Holocene sedimentary environment transform and onset time of Pearl River Delta progradation
-
摘要:
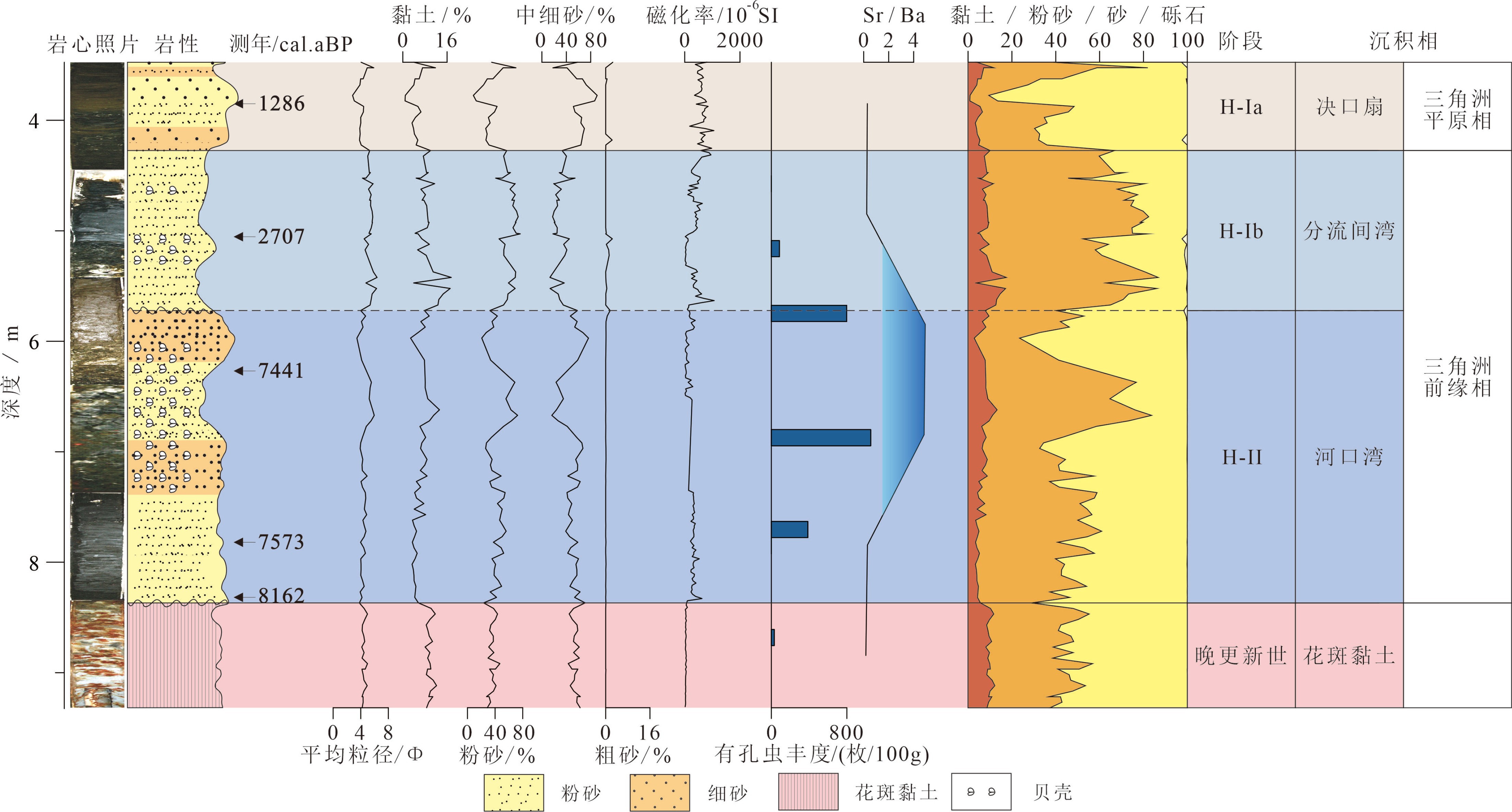
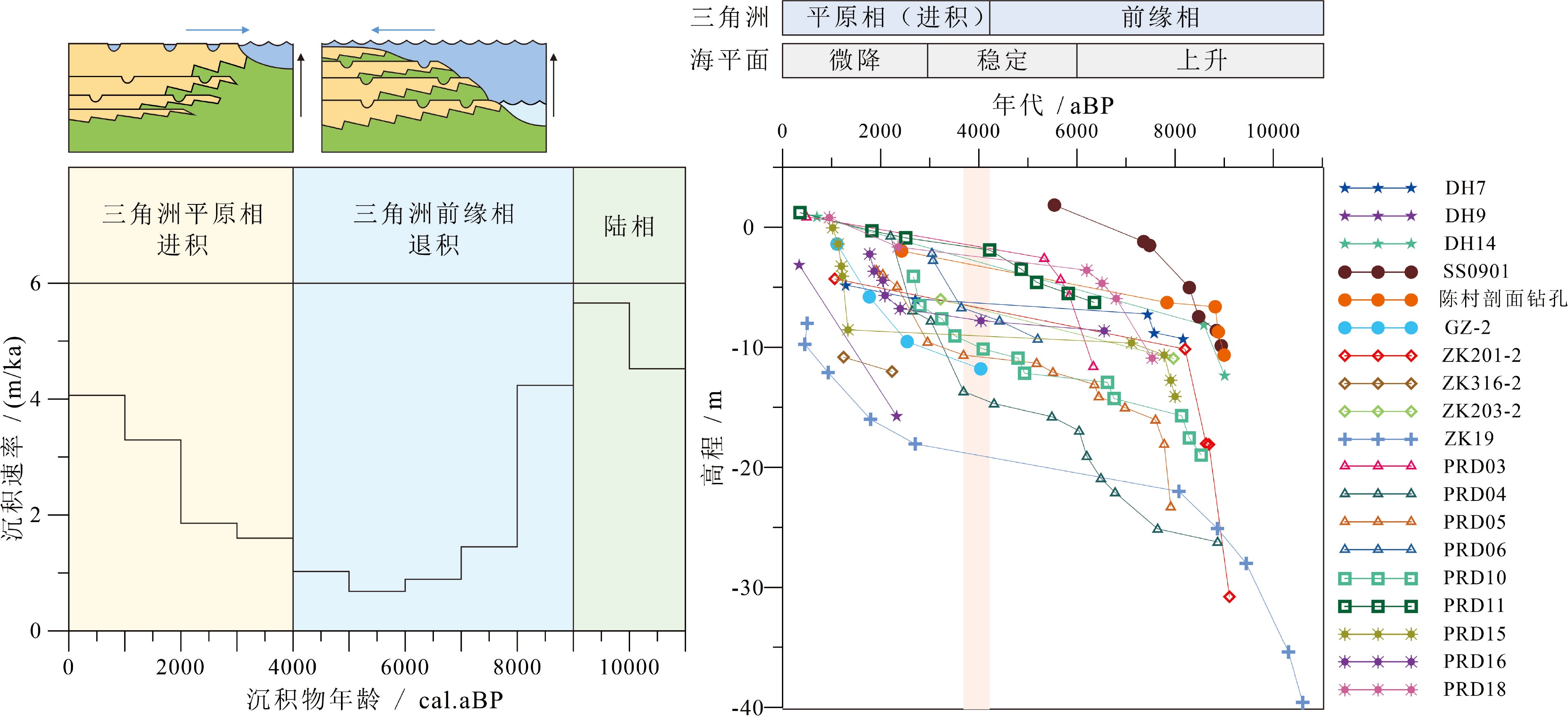
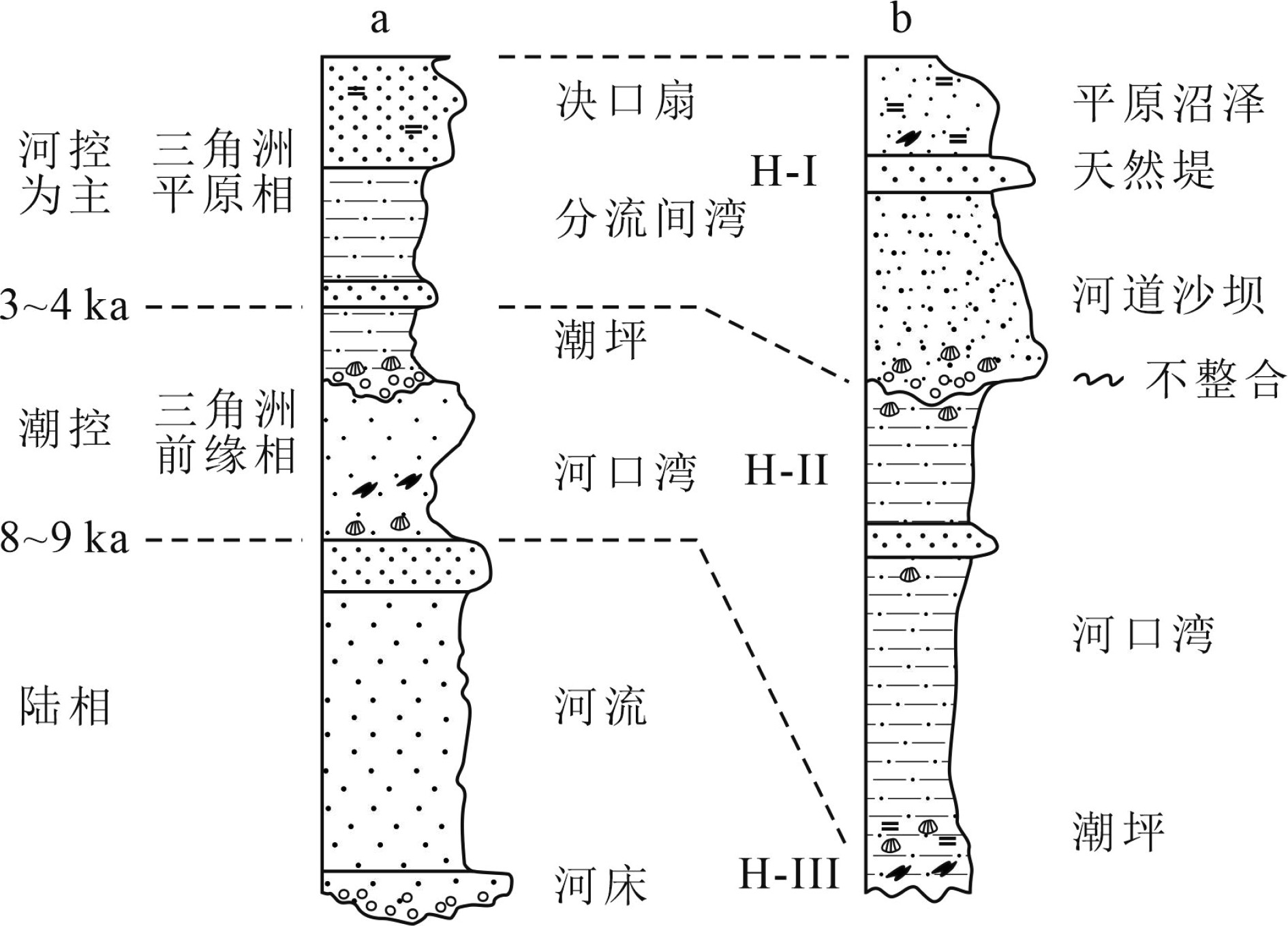
全新世是现代珠江三角洲平原形成的重要阶段,西江、北江和东江的河流物源为全新世海-陆交互相沉积提供了最主要的物质来源。然而,珠江三角洲早全新世以来的海进-海退沉积序列反映的沉积速率变化,以及退积-进积过程和起始年代因三角洲地区复杂的地形地貌而存在时空差异。此外,许多地点钻孔揭示出海-陆沉积模式转换过程中存在大量的沉积间断。本文对珠江三角洲的两个典型钻孔进行了详细的岩性、粒度等环境指标的分析,结合区域内20余个钻孔的横向对比,对全新世的海-陆沉积环境与模式转换进行了深入探讨。结果表明,全新世海相沉积底部年代为穿时性分布,在伶仃洋约为11 kaBP,海侵沿着深切河谷深入到番禺-三水一带的年代延迟至9~8 kaBP;高海面期不同地点存在三角洲前缘相的河口湾、潮坪等多种沉积环境,同时,早—中全新世三角洲前缘沉积环境受到古地形影响,在一些地点存在许多极高沉积速率的堆积体(可达~4 cm/a)。全新世沉积由海进的退积模式转变为海退的进积模式在大量钻孔中都有明显体现,通常表现为细粒组分的粉砂含量增多,磁化率快速升高,海洋有孔虫含量降低等;其沉积环境通常由滨海相转变为网状水系下的分流间湾、决口扇或河流冲积相。由潮汐作用为主的三角洲前缘沉积模式转换至平原相的发生时间主要集中在4~3 kaBP,并且许多地点的沉积动力转换的接触界面表现为明显的沉积间断,即晚全新世强烈的河流冲积和三角洲平原快速推进导致对原先较老沉积物的侵蚀作用。
Abstract:The Pearl River Delta is mainly formed in Holocene by the sediments from the Xijiang, Beijiang and Dongjiang rivers as the results of sea-land interaction. Owing to the complexity of topography in the deltaic area, there remain some key questions to be solved, such as the spatio- temporal variation in depositional processes, onset time of delta progradation, variation in sedimentation rate and transgression -regression patterns. Boreholes at many sites have revealed that there are significant sedimentary discontinuities during the transformation from marine to fluvial environment and vice versa. In this paper, detailed investigation is devoted to the lithology, grain size distribution, magnetic susceptibility, microfossils and chronology of two typical cores, upon the correlation with over 20 cores from the region. Sea-land interaction models are established for the deltaic sequences. Results show that the age of the bottom of the marine sediments is diachronous from place to place. It is about 11 kaBP in the Lingding estuary, but 9~8 kaBP in the Panyu-Sanshui area due to the time delay during sea water transgression following the incised-valley; Various sedimentary environments such as estuaries and tidal flats as the components of the delta front facies appeared in different localities during high sea-level period. Affected by the land topography, sedimentation rate in some places may be as high as~4 cm/a. In many drilling holes, the transformation from marine progradation to retrogradation is often observed, while the fine sand components increase in contents, magnetic susceptibility rapidly increases, and the amount of ocean foraminifera decreases. At the same time, facies changes occur from coastal facies to tributary bays, crevasse splay, or river alluvial facies under a reticulated water system. The delta front facies, mostly tide-dominated, transformed to the delta plain facies around 4~3 kaBP, with distinct discontinuities, indicating the intensification of late Holocene underwater erosion by the Pearl River.
-

-
图 5 珠江三角洲西江至虎门出口一线的全新世联孔剖面(引用文献见表1)
Figure 5.
表 1 本研究和引用的珠江三角洲剖面钻孔信息
Table 1. Coordinates of study and sited cores from the Pearl River Delta in this work
序号 钻孔编号 地点 孔口高程/m 北纬 东经 文献 1 SS0901 佛山市三水区 4.8 23°10′06.07″ 112°50′35.90″ [9] 2 陈村钻孔剖面 佛山市顺德区 2.4 22°58′35.00″ 113°12′28.00″ [18] 3 DH14 佛山市顺德区 5 22°57′49.47″ 113°03′39.45″ 本文 4 PRD09 广州市番禺区 1.07 22°55′20.00″ 113°25′39.00″ [19] 5 PRD15 广州市番禺区 − 22°54′49.00″ 113°31′02.00″ [20] 6 PRD16 广州市番禺区 1.73 22°52′28.00″ 113°32′45.00″ [21] 7 PRD20 佛山市顺德区 1.56 22°51′54.00″ 113°15′23.00″ [11] 8 PRD06 佛山市顺德区 2.73 22°51′18.00″ 113°08′40.00″ [20] 9 PRD10 中山市东凤镇 2.68 22°43′22.00″ 113°14′42.00″ [20] 10 GZ-2 广州市南沙区 1 22°42′20.34″ 113°30′49.86″ [22] 11 ZK201-2 中山市三角镇 4 22°41′03.12″ 113°27′25.20″ [23] 12 ZK316-2 广州市南沙区 1 22°40′52.00″ 113°35′06.00″ [10] 13 PRD18 中山市三角镇 2.02 22°40′41.00″ 113°25′55.00″ [20] 14 DH7 中山市三角镇 −1 22°40′33.49″ 113°23′44.09″ 本文 15 ZK203-2 中山市三角镇 −1 22°40′19.88″ 113°27′22.39″ [24] 16 PRD03 中山市小榄镇 − 22°39′11.02″ 113°16′17.40″ [20] 17 PRD11 中山市东升镇 − 22°37′58.00″ 113°16′58.00″ [20] 18 PRD02 中山市东升镇 2 22°37′05.40″ 113°17′21.05″ [25] 19 DH9 广州市南沙区 3 22°36′23.67″ 113°38′06.59″ 本文 20 PRD05 江门市新会区 1.12 22°31′24.00″ 113°11′02.00″ [7] 21 PRD04 江门市新会区 − 22°29′22.99″ 113°11′38.04″ [20] 22 ZK19 伶仃洋 −5 22°22′55.81″ 113°41′54.88″ [12] 表 2 DH7、DH14钻孔沉积物的测年结果
Table 2. Information of age dating of samples from the cores DH7 and DH14
取样编号 实验室编号 深度/m 测年材料 测试方法 测试年龄/aBP 校正年龄/cal. aBP(置信95%) DH7-1-50 Beta - 503602 3.85 贝壳 AMS 14C 1 810±30 1 384~1 188 DH7-2-66 5.01 有机质 AMS 14C 2 540±30 2 728~2 685 DH7-3-92 6.27 贝壳 AMS 14C 6 930±30 7 509~7 372 DH7-5-47 Beta - 503591 7.82 贝壳 AMS 14C 7 170±30 7 663~7 483 DH7-5-97 8.32 贝壳 AMS 14C 7 700±30 8 272~8 052 DH14-2-78 Beta - 503600 5.13 泥炭 AMS 14C 770±30 734~668 DH14-11-78 Beta - 503599 14.13 植物碎屑 AMS 14C 7 800±30 8 638~8 536 DH14-15 19CZ-24 19.30 粗颗粒石英 OSL-SAR 9 010±430 − -
[1] 黄镇国, 李平日, 张仲英, 等. 珠江三角洲第四纪沉积特征[J]. 地质论评, 1985, 31(2):159-164 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.1985.02.008
HUANG Zhenguo, LI Pingri, ZHANG Zhongying, et al. Characteristics of the Quaternary deposits in the Zhujiang (Pearl) delta [J]. Geological Review, 1985, 31(2): 159-164. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.1985.02.008
[2] 郑卓, 汤永杰, 郑艳伟, 等. 西江―北江及珠江三角洲汇流区全新世泥炭腐木层时空分布与环境变化[J]. 热带地理, 2016, 36(3):313-325
ZHENG Zhuo, TANG Yongjie, ZHENG Yanwei, et al. Environmental changes inferred from spatial-temporal distribution of Holocene buried peat layers in lower reaches of the Xijiang and Beijiang and the river confluence of Pearl River Delta [J]. Tropical Geography, 2016, 36(3): 313-325.
[3] 陈国能, 张珂, 贺细坤, 等. 珠江三角洲晚更新世以来的沉积—古地理[J]. 第四纪研究, 1994(1):67-74 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.1994.01.007
CHEN Guoneng, ZHANG Ke, HE Xikun, et al. Paleo-geographic evolution of the Pearl River Delta since the Late Pleistocene [J]. Quaternary Sciences, 1994(1): 67-74. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.1994.01.007
[4] 李平日, 黄镇国, 张仲英, 等. 珠江三角洲的第四纪地层[J]. 地理科学, 1984, 4(2):133-142
LI Pingri, HUANG Zhenguo, ZHANG Zhongying, et al. Quaternary stratigraphy in the Zhujiang Delta [J]. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 1984, 4(2): 133-142.
[5] 宗永强, 黄光庆, 熊海仙, 等. 珠江三角洲晚第四纪地层、海平面变化与构造运动的关系[J]. 热带地理, 2016, 36(3):326-333
ZONG Yongqiang, HUANG Guangqing, XIONG Haixian, et al. Relationship between Late Quaternary lithostratigraphy, sea-level change and tectonics in the Pearl River Delta [J]. Tropical Geography, 2016, 36(3): 326-333.
[6] Zong Y Q, Yu F L, Huang G Q, et al. The history of water salinity in the Pearl River estuary, China, during the Late Quaternary [J]. Earth Surface Processes and Landforms, 2010, 35(10): 1221-1233. doi: 10.1002/esp.2030
[7] Liu C L, Fürsich F T, Wu J, et al. Late Quaternary palaeoenvironmental changes documented by microfaunas and shell stable isotopes in the southern Pearl River Delta plain, South China [J]. Journal of Palaeogeography, 2013, 2(4): 344-361.
[8] 陈双喜, 赵信文, 黄长生, 等. 珠江三角洲晚第四纪环境演化的沉积响应[J]. 地质通报, 2016, 35(10):1734-1744 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2016.10.021
CHEN Shuangxi, ZHAO Xinwen, HUANG Changsheng, et al. Sedimentary response to the Late Quaternary envi-ronmental evolution in Pearl River Delta [J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2016, 35(10): 1734-1744. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2016.10.021
[9] 黄康有, 何嘉卉, 宗永强, 等. 珠江三角洲三水盆地早全新世以来孢粉分析与古环境重建[J]. 热带地理, 2016, 36(3):364-373
HUANG Kangyou, HE Jiahui, ZONG Yongqiang, et al. Holocene paleoenvironment reconstruction based on pollen data in the Sanshui Basin, northern Pearl River Delta [J]. Tropical Geography, 2016, 36(3): 364-373.
[10] 余少华, 陈芳, 谢叶彩, 等. 珠江口万顷沙晚第四纪沉积及古环境重建[J]. 热带地理, 2016, 36(3):374-387
YU Shaohua, CHEN Fang, XIE Yecai, et al. Paleoenvironment reconstruction and sedimentary record in the Wanqingsha area of the Pearl River Estuary [J]. Tropical Geography, 2016, 36(3): 374-387.
[11] 殷鉴, 刘春莲, 吴洁, 等. 珠江三角洲中部晚更新世以来的有孔虫记录与古环境演化[J]. 古地理学报, 2016, 18(4):677-690 doi: 10.7605/gdlxb.2016.04.050
YIN Jian, LIU Chunlian, WU Jie, et al. Foraminiferal records and palaeoenvironmental changes since the Late Pleistocene in central Pearl River Delta [J]. Journal of Palaeogeography, 2016, 18(4): 677-690. doi: 10.7605/gdlxb.2016.04.050
[12] 瓦西拉里, 王建华, 陈慧娴, 等. 伶仃洋ZK19孔晚第四纪沉积地球化学特征及其古环境意义[J]. 热带地理, 2016, 36(3):343-354
WAXI Lali, WANG Jianhua, CHEN Huixian, et al. Major and trace elements geochemistry and paleoenvironmental implications of borehole ZK19 in the Lingdingyang Bay of the Pearl River Estuary [J]. Tropical Geography, 2016, 36(3): 343-354.
[13] 蓝先洪. 珠江三角洲晚第四纪沉积特征[J]. 沉积学报, 1996, 14(2):155-162
LAN Xianhong. Sedimentary characteristics of Late Quaternary in the Zhujiang River Delta [J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 1996, 14(2): 155-162.
[14] 戴仕宝, 杨世伦, 蔡爱民. 51年来珠江流域输沙量的变化[J]. 地理学报, 2007, 62(5):545-554 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0375-5444.2007.05.011
DAI Shibao, YANG Shilun, CAI Aimin. Variation of sediment discharge of the Pearl River Basin from 1955 to 2005 [J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2007, 62(5): 545-554. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0375-5444.2007.05.011
[15] 韦惺, 吴超羽. 珠江三角洲沉积体与河网干流河道的形成发育[J]. 海洋学报, 2018, 40(7):66-78
WEI Xing, WU Chaoyu. The formation and development of the deposition bodies and main channels in the Zhujiang River Delta [J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2018, 40(7): 66-78.
[16] 黄镇国, 李平日, 张仲英, 等. 珠江三角洲形成发育演变[M]. 广州: 科学普及出版社广州分社, 1982.
HUANG Zhenguo, LI Pingri, ZHANG Zhongying, et al. Evolution of the Pearl River Delta[M]. Guanzhou: Science Popularization Press Guangzhou Branch, 1982.
[17] 赵焕庭. 珠江河口演变[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 1990.
ZHAO Huanting. Evolution of the Pearl River Estuary[M]. Beijing: China Ocean Press, 1990.
[18] 赵信文, 陈双喜, 黄长生, 等. 珠江三角洲陈村钻孔剖面沉积特征及有机碳同位素古环境意义[J]. 地质通报, 2014, 33(10):1635-1641 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2014.10.023
ZHAO Xinwen, CHEN Shuangxi, HUANG Changsheng, et al. The sedimentary characteristics of core section from Chencun Village in Pearl River Delta, and their organic carbon isotopic palaeoenvironmental implications [J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2014, 33(10): 1635-1641. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2014.10.023
[19] 刘春莲, 杨婷婷, 吴洁, 等. 珠江三角洲晚第四纪风化层稀土元素地球化学特征[J]. 古地理学报, 2012, 14(1):125-132 doi: 10.7605/gdlxb.2012.01.011
LIU Chunlian, YANG Tingting, WU Jie, et al. REE geochemical characteristics of mottled clays of the Late Quaternary in the Pearl River Delta [J]. Journal of Palaeogeography, 2012, 14(1): 125-132. doi: 10.7605/gdlxb.2012.01.011
[20] 韦惺. 全新世以来珠江三角洲的沉积演变模式研究[D]. 中山大学博士学位论文, 2010: 1-210.
WEI Xing. Evolution pattern of the Zhujiang River Delta since Holocene[D]. Doctor Dissertation of Sun Yat-sen University, 2010: 1-210.
[21] 庄畅, 刘春莲, 吴洁, 等. 珠江三角洲PRD16孔微体生物记录与晚更新世以来的古环境重建[J]. 中山大学学报: 自然科学版, 2013, 52(3):128-132
ZHUANG Chang, LIU Chunlian, WU Jie, et al. Microfossil records of borehole PRD16 and palaeoenvironment since the Late Pleistocene in the Pearl River Delta [J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Sunyatseni, 2013, 52(3): 128-132.
[22] 王建华, 曹玲珑, 王晓静, 等. 珠江三角洲万顷沙地区晚第四纪沉积相与古环境演变[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2009, 29(6):35-41
WANG Jianhua, CAO Linglong, WANG Xiaojing, et al. Evolution of sedimentary facies and paleoenvironment during the Late Quaternary in Wanqingsha area of the Pearl River Delta [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2009, 29(6): 35-41.
[23] 陈炽新, 吴聪, 谢叶彩, 等. 珠江三角洲中山地区ZK201-2钻孔硅藻组合及古环境意义[J]. 微体古生物学报, 2014, 31(4):335-346
CHEN Chixin, WU Cong, XIE Yecai, et al. Diatom assemblages from borehole ZK201-2 in Zhongshan area of the Zhujiang River Delta Guangdong, S. China and their paleoenvironment significance [J]. Acta Micropalaeontologica Sinica, 2014, 31(4): 335-346.
[24] 谢叶彩, 王强, 龙桂, 等. 珠江口小榄镇-万顷沙地区晚更新世以来的海侵层序[J]. 古地理学报, 2014, 16(6):835-852 doi: 10.7605/gdlxb.2014.06.067
XIE Yecai, WANG Qiang, LONG Gui, et al. Transgressive sequence since the Late Pleistocene in Xiaolan Town-Wanqingsha area, Zhujiang River estuary [J]. Journal of Palaeogeography, 2014, 16(6): 835-852. doi: 10.7605/gdlxb.2014.06.067
[25] 韦惺, 吴超羽. 全新世以来珠江三角洲的地层层序和演变过程[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2011, 54(10):1523-1541 doi: 10.1007/s11430-011-4238-6
WEI Xing, WU Chaoyu. Holocene delta evolution and sequence stratigraphy of the Pearl River Delta in South China [J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 2011, 54(10): 1523-1541. doi: 10.1007/s11430-011-4238-6
[26] 黄镇国, 李平日, 张仲英, 等. 珠江三角洲第四系微量元素的指相意义[J]. 热带地理, 1983(1):42-49, 53
HUANG Zhenguo, LI Pingri, ZHANG Zhongying, et al. The referential phase significance of quaternary trace elements in the Pearl River Delta [J]. Tropical Geography, 1983(1): 42-49, 53.
[27] 蓝先洪, 马道修, 徐明广, 等. 珠江三角洲若干地球化学标志及指相意义[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 1987, 7(1):41-51
LAN Xianhong, MA Daoxiu, XU Mingguang, et al. Some geochemical indicators of the Pearl River Delta and their facies significance [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 1987, 7(1): 41-51.
[28] Kissel C, Laj C, Mazaud A, et al. Magnetic anisotropy and environmental changes in two sedimentary cores from the Norwegian Sea and the North Atlantic [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1998, 164(3-4): 617-626. doi: 10.1016/S0040-1951(98)00223-6
[29] 张振克, 吴瑞金, 王苏民. 岱海湖泊沉积物频率磁化率对历史时期环境变化的反映[J]. 地理研究, 1998, 17(3):297-302 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0585.1998.03.011
ZHANG Zhenke, WU Ruijin, WANG Sumin. Implication of magnetic frequency dependent susceptibility on environmental variation from lacustrine sediment in Daihai Lake [J]. Geographical Research, 1998, 17(3): 297-302. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0585.1998.03.011
[30] 杨晓强, 李华梅. 泥河湾盆地沉积物磁化率及粒度参数对沉积环境的响应[J]. 沉积学报, 1999, 17(S1):763-768
YANG Xiaoqiang, LI Huamei. The sediment susceptibility and grain-size profile respond to change of depositional environment in Nihewan Basin [J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 1999, 17(S1): 763-768.
[31] 吴海斌, 陈发虎, 王建民, 等. 干旱区湖泊沉积物磁组构参数量值特征与环境变化研究[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 1999, 19(2):95-102
WU Haibin, CHEN Fahu, WANG Jianmin, et al. Study on magnetic fabric parameters of lake sediments in arid area and environmental changes [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 1999, 19(2): 95-102.
[32] 杨晓强, 李华梅. 陆相断陷湖盆沉积物磁组构特征及环境意义——以泥河湾盆地为例[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2000, 20(3):43-52
YANG Xiaoqiang, LI Huamei. Magnetic anisotropy and its environmental significance in limnal faulted basin—Taking the Nihewan Basin as an example [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2000, 20(3): 43-52.
[33] 王秋良, 袁胜元, 李长安. 江汉平原江陵剖面有机碳含量、碳同位素和磁化率的古气候意义[J]. 地质科技情报, 2006, 25(4):59-62 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7849.2006.04.011
WANG Qiuliang, YUAN Shengyuan, LI Chang’an. Paleoclimate significance of the total organic carbon and organic carbon isotope and magnetic susceptibility of the Jiangling Section, Jianghan Plain, Hubei Province [J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2006, 25(4): 59-62. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7849.2006.04.011
[34] 张玉芬, 李长安, 王秋良, 等. 江汉平原沉积物磁学特征及对长江三峡贯通的指示[J]. 科学通报, 2008, 53(4):584-590 doi: 10.1007/s11434-008-0111-1
ZHANG Yufen, LI Chang’an, WANG Qiuliang, et al. Magnetism parameters characteristics of drilling deposits in Jianghan Plain and indication for forming of the Yangtze River Three Gorges [J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2008, 53(4): 584-590. doi: 10.1007/s11434-008-0111-1
[35] 汪品先, 闵秋宝, 卞云华. 南黄海西北部底质中有孔虫、介形虫分布规律及其地质意义[M]//汪品先. 海洋微体古生物论文集. 北京: 海洋出版社, 1980.
WANG Pinxian, MIN Qiubao, BIAN Yunhua. The distribution and geological significance of foraminifera and ostracoda in the sediment of the northwestern South Yellow Sea[M]//WANG Pinxian. Marine Microbody Paleontology. Beijing: China Ocean Press, 1980.
[36] Buck K F, C Olson H C, Austin J A Jr. Paleoenvironmental evidence for latest Pleistocene sea-level fluctuations on the New Jersey outer continental shelf: combining high-resolution sequence stratigraphy and foraminiferal analysis [J]. Marine Geology, 1999, 154(1-4): 287-304. doi: 10.1016/S0025-3227(98)00119-4
[37] Murray J W. Ecology and Applications of Benthic Foraminifera[M]. New York: Cambridge University Press, 2006.
[38] 董艺辛, 刘春莲, 阴家润, 等. 珠江三角洲晚第四纪环境演变的微体生物记录[J]. 古脊椎动物学报, 2007, 45(2):161-172 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3118.2007.02.008
DONG Yixin, LIU Chunlian, YIN Jiarun, et al. Late Quaternary microfaunas and paleoenvironmental changes recorded in core sediments of the Pearl River Delta, South China [J]. Vertebrata Palasiatica, 2007, 45(2): 161-172. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3118.2007.02.008
[39] 周洋, 谢叶彩, 陈芳, 等. 珠江三角洲ZK201-2孔晚更新世以来微体生物群与古环境[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2015, 35(4):113-123
ZHOU Yang, XIE Yecai, CHEN Fang, et al. Microfaunas in hole ZK201-2 at Zhujiang River Delta since late pleistocene and their implications for paleoenvironments [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2015, 35(4): 113-123.
[40] Zong Y Q, Huang K Y, Yu F L, et al. The role of sea-level rise, monsoonal discharge and the palaeo-landscape in the early Holocene evolution of the Pearl River delta, southern China [J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2012, 54: 77-88. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2012.01.002
[41] 龙云作, 霍春兰. 珠江三角洲晚第四纪沉积特性[J]. 海洋科学, 1990(4):7-14
LONG Yunzuo, HUO Chunlan. The sedimentation characteristics of Zhujiang River Delta in Late Quaternary [J]. Marine Sciences, 1990(4): 7-14.
[42] 黄镇国, 宗永强. 应用粒度参数区分沉积相——以珠江三角洲为例[J]. 热带地理, 1982, 2(2):37-42
HUANG Zhenguo, ZONG Yongqiang. The application of particle size parameters to distinguish sedimentary facies - A case study of the Pearl River Delta [J]. Tropical Geography, 1982, 2(2): 37-42.
[43] 贾良文, 何志刚, 莫文渊, 等. 全新世以来珠江三角洲快速沉积体的初步研究[J]. 海洋学报, 2010, 32(2):87-95
JIA Liangwen, HE Zhigang, MO Wenyuan, et al. A preliminary study on rapid deposition bodies in the Zhujiang Delta since Holocene [J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2010, 32(2): 87-95.
[44] 王晓静, 王建华, 曹玲珑, 等. 广州地区晚第四纪孢粉气候研究[J]. 中山大学学报: 自然科学版, 2010, 49(3):113-121
WANG Xiaojing, WANG Jianhua, CAO Linglong, et al. Late Quaternary pollen records and climate significance in Guangzhou [J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Sunyatseni, 2010, 49(3): 113-121.
[45] 张生, 朱诚, 张强, 等. 太湖地区新石器时代以来文化断层的成因探讨[J]. 南京大学学报: 自然科学版, 2002, 38(1):64-73
ZHANG Sheng, ZHU Cheng, ZHANG Qiang, et al. Cultural interruptions since the Neolithic Age recorded in the Diagnostic sediment in the Taihu Lake region, Esastern China [J]. Journal of Nanjing University: Natural Sciences, 2002, 38(1): 64-73.
[46] 张强, 姜彤, 施雅风, 等. 长江三角洲地区1万年以来洪水与气候变化的关系[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2003, 23(3):11-15
ZHANG Qiang, JIANG Tong, SHI Yafeng, et al. Relationship between climatic changes and the flooding occurrence since the Holocene in the Yangtze River Delta region [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2003, 23(3): 11-15.
[47] 张强, 朱诚, 姜逢清, 等. 南京江北地区晚更新世以来环境演变研究[J]. 地理科学, 2001, 21(6):498-504 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0690.2001.06.004
ZHANG Qiang, ZHU Cheng, JIANG Fengqing, et al. Environmental changes since Late-Pleistocene in north-bank of Yangtze River, Nanjing [J]. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 2001, 21(6): 498-504. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0690.2001.06.004
-




 下载:
下载: