Geochemical characteristics of major elements and their paleoenvironmental significance of the Xianjingyuan loess in Shandong Province
-
摘要:
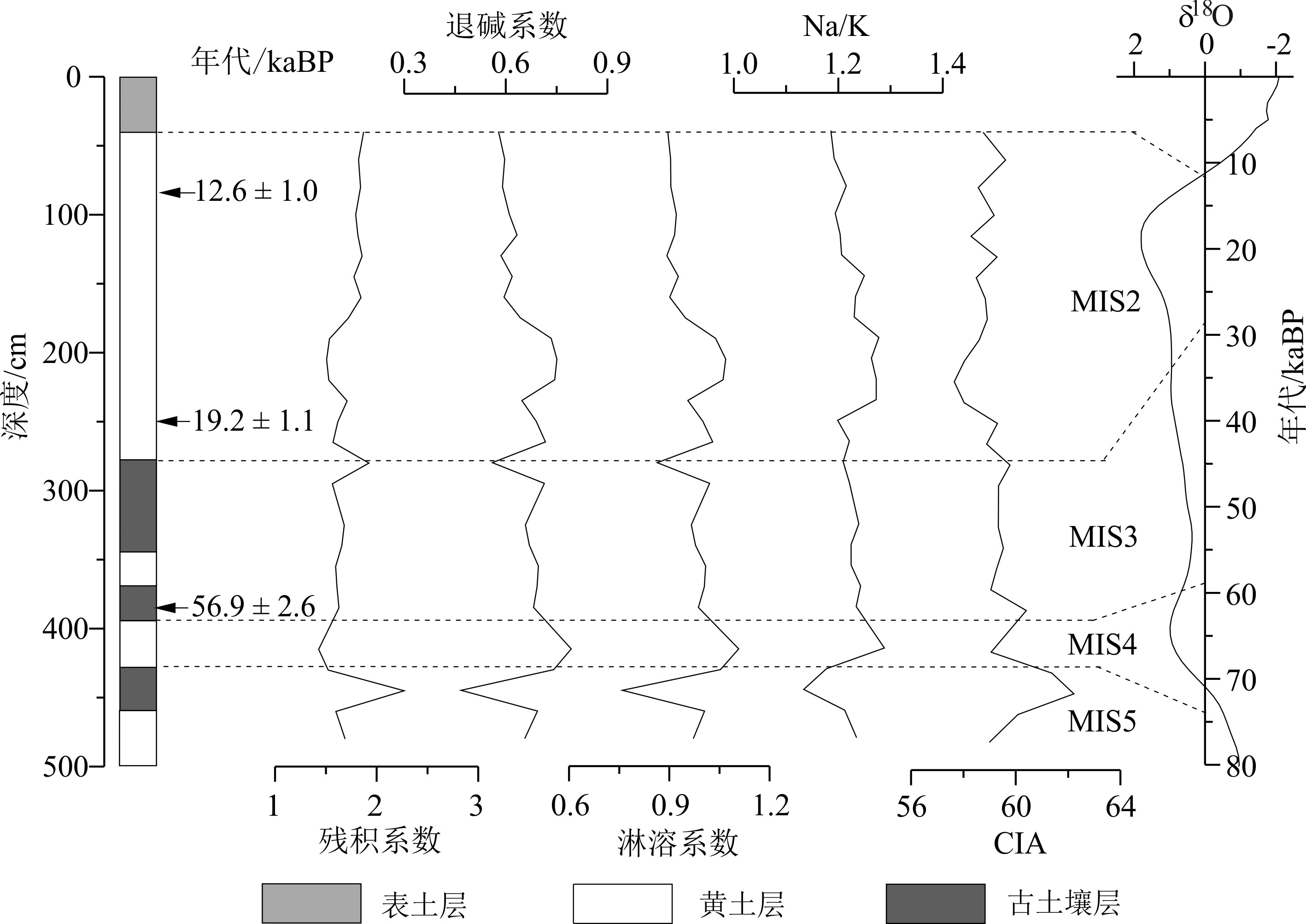
通过对南长山岛仙境源黄土的常量元素组成特征进行分析,结合风化判别指标和元素综合参数探讨了该黄土堆积过程中经历的化学风化强度与气候变化特征,并将其与砣矶岛黄土、平阴黄土以及洛川黄土-古土壤进行对比,结果表明:(1)仙境源黄土的主要化学成分为SiO2、Al2O3和CaO,常量元素含量呈SiO2>Al2O3>CaO>Fe2O3>K2O>Na2O>MgO>TiO2>P2O5>MnO的组合特征;(2)仙境源黄土整体处于初等化学风化阶段,并在堆积过程中先后经历了5次暖湿与冷干的气候变化,该区气候环境与全球气候环境的变化之间存在较好的响应关系;(3)山东的粉尘物源和古气候环境总体上存在较高相似性,但因海陆位置与地形的影响使气候环境存在区域性的差异,而仙境源黄土与平阴黄土之间明显的差异表明二者粉尘物源存在差别;(4)对于仙境源黄土与洛川黄土-古土壤在元素组成与风化强度上存在的明显差异,我们认为主要是因粉尘的物源不同导致。
Abstract:The loess deposited in the Miaodao Islands has great significance to the revealing of paleoclimatic and paleoenvironmental changes. In this study, we analyzed the compositional characteristics of the major elements of the Xianjingyuan loess on the Nanchangshan island. Combined with the chemical weathering indexes and integrated elemental parameters, we discussed in this paper the characteristics and intensity of chemical weathering and climate changes during the accumulation of Xianjingyuan loess. Also made are comparisons to the Tuoji loess, Pingyin loess and Luochuan loess-palaeosol. It is revealed that: (1) The Xianjingyuan loess is dominated by the major elements of SiO2, Al2O3 and CaO, and the abundance of major elements are in an order of SiO2>Al2O3>CaO>TFe2O3>K2O>Na2O>MgO>TiO2>P2O5>MnO; (2) Chemical weathering indicators indicated that the Xianjingyuan loess was in an initial stage of chemical weathering; and the integrated element parameters suggest that the region had experienced five times of climatic change from warm and humid to cold and dry, and the climate environment of Xianjingyuan has a good response to the global climate environment; (3) The dust sources and the paleoclimate environment are highly similar to the loess found in Shandong Province, but the regional environment was effected by geographic location and topographic conditions, the obvious difference between Xianjingyuan loess and Pingyin loess suggest that there is difference in dust sources; (4) the difference between the major elements and chemical weathering in Xianjingyuan loess and Luochuan loess-palaeosol owes its origin to the difference of dust sources.
-
Key words:
- major elements /
- chemical weathering /
- environmental evolution /
- Shandong loess
-

-
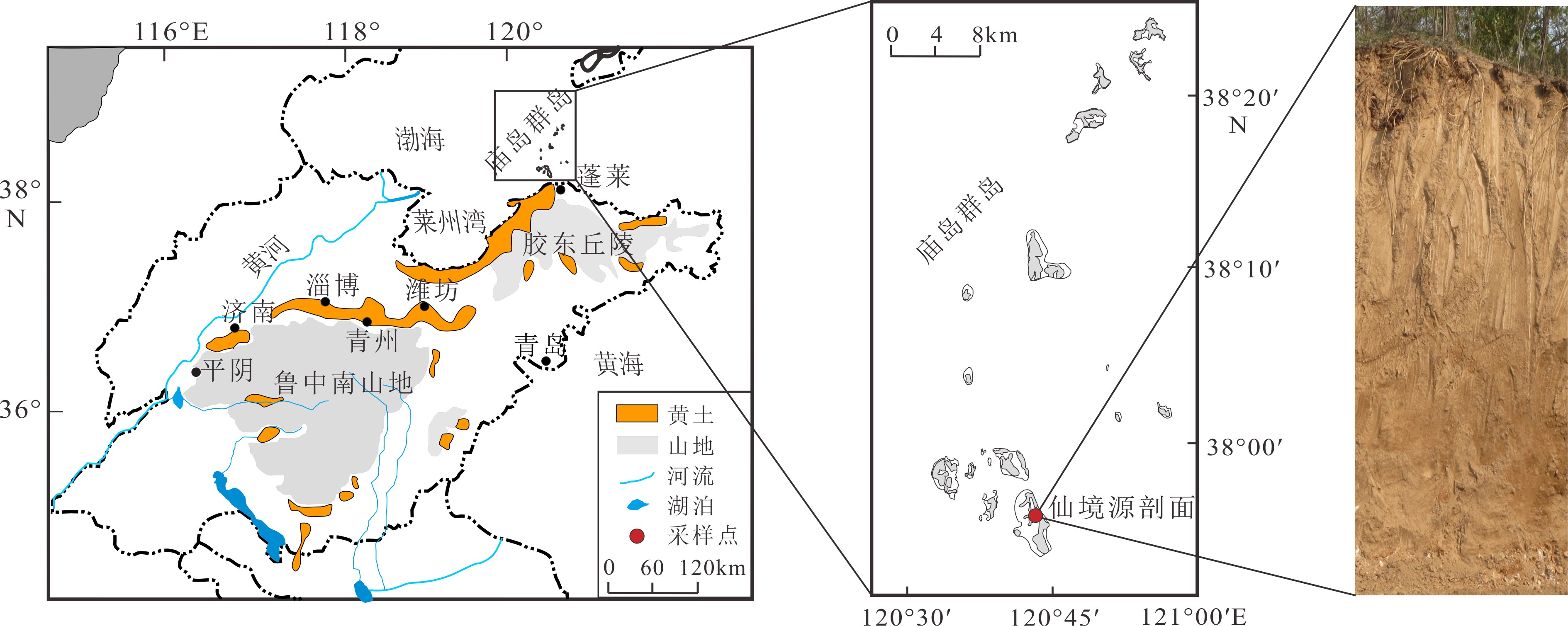
图 1 仙境源剖面地理位置[24]
Figure 1.
表 1 仙境源黄土与砣矶岛黄土、平阴黄土、洛川黄土-古土壤的常量元素含量
Table 1. Major elements contents of Xiangjiangyuan loess, Tuoji loess, Pingyin loess and Luochuan loess-paleoaol
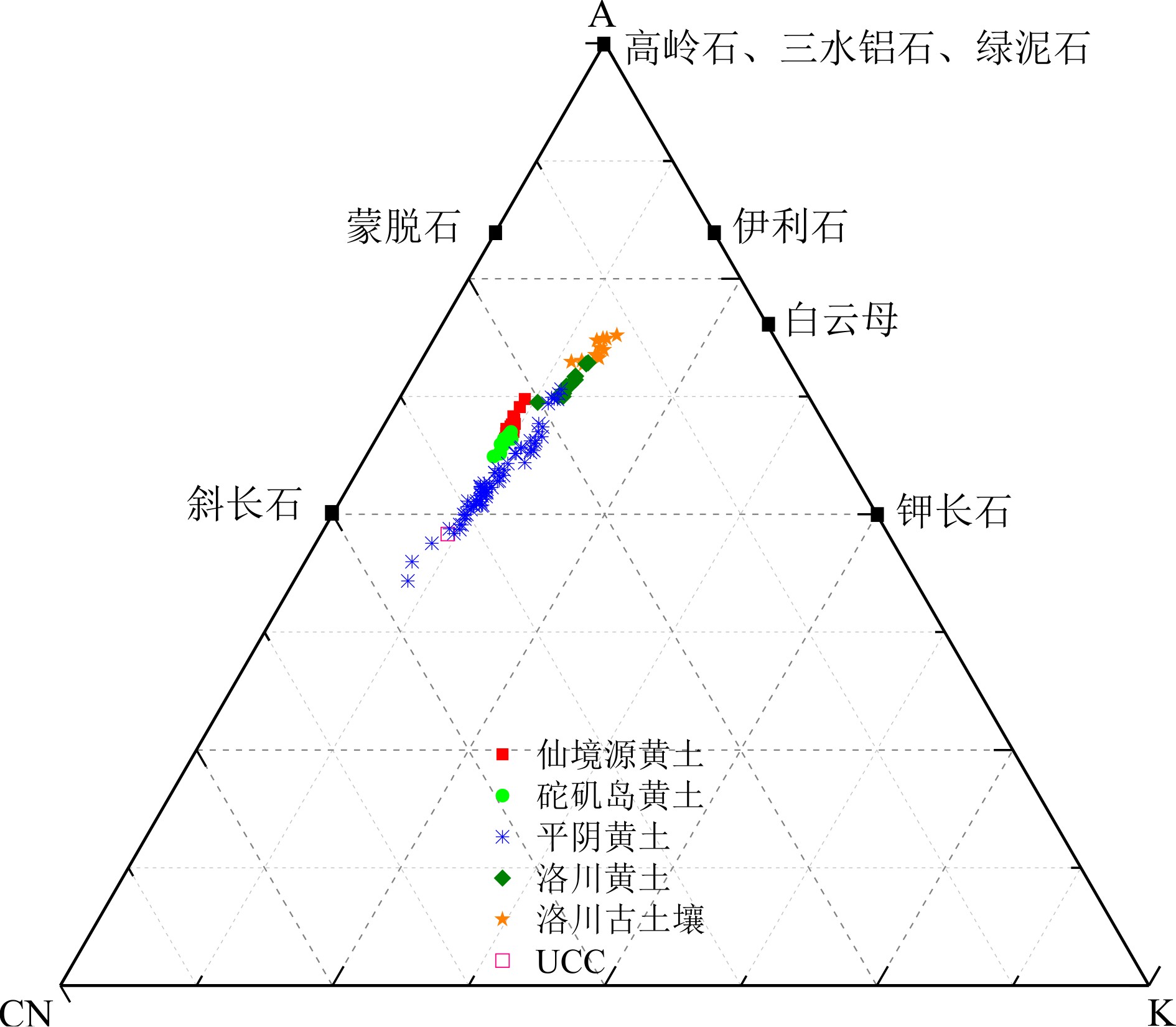
% 样品名称 SiO2 Al2O3 TFe2O3 K2O Na2O CaO MgO MnO TiO2 P2O5 仙境源黄土(n=27) 最大 69.88 13.02 4.37 2.30 1.85 7.48 1.66 0.07 0.73 0.11 最小 61.56 11.26 3.51 2.06 1.61 4.42 1.00 0.06 0.62 0.06 平均 65.47 11.81 3.78 2.17 1.75 6.00 1.47 0.07 0.67 0.08 砣矶岛黄土[23](n=13) 平均 66.95 11.63 3.76 2.23 1.87 4.94 1.56 0.07 0.69 0.10 平阴黄土[24](n=70) 平均 69.28 11.94 4.00 2.68 2.27 7.76 1.44 − − − 洛川黄土[10](n=13) 平均 67.10 13.99 4.62 2.99 1.73 1.03 2.22 0.07 0.72 0.15 洛川古土壤[10](n=12) 平均 64.85 14.93 5.17 3.18 1.39 0.82 2.21 0.08 0.76 0.11 UCC[26] 平均 66.00 15.20 5.00 3.40 3.90 4.20 2.20 0.07 0.68 0.50 -
[1] 刘东生, 安芷生, 郑洪汉. 黄土与环境[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1985.
LIU Tungsheng, AN Zhisheng, ZHENG Honghan. Loess and Environment[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1985.
[2] 周家兴, 于娟, 杨丽君, 等. 铜川地区早中全新世黄土沉积特征及其古气候意义[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2020, 40(1):160-166
ZHOU Jiaxing, YU Juan, YANG Lijun, et al. Sedimentary characteristics of the Early and Middle Holocene loess in Tongchuan aere and their implications for paleoclimate [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2020, 40(1): 160-166.
[3] Smalley I, Marković S B. Controls on the nature of loess particles and the formation of loess deposits [J]. Quaternary International, 2019, 502: 160-164. doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2017.08.021
[4] 王攀, 张培新, 杨振京, 等. 靖边黄土剖面记录的末次冰期以来的气候变化[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2019, 39(3):162-170
WANG Pan, ZHANG Peixin, YANG Zhenjing, et al. Climate change since the last glacial stage recorded in Jingbian loess section [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2019, 39(3): 162-170.
[5] Liu B, Jin H L, Sun Z, et al. Geochemical weathering of Aeolian sand and its palaeoclimatic implications in the Mu Us Desert, northern China, since the Late Holocene [J]. Journal of Arid Land, 2016, 8(5): 647-659. doi: 10.1007/s40333-016-0014-y
[6] 毛沛妮, 庞奖励, 黄春长, 等. 汉江上游黄土常量元素地球化学特征及区域对比[J]. 地理学报, 2017, 72(2):279-291 doi: 10.11821/dlxb201702008
MAO Peini, PANG Jiangli, HUANG Chunchang, et al. Chemical weathering characteristics and regional comparative study of the loess deposits in the upper Hanjiang River [J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2017, 72(2): 279-291. doi: 10.11821/dlxb201702008
[7] 凌超豪, 张智, 贾玉连, 等. 元素地球化学揭示的长江中下游下蜀黄土物源及其环境意义[J]. 地层学杂志, 2018, 42(3):328-335
LING Chaohao, ZHANG Zhi, JIA Yulian, et al. Geochemical evidence for provenance of Xiashu loess in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze river and its environmental implication [J]. Journal of Stratigraphy, 2018, 42(3): 328-335.
[8] 赵万苍, 刘连文, 陈骏, 等. 中国沙漠元素地球化学区域特征及其对黄土物源的指示意义[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2019, 62(9):1428-1440 doi: 10.1007/s11430-018-9354-y
ZHAO Wancang, LIU Lianwen, CHEN Jun, et al. Geochemical characterization of major elements in desert sediments and implications for the Chinese loess source [J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 2019, 62(9): 1428-1440. doi: 10.1007/s11430-018-9354-y
[9] 杜慧荣, 谢远云, 康春国, 等. 哈尔滨黄土的粒度与地球化学特征及其对粉尘物源的指示[J]. 中国沙漠, 2020, 40(1):64-76
DU Huirong, XIE Yuanyun, KANG Chunguo, et al. Grain-size and geochemical compositions of the Harbin loess deposits and their implications for eolian dust provenances [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2020, 40(1): 64-76.
[10] 陈骏, 安芷生, 刘连文, 等. 最近2.5Ma以来黄土高原风尘化学组成的变化与亚洲内陆的化学风化[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 2001, 31(2):136-145 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7240.2001.02.007
CHEN Jun, AN Zhisheng, LIU Lianwen, et al. Variations in chemical compositions of the Aelion dust in Chinese Loess Plateau over the past 2.5Ma and chemical weathering in Asian island [J]. Science in China: Series D, 2001, 31(2): 136-145. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7240.2001.02.007
[11] 李徐生, 韩志勇, 杨守业, 等. 镇江下蜀黄土剖面的化学风化强度与元素迁移特征[J]. 地理学报, 2007, 62(11):1174-1184 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0375-5444.2007.11.006
LI Xusheng, HAN Zhiyong, YANG Shouye, et al. Chemical weathering intensity and element migration features of the Xiashu loess profile in Zhenjiang [J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2007, 62(11): 1174-1184. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0375-5444.2007.11.006
[12] 张玉芬, 邵磊, 熊德强. “巫山黄土”元素地球化学特征及成因和物源意义[J]. 沉积学报, 2014, 31(1):78-84
ZHANG Yufen, SHAO Lei, XIONG Deqiang. Elemental compositions of the "Wushan Loess": implications for origin and sediment source [J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2014, 31(1): 78-84.
[13] Hao Q Z, Guo Z T, Qiao Y S, et al. Geochemical evidence for the provenance of middle Pleistocene loess deposits in southern China [J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2010, 29(23-24): 3317-3326. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2010.08.004
[14] Xiong S F, Ding Z L, Zhu Y J, et al. A ~6 Ma chemical weathering history, the grain size dependence of chemical weathering intensity, and its implications for provenance change of the Chinese loess-red clay deposit [J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2010, 29(15-16): 1911-1922. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2010.04.009
[15] Xie Y Y, Kang C G, Chi Y P, et al. The loess deposits in northeast China: The linkage of loess accumulation and geomorphic-climatic features at the easternmost edge of the Eurasian loess belt [J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2019, 181: 103914. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2019.103914
[16] Tian S C, Sun J M, Lü L X, et al. Optically stimulated luminescence dating of late Quaternary loess deposits in the coastal region of North China: Provenance and paleoclimatic implications [J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2019, 218: 160-177. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2019.06.022
[17] 黎武标, 李志文, 王志刚, 等. 粒度端元揭示的芝罘剖面末次间冰期: 末次冰期气候环境变化特征[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2019, 39(2):177-187
LI Wubiao, LI Zhiwen, WANG Zhigang, et al. Climatic environment changes during the last interglacial-glacial cycle in Zhifu loess section: Revealed by grain-size end-member algorithm [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2019, 39(2): 177-187.
[18] 刘乐军, 李培英, 王永吉. 鲁中黄土粒度特征及其成因探讨[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2000, 20(1):81-86
LIU Lejun, LI Peiying, WANG Yongji. The Grain-size properties and genesis of the loess in central Shandong Province [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2000, 20(1): 81-86.
[19] 张祖陆, 辛良杰, 聂晓红. 山东地区黄土研究综述[J]. 地理科学, 2004, 24(6):746-752 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0690.2004.06.018
ZHANG Zulu, XIN Liangjie, NIE Xiaohong. A summary of loessial researches in Shandong [J]. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 2004, 24(6): 746-752. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0690.2004.06.018
[20] 曹家欣, 李培英, 石宁. 山东庙岛群岛的黄土[J]. 中国科学: B辑, 1988, 31(1):120-127
CAO Jiaxin, LI Peiying, SHI Ning. Study on the loess of Miaodao islands in Shandong province [J]. Scientia China (Series B), 1988, 31(1): 120-127.
[21] 于洪军. 中国东部陆架黄土成因的新探索[J]. 第四纪研究, 1999, 7(4):367-372
YU Hongjun. A new exploration on the origin of loess in the shelf area of the Eastern China seas [J]. Quaternary Sciences, 1999, 7(4): 367-372.
[22] 王萧风, 郑祥民, 许健, 等. 山东长岛黄土沉积物的磁性与碳酸盐特征及其环境意义初探[J]. 云南地理环境研究, 2007, 19(4):133-138 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7852.2007.04.026
WANG Xiaofeng, ZHENG Xiangmin, XU Jian, et al. The primary research on magnetic measurements and CaCO3 from loess sediments of Changdao in Shandong [J]. Yunnan Geographic Environment Research, 2007, 19(4): 133-138. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7852.2007.04.026
[23] Xu S J, Kong F B, Jia G J, et al. An integrated OSL chronology, sedimentology and geochemical approach to loess deposits from Tuoji Island, Shandong Province: Implications for the late quaternary paleoenvironment in East China [J]. Aeolian Research, 2018, 31: 105-116. doi: 10.1016/j.aeolia.2017.07.007
[24] 徐树建, 倪志超, 丁新潮. 山东平阴黄土剖面常量元素地球化学特征[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2016, 35(2):353-359 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2016.02.017
XU Shujian, NI Zhichao, DING Xinchao. Geochemical characteristics of major elements of the Pingyin loess in Shandong Province [J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 2016, 35(2): 353-359. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2016.02.017
[25] Xu S J, Ding X C, Yu L P, et al. Palaeoclimatic implications of Aeolian sediments on the Miaodao Islands, Bohai Sea, East China, based on OSL dating and proxies [J]. Aeolian Research, 2015, 19: 259-266. doi: 10.1016/j.aeolia.2015.02.001
[26] Taylor S R, McLennan S M. The continental crust Its composition and evolution: An examination of the geochemical record preserved in sedimentary rocks[M]. Oxford: Blackwell, 1985.
[27] 路硕, 尹功明, 宋为娟, 等. 合肥下蜀土地球化学特征及其古气候意义[J]. 地质力学学报, 2019, 25(3):428-439 doi: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.2019.25.03.040
LU Shuo, YIN Gongming, SONG Weijuan, et al. Geochemical characteristics and paleoclimate implications of Hefei Xiashu loess [J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2019, 25(3): 428-439. doi: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.2019.25.03.040
[28] Nesbit H W, Young G M. Early proterozoic climates and plate motions inferred from major element chemistry of lutites [J]. Nature, 1982, 299(5885): 715-717. doi: 10.1038/299715a0
[29] Qiao Y S, Hao Q Z, Peng S S, et al. Geochemical characteristics of the eolian deposits in southern China, and their implications for provenance and weathering intensity [J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2011, 308(3-4): 511-523.
[30] McLennan S M. Weathering and global denudation [J]. The Journal of Geology, 1993, 101(2): 295-303. doi: 10.1086/648222
[31] 张威, 董应巍, 于洋, 等. 辽南黄土化学风化特点及其环境意义[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2013, 33(6):163-171
ZHANG Wei, DONG Yingwei, YU Yang, et al. Chemical weathering of the loess in the south of Liaoning Province and its implications for environmental change [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2013, 33(6): 163-171.
[32] Buggle B, Glaser B, Hambach U, et al. An evaluation of geochemical weathering indices in loess-paleosol studies [J]. Quaternary International, 2011, 240(1-2): 12-21. doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2010.07.019
[33] Yang S L, Ding F, Ding Z L. Pleistocene chemical weathering history of Asian arid and semi-arid regions recorded in loess deposits of China and Tajikistan [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2006, 70(7): 1695-1709. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2005.12.012
[34] 梁敏豪, 杨胜利, 成婷, 等. 青藏高原东部黄土沉积元素地球化学示踪[J]. 沉积学报, 2018, 36(5):927-936
LIANG Minhao, YANG Shengli, CHENG Ting, et al. Geochemical evidence for the provenance of loess deposits in the Eastern Xizang Plateau [J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2018, 36(5): 927-936.
[35] 刁桂仪, 文启忠. 黄土风化成土过程中主要元素迁移序列[J]. 地质地球化学, 1999, 27(1):21-26
DIAO Guiyi, WEN Qizhong. The migration series of major elements during loess pedogenesis [J]. Geology-Geochemistry, 1999, 27(1): 21-26.
[36] 李传想, 宋友桂, 王乐民. 新疆伊犁黄土元素地球化学特征及古环境意义[J]. 新疆地质, 2012, 30(1):103-108 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8845.2012.01.020
LI Chuanxiang, SONG Yougui, WANG Lemin. Geochemical characteristics and paleoen-vironmental significance of the loess in the lli Region, Xinjiang [J]. Xinjiang Geology, 2012, 30(1): 103-108. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8845.2012.01.020
[37] 张文翔, 史正涛, 张虎才, 等. 中国西风区伊犁盆地塔勒德黄土-古土壤元素地球化学特征及环境意义[J]. 第四纪研究, 2011, 31(5):812-821 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7410.2011.05.06
ZHANG Wenxiang, SHI Zhengtao, ZHANG Hucai, et al. Geochemical characteristics and environmental significance of the Talede loess-paleosol sequence in Westerly Area of China [J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2011, 31(5): 812-821. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7410.2011.05.06
[38] 胡梦珺, 杨爱丽, 张文丽. 常量元素氧化物含量及其比值揭示的中晚全新世以来玛曲高原的环境演变[J]. 中国沙漠, 2015, 35(2):313-321 doi: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2015.00002
HU Mengjun, YANG Aili, ZHANG Wenli. Environmental evolution since the Middle-Late Holocene in the Maqu Plateau reflected by constant element oxides content and ratios [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2015, 35(2): 313-321. doi: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2015.00002
[39] 赵锦慧, 王丹, 鹿化煜, 等. 西宁地区黄土地球化学元素所揭示的古气候变化[J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 2006, 20(5):104-108 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-7578.2006.05.021
ZHAO Jinhui, WANG Dan, LU Huayu, et al. Variations of geochemical elements in Xining loess deposit and the Paleoclimatic implications [J]. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 2006, 20(5): 104-108. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-7578.2006.05.021
[40] 雒聪文, 马玉贞, 王凯, 等. 东亚地区MIS 5时期孢粉记录的植被与气候研究进展[J]. 地理科学进展, 2019, 34(5):540-551
LUO Congwen, MA Yuzhen, WANG Kai, et al. Vegetation and climate inferred from pollen record in East Asian region during MIS 5: A review [J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2019, 34(5): 540-551.
[41] 肖景义, 陈建强, 许哲平, 等. 邯郸地区晚更新世以来植被波动特征及其对气候变化的响应[J]. 沉积学报, 2010, 28(6):1206-1212
XIAO Jingyi, Chen Jianqiang, XU Zheping, et al. Characteristics of vegetation fluctuation as well as consequent impact on climate since late Pleistocene in Handan area, Hebei [J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2010, 28(6): 1206-1212.
[42] 李玉嵩, 陈建强, 赵硕, 等. 唐山地区晚更新世以来的孢粉组合特征及其与邻区的对比[J]. 地球学报, 2011, 32(2):178-188 doi: 10.3975/cagsb.2011.02.06
LI Yusong, CHEN Jianqiang, ZHAO Shuo, et al. Sporepollen assemblages in Tangshan area since late Pleistocene with a correlation to those in adjacent areas [J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2011, 32(2): 178-188. doi: 10.3975/cagsb.2011.02.06
[43] 李小燕, 赵泉鸿, 姚政权, 等. 渤海百万年以来的海侵记录: BH08孔有孔虫和介形类证据[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2015, 35(6):93-108
LI Xiaoyan, ZHAO Quanhong, YAO Zhengquan, et al. Transgressive records of last million years in the Bohai Sea, China: Evidence from foraminifera and ostracoda of core BH08 [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2015, 35(6): 93-108.
[44] Liu J, Saito Y, Wang H, et al. Stratigraphic development during the Late Pleistocene and Holocene offshore of the Yellow River delta, Bohai Sea [J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2009, 36(4-5): 318-331. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2009.06.007
[45] 仇建东, 刘健, 白伟明. 深海氧同位素第3阶段古气候: 海平面变化研究进展[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2012, 28(11):12-16
QIU Jiandong, LIU Jian, BAI Weiming. Progress of the studies of paleoclimate and sea level changes in the marine oxygen isotope stage 3 [J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2012, 28(11): 12-16.
[46] 皱建军, 石学法, 刘焱光, 等. 末次冰期以来日本海陆源沉积的地球化学记录及其对海平面和气候变化的响应[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2010, 30(2):75-86
ZOU Jianjun, SHI Xuefa, LIU Yanguang, et al. Geochemical record of terrigenous sediments from the sea of Japan since Last Glacial and its response to sea level and climate change [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2010, 30(2): 75-86.
[47] 伍婧, 刘强, 储国强, 等. 晚冰期大兴安岭植被气候变化的气孔器记录[J]. 科学通报, 2016, 61(36):3940-3945 doi: 10.1360/N972016-01181
WU Jing, LIU Qiang, CHU Guoqiang, et al. Vegetation history and climate change recorded by stomata evidence during the late glacial in the Great Khingan Mountain Region, Northeastern China [J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2016, 61(36): 3940-3945. doi: 10.1360/N972016-01181
[48] 管清玉, 潘保田, 高红山, 等. 两高分辨率黄土剖面末次冰消期气候事件的差异探讨[J]. 中国沙漠, 2007, 27(2):177-181 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-694X.2007.02.002
GUAN Qingyu, PAN Baotian, GAO Hongshan, et al. Discuss on difference of climate change events recorded in two high-resolution loess sections in last deglaciation [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2007, 27(2): 177-181. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-694X.2007.02.002
-



 下载:
下载: