Distribution of benthic forminifera in the surficial sediments of Changjiang distal delta and its environmental implications
-
摘要:
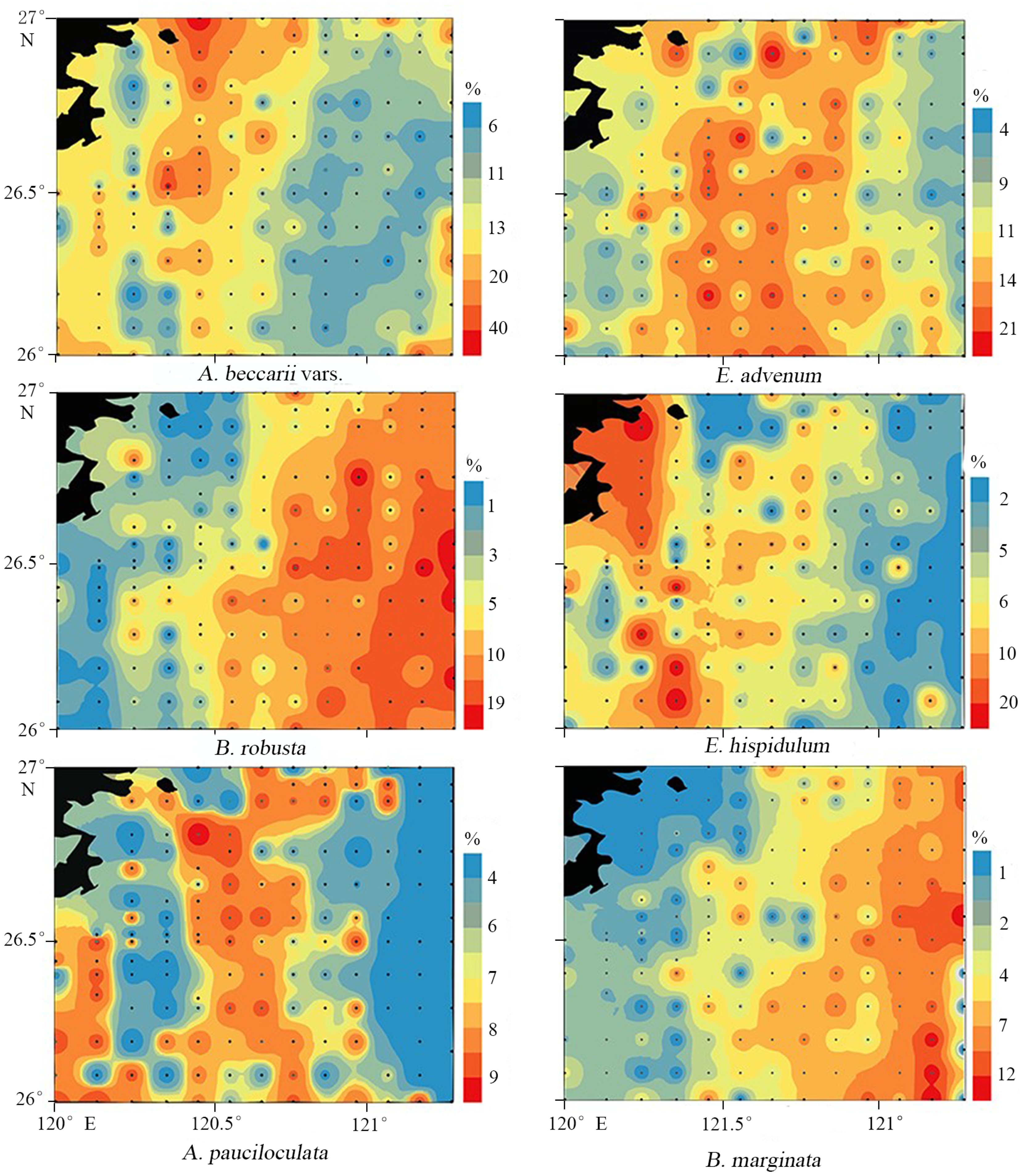
长江远端三角洲是东海内陆架泥质沉积体重要组成部分,是全新世高海平面时期以来形成的重要地貌单元,其包含了高分辨率沉积环境与气候变化信息,对该地区现代沉积环境及其影响条件的分析将有助于长时间尺度古记录识别与反演。对研究区海域145个站位的表层沉积物样品进行了底栖有孔虫化石分析,鉴定结果表明该地区底栖有孔虫有52种,以玻璃壳体类型为主,平均含量占底栖有孔虫总量的90.6 %,其次为瓷质壳,胶结壳含量最低。进一步因子分析结果表明,研究区底栖有孔虫可划分为4个组合:组合Ⅰ(Ammonia beccarii vars.-Quinqueloculina spp.)分布在研究区西部近岸浅水区,组合Ⅱ(Bolivina robusta-Bulimina marginata-Hanzawaia spp.)分布于研究区东南部水深较大处,组合Ⅲ(Elphidium hispidulum-Fursenkoina schreibersiana)呈带状分布于近岸,组合Ⅳ(Elphidium advenum-Ammonia pauciloculata)分布区域位于组合Ⅰ和组合Ⅱ之间。组合Ⅰ可能指示区域水体环境受闽浙沿岸水团影响;组合Ⅱ可能指示区域水体环境受台湾暖流水团影响;组合Ⅲ的分布可能与夏季闽江水与外海水混合发生水体层化有关;组合Ⅳ可能指示区域水体环境受季节性闽浙沿岸水与台湾暖流水团影响。
Abstract:The distal end of the Yangtze River delta, as a part of the muddy sediments on the continental shelf of the East China Sea, is formed right after the high sea level of Holocene and contains high-resolution information of environmental and climatic changes. In order to make better interpretation of the long-term paleoenvironmental records, 145 surface samples collected from the northern coastal waters of Fujian Province have been quantitatively analyzed for foraminifera distribution. 52 species of benthonic foraminifera were identified dominated by hyaline Rotaliida, followed successively by porcelaneous Miliolina, and agglutinated Textulariida. Four assemblages have been recognizeded based on factor analysis: The Assemblage I (Ammonia beccarii vars. -Quinqueloculina spp.) is mainly distributed in the shallow-water environment possibly related to the Minzhe coastal current; The Assemblage II (Bolivina robusta-Bulimina marginata-Hanzawaia spp.) indicates the environment predominated by the warm current coming from Taiwan; The Assemblage III (Elphidium hispidulum-Fursenkoina schreibersiana) is distributed in a ribbon pattern near the shore, where the water from the Minjiang River is stratified with sea water in summer; The Assemblage IV (Elphidium advenum-Ammonia pauciloculata) is restricted in some local areas between the Assemblage I and II, possibly indicating an environment dominated by mixed water mass. The research results suggest that the combination and distribution of benthic foraminifera in the study area are not only affected by material source, but also constrained by their dynamic environment, which is of great significance to the reconstruction of paleoenvironment in the areas as such.
-
Key words:
- distal delta /
- benthic foraminifera /
- water mass distribution /
- factor analysis /
- surface sediment
-

-
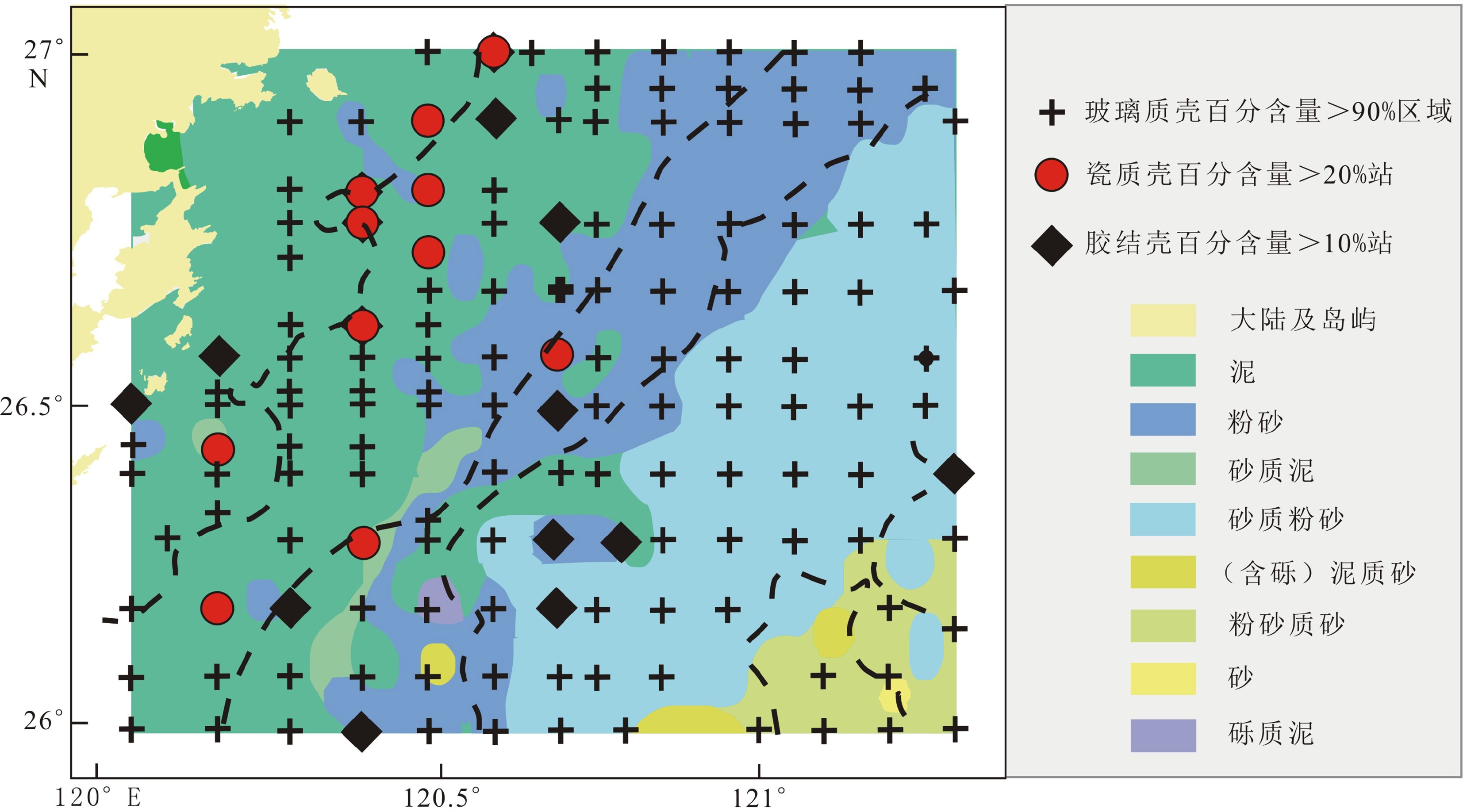
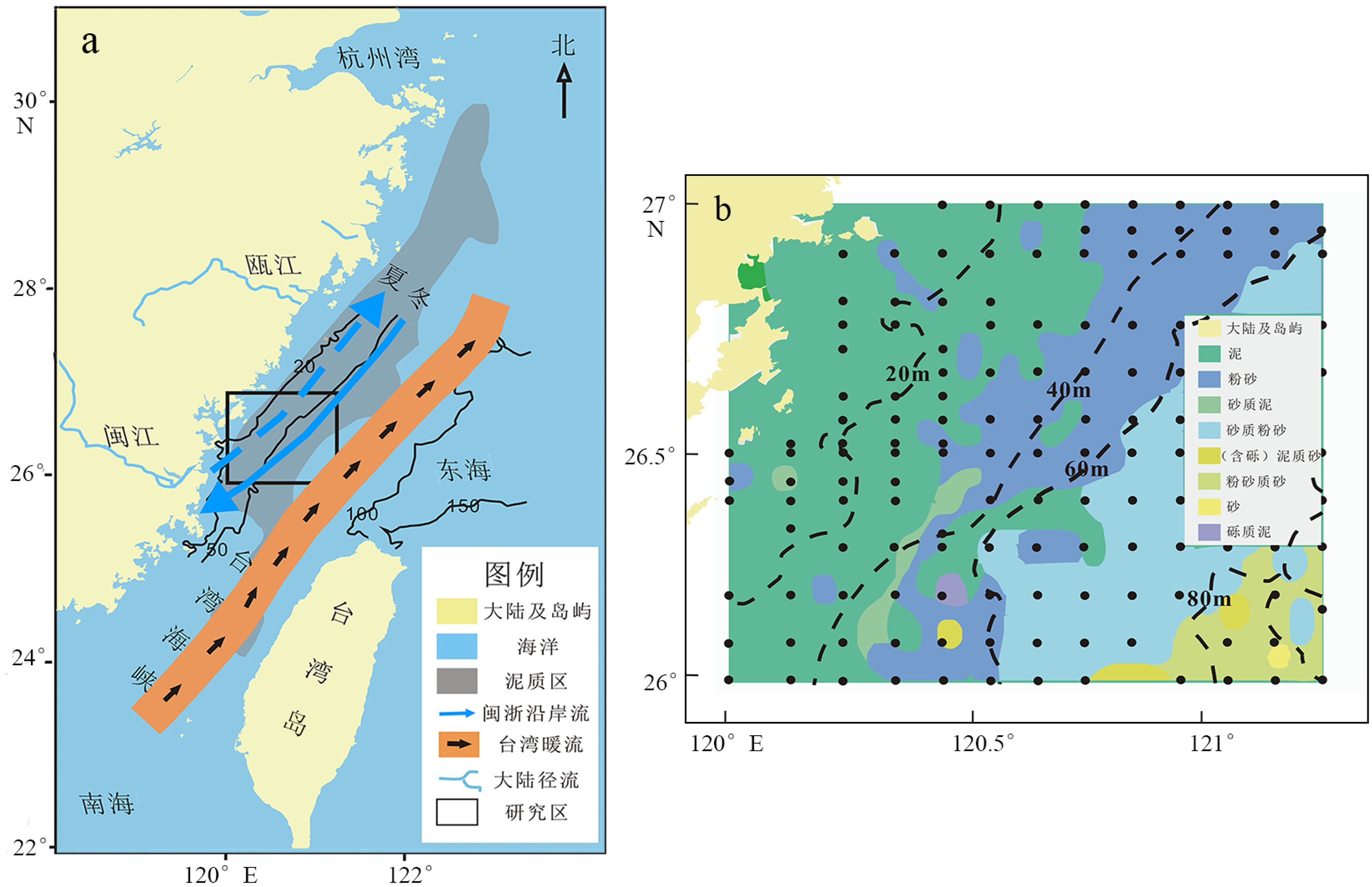
图 1 研究区域水文(a)与取样位置(b)[23]
Figure 1.
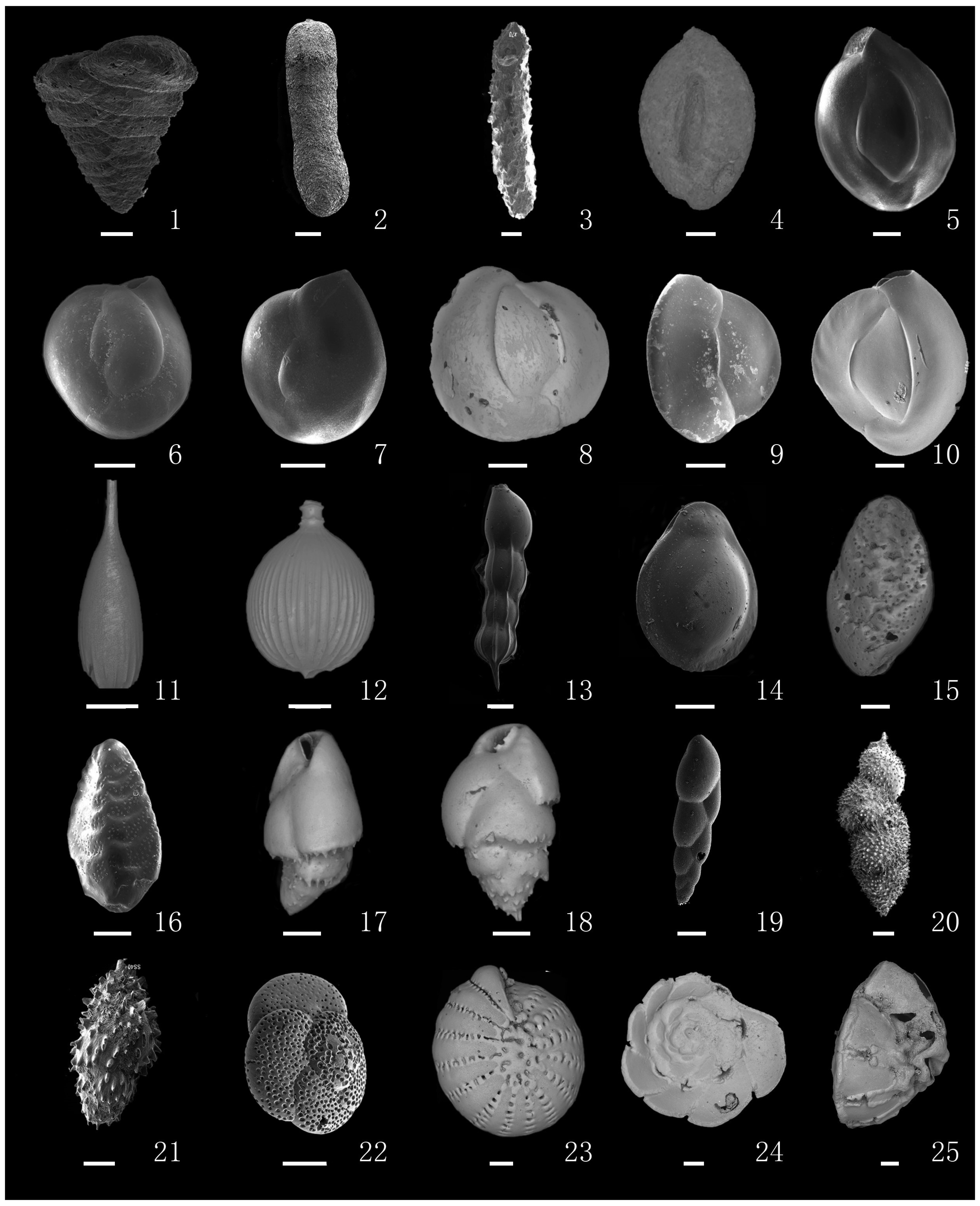
图 2 研究区部分有孔虫(图版1)(比例尺=100 μm。 1Textularia sagittula(Defrance), 2 Martinottiella communis(d' Orbigny), 3 Martinottiella sp., 4 Sigmoilopsis asperula(Karrer), 5 Quinqueloculina seminula(Linné), 6-7 Quinqueloculina akneriana rotunda(Gerke), 8-10 Quinqueloculina lamarckiana d'Orbigny, 11 Lagena doveyensis Haynes, 12 Lagena spicata Cushman et McCulloch,13 Dentalina decepta(Bagg), 14 Fissurina marginata(Montagu), 15-16 Bolivina robusta Brady, 17-18 Bulimina marginata d' Orbigny,19 Virgulopsis orientalis Ho et Hu, 20 Uvigerina asperula Czjek, 21 Uvigerina aculeata d' Orbigny, 22 Rosalina sp., 23 Pseudorotalia indopacifica(Thalmann), 24-25 Rotalinoides compressiuscula(Brady))
Figure 2.
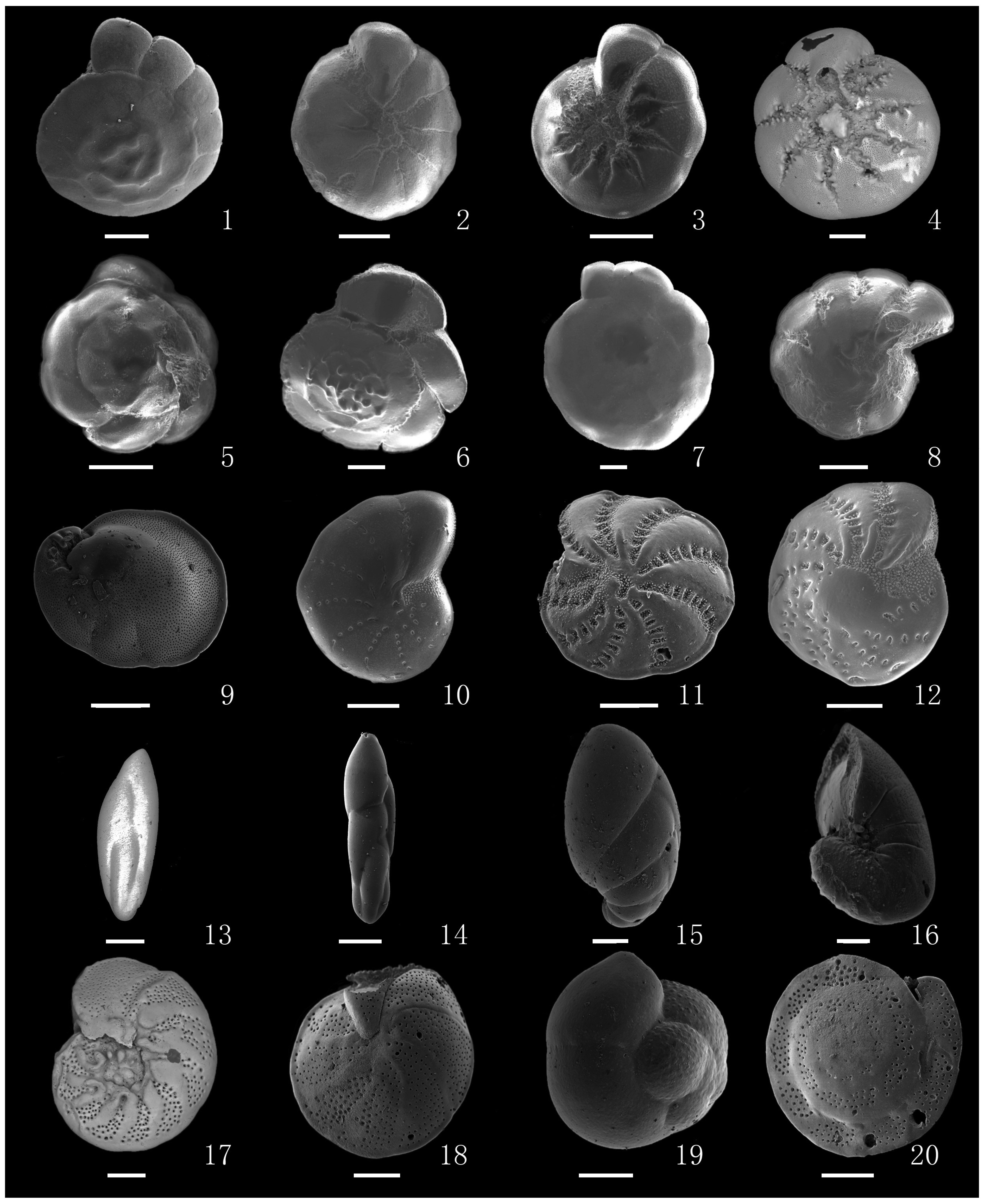
图 3 研究区部分有孔虫(图版2)(比例尺=100 μm。1-4 Ammonia beccarii(Linné)vars., 5-8 Rotalidium annectens(Parker & Jones), 9 Cancris sp.,10 Cribrinonion porisuturalis S.Y.Zheng, 11-12 Elphidium advenum(Cushman),13-14 Fursenkoina schreibersiana(Czjzek), 15-16 Florilus cf. atlanticus(Cushman), 17-18 Hanzawaia nipponica Asano, 19 Gyroidina sp.,20 Heterolepa dutemplei(d' Orbigny))
Figure 3.
表 1 研究区底栖有孔虫因子分析结果
Table 1. Factor analysis results of benthic foraminifera
底栖有孔虫属种 因子1 因子2 因子3 因子4 Ammonia convexidorsa −0.006 −0.028 −0.627 −0.072 Ammonia ketienziensis 0.259 0.031 −0.616 −0.099 Ammonia maruhasii 0.023 0.013 −0.636 0.042 Ammonia pauciloculata 1.013 −0.070 −0.865 1.522 Ammonia beccarii vars. 4.400 0.891 0.038 −0.045 Bolivina robusta −0.924 4.003 0.009 −0.618 Bolivina spathulata −0.578 1.698 0.076 0.326 Bulimina marginata −0.276 1.774 0.314 0.754 Cancris sp. −0.027 0.048 −0.032 0.222 Cribrononion spp. 0.494 0.269 −0.144 −0.140 Elphidium advenum 0.529 0.919 −1.322 4.350 Elphidium hispidulum −0.358 −0.110 −3.372 −0.006 Fissurina sp. −0.012 0.027 −0.015 0.028 Florilus cf. atlanticus −0.084 0.517 −0.127 0.473 Fursenkoina schreibersiana −0.601 0.092 −3.303 −0.889 Hanzawaia spp. 0.645 1.708 0.051 −1.592 Heterolepa dutemplei 0.240 0.767 −0.272 −0.757 Hyalinea balthica −0.064 0.460 0.119 −0.208 Lagena spp. −0.039 0.075 −0.047 0.250 Martinottiella spp. 0.022 0.262 −0.113 0.138 Nonion sp. 0.121 0.960 0.209 −0.571 Pseudoeponides nakazatoensis 0.120 0.040 −0.055 0.577 Pseudorotalia sp. 0.098 0.025 −0.007 0.052 Quinqueloculina spp. 2.262 −0.348 −0.117 −0.008 Rosalina sp. 0.056 0.072 0.057 0.028 Rotalidium annectens 0.079 −0.298 −2.284 −1.295 Rotalinoides compressiuscula 1.564 0.605 −0.663 −1.517 Sigmoilina spp. 0.570 0.352 0.166 −0.409 Spiroloculina communis 0.415 0.192 0.122 0.314 Textularia sagittula 0.557 −0.187 −0.171 −0.028 Uvigerina spp. −0.597 1.533 −0.050 0.658 Virgulopsis orientalis −0.094 0.310 −0.033 0.181 -
[1] 伍伯瑜. 台湾海峡及其邻近水域的流型和水文特征[J]. 海洋通报, 1983, 2(4):1-8
WU Boyu. The current pattern and hydrologic character in the Taiwan Straits and its adjacent waters [J]. Marine Science Bulletin, 1983, 2(4): 1-8.
[2] 潘玉球, 曹欣中, 许建平. 浙江沿岸上升流锋区特征及其成因的初步探讨[J]. 海洋湖沼通报, 1982(3):1-7
PAN Yuqiu, CAO Xinzhong, XU Jianping. A preliminary investigation of the cause and characteristics of the upwelling front zone off Zhejiang [J]. Transactions of Oceanology and Limnology, 1982(3): 1-7.
[3] 曾刚. 福建近海沿岸水及其水文状况[J]. 海洋通报, 1986, 5(3):32-37
ZENG Gang. The coastal water and its hydrographic states in the nearshore waters along Fujian province [J]. Marine Science Bulletin, 1986, 5(3): 32-37.
[4] Li C S, Shi X F, Kao S J, et al. Rare earth elements in fine-grained sediments of major rivers from the high-standing island of Taiwan [J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2013, 69: 39-47. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2013.03.001
[5] Liu S F, Shi X F, Liu Y G, et al. Concentration distribution and assessment of heavy metals in sediments of mud area from inner continental shelf of the East China Sea [J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2011, 64(2): 567-579. doi: 10.1007/s12665-011-0941-z
[6] Qiao S Q, Yang Z S, Liu J P, et al. Records of late-Holocene East Asian winter monsoon in the East China Sea: Key grain-size component of quartz versus bulk sediments [J]. Quaternary International, 2011, 230(1-2): 106-114. doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2010.01.020
[7] 沈林南, 吴祥恩, 李超, 等. 福建三沙湾表层沉积硅藻分布特征及其与环境因子的关系[J]. 应用海洋学学报, 2014, 33(2):212-221 doi: 10.3969/J.ISSN.2095-4972.2014.02.009
SHEN Linnan, WU Xiang’en, LI Chao, et al. Distribution characteristics of diatom in surface sediment and its relation with environment factors in Sansha Bay of Fujian [J]. Journal of Applied Oceanography, 2014, 33(2): 212-221. doi: 10.3969/J.ISSN.2095-4972.2014.02.009
[8] 田丰歌, 徐兆礼. 福建中部近海浮游动物数量分布与水团变化的关系[J]. 生态学报, 2012, 32(4):1097-1104 doi: 10.5846/stxb201012261848
TIAN Fengge, XU Zhaoli. Relating the distribution of zooplankton abundance in the coastal waters of central Fujian Province to the seasonal variation of water masses [J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2012, 32(4): 1097-1104. doi: 10.5846/stxb201012261848
[9] Li X Y, Jian Z M, Shi X F, et al. A Holocene record of millennial-scale climate changes in the mud area on the inner shelf of the East China Sea [J]. Quaternary International, 2015, 384: 22-27. doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2014.11.030
[10] 汪品先, 闵秋宝, 卞云华, 等. 东海表层沉积中有孔虫、介形虫组合分布的初步研究[J]. 同济大学学报, 1979(2):90-108
WANG Pinxian, MIN Qiubao, BIAN Yunhua, et al. A preliminary study of Foramiriferal and Ostracod assemblages' distribution in bottom sediments of the East China Sea [J]. Journal of Tongji University, 1979(2): 90-108.
[11] 郑执中, 郑守仪, 傅钊先. 东海底栖有孔虫区系的初步分析[J]. 科学通报, 1979, 24(19):903-906 doi: 10.1360/csb1979-24-19-903
ZHENG Zhizhong, ZHENG Shouyi, FU Zhaoxian. Preliminary analysis of benthic foraminifera in the East China Sea [J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 1979, 24(19): 903-906. doi: 10.1360/csb1979-24-19-903
[12] 张江勇, 汪品先. 深海研究中的底栖有孔虫: 回顾与展望[J]. 地球科学进展, 2004, 19(4):545-551 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.2004.04.009
ZHANG Jiangyong, WANG Pinxian. Benthic foraminifera in deep-sea research: retrospect and prospect [J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2004, 19(4): 545-551. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.2004.04.009
[13] 陈荣华. 浙江海岸带表层沉积物中有孔虫的分布及其影响因子[J]. 东海海洋, 1990, 8(3):35-48
CHEN Ronghua. Distribution and influencing factors of foraminifera in surface sediments of coastal zone of Zhejiang Province [J]. Donghai Marine Science, 1990, 8(3): 35-48.
[14] 方惠瑛. 台湾海峡表层沉积物中底栖有孔虫分布特征[J]. 台湾海峡, 1998(1):43-49
FANG Huiying. Benthic foraminifera in surface sediments of Taiwan Strait [J]. Journal of Oceanography in Taiwan Strait, 1998(1): 43-49.
[15] 周洋, 陈芳, 孙桂华, 等. 台湾海峡西北部平潭岛海域表层沉积物中底栖有孔虫分布及其环境控制因素[J]. 微体古生物学报, 2014, 34(1):54-63
ZHOU Yang, CHEN Fang, SUN Guihua, et al. Benthic foraminiferal distribution in surface sediments of the northwest Taiwan Strait near the Pingtan Island and its environmental controlling factors [J]. Acta Micropalaeontologica Sinica, 2014, 34(1): 54-63.
[16] 陈峰. 福建近岸海底地形的初步研究[J]. 台湾海峡, 1982(2):83-90
CHEN Feng. A preliminary study of underwater morphology along the Fujian coast [J]. Journal of Oceanography in Taiwan Strait, 1982(2): 83-90.
[17] 王翠, 郭晓峰, 方婧, 等. 闽浙沿岸流扩展范围的季节特征及其对典型海湾的影响[J]. 应用海洋学学报, 2018, 37(1):1-8 doi: 10.3969/J.ISSN.2095-4972.2018.01.001
WANG Cui, GUO Xiaofeng, FANG Jing, et al. Characteristics of seasonal spatial expansion of Fujian and Zhejiang Coastal Current and their bay effects [J]. Journal of Applied Oceanography, 2018, 37(1): 1-8. doi: 10.3969/J.ISSN.2095-4972.2018.01.001
[18] Jan S, Wang J, Chern C S, et al. Seasonal variation of the circulation in the Taiwan Strait [J]. Journal of Marine Systems, 2002, 35(3-4): 249-268. doi: 10.1016/S0924-7963(02)00130-6
[19] 汪品先, 章纪军, 赵泉鸿, 等. 东海底质中的有孔虫和介形虫[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 1988.
WANG Pinxian, ZHNG Jijun, ZHAO Quanhong, et al. Foraminifera and Ostracods in the Sediments of the East China Sea[M]. Beijing: China Ocean Press, 1988.
[20] 石学法, 刘升发, 乔淑卿, 等. 东海闽浙沿岸泥质区沉积特征与古环境记录[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2010, 30(4):19-30 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1140.2010.04019
SHI Xuefa, LIU Shengfa, QIAO Shuqing, et al. Depositional features ang palaeoenvironmental records of the mud deposits in Min-Zhe coastal mud area, East China sea [J]. Marine Geology and Quaternary Geology, 2010, 30(4): 19-30. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1140.2010.04019
[21] Li G X, Li P, Liu Y, et al. Sedimentary system response to the global sea level change in the East China Seas since the last glacial maximum [J]. Earth Science Reviews, 2014, 139: 390-405. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2014.09.007
[22] Lei Y L, Li T G. Atlas of Benthic Foraminifera from China Seas[M]. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer, 2016.
[23] 丛静艺, 袁忠鹏, 胡刚, 等. 长江远端三角洲多源沉积分异作用及其动力机制[J]. 沉积学报, 2020, 38(3):528-537
CONG Jingyi, YUAN Zhongpeng, HU Gang, et al.
Sedimentary differentiation and hydrodynamic environment of multi-sourced sediment in the Changjiang Distal Delta [J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2020, 38(3): 528-537. [24] 史光辉. 东海陆架泥质区底栖有孔虫记录及其环境意义[D]. 中国海洋大学硕士学位论文, 2014.
SHI Guanghui. Benthic foraminifera response to changes in paleoenviornments of Mud area on the East China Sea shelf[D]. Master Dissertation of Ocean University of China, 2014.
[25] Jian Z M, Wang L J, Kienast M, et al. Benthic foraminiferal paleoceanography of the South China Sea over the last 40, 000 years [J]. Marine Geology, 1999, 156(1-4): 159-186. doi: 10.1016/S0025-3227(98)00177-7
[26] 类彦立, 李铁刚. 奥茅卷转虫 Ammonia aomoriensis (Asano, 1951)与毕克卷转虫 Ammonia beccarii (Linnaeus, 1758)(有孔虫)的分类学以及在黄东海分布的温盐深特征比较研究[J]. 微体古生物学报, 2015, 32(01):1-19
LEI Yanli, LI Tiegang. Ammonia aomoriensis (asano, 1951) and Ammonia beccarii (linnaeus, 1758) (foraminifera) : comparisons on theirtaxonomy and ecological distributions correlated to temperature,salinity and depth in the yellow SEA [J]. Acta Micropalaeontologica Sinica, 2015, 32(01): 1-19.
[27] Murray J W. Ecology and Palaeoecology of Benthic Foraminifera[M]. Harlow: Longman Scientific and Technical, 1991.
[28] Dong S S, Lei Y L, Li T G, et al. Responses of benthic foraminifera to changes of temperature and salinity: Results from a laboratory culture experiment [J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 2019, 62(2): 459-472. doi: 10.1007/s11430-017-9269-3
[29] 李小艳, 石学法, 程振波, 等. 渤海莱州湾表层沉积物中底栖有孔虫分布特征及其环境意义[J]. 微体古生物学报, 2010, 27(1):38-44
LI Xiaoyan, SHI Xuefa, CHENG Zhenbo, et al. Distribution of benthic foraminifera in surface sediments of the Laizhou Bay, Bohai Sea and its environmental significance [J]. Acta Micropalaeontologica Sinica, 2010, 27(1): 38-44.
[30] 王海霞, 赵全民, 李铁刚, 等. 辽东湾表层沉积物中底栖有孔虫分布及其与沉积环境的关系[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2011, 31(2):87-94 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1140.2011.02087
WANG Haixia, ZHAO Quanmin, LI Tiegang, et al. Distribution of benthic foraminifera in surface sediments of the Liaodong Bay and its bearing on sedimentary environments [J]. Marine Geology and Quaternary Geology, 2011, 31(2): 87-94. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1140.2011.02087
[31] Zhao B C, Yan X X, Wang Z H, et al. Sedimentary evolution of the Yangtze River mouth (East China Sea) over the past 19, 000 years, with emphasis on the Holocene variations in coastal currents [J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2018, 490: 431-449. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2017.11.023
[32] Kaiho K. Benthic foraminiferal dissolved-oxygen index and dissolved-oxygen levels in the modern ocean [J]. Geology, 1994, 22(8): 719-722. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1994)022<0719:BFDOIA>2.3.CO;2
[33] Mazumder A, Nigam R. Bathymetric preference of four major genera of rectilinear benthic foraminifera within oxygen minimum zone in Arabian Sea off central west coast of India [J]. Journal of Earth System Science, 2014, 123(3): 633-639. doi: 10.1007/s12040-014-0419-y
[34] 刘海霞, 李道季, 高磊, 等. 长江口夏季低氧区形成及加剧的成因分析[J]. 海洋科学进展, 2012, 30(2):186-197 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2012.02.004
LIU Haixia, LI Daoji, GAO Lei, et al. Study on main influencing factors of formation and deterioration of summer hypoxia off the Yangtze River Estuary [J]. Advances in Marine Science, 2012, 30(2): 186-197. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2012.02.004
[35] 王巧宁, 颜天, 周名江. 近岸和河口低氧成因及其影响的研究进展[J]. 海洋环境科学, 2012, 31(5):775-778
WANG Qiaoning, YAN Tian, ZHOU Mingjiang. Research progress on cause of hypoxia and its influence in coastal and estuary region [J]. Marine Environmental Science, 2012, 31(5): 775-778.
[36] 韦钦胜, 王保栋, 于志刚, 等. 夏季长江口外缺氧频发的机制及酸化问题初探[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2017, 60(2):360-381 doi: 10.1007/s11430-015-5542-8
WEI Qinsheng, WANG Baodong, YU Zhigang, et al. Mechanisms leading to the frequent occurrences of hypoxia and a preliminary analysis of the associated acidification off the Changjiang estuary in summer [J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 2017, 60(2): 360-381. doi: 10.1007/s11430-015-5542-8
[37] 叶丰, 黄小平. 近岸海域缺氧现状、成因及其生态效应[J]. 海洋湖沼通报, 2010(3):91-99 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6482.2010.03.014
YE Feng, HUANG Xiaoping. The status, causes, and ecological effects of coastal hypoxia [J]. Transactions of Oceanology and Limnology, 2010(3): 91-99. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6482.2010.03.014
[38] 翁学传, 张启龙, 颜廷壮, 等. 台湾海峡中、北部海域春、夏季水团分析[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 1992, 23(3):235-244
WENG Xuechuan, ZHANG Qilong, YAN Tingzhuang, et al. Analysis of water masses in the middle and northern Taiwan strait in spring and summer [J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 1992, 23(3): 235-244.
[39] 许金电, 黄奖, 邱云, 等. 浙闽沿岸水的空间结构特征及生消过程[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2015, 34(1):1-7 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5470.2015.01.001
XU Jindian, HUANG Jiang, QIU Yun, et al. Spatial structure characteristics of Zhejiang and Fujian coastal water and their evolution [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2015, 34(1): 1-7. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5470.2015.01.001
[40] 潘玉球, 徐端蓉, 许建平. 浙江沿岸上升流区的锋面结构、变化及其原因[J]. 海洋学报, 1985, 7(4):401-411
PAN Yuqiu, XU Ruirong, XU Jianping. Preliminary study on the characteristics and causes of upwelling front along the coast of Zhejiang province [J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 1985, 7(4): 401-411.
[41] 喻祖祥, 苏育嵩, 俞光耀, 等. 长江口及济州岛附近海域变性水团的初步分析[J]. 山东海洋学院学报, 1984, 14(3):1-12
YU Zuxiang, SU Yusong, YU Guangyao, et al. A preliminary analysis of modified water masses in the sea area near the Yangtze River mouth and the Chijudo island [J]. Journal of Shandong College of Oceanology, 1984, 14(3): 1-12.
[42] 桂峰, 王柳柱, 赵晟, 等. 舟山港表层沉积物中底栖有孔虫组合特征初步研究[J]. 微体古生物学报, 2013, 30(4):415-422
GUI Feng, WANG Liuzhu, ZHAO Shen, et al. Benthic foraminiferal characteristics in surface sediments of the Zhoushan harbour, Zhejiang, China [J]. Acta Micropalaeontologica Sinica, 2013, 30(4): 415-422.
-



 下载:
下载: