“Source to sink” analysis of a sea basin: The Quaternary deepwater turbidite fan system in Pearl River Valley-Northwest subbasin, Northern South China Sea
-
摘要:
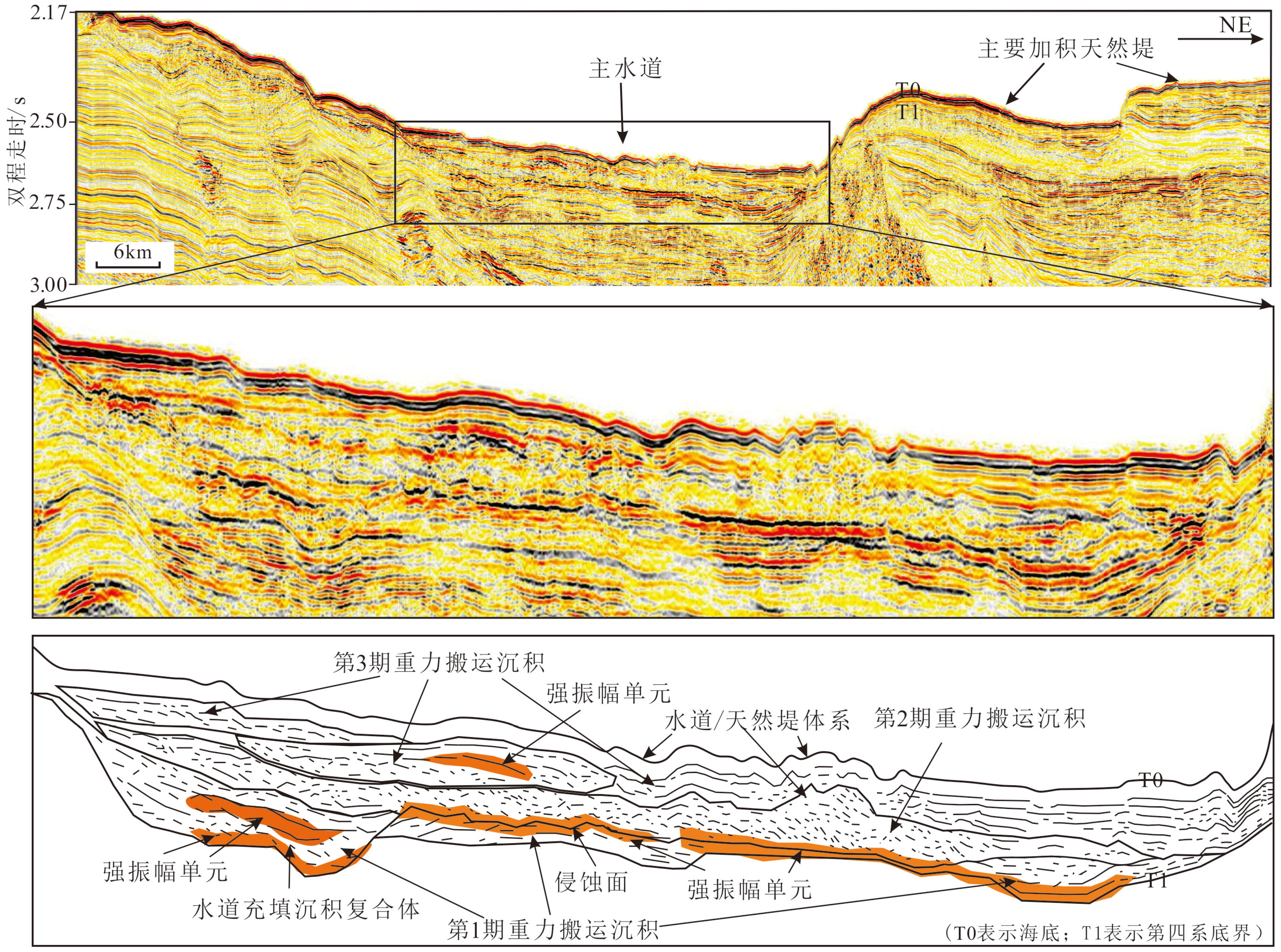
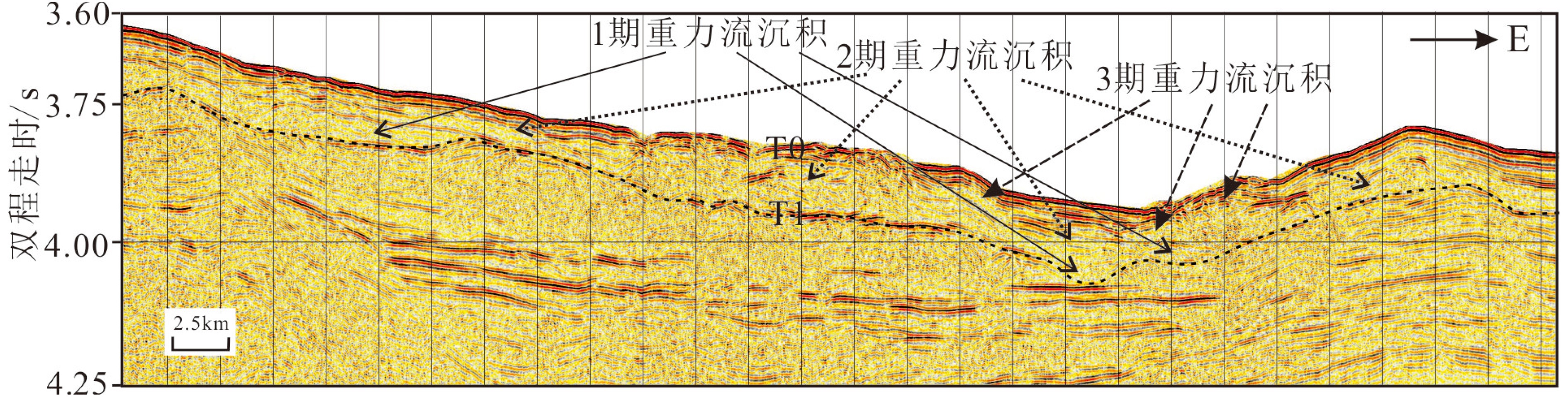
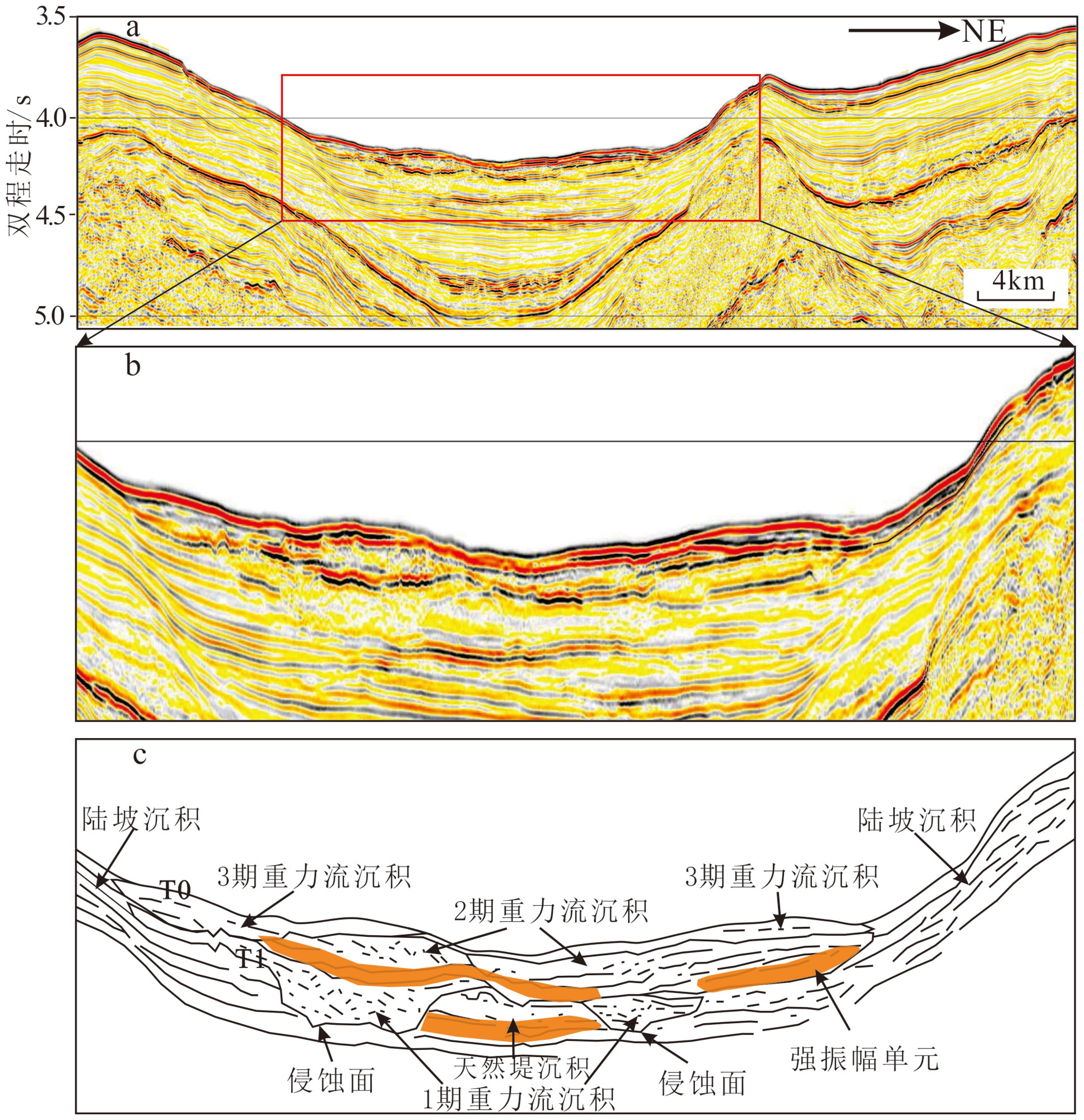
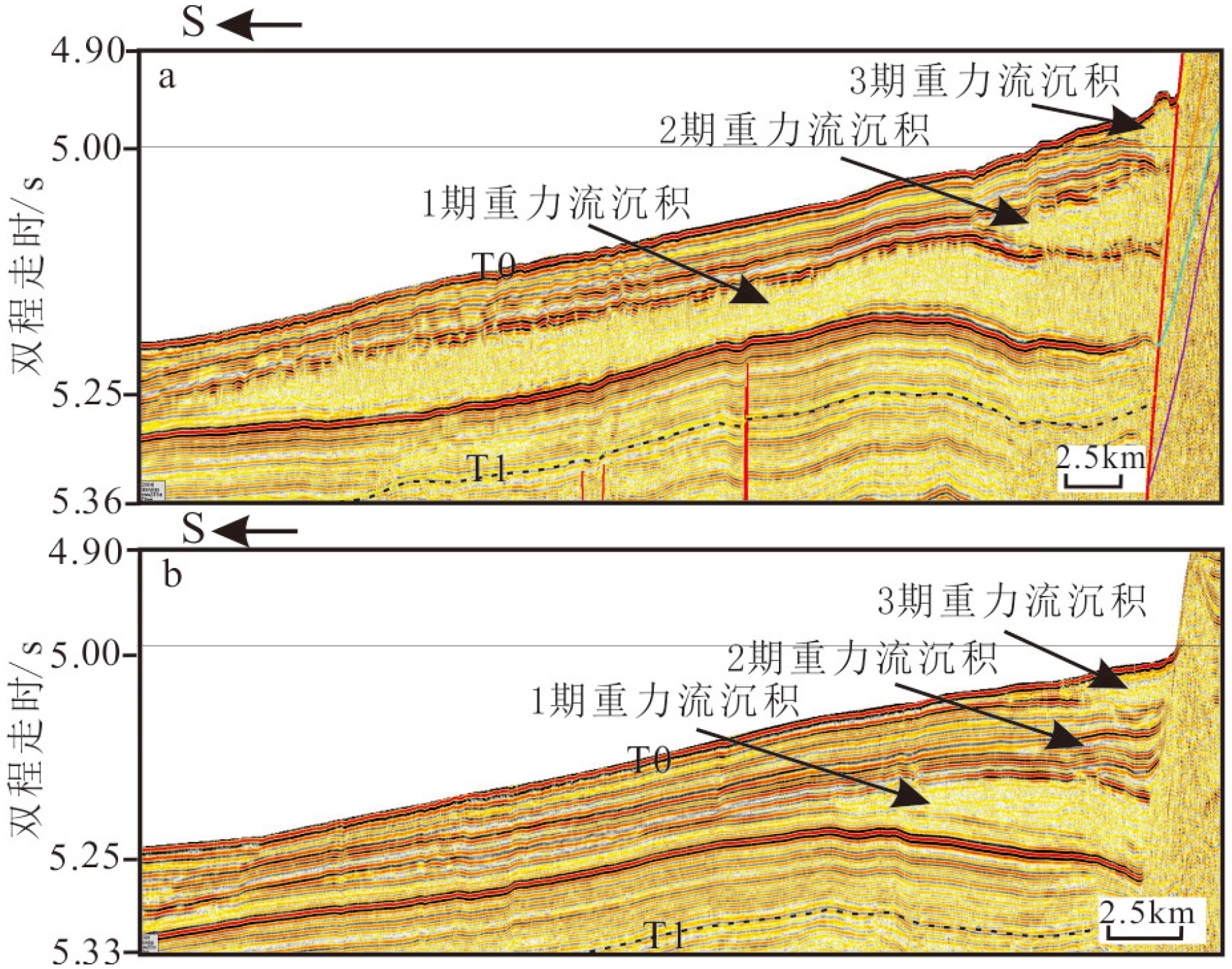
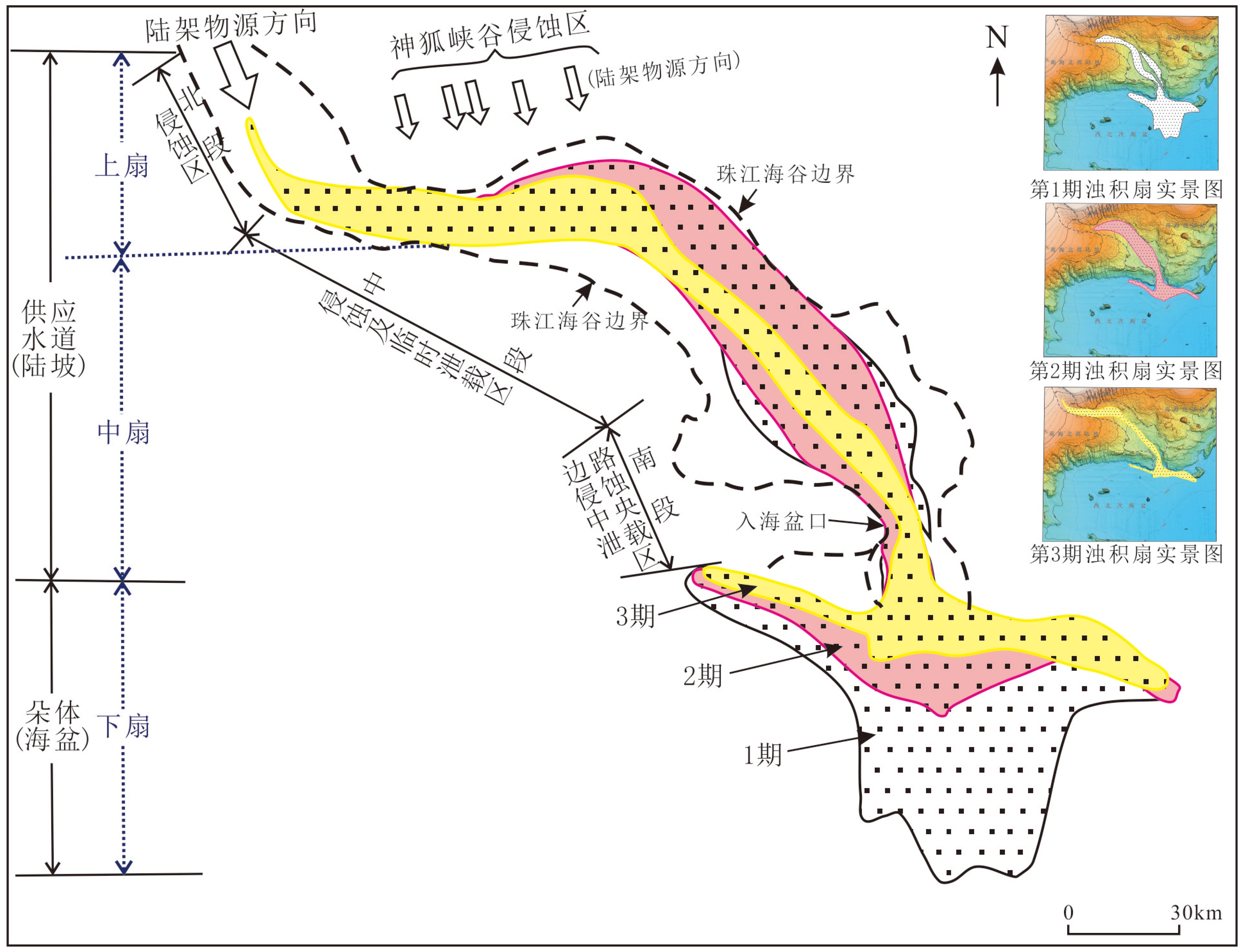
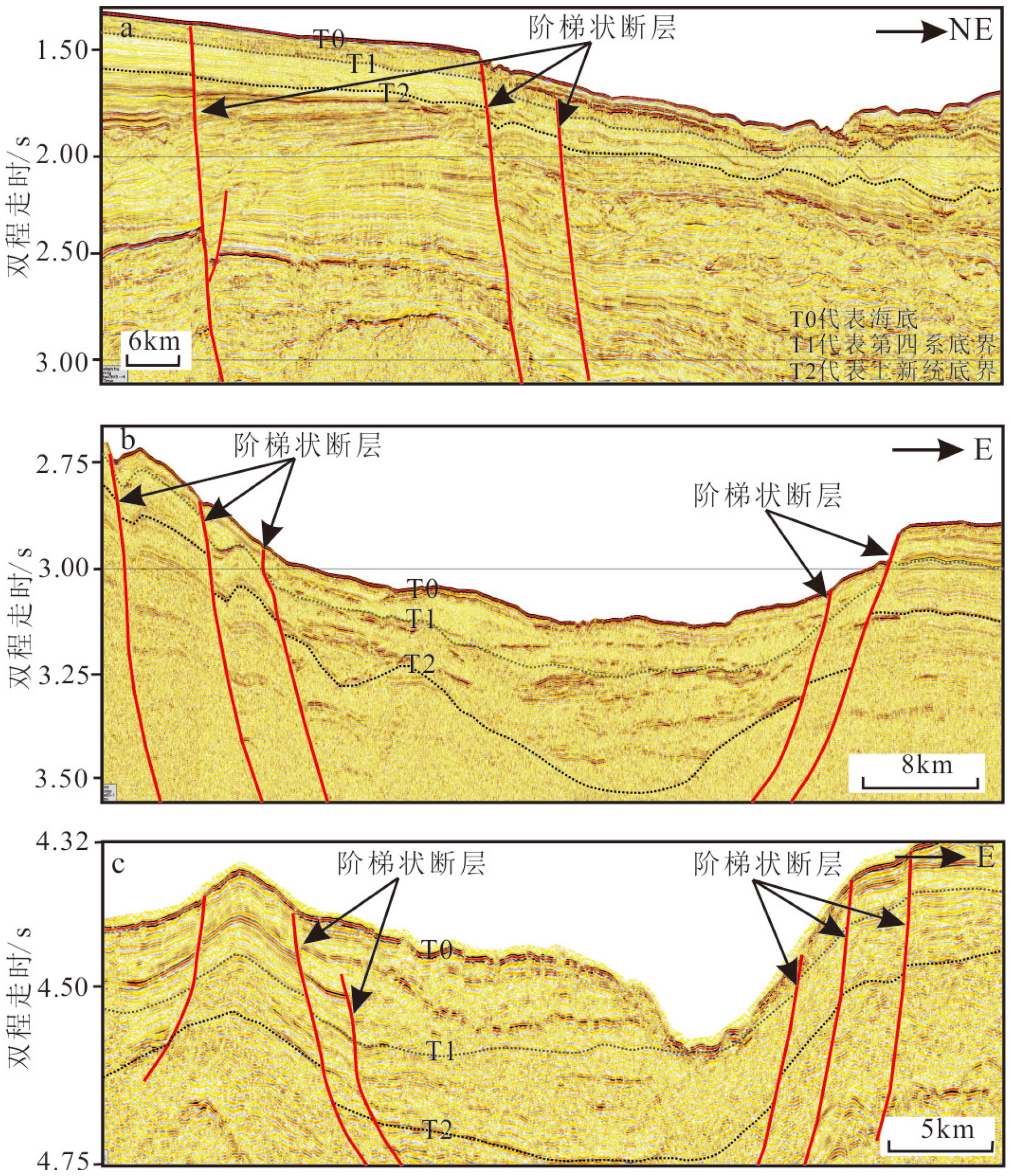
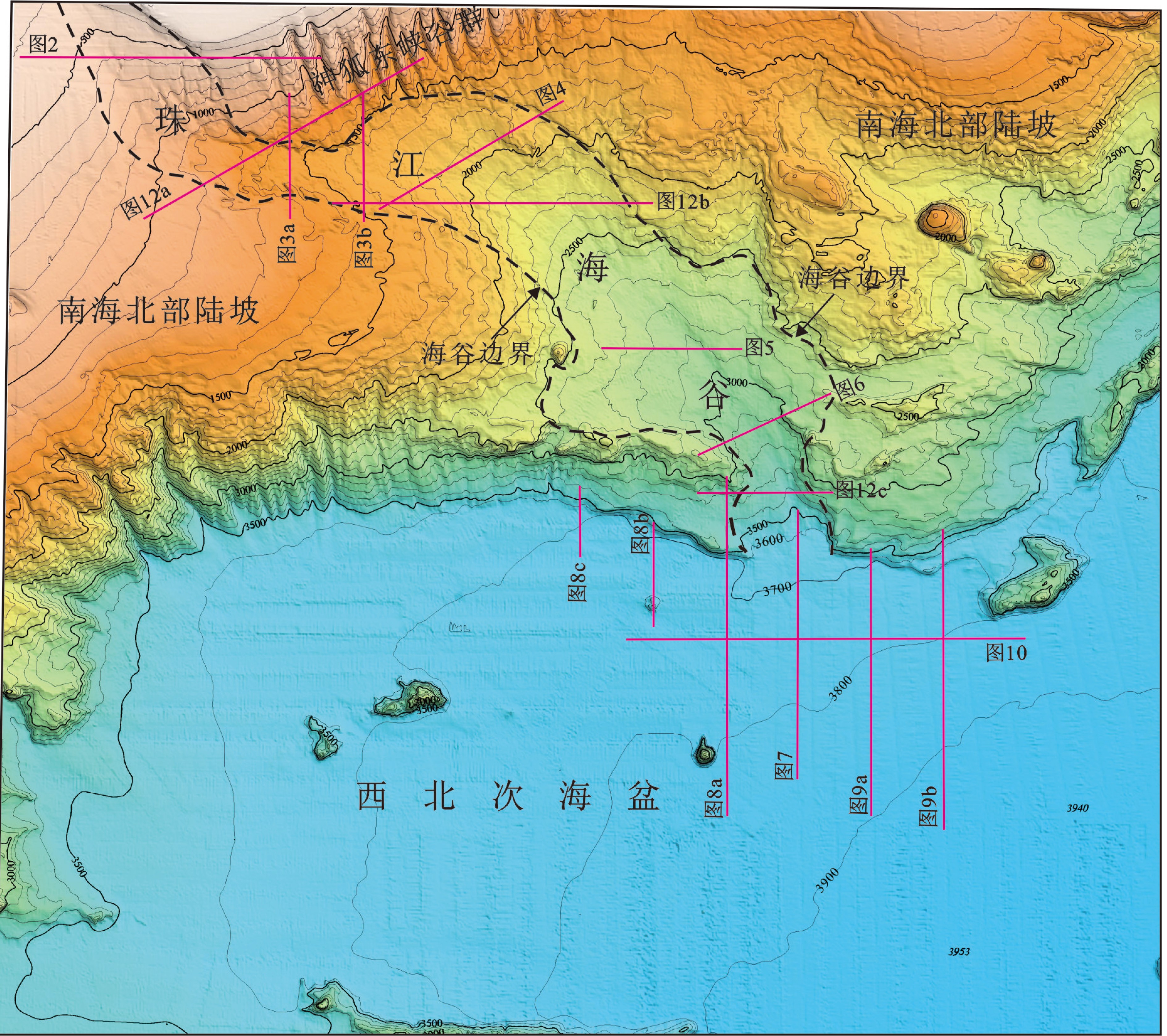
运用近年来采集的高分辨率地震资料和多波束测深数据,在珠江海谷及西北次海盆深海平原区发现大规模发育的第四纪重力流沉积体系,该沉积体系沿珠江海谷以北西-南南东方向贯穿整个北部陆坡,进入西北次海盆后呈扇形展开,形成珠江海谷-西北次海盆大型深水浊积扇系统。据沉积体系空间展布特征差异,将珠江海谷划分为北、中、南三段,北段为过路侵蚀和水道下切,中段以水道充填和天然堤沉积为主,南段以水道-天然堤和朵叶体沉积共存为特征,揭示出北部陆坡珠江海谷是珠江口外陆缘物质输送海盆深海平原的主要通道;海盆区总体以朵叶体发育为特色,呈扇形展布。深水扇系统可分为三期次沉积体,其区域结构记录了重力流沉积物从侵蚀、卸载到南海海盆作为限制性盆地接收陆源沉积物的全过程,为“源-渠-汇”的研究构建了一个完美的范例。本文以珠江海谷-西北次海盆第四纪深水浊积扇沉积体系为例,完整地揭示了水道-扇体的组构和特征,清晰呈现了陆坡-海盆砂体展布的规律,可为建立南海北部新近纪早期深水扇形成模式提供参考,有助于指导南海深水油气勘探工作。
Abstract:Using high resolution seismic profiles and multi-beam echo-sounding data acquired in recent years, a large complicated Quaternary deepwater gravity flow depositional system is identified in the Pearl River Valley (PRV) and Northwestern subbasin (NW subbasin) of the northern South China Sea (SCS). It runs through the whole continental slope along a channel in NW-SSE direction, discharged in the NW subbasin to form a deepwater turbidite fan system. Extending from the northern valley to the southern sea basin, it is more than 320 km long longitudinally. From the aerial view, the turbidite fan shows different features on continental slope and in sea basin. In the slope area, it may be divided into three sections, the north, middle and south sections respectively. The north section is mainly an incised channel under erosion. The middle section shows channel filling and natural levee, while the southern section is composed of the channel-levee complexes and lobes. In the NW subbasin, it is characterized by lobes with large scale of fan-shaped sand bodies, extending for 70 km towards the south direction. The Pearl River Valley, which goes through the continental slope of northern South China Sea, is the main passage for sediments to be transported from the continental margin into the abyssal plain. Vertically, the turbidite fan could be subdivided into three phases and the depocenters of the three phases are not consistent. The first phase of the fan or the oldest deposit is the largest in scale comparing to the other two. The three fans migrate along the slope, suggesting a retrogression towards continent owing to the rising of relative sea level during Quaternary. The regional pattern of the PRV-NW subbasin turbidite fan system has recorded a rather completed process for a gravity flow moving from continent erosion to sediment unloading and provided a perfect example for a “source-conduit-sink” system. This paper carefully described the system and has provided a reference for the depositional model of the deepwater fan in early Neogene in the northern South China Sea, which is significant to prospecting of deepwater oil and gas resources.
-

-
[1] Moore G T. Interaction of rivers and oceans: Pleistocene petroleum potential [J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1969, 53(12): 2421-2430.
[2] Anthony E J, Julian M. Source-to-sink sediment transfers, environmental engineering and hazard mitigation in the steep Var River catchment, French Riviera, southeastern France [J]. Geomorphology, 1999, 31(1-3): 337-354.
[3] Sømme T O, Jackson C A L, Vaksdal M. Source-to-sink analysis of ancient sedimentary systems using a subsurface case study from the Mør-Trøndelag area of southern Norway: Part 1-depositional setting and fan evolution [J]. Basin Research, 2013, 25(5): 489-511. doi: 10.1111/bre.12013
[4] Sømme T O, Jackson C A L. Source-to-sink analysis of ancient sedimentary systems using a subsurface case study from the Mør-Trøndelag area of southern Norway: Part 2-sediment dispersal and forcing mechanisms [J]. Basin Research, 2013, 25(5): 512-531. doi: 10.1111/bre.12014
[5] Sømme T O, Helland-Hansen W, Martinsen O J, et al. Relationships between morphological and sedimentological parameters in source-to-sink systems: A basis for predicting semi-quantitative characteristics in subsurface systems [J]. Basin Research, 2009, 21(4): 361-387. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2117.2009.00397.x
[6] 庞雄, 彭大钧, 陈长民, 等. 三级“源-渠-汇”耦合研究珠江深水扇系统[J]. 地质学报, 2007, 81(6):857-864 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2007.06.016
PANG Xiong, PENG Dajun, CHEN Changmin, et al. Three hierarchies “Source-Conduit-Sink” coupling analysis of the Pearl River deep-water fan system [J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2007, 81(6): 857-864. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2007.06.016
[7] 林畅松, 夏庆龙, 施和生, 等. 地貌演化、源-汇过程与盆地分析[J]. 地学前缘, 2015, 22(1):9-20
LIN Changsong, XIA Qinglong, SHI Hesheng, et al. Geomorphological evolution, source to sink system and basin analysis [J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2015, 22(1): 9-20.
[8] 徐长贵, 杜晓峰, 徐伟, 等. 沉积盆地“源-汇”系统研究新进展[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2017, 38(1):1-11 doi: 10.11743/ogg20170101
XU Changgui, DU Xiaofeng, XU Wei, et al. New advances of the “Source-to-Sink”system research in sedimentary basin [J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2017, 38(1): 1-11. doi: 10.11743/ogg20170101
[9] 汪品先. 深海沉积与地球系统[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2009, 29(4):1-11
WANG Pinxian. Deep sea sediments and earth system [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2009, 29(4): 1-11.
[10] M. Richards, M. Bowman, H Reading. Submarine-fan systems i: characterization and stratigraphic prediction [J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 1998, 15(7): 689-717. doi: 10.1016/S0264-8172(98)00036-1
[11] 庞雄, 陈长民, 彭大钧, 等. 南海珠江深水扇系统及油气[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2007: 1-303.
PANG Xiong, CHEN Changmin, PENG Dajun, et al. The Pearl River deepwater fan systems & petroleum in South China Sea[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2007:1-303.
[12] Stow D A V, Johansson M. Deep-water massive sands: nature, origin and hydrocarbon implications [J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2000, 17(2): 145-174. doi: 10.1016/S0264-8172(99)00051-3
[13] Shanmugam G. Deep-water Processes and Facies Models: Implications for Sandstone Petroleum Reservoirs[M]. Amsterdam:Elsevier, 2006.
[14] Kolla V, Posamentier H W, Wood L J. Deep-water and fluvial sinuous channels-Characteristics, similarities and dissimilarities, and modes of formation [J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2007, 24(6-9): 388-405. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2007.01.007
[15] Bourget J, Zaragosi S, Mulder T, et al. Hyperpycnal-fed turbidite lobe architecture and recent sedimentary processes: A case study from the Al Batha turbidite system, Oman margin [J]. Sedimentary Geology, 2010, 229(3): 144-159. doi: 10.1016/j.sedgeo.2009.03.009
[16] 彭大均, 庞雄, 陈长民, 等. 南海珠江深水扇系统的形成特征与控制因素[J]. 沉积学报, 2006, 24(1):10-19 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0550.2006.01.002
PENG Dajun, PANG Xiong, CHEN Changmin, et al. The characteristics and controlling factors for the formation of deep-water fan system in South China Sea [J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2006, 24(1): 10-19. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0550.2006.01.002
[17] 王昌勇, 杨宝泉, 高博禹, 等. 荔湾3-1井区珠江组深水扇高分辨率层序分析及应用[J]. 沉积学报, 2011, 29(6):1122-1129
WANG Changyong, YANG Baoquan, GAO Boyu, et al. High-Resolution Sequence Stratigraphy Analysis and Application in Deepwater Fan of Zhujiang Formation, Liwan3-1 Area [J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2011, 29(6): 1122-1129.
[18] 朱伟林, 钟锴, 李友川, 等. 南海北部深水区油气成藏与勘探[J]. 科学通报, 2012, 57(20):1833-1841 doi: 10.1360/csb2012-57-20-1833
ZHU Weilin, ZHONG Kai, LI Youchuan, et al. Characteristics of hydrocarbon accumulation and exploration potential of the northern South China Sea Deep-water Basins [J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2012, 57(20): 1833-1841. doi: 10.1360/csb2012-57-20-1833
[19] 施和生, 柳保军, 颜承志, 等. 珠江口盆地白云-荔湾深水区油气成藏条件与勘探潜力[J]. 中国海上油气, 2010, 22(6):369-374 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1506.2010.06.003
SHI Hesheng, LIU Baojun, YAN Chengzhi, et al. Hydrocarbon accumulation conditions and exploration potential in Baiyun-Liwan deepwater Area, Pearl River Month basin [J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2010, 22(6): 369-374. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1506.2010.06.003
[20] 李云, 郑荣才, 高博禹, 等. 深水扇沉积研究现状和展望——以珠江口盆地白云凹陷珠江深水扇系统为例[J]. 地质论评, 2010, 56(4):549-560
LI Yun, ZHENG Rongcai, GAO Boyu, et al. Reviews and prospects on submarine fan deposition: A case study of Zhujiang submarine fan system in Baiyun depression, Pearl River Mouth Basin [J]. Geological Review, 2010, 56(4): 549-560.
[21] 李胜利, 于兴河, 刘玉梅, 等. 水道加朵体型深水扇形成机制与模式: 以白云凹陷荔湾3-1地区珠江组为例[J]. 地学前缘, 2012, 19(2):32-40
LI Shengli, YU Xinghe, LIU Yumei, et al. Formation mechanism and pattern of deep-water fan with channel and lobe: A case study of the ZhuJiang Formation in Liwan 3-1 area, Baiyun Depression [J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2012, 19(2): 32-40.
[22] 王大伟, 吴时国, 王英民, 等. 琼东南盆地深水重力流沉积旋回[J]. 科学通报, 2015, 60(10):933-943 doi: 10.1360/N972014-00477
WANG Dawei, Wu Shiguo, Wang Yingmin, et al. Deep-water sediment cycles in the Qiongdongnan Basin (in Chinese) [J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2015, 60(10): 933-943. doi: 10.1360/N972014-00477
[23] 何小胡, 钟泽红, 董贵能, 等. 莺琼盆地新近纪海流的研究新进展及深水油气勘探的启示[J]. 天然气勘探与开发, 2015, 38(1):5-8 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-3177.2015.01.002
HE Xiaohu, ZHONG Zehong, DONG Guineng, et al. Neogene ocean current in YingQiong basin: implication of deepwater oil and gas exploration [J]. Natural Gas Exploration & Development., 2015, 38(1): 5-8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-3177.2015.01.002
[24] 王亚辉, 张道军, 赵鹏肖, 等. 南海北部琼东南盆地中央峡谷成因新认识[J]. 海洋学报, 2016, 38(11):97-124
WANG Yahui, ZHANG Daojun, ZHAO Pengxiao, et al. A new consideration on the genetic mechanism of the central canyon in the Qiongdongnan Basin, the northern South China Sea [J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2016, 38(11): 97-124.
[25] 林畅松, 刘景彦, 蔡世祥, 等. 莺琼盆地大型下切谷和海底重力流体系的沉积构成和发育背景[J]. 科学通报, 2001, 46(1):69-72 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2001.01.018
LIN Changsong, LIU Jingyan, CAI Shixiang, et al. sedimentation and evolution background of old large incised channel and submarine gravity flow system in Ying-Qiong basin [J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2001, 46(1): 69-72. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2001.01.018
[26] 苏明, 张成, 解习农, 等. 深水峡谷体系控制因素分析——以南海北部琼东南盆地中央峡谷体系为例[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2014, 44(8):1807-1820
SU Ming, ZHANG Cheng, XIE Xinong, et al. Controlling factors on the submarine canyon system: a case study of the Central Canyon System in the Qiongdongnan Basin, northern South China Sea [J]. Science China: Earth Sciences, 2014, 44(8): 1807-1820.
[27] 王振峰, 孙志鹏, 张迎朝, 等. 南海北部琼东南盆地深水中央峡谷大气田分布与成藏规律[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2016, 21(4):54-64 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2016.04.006
WANG Zhenfeng, SUN Zhipeng, ZHANG Yingzhao, etc al. Distribution and hydrocarbon accumulation mechanism of the giant deepwater Central Canyon gas field in Qiongdongnan Basin, northern South China Sea [J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2016, 21(4): 54-64. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2016.04.006
[28] 刘睿, 周江羽, 张莉, 等. 南海西北次海盆深水扇系统沉积演化特征[J]. 沉积学报, 2013, 31(4):706-716
LIU Rui, ZHOU Jiangyu, ZHANG Li, etc. Depositional Architecture and Evolution of Deep water Fan System in the Northwestern Sub-Basin, South China Sea [J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2013, 31(4): 706-716.
[29] 杨胜雄, 邱燕, 朱本铎. 南海地质地球物理图系(1:200万)[M]. 天津: 中国航海图书出版社出版发行, 2015年5月第一版.
YANG Shengxiong, QIU Yan, ZHU Benduo. Atlas of Geology and geophysics of South China Sea(1:2000000)[M]. Tianjin:China Navigation Publication Press, 2015.
[30] 庞雄, 陈长民, 彭大钧, 等. 南海北部白云深水区之基础地质[J]. 中国海上油气, 2007, 20(4):215-222
PANG Xiong, CHEN Changmin, PENG Dajun, et al. Basic geology of Baiyun deep-water area in the northern South China Sea [J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2007, 20(4): 215-222.
[31] 张远泽, 漆家福, 吴景富. 南海北部新生代盆地断裂系统及构造动力学影响因素[J]. 地球科学, 2019,44(2): 603-625.
ZHANG Yuanze, QI Jiafu, WU Jingfu. Cenozoic faults systems and its geodynamics of the continental margin basins in the northern of South China Sea[J]. Earth Science, 2019,44(2): 603-625.
[32] 鲁宝亮, 王璞珺, 张功成等. 南海区域断裂特征及其基底构造格局[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2015,30(4):1544-1553
LU Baoliang, WANG Pujun, ZHANG Gongcheng, et al. Characteristic of regional fractures in South China Sea and its basement tectonic framework [J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2015,30(4): 1544-1553.
[33] Walker R G. Deep-water sandstone facies and ancient submarine fans: models for exploration for stratigraphic traps [J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1978, 62(6): 932-966.
[34] Shanmugam G. 50 years of the turbidite paradigm (1950s-1990s): deep-water processes and facies models: a critical perspective [J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2000, 17(2): 285-342. doi: 10.1016/S0264-8172(99)00011-2
[35] Lopez M. Architecture and depositional pattern of the Quaternary deep sea fan of the Amazon [J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2001, 18(4): 479-486. doi: 10.1016/S0264-8172(00)00071-4
[36] Reading H G, Richards M. Turbidite systems in deep-water basin margins classified by grain-size and feeder system [J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1994, 78(5): 792-822.
[37] Gervais A, Savoye B, Mulder T, et al. Sandy modern turbidite lobes: A new insight from high resolution seismic data [J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2006, 23(4): 485-502. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2005.10.006
[38] Deptuck M E, Sylvester Z, Pirmez C, et al. Migration-aggradation history and 3-D seismic geomorphology of submarine channels in the Pleistocene Benin-major Canyon, western Niger Delta slope [J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2007, 24(6-9): 406-433. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2007.01.005
[39] Sun Q L, Alves T M, Lu X Y, et al. True volumes of slope failure estimated from a Quaternary mass-transport deposit in the northern South China Sea[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2018, 45(6): 2642-2651, doi: 10.1002/2017GL076484.
-



 下载:
下载: