Research progress of the Holocene paleoflood in the Yellow River basin and a future prospect
-
摘要:
全新世古洪水研究能够弥补近现代洪水监测记录在时间和空间上的局限性,更加科学地查明洪灾规律及机制,已逐步成为当今全球变化研究的热点之一。黄河流域由于独特的地质地貌条件,历史时期以来洪灾频发、影响巨大,而且现今洪水风险依然很大,是我国古洪水研究的重点区域。本文围绕近十年来黄河流域全新世古洪水研究在沉积特征、古水文重建、年代框架及其与文明兴衰关系等方面的研究成果,综述了当前研究中面临的主要问题和发展趋势,认为应加强流域内不同地貌位置的古洪水研究,综合分析、交互验证,完善黄河流域全新世古洪水序列及年代框架,深入挖掘“区域气候背景-异常洪水事件-人类活动”之间的相互关系,为全球变化背景下黄河流域洪水预测、防治及风险评估等提供科学依据。
Abstract:The study of Holocene paleoflood can remedy the limitation of modern flood monitoring records in time and space, and more scientifically identify the flooding regulations and mechanisms. It has gradually become one of the hotspots of the research of global changes. Due to the unique geological conditions in the Yellow River basin, floods have frequently happened in the Holocene history. The present flood risk is still very high in the basin, and therefore, it is one of the key areas of paleoflood research in China. This paper focuses on the research results of the paleoflood in the Yellow River basin published in the past ten years with special interests in sedimentary characteristics, hydrological reconstruction, chronological framework, and its relation to the rise and fall of civilization. Key problems and development trends of the current researches are also discussed, and it is suggested that the records of ancient floods at different geomorphologic locations in the basin should be further collected.
-
Key words:
- paleoflood /
- slack-water deposits /
- the Holocene /
- the Yellow River basin
-

-
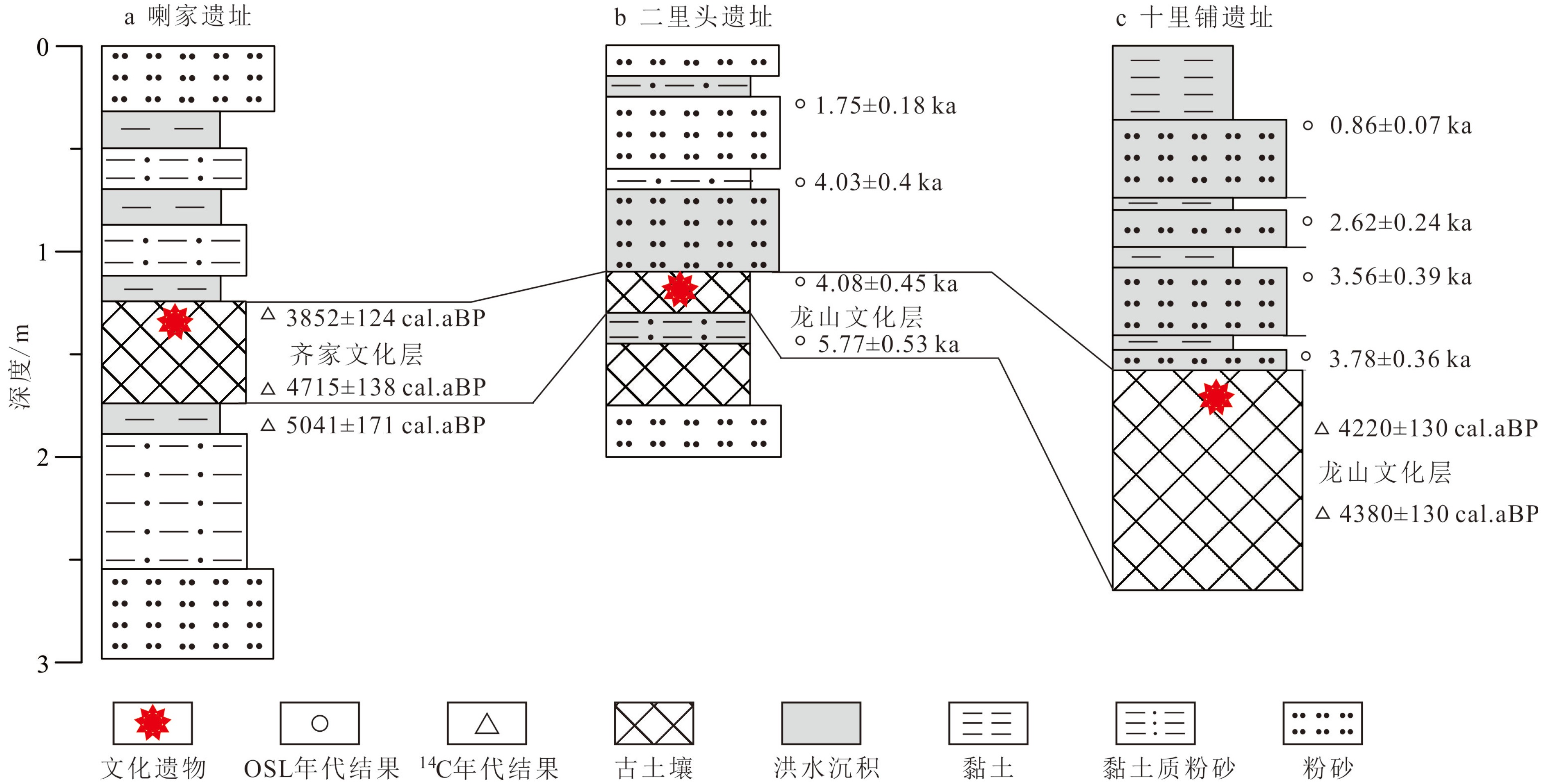
图 3 黄河洪泛平原异常洪沉积模式及相应频率曲线 (据文献[59]改编)
Figure 3.
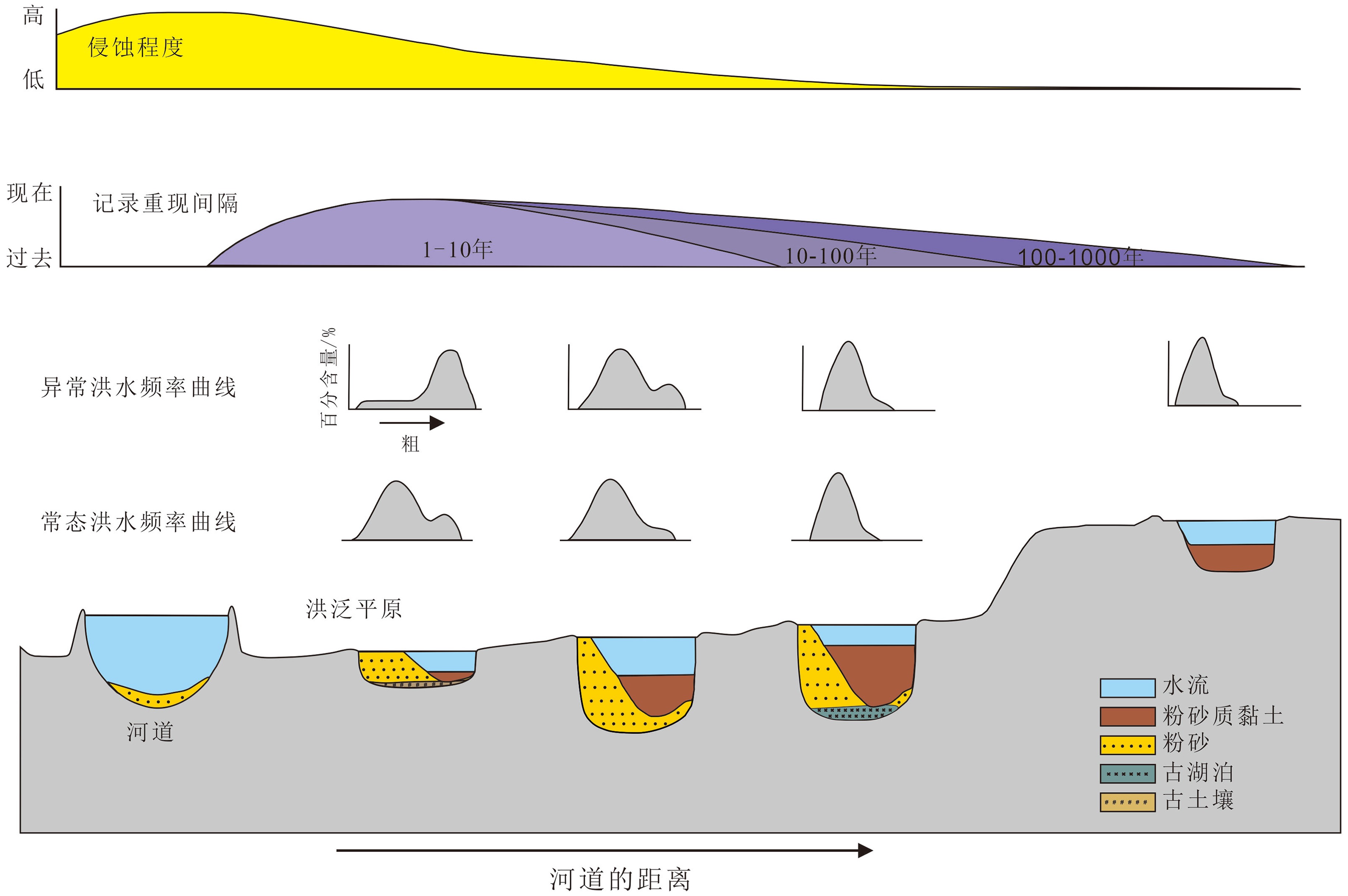
图 4 黄河下游洪水沉积频率曲线图 (据文献[48]改编)
Figure 4.
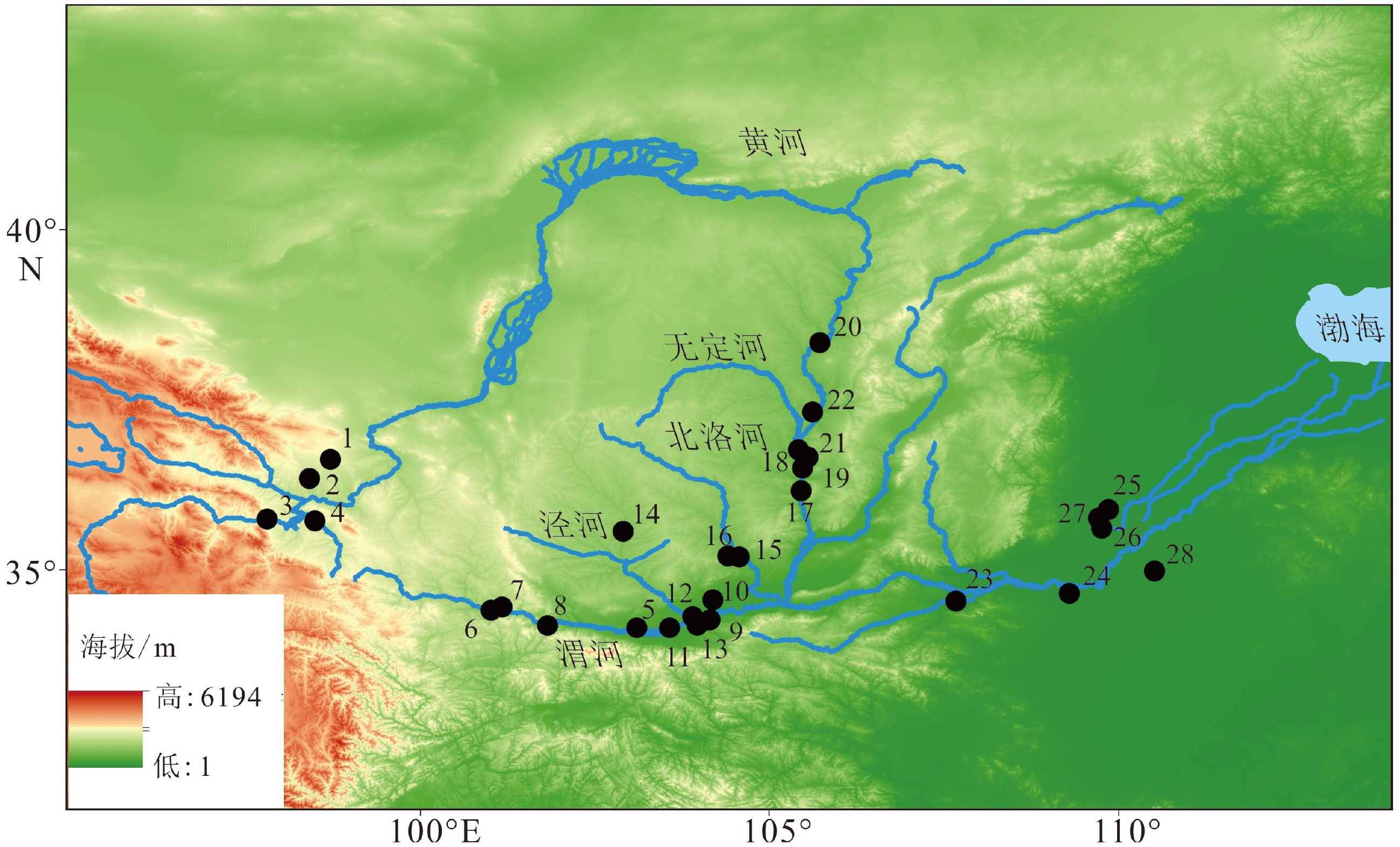
表 1 黄河流域古洪水水文信息重建
Table 1. Comparison of paleoflood hydrological information of some research sites in the Yellow River Basin
河段 古洪水期次 古洪水水位/m 古洪水洪峰流量/
(m3/s)近现代洪水实测最大
洪峰流量/(m3/s)方法 来源 上游靖远-景泰段 3200~3000 1310.3 12750~16310 5600 HEC-RAS [16] 洮河 480~300 1756.43~1759.75 4685~6700 2370 HEC-RAS [17] 渭河 1800~1600 1068.63~1073.15 11420~20100 4920 HEC-RAS [19] 晋陕峡谷马头关段 1900~1700
3400~3000520.1~524.5 25200~51500 24000 HEC-RAS [18] 晋陕峡谷龙门段 3200~2800 407.53~408.14 46280~48800 24000 HEC-RAS [23] 晋陕峡谷柳林滩段 3200~3000 640.05~640.91 48190~52260 24000 比降-面积 [24] 北洛河 7600~7400
5800~5000
4200~4000635.85 12600~14100 6280 比降-面积 [10] 延河 9500~8500 778.3 15000 6860 HEC-RAS [25] 表 2 黄河流域全新世古洪水研究剖面位置及年代数据
Table 2. The age data and location of the Holocene paleoflood research profiles
序号 河段 剖面位置 经纬度 年代获取方法 洪水时间/aBP 数据来源 1 上游 景泰峡谷段 36.7167°N
103.7167°E光释光测年 3200~3000 [14] [16] 2 喇家遗址剖面 36.4417°N
103.4172°E光释光测年、 放射性碳测年 4380~3970
2850~2720
2310~2140[26] 3 积石峡 35.8603°N
102.8147°E放射性碳测年 3870 [27] 4 洮河 35.8333°N、103.5000°E 光释光测年、考古年代、地层对比 300~480 [17] 5 中游 漆水河杨凌段 34.2989°N
108.1125°E光释光测年、考古年代 4300~4000
3100~3000[7] 6 渭河上游 34.5583°N
106.0278°E光释光测年、考古年代 1800~1600 [28] 7 渭河天水段 34.6000°N
106.1850°E地层对比、考古年代 3200~3000
1800~1600[19] 8 渭河宝鸡段 34.3333°N
106.8333°E地层对比、考古年代 3200~3000 [29] 9 渭河千河流域 34.4667°N
108.9167°E光释光测年 6000~5000 [30] 10 渭河支流石川河 34.7056°N
109.1997°E光释光测年、放射性碳测年 8900~9200
6200~6600
4100~4700
3700~3900
2300~2600[31] 11 渭河临潼段 34.4167°N
109.1667°E光释光测年 3200~3000 [32] 12 渭河咸阳段 34.3000°N
108.5833°E光释光测年 3200~2800 [33] [34] 13 泾河高陵段 34.3333°N
108.9833°E光释光测年、考古年代 4200~4000
3200~2800[35] [36] 14 马莲河合水段 35.6861°N
107.9167°E地层对比 4200~4000 [37] 15 北洛河白水段 35.3167°N
109.5806°E地层对比 4500~4000 [38] 16 北洛河宜君段 35.3333°N
109.4167°E光释光测年 地层对比 7600~7400
5800~5000
4200~4000[10] 17 晋陕峡谷吉县段 36.2667°N
110.4667°E光释光测年、地层对比 9000~8500
3200~3000[39] 18 晋陕峡谷永和关段 36.8533°N110.4269°E 光释光测年、地层对比 3200~3000 [20] 19 晋陕峡谷马头关段 36.5904°N
110.4849°E光释光测年 3400~3000
1900~1700[18] 20 晋陕峡谷柳林滩段 38.3818°N
110.7383°E光释光测年 10800~10200
10600~9600[15] 21 晋陕峡谷龙门段 36.7500°N
110.5625°E光释光测年 地层对比 3200~2800
1800~1700
770~610[40] [41] 22 晋陕峡谷吴堡段 37.3917°N
110.6306°E光释光测年、地层对比 3200~2900 [42] 23 二里头遗址剖面 34.6887°N
112.6875°E光释光测年、放射性碳测年 6000~5500
4000~3800
1800~1700[43] 24 下游 开封段 34.7943°N
114.3069°E放射性碳测年 考古年代 308 [44] 25 内黄三杨庄剖面 35.7275°N
114.7734°E放射性碳测年、考古年代 4200~2000 [45] 26 内黄大张龙剖面 35.9946°N
114.8692°E放射性碳测年 902~822 [46] 27 内黄岸上剖面 35.8757°N
114.723°E光释光测年、放射性碳测年、考古年代 4200~3000 [47] 28 菏泽段 35.1150°N
115.5310°E光释光测年、放射性碳测年、考古年代 4000~3500 [48] -
[1] 朴世龙, 张新平, 陈安平, 等. 极端气候事件对陆地生态系统碳循环的影响[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2019, 62(10):1551-1563 doi: 10.1007/s11430-018-9363-5
PIAO Shilong, ZHANG Xinping, CHEN Anping, et al. The impacts of climate extremes on the terrestrial carbon cycle: A review [J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 2019, 62(10): 1551-1563. doi: 10.1007/s11430-018-9363-5
[2] Baker V R, Pickup G. Flood geomorphology of the Katherine Gorge, northern Territory, Australia [J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 1987, 98(6): 635-646. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(1987)98<635:FGOTKG>2.0.CO;2
[3] Baker V R. Paleoflood hydrology: Origin, progress, prospects [J]. Geomorphology, 2008, 101(1-2): 1-13. doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2008.05.016
[4] Wilhelm B, Ballesteros Cánovas J A, Macdonald N, et al. Interpreting historical, botanical, and geological evidence to aid preparations for future floods [J]. WIREs Water, 2019, 6(1): e1318. doi: 10.1002/wat2.1318
[5] Liu W M, Carling P A, Hu K H, et al. Outburst floods in China: a review [J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2019, 197: 102895. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2019.102895
[6] Kozlowski T T. Extent, causes, and impacts of flooding[M]//Kozlowski T T. Flooding and Plant Growth. San Diego: Academic Press, 1984: 1-7.
[7] 黄春长, 庞奖励, 查小春, 等. 黄河流域关中盆地史前大洪水研究—以周原漆水河谷地为例[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2011, 41(11):1658-1669 doi: 10.1360/zd-2011-41-11-1658
HUANG Chunchang, PANG Jiangli, ZHA Xiaochun, et al. Prehistorical floods in the Guanzhong basin in the Yellow River drainage area: a case study along the Qishuihe River valley over the Zhouyuan loess tableland [J]. Science Sinica Terrae, 2011, 41(11): 1658-1669. doi: 10.1360/zd-2011-41-11-1658
[8] Yang D Y, Yu G, Xie Y B, et al. Sedimentary records of large Holocene floods from the middle reaches of the Yellow River, China [J]. Geomorphology, 2000, 33(1-2): 73-88. doi: 10.1016/S0169-555X(99)00111-7
[9] 谢悦波, 费宇红, 沈起鹏. 古洪水平流沉积与水位[J]. 地球学报, 2001, 22(4):320-323 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1006-3021.2001.04.008
XIE Yuebo, FEI Yuhong, SHEN Qipeng. Slackwater deposits and flow peak level of a paleoflood [J]. Acta Geoscientia Sinica, 2001, 22(4): 320-323. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1006-3021.2001.04.008
[10] Zhang Y Z, Huang C C, Pang J L, et al. Holocene palaeoflood events recorded by slackwater deposits along the middle Beiluohe River valley, middle Yellow River basin, China [J]. Boreas, 2015, 44(1): 127-138. doi: 10.1111/bor.12095
[11] Benito G, Macklin M G, Panin A, et al. Recurring flood distribution patterns related to short-term Holocene climatic variability [J]. Scientific Reports, 2015, 5: 16398. doi: 10.1038/srep16398
[12] 李晓刚. 黄河流域古洪水研究进展[J]. 商洛学院学报, 2013, 27(2):57-63 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-0033.2013.02.015
LI Xiaogang. Advances of paleoflood research in the Yellow River Basin [J]. Journal of Shangluo University, 2013, 27(2): 57-63. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-0033.2013.02.015
[13] 陈莹璐, 黄春长, 张玉柱, 等. 黄河源区玛曲段末次冰消期古洪水事件及其光释光测年研究[J]. 冰川冻土, 2017, 39(3):549-562
CHEN Yinglu, HUANG Chunchang, ZHANG Yuzhu, et al. Study of the sedimentology and OSL dating of the Last Deglaciation paleoflood events along Maqu section in the source regions of the Yellow River [J]. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology, 2017, 39(3): 549-562.
[14] 赵雪如, 黄春长, 庞奖励, 等. 黄河上游靖远金坪段全新世古洪水沉积物特征[J]. 山地学报, 2016, 34(2):173-180
ZHAO Xueru, HUANG Chunchang, PANG Jiangli, et al. Sediment characteristics of the palaeoflood slackwater deposits at Jingyuan-Jinping site in the upper reaches of the Yellow River [J]. Mountain Research, 2016, 34(2): 173-180.
[15] 刘雯瑾, 黄春长, 庞奖励, 等. 黄河柳林滩段全新世古洪水滞流沉积物物源研究[J]. 水土保持学报, 2016, 30(2):136-142
LIU Wenjin, HUANG Chunchang, PANG Jiangli, et al. Study on provenance of Holocene flood slackwater deposits in the Liulintan reach of the Yellow River [J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2016, 30(2): 136-142.
[16] Hu G M, Huang C C, Zhou Y L, et al. Extreme paleoflood events 3200-3000 a BP in the Jingyuan–Jingtai reaches of the upper Yellow River, China [J]. The Holocene, 2016, 26(5): 790-800. doi: 10.1177/0959683615618257
[17] 胡迎, 黄春长, 周亚利, 等. 黄河上游洮河流域全新世古洪水水文学研究[J]. 干旱区地理, 2017, 40(5):1029-1037
HU Ying, HUANG Chunchang, ZHOU Yali, et al. Hydrological studies of the Holocene palaeoflood in the Taohe River basin of the upper Yellow River [J]. Arid Land Geography, 2017, 40(5): 1029-1037.
[18] 刘雯瑾, 黄春长, 庞奖励, 等. 黄河马头关段全新世古洪水水文恢复及气候背景研究[J]. 干旱区地理, 2017, 40(1):85-93
LIU Wenjin, HUANG Chunchang, PANG Jiangli, et al. Holocene Palaeoflood and climatic changes at the Matouguan Reach of the Yellow River [J]. Arid Land Geography, 2017, 40(1): 85-93.
[19] 石彬楠, 黄春长, 庞奖励, 等. 渭河上游天水东段全新世古洪水水文学恢复研究[J]. 干旱区地理, 2016, 39(3):573-581
SHI Binnan, HUANG Chunchang, PANG Jiangli, et al. Hydrological reconstructions of the Holocene Palaeoflood in the Tianshui East Reach of the upper Weihe River [J]. Arid Land Geography, 2016, 39(3): 573-581.
[20] 黄春长, 李晓刚, 庞奖励, 等. 黄河永和关段全新世古洪水研究[J]. 地理学报, 2012, 67(11):1493-1504 doi: 10.11821/xb201211006
HUANG Chunchang, LI Xiaogang, PANG Jiangli, et al. Palaeoflood sedimentological and hydrological studies on the Yongheguan reach in the middle Yellow River [J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2012, 67(11): 1493-1504. doi: 10.11821/xb201211006
[21] 刘涛. 河流古洪水水文学重建的多种方法比较研究——以黄河中游和汉江上游为例[D]. 陕西师范大学硕士学位论文, 2015.
LIU Tao. Comparative study of hydrological reconstructions of Paleoflood: case studies of bedrock gorge reach in the middle Yellow River basin and upper Hanjiang River basin[D]. Master Dissertation of Shaanxi Normal University, 2015.
[22] Baker V R. Palaeoflood hydrology in a global context [J]. CATENA, 2006, 66(1-2): 161-168. doi: 10.1016/j.catena.2005.11.016
[23] 胡贵明, 黄春长, 周亚利, 等. 黄河靖远-景泰段全新世古洪水水文事件水文指标模拟及气候背景分析[J]. 资源科学, 2015, 37(10):2059-2067
HU Guiming, HUANG Chunchang, ZHOU Yali, et al. Hydrological reconstructions and climate events of the Holocene paleoflood in the Jingyuan-Jingtai reach on the Yellow River [J]. Resources Science, 2015, 37(10): 2059-2067.
[24] 范龙江, 黄春长, 庞奖励, 等. 黄河柳林段全新世特大洪水水文学研究[J]. 土壤通报, 2014, 45(3):524-530
FAN Longjiang, HUANG Chunchang, PANG Jiangli, et al. Palaeoflood hydrological studies in the Lianghekou reach in the middle Yellow River [J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2014, 45(3): 524-530.
[25] Guo Y Q, Huang C C, Pang J L, et al. Reconstruction palaeoflood hydrology using slackwater flow depth method in the Yanhe River valley, middle Yellow River basin, China [J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2017, 544: 156-171. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2016.11.017
[26] Ma M M, Dong G H, Chen F H, et al. Process of paleofloods in Guanting basin, Qinghai Province, China and possible relation to monsoon strength during the mid-Holocene [J]. Quaternary International, 2014, 321: 88-96. doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2012.05.031
[27] Wu Q L, Zhao Z J, Liu L, et al. Outburst flood at 1920 BCE supports historicity of China's Great flood and the Xia Dynasty [J]. Science, 2016, 353(6299): 579-582. doi: 10.1126/science.aaf0842
[28] 朱向锋, 黄春长, 庞奖励, 等. 渭河天水峡谷全新世特大洪水水文学研究[J]. 地理科学进展, 2010, 29(7):840-846 doi: 10.11820/dlkxjz.2010.07.010
ZHU Xiangfeng, HUANG Chunchang, PANG Jiangli, et al. Palaeo-Hydrologrcal studies of the Holocene extreme floods in the Tianshui Gorges of the Weihe River [J]. Progress in Geography, 2010, 29(7): 840-846. doi: 10.11820/dlkxjz.2010.07.010
[29] 万红莲, 黄春长, 庞奖励, 等. 渭河宝鸡峡全新世古洪水事件研究[J]. 陕西师范大学学报: 自然科学版, 2010, 38(2):76-82
WAN Honglian, HUANG Chunchang, PANG Jiangli, et al. Palaeoflood events in the Baojixia Gorges of the Weihe River [J]. Journal of Shaanxi Normal University: Natural Science Edition, 2010, 38(2): 76-82.
[30] 王恒松, 黄春长, 周亚利, 等. 关中西部千河流域全新世古洪水事件光释光测年研究[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2012, 42(3):390-401 doi: 10.1360/zd-2012-42-3-390
WANG Hengsong, HUANG Chunchang, ZHOU Yali, et al. OSL dating of the Holocene paleoflood events on the Qianhe River in the Guanzhong Basin, China [J]. Scientia Sinica Terrae, 2012, 42(3): 390-401. doi: 10.1360/zd-2012-42-3-390
[31] He Z, Long H, Yang L H, et al. Luminescence dating of a fluvial sequence using different grain size fractions and implications on Holocene flooding activities in Weihe Basin, central China [J]. Quaternary Geochronology, 2019, 49: 123-130. doi: 10.1016/j.quageo.2018.05.007
[32] 王恒松, 黄春长, 周亚利, 等. 全新世古洪水事件光释光测年研究——以渭河下游临潼段为例[J]. 地球学报, 2012, 33(2):227-235
WANG Hengsong, HUANG Chunchang, ZHOU Yali, et al. OSL dating of the Holocene paleoflood events: a case study of the Lintong segment in the lower Weihe River Valley [J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2012, 33(2): 227-235.
[33] 赵梅, 查小春, 黄春长, 等. 渭河中游全新世晚期古洪水沉积物特征[J]. 干旱区研究, 2012, 29(5):920-925
ZHAO Mei, ZHA Xiaochun, HUANG Chunchang, et al. Analysis on depositional features of the Late Holocene Paleo-flood slackwater deposit in middle reaches of the Weihe River [J]. Arid Zone Research, 2012, 29(5): 920-925.
[34] 王恒松, 黄春长, 周亚利, 等. 渭河咸阳段全新世古洪水事件光释光测年研究[J]. 沉积学报, 2012, 30(2):346-355
WANG Hengsong, HUANG Chunchang, ZHOU Yali, et al. OSL dating of the Palaeoflood events in the middle reaches of the Weihe River [J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2012, 30(2): 346-355.
[35] 顾洪亮, 黄春长, 周亚利, 等. 关中盆地杨官寨遗址古洪水事件释光测年[J]. 地理研究, 2012, 31(10):1837-1848
GU Hongliang, HUANG Chunchang, ZHOU Yali, et al. OSL dating study on the Palaeoflood events recorded in the Yangguanzhai Neolithic ruins in the Guanzhong basin [J]. Geographical Research, 2012, 31(10): 1837-1848.
[36] 张玉柱, 黄春长, 庞奖励, 等. 泾河下游全新世古洪水滞流沉积物研究[J]. 土壤通报, 2012, 43(3):521-528
ZHANG Yuzhu, HUANG Chunchang, PANG Jiangli, et al. Sedimentary studies of the Holocene flood slackwater deposits in the lower reaches of the Jinghe River [J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2012, 43(3): 521-528.
[37] 周芳, 查小春, 黄春长, 等. 马莲河全新世古洪水沉积学和水文学研究[J]. 地理科学进展, 2011, 30(9):1081-1087 doi: 10.11820/dlkxjz.2011.09.002
ZHOU Fang, ZHA Xiaochun, HUANG Chunchang, et al. Study on Holocene paleoflood in Malian River Basin [J]. Progress in Geography, 2011, 30(9): 1081-1087. doi: 10.11820/dlkxjz.2011.09.002
[38] 赵明, 黄春长, 庞奖励, 等. 北洛河中游白水段峡谷全新世特大洪水水文学研究[J]. 自然灾害学报, 2011, 20(5):155-161
ZHAO Ming, HUANG Chunchang, PANG Jiangli, et al. Palaeo-flood hydrological studies in the middle reaches of Beiluo River [J]. Journal of Natural Disasters, 2011, 20(5): 155-161.
[39] 郝高建, 黄春长, 刑莹莹, 等. 黄河晋陕峡谷吉县段全新世古洪水平流沉积特征研究[J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 2011, 25(3):106-112
HAO Gaojian, HUANG Chunchang, XING Yingying, et al. Sedimentary characteristics of the slackwater deposits of Holocene extreme floods in the FJJ section in the Yellow River valley, Ji county [J]. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 2011, 25(3): 106-112.
[40] 石彬楠, 黄春长, 庞奖励, 等. 黄河龙门段商周转折时期的古洪水事件及气候背景[J]. 湖泊科学, 2017, 29(1):234-245 doi: 10.18307/2017.0125
SHI Binnan, HUANG Chunchang, PANG Jiangli, et al. Palaeoflood events and climate change at the turning time from the Shang to Zhou dynasty in the Longmen reach of the Yellow River [J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 2017, 29(1): 234-245. doi: 10.18307/2017.0125
[41] Zhao X R, Huang C C, Pang J L, et al. Holocene climatic events recorded in palaeoflood slackwater deposits along the middle Yiluohe River valley, middle Yellow River basin, China [J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2016, 123: 85-94. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2016.04.002
[42] Fan L J, Huang C C, Pang J L, et al. Sedimentary records of palaeofloods in the Wubu Reach along the Jin-Shaan gorges of the middle Yellow River, China [J]. Quaternary International, 2015, 380-381: 368-376. doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2014.04.055
[43] Zhang Y Z, Huang C C, Tan Z H, et al. Prehistoric and historic overbank floods in the Luoyang Basin along the Luohe River, middle Yellow River basin, China [J]. Quaternary International, 2019, 521: 118-128. doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2019.06.023
[44] Storozum M, Lu P, Wang S Y, et al. Geoarchaeological evidence of the AD 1642 Yellow River flood that destroyed Kaifeng, a former capital of dynastic China [J]. Scientific Reports, 2020, 10(1): 3765. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-60169-1
[45] 司徒克, 秦臻, 刘海旺, 等. 河南省内黄县河流地质考古研究[J]. 第四纪研究, 2020, 40(2):579-593 doi: 10.11928/j.issn.1001-7410.2020.02.26
Storozum M J, QIN Zhen, LIU Haiwang, et al. The alluvial geoarchaeology of Neihuang County, Henan Province [J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2020, 40(2): 579-593. doi: 10.11928/j.issn.1001-7410.2020.02.26
[46] Storozum M J, Zhen Q, Ren X L, et al. The collapse of the North Song dynasty and the AD 1048-1128 Yellow River floods: Geoarchaeological evidence from northern Henan Province, China [J]. The Holocene, 2018, 28(11): 1759-1770. doi: 10.1177/0959683618788682
[47] Kidder T, Liu H W, Xu Q H, et al. The alluvial geoarchaeology of the Sanyangzhuang site on the Yellow River Floodplain, Henan Province, China [J]. Geoarchaeology, 2012, 27(4): 324-343. doi: 10.1002/gea.21411
[48] Yu S Y, Hou Z F, Chen X X, et al. Extreme flooding of the lower Yellow River near the Northgrippian-Meghalayan boundary: evidence from the Shilipu archaeological site in southwestern Shandong Province, China [J]. Geomorphology, 2020, 350: 106878. doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2019.106878
[49] 张俊娜, 夏正楷. 中原地区4 ka BP前后异常洪水事件的沉积证据[J]. 地理学报, 2011, 66(5):685-697 doi: 10.11821/xb201105011
ZHANG Junna, XIA Zhengkai. Deposition evidences of the 4 ka BP Flood events in Central China Plains [J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2011, 66(5): 685-697. doi: 10.11821/xb201105011
[50] Storozum M, Liu H W, Qin Z, et al. Early evidence of irrigation technology in the North China Plain: Geoarchaeological investigations at the Anshang Site, Neihuang County, Henan Province, China [J]. Geoarchaeology, 2018, 33(2): 143-161. doi: 10.1002/gea.21634
[51] 李中轩, 朱诚, 吴国玺, 等. 河南省史前人类遗址的时空分布及其驱动因子[J]. 地理学报, 2013, 68(11):1527-1537 doi: 10.11821/dlxb201311008
LI Zhongxuan, ZHU Cheng, WU Guoxi, et al. Spatial and temporal distribution of prehistoric human sites and its driving factors in Henan province [J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2013, 68(11): 1527-1537. doi: 10.11821/dlxb201311008
[52] Dong G H, Zhang F Y, Liu F W, et al. Multiple evidences indicate no relationship between prehistoric disasters in Lajia site and outburst flood in upper Yellow River valley, China [J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 2018, 61(4): 441-449. doi: 10.1007/s11430-017-9079-3
[53] Han J C. Comment on “Outburst flood at 1920 BCE supports historicity of China’s Great Flood and the Xia dynasty” [J]. Science, 2017, 355(6332): 1382.
[54] Huang C C, Zhou Y L, Zhang Y Z, et al. Comment on “Outburst flood at 1920 BCE supports historicity of China’s Great Flood and the Xia dynasty” [J]. Science, 2017, 355(6332): 1382.
[55] Wu W X, Dai J H, Zhou Y, et al. Comment on “Outburst flood at 1920 BCE supports historicity of China’s Great Flood and the Xia dynasty” [J]. Science, 2017, 355(6332): 1382.
[56] Merz B, Aerts J, Arnbjerg-Nielsen K, et al. Floods and climate: emerging perspectives for flood risk assessment and management [J]. Natural Hazards and Earth System Sciences, 2014, 14(7): 1921-1942. doi: 10.5194/nhess-14-1921-2014
[57] Hall J, Arheimer B, Borga M, et al. Understanding flood regime changes in Europe: a state-of-the-art assessment [J]. Hydrology and Earth System Sciences, 2014, 18(7): 2735-2772. doi: 10.5194/hess-18-2735-2014
[58] Lewin J, Macklin M G. Preservation potential for Late Quaternary river alluvium [J]. Journal of Quaternary Science, 2003, 18(2): 107-120. doi: 10.1002/jqs.738
[59] Toonen W H J, Munoz S E, Cohen K M, et al. High-Resolution sedimentary Paleoflood records in alluvial river environments: a review of recent methodological advances and application to flood hazard assessment[M]//Herget J, Fontana A. Palaeohydrology: Traces, Tracks and Trails of Extreme Events. Cham: Springer, 2020: 213-228.
[60] Yu S Y, Chen X X, Cheng P, et al. Freshwater radiocarbon reservoir age in the lower Yellow River floodplain during the Late Holocene [J]. The Holocene, 2018, 28(1): 119-126. doi: 10.1177/0959683617715699
[61] Matsumoto D, Sawai Y, Yamada M, et al. Erosion and sedimentation during the September 2015 flooding of the Kinu River, central Japan [J]. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6: 34168. doi: 10.1038/srep34168
[62] Toonen W H J, Winkels T G, Cohen K M, et al. Lower Rhine historical flood magnitudes of the last 450 years reproduced from grain-size measurements of flood deposits using End Member Modelling [J]. CATENA, 2015, 130: 69-81. doi: 10.1016/j.catena.2014.12.004
[63] Peng F, Kasse C, Prins M A, et al. Paleoflooding reconstruction from Holocene levee deposits in the Lower Meuse valley, the Netherlands [J]. Geomorphology, 2020, 352: 107002. doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2019.107002
[64] Shen H Y, Yu L P, Zhang H M, et al. OSL and radiocarbon dating of flood deposits and its paleoclimatic and archaeological implications in the Yihe River Basin, East China [J]. Quaternary Geochronology, 2015, 30: 398-404. doi: 10.1016/j.quageo.2015.03.005
[65] Zhao H, Liu Z, Song L, et al. OSL dating of flood sediments in the North China Plain [J]. Quaternary Geochronology, 2019, 49: 101-107. doi: 10.1016/j.quageo.2018.07.010
[66] 杨铭, 王松娜, 康树刚, 等. 河南三杨庄剖面光释光年代学研究[J]. 地球环境学报, 2018, 9(6):580-588
YANG Ming, WANG Songna, KANG Shugang, et al. Optically stimulated luminescence dating of Sanyangzhuang profile, Henan Province [J]. Journal of Earth Environment, 2018, 9(6): 580-588.
[67] Yu S Y, Li C H, Chen X X, et al. Rates of organic carbon burial in a floodplain lake of the Lower Yellow River Area during the Late Holocene [J]. Radiocarbon, 2014, 56(3): 1129-1138. doi: 10.2458/56.17923
[68] Huang C C, Pang J L, Zha X C, et al. Extraordinary floods related to the climatic event at 4200 a BP on the Qishuihe River, middle reaches of the Yellow River, China [J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2011, 30(3-4): 460-468. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2010.12.007
[69] 周晓龙, 于学峰. 长江、黄河流域全新世古洪水事件对比研究[J]. 地球环境学报, 2013, 4(5):1427-1436 doi: 10.7515/JEE201305001
ZHOU Xiaolong, YU Xuefeng. Correlation studies on palaeoflood events in the drainage area of Yangtze and Yellow River during the Holocene [J]. Journal of Earth Environment, 2013, 4(5): 1427-1436. doi: 10.7515/JEE201305001
[70] Tan L C, Shen C C, Cai Y J, et al. Great flood in the middle-lower Yellow River reaches at 4000 a BP inferred from accurately-dated stalagmite records [J]. Science Bulletin, 2018, 63(4): 206-208. doi: 10.1016/j.scib.2018.01.023
[71] Yang Q, Ma Z G, Xu B L. Modulation of monthly precipitation patterns over East China by the Pacific Decadal Oscillation [J]. Climatic Change, 2017, 144(3): 405-417. doi: 10.1007/s10584-016-1662-9
[72] Su K, Kidder T R. Humans and climate change in the middle and lower Yellow River of China [J]. Quaternary International, 2019, 521: 111-117. doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2019.06.031
-



 下载:
下载: