Seasonal distribution of suspended sediments in the water northeast to Shandong Peninsula and its controlling factors
-
摘要:
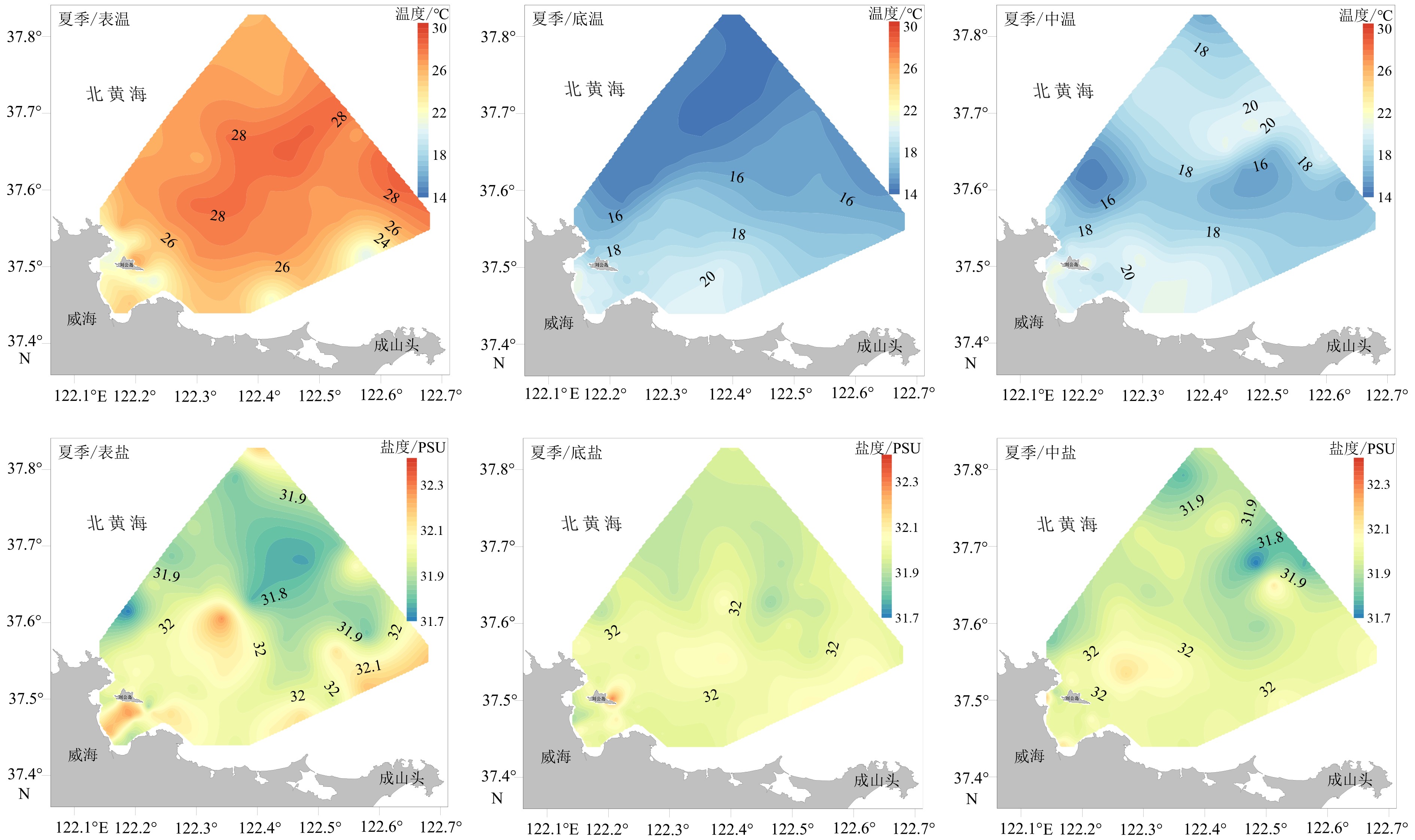
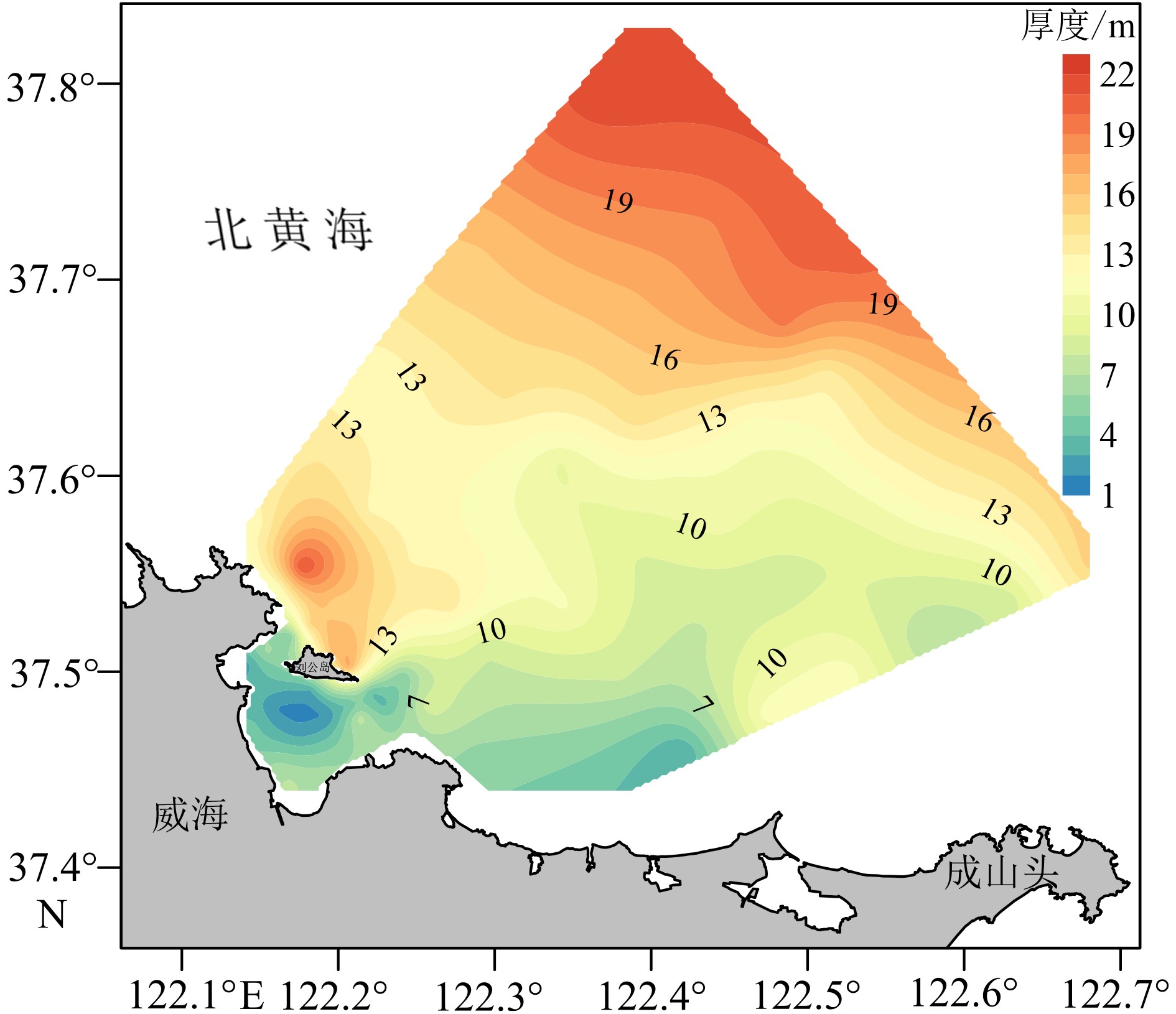
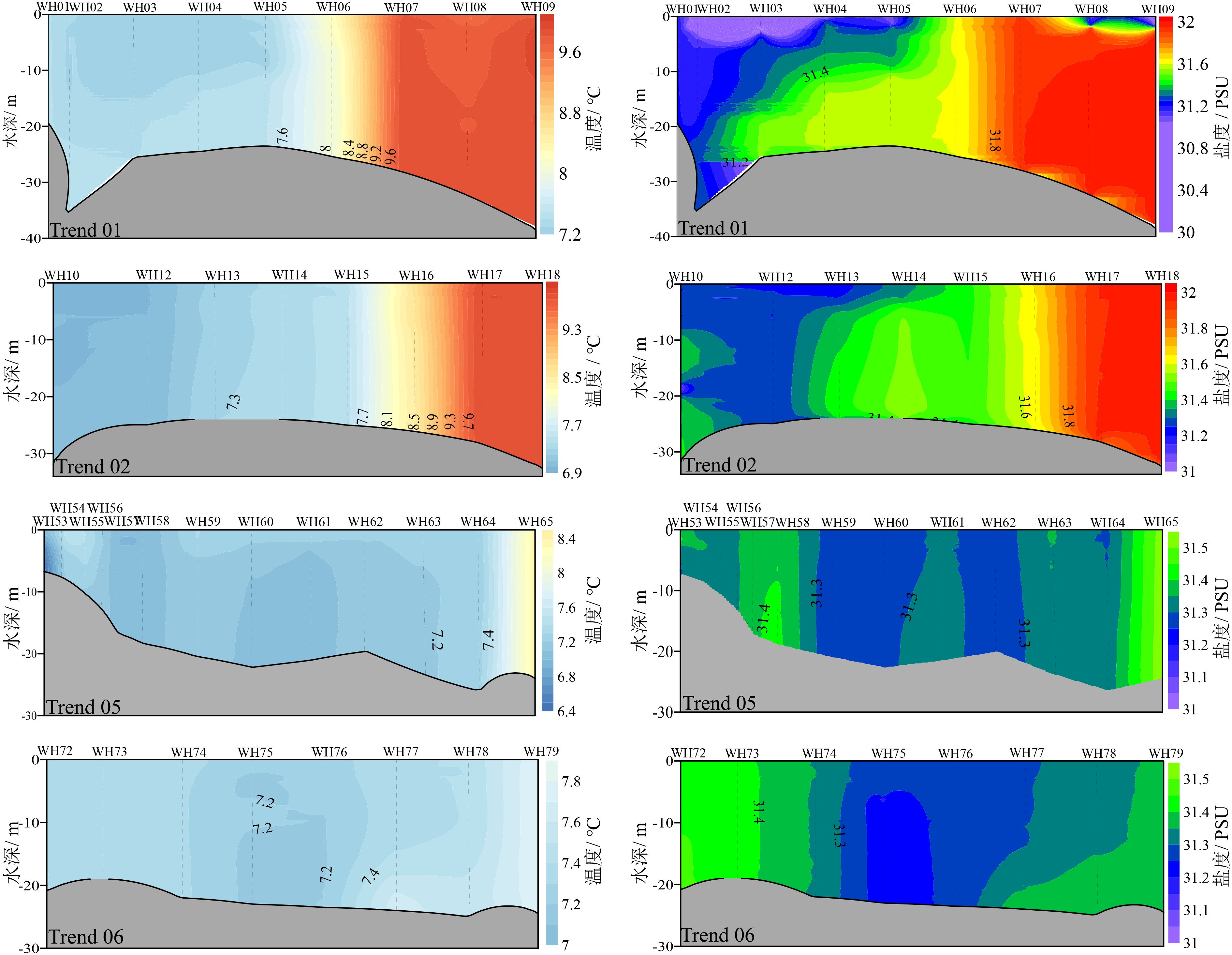
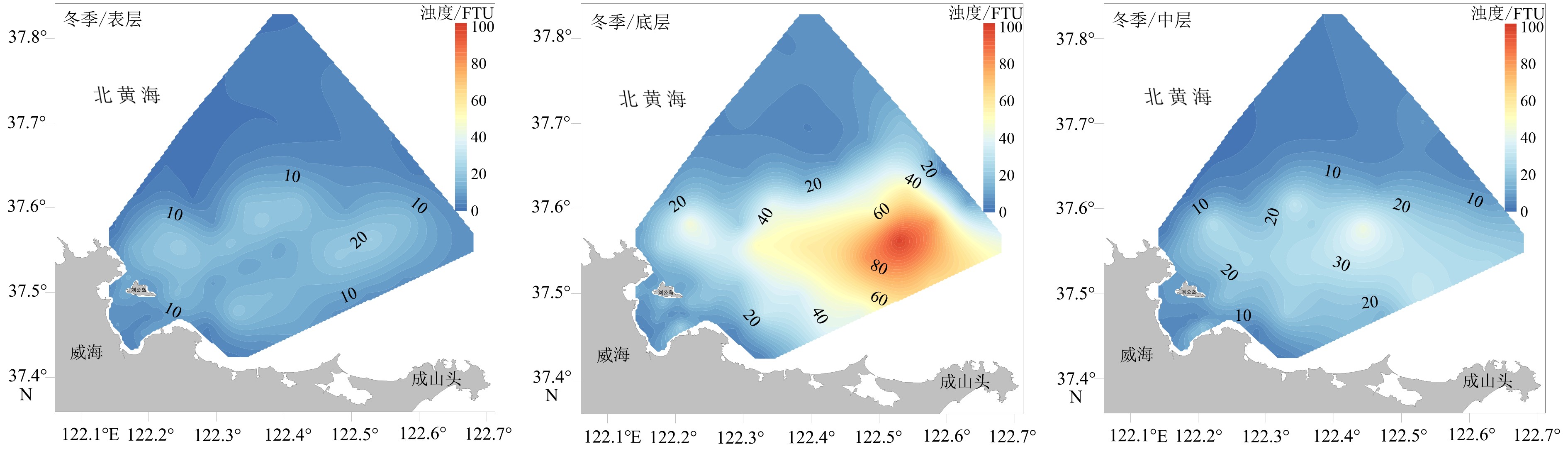
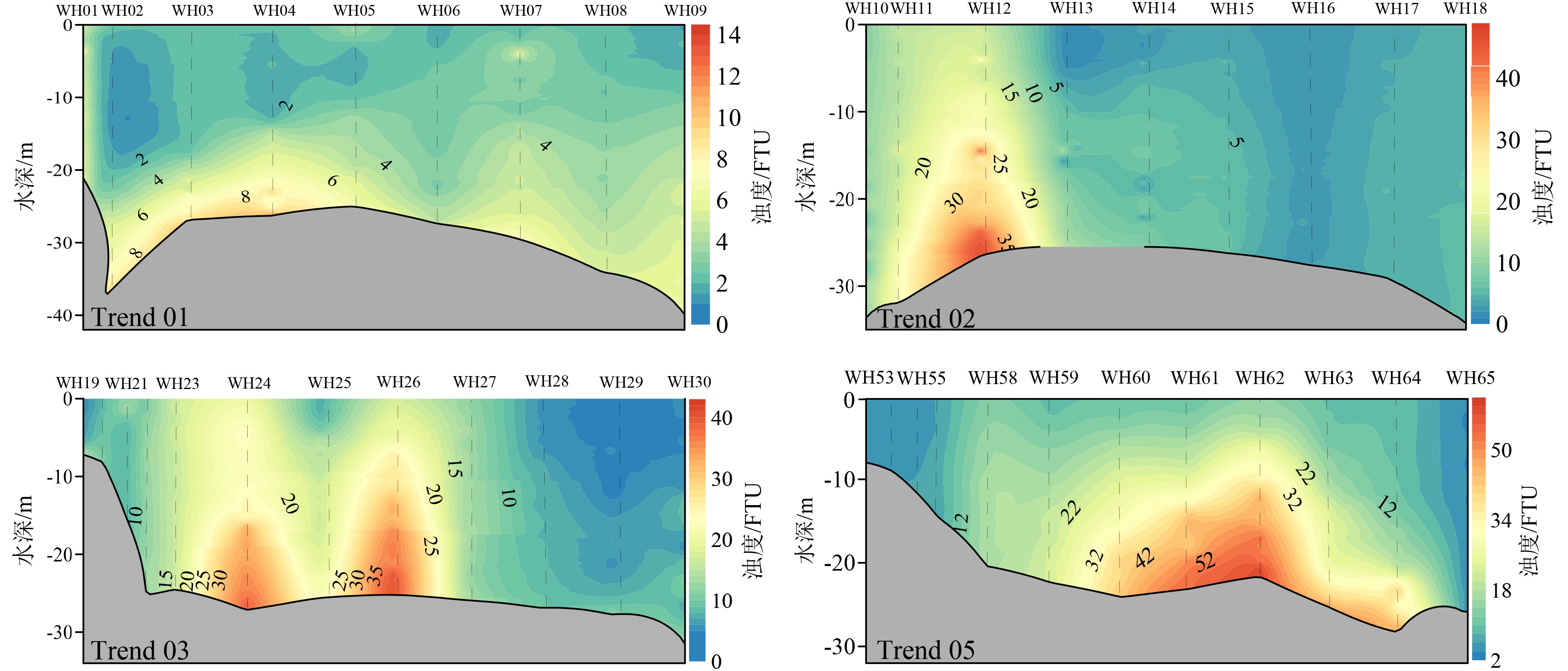
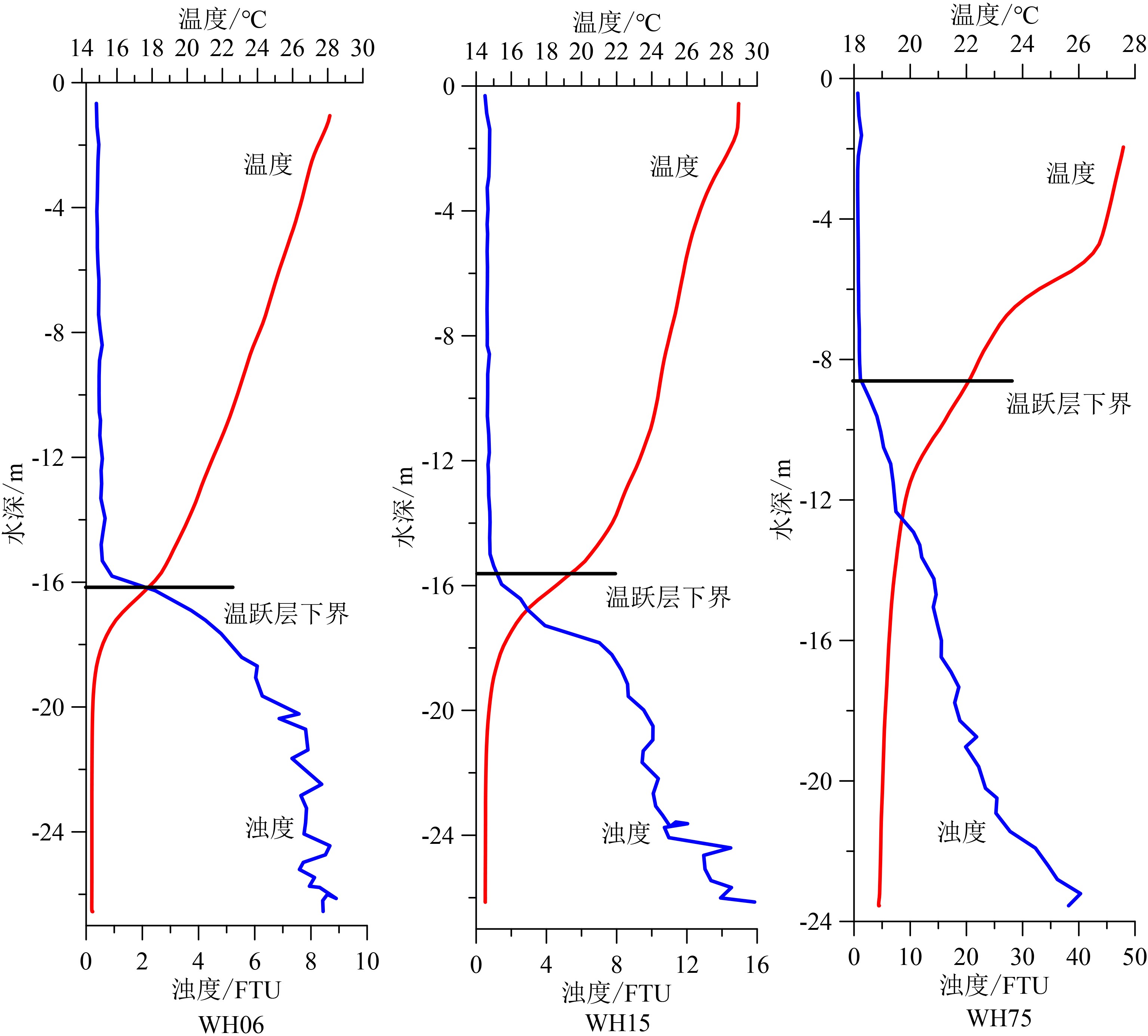
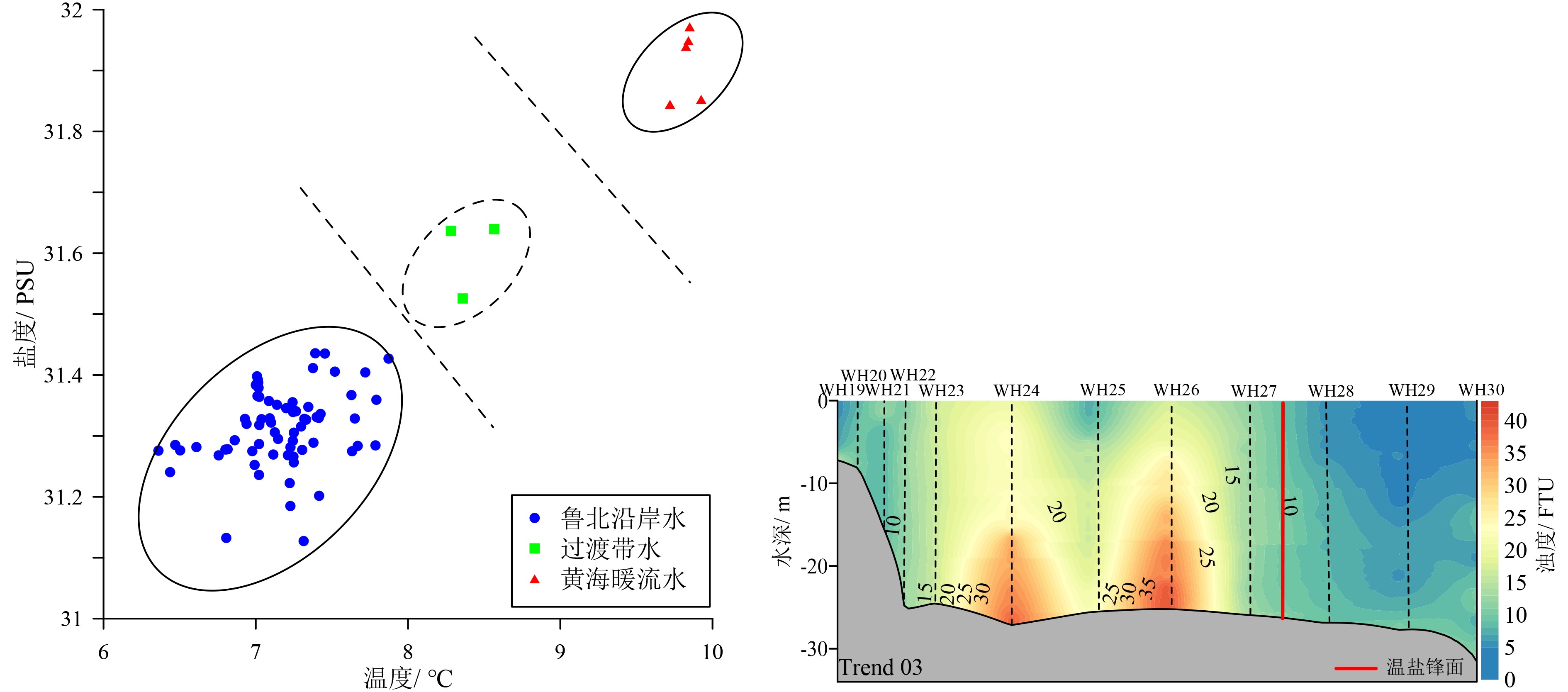
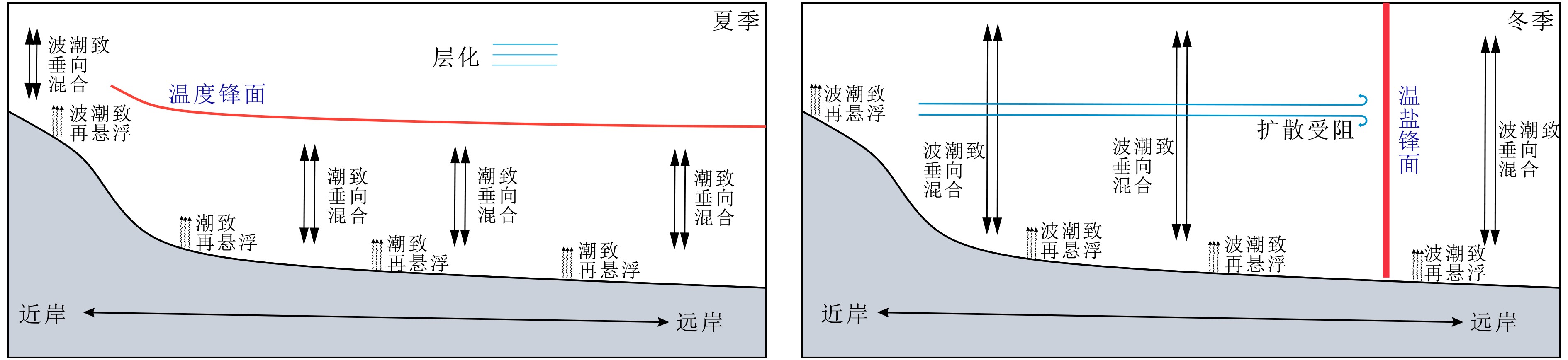
基于2018年山东半岛东北部海域冬、夏两季悬浮体浓度、浊度及水温和盐度调查资料,分析了研究区水体悬浮体浓度的季节性变化,探讨了其控制因素。结果表明:夏季浊度在0.2~37.8FTU之间变化,冬季浊度在1.5~100.1FTU之间变化,均表现为底高表低、东高西低的特征。夏季水温分层明显,表现为表层高、底层低的特征,盐度整体无明显变化;冬季温盐垂向上混合均匀,平面上表现为近岸低温低盐水体向远岸高温高盐水体的过渡。悬浮体浓度分布受潮流、波浪、温跃层和温盐锋面等因素影响。夏季,悬浮体垂向上受到温跃层影响,底层悬浮体难以向表层输运;平面上潮混合和波浪差异性作用阻碍了悬浮体的水平输运。冬季,强风浪促使悬浮体垂向混合剧烈,表层悬浮体浓度明显较夏季变高;平面上沿岸流和黄海暖流形成的温、盐锋面阻碍了水团间悬浮体的输运。
Abstract:Based on the characteristics of suspended matter, such as sediment content, turbidity, temperature and salinity, acquired in the summer and winter of 2018 in the water northeast to the Shandong Peninsula, we studied the seasonal variation of suspended sediment and it’s controlling factors. The results show that the turbidity varies from 0.2 to 37.8 FTU in summer, 1.5 to 100.1 FTU in winter, of which both are high on the bottom and low on the surface and high in the east and low in the west. Concerning water temperature, it is obviously stratified in summer, high on the surface and low on the bottom. However, there is no obvious changes as far as salinity is considered. In the winter time, both the temperature and salinity show a transition from the low temperature and low salinity water mass near the shore to the high temperature and high salinity water mass off the coast on plane, and evenly mixed in vertical direction. The distribution of suspended sediment content is controlled by various factors, such as tide, wave, thermocline, temperature and salinity fronts. In summer, affected by the thermocline vertically, the suspended sediments in bottom water are difficult to move into the upper layer, while tidal mixing and wave differentiation will accelerate the exchange of suspended sediment between the near shore and the far shore areas. However, the content of surface suspended matter is significantly higher in winter, because of the intensification of vertical mixing by strong wind and waves. The temperature and salinity front, formed by the coastal current and the Yellow Sea warm current, will block the exchanges of suspended sediments between water masses.
-
Key words:
- suspended sediment content /
- thermocline /
- fronts /
- Shandong Peninsula
-

-
图 1 黄海冬季环流及夏季冷水团分布图[23]
Figure 1.
图 13 黄海M2分潮潮流椭圆及最大潮流分布图[25]
Figure 13.
表 1 夏季温度、盐度
Table 1. Water temperature and salinity in summer
层位 表层 中层 底层 温度/℃ 盐度/PSU 温度/℃ 盐度/PSU 温度/℃ 盐度/PSU 最大值 28.8 32.28 21.7 32.25 21.0 32.31 最小值 20.4 31.71 15.0 31.70 14.2 31.85 平均值 25.4 32.00 18.6 31.98 17.4 31.99 表 2 冬季水温和盐度特征值
Table 2. Water temperature and salinity in winter
层位 表层 中层 底层 温度/℃ 盐度/PSU 温度/℃ 盐度/PSU 温度/℃ 盐度/PSU 最大值 9.9 31.97 9.9 31.99 9.9 31.99 最小值 6.4 31.13 6.3 31.19 6.3 31.15 平均值 7.4 31.36 7.4 31.39 7.4 31.38 表 3 冬季和夏季水体浊度特征值
Table 3. Water turbidity in winter and summer
FTU 夏季 冬季 表层 中层 底层 表层 中层 底层 最大值 2.3 8.9 37.8 22.4 44.0 100.1 最小值 0.2 0.2 2.9 1.5 2.3 3.9 平均值 0.6 2.5 9.3 9.2 13.0 23.4 -
[1] Bian C W, Jiang W S, Quan Q, et al. Distributions of suspended sediment concentration in the Yellow Sea and the East China Sea based on field surveys during the four seasons of 2011 [J]. Journal of Marine Systems, 2013, 121-122: 24-35. doi: 10.1016/j.jmarsys.2013.03.013
[2] Bouchez J, Gaillardet J, France‐Lanord C, et al. Grain size control of river suspended sediment geochemistry: Clues from Amazon River depth profiles [J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2011, 12(3): Q03008.
[3] Bian C W, Jiang W S, Greatbatch R J, et al. The suspended sediment concentration distribution in the Bohai Sea, Yellow Sea and East China Sea [J]. Journal of Ocean University of China, 2013, 12(3): 345-354. doi: 10.1007/s11802-013-1916-3
[4] Yuan D L, Zhu J R, Li C Y, et al. Cross-shelf circulation in the Yellow and East China Seas indicated by MODIS satellite observations [J]. Journal of Marine Systems, 2008, 70(1-2): 134-149. doi: 10.1016/j.jmarsys.2007.04.002
[5] Muslim I, Jones G. The seasonal variation of dissolved nutrients, chlorophyll a and suspended sediments at Nelly Bay, Magnetic Island [J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2003, 57(3): 445-455. doi: 10.1016/S0272-7714(02)00373-6
[6] Lu J, Qiao F L, Wang X H, et al. A numerical study of transport dynamics and seasonal variability of the Yellow River sediment in the Bohai and Yellow seas [J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2011, 95(1): 39-51. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2011.08.001
[7] Bi N S, Yang Z S, Wang H J, et al. Seasonal variation of suspended-sediment transport through the southern Bohai Strait [J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2011, 93(3): 239-247. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2011.03.007
[8] Yang Z S, Liu J P. A unique Yellow River-derived distal subaqueous delta in the Yellow Sea [J]. Marine Geology, 2007, 240(1-4): 169-176. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2007.02.008
[9] Liu J P, Milliman J D, Gao S, et al. Holocene development of the Yellow River’s subaqueous delta, North Yellow Sea [J]. Marine Geology, 2004, 209(1-4): 45-67. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2004.06.009
[10] Qiao S Q, Shi X F, Wang G Q, et al. Sediment accumulation and budget in the Bohai Sea, Yellow Sea and East China Sea [J]. Marine Geology, 2017, 390: 270-281. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2017.06.004
[11] 窦衍光, 李军, 杨守业. 山东半岛东部海域表层沉积物元素组成及物源指示意义[J]. 海洋学报, 2012, 34(1):109-119
DOU Yanguang, LI Jun, YANG Shouye. Element compositions and provenance implication of surface sediments in offshore areas of the eastern Shandong Peninsula in China [J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2012, 34(1): 109-119.
[12] 蓝先洪, 李日辉, 密蓓蓓, 等. 渤海东部和黄海北部表层沉积物稀土元素的分布特征与物源判别[J]. 地球科学, 2016, 41(3):463-474
LAN Xianhong, LI Rihui, MI Beibei, et al. Distribution characteristics of rare earth elements in surface sediment and their provenance discrimination in the eastern Bohai and northern Yellow Seas [J]. Earth Science, 2016, 41(3): 463-474.
[13] Li Y, Li A C, Huang P, et al. Clay minerals in surface sediment of the north Yellow Sea and their implication to provenance and transportation [J]. Continental Shelf Research, 2014, 90: 33-40. doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2014.01.020
[14] Wang A M, Ralston D K, Bi N S, et al. Seasonal variation in sediment transport and deposition on a muddy clinoform in the Yellow Sea [J]. Continental Shelf Research, 2019, 179: 37-51. doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2019.04.009
[15] 王勇智, 张永强, 孙惠凤. 山东半岛东部海域悬浮体分布季节变化及其冬季输送通量研究[J]. 沉积学报, 2019, 37(3):541-549
WANG Yongzhi, ZHANG Yongqiang, SUN Huifeng. Seasonal variation of suspended matter distribution and flux in coastal waters of eastern Shandong Peninsula [J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2019, 37(3): 541-549.
[16] 赵一阳, 朴龙安, 秦蕴珊, 等. 南黄海沉积学研究新进展——中韩联合调查[J]. 海洋科学, 1998(1):34-37
ZHAO Yiyang, PARK Y A, QIN Yunshan, et al. Recent development in the southern Yellow Sea sedimentology——The China-Korea Joint investigation [J]. Marine Sciences, 1998(1): 34-37.
[17] 边昌伟. 中国近岸泥沙在渤海、黄海和东海的输运[D]. 中国海洋大学博士学位论文, 2012.
BIAN Changwei. Chinese coastal sediment transport in the Bohai Sea, Yellow Sea and East China Sea[D]. Doctor Dissertation of Ocean University of China, 2012.
[18] Zeng X M, He R Y, Xue Z, et al. River-derived sediment suspension and transport in the Bohai, Yellow, and East China Seas: A preliminary modeling study [J]. Continental Shelf Research, 2015, 111: 112-125. doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2015.08.015
[19] 杨作升, 戴慧敏, 王开荣. 1950~2000年黄河入海水沙的逐日变化及其影响因素[J]. 中国海洋大学学报, 2005, 35(2):237-244
YANG Zuosheng, DAI Huimin, WANG Kairong. Daily variations of water discharge and Sediment discharge into the sea from Yellow River from 1950 to 2000 and relevant influential factors that generate these changes [J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 2005, 35(2): 237-244.
[20] 李广雪, 岳淑红, 赵东波, 等. 黄河口快速沉积及其动力过程(英文)[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2004, 24(3):29-36
LI Guangxue, YUE Shuhong, ZHAO Dongbo, et al. Rapid deposition and dynamic processes in the modern Yellow River Mouth [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2004, 24(3): 29-36.
[21] 齐君, 李凤业, 宋金明, 等. 北黄海沉积速率及其沉积通量[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2004, 24(2):9-14
QI Jun, LI Fengye, SONG Jinming, et al. Sedimentation rate and flux of the North Yellow Sea [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2004, 24(2): 9-14.
[22] 程鹏. 北黄海细颗粒物质的沉积特征与输运过程[D]. 中国科学院海洋研究所博士学位论文, 2000.
CHENG Peng. Sediment characteristics and transport processes of fine-grained material over the northern Yellow Sea[D]. Doctor Dissertation of Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2000.
[23] 苏纪兰. 中国近海水文[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 2005: 207-246.
SU Jilan. China's Offshore Hydrology[M]. Beijing: China Ocean Press, 2005: 207-246.
[24] 王爱美. 黄海中部泥质沉积区温度锋面及层化的时空变化及其沉积效应[D]. 中国海洋大学, 2019.
WANG Aimei. Thermal front and stratification effect on the sediment transport and deposition at a muddy clinoform in the Yellow Sea[D]. Ocean University of China, 2019.
[25] Xu L L, Wu D X, Lin X P, et al. The study of the Yellow Sea warm current and its seasonal variability [J]. Journal of Hydrodynamics, 2009, 21(2): 159-165. doi: 10.1016/S1001-6058(08)60133-X
[26] Yu F, Zhang Z X, Diao X Y, et al. Observational evidence of the Yellow Sea warm current [J]. Chinese Journal of Oceanology and Limnology, 2010, 28(3): 677-683. doi: 10.1007/s00343-010-0006-2
[27] 管秉贤. 黃海冷水团的水温变化以及环流特征的初步分析[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 1963, 5(4):255-284
GUAN Bingxian. A preliminary study of the temperature variations and the characteristics of the circulation of the cold water mass of the Yellow Sea [J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 1963, 5(4): 255-284.
[28] 赫崇本, 汪圆祥, 雷宗友, 等. 黄海冷水团的形成及其性质的初步探讨[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 1959, 2(1):11-15
HO C P, WANG Yuanxiang, LEI Zongyou, et al. A prelimenary study of the formation of Yellow Sea cold mass and its properties [J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 1959, 2(1): 11-15.
[29] 冷星, 朱龙海, 胡日军. 山东半岛东部海域泥质区冬季悬浮泥沙时空变化及输运机制[J]. 中国海洋大学学报, 2019, 49(4):106-116, 8
LENG Xin, ZHU Longhai, HU Rijun. The spatiotemporal change and transport mechanism of suspended sediment in the mud area of the eastern sea of Shandong Peninsulain winter [J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 2019, 49(4): 106-116, 8.
[30] 秦蕴珊, 李凡. 渤海海水中悬浮体的研究[J]. 海洋学报, 1982, 14(2):191-200
QIN Yunshan, LI Fan. Study on the suspended matter of the sea water of the Bohai gulf [J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 1982, 14(2): 191-200.
[31] 苏健, 江文胜, 孙文心. 渤海中南部悬浮物海洋调查资料分析[J]. 青岛海洋大学学报, 2001, 31(5):647-652
SU Jian, JIANG Wensheng, SUN Wenxin. Analysis of SPM Data Obtained in Ocean Investigation in the Bohai Sea [J]. Journal of Ocean University of Qingdao, 2001, 31(5): 647-652.
[32] 王勇智, 乔璐璐, 杨作升, 等. 夏、冬季山东半岛东北部沿岸悬浮物输送机制的初步研究[J]. 泥沙研究, 2012(5):49-57 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0468-155X.2012.05.008
WANG Yongzhi, QIAO Lulu, YANG Zuosheng, et al. Research on suspended sediment transport mechanisms along northeast coast of Shandong Peninsula in summer and in winter [J]. Journal of Sediment Research, 2012(5): 49-57. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0468-155X.2012.05.008
[33] 江伟, 邢博, 楼伟, 等. 海洋温跃层分析方法比较[J]. 海洋预报, 2016, 33(3):41-49 doi: 10.11737/j.issn.1003-0239.2016.03.006
JIANG Wei, XING Bo, LOU Wei, et al. Comparisons of three thermocline detection methods [J]. Marine Forecasts, 2016, 33(3): 41-49. doi: 10.11737/j.issn.1003-0239.2016.03.006
[34] 朱学明, 鲍献文, 宋德海, 等. 渤、黄、东海潮汐、潮流的数值模拟与研究[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2012, 43(6):1103-1113 doi: 10.11693/hyhz201206011011
ZHU Xueming, BAO Xianwen, SONG Dehai, et al. Numerical study on the tides and tidal currents in Bohai Sea, Yellow Sea and East China Sea [J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2012, 43(6): 1103-1113. doi: 10.11693/hyhz201206011011
[35] 苏纪兰. 中国近海的环流动力机制研究[J]. 海洋学报(中文版), 2001, 23(4):1-16
SU Jilan. A review of circulation dynamics of the coastal oceans near China [J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2001, 23(4): 1-16.
[36] 赵保仁. 黄海冷水团锋面与潮混合[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 1985, 16(6):451-460
ZHAO Baoren. The fronts of the Huanghai Sea cold water mass induced by tidal mixing [J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 1985, 16(6): 451-460.
[37] 郑铁民, 赵一阳, 李凡, 等. 南黄海夏季海水中悬浮体的研究[J]. 海洋学报, 1990, 12(6):749-757
ZHENG Tiemin, ZHAO Yiyang, LI Fan, et al. Study on the suspended matter of the sea water of the south Yellow Sea in summer [J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 1990, 12(6): 749-757.
[38] Zhong W, Zhu L H, Dong P, et al. Mechanisms of sediment trapping in coastal embayments off the Shandong Peninsula in summer—A case study in Weihai Bay [J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2020, 236: 106623. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2020.106623
[39] Qiao L L, Liu Y, Chen J J, et al. Distribution and its mechanism of suspended particulate matters in the southern Huanghai Sea and the East China Sea in summer [J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2011, 30(5): 94-100. doi: 10.1007/s13131-011-0151-2
[40] Acha E M, Mianzan H W, Guerrero R A, et al. Marine fronts at the continental shelves of austral South America: physical and ecological processes [J]. Journal of Marine Systems, 2004, 44(1-2): 83-105. doi: 10.1016/j.jmarsys.2003.09.005
[41] Chen C T A. Chemical and physical fronts in the Bohai, Yellow and East China seas [J]. Journal of Marine Systems, 2009, 78(3): 394-410. doi: 10.1016/j.jmarsys.2008.11.016
[42] Belkin I M, Cornillon P C, Sherman K. Fronts in Large Marine Ecosystems [J]. Progress in Oceanography, 2009, 81(1-4): 223-236. doi: 10.1016/j.pocean.2009.04.015
[43] Zang Z C, Xue Z G, Bi N S, et al. Seasonal and Intra-seasonal Variations of Suspended-Sediment Distribution in the Yellow Sea [J]. Continental Shelf Research, 2017, 148: 116-129. doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2017.08.016
[44] Isobe A. Recent advances in ocean-circulation research on the Yellow Sea and East China Sea shelves [J]. Journal of Oceanography, 2008, 64(4): 569-584. doi: 10.1007/s10872-008-0048-7
[45] 张凯南. 北黄海冷水团对悬浮体物质组成和沉积环境的影响机制[D]. 中国科学院大学(中国科学院海洋研究所)博士学位论文, 2018.
ZHANG Kainan. The influence of the North Yellow Sea cold water mass on the properties of suspended particulate matter and sedimentary environment[D]. Doctor Dissertation of Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2018.
-




 下载:
下载: