Seismic sequence and evolution model of isolated carbonate platform—A case from Yongle Atoll, Xisha Islands
-
摘要:
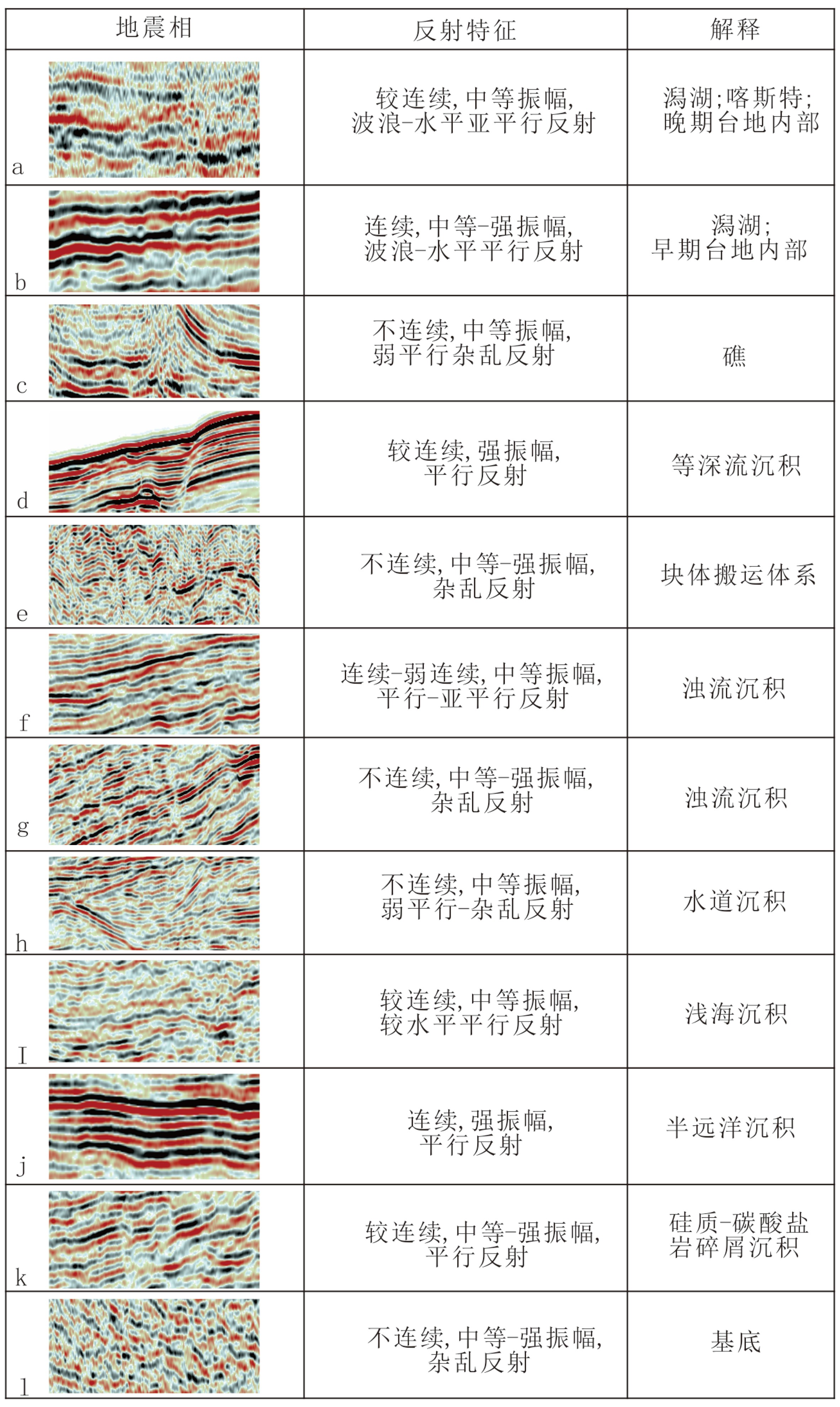
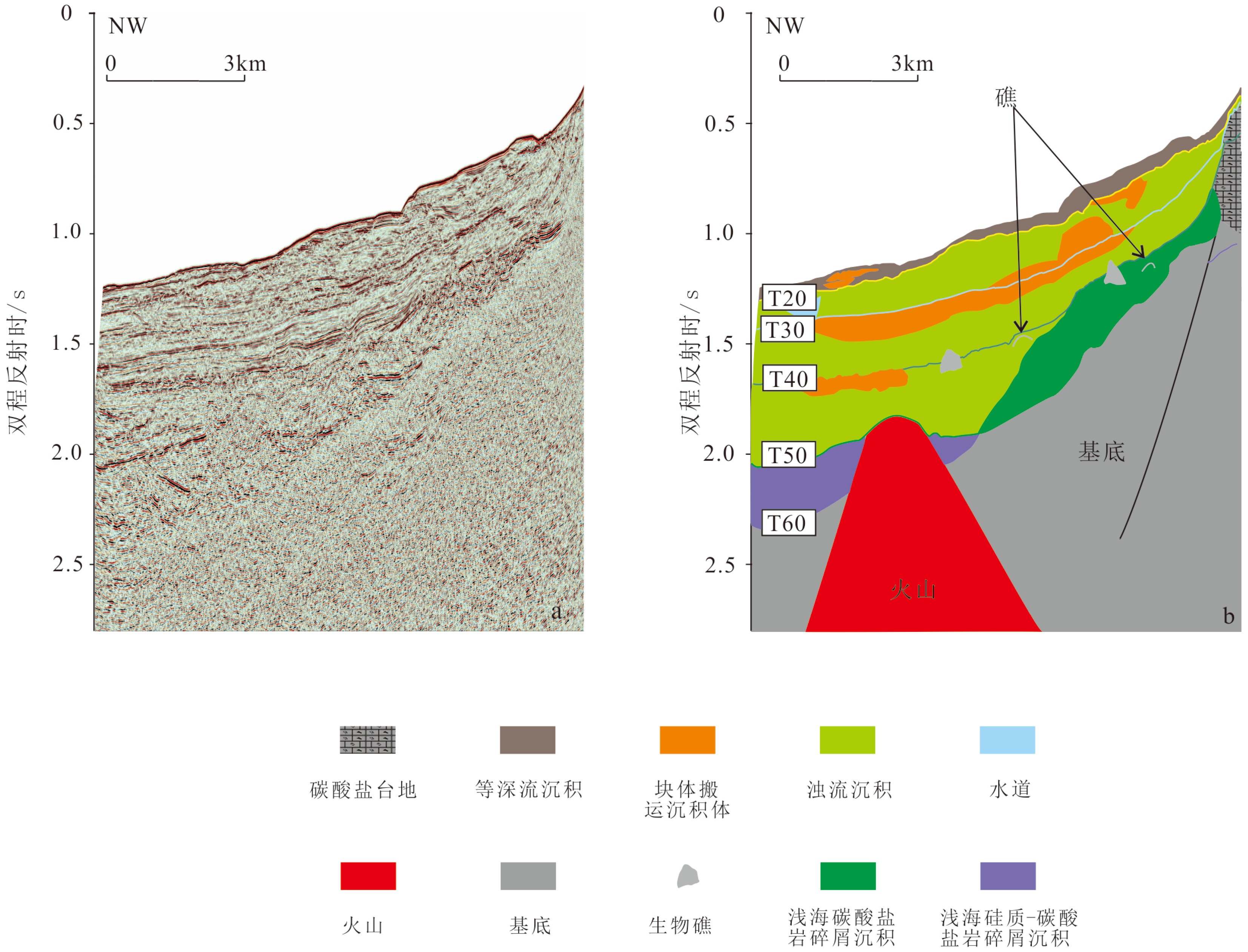
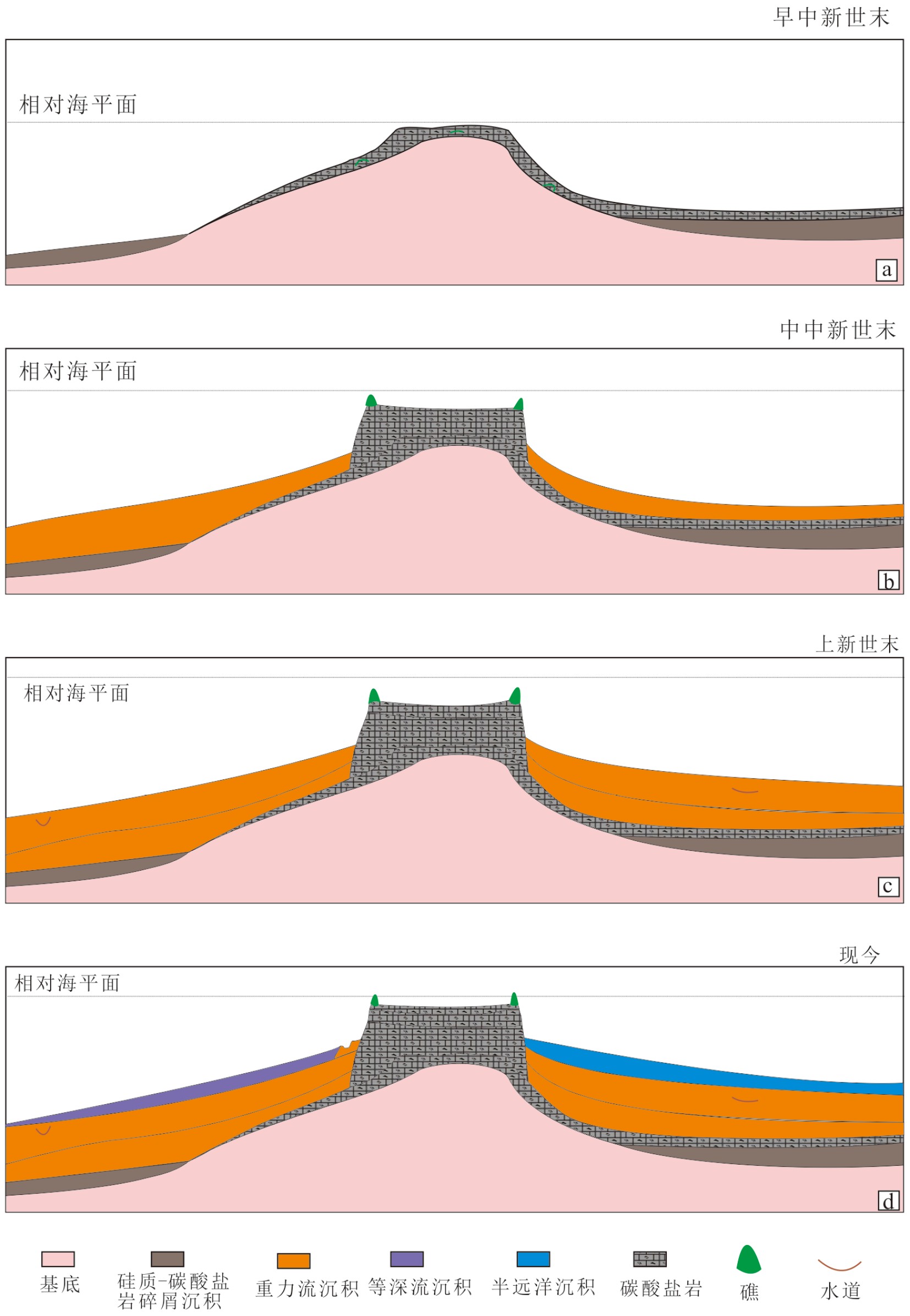
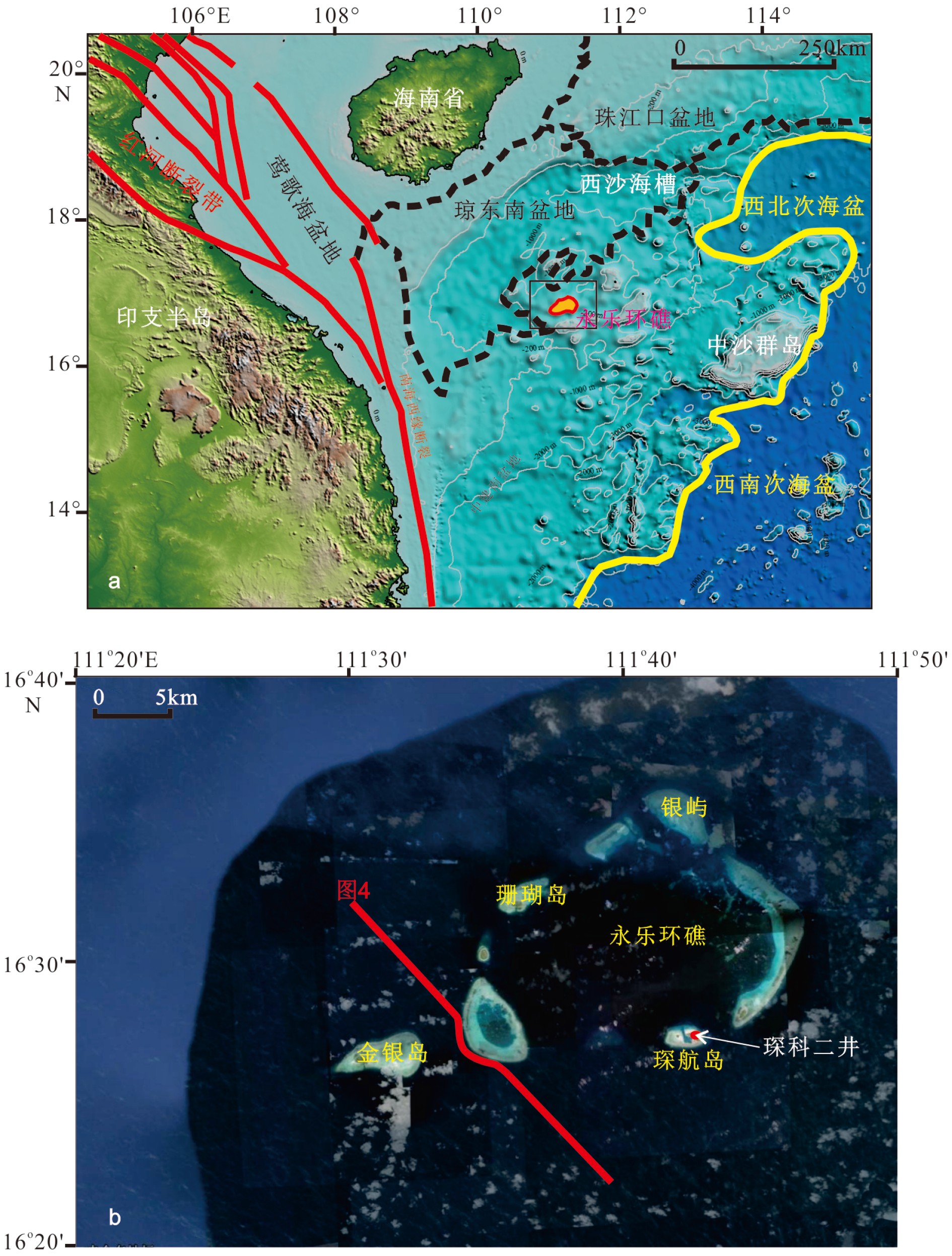
永乐环礁作为典型的现代孤立碳酸盐台地,记录了西沙海域生物礁以及碳酸盐台地的整个兴衰历史。根据新采集的高分辨率多道地震数据,结合永乐环礁琛科2井以及永乐环礁东部西科1井的研究结果,对永乐环礁内部进行层序地层学研究,讨论了永乐环礁的演化过程,建立了西沙孤立碳酸盐台地的发育模式。根据地震反射同相轴特征变化,自下而上划分出Sq1(下中新统)、Sq2(中中新统)、Sq3(上中新统)、Sq4(上新统)、Sq5(第四系)5个层序,建立了永乐环礁的年代地层格架。重建了永乐碳酸盐台地自中新世以来的演化历史:台地顶部自中新世以来沉积环境相对稳定,以潟湖为主;而台地斜坡早中新世为滨浅海环境,发育生物礁,中中新世至今为半深海沉积环境,斜坡区有水道侵蚀,发育源于台地顶部的重力流沉积,在台地西部的斜坡区还发现了第四纪等深流沉积。综上,将西沙孤立碳酸盐台地发育演化划分为早中新世萌芽期、中中新世繁盛期、晚中新世—上新世淹没期、第四纪现代环礁4个阶段。本次研究弥补了以往对西沙孤立碳酸盐台地发育演化研究的不足。
Abstract:The Yongle Atoll is a typical modern isolated carbonate platform, which has recorded a complete evolutionary history of biological reefs and carbonate platforms in the Xisha Area. Based on the newly acquired high-resolution multi-channel seismic data, combined with the research results of Well CK-2 in the Yongle Atoll and Well XK-1in the east of Yongle Atoll, the sequence stratigraphy of the Yongle Atoll is studied, the evolution of the Atoll discussed, and the evolutionary model for the Xisha isolated carbonate platform established. Based on the change in seismic reflection isophase characteristics, five sequences, i.e. Sq1 (Lower Miocene), Sq2 (Middle Miocene), Sq3 (Upper Miocene), Sq4 (Pliocene), and Sq5 (Quaternary) were divided from the bottom up, And the chronostratigraphic framework of the Yongle Atoll was established upon the basis. The depositional environment of the platform dominated by lagoons has been relatively stable since Miocene. The platform slope used to be a neritic environment in Early Miocene where biological reefs well developed. It has been a bathyal sedimentary environment since Miocene up to the present. Gravity flow deposits originated from the top of the platform, as Quaternary contour current deposits are also observed on the western slope of the platform. The development and evolution of the isolated carbonate platform in the Xisha may be divided into four stages: initiation in Early Miocene, large-scale carbonate platform growth in Middle Miocene, drowning period in Late Miocene-Pleistocene, and an atoll at present. This study makes up the shortcomings of previous studies on the development and evolution of isolated carbonate platforms in the Xisha Islands.
-

-
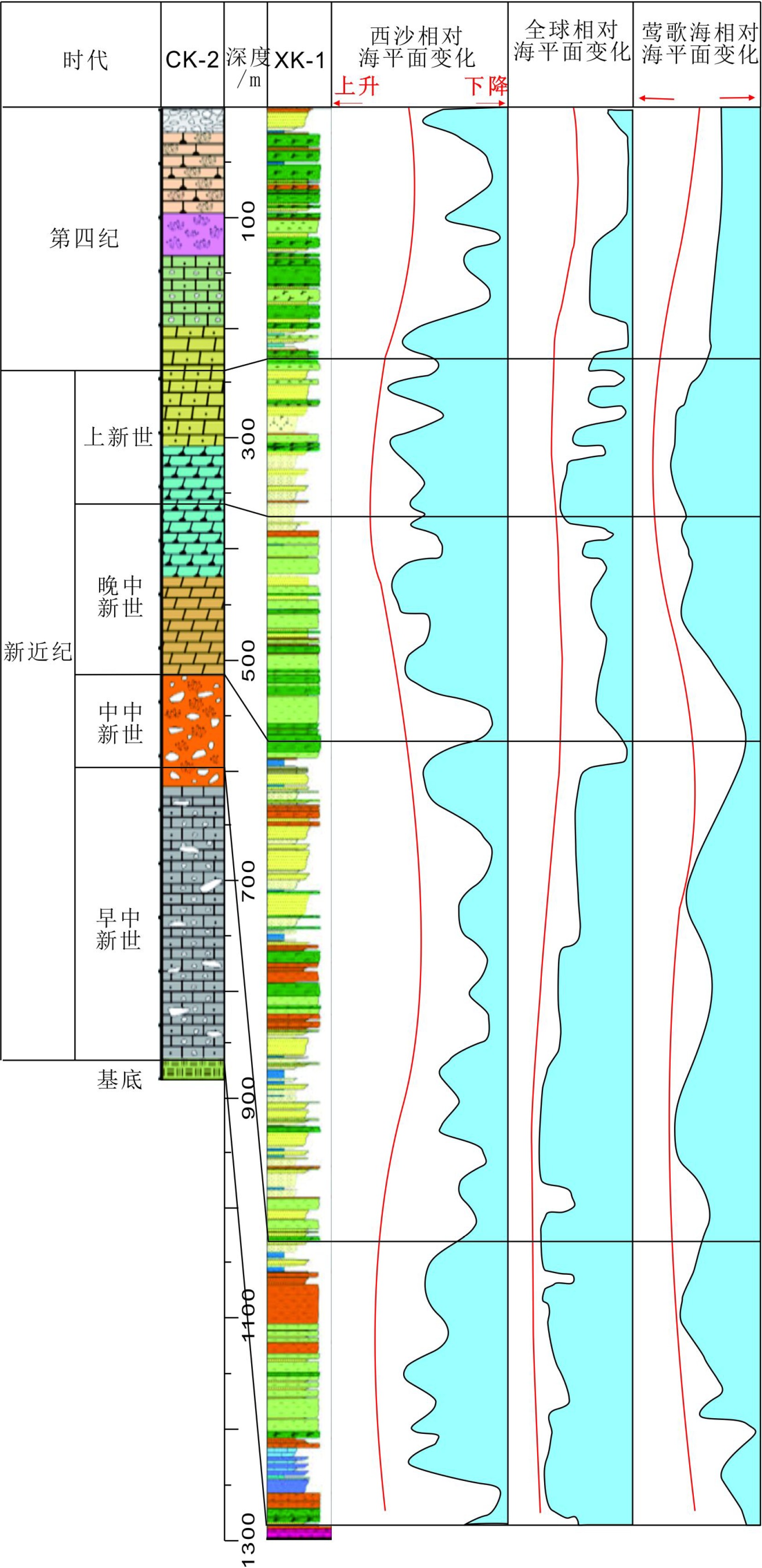
图 2 西沙碳酸盐台地地震层序划分[10]
Figure 2.
表 1 岛礁地震探测航次采集参数对比
Table 1. Comparison of seismic acquisition parameters for reef island
采集参数 2010年巴哈马Caranar航次 2007年马尔代夫M74/4航次 2017年永乐环礁高分辨率地震探测航次 接受道数/道 96 144 128 测线间距/km 斜坡区2.5 不详 主测线2.5~5 道间距/m 6.25 6.25 3.125 最小偏移距/m 不详 不详 69.7 炮间距/m 不详 25 12.5 震源容量 Mini-GI 24in3 组合Mini-GI 105in3 组合Mini-GI 520in3 信号频道/Hz 40~350 主频100~120 主频100~120 -
[1] Vail P R, Colin J P, Duchene R J, et al. Sequence stratigraphy and its application to the chronostratigraphic correlation of the paris basin jurassic [J]. Bulletin Societe Geologique France, 1987, 3(7): 1301-1330.
[2] Posamentier H W, Vail P R. Eustatic controls on clastic deposition II-Sequence and systems tract models[M]//Sea-Level Changes: An Integrated Approach.Tulsa, Okla: SEPM, 1988: 125-154.
[3] Betzler C, Hübscher C, Lindhorst S, et al. Monsoon-induced partial carbonate platform drowning (Maldives, Indian Ocean) [J]. Geology, 2009, 37(10): 867-870. doi: 10.1130/G25702A.1
[4] Eberli G P, Ginsburg R N. Comment and reply on “Segmentation and coalescence of Cenozoic carbonate platforms, northwestern Great Bahama Bank”: Reply [J]. Geology, 1987, 15(11): 1082.
[5] Schlager W, Warrlich G. Record of sea-level fall in tropical carbonates [J]. Basin Research, 2009, 21(2): 209-224. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2117.2008.00383.x
[6] Wilson M E J. Cenozoic carbonates in Southeast Asia: implications for equatorial carbonate development [J]. Sedimentary Geology, 2002, 147(3-4): 295-428. doi: 10.1016/S0037-0738(01)00228-7
[7] Wilson M E J. Global and regional influences on equatorial shallow-marine carbonates during the Cenozoic [J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2008, 265(3-4): 262-274. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2008.05.012
[8] Fournier F, Montaggioni L, Borgomano J. Paleoenvironments and high-frequency cyclicity from Cenozoic South-East Asian shallow-water carbonates: a case study from the Oligo-Miocene buildups of Malampaya (Offshore Palawan, Philippines) [J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2004, 21(1): 1-21. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2003.11.012
[9] Webster J M, Wallace L, Silver E, et al. Drowned carbonate platforms in the Huon Gulf, Papua New Guinea [J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2004, 5(11): Q11008.
[10] Rankey E C. Seismic architecture and seismic geomorphology of heterozoan carbonates: Eocene-Oligocene, Browse Basin, Northwest Shelf, Australia [J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2017, 82: 424-443. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2017.02.011
[11] Principaud M, Ponte J P, Mulder T, et al. Slope-to-basin stratigraphic evolution of the northwestern Great Bahama Bank (Bahamas) during the Neogene to Quaternary: interactions between downslope and bottom currents deposits [J]. Basin Research, 2017, 29(6): 699-724. doi: 10.1111/bre.12195
[12] Fan T L, Yu K F, Zhao J X, et al. Strontium isotope stratigraphy and paleomagnetic age constraints on the evolution history of coral reef islands, northern South China Sea [J]. GSA Bulletin, 2020, 132(3-4): 803-816. doi: 10.1130/B35088.1
[13] Jiang W, Yu K F, Fan T L, et al. Coral reef carbonate record of the Pliocene-Pleistocene climate transition from an atoll in the South China Sea [J]. Marine Geology, 2019, 411: 88-97. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2019.02.006
[14] Wang R, Jones B, Yu K F. Island dolostones: Genesis by time-transgressive or event dolomitization [J]. Sedimentary Geology, 2019, 390: 15-30. doi: 10.1016/j.sedgeo.2019.07.002
[15] Wang R, Yu K F, Jones B, et al. Evolution and development of Miocene “island dolostones” on Xisha Islands, South China Sea [J]. Marine Geology, 2018, 406: 142-158. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2018.09.006
[16] Zhang Y, Yu K F, Qian H D, et al. The basement and volcanic activities of the Xisha Islands: Evidence from the kilometre-scale drilling in the northwestern South China Sea [J]. Geological Journal, 2020, 55: 571-583. doi: 10.1002/gj.3416
[17] 罗威, 张道军, 刘新宇, 等. 西沙地区西科1井综合地层学研究[J]. 地层学杂志, 2018, 42(4):485-498
LUO Wei, ZHANG Daojun, LIU Xinyu, et al. A comprehensive stratigraphic study of Well XK-1 in the Xisha area [J]. Journal of Stratigraphy, 2018, 42(4): 485-498.
[18] 张功成. 南海北部陆坡深水区构造演化及其特征[J]. 石油学报, 2010, 31(4):528-533, 541 doi: 10.7623/syxb201004002
ZHANG Gongcheng. Tectonic evolution of deepwater area of northern continental margin in South China Sea [J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2010, 31(4): 528-533, 541. doi: 10.7623/syxb201004002
[19] Qiu X L, Ye S Y, Wu S M, et al. Crustal structure across the xisha trough, northwestern South China Sea [J]. Tectonophysics, 2001, 341(1-4): 179-193. doi: 10.1016/S0040-1951(01)00222-0
[20] 朱伟林, 谢习农, 王振峰, 等. 南海西沙隆起基底成因新认识[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2017, 47(12):1460-1468 doi: 10.1360/N072017-00011
ZHU Weilin, XIE Xinong, WANG Zhenfeng, et al. New insights on the origin of the basement of the Xisha uplift, South China Sea [J]. Scientia Sinica Terrae, 2017, 47(12): 1460-1468. doi: 10.1360/N072017-00011
[21] Li C F, Li J B, Ding W W, et al. Seismic stratigraphy of the central South China Sea basin and implications for neotectonics [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research-Solid Earth, 2015, 120(3): 1377-1399. doi: 10.1002/2014JB011686
[22] 吴时国, 张新元. 南海共轭陆缘新生代碳酸盐台地对海盆构造演化的响应[J]. 地球科学—中国地质大学学报, 2015, 40(2):234-248 doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2015.017
WU Shiguo, ZHANG Xinyuan. Response of cenozoic carbonate platform on tectonic evolution in the conjugated margin of South China Sea [J]. Earth Science-Journal of China University of Geosciences, 2015, 40(2): 234-248. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2015.017
[23] 马玉波, 吴时国, 杜晓慧, 等. 西沙碳酸盐岩建隆发育模式及其主控因素[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2011, 31(4):59-67
MA Yubo, WU Shiguo, DU Xiaohui, et al. Evolutionary model and control factors of Xisha carbonate buildup [J]. Marine Geology & Qaternary Geology, 2011, 31(4): 59-67.
[24] Wu S G, Yang Z, Wang D W, et al. Architecture, development and geological control of the Xisha carbonate platforms, northwestern South China Sea [J]. Marine Geology, 2014, 350: 71-83. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2013.12.016
[25] 杨振, 张光学, 张莉, 等. 西沙海域中新世碳酸盐台地的时空分布及其油气成藏模式[J]. 地质学报, 2017, 91(6):1360-1373 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2017.06.014
YANG Zhen, ZHANG Guangxue, ZHANG Li, et al. The spatial-temporal distribution of miocene carbonate platform in the Xisha sea area and its model of hydrocarbon accumulation [J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2017, 91(6): 1360-1373. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2017.06.014
[26] Shao L, Li Q Y, Zhu W L, et al. Neogene carbonate platform development in the NW South China Sea: Litho-, bio- and chemo-stratigraphic evidence [J]. Marine Geology, 2017, 385: 233-243. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2017.01.009
[27] Ma Y B, Wu S G, Lv F L, et al. Seismic characteristics and development of the Xisha carbonate platforms, northern margin of the South China Sea [J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2011, 40(3): 770-783. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2010.11.003
[28] 张汉羽, 吴时国, 韩孝辉, 等. 岛礁地震资料特征分析及处理流程——以西沙永乐环礁为例[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2018, 38(6):172-184
ZHANG Hanyu, WU Shiguo, HAN Xiaohui, et al. Characteristics of seismic data and its processing procedures in the areas of Reef Islands—a case from Yongle Atoll of Xisha Islands [J]. Marine Geology & Qaternary Geology, 2018, 38(6): 172-184.
[29] 刘刚, 何其江, 李亮, 等. 西沙群岛永乐环礁瀉湖沉积速率及地球化学特征[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2018, 38(6):69-77
LIU Gang, HE Qijiang, LI Liang, et al. Sedimentation rate and geochemical characters of the lagoonal deposits in the Yongle Atoll, Xisha Islands [J]. Marine Geology & Qaternary Geology, 2018, 38(6): 69-77.
[30] Shao L, Cui Y C, Qiao P J, et al. Sea-level changes and carbonate platform evolution of the Xisha Islands (South China Sea) since the Early Miocene [J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2017, 485: 504-516. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2017.07.006
[31] Betzler C, Fürstenau J, Lüdmann T, et al. Sea-level and ocean-current control on carbonate-platform growth, Maldives, Indian Ocean [J]. Basin Research, 2013, 25(2): 172-196. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2117.2012.00554.x
[32] 王子兰, 王仕俭, 李素闪, 等. GeoEast处理解释一体化应用[J]. 天然气工业, 2007, 27(S1):222-224
WANG Zilan, WANG Shijian, LI Sushan, et al. GeoEast processing and interpretation of integrated applications [J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2007, 27(S1): 222-224.
[33] Fontaine J M, Cussey R, Lacaze J, et al. Seismic interpretation of carbonate depositional environments [J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1987, 71(3): 281-297.
[34] Paumard V, Zuckmeyer E, Boichard R, et al. Evolution of Late Oligocene-Early Miocene attached and isolated carbonate platforms in a volcanic ridge context (Maldives type), Yadana field, offshore Myanmar [J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2017, 81: 361-387. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2016.12.012
[35] Shahzad K, Betzker C, Ahmed N, et al. Growth and demise of a Paleogene isolated carbonate platform of the Offshore Indus Basin, Pakistan: effects of regional and local controlling factors [J]. International Journal of Earth Sciences, 2018, 107(2): 481-504. doi: 10.1007/s00531-017-1504-7
[36] Shahzad K, Betzker C, Qayyum F. Controls on the Paleogene carbonate platform growth under greenhouse climate conditions (Offshore Indus Basin) [J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2019, 101: 519-539. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2018.12.025
-



 下载:
下载: