Investigation of gravity flow deposits on the Lingshui slope of the northern South China Sea
-
摘要:
深水沉积环境复杂、浅层沉积物土质差异明显、重力流沉积多样,对深水海洋工程水下设施的设计、施工和运营安全提出了新的挑战。通过二维/三维数字地震等方式能够识别出数百米的滑坡体,但是对于海洋工程上所关注的浅层海底的重力流沉积体系,其分析能力有限。以南海北部陵水区块为例,通过船载多波束的后向散射成果、自主水下航行器(AUV)搭载的浅地层剖面资料,结合重力活塞取样器(JPC)取样和碳14测年(AMS14C)等资料综合分析,对深水海底浅层重力流沉积的形成和分布模式进行探讨。研究表明,船载多波束后向散射图能够较为准确地识别区域性重力流沉积区域,以及表层沉积物的变化,AUV搭载的浅地层剖面能够精确地识别地层的纵向差异,JPC取样能够获取重力流沉积样品及其物理力学参数,以上资料的综合分析,是准确识别、研究和认识现代重力流沉积体系的重要方法。研究区内最近的2期重力流沉积分别发生于5.5 kaBP左右和45 kaBP前,重力流的发生一般都是由上陆坡区海底峡谷的活动引起的。最近的一期重力流事件中,先后发生了浊流沉积和块状搬运体(MTDs)沉积,MTDs沉积过程中会对下伏地层产生明显的冲蚀现象。在重力流沉积区进行水下结构物设计和施工时,应特别关注重力流沉积引起的地形坡度变化,以及地层中土质成分的差异,可能对水下结构物的安装和维护产生的影响。
Abstract:Deep-water environment is rather complex. Within the shallow part of the environment, there occur various gravity flow deposits, that become new challenges to the design, construction and operation of underwater facilities. The landslides on scale of hundreds of meters can be identified by 2D/3D digital seismic survey, but the recognition of gravity flow depositional system on the shallow seabed, which is concerned by marine engineers, is limited. Taking the Lingshui block in the north of the South China Sea as an example, this paper discussed the formation and distribution models of shallow gravity flow deposits in the deep sea bottom with the results of MBES backscattering on board, the sub-bottom profile data carried by the Autonomous Underwater Vehicle (AUV), combined with the data of Jumbo Piston Corer (JPC) sampling and AMS14C dating. The results show that the MBES backscatter result can accurately identify the region of gravity flow deposition and the changes of surface sediments, the Sub-bottom profiler carried by AUV can accurately identify the vertical differences of strata, and JPC sampling can obtain the gravity flow deposits as well as their physical and mechanical parameters. The comprehensive analysis of the above data founded the basis to accurately identify, study and recognize the present situation of the gravity flow depositional system. The latest two periods of gravity flow deposition in the study area occurred about 5.5 ka and 45 ka ago, respectively. Generally, the gravity flow is caused by the activity of submarine canyon on the upper slope. In the latest gravity flow event, turbidity current deposition and MTDS deposition took place successively, and the MTDS deposition produced obvious erosion to the underlying strata. In the design and construction of underwater structures in the gravity flow active area, special attention should be paid to the change of terrain slope caused by gravity flow deposition and the difference of soil composition in the stratum, which may affect the installation and maintenance of underwater facilities.
-
Key words:
- backscatter /
- gravity flow deposition /
- turbidity /
- deep-water sedimentary model
-

-
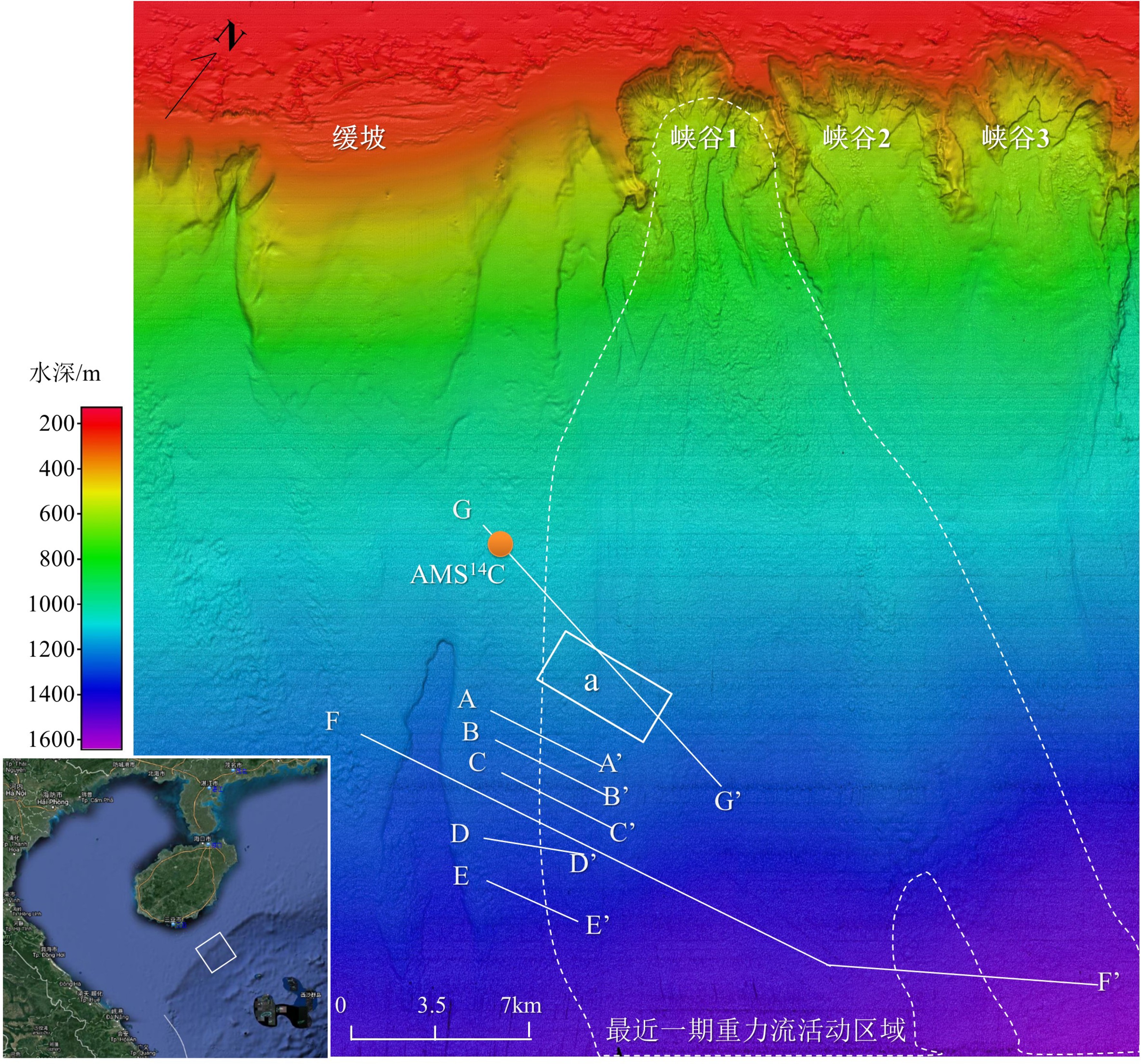
图 2 通过碳14C测年推算重力流发生年代(图1中的G-G’)
Figure 2.
图 3 通过地形识别最近一期MTDs沉积(位于图1中的a区域)
Figure 3.
图 7 浅地层剖面——近期浊流与MTDs沉积(图1中的E-E’)
Figure 7.
图 9 浅地层剖面——浊流堆积在海底凹陷处(图1中的D-D’)
Figure 9.
图 11 调查区域水深光照图及东-西向浅地层剖面(图1中的F-F’)
Figure 11.
表 1 浊流沉积JPC取样土质参数
Table 1. Soil parameters for JPC Sampling in turbidity area
样品深度/ m 含水/ % 容重/(kN/m3) 界限含水量/% 200#/ % 颗粒密度 液限 塑限 塑性指数 0.5 113 13.8 89.2 39.4 49.8 94 2.7 1.3 80 15.2 71.1 31.6 39.5 96 2.71 2 117 13.7 81 40.7 40.3 93 2.69 2.7 130 13.4 101.7 45.1 56.6 95 2.7 3.5 133 13.1 105.1 45.5 59.6 93 2.7 4.2 112 13.6 104 44.6 59.4 96 2.7 4.9 119 13.5 94.3 40.4 53.9 97 2.7 -
[1] Heezen B C, Ewing W M. Turbidity currents and submarine slumps and the 1929 Grand Banks (Newfoundland) earthquake [J]. American Journal Science Series, 1952, 250: 849-873. doi: 10.2475/ajs.250.12.849
[2] Parker G, Garcia M, Fukushima Y, et al. Experiments on turbidity currents over an erodible bed [J]. Journal of Hydraulic Research, 1987, 25: 123-147. doi: 10.1080/00221688709499292
[3] Garcia M. Depositional turbidity currents laden with poorly sorted sediment [J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 1994, 120: 1 240-1 263. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9429(1994)120:11(1240)
[4] Huang H, Imran J, Pirmez C. Numerical modeling of poorly sorted depositional turbidity currents [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 2007, 112: 1-15.
[5] Bouma A H, Normark W R, Barnes N E. Submarine Fans and Related Turbidite Systems [M]. New York: Springer Verlag, 1985: 351.
[6] Talling P J, Masson D G, Sumner E J, et al. Subaqueous sediment density flows: Depositional processes and deposit types [J]. Sedimentology, 2012, 59(7): 1 937-2 003. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3091.2012.01353.x
[7] Bouma A H. Sedimentology of Some Flysch Deposits: A Graphic Approach to Facies Interpretation[M]. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 1962: 168.
[8] 秦志亮. 南海北部陆坡块体搬运沉积体系的沉积过程、分布及成因研究[D]. 中国科学院研究生院. 2012.
QIN Zhiliang. Study on the sedimentary process, distribution and genesis of the transport sedimentary system on the northern continental slope of the South China Sea [D]. Graduate School of Chinese Academy of Sciences. 2012.
[9] 邵磊, 李学杰, 耿建华, 等. 南海北部深水底流沉积作用[J]. 中国科学: D辑: 地球科学, 2007(6):771-777
SHAOLei, LI Xuejie, GENG Jianhua, et al. Deepwater undercurrent sedimentation in the northern South China Sea [J]. Chinese Science: part D: Geoscience, 2007(6): 771-777.
[10] 王大伟, 吴时国, 董冬冬, 等. 琼东南盆地第四纪块体搬运体系的地震特征[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2009(3):69-74
WANG Dawei, WU Shiguo, DONG Dongdong, et al. Seismic characteristics of Quaternary block transport system in Qiongdongnan Basin [J]. Marine Geology and Quaternary Geology, 2009(3): 69-74.
[11] 王俊勤, 张广旭, 陈端新, 等. 琼东南盆地陵水研究区海底地质灾害类型、分布和成因机制[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2019(4):87-95
WANG Junqin, Zhang GUANGXU, CHEN Duanxin, et al. Types, distribution and genetic mechanism of submarine geological disasters in Lingshui study area of Qiongdongnan Basin [J]. Marine Geology and Quaternary Geology, 2019(4): 87-95.
[12] 王大伟, 吴时国, 秦志亮, 等. 南海陆坡大型块体搬运体系的结构与识别特征[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2009(5):65-72
WANG Dawei, WU Shiguo, QIN Zhiliang, et al. Structure and identification characteristics of large block transport system on the continental slope of the South China Sea [J]. Marine Geology and Quaternary Geology, 2009(5): 65-72.
[13] 袁圣强, 吴时国, 赵宗举, 等. 南海北部陆坡深水区沉积物输送模式探讨[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2010(4):39-48
YUAN Shengqiang, WU Shiguo, ZHAO Zongju, et al. Discussion on sediment transport model in deep water area of northern continental slope of South China Sea [J]. Marine geology and Quaternary geology, 2010(4): 39-48.
[14] 张娜, 姜涛, 张道军. 琼东南盆地海底地形地貌特征及其对深水沉积的控制[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2012(5):27-33
ZHANG Na, JIANG Tao, ZHANG Daojun. Seafloor topography and geomorphology in Qiongdongnan Basin and its control on deep-water sedimentation [J]. Marine Geology and Quaternary Geology, 2012(5): 27-33.
[15] 庞雄, 陈长民, 朱明. 深水沉积研究前缘问题[J]. 地质论评, 2007(1):36-42 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.2007.01.006
PANG Xiong, CHEN Changmin, ZHU Ming. Frontier problems in the study of deep-water sedimentation [J]. A review of geology, 2007(1): 36-42. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.2007.01.006
[16] 徐景平. 海底浊流研究百年回顾[J]. 中国海洋大学学报: 自然科学版, 2014(10):98-105
XU Jingping. A hundred-year review of the study of submarine turbidity current [J]. Journal of Ocean University of China: natural Science Edition, 2014(10): 98-105.
[17] 姜辉. 浊流沉积的动力学机制与响应[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2010, 8(8):428-435
JIANG Hui. Dynamic mechanism and response of turbidity current deposition [J]. Petroleum and natural gas geology, 2010, 8(8): 428-435.
[18] 李利阳. 浊流沉积研究的新进展: 鲍马序列、海底扇的重新审视[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质, 2015(4):106-112 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-3850.2015.04.015
LI Liyang. New progress in the study of turbidite deposits: re-examination of Baoma sequence and subsea fan [J]. Sedimentation and Tethys geology, 2015(4): 106-112. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-3850.2015.04.015
[19] 孙国桐. 深水重力流沉积研究进展[J]. 地质科技情报, 2015(3):30-36
SUN Guotong. Research progress of gravity flow deposition in deep water [J]. Geological science and technology information, 2015(3): 30-36.
[20] 梁建设, 田兵, 王琪, 等. 深水沉积理论研究现状、存在问题及发展趋势[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2017(10):1488-1496
LIANG Jian, TIAN Bing, WANG Qi, et al. Research status, existing problems and development trend of deepwater sedimentation theory [J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2017(10): 1488-1496.
[21] Laval A, Cremer M, Beghin P, et al. Density surges: Two-dimensional experiments [J]. Sedimentology, 2010, 35(1): 73-84.
[22] MarrJ G, Harff P A, Shanmugam G, et al. Experiments on subaqueous sandy gravity flows: The role of clay and water content in flow dynamics and depositional structures [J]. Geo-logical Society of America Bulletin, 2001, 113(11): 1377-1386. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(2001)113<1377:EOSSGF>2.0.CO;2
[23] Yin M, Rui Y. Laboratory study on submarine debris flow [J]. Marine Georesources & Geotechnology, 2018, 36(8): 950-958.
-



 下载:
下载:









