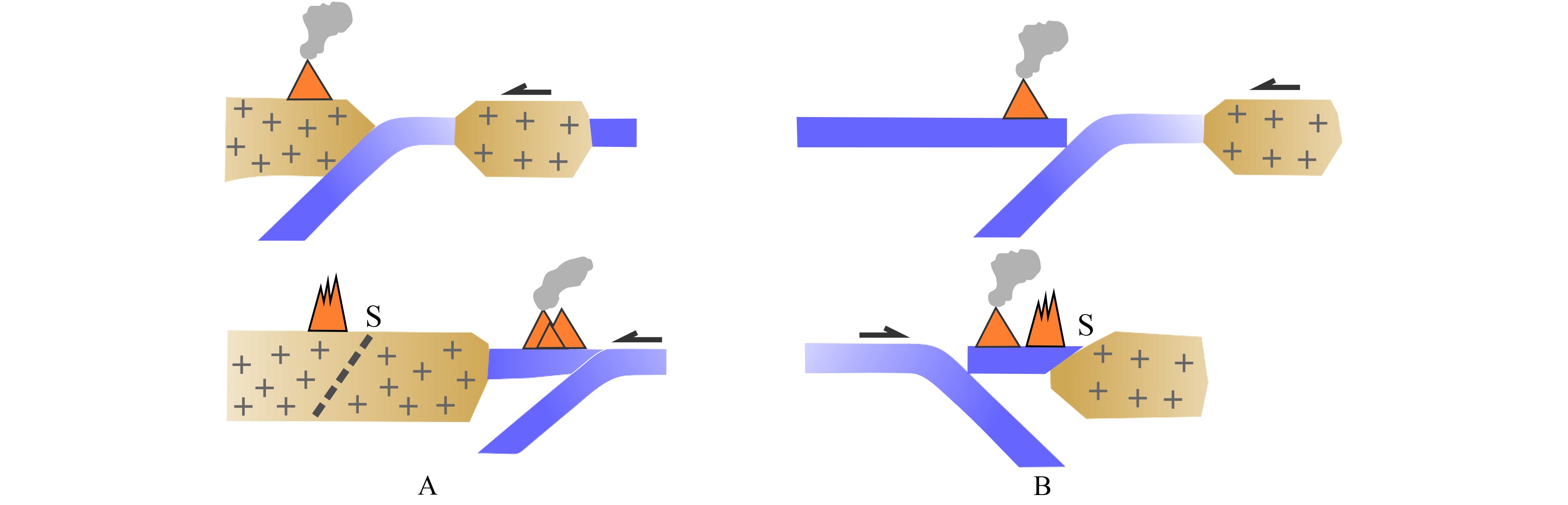
图 4 PN-SL俯冲体系关键构造演化阶段模式图(修改自Schellart等[3])
Figure 4.
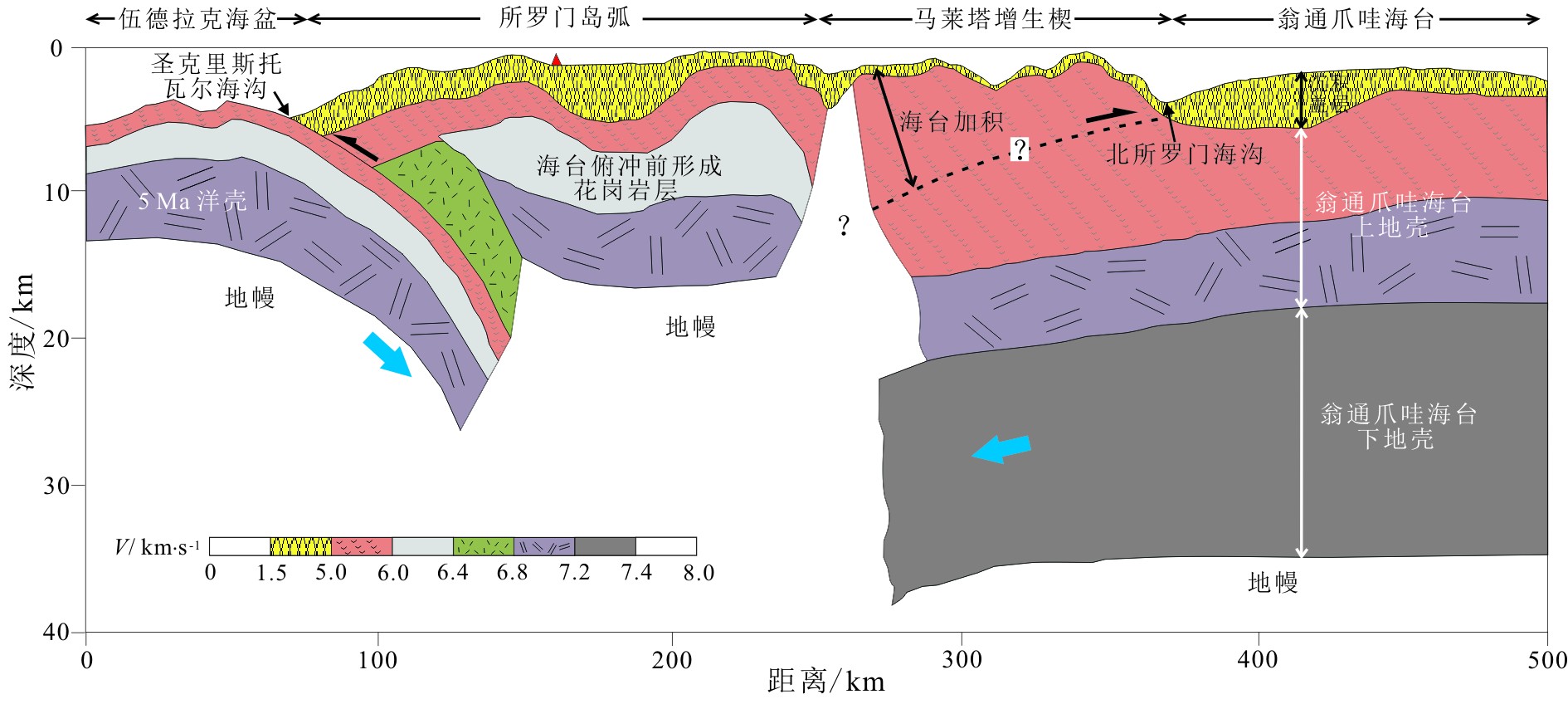
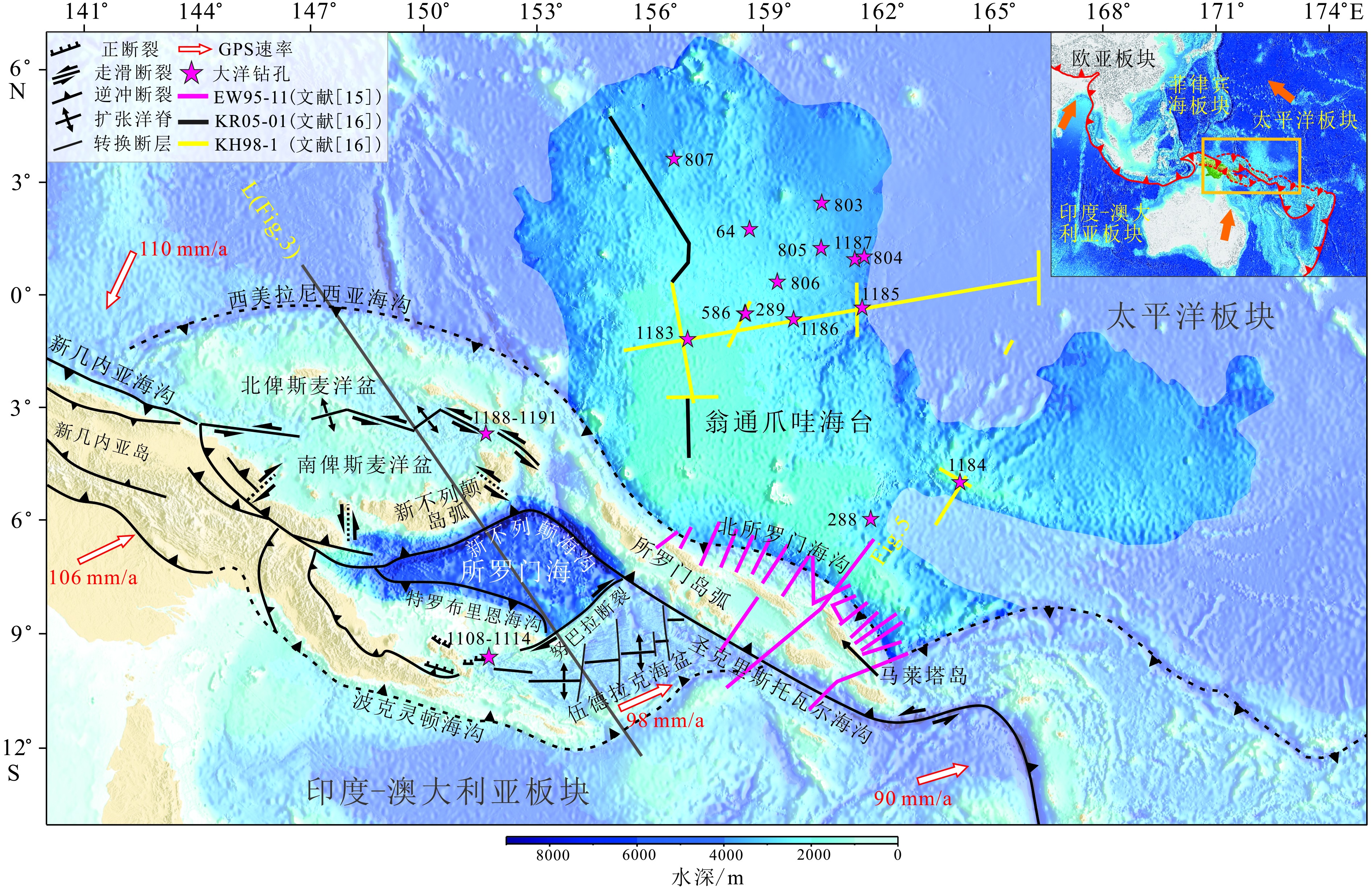
图 5 翁通爪哇海台与PN-SL俯冲体系拼贴构造结构剖面(测线位置见图1)
Figure 5.
图 7 翁通爪哇海台俯冲碰撞诱发PN-SL俯冲体系“反向、多向俯冲”示意图(修改自Holm等[4])
Figure 7.
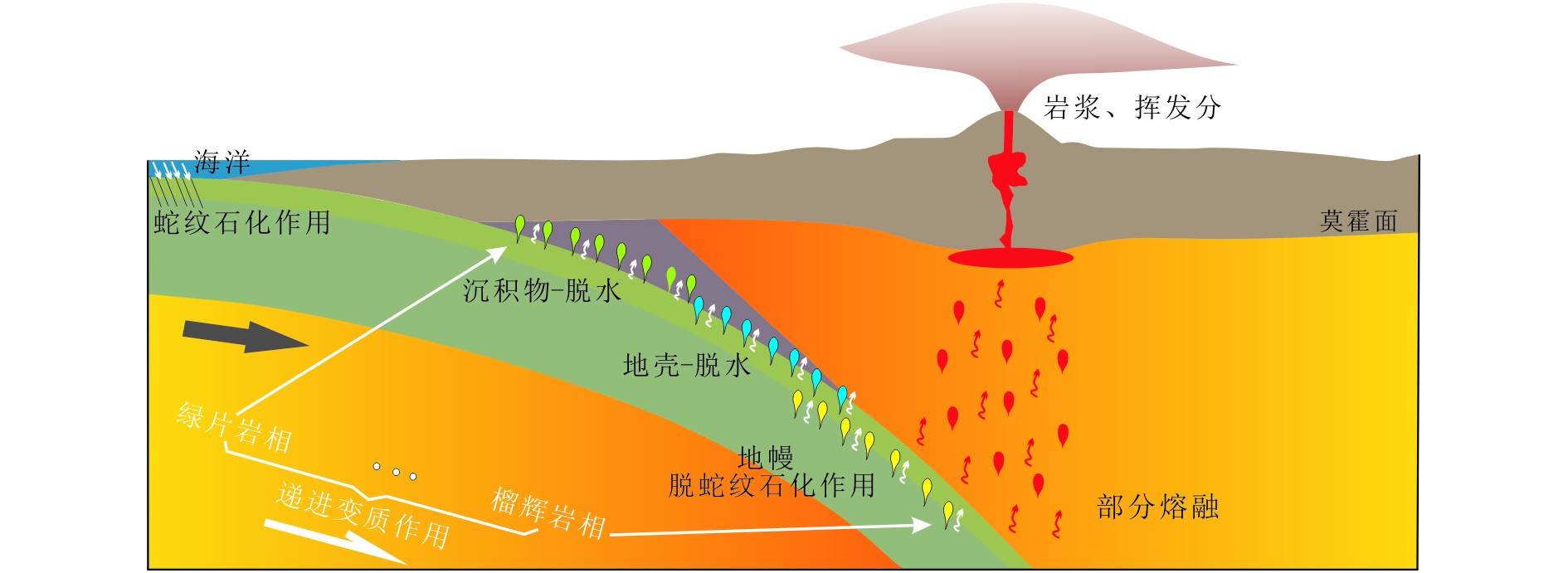
图 8 俯冲体系流体分布及迁移示意图(修改自Rüpke等[101])
Figure 8.
-
[1] Wessel P, Kroenke L W. Ontong Java Plateau and late Neogene changes in Pacific plate motion [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 2000, 105(B12): 28255-28277. doi: 10.1029/2000JB900290
[2] Stotz I L, Iaffaldano G, Davies D R. Late Miocene Pacific plate kinematic change explained with coupled global models of mantle and lithosphere dynamics [J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2017, 44(14): 7177-7186. doi: 10.1002/2017GL073920
[3] Schellart W P, Lister G S, Toy V G. A Late Cretaceous and Cenozoic reconstruction of the Southwest Pacific region: Tectonics controlled by subduction and slab rollback processes [J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2006, 76(3-4): 191-233. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2006.01.002
[4] Holm R J, Rosenbaum G, Richards S W. Post 8 Ma reconstruction of Papua New Guinea and Solomon Islands: Microplate tectonics in a convergent plate boundary setting [J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2016, 156: 66-81. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2016.03.005
[5] Both R, Crook K, Taylor B, et al. Hydrothermal chimneys and associated fauna in the Manus Back-Arc Basin, Papua New Guinea [J]. Eos, Transactions American Geophysical Union, 1986, 67(21): 489-490. doi: 10.1029/EO067i021p00489
[6] Cooper P A, Taylor B. Polarity reversal in the Solomon Islands arc [J]. Nature, 1985, 314(6010): 428-430. doi: 10.1038/314428a0
[7] Petterson M G, Babbs T, Neal C R, et al. Geological-tectonic framework of Solomon Islands, SW Pacific: Crustal accretion and growth within an intra-oceanic setting [J]. Tectonophysics, 1999, 301(1-2): 35-60. doi: 10.1016/S0040-1951(98)00214-5
[8] Chadwick J, Perfit M, McInnes B, et al. Arc lavas on both sides of a trench: Slab window effects at the Solomon Islands triple junction, SW Pacific [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2009, 279(3-4): 293-302. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2009.01.001
[9] Schuth S, König S, Münker C. Subduction zone dynamics in the SW Pacific plate boundary region constrained from high-precision Pb isotope data [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2011, 311(3-4): 328-338. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2011.09.006
[10] Taylor B. Bismarck Sea: Evolution of a back-arc basin [J]. Geology, 1979, 7(4): 171-174. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1979)7<171:BSEOAB>2.0.CO;2
[11] Wallace L M, Stevens C, Silver E, et al. GPS and seismological constraints on active tectonics and arc-continent collision in Papua New Guinea: Implications for mechanics of microplate rotations in a plate boundary zone [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 2004, 109(B5): B05404.
[12] Cooper P, Taylor B. Seismotectonics of New Guinea: A model for arc reversal following arc-continent collision [J]. Tectonics, 1987, 6(1): 53-67. doi: 10.1029/TC006i001p00053
[13] Holm R J, Richards S W. A re-evaluation of arc-continent collision and along-arc variation in the Bismarck Sea region, Papua New Guinea [J]. Australian Journal of Earth Sciences, 2013, 60(5): 605-619. doi: 10.1080/08120099.2013.824505
[14] Westaway R. Active low-angle normal faulting in the Woodlark extensional province, Papua New Guinea: A physical model [J]. Tectonics, 2005, 24(6): TC6003.
[15] Phinney E J, Mann P, Coffin M F, et al. Sequence stratigraphy, structural style, and age of deformation of the Malaita accretionary prism (Solomon arc-Ontong Java Plateau convergent zone) [J]. Tectonophysics, 2004, 389(3-4): 221-246. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2003.10.025
[16] Inoue H, Coffin M F, Nakamura Y, et al. Intrabasement reflections of the Ontong Java Plateau: Implications for plateau construction [J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2008, 9(4): Q04014.
[17] Baldwin S L, Fitzgerald P G, Webb L E. Tectonics of the New Guinea region [J]. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 2012, 40(1): 495-520. doi: 10.1146/annurev-earth-040809-152540
[18] Holm R J, Spandler C, Richards S W. Melanesian arc far-field response to collision of the Ontong Java Plateau: Geochronology and petrogenesis of the Simuku Igneous Complex, New Britain, Papua New Guinea [J]. Tectonophysics, 2013, 603: 189-212. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2013.05.029
[19] McInnes B I A, Gregoire M, Binns R A, et al. Hydrous metasomatism of oceanic sub-arc mantle, Lihir, Papua New Guinea: petrology and geochemistry of fluid-metasomatised mantle wedge xenoliths [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2001, 188(1-2): 169-183. doi: 10.1016/S0012-821X(01)00306-5
[20] Bénard A, Woodland A B, Arculus R J, et al. Variation in sub-arc mantle oxygen fugacity during partial melting recorded in refractory peridotite xenoliths from the West Bismarck Arc [J]. Chemical Geology, 2018, 486: 16-30. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2018.03.004
[21] Eguchi T, Fujinawa Y, Ukawa M, et al. Earthquakes associated with the back-arc opening in the eastern Bismarck Sea: activity, mechanisms, and tectonics [J]. Physics of the Earth and Planetary Interiors, 1989, 56(3-4): 189-209. doi: 10.1016/0031-9201(89)90157-X
[22] Bird P. An updated digital model of plate boundaries [J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2003, 4(3): 1027.
[23] Binns R A, Scott S D. Actively forming polymetallic sulfide deposits associated with felsic volcanic rocks in the Eastern Manus Back-arc basin, Papua New Guinea [J]. Economic Geology, 1993, 88(8): 2226-2236. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.88.8.2226
[24] Crook K A W, Taylor B. Structure and Quaternary tectonic history of the Woodlark triple junction region, Solomon islands [J]. Marine Geophysical Researches, 1994, 16(1): 65-89. doi: 10.1007/BF01812446
[25] Taylor B, Goodliffe A, Martinez F, et al. Continental rifting and initial sea-floor spreading in the Woodlark basin [J]. Nature, 1995, 374(6522): 534-537. doi: 10.1038/374534a0
[26] Abers G A, Mutter C Z, Fang J. Shallow dips of normal faults during rapid extension: Earthquakes in the Woodlark-D’Entrecasteaux rift system, Papua New Guinea [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 1997, 102(B7): 15301-15317. doi: 10.1029/97JB00787
[27] Abers G A, Ferris A, Craig M, et al. Mantle compensation of active metamorphic core complexes at Woodlark rift in Papua New Guinea [J]. Nature, 2002, 418(6900): 862-865. doi: 10.1038/nature00990
[28] Bruns T R, Vedder J G, Cooper A K. Geology of the Shortland basin region, central Solomons Trough, Solomon Islands-review and new findings[C]//Vedder J G, Bruns T R. Geology and offshore resources of Pacific island arcs-Solomon Islands and Bougainville, Papua New Guinea Regions, Earth Science Series. Houston, Texas: Circum-Pacific Council for Energy and Mineral Resources, 1989: 125-144.
[29] Mann P, Taira A. Global tectonic significance of the Solomon Islands and Ontong Java Plateau convergent zone [J]. Tectonophysics, 2004, 389(3-4): 137-190. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2003.10.024
[30] Zhang Z, Li S Z, Tian J W, et al. Formation mechanism of the moniliform seamounts outside the West Melanesian Trench [J]. Geological Journal, 2018, 53(4): 1604-1610. doi: 10.1002/gj.2979
[31] Hall R, Spakman W. Subducted slabs beneath the eastern Indonesia-Tonga region: insights from tomography [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2002, 201(2): 321-336. doi: 10.1016/S0012-821X(02)00705-7
[32] Abers G A, Roecker S W. Deep structure of an Arc-Continent collision: Earthquake relocation and inversion for upper mantle P and S wave velocities beneath Papua New Guinea [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 1991, 96(B4): 6379-6401. doi: 10.1029/91JB00145
[33] Woodhead J, Hergt J, Sandiford M, et al. The big crunch: Physical and chemical expressions of arc/continent collision in the Western Bismarck arc [J]. Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, 2010, 190(1-2): 11-24. doi: 10.1016/j.jvolgeores.2009.03.003
[34] Mohiuddin A, Long M D, Lynner C. Mid-mantle seismic anisotropy beneath southwestern Pacific subduction systems and implications for mid-mantle deformation [J]. Physics of the Earth and Planetary Interiors, 2015, 245: 1-14. doi: 10.1016/j.pepi.2015.05.003
[35] 张培震, 张会平, 郑文俊, 等. 东亚大陆新生代构造演化[J]. 地震地质, 2014, 36(3):574-585 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2014.03.003
ZHANG Peizhen, ZHANG Huiping, ZHENG Wenjun, et al. Cenozoic tectonic evolution of continental Eastern Asia [J]. Seismology and Geology, 2014, 36(3): 574-585. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2014.03.003
[36] Seton M, Müller R D, Zahirovic S, et al. Global continental and ocean basin reconstructions since 200 Ma [J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2012, 113(3-4): 212-270. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2012.03.002
[37] Schellart W P, Spakman W. Australian plate motion and topography linked to fossil New Guinea slab below Lake Eyre [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2015, 421: 107-116. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2015.03.036
[38] Zahirovic S, Matthews K J, Flament N, et al. Tectonic evolution and deep mantle structure of the eastern Tethys since the latest Jurassic [J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2016, 162: 293-337. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2016.09.005
[39] Crawford A J, Meffre S, Symonds P A. 120 to 0 Ma tectonic evolution of the southwest Pacific and analogous geological evolution of the 600 to 220 Ma Tasman Fold Belt System[C]//Evolution and Dynamics of the Australian Plate. Geological Society of Australia Special Publication, 2003, 22: 377-397.
[40] Petterson M G, Neal C R, Mahoney J J, et al. Structure and deformation of north and central Malaita, Solomon Islands: tectonic implications for the Ontong Java Plateau-Solomon arc collision, and for the fate of oceanic plateaus [J]. Tectonophysics, 1997, 283(1-4): 1-33. doi: 10.1016/S0040-1951(97)00206-0
[41] Davies H L. The geology of New Guinea - the cordilleran margin of the Australian continent [J]. Episodes, 2012, 35(1): 87-102.
[42] Sun W D, Arculus R J, Kamenetsky V S, et al. Release of gold-bearing fluids in convergent margin magmas prompted by magnetite crystallization [J]. Nature, 2004, 431(7011): 975-978. doi: 10.1038/nature02972
[43] Sun W D, Bennett V C, Eggins S M, et al. Enhanced mantle-to-crust rhenium transfer in undegassed arc magmas [J]. Nature, 2003, 422(6929): 294-297. doi: 10.1038/nature01482
[44] Sun W D, Ding X, Hu Y H, et al. The golden transformation of the Cretaceous plate subduction in the west Pacific [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2007, 262(3-4): 533-542. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2007.08.021
[45] Holm R J, Spandler C, Richards S W. Continental collision, orogenesis and arc magmatism of the Miocene Maramuni arc, Papua New Guinea [J]. Gondwana Research, 2015, 28(3): 1117-1136. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2014.09.011
[46] Petterson M G, Haldane M I, Smith D J, et al. Geochemistry and petrogenesis of the Gallego Volcanic Field, Solomon Islands, SW Pacific and geotectonic implications [J]. Lithos, 2011, 125(3-4): 915-927. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2011.05.008
[47] Soustelle V, Tommasi A, Demouchy S, et al. Melt-rock interactions, deformation, hydration and seismic properties in the sub-arc lithospheric mantle inferred from xenoliths from seamounts near Lihir, Papua New Guinea [J]. Tectonophysics, 2013, 608: 330-345. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2013.09.024
[48] 崔华伟, 万永革, 黄骥超, 等. 2015年3月新不列颠Ms7.4地震震源及邻区构造应力场特征[J]. 地球物理学报, 2017, 60(3):985-998 doi: 10.6038/cjg20170313
CUI Huawei, WAN Yongge, HUANG Jichao, et al. The tectonic stress field in the source of the New Britain Ms 7.4 earthquake of March 2015 and adjacent areas [J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2017, 60(3): 985-998. doi: 10.6038/cjg20170313
[49] Chen T, Luo H P, Furlong K P. A Bayesian rupture model of the 2007 Mw 8.1 Solomon Islands earthquake in Southwest Pacific with coral reef displacement measurements [J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2017, 139: 92-97.
[50] Yang G L, Shen C Y, Wang J P, et al. Isostatic anomaly characteristics and tectonism of the New Britain Trench and neighboring Papua New Guinea [J]. Geodesy and Geodynamics, 2018, 9(5): 404-410. doi: 10.1016/j.geog.2018.04.006
[51] Mahoney J J, Storey M, Duncan R A, et al. Geochemistry and age of the Ontong Java Plateau[C]//Pringle M S, Sager W W, Sliter W V, et al. The Mesozoic Pacific: Geology, Tectonics, and Volcanism: A Volume in Memory of Sy Schlanger. Washington, D.C.: AGU, 1993, 77: 233-261.
[52] Taylor B. The single largest oceanic plateau: Ontong Java-Manihiki-Hikurangi [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2006, 241(3-4): 372-380. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2005.11.049
[53] Hanyu T, Tejada M L G, Shimizu K, et al. Collision-induced post-plateau volcanism: Evidence from a seamount on Ontong Java Plateau [J]. Lithos, 2017, 294-295: 87-96. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2017.09.029
[54] Chandler M T, Wessel P, Sager W W. Analysis of Ontong Java Plateau palaeolatitudes: evidence for large-scale rotation since 123 Ma? [J]. Geophysical Journal International, 2013, 194(1): 18-29. doi: 10.1093/gji/ggt075
[55] Chandler M T, Wessel P, Taylor B, et al. Reconstructing Ontong Java Nui: Implications for Pacific absolute plate motion, hotspot drift and true polar wander [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2012, 331-332: 140-151. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2012.03.017
[56] Hall S, Riisager P. Palaeomagnetic palaeolatitudes of the Ontong Java Plateau from 120 to 55 Ma: implications for the apparent polar wander path of the Pacific Plate [J]. Geophysical Journal International, 2007, 169(2): 455-470. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-246X.2007.03338.x
[57] Gladczenko T P, Coffin M F, Eldholm O. Crustal structure of the Ontong Java Plateau: Modeling of new gravity and existing seismic data [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 1997, 102(B10): 22711-22729. doi: 10.1029/97JB01636
[58] Klosko E R, Russo R M, Okal E A, et al. Evidence for a rheologically strong chemical mantle root beneath the Ontong-Java Plateau [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2001, 186(3-4): 347-361. doi: 10.1016/S0012-821X(01)00235-7
[59] Taira A, Mann P, Rahardiawan R. Incipient subduction of the Ontong Java Plateau along the North Solomon trench [J]. Tectonophysics, 2004, 389(3-4): 247-266. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2004.07.052
[60] Tommasi A, Ishikawa A. Microstructures, composition, and seismic properties of the Ontong Java Plateau mantle root [J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2014, 15(11): 4547-4569. doi: 10.1002/2014GC005452
[61] Covellone B M, Savage B, Shen Y. Seismic wave speed structure of the Ontong Java Plateau [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2015, 420: 140-150. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2015.03.033
[62] Tharimena S, Rychert C A, Harmon N. Seismic imaging of a mid-lithospheric discontinuity beneath Ontong Java Plateau [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2016, 450: 62-70. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2016.06.026
[63] Ely J C, Neal C R. Using platinum-group elements to investigate the origin of the Ontong Java Plateau, SW Pacific [J]. Chemical Geology, 2003, 196(1-4): 235-257. doi: 10.1016/S0009-2541(02)00415-1
[64] Fitton J G, Godard M. Origin and evolution of magmas on the Ontong Java Plateau [J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 2004, 229(1): 151-178. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.2004.229.01.10
[65] Ishikawa A, Kuritani T, Makishima A, et al. Ancient recycled crust beneath the Ontong Java Plateau: Isotopic evidence from the garnet clinopyroxenite xenoliths, Malaita, Solomon Islands [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2007, 259(1-2): 134-148. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2007.04.034
[66] Ishikawa A, Pearson D G, Dale C W. Ancient Os isotope signatures from the Ontong Java Plateau lithosphere: Tracing lithospheric accretion history [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2011, 301(1-2): 159-170. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2010.10.034
[67] Tejada M L G, Suzuki K, Hanyu T, et al. Cryptic lower crustal signature in the source of the Ontong Java Plateau revealed by Os and Hf isotopes [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2013, 377-378: 84-96. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2013.07.022
[68] Demouchy S, Ishikawa A, Tommasi A, et al. Characterization of hydration in the mantle lithosphere: Peridotite xenoliths from the Ontong Java Plateau as an example [J]. Lithos, 2015, 212-215: 189-201. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2014.11.005
[69] Knesel K M, Cohen B E, Vasconcelos P M, et al. Rapid change in drift of the Australian plate records collision with Ontong Java plateau [J]. Nature, 2008, 454(7205): 754-757. doi: 10.1038/nature07138
[70] Korenaga J. Why did not the Ontong Java Plateau form subaerially? [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2005, 234(3-4): 385-399. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2005.03.011
[71] Ingle S, Coffin M F. Impact origin for the greater Ontong Java Plateau? [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2004, 218(1-2): 123-134. doi: 10.1016/S0012-821X(03)00629-0
[72] Roberge J, Wallace P J, White R V, et al. Anomalous uplift and subsidence of the Ontong Java Plateau inferred from CO2 contents of submarine basaltic glasses [J]. Geology, 2005, 33(6): 501-504. doi: 10.1130/G21142.1
[73] Ito G, van Keken P E. Hot spots and melting anomalies [J]. Treatise on Geophysics, 2007, 7: 371-435. doi: 10.1016/B978-044452748-6/00123-1
[74] Neal C R, Mahoney J J, Kroenke L W, et al. The Ontong Java Plateau[C]//Mahoney J J, Coffin M F. Large Igneous Provinces: Continental, Oceanic, and Planetary Flood Volcanism. American Geophysical Union Geophysical Monograph Series, 1997, 100: 183-216.
[75] Ito G, Clift P D. Subsidence and growth of Pacific Cretaceous plateaus [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1998, 161(1-4): 85-100. doi: 10.1016/S0012-821X(98)00139-3
[76] Tejada M L G, Mahoney J J, Neal C R, et al. Basement geochemistry and geochronology of central Malaita, Solomon Islands, with implications for the origin and evolution of the Ontong Java Plateau [J]. Journal of Petrology, 2002, 43(3): 449-484. doi: 10.1093/petrology/43.3.449
[77] Richardson W P, Okal E A, Van der Lee S. Rayleigh-wave tomography of the Ontong-Java Plateau [J]. Physics of the Earth and Planetary Interiors, 2000, 118(1-2): 29-51. doi: 10.1016/S0031-9201(99)00122-3
[78] Miura S, Suyehiro K, Shinohara M, et al. Seismological structure and implications of collision between the Ontong Java Plateau and Solomon Island Arc from ocean bottom seismometer-airgun data [J]. Tectonophysics, 2004, 389(3-4): 191-220. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2003.09.029
[79] Smart K A, Tappe S, Ishikawa A, et al. K-rich hydrous mantle lithosphere beneath the Ontong Java Plateau: Significance for the genesis of oceanic basalts and Archean continents [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2019, 248: 311-342. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2019.01.013
[80] Stern R J. Subduction initiation: spontaneous and induced [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2004, 226(3-4): 275-292. doi: 10.1016/S0012-821X(04)00498-4
[81] Stern R J, Gerya T. Subduction initiation in nature and models: A review [J]. Tectonophysics, 2018, 746: 173-198. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2017.10.014
[82] Maruyama S, Utsunomiya A, Ishikawa A. Ontong-Java Plateau, the World's largest Oceanic Plateau, has Been subducted 50%, with the Remaining 50% on the Surface, and with a < 1% accretion on the hanging wall of the Solomon Islands [J]. Journal of Geography, 2011, 120(6): 1035-1044. doi: 10.5026/jgeography.120.1035
[83] Stern R J. 板块构造启动的时间和机制: 理论和经验探索[J]. 科学通报, 2007, 52(5):578-591 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2007.05.014
STERN R J. When and how did plate tectonics begin? Theoretical and empirical considerations [J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2007, 52(5): 578-591. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2007.05.014
[84] Niu Y L, O'Hara M J, Pearce J A. Initiation of subduction zones as a consequence of lateral compositional buoyancy contrast within the lithosphere: a petrological perspective [J]. Journal of Petrology, 2003, 44(5): 851-866. doi: 10.1093/petrology/44.5.851
[85] Hall C E, Gurnis M, Sdrolias M, et al. Catastrophic initiation of subduction following forced convergence across fracture zones [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2003, 212(1-2): 15-30. doi: 10.1016/S0012-821X(03)00242-5
[86] Gurnis M, Hall C, Lavier L. Evolving force balance during incipient subduction [J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2004, 5(7): Q07001.
[87] Nikolaeva K, Gerya T V, Marques F O. Subduction initiation at passive margins: Numerical modeling [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 2010, 115(B3): B03406.
[88] Ishizuka O, Tani K, Reagan M K, et al. The timescales of subduction initiation and subsequent evolution of an oceanic island arc [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2011, 306(3-4): 229-240. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2011.04.006
[89] Musgrave R J. Paleomagnetism and tectonics of Malaita, Solomon islands [J]. Tectonics, 1990, 9(4): 735-759. doi: 10.1029/TC009i004p00735
[90] Honza E, Davies H L, Keene J B, et al. Plate boundaries and evolution of the Solomon Sea region [J]. Geo-Marine Letters, 1987, 7(3): 161-168. doi: 10.1007/BF02238046
[91] Hall R. Cenozoic geological and plate tectonic evolution of SE Asia and the SW Pacific: computer-based reconstructions, model and animations [J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2002, 20(4): 353-431. doi: 10.1016/S1367-9120(01)00069-4
[92] 李忠海, 刘明启, GERYA T. 俯冲隧道中物质运移和流体-熔体活动的动力学数值模拟[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2015, 58(8):1251-1268
LI Zhonghai, LIU Mingqi, GERYA T. Material transportation and fluid-melt activity in the subduction channel: numerical modeling [J]. Science China: Earth Sciences, 2015, 58(8): 1251-1268.
[93] Hacker B R, Peacock S M, Abers G A, et al. Subduction factory 2. Are intermediate-depth earthquakes in subducting slabs linked to metamorphic dehydration reactions? [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 2003, 108(b1): 2030.
[94] 郑永飞, 陈仁旭, 徐峥, 等. 俯冲带中的水迁移[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2016, 59(4):651-682
ZHENG Yongfei, CHEN Renxu, XU Zheng, et al. The transport of water in subduction zones [J]. Science China: Earth Sciences, 2016, 59(4): 651-682.
[95] Sumino H, Burgess R, Mizukami T, et al. Seawater-derived noble gases and halogens preserved in exhumed mantle wedge peridotite [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2010, 294(1-2): 163-172. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2010.03.029
[96] Alt J C, Garrido C J, Shanks W C III, et al. Recycling of water, carbon, and sulfur during subduction of serpentinites: A stable isotope study of Cerro del Almirez, Spain [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2012, 327-328: 50-60. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2012.01.029
[97] Stern R J. Subduction zones [J]. Reviews of Geophysics, 2002, 40(4): 1012. doi: 10.1029/2001RG000108
[98] van der Lee S, Regenauer-Lieb K, Yuen D A. The role of water in connecting past and future episodes of subduction [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2008, 273(1-2): 15-27. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2008.04.041
[99] 孙卫东, 凌明星, 杨晓勇, 等. 洋脊俯冲与斑岩铜金矿成矿[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2010, 53(4):475-484
SUN Weidong, LING Mingxing, YANG Xiaoyong, et al. Ridge subduction and porphyry copper-gold mineralization: An overview [J]. Science China: Earth Sciences, 2010, 53(4): 475-484.
[100] Ribeiro J M, Lee C T A. An imbalance in the deep water cycle at subduction zones: The potential importance of the fore-arc mantle [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2017, 479: 298-309. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2017.09.018
[101] Rüpke L H, Morgan J P, Hort M, et al. Serpentine and the subduction zone water cycle [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2004, 223(1-2): 17-34. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2004.04.018
[102] Gerya T V, Stern R J, Baes M, et al. Plate tectonics on the Earth triggered by plume-induced subduction initiation [J]. Nature, 2015, 527(7577): 221-225. doi: 10.1038/nature15752
[103] Shao W Y, Chung S L, Chen W S, et al. Old continental zircons from a young oceanic arc, Eastern Taiwan: Implications for Luzon subduction initiation and Asian accretionary orogeny [J]. Geology, 2015, 43(6): 479-482. doi: 10.1130/G36499.1
[104] MacKenzie L S, Abers G A, Rondenay S, et al. Imaging a steeply dipping subducting slab in Southern Central America [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2010, 296(3-4): 459-468. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2010.05.033
[105] Zhao D P. Big mantle wedge, anisotropy, slabs and earthquakes beneath the Japan Sea [J]. Physics of the Earth and Planetary Interiors, 2017, 270: 9-28. doi: 10.1016/j.pepi.2017.06.009
[106] Dymkova D, Gerya T. Porous fluid flow enables oceanic subduction initiation on Earth [J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2013, 40(21): 5671-5676. doi: 10.1002/2013GL057798
[107] Leng W, Gurnis M. Subduction initiation at relic arcs [J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2015, 42(17): 7014-7021. doi: 10.1002/2015GL064985
[108] Nair R, Chacko T. Role of oceanic plateaus in the initiation of subduction and origin of continental crust [J]. Geology, 2008, 36(7): 583-586. doi: 10.1130/G24773A.1
[109] Korenaga J. Thermal cracking and the deep hydration of oceanic lithosphere: A key to the generation of plate tectonics? [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 2007, 112(B5): B05408.
[110] 李忠海. 大陆俯冲-碰撞-折返的动力学数值模拟研究综述[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2014, 57(1):47-69
LI Zhonghai. A review on the numerical geodynamic modeling of continental subduction, collision and exhumation [J]. Science China: Earth Sciences, 2014, 57(1): 47-69.
[111] 冷伟, 毛伟. 俯冲带热结构的动力学模型研究[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2015, 58(7):1070-1083
LENG Wei, MAO Wei. Geodynamic modeling of thermal structure of subduction zones [J]. Science China: Earth Sciences, 2015, 58(7): 1070-1083.
[112] Nakao A, Iwamori H, Nakakuki T. Effects of water transportation on subduction dynamics: Roles of viscosity and density reduction [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2016, 454: 178-191. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2016.08.016
[113] Arcay D, Tric E, Doin M P. Numerical simulations of subduction zones: Effect of slab dehydration on the mantle wedge dynamics [J]. Physics of the Earth and Planetary Interiors, 2005, 149(1-2): 133-153. doi: 10.1016/j.pepi.2004.08.020
[114] Baes M, Gerya T, Sobolev S V. 3-D thermo-mechanical modeling of plume-induced subduction initiation [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2016, 453: 193-203. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2016.08.023
-



 下载:
下载: