Application of micro-XRF technology to rapid and nondestructive detection of inorganic elements in ocean minerals
-
摘要:
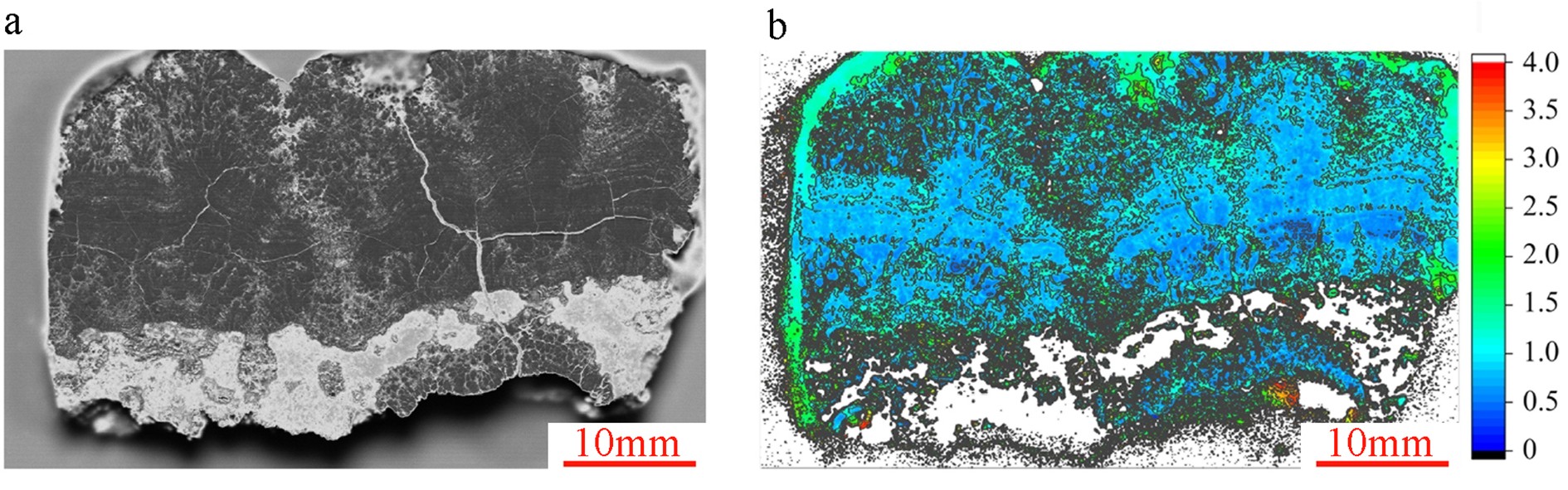
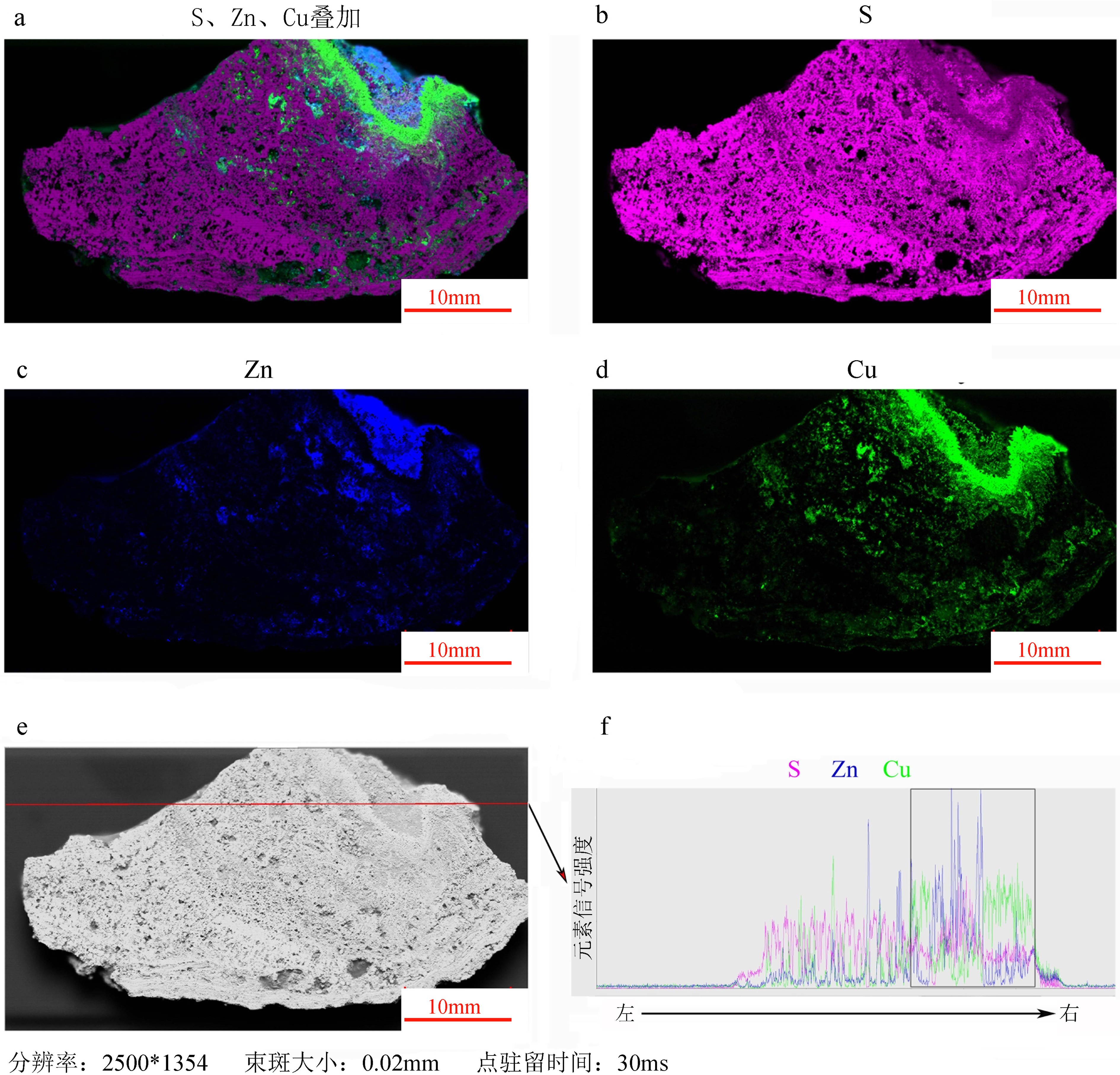
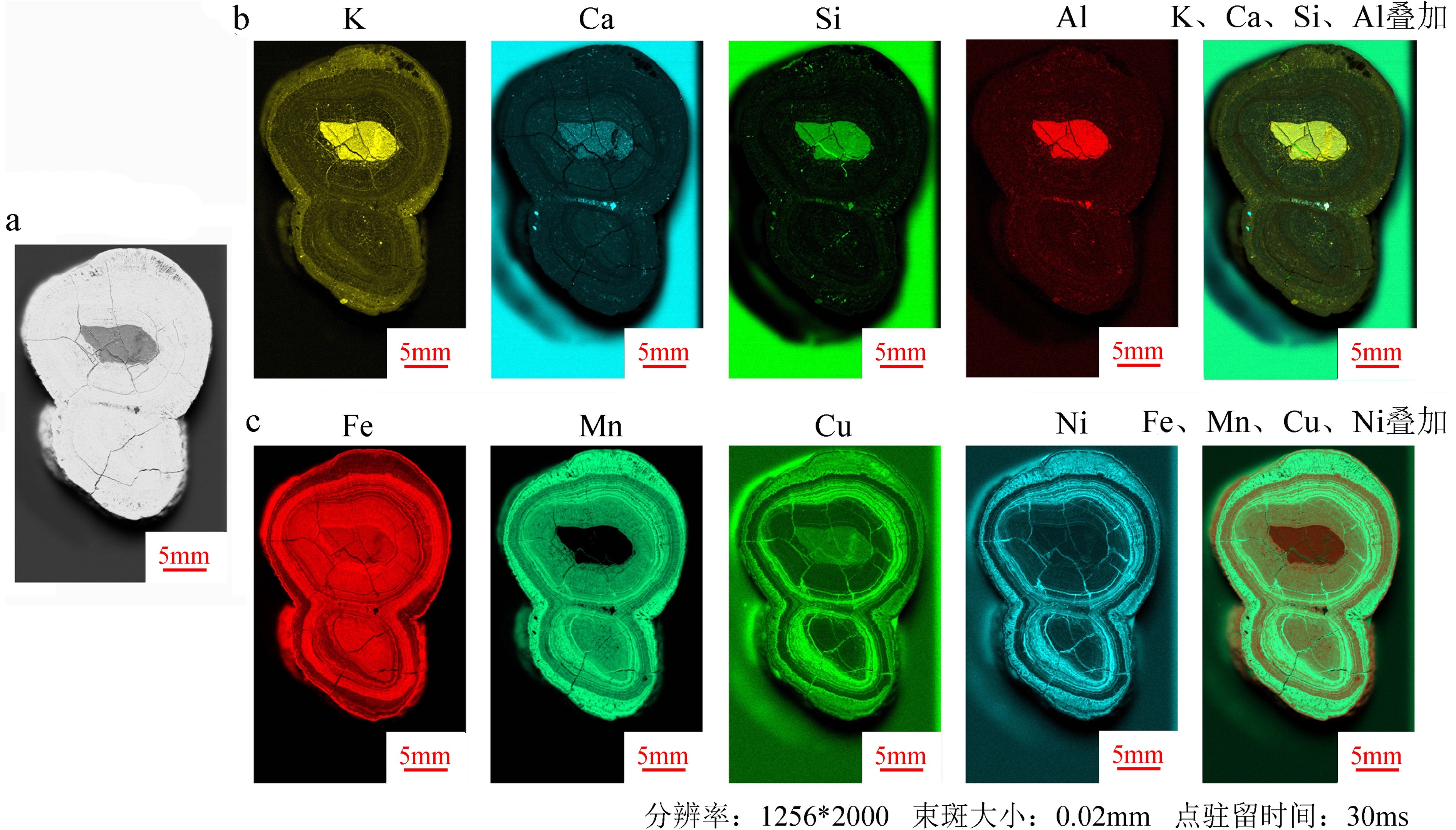
深海固体矿产主要由铁锰结核、富钴结壳和多金属热液硫化物组成,元素在矿产中原位的分布和含量,对了解矿物成因、品位以及评估其经济价值有重要指示作用。本研究利用微区XRF分析技术对铁锰结核、富钴结壳、热液硫化物3种大洋类型矿产样品,进行高分辨、原位和无损的多元素空间分布检测,结果显示了不同元素在3种类型矿物中的空间分布特征。通过对测试数据进一步处理和优化成图流程,可以获得特定元素在矿物中半定量分布图,并对不同元素在矿物空间分布的差异性和相关性进行对比分析,从而建立一种肉眼可见的测试大洋矿产资源样品中元素原位分布的新方法。
Abstract:A great amount of solid minerals, such as ferromanganese nodules, cobalt-bearing crusts and polymetallic hydrothermal sulfides, occur in the deep ocean. The in-situ distribution of the contents of various elements in the minerals are important indicators to their genesis, identification, grade and evaluation of economic value. In this study, three types of mineral samples, including ferromanganese nodules, cobalt-bearing crusts and polymetallic hydrothermal sulfides, were analyzed with micro-XRF technology, and high-resolution, in-situ and non-destructive multi-element mapping analysis was adopted to reveal the difference in spatial distribution of different elements in different types of mineral samples. Through the analysis of test data and the optimization of mapping process, we can compare the correlation and difference in specific element distribution and semi-quantitative content, so as to establish a new method for disclosing the visible deep-sea mineral element distribution psatterns.
-
Key words:
- nodules /
- crusts /
- hydrothermal sulfides /
- micro-XRF /
- element distribution /
- in situ /
- nondestructive
-

-
表 1 微区XRF在结核、结壳样品中的平行性验证
Table 1. Verification of parallelism of micro-XRF in nodule and crust samples
元素 结核样品 结壳样品点1 结壳样品点2 5次点扫
均值/%5次点扫标准
偏差/%相对标准
偏差/%5次点扫
均值/%5次点扫标准
偏差/%相对标准
偏差/%5次点扫
均值/%5次点扫标准
偏差/%相对标准
偏差/%Mg 0.098 0.035 35.3 0.113 0.023 20.0 0.063 0.046 74.1 Al 0.597 0.020 3.3 0.320 0.018 5.5 1.820 0.107 5.9 Si 1.873 0.013 0.7 1.961 0.050 2.6 7.834 0.303 3.9 P 0.252 0.004 1.8 0.382 0.009 2.3 0.286 0.036 12.7 S 0.222 0.006 2.7 0.259 0.002 0.8 0.170 0.017 10.0 Cl 2.296 0.019 0.8 1.348 0.028 2.1 1.569 0.012 0.8 K 0.788 0.004 0.5 0.682 0.005 0.8 1.354 0.039 2.9 Ca 4.011 0.012 0.3 5.147 0.017 0.3 5.857 0.026 0.4 Ti 2.391 0.006 0.3 2.668 0.008 0.3 1.777 0.009 0.5 V 0.258 0.006 2.5 0.329 0.009 2.8 0.281 0.022 7.7 Cr 0.286 0.008 2.9 0.245 0.009 3.7 0.499 0.010 2.1 Mn 50.880 0.037 0.1 44.081 0.049 0.1 34.971 0.461 1.3 Fe 32.746 0.069 0.2 39.651 0.079 0.2 41.289 0.154 0.4 Co 1.269 0.007 0.5 1.066 0.012 1.1 0.506 0.031 6.2 Ni 0.761 0.004 0.5 0.534 0.003 0.6 0.594 0.008 1.4 Cu 0.303 0.004 1.5 0.170 0.004 2.2 0.252 0.005 1.8 Zn 0.157 0.008 5.0 0.150 0.010 6.4 0.142 0.007 5.2 Sr 0.081 0.002 2.4 0.104 0.002 2.3 0.107 0.003 2.8 Pb 0.730 0.014 2.0 0.788 0.014 1.7 0.629 0.012 1.9 表 2 微区XRF在热液硫化物样品中的平行性验证
Table 2. Verification of parallelism of micro-XRF in hydrothermal sulfide
元素 热液硫化物点1 热液硫化物点2 热液硫化物点3 5次点扫
均值/%5次点扫标准
偏差/%相对标准
偏差/%5次点扫
均值/%5次点扫标准
偏差/%相对标准
偏差/%5次点扫
均值/%5次点扫标准
偏差/%相对标准
偏差/%Al 0.484 0.065 13.5 0.178 0.022 12.3 0.180 0.022 12.4 Si 1.076 0.242 22.5 0.102 0.013 12.7 1.045 0.021 2.0 S 26.594 0.917 3.4 42.930 0.424 1.0 34.685 0.084 0.2 Cl 1.954 0.279 14.3 0.671 0.419 62.4 3.446 0.021 0.6 K 0.161 0.008 4.8 0.066 0.005 7.0 0.324 0.015 4.8 Ca 0.067 0.034 49.8 0.008 0.001 7.2 0.034 0.003 7.6 V 0.098 0.013 13.3 0.204 0.038 18.8 2.422 0.031 1.3 Cr 1.102 0.200 18.2 54.463 0.681 1.2 19.171 0.059 0.3 Fe 39.325 0.472 1.2 0.017 0.001 8.1 0.023 0.002 7.1 Cu 27.629 0.633 2.3 0.223 0.005 2.4 6.521 0.133 2.0 Zn 1.511 0.235 15.5 1.138 0.106 9.3 32.146 0.240 0.7 表 3 微区XRF在黄铁矿标样中的准确度验证
Table 3. Accuracy verification of micro-XRF in pyrite standard sample
黄铁矿标样K18 点1/% 点2/% 点3/% 3次点扫相对标准偏差/% 3次点扫均值/% 标样理论值/% 检测误差/% Fe 43.01 43.51 43.36 0.59 43.29 46.64 7.18 S 53.38 53.32 52.93 0.46 53.21 53.19 0.04 表 4 微区XRF在闪锌矿标样中的准确度验证
Table 4. Accuracy verification of micro-XRF in sphalerite standard sample
闪锌矿标样 K52 点1/% 点2/% 点3/% 3次点扫相对标准偏差/% 3次点扫均值/% 标样理论值/% 检测误差/% Zn 62.96 62.33 63.62 1.02 62.97 66.96 5.96 S 33.68 33.72 33.41 0.50 33.60 32.71 2.72 表 5 不同单点驻留时间下的微区XRF面扫结果比对
Table 5. Comparison of micro-XRF area scanning results under different point dwell time
元素 100ms/% 50 ms/% 30 ms/% 20 ms/% 10 ms/% Al 0.11 0.13 0.10 0.12 0.12 Si 0.52 0.53 0.52 0.52 0.51 S 43.35 43.24 43.34 43.23 43.33 Cl 4.00 3.91 3.90 3.94 3.95 K 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.03 Ca 0.10 0.11 0.11 0.11 0.11 Cr 1.67 1.67 1.70 1.67 1.67 Fe 45.90 46.06 46.02 46.07 45.99 Cu 1.39 1.40 1.38 1.40 1.38 Zn 2.86 2.87 2.84 2.86 2.86 As 0.05 0.05 0.05 0.05 0.05 Cd 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02 -
[1] 高亚峰. 海洋矿产资源及其分布[J]. 海洋信息, 2009(1):13-14 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-1724.2009.01.005
GAO Yafeng. Marine mineral resources and their distribution [J]. Marine Information, 2009(1): 13-14. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-1724.2009.01.005
[2] 崔木花, 董普, 左海凤. 我国海洋矿产资源的现状浅析[J]. 海洋开发与管理, 2005, 22(5):16-21 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9857.2005.05.002
CUI Muhua, DONG Pu, ZUO Haifeng. Brief analysis on the current situation of the marine mineral resources of China [J]. Ocean Development and Management, 2005, 22(5): 16-21. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9857.2005.05.002
[3] Hein J R, Mizell K, Koschinsky A, et al. Deep-ocean mineral deposits as a source of critical metals for high- and green-technology applications: Comparison with land-based resources [J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2013, 51: 1-14. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2012.12.001
[4] Kuhn T, Wegorzewski A, Rühlemann C, et al. Composition, formation, and occurrence of polymetallic nodules[M]//Sharma R. Deep-Sea Mining: Resource Potential, Technical and Environmental Considerations. Cham: Springer International Publishing, 2017: 23-63.
[5] Hein J R, Koschinsky A. Deep-ocean ferromanganese crusts and nodules[M]//Turekian K K. Treatise on Geochemistry. 2nd ed. Oxford: Elsevier, 2014: 273-291.
[6] 朱节清, 王毅民. 锰结核微区元素分布及生长速率变化研究[J]. B辑, 1993, 23(4):417-422
ZHU Jieqing, WANG Yimin. Study on element distribution and growth rate of manganese nodules [J]. Chinese Science: Chemistry, Life science and Geoscience, 1993, 23(4): 417-422.
[7] 赵宏樵, 郑存江, 初凤友, 等. 富钴结壳中成矿元素的微区分布特征及其地质意义[J]. 海洋学研究, 2009, 27(2):84-89 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-909X.2009.02.012
ZHAO Hongqiao, ZHENG Cunjiang, CHU Fengyou, et al. Mirco-area distribution characteristics of the elements in co-rich crust and its geological significance [J]. Journal of Marine Sciences, 2009, 27(2): 84-89. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-909X.2009.02.012
[8] 龙晓军, 赵广涛, 杨胜雄, 等. 西太平洋麦哲伦海山富钴结壳成分特征及古环境记录[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2015, 35(5):47-55
LONG Xiaojun, ZHAO Guangtao, YANG Shengxiong, et al. Chemical composition and paleoenvironmental record of the co-rich crust from Magellan seamount in Western Pacific [J]. Marine Geology and Quaternary Geology, 2015, 35(5): 47-55.
[9] German C R, Seyfried W E Jr. Hydrothermal processes[M]//Holland H D, Turekian K K. Treatise on Geochemistry. 2nd ed. Oxford: Elsevier, 2014: 191-233.
[10] 李目. 我国科学家首次在大洋中脊发现新的海底热液活动区[J]. 北京大学学报: 自然科学版, 2007, 43(3):389
LI Mu. The first discovery of a new hydrothermal active area in the mid ocean ridge by Chinese scientists [J]. Journal of Peking University: Natural Science, 2007, 43(3): 389.
[11] Böning P, Bard E, Rose J. Toward direct, micron-scale XRF elemental maps and quantitative profiles of wet marine sediments [J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2007, 8(5): Q05004.
[12] Sorrel P, Oberhänsli H, Boroffka N, et al. Control of wind strength and frequency in the Aral Sea basin during the late Holocene [J]. Quaternary Research, 2007, 67(3): 371-382. doi: 10.1016/j.yqres.2006.12.003
[13] 梁述廷, 刘玉纯, 刘瑱, 等. X射线荧光光谱微区分析在铅锌矿石鉴定上的应用[J]. 岩矿测试, 2013, 32(6):897-902 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2013.06.009
LIANG Shuting, LIU Yuchun, LIU Zhen, et al. Application of in-situ micro-X-ray fluorescence spectrometry in the identification of lead-zinc ore [J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2013, 32(6): 897-902. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2013.06.009
[14] 杨海, 葛良全, 谷懿, 等. 原位微区X射线荧光分析在矿物学研究中的应用[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析, 2013(11):3137-3141 doi: 10.3964/j.issn.1000-0593(2013)11-3137-05
YANG Hai, GE Liangquan, GU Yi, et al. Application of in situ micro energy dispersive X-ray fluorescence analysis in mineralogy [J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2013(11): 3137-3141. doi: 10.3964/j.issn.1000-0593(2013)11-3137-05
[15] 刘勇胜, 胡兆初, 李明, 等. LA-ICP-MS在地质样品元素分析中的应用[J]. 科学通报, 2013, 58(32):3863-3878 doi: 10.1007/s11434-013-5901-4
LIU Yongsheng, HU Zhaochu, LI Ming, et al. Applications of LA-ICP-MS in the elemental analyses of geological samples [J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2013, 58(32): 3863-3878. doi: 10.1007/s11434-013-5901-4
[16] 宋佳泽, 黄湘通, 杨守业, 等. 南黄海牡蛎壳元素组成的原位微区分析及环境指示[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2020, 40(2):70-79
SONG Jiaze, HUANG Xiangtong, YANG Shouye, et al. In-situ microanalysis of elemental ratios in a single oyster shell from the South Yellow Sea, China and its environmental implications [J]. Marine Geology and Quaternary Geology, 2020, 40(2): 70-79.
[17] 吴石头, 王亚平, 许春雪. 激光剥蚀电感耦合等离子体质谱元素微区分析标准物质研究进展[J]. 岩矿测试, 2015, 34(5):503-511
WU Shitou, WANG Yaping, XU Chunxue. Research progress on reference materials for in situ elemental analysis by laser ablation-inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry [J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2015, 34(5): 503-511.
[18] 沈亚婷. 原位微区同步辐射X射线荧光和近边吸收谱研究拟南芥幼苗及根际土壤中铅分布与形态特征[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析, 2014, 34(3):818-822 doi: 10.3964/j.issn.1000-0593(2014)03-0818-05
SHEN Yating. Distribution and speciation of Pb in Arabidopsis thaliana shoot and rhizosphere soil by in situ synchrotron radiation micro X-ray fluorescence and X-ray absorption near edge structure [J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2014, 34(3): 818-822. doi: 10.3964/j.issn.1000-0593(2014)03-0818-05
[19] 袁静, 罗立强. 同步辐射微区X射线荧光和吸收谱技术在大气、土壤和动植物分析中的应用[J]. 核技术, 2014, 37(8):1-11
YUAN Jing, LUO Liqiang. Synchrotron μ-XRF and XAFS in element distribution and speciation of air, soil and biological samples [J]. Nuclear Techniques, 2014, 37(8): 1-11.
[20] 凡小盼, 赵雄伟, 高强. 同步辐射微束X射线荧光技术在早期黄铜研究中的应用[J]. 电子显微学报, 2014, 33(4):349-356 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6281.2014.04.012
FAN Xiaopan, ZHAO Xiongwei, GAO Qiang. The application of synchrotron radiation μ-X-ray fluorescence technology to early brass research [J]. Journal of Chinese Electron Microscopy Society, 2014, 33(4): 349-356. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6281.2014.04.012
[21] van der Ent A, Przybyłowicz W J, de Jonge M D, et al. X-ray elemental mapping techniques for elucidating the ecophysiology of hyperaccumulator plants [J]. New Phytologist, 2018, 218(2): 432-452. doi: 10.1111/nph.14810
-



 下载:
下载: