Turbidite records since 36.6 ka at the Yingqiong continental slope in the northwest of South China Sea
-
摘要:
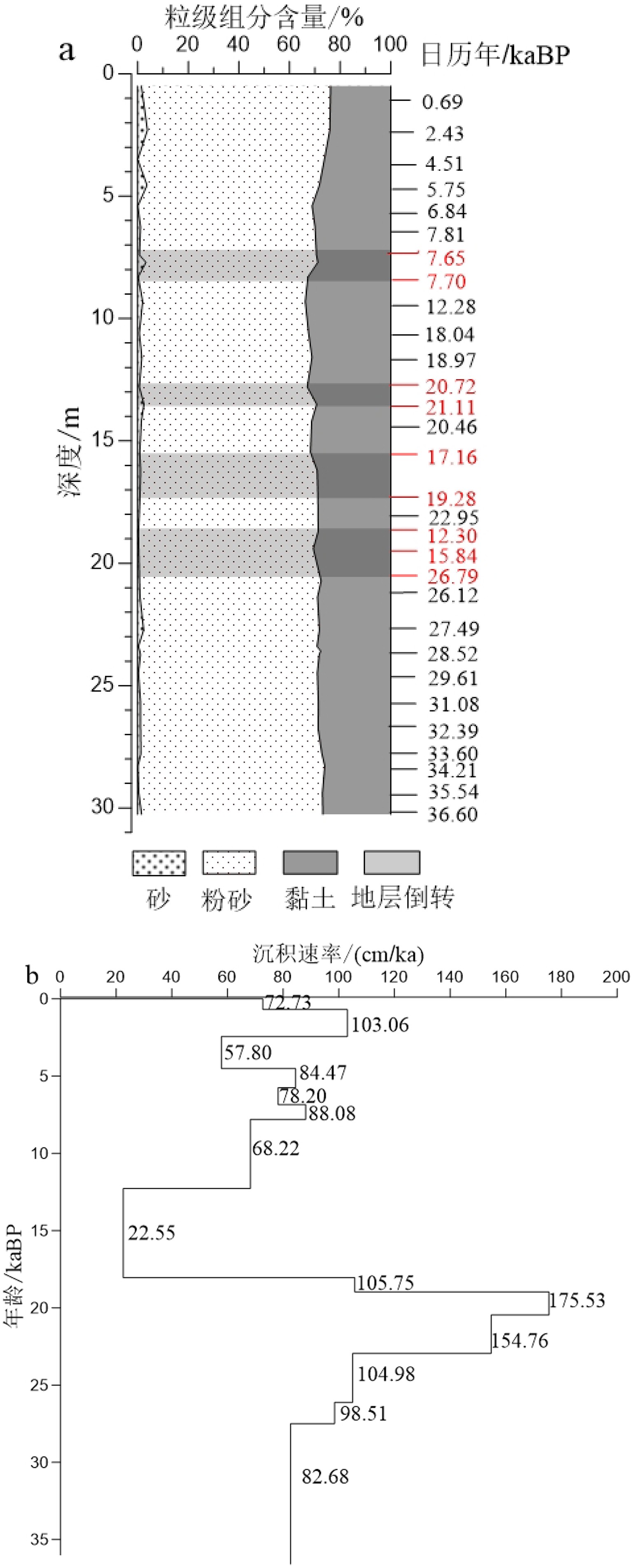
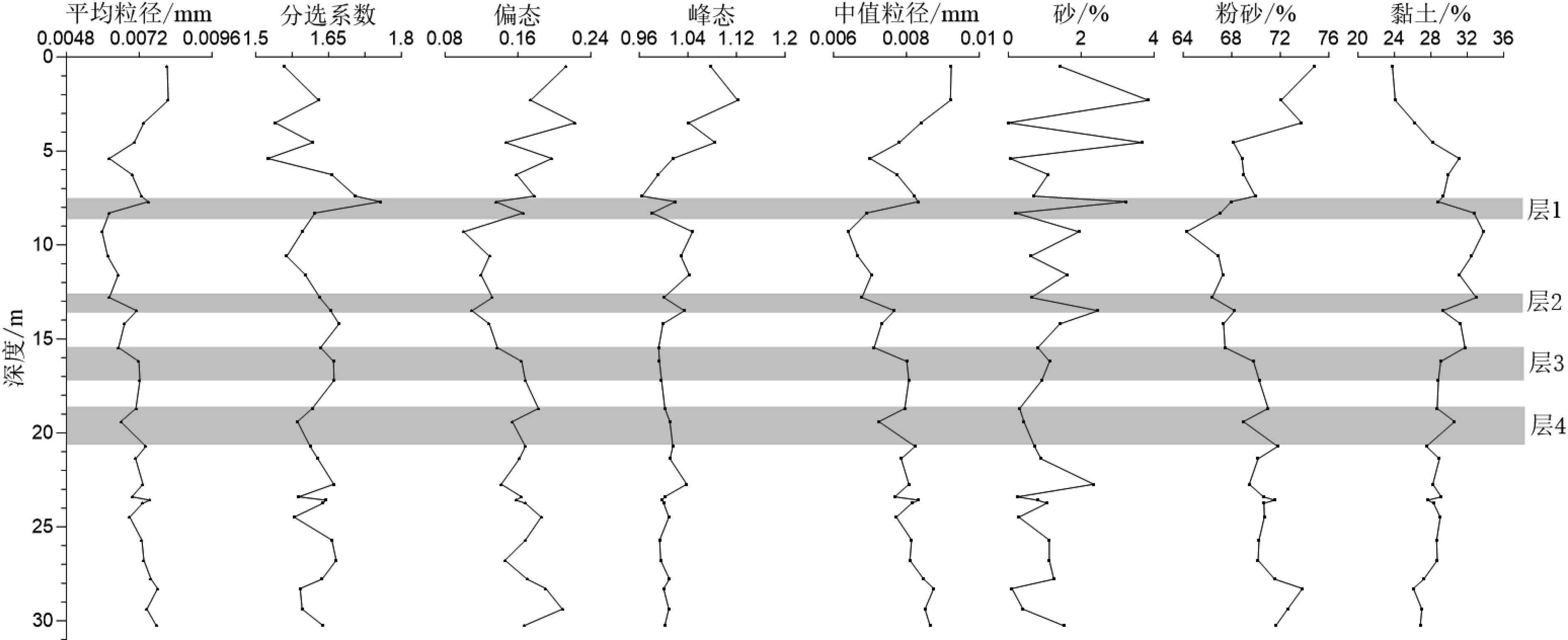
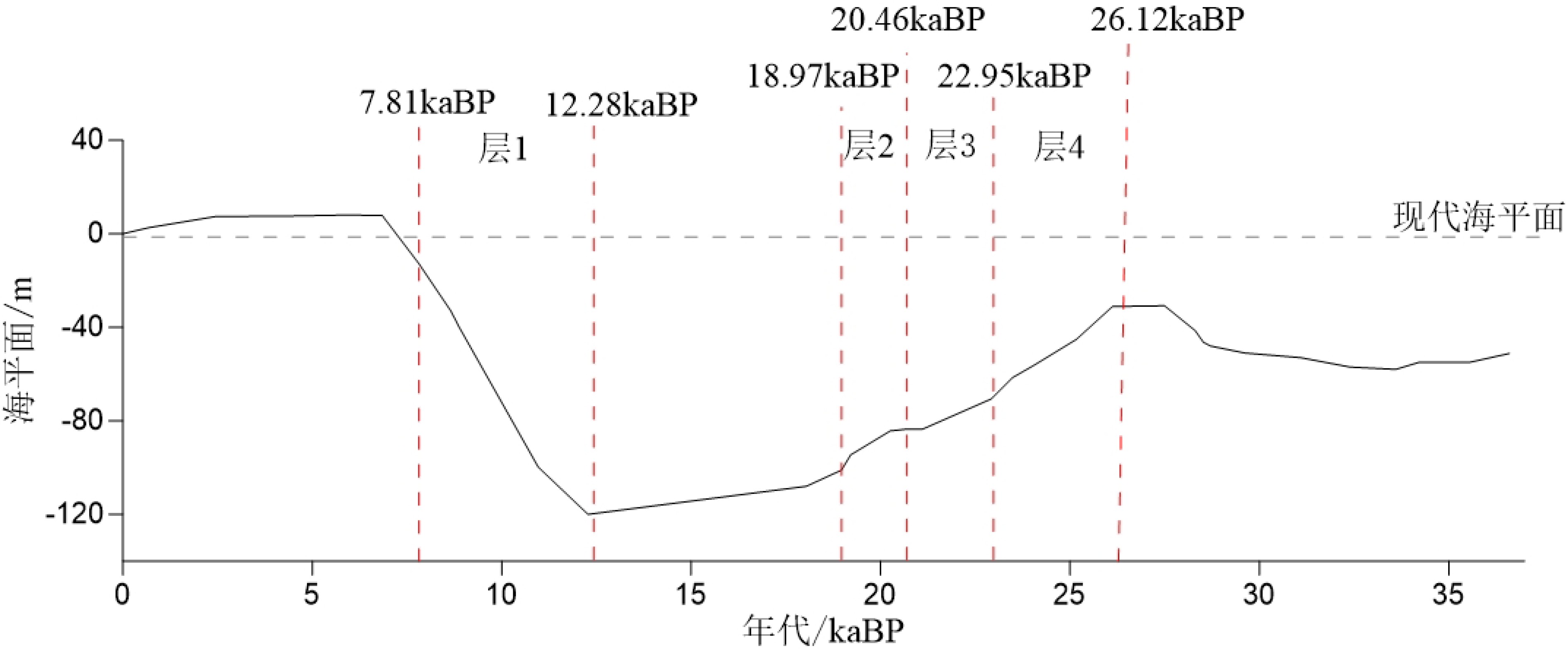
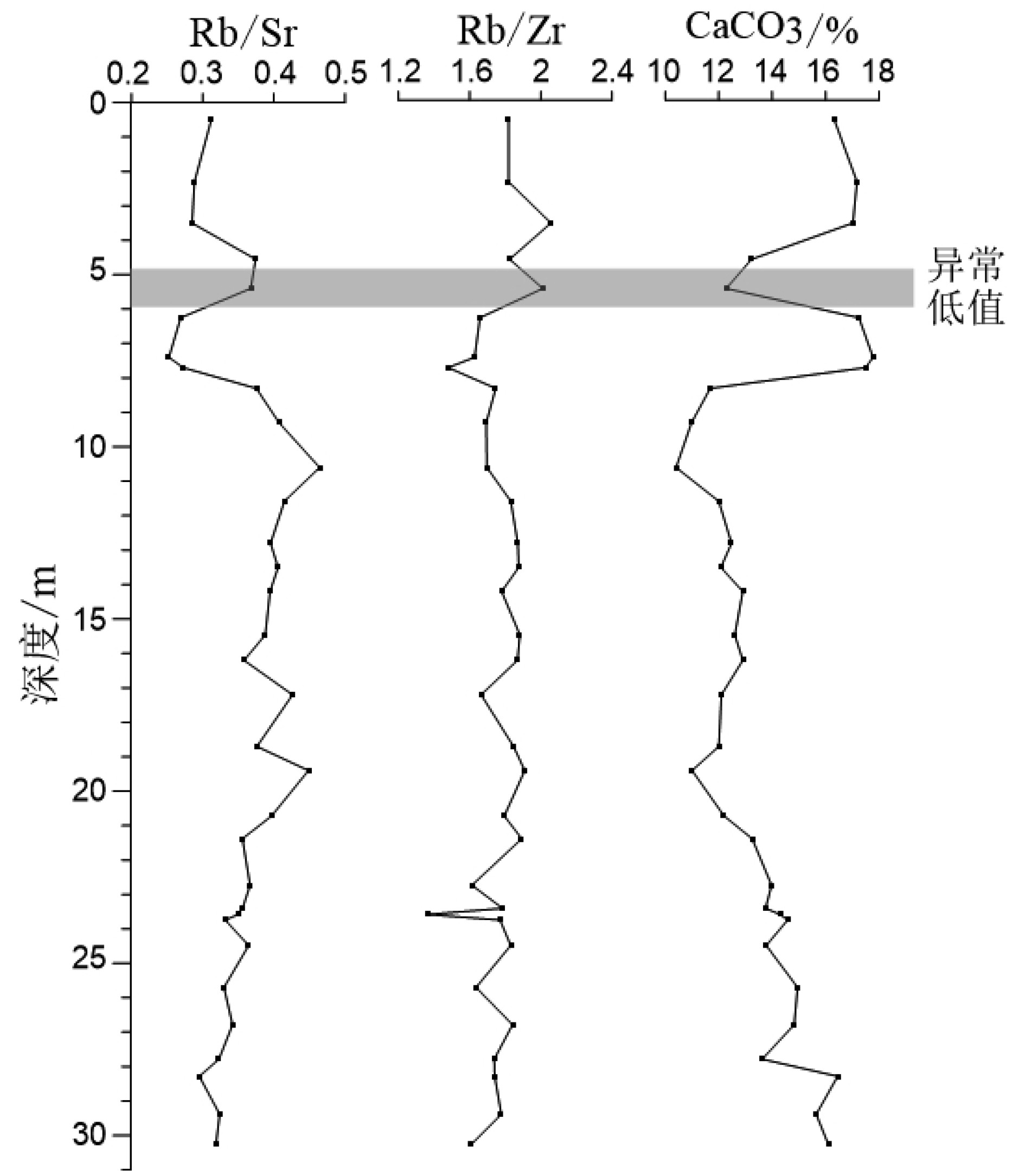
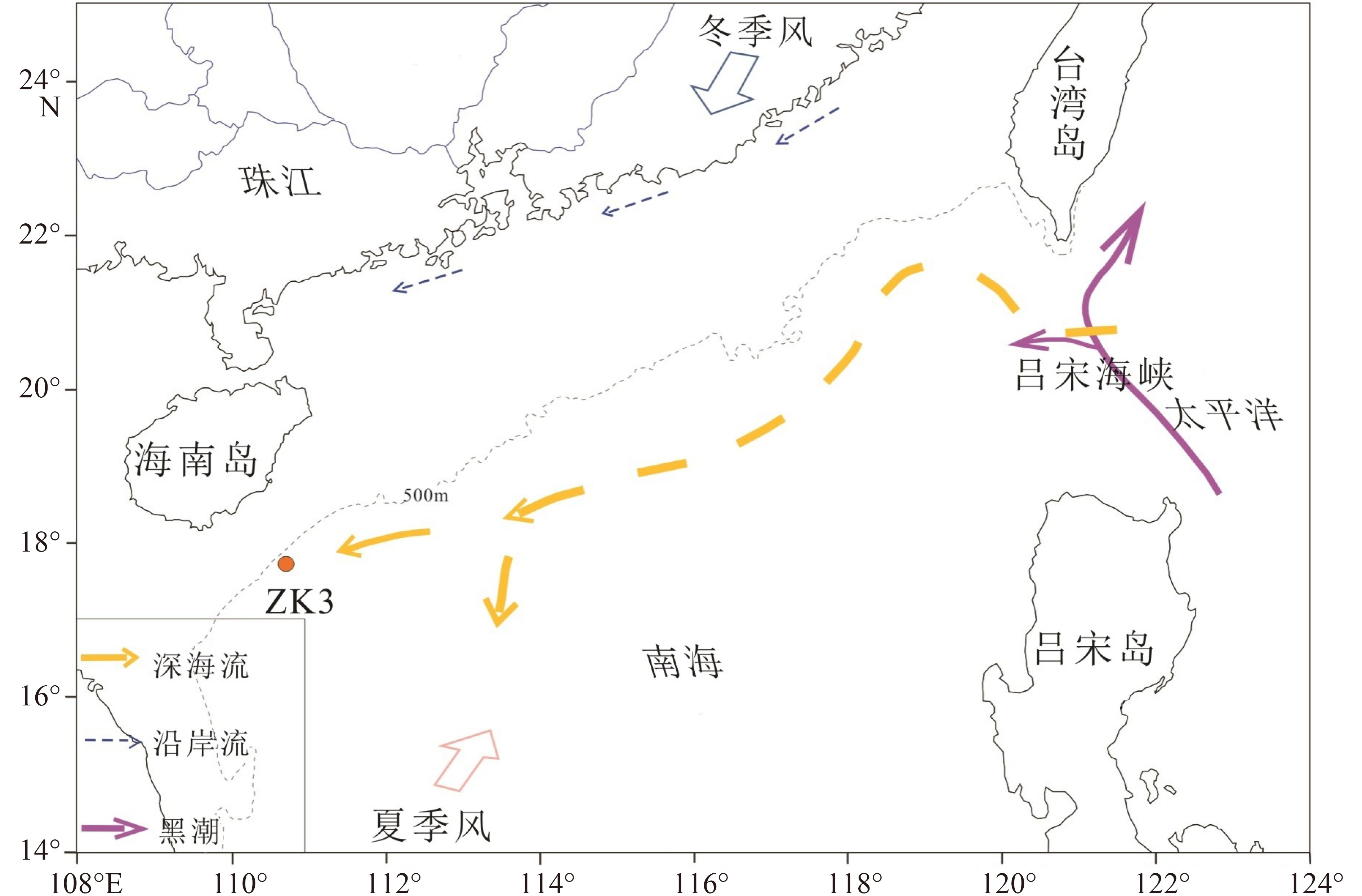
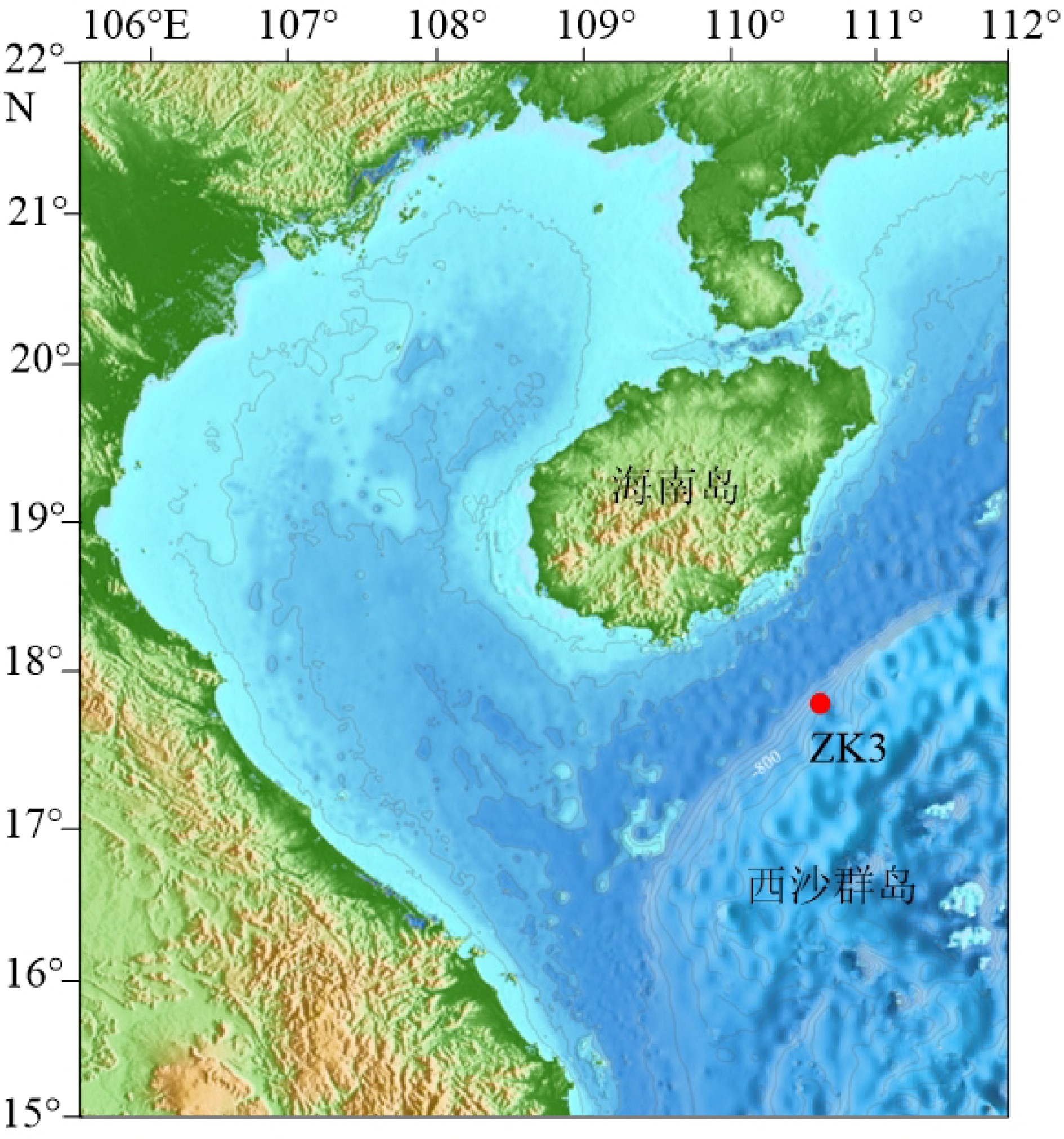
对取自南海西北部莺琼陆坡的ZK3岩心进行了AMS14C测年、沉积物粒度分析、地球化学元素分析等,结合萨哈-兰迪姆相浊流环境判别及C-M图的分析结果,识别了南海西北部莺琼陆坡的浊流沉积,讨论了浊流发育的成因及环境气候变化对南海陆坡沉积环境的影响。研究表明:ZK3岩心主要发育了36.6 kaBP以来的晚更新世和全新世地层,浊流沉积发育,初步识别出7.4~8.3、12.8~13.5、15.5~17.2、18.7~20.7 m这4个特征明显的浊积层,其中有3次浊积事件发生于末次冰期。有利的地形、丰富的物源、活跃的海平面变化及气候变化是触发浊流的主要因素。
Abstract:The cores of ZK3 collected from the Yingqiong slope in the northwest of South China Sea were dated with AMS14C dating, and analyzed for grain sizes and geochemical elements. The Shakha-Landim method for discrimination of turbidity environment and the C-M diagram for turbidite deposits, are also used to recognize the turbidity sediments. Detailed discussion is devoted to the formation of turbidity current and the impacts of the climate change onto the sedimentary environment. The study shows that sediments of core ZK3 were deposited in the time of Pleistocene and Holocene since 36.6 ka. Four layers of turbidite with obvious features occur in the intervals of 7.4~8.3, 12.8~13.5, 15.5~17.2 and 18.7~20.7 m respectively, corresponding to three turbidity events during the last glacial stage. Favorable topography, abundant material supply, active sea level fluctuation and climate change are the main causes for the origin of the turbidity currents.
-
Key words:
- turbidity sedimentation /
- grain size /
- sea level change /
- northwestern of South China Sea
-

-
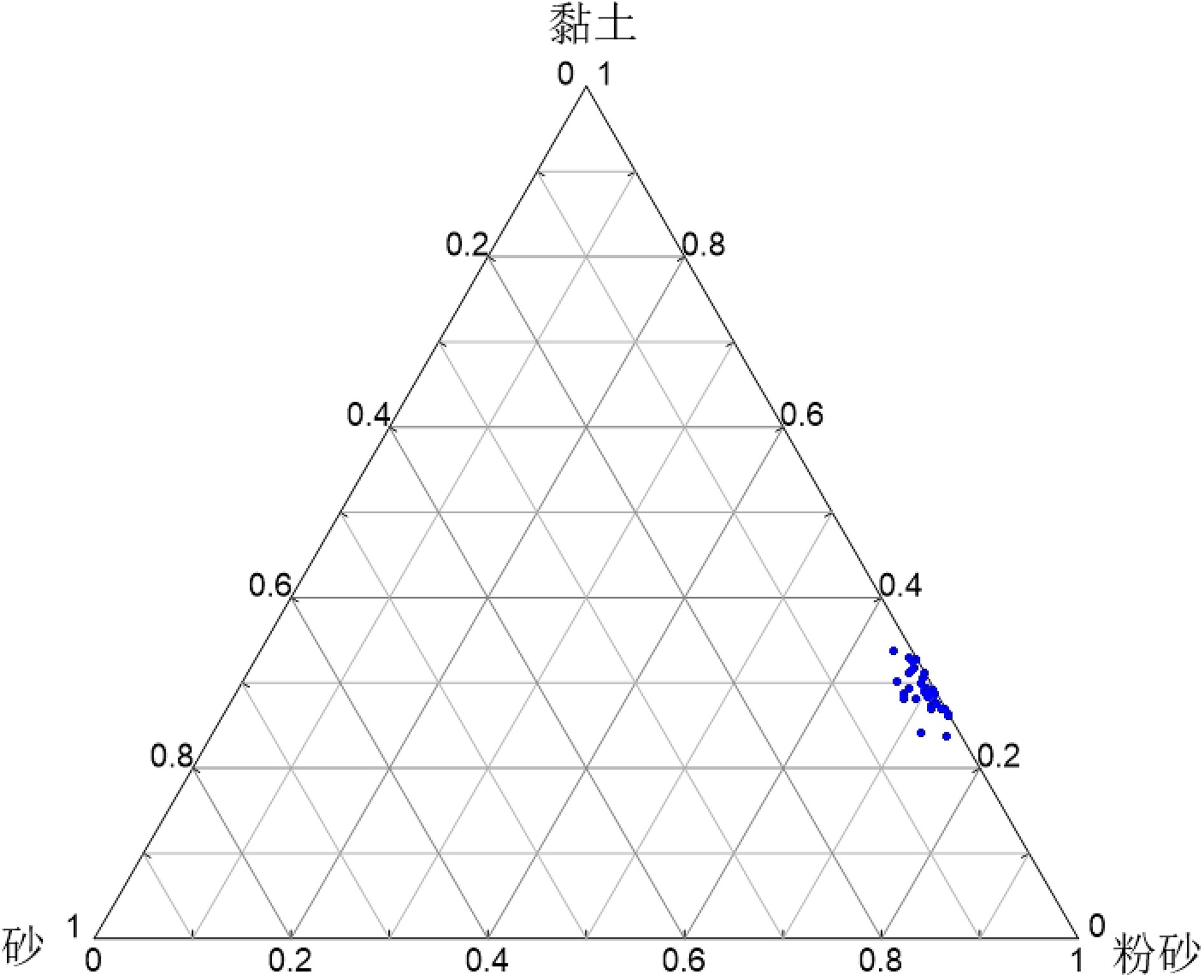
表 1 ZK3岩心沉积物组成与粒度参数
Table 1. Composition and grain size parameters of the sediments from core ZK3
粒度参数 砂/% 粉砂/% 黏土/% Md Mz σI SkI Kg 平均值 1.16 69.83 29.01 0.008 0.007 1.625 0.161 1.016 最大值 3.85 74.80 33.79 0.009 0.008 1.756 0.223 1.122 最小值 0.00 64.28 23.78 0.006 0.006 1.525 0.100 0.965 表 2 ZK3岩心各层位萨哈-兰迪姆相浊流环境判别结果
Table 2. Identification of Turbidity current environment with Sakha-Landim facies diagram for each layer of core ZK3
层位 Y值 层位 Y值 ZK3 S-9-7.40 5.619 ZK3 S-29-16.20 5.697 ZK3 S-10-7.70 5.606 ZK3 S-31-17.20 5.741 ZK3 S-11-8.30 5.657 ZK3 S-35-18.70 5.885 ZK3 S-22-12.80 5.530 ZK3 S-37-19.40 5.748 ZK3 S-24-13.50 5.549 ZK3 S-41-20.70 5.860 ZK3 S-28-15.50 5.521 − − -
[1] 傅飘儿, 庄畅, 刘坚, 等. 南海西沙海槽XH-CL16柱状沉积物稀土元素特征及其物源[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2015, 35(4):63-71
FU Piaoer, ZHUANG Chang, LIU Jian, et al. Rare earth elements geochemistry and provenance of the sediments from core XH-Cl16 in the XiSha Trough, South China Sea [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2015, 35(4): 63-71.
[2] 汪品先. 南海——我国深海研究的突破口[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2009, 28(3):1-4 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5470.2009.03.001
WANG Pinxian. Toward scientific breakthrough in the South China Sea [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2009, 28(3): 1-4. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5470.2009.03.001
[3] Steinke S, Kienast M, Hanebuth T. On the significance of sea-level variations and shelf paleo-morphology in governing sedimentation in the southern South China Sea during the last deglaciation [J]. Marine Geology, 2003, 201(1-3): 179-206. doi: 10.1016/S0025-3227(03)00216-0
[4] Hanebuth T, Stattegger K, Grootes P M. Rapid flooding of the Sunda shelf: a late-glacial sea-level record [J]. Science, 2000, 288(5468): 1033-1035. doi: 10.1126/science.288.5468.1033
[5] 章伟艳, 张富元, 张霄宇. 南海东部海域柱样沉积物浊流沉积探讨[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2003, 22(3):36-43 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5470.2003.03.006
ZHANG Weiyan, ZHANG Fuyuan, ZHANG Xiaoyu. Characteristics of turbidity deposits from sediment cores in eastern South China Sea [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2003, 22(3): 36-43. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5470.2003.03.006
[6] Ducassou M, Migeon S, Mulder T, et al. Evolution of the Nile deep-sea turbidite system during the Late Quaternary: influence of climate change on fan sedimentation [J]. Sedimentology, 2009, 56(7): 2061-2090. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3091.2009.01070.x
[7] Weaver P P E, Kuijpers A. Climatic control of turbidite deposition on the Madeira Abyssal Plain [J]. Nature, 1983, 306(5941): 360-363. doi: 10.1038/306360a0
[8] 冯文科, 石要红, 陈玲辉. 南海北部外陆架和上陆坡海底滑坡稳定性研究[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 1994(2):81-94
FENG Wenke, SHI Yaohong, CHEN Linghui. Research for seafloor landslide stability on the outer continental shelf and the upper continental slope in the Northern South China Sea [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 1994(2): 81-94.
[9] 李军, 赵京涛. 冲绳海槽中部沉积物稀土元素地球化学特征及其在古环境变化研究的应用[J]. 自然科学进展, 2009, 19(12):1333-1342 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-008X.2009.12.007
LI Jun, ZHAO Jingtao. Geochemical characteristics of rare earth elements in the sediments of the Central Okinawa Trough and its application in the study of paleoenvironmental changes [J]. Progress in Natural Science, 2009, 19(12): 1333-1342. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-008X.2009.12.007
[10] Bouma A H. Sedimentology of Some Flysch Deposits: a Graphic Approach to Facies Interpretation[M]. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 1962.
[11] Shanmugam G. The Bouma Sequence and the turbidite mind set [J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 1997, 42(4): 201-229. doi: 10.1016/S0012-8252(97)81858-2
[12] 葛黄敏, 李前裕, 成鑫荣, 等. 南海北部晚第四纪高分辨率浮游氧同位素地层学及其古气候信息[J]. 地球科学——中国地质大学学报, 2010, 35(4):515-525 doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2010.067
GE Huangmin, LI Qianyu, CHENG Xinrong, et al. Late quaternary high resolution monsoon records in planktonic stable isotopes from Northern South China Sea [J]. Earth Science—Journal of China University of Geosciences, 2010, 35(4): 515-525. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2010.067
[13] 袁迎如. 冲绳海槽沉积物的粒度[J]. 东海海洋, 1986, 4(3):42-49
YUAN Yingru. Grain size of the sediments in Okymawa Trough [J]. Donghai Marine Science, 1986, 4(3): 42-49.
[14] 刘宝君, 曾允孚. 岩相古地理基础和工作方法[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1985: 271-284.
LIU Baojun, ZENG Yunfu. Lithofacies Paleogeography Foundation and Working Method[M]. Beijing: Geological Press, 1985: 271-284.
[15] 姜衡. 神狐海域含水合物浊流沉积体差异性对比研究[D]. 中国地质大学(北京)硕士学位论文, 2018.
JIANG Heng. Comparative study on the difference of hydrate-bearing turbidites in the Shenhu Sea Area[D]. Master Dissertation of China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2018.
[16] Ashley G M. Interpretation of polymodal sediments [J]. The Journal of Geology, 1978, 86(4): 411-421. doi: 10.1086/649710
[17] 李小洁. 南海北部沉积物记录的早更新世气候变化[D]. 中国科学院研究生院(地球环境研究所)硕士学位论文, 2015.
LI Xiaojie. The early Pleistocene climate change recorded in the northern South China Sea sediments[D]. Master Dissertation of the University of Chinese Academy of Sciences (Institute of Earth Environment), 2015.
[18] 李明坤. 南海西北部36 kyr BP以来的古气候环境演变与驱动机制[D]. 中国科学院大学(中国科学院广州地球化学研究所)博士学位论文, 2018.
LI Mingkun. Paleoclimate and paleoenvironment evolutions in the Northwestern South China Sea over the past 36 kyr BP and the forcing mechanisms[D]. Doctor Dissertation of University of Chinese Academy of Sciences (Guangzhou Institute of Geochemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences), 2018.
[19] 文琼英, 张川波. 浊流沉积机理及其特征[J]. 海洋科学, 1982(4):56-58
WEN Qiongying, ZHANG Chuanbo. Mechanism and characteristics of turbidity deposition [J]. Marine Sciences, 1982(4): 56-58.
[20] 李波, 王艳, 钟和贤, 等. 花东海盆浊流沉积的磁性特征及其环境意义[J]. 地球物理学报, 2016, 59(9):3330-3342 doi: 10.6038/cjg20160917
LI Bo, WANG Yan, ZHONG Hexian, et al. Magnetic properties of turbidites in the Huatung Basin and their environmental implications [J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2016, 59(9): 3330-3342. doi: 10.6038/cjg20160917
[21] Hesse R. Turbiditic and non-turbiditic mudstone of Cretaceous flysch sections of the East Alps and other basins [J]. Sedimentology, 1975, 22(3): 387-416. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3091.1975.tb01638.x
[22] Passega R. Texture as characteristic of clastic deposition [J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1957, 41(9): 1952-1984.
[23] Shiki T, Kumon F, Inouchi Y, et al. Sedimentary features of the seismo-turbidites, Lake Biwa, Japan [J]. Sedimentary Geology, 2000, 135(1-4): 37-50. doi: 10.1016/S0037-0738(00)00061-0
[24] 周杨锐, 朱友生, 周松望, 等. 南海北部东沙隆起西侧陆坡坡折处浊流沉积[J]. 海洋科学, 2018, 42(2):23-33 doi: 10.11759/hykx20171101003
ZHOU Yangrui, ZHU Yousheng, ZHOU Songwang, et al. Turbidites at the continental slope on the west side of Dongsha uplift in the northern South China Sea [J]. Marine Sciences, 2018, 42(2): 23-33. doi: 10.11759/hykx20171101003
[25] 赵玉龙, 刘志飞, COLIN C, et al. 南海南部末次冰期浊流沉积的高分辨率沉积学和地球化学研究[J]. 科学通报, 2011, 56(33):3558-3565 doi: 10.1007/s11434-011-4685-7
ZHAO Yulong, LIU Zhifei, COLIN C, et al. Turbidite deposition in the southern South China Sea during the last glacial: evidence from grain-size and major elements records [J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2011, 56(33): 3558-3565. doi: 10.1007/s11434-011-4685-7
[26] Shanmugam G, Moiola R J. Eustatic control of turbidites and winnowed turbidites [J]. Geology, 1982, 10(5): 231-235. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1982)10<231:ECOTAW>2.0.CO;2
[27] 钱星, 张莉, 易海, 等. 南海北部双峰南陆坡深水区早—中中新世沉积充填特征及其影响因素[J]. 石油实验地质, 2015, 37(6):751-757 doi: 10.11781/sysydz201506751
QIAN Xing, ZHANG Li, YI Hai, et al. Sedimentary filling characteristics and the main controlling factors during the Early-Middle Miocene in the deep-water area of Shuangfengnan Slope in the northern South China Sea [J]. Petroleum Geology and Experiment, 2015, 37(6): 751-757. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201506751
[28] 雷艳, 胡建芳, 向荣, 等. 末次盛冰期以来南海北部神狐海域沉积有机质的组成特征及其古气候/环境意义[J]. 海洋学报, 2017, 39(11):75-84
LEI Yan, HU Jianfang, Xiang Rong, et al. Composition of sedimentary organic matter in Shenhu, northern South China Sea since the Last Glacial Maximum and its implication for paleoclimate [J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2017, 39(11): 75-84.
[29] 葛倩, 孟宪伟, 初凤友, 等. 南海北部ZHS-176孔古海洋学记录: 氧同位素和有机碳[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2012, 32(5):73-80
GE Qian, MENG Xianwei, CHU Fengyou, et al. Paleoceanographic records of core ZHS-176 from the northern South China Sea: oxygen isotope and organic carbon [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2012, 32(5): 73-80.
[30] 徐海. 中国全新世气候变化研究进展[J]. 地质地球化学, 2001, 29(2):9-16 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9250.2001.02.002
XU Hai. Advance in research on the Holocene climate fluctuations [J]. Geology-Geochemistry, 2001, 29(2): 9-16. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9250.2001.02.002
[31] 李牛, 陈多福. 南海北部陆坡神狐海域富有孔虫沉积层的特征及成因[J]. 地球化学, 2015, 44(6):564-570 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0379-1726.2015.06.005
LI Niu, CHEN Duofu. Characteristics and origin of the Foraminifera-rich sedimentary layers in Shenhu area on the northern continental slope of the South China Sea [J]. Geochimica, 2015, 44(6): 564-570. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0379-1726.2015.06.005
[32] 葛倩, 孟宪伟, 初凤友, 等. 近3万年来南海北部碳酸盐旋回及古气候意义[J]. 海洋学研究, 2008, 26(1):18-21 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-909X.2008.01.003
GE Qian, MENG Xianwei, CHU Fengyou, et al. The carbonate cycles in the northern South China Sea during the last 30 ka and the paleoclimatic significance [J]. Journal of Marine Sciences, 2008, 26(1): 18-21. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-909X.2008.01.003
[33] 叶芳, 刘志飞, 拓守廷, 等. 南海北部中更新世0.78~1.0Ma期间的陆源碎屑粒度记录[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2007, 27(2):77-83
YE Fang, LIU Zhifei, TUO Shouting, et al. Grain size record of terrigenous clast during mid-pleistocene transition (0.78~1.0 Ma) in the northern South China Sea [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2007, 27(2): 77-83.
[34] 陈隆勋, 朱乾根, 罗会帮. 东亚季风[M]. 北京: 气象出版社, 1991: 28-61.
CHEN Longxun, ZHU Qiangen, LUO Huibang. East Asian Monsoon[M]. Beijing: China Meteorological Press, 1991: 28-61.
[35] 刘伟. 南海北部陆坡MIS5以来的古环境记录[D]. 中国地质大学(北京)博士学位论文, 2012.
LIU Wei. Paleoclimatic records from northern slope of South China Sea since the Marine Isotope Stage 5[D]. Doctor Dissertation of China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2012.
[36] 庞雄. 深水重力流沉积的层序地层结构与控制因素——南海北部白云深水区重力流沉积层序地层学研究思路[J]. 中国海上油气, 2012, 24(2):1-8 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1506.2012.02.001
PANG Xiong. Sequence stratigraphy configuration of deepwater gravity-flow sediments and its controls: a line of thinking in sequence stratigraphy of gravity-flow sediments in Baiyun deepwater area, the northern South China Sea [J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2012, 24(2): 1-8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1506.2012.02.001
[37] 邵磊, 李学杰, 耿建华, 等. 南海北部深水底流沉积作用[J]. 中国科学 D辑: 地球科学, 2007, 50(7):1060-1066 doi: 10.1007/s11430-007-0015-y
SHAO Lei, LI Xuejie, GENG Jianhua, et al. Deep water bottom current deposition in the northern South China Sea [J]. Science in China Series D: Earth Sciences, 2007, 50(7): 1060-1066. doi: 10.1007/s11430-007-0015-y
[38] 李华, 王英民, 徐强, 等. 南海北部珠江口盆地重力流与等深流交互作用沉积特征、过程及沉积模式[J]. 地质学报, 2014, 88(6):1120-1129
LI Hua, WANG Yingmin, XU Qiang, et al. Interactions between down-slope and along-slope processes on the northern slope of South China Sea: products, processes, and depositional model [J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2014, 88(6): 1120-1129.
[39] 田洁. 南海西北陆坡区新生代碳酸盐台地周缘深水沉积体系研究[D]. 中国科学院研究生院(海洋研究所)博士学位论文, 2015.
TIAN Jie. Characteristics and evolution of Cenozoic periplatform deep-water sedimentary system in the Xisha area, northern continental margin of the South China sea[D]. Doctor Dissertation of the Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2015.
[40] 陈慧. 南海西北次海盆西北陆缘深水沉积体系及其演化研究[D]. 中国地质大学博士学位论文, 2014.
CHEN Hui. Characteristics and evolution of deep-water sedimentary systems on the northwestern margin slopes of the northwest sub-basin, South China Sea[D]. Doctor Dissertation of China University of Geosciences, 2014.
[41] Liu Z F, Zhao Y L, Colin C, et al. Source-to-sink transport processes of fluvial sediments in the South China Sea [J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2016, 153: 238-273. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2015.08.005
[42] Lee H J, Chough S K, Yoon S H. Slope-stability change from late Pleistocene to Holocene in the Ulleung Basin, East Sea (Japan Sea) [J]. Sedimentary Geology, 1996, 104(1-4): 39-51. doi: 10.1016/0037-0738(95)00119-0
[43] 张明书. 冲绳海槽的晚第四纪浊流沉积[J]. 长春地质学院学报, 1988, 18(1):19-28
ZHANG Mingshu. Late quaternary turbidites in the Okinawa Trough [J]. Journal of Changchun University of Earth Science, 1988, 18(1): 19-28.
-



 下载:
下载: