Sand waves in the shelf area off Xiamen Bay
-
摘要:
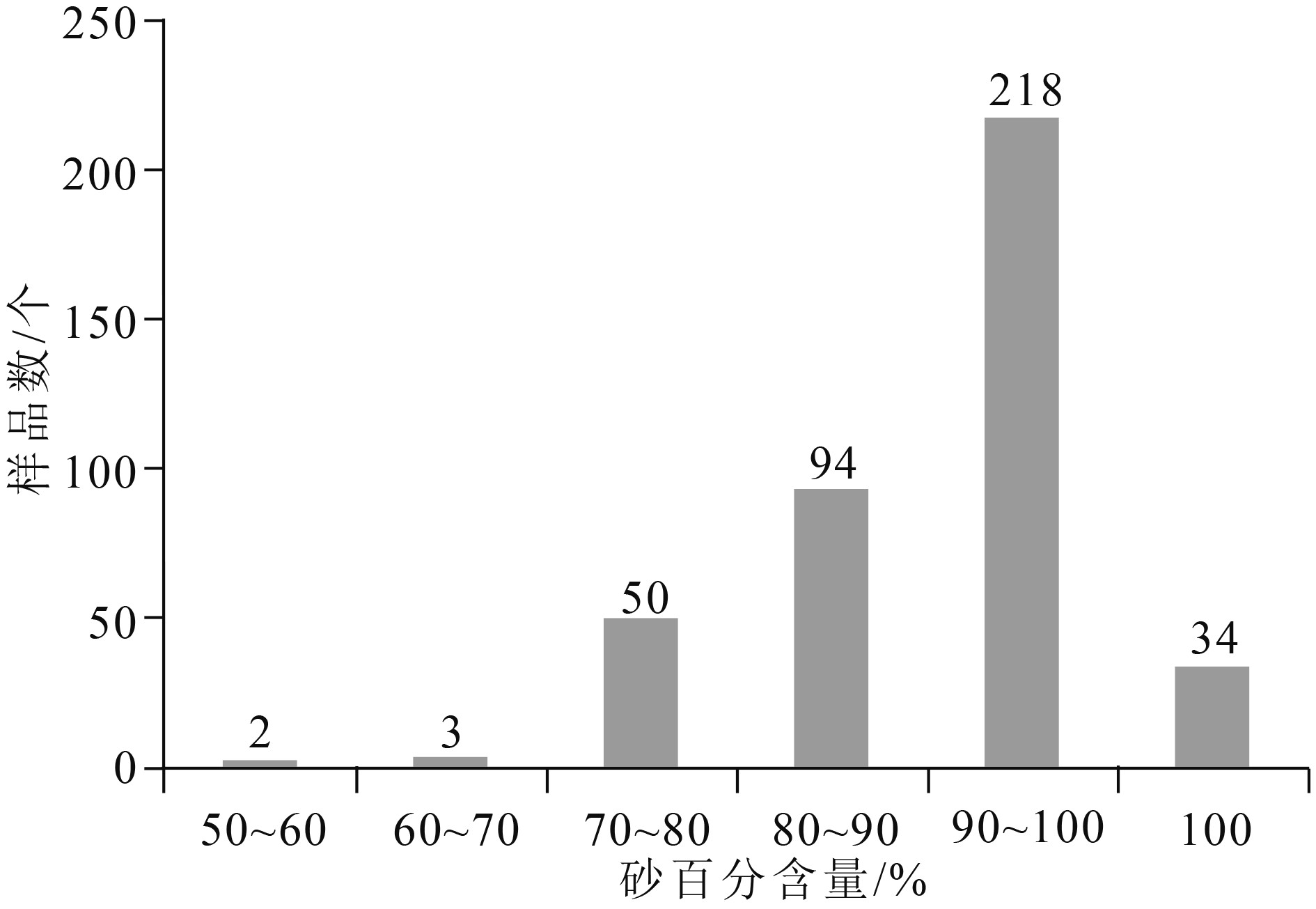
利用2014–2017年在台湾海峡西部采集的多波束、单道地震剖面、沉积物粒度样品及海流监测资料,在厦门湾近岸陆架区识别出一系列海底沙波,并对沙波的形态特征、分布规律和沉积物组成特征进行分析,探讨水动力条件及其对沙波发育的影响。结果表明沙波发育区水深一般为10~60 m,地形较平缓开阔,坡度一般为0°~1°;平面上沙波区呈一系列NW-SE向条带状坡地,波脊呈线性或新月形,波脊轴线为SW-NE方向,沙波波长为120~800 m,波高2~12 m,沙波指数较大(>30)。地震剖面显示,波形形态主要分为三类:近对称性沙波、非对称性沙波及叠合沙波。近对称性沙纹的波高较大,沙波指数小;非对称性沙波的波长较长,沙波指数大;稳定沙波经后期水流“改造、激活”形成叠合沙波。砂含量较高,沉积物类型以砂、粉砂质砂及砂质粉砂为主,多为细砂—中砂。厦门湾口外的近岸陆架区水动力较强,流系复杂,总体受浙闽沿岸流、南海表层流和黑潮分支的影响。本区为不正规半日潮,流速为0.3~0.7 m/s,落潮流以S向为主,涨潮流向以NNE向为主,潮流作用对沙波的发育和改造起重要影响。
Abstract:Based on the multi-beam and single-channel seismic data, sediment grain size distribution data and current data collected from the period of 2014–2017, seafloor sand waves are discovered on the shelf off Xiamen Bay. This paper deals with the morphological features, distribution patterns and sediment composition of the sand waves. Hydrodynamic conditions and their bearing on sand waves are discussed. The results show that the sand waves are mainly developed in the offshore area of 10~60 m in water depth with a slope of 0~1 degree, where the sea bottom is relatively gentle and open. Crests of sand waves show a parallel pattern extending in a NW-SE direction. The axis of the sand wave ridge is SW-NE. Most of the sand waves are 2~12 m high and 0.12~0.8 km long with large sand wave index (>30). In the seismic profiles, there are three types of waves i.e. symmetric sand waves, asymmetric sand waves and superimposed sand waves. The symmetrical sand waves are characterized by larger wave height and smaller wave index, while the asymmetrical sand wave by longer wave length and larger sand wave index. The stable sand wave is a kind of superimposed sand wave reformed and reactivated by the flow in later stage. The offshore shelf of Xiamen Bay and its adjacent waters are rich in sand. The bottom sediments are dominated by silt and fine-medium sand, controlled by hydrological dynamics of the area. Affected by the Zhejiang-Fujian coastal current, the surface current of the South China Sea and the branch of Kuroshio current, the current system of the study area is strong and complicated. With regard to the tidal system, the study area is dominated by irregular semi-diurnal tides with a velocity of 0.3~0.7m/s. Tidal currents play an important role in the development and transformation of sand waves.This paper clarified the distribution pattern, and sediment characteristics of the seafloor sand wave, and provided useful foundation for submarine engineering construction in the study area.
-
Key words:
- submarine sand waves /
- distribution /
- morphological characteristics /
- classification /
- Xiamen Bay
-

-
表 1 研究区沙波形态参数特征统计
Table 1. Statistical table of sand wave shape parameters in the study area
测线名称 测线方向 水深/m 沙波类型 波形尺度/m 沙波指数(L/H) 沉积物类型 潮流运动方向 备注 波长(L) 波高(H) AB W-E 40 近对称沙波 120 3.6 33.3 粉砂质砂 EW向 最小波长 AB W-E 42 近对称沙波 390 11.4 34.2 粉砂质砂 EW向 最大波长 BC SW-NE 56 非对称沙波 300 3 100 砂 NE向 最小波长 BC SW-NE 48 非对称沙波 465 4.5 103.3 砂 NE向 最大波长 -
[1] 王嵘, 张永战, 夏非, 等. 南黄海辐射沙脊群海域底质粒度特征及其输运趋势[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2012, 32(6):1-8
WANG Rong, ZHANG Yongzhan, XIA Fei, et al. Grain size distribution and transportation trends of bottom sediments in the sand ridge field of the South Yellow Sea, China [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2012, 32(6): 1-8.
[2] 赵月霞, 刘保华, 李西双, 等. 胶州湾湾口海底沙波地形地貌特征及其活动性研究[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2006, 37(5):464-471 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.2006.05.013
ZHAO Yuexia, LIU Baohua, LI Xishuang, et al. Topography feature and migration of submarine sand waves in Jiaozhoy Bay mouth [J]. Oceanologia Et Limnologia Sinica, 2006, 37(5): 464-471. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.2006.05.013
[3] 王昆山, 姜晓黎, 叶青, 等. 南黄海潮流沙脊区表层沉积物重矿物分布及来源[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2013, 33(5):1-11
WANG Kunshan, JIANG Xiaoli, YE Qing, et al. Distribution and source of heavy minerals in the surface sediment of the tidal sand ridges area in South Yellow Sea [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2013, 33(5): 1-11.
[4] 庄丽华, 阎军, 徐涛, 等. 扬子浅滩东南海域海底潮流沙脊、沙波特征[J]. 海洋科学, 2017, 41(1):11-17 doi: 10.11759/hykx20160614001
ZHUANG Lihua, YAN Jun, XU Tao, et al. Bedform of tidal sand ridges on the southeast Yangtze Shoal on continental shelf in the East Sea [J]. Marine Sciences, 2017, 41(1): 11-17. doi: 10.11759/hykx20160614001
[5] 鲍晶晶. 台湾浅滩沙波动力特征研究[D]. 中国地质大学博士学位论文, 2014.
BAO Jingijng. A dissertation submitted to China University of Geosciences for the Doctor Degree of Marine geology[D]. Doctor Dissertation of China University of Geosciences, 2014.
[6] 杜晓琴, 李炎, 高抒. 台湾浅滩大型沙波、潮流结构和推移质输运特征[J]. 海洋学报, 2008, 30(5):124-136
DU Xiaoqin, LI Yan, GAO Shu. Characteristics of the large-scale sandwaves, tidal flow structure and bedload transport over the Taiwan Bank in southern China [J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2008, 30(5): 124-136.
[7] 余威, 吴自银, 周洁琼, 等. 台湾浅滩海底沙波精细特征、分类与分布规律[J]. 海洋学报, 2015, 37(10):11-25
YU Wei, WU Ziyin, ZHOU Jieqiong, et al. Meticulous characteristics, classification and distribution of seabed sand wave on the Taiwan bank [J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2015, 37(10): 11-25.
[8] 邱燕, 彭学超, 王英民, 等. 南海北部海域第四系侵蚀过程与沉积响应[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2017, 143-146.
QIU Yan, PENG Xuechao, WANG Yingmin, et al. Erosive Process and Sedimentary Characteristics of the Quaternary Sediments in the Northern South China Sea[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2017, 143-146.
[9] 彭学超, 吴庐山, 崔兆国, 等. 南海东沙群岛以北海底沙波稳定性分析[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2006, 25(3):21-27 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5470.2006.03.004
PENG Xuechao, WU Lushan, CUI Zhaoguo, et al. A stability analysis of seabed sand waves in waters north of Dongsha Islands of South China Sea [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2006, 25(3): 21-27. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5470.2006.03.004
[10] 栾锡武, 彭学超, 王英民, 等. 南海北部陆架海底沙波基本特征及属性[J]. 地质学报, 2010, 84(2):233-245
LUAN Xiwu, PENG Xuechao, WANG Yingmin, et al. Characteristics of sand waves on the northern South China Sea shelf and its formation [J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2010, 84(2): 233-245.
[11] 张晶晶, 庄振业, 曹立华. 南海北部陆架陆坡沙波底形[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2015, 31(7):11-19
ZHANG Jingjing, ZHUANG Zhenye, CAO Lihua. Bed forms on the northern shelf and slope of the South China Sea [J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2015, 31(7): 11-19.
[12] 吴建政, 胡日军, 朱龙海, 等. 南海北部海底沙波研究[J]. 中国海洋大学学报, 2006, 36(6):1019-1023
WU Jianzheng, HU Rijun, ZHU Longhai, et al. Study on the seafloor sandwaves in the northern South China Sea [J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 2006, 36(6): 1019-1023.
[13] 曹立华, 徐继尚, 李广雪, 等. 海南岛西部岸外沙波的高分辨率形态特征[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2006, 26(4):15-22
CAO Lihua, XU Jishang, LI Guangxue, et al. High-resolution morphological characteristics of sand waves off the west Hainan Island [J]. Marine Geology and Quaternary Geology, 2006, 26(4): 15-22.
[14] 李泽文, 阎军, 栾振东, 等. 海南岛西南海底沙波形态和活动性的空间差异分析[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2010, 26(7):24-32
LI Zewen, YAN Jun, LAN Zhendong, et al. Analysis on spatial differences of morphology and mobility of the submarine sand waves in southwest Hainan Island [J]. Marine Geology Letters, 2010, 26(7): 24-32.
[15] 李近元. 海南东方岸外海底沙波运移及浅地层结构分析研究[D]. 中国科学院大学硕士学位论文, 2010.
LI Jinyuan. 2010. The analysis of sand wares and shallow seismic profile in the sea area to the southwest of Hainan Island[D]. Master Dissertation of University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2010.
[16] 郭立, 马小川, 阎军. 北部湾东南海域海底沙波发育分布特征及控制因素[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2017, 37(1):67-76
GUO Li, MA Xiaochuan, YAN Jun. Distribution pattern and control factors of sand waves in southeast Beibu gulf [J]. Marine Geology and Quaternary Geology, 2017, 37(1): 67-76.
[17] 蔺爱军, 胡毅, 林桂兰, 等. 海底沙波研究进展与展望[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2017, 32(3):1366-1377 doi: 10.6038/pg20170356
LIN Aijun, HU Yi, LIN Guilan, et al. Progress and perspective of submarine sand waves researches [J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2017, 32(3): 1366-1377. doi: 10.6038/pg20170356
[18] 单红仙, 沈泽中, 刘晓磊, 等. 海底沙波分类与演化研究进展[J]. 中国海洋大学学报, 2017, 47(10):73-82
SHAN Hongxian, SHEN Zezhong, LIU Xiaolei, et al. Classification and evolution of submarine sandwave: a review [J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 2017, 47(10): 73-82.
[19] 杨胜雄, 邱燕, 朱本铎, 等. 南海地质地球物理图系(1: 200万)[M]. 天津: 中国航海图书出版社, 2015.
YANG Shengxiong, QIU Yan, ZHU Benduo, et al. Geological and Geophysical Maps of the South China Sea (1: 2000000)[M]. Tianjin: China Navigation Book Publishing House, 2015.
[20] 胡建宇. 台湾海峡及其邻近海区海洋动力环境特征的研究[D]. 厦门大学博士学位论文, 2002.
HU Jianyu. A study on the characteristics of marine dynamic environment in the Taiwan Strait and its adjacent sea areas[D]. Doctor Dissertation of Xiamen University, 2002.
[21] 綦梦楠. 厦门湾及邻近海域潮汐潮流数值模拟与预报研究[D]. 中国海洋大学硕士学位论文, 2014.
QI Mengnan. A study on numerical simulation and forecast of tides and tidal currents in Xiamen Bay and its adjacent waters[D]. Master Dissertation of Ocean University of China, 2014.
[22] 王文介. 南海北部的潮波传播与海底沙脊和沙波发育[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2000, 19(1):1-7 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5470.2000.01.001
WANG Wenjie. Propagation of tidal waves and development of sea-bottom sand ridges and sand ripples in northern South China Sea [J]. Tropic Oceanology, 2000, 19(1): 1-7. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5470.2000.01.001
[23] 张志欣. 中国近海沿岸流及毗邻流系的观测与分析研究[D]. 中国海洋大学博士学位论文, 2014.
ZHAO Zhixin. Observation and analysis of the coastal current and its adjacent current system in the China offshore waters[D]. Doctor Dissertation of Ocean University of China, 2014.
[24] 关明. 台湾海峡沙波数值模拟[D]. 大连理工大学硕士学位论文, 2017.
GUAN Ming. Sand wave numerical simulation in Taiwan Strait[D]. Master Dissertation of Dalian University of Technology, 2017.
[25] 刘振夏, 夏东兴. 中国近海潮流沉积沙体[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 2004.
LIU Zhenxia, XIA Dongxing. Tidal Sands in the China Seas[M]. Beijing: China Ocean Press, 2004.
-




 下载:
下载: