Evolution characteristics of biogas in seabed sediments and their influencing factors on gas sources
-
摘要:
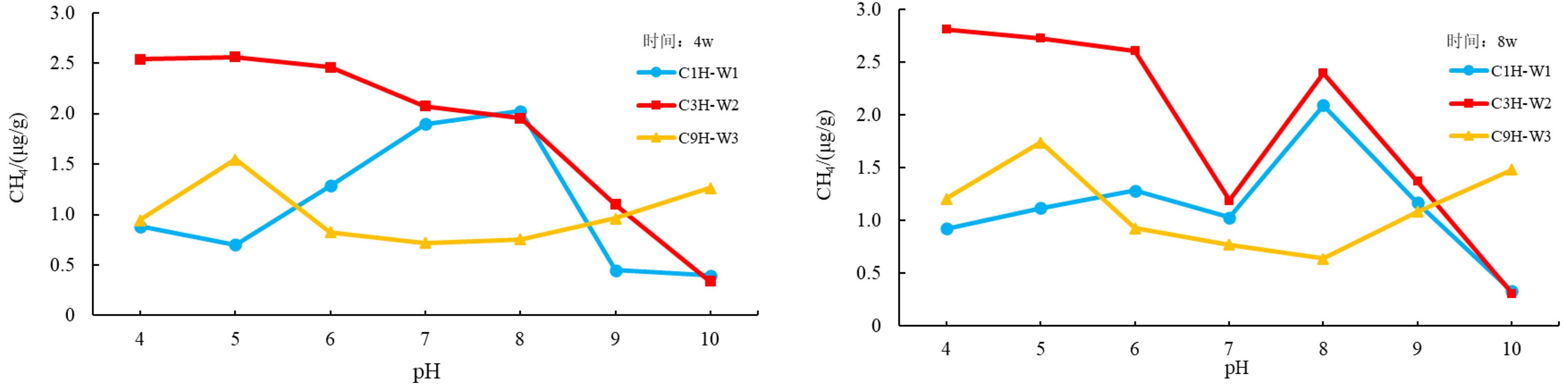
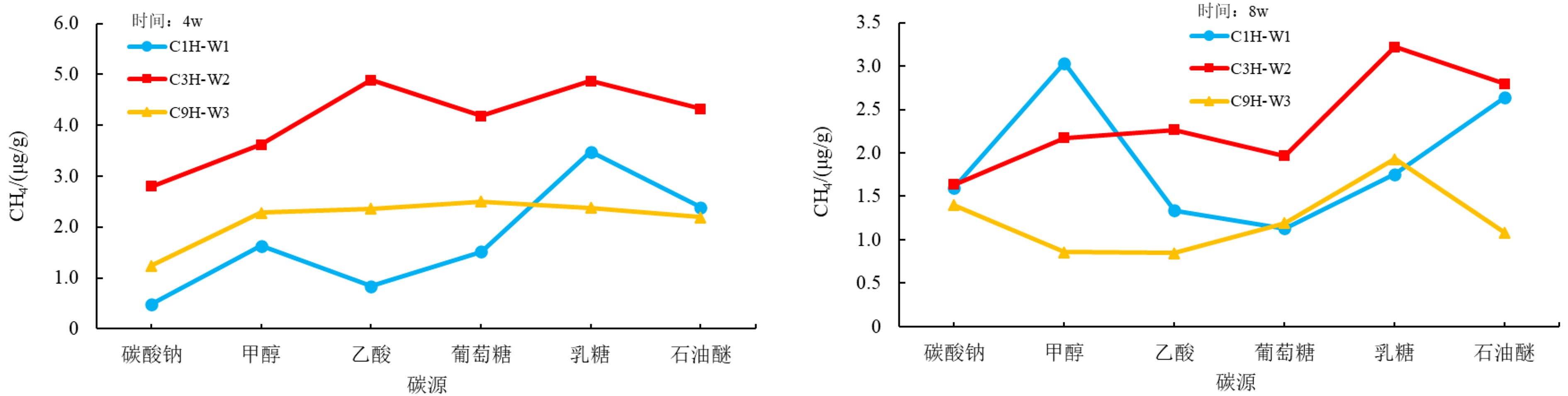
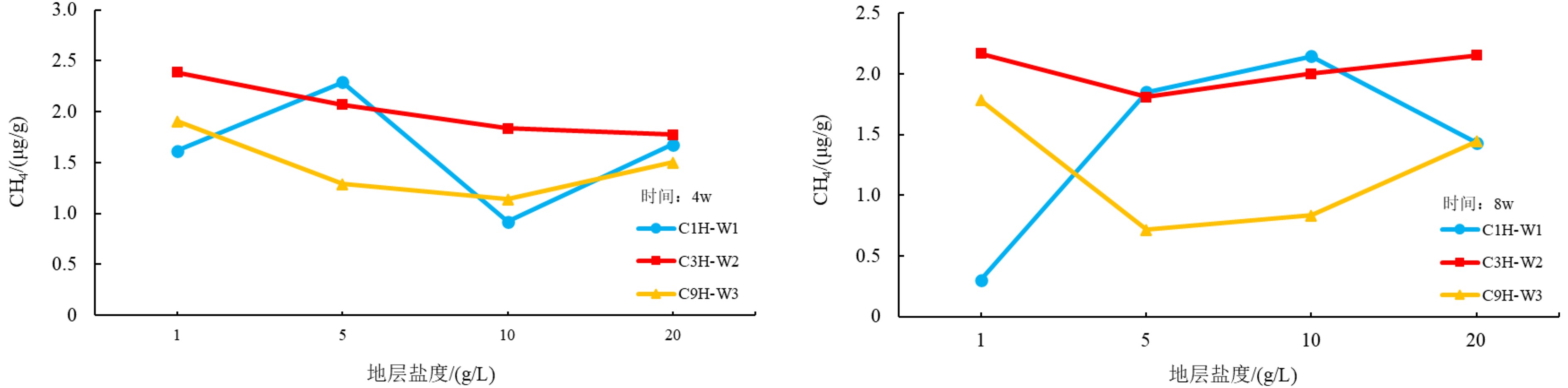
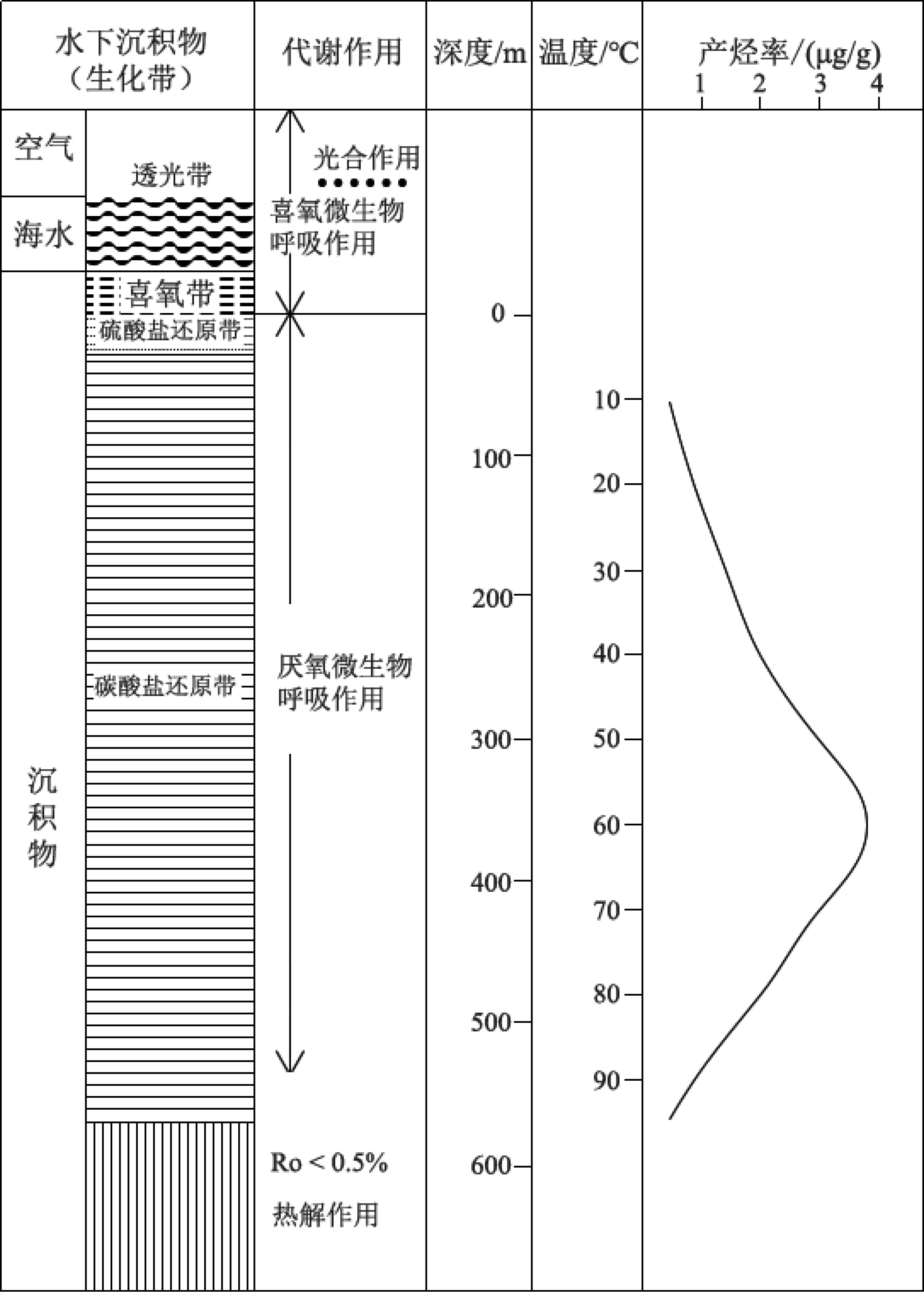
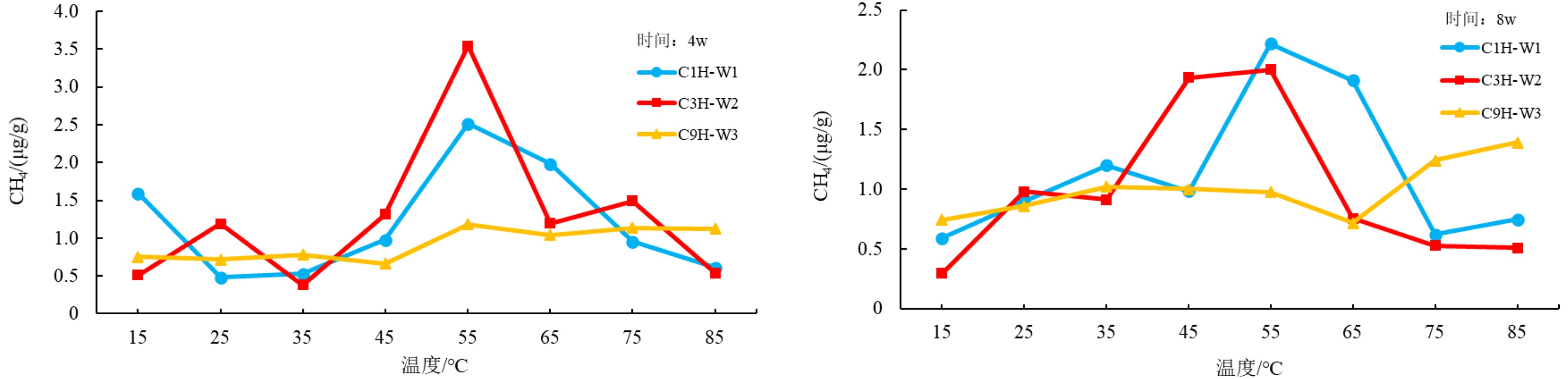
为研究海洋天然气水合物生物气源的影响因素及演化模式,选择了某海域3个海底沉积物样品进行微生物演化模拟实验。通过改变生气条件,分析不同温度、pH、碳源、碳源浓度、氮源和地层盐度对海底沉积物产甲烷菌生物气生成的影响。实验结果表明:某海域产甲烷菌在55 ℃时CH4产气量最高;pH为6~8时CH4产气量较高,且pH为10时仍有CH4产出;加入氮源、碳源都有一定程度的促进作用,但过高的碳源浓度会抑制CH4产气量;地层盐度的变化对CH4产气量影响不明显。根据不同温度微生物演化及产气率可将生物气演化分早期、高峰期和晚期3个阶段;pH为6~8、碳源选取乳糖(双糖)且浓度2.0 mL/L以及蛋白质为主要氮源时明显促进产甲烷菌产气率;按照采样点海域地温梯度及环境条件,认为采样点所在海域海底生物气源岩埋藏深度大约为200~500 m,具有弱碱性、弱径流水动力条件的地区可以作为重点勘查地区。
Abstract:In order to seek for the influencing factors on the biogenic gas sources in marine natural gas hydrate deposits and its genetic model, three marine sediment samples were collected for microbial evolution experiment. Various biogas production conditions, such as temperatures, pH, carbon source, carbon source concentration, nitrogen source, and formation salinity are changed to look for their effects on the biogas production by methanogenic bacteria in seabed sediments. The experimental results suggest that the methanogenic bacteria reach the highest methane production rate when temperature is at 55 ℃. The production remains high when pH changes between 6~8, and there is still methane gas produced until pH increased to 10. Both the nitrogen or carbon have certain degrees of promoting effect. However, carbon source concentration will inhibit methane gas production if it is too high. Change of formation salinity have no significant effect on methane gas production as the experiment indicates. According to the microbial evolution and gas production rate at different temperatures, biogas evolution can be divided into three stages: early stage, peak stage and late stage. When pH is between 6~8, and lactose (disaccharide) in concentration of 2.0 ml/L is selected as carbon source, and protein selected as the main nitrogen source, the biogas production rate of methanogens is significantly enhanced. Based on the geothermal gradient and environmental conditions of the sampling area, it is inferred that the major biogenic gas source rock is buried in a depth of about 200~500 m, and the area with weak alkalinity and weak runoff is the most favorable exploration target.
-
Key words:
- methanogen /
- gas production potential /
- biogas /
- simulation experiment /
- sediment
-

-
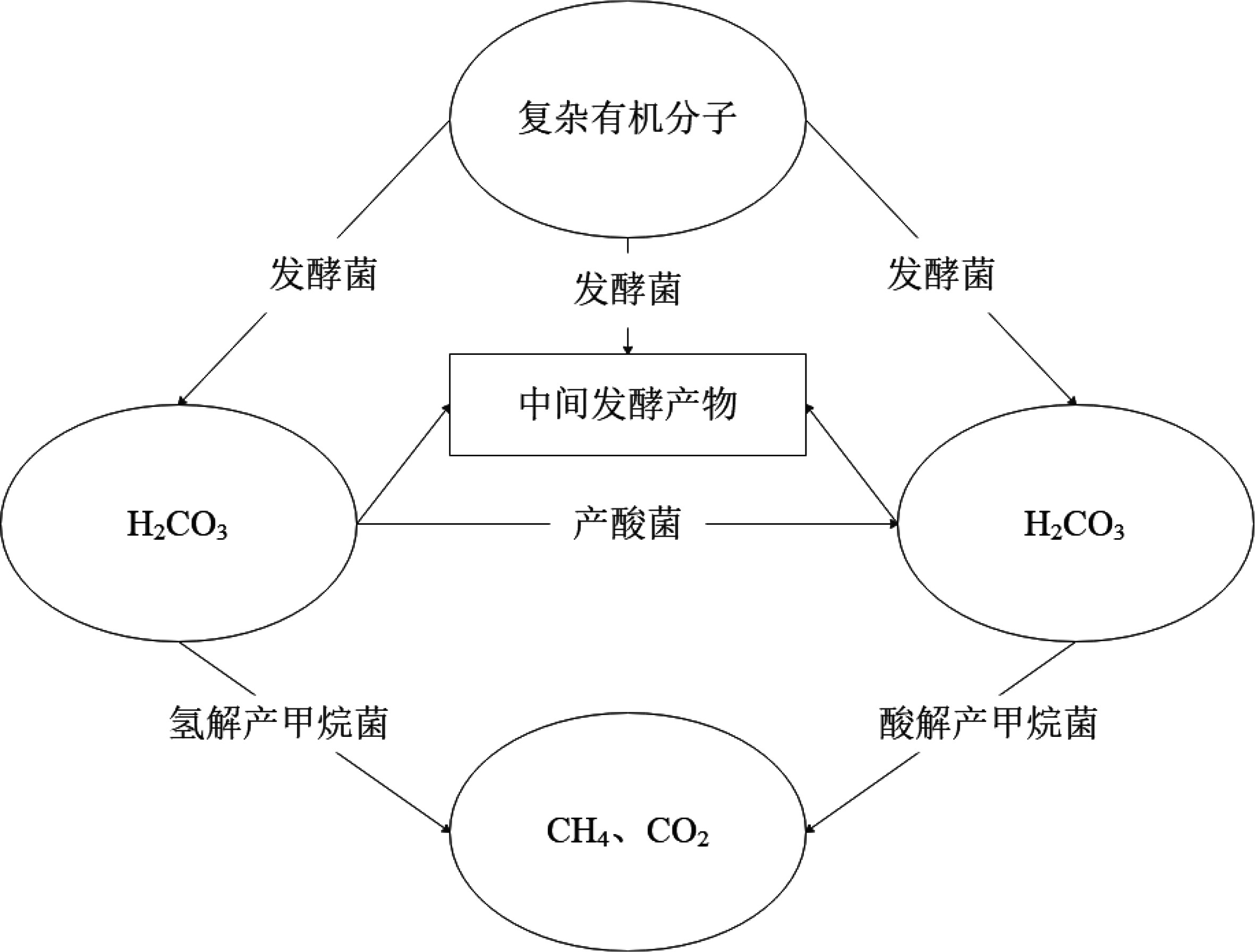
图 4 生物甲烷形成途径示意图[28]
Figure 4.
表 1 实验用样品基础信息表
Table 1. Basic information of experiment samples
样品编号 采样深度/m 含水量/% 含碳量/% 含硫量/% 母质类型 C1H 2.5 46.80 0.74 0.15 ⅡB C3H 7.5 38.00 0.85 0.31 ⅡB C9H 22.5 40.00 0.87 0.66 ⅡB 表 2 不同控制因素实验设计表
Table 2. Experimental design upon different control factors
影响条件 影响条件设置 备注 温度/℃ 15、25、35、45、55、65、75、85 使用不同水浴培养箱来控制不同温度 pH值 4.0、5.0、6.0、7.0、8.0、9.0、10.0 使用无菌无氧1 mol/L的HCl和NaOH溶液来调节pH值 碳源 碳酸钠、甲醇、乙酸、葡萄糖、乳糖、石油醚 碳酸钠、葡萄糖、乳糖为1 g/L,甲醇、乙酸、石油醚为1.0 mL/L 碳源浓度/(mL/L) 0.1、0.5、1.0、2.0、5.0 选用乙酸作为碳源 氮源 硝酸钠、亚硝酸钠、氯化铵、蛋白胨、酵母膏 试剂浓度均为1 g/L 盐度/(g/L) 1、5、10、20 使用1 000 mL蒸馏水配置对应盐度 -
[1] 张光学, 黄永样, 祝有海, 等. 南海天然气水合物的成矿远景[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2002, 22(1):75-81
ZHANG Guangxue, HUANG Yongxiang, ZHU Youhai, et al. Prospect of gas hydrate resources in the South China Sea [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2002, 22(1): 75-81.
[2] 吴必豪, 张光学, 祝有海, 等. 中国近海天然气水合物的研究进展[J]. 地学前缘, 2003, 10(1):177-189 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2003.01.021
WU Bihao, ZHANG Guangxue, ZHU Youhai, et al. Progress of gas hydrate investigation in China offshore [J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2003, 10(1): 177-189. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2003.01.021
[3] Davis K J, Gerlach R. Transition of biogenic coal-to-methane conversion from the laboratory to the field: A review of important parameters and studies [J]. International Journal of Coal Geology, 2018, 185: 33-43. doi: 10.1016/j.coal.2017.11.006
[4] Green M S, Flanegan K C, Gilcrease P C. Characterization of a methanogenic consortium enriched from a coalbed methane well in the Powder River Basin, U. S. A. [J]. International Journal of Coal Geology, 2008, 76(1-2): 34-45. doi: 10.1016/j.coal.2008.05.001
[5] 张祥, 纪宗兰, 杨银山, 等. 关于生物气源岩评价标准的讨论--以柴达木盆地第四系生物气为例[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2004, 15(5):465-470 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-1926.2004.05.005
ZHANG Xiang, JI Zonglan, YANG Yinshan, et al. Discussion of evaluation criterion for the source rock of biological gas: taking quaternary biological gas in Qaidamu basin as the example [J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2004, 15(5): 465-470. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-1926.2004.05.005
[6] 仇天雷, 承磊, 罗辉, 等. 一株近海沉积物中产甲烷菌的分离及鉴定[J]. 中国沼气, 2006, 25(2):3-6, 10 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1166.2006.02.001
QIU Tianlei, CHENG Lei, LUO Hui, et al. Isolation and characterization of methanogens from sediments in Jiaozhou Bay [J]. China Biogas, 2006, 25(2): 3-6, 10. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1166.2006.02.001
[7] Park S Y, Liang Y. Biogenic methane production from coal: A review on recent research and development on microbially enhanced coalbed methane (MECBM) [J]. Fuel, 2016, 166: 258-267. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2015.10.121
[8] 丁芳芳. 煤层中产甲烷微生物的培养及产气[D]. 合肥: 合肥工业大学, 2013.
DING Fangfang. The culture of methanogenic organism and gas production in coalbed[D]. Hefei: Hefei University of Technology, 2013.
[9] Formolo M, Martini A, Petsch S. Biodegradation of sedimentary organic matter associated with coalbed methane in the Powder River and San Juan Basins, U. S. A. [J]. International Journal of Coal Geology, 2008, 76(1-2): 86-97. doi: 10.1016/j.coal.2008.03.005
[10] Pandey R, Harpalani S, Feng R M, et al. Changes in gas storage and transport properties of coal as a result of enhanced microbial methane generation [J]. Fuel, 2016, 179: 114-123. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2016.03.065
[11] Strąpoć D, Picardal F W, Turich C, et al. Methane-producing microbial community in a coal bed of the Illinois Basin [J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2008, 74(8): 2424-2432. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02341-07
[12] Jones E J P, Voytek M A, Warwick P D, et al. Bioassay for estimating the biogenic methane-generating potential of coal samples [J]. International Journal of Coal Geology, 2008, 76(1-2): 138-150. doi: 10.1016/j.coal.2008.05.011
[13] Goldstein R H. Fluid inclusions in sedimentary and diagenetic systems [J]. Lithos, 2001, 55(1-4): 159-193. doi: 10.1016/S0024-4937(00)00044-X
[14] 王爱宽, 秦勇. 生物成因煤层气实验研究现状与进展[J]. 煤田地质与勘探, 2010, 38(5):23-27 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2010.05.005
WANG Aikuan, QIN Yong. Research status and progress of experimental study on biogenic coalbed methane [J]. Coal Geology & Exploration, 2010, 38(5): 23-27. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2010.05.005
[15] 郭红玉, 符超勇, 拜阳, 等. 生物产气对煤层气可采性指标的影响[J]. 天然气工业, 2017, 37(2):46-51 doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2017.02.006
GUO Hongyu, FU Chaoyong, BAI Yang, et al. Influence of biogenic gas production on coalbed methane recoverability parameters [J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2017, 37(2): 46-51. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2017.02.006
[16] 李明宅, 张洪年, 刘华, 等. 生物气模拟试验的进展[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 1996, 17(2):117-122 doi: 10.11743/ogg19960205
LI Mingzhai, ZHANG Hongnian, LIU Hua, et al. Advances in simulated test of biogas [J]. Oli & Gas Geology, 1996, 17(2): 117-122. doi: 10.11743/ogg19960205
[17] 钱贻伯, 连莉文, 尹小波, 等. 地质沉积物中残留有机质生化产甲烷作用的可行性研究[J]. 中国沼气, 1996, 14(3):13-16
QIAN Yibo, LIAN Liwen, YIN Xiaobo, et al. A study on bio-methanogenesis of remanent organic matter in geology sediment [J]. China Biogas, 1996, 14(3): 13-16.
[18] 陆伟文, 海秀珍. 生物气模拟生成实验及地层中生物气生成量之估算[J]. 石油实验地质, 1991, 13(1):65-76 doi: 10.11781/sysydz199101065
LU Weiwen, HAI Xiuzhen. Simulation experiments on biogas generation and estimation of generation amount of biogas in strata [J]. Petroleum Geology & Experimental, 1991, 13(1): 65-76. doi: 10.11781/sysydz199101065
[19] 邓宇, 钱贻伯, 林世平. 藻类的产甲烷及产烃潜力实验[J]. 中国沼气, 2000, 18(4):24 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1166.2000.04.005
DENG Yu, QIAN Yibo, LIN Shiping. Methane and hydrocarbon production potential of algae [J]. China Biogas, 2000, 18(4): 24. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1166.2000.04.005
[20] 戚厚发, 关德师, 钱贻伯, 等. 中国生物气成藏条件[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 1997: 48-61.
QI Houfa, GUAN Deshi, QIAN Yibo, et al. Biogas Accumulation Conditions in China[M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 1997: 48-61.
[21] 李美群, 邓洁红, 熊兴耀, 等. 产甲烷菌的研究进展[J]. 酿酒科技, 2009(5):90-93
LI Meiqun, DENG Jiehong, XIONG Xingyao, et al. Research progress in psychrophilic methanogenic bacteria [J]. Liquor-Making Science & Technology, 2009(5): 90-93.
[22] 王娜, 刘晨光, 袁文杰, 等. 氧化还原电位控制下自絮凝酵母高浓度乙醇发酵[J]. 化工学报, 2012, 63(4):1168-1174 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0438-1157.2012.04.025
WANG Na, LIU Chenguang, YUAN Wenjie, et al. ORP control on very high gravity ethanol fermentation by flocculating yeast [J]. CIESC Journal, 2012, 63(4): 1168-1174. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0438-1157.2012.04.025
[23] 关德师, 戚厚发, 钱贻伯, 等. 生物气的生成演化模式[J]. 石油学报, 1997, 18(3):31-36 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2697.1997.03.005
GUAN Deshi, QI Houfa, QIAN Yibo, et al. Generation and evolution model of biogenic gas [J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 1997, 18(3): 31-36. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2697.1997.03.005
[24] 姜乃煌, 宋孚庆, 任冬苓, 等. 甲烷菌发酵阶段划分[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 1993, 20(4):39-43
JIANG Naihuang, SONG Fuqing, REN Dongling, et al. Determination of different stages of methanobacteria fermentation [J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 1993, 20(4): 39-43.
[25] 孔媛, 雷怀彦, 许江, 等. 南海北部天然气水合物的形成分解与微生物的偶联关系[J]. 厦门大学学报: 自然科学版, 2018, 57(6):768-777
KONG Yuan, LEI Huaiyan, XU Jiang, et al. The Coupling between microorganisms and natural gas hydrates in the northern South China Sea [J]. Journal of Xiamen University: Natural Science, 2018, 57(6): 768-777.
[26] Clayton C. Source volumetrics of biogenic gas generation[M]//Vially R. Bacterial Gas. Paris: Editions Technip, 1992: 191-240.
[27] 陈浩, 秦勇, 邓泽, 等. 二连盆地吉尔嘎朗图凹陷低煤阶煤层生物产气影响因素[J]. 天然气工业, 2018, 38(6):27-32 doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2018.06.004
CHEN Hao, QIN Yong, DENG Ze, et al. Factors influencing the biogenic gas production of low rank coal beds in the Jiergalangtu sag, Erlian Basin [J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2018, 38(6): 27-32. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2018.06.004
[28] 张水昌, 赵文智, 李先奇, 等. 生物气研究新进展与勘探策略[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2005, 32(4):90-96 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0747.2005.04.015
ZHANG Shuichang, ZHAO Wenzhi, LI Xianqi, et al. Advances in biogenic gas studies and play strategies [J]. Petroleum Exploration & Development, 2005, 32(4): 90-96. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0747.2005.04.015
[29] 尹小波, 连莉文, 徐洁泉, 等. 产甲烷过程的独特酶类及生化监测方法[J]. 中国沼气, 1998, 16(3):8-12
YIN Xiaobo, LIAN Liwen, XU Jiequan, et al. Unique enzymes and biochemical monitoring methods in methanogenesis [J]. China Biogas, 1998, 16(3): 8-12.
[30] 李本亮, 王明明, 冉启贵, 等. 地层水含盐度对生物气运聚成藏的作用[J]. 天然气工业, 2003, 23(5):16-20 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0976.2003.05.005
LI Benliang, WANG Mingming, RAN Qigui, et al. Effect of the salinity of formation water on biogas migration, accumulation and reservoir formation [J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2003, 23(5): 16-20. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0976.2003.05.005
[31] 苏现波, 徐影, 吴昱, 等. 盐度、pH对低煤阶煤层生物甲烷生成的影响[J]. 煤炭学报, 2011, 36(8):1302-1306
SU Xianbo, XU Ying, WU Yu, et al. Effect of salinity and pH on biogenic methane production of low-rank coal [J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2011, 36(8): 1302-1306.
[32] 林小云, 高甘霖, 徐莹, 等. 生物成因气生成演化模式探讨[J]. 特种油气藏, 2015, 22(1):1-7 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6535.2015.01.001
LIN Xiaoyun, GAO Ganlin, XU Ying, et al. Discussion on generation and evolution mode of biogenetic gas [J]. Special Oil & Gas Reservoirs, 2015, 22(1): 1-7. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6535.2015.01.001
[33] 苏丕波, 梁金强, 沙志彬, 等. 神狐深水海域天然气水合物成藏的气源条件[J]. 西南石油大学学报(自然科学版), 2014, 36(2):1-8 doi: 10.11885/j.issn.1674-5086.2013.10.16.01
SU Peibo, LIANG Jinqiang, SHA Zhibin, et al. Gas source conditions for gas hydrate accumulation in Shenhu deep water area [J]. Journal of Southwest Petroleum University (Science & Natural Edition), 2014, 36(2): 1-8. doi: 10.11885/j.issn.1674-5086.2013.10.16.01
[34] 方银霞, 申屠海港, 金翔龙. 冲绳海槽天然气水合物稳定带厚度的计算[J]. 矿床地质, 2002, 21(4):414-418 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2002.04.013
FANG Yinxia, SHENTU Haigang, JIN Xianglong. Computation of thickness of hydrate stability zone in Okinawa trough [J]. Mineral Deposits, 2002, 21(4): 414-418. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2002.04.013
[35] 方银霞, 黎明碧, 金翔龙, 等. 东海冲绳海槽天然气水合物的形成条件[J]. 科技通报, 2003, 19(1):1-5 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7119.2003.01.001
FANG Yinxia, LI Mingbi, JIN Xianglong, et al. Formation condition of gas hydrate in okinawa trough of the East China Sea [J]. Science and Technology Bulletin, 2003, 19(1): 1-5. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7119.2003.01.001
[36] 黄保家, 肖贤明, 董伟良. 莺歌海盆地烃源岩特征及天然气生成演化模式[J]. 天然气工业, 2002, 22(1):26-30 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0976.2002.01.007
HUANG Baojia, XIAO Xianming, DONG Weiliang. Characteristics of Hydrocarbon Source Rocks and Generation & Evolution Model of Natural Gas in Yinggehai Basi [J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2002, 22(1): 26-30. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0976.2002.01.007
[37] 李明宅, 张洪年, 郜建军. 生物气的生成演化模式和初次运移特征[J]. 石油实验地质, 1995, 17(2):147-155 doi: 10.11781/sysydz199502147
LI Mingzhai, ZHANG Hongnian, GAO Jianjun. Generation and evolution models and pkimary migrationation features of biogases [J]. Petroleum Geology & Experimental, 1995, 17(2): 147-155. doi: 10.11781/sysydz199502147
-



 下载:
下载: