Geochemistry of rare earth elements and yttrium in ferromanganese crusts from Kocebu Guyot in the Western Pacific
-
摘要:
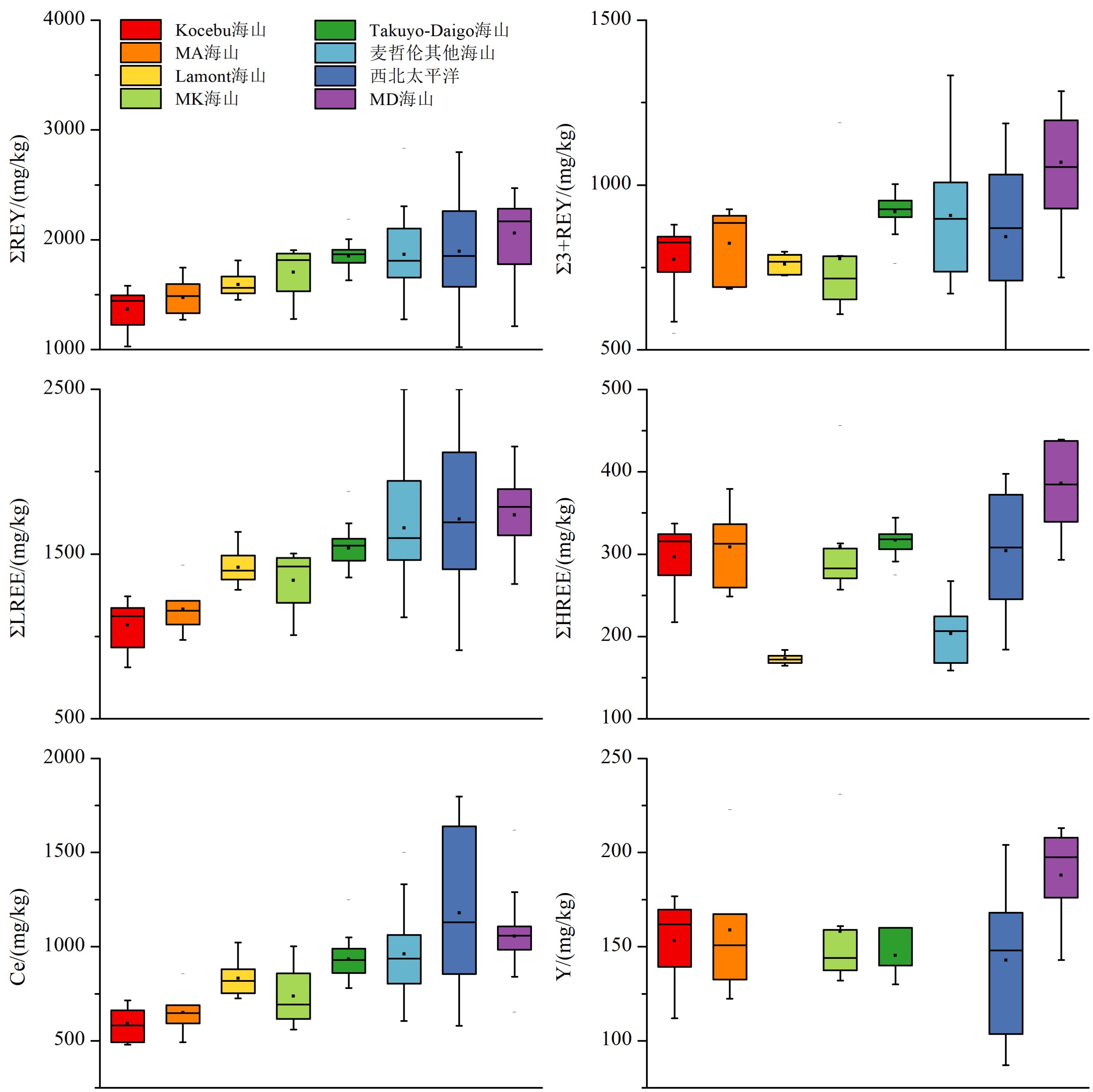
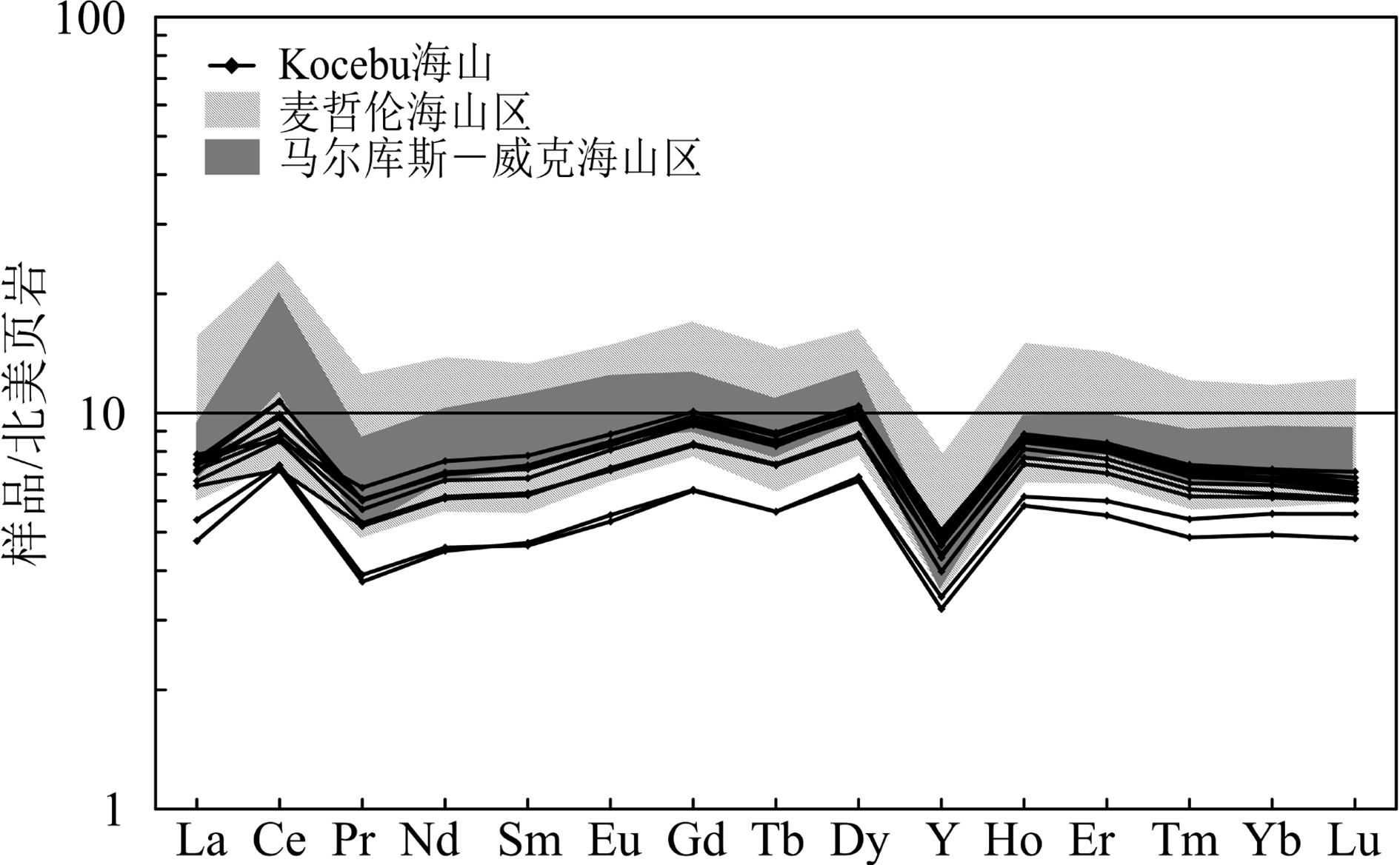
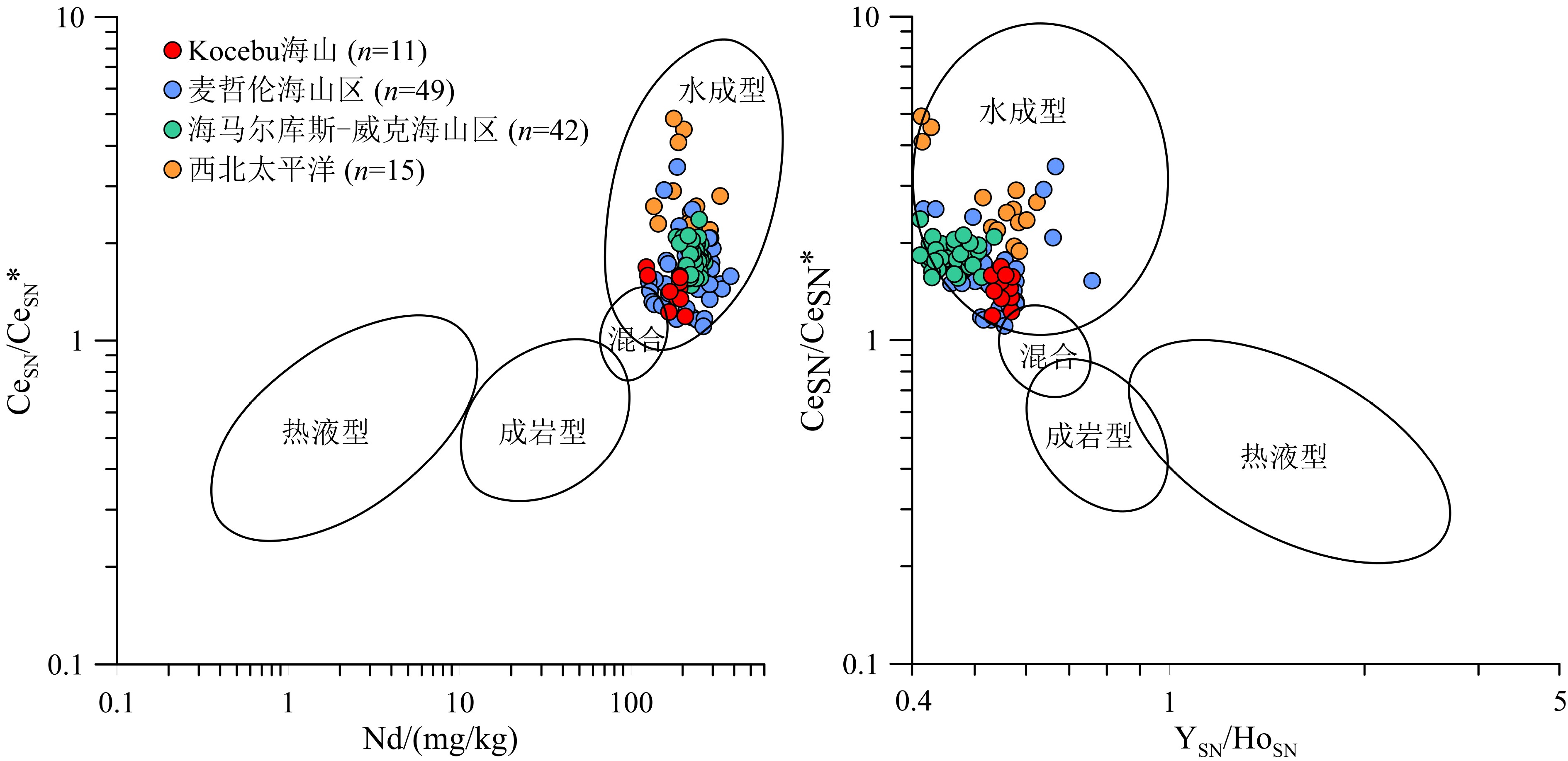
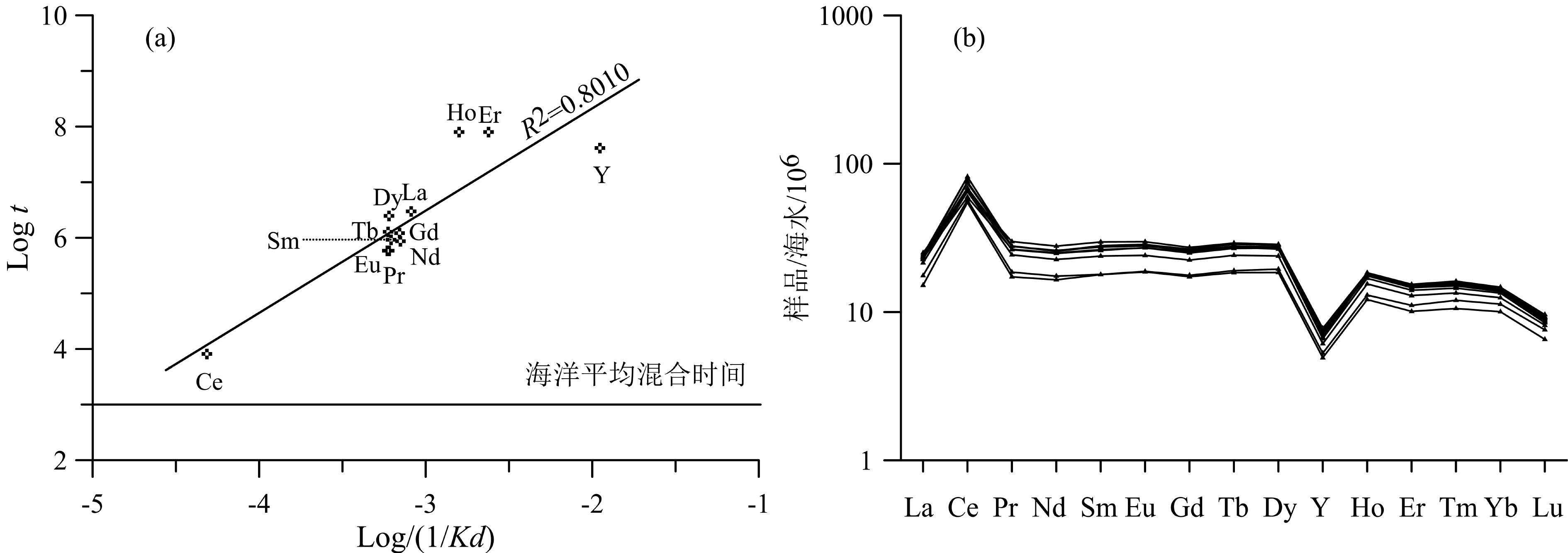
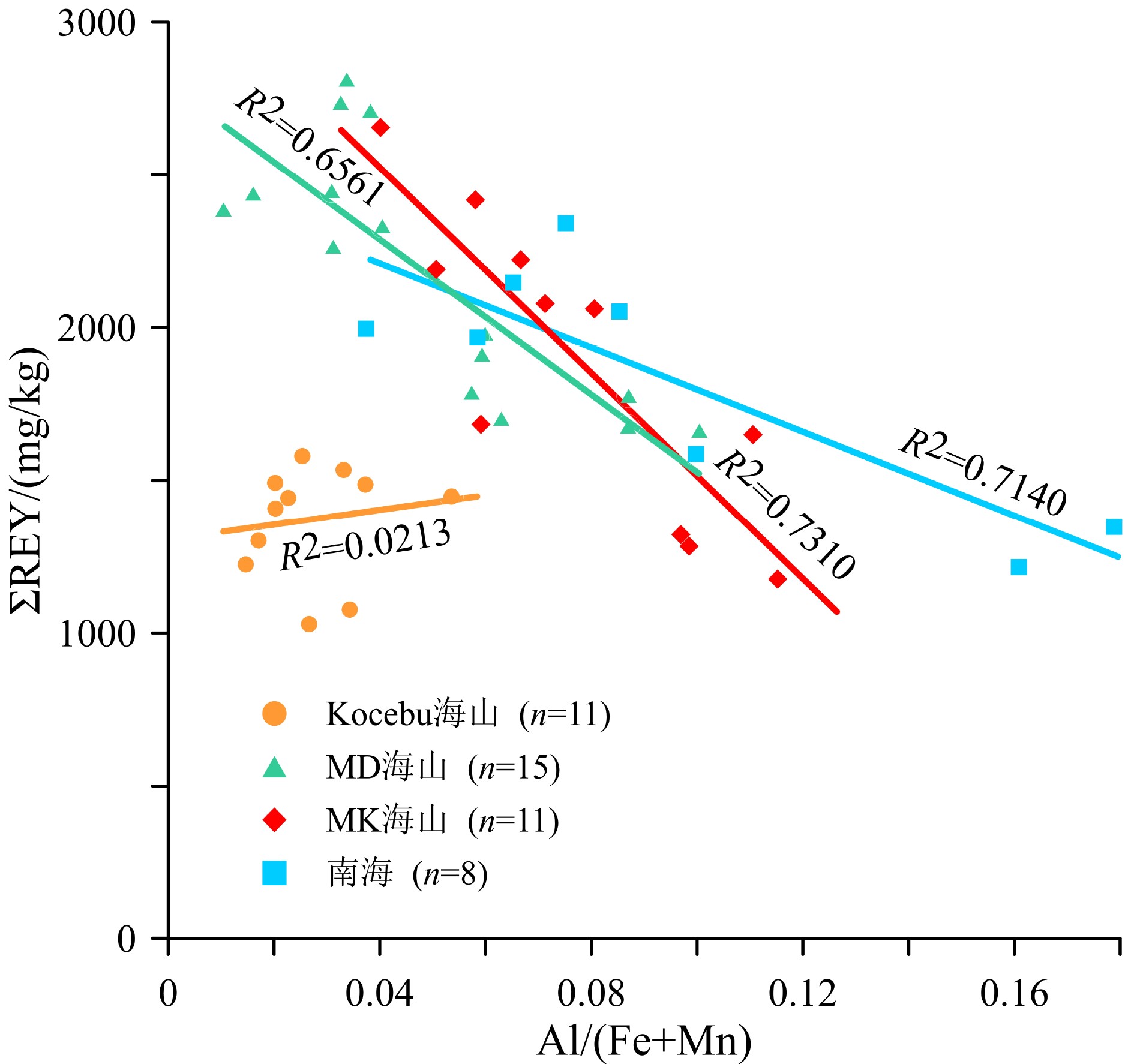
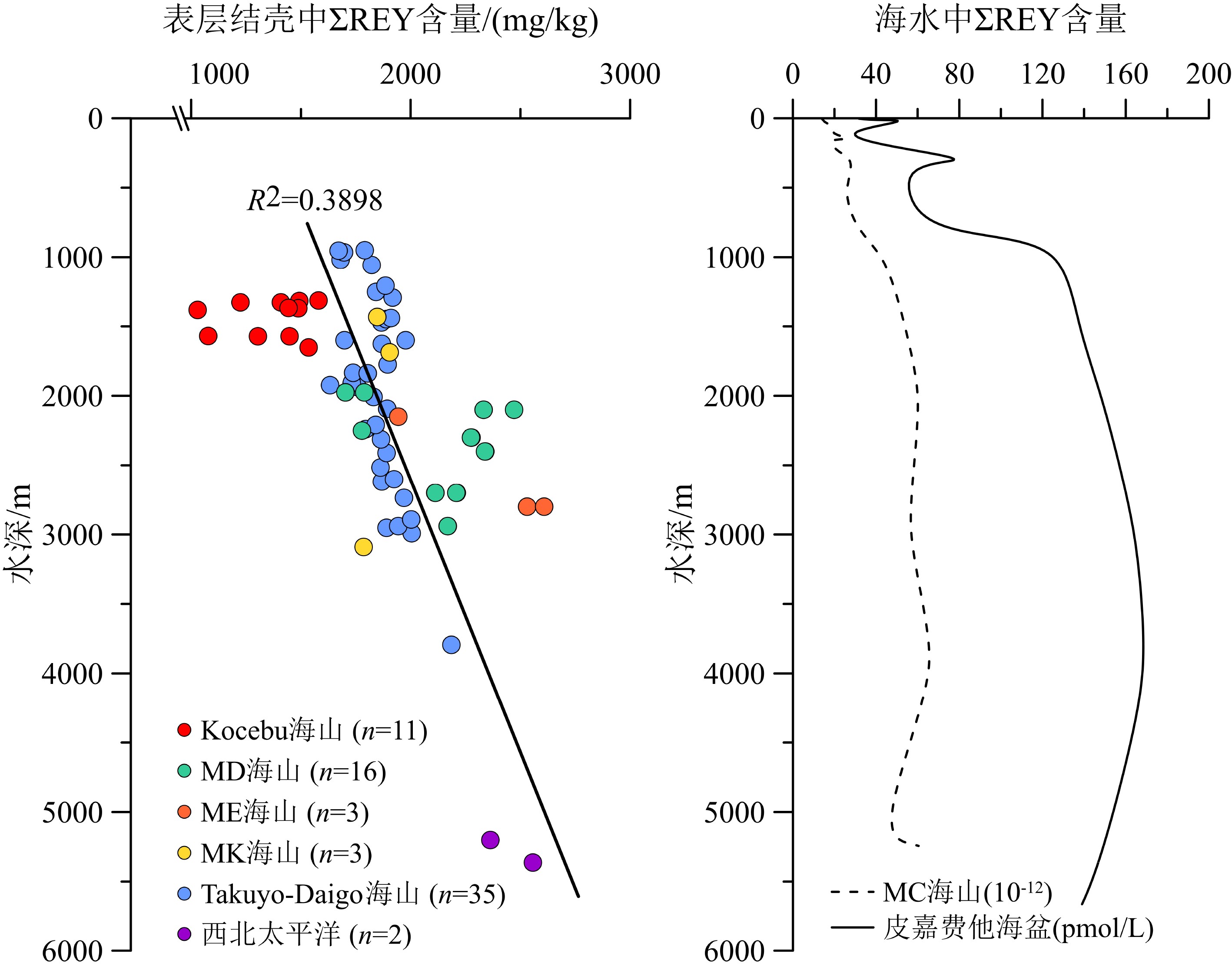
西太平洋麦哲伦海山区是全球重要的铁锰结壳资源分布区,具有丰富的稀土元素资源潜力。本文对采自麦哲伦海山区Kocebu海山的11个铁锰结壳表层样(<1 mm)进行稀土元素地球化学研究,探讨其含量特征、成因和影响稀土元素富集的环境因素。结果表明:Kocebu海山铁锰结壳表层样品ΣREY(Rare earth elements and yttrium)平均含量为1 366 mg/kg,低于前人在麦哲伦海山区其他海山以及邻近的马尔库斯–威克海山区的分析结果;样品轻稀土富集和Ce正异常(平均值为1.45)特征以及稀土元素成因图解、配分曲线和分配系数曲线等均表明该海山结壳属于水成成因;海水中稀土元素含量和溶解氧含量是控制结壳生长的关键环境参数,二者在Kocebu海山所在海区的浅水环境中含量较低;结壳ΣREY含量偏低与采样点水深较浅导致的海水稀土元素含量和溶解氧含量较低密切相关,受碎屑矿物的稀释作用影响较小。在开展铁锰结壳地球化学特征研究和资源勘探评价时应充分考虑采样水深的分布范围,局部水深样品的分析结果可能导致研究结果出现较大偏差。
Abstract:The Magellan Seamounts in the Western Pacific, as an important contract area for ferromanganese crusts exploration, contain high potential of rare earth resources. In this paper, the geochemistry of rare earth elements and yttrium (REY) from 11 top surface ferromanganese crust samples (<1 mm) collected from the Kocebu Guyot were studied. We analyzed the REY composition characteristics and genetic type of the samples and discussed the factors which control the enrichment of REY. The results show that the average REY abundance (ΣREY) of the crusts is 1366 mg/kg, which is lower than that from other seamounts in Magellan Seamounts and Marcus-Wake Seamounts. The Kocebu Guyot is characterized by enriched light REE and high positive Ce anomalies (mean δCe value 1.45). Genetic discrimination diagram, normalized REY plots and REY partition coefficient patterns indicate that all the crusts are hydrogenetic in origin. REY abundance and dissolved oxygen content in seawater should be regarded as primary environmental parameters controlling the growth of crusts. The lower REY abundance in the samples is related to the water depth and affected by lower REY and oxygen content in shallower waters near Kocebu Guyot, but not observably diluted by detrital minerals. Geochemistry research and resource evaluation of ferromanganese crusts in seamount areas should take the influence of water depth into further consideration, the analysis of samples from limited water depth may cause large deviations in the research results.
-
Key words:
- ferromanganese crusts /
- rare earth elements /
- geochemistry /
- genesis /
- Magellan Seamounts
-

-
图 4 Kocebu海山铁锰结壳成因类型判别图解[34]
Figure 4.
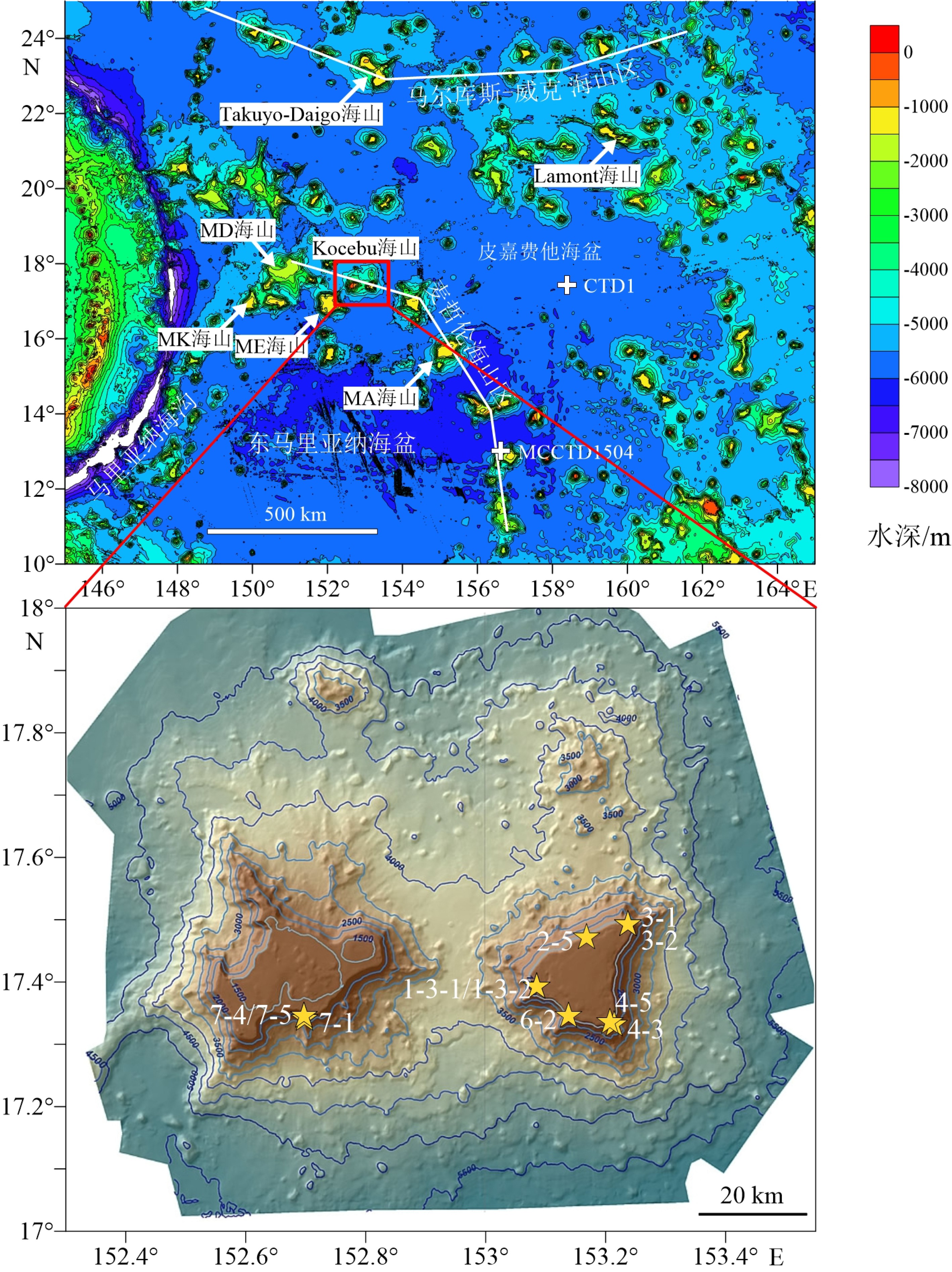
表 1 Kocebu海山铁锰结壳采样信息
Table 1. The sampling information of Fe-Mn crusts from Kocebu Guyot
样品编号 北纬 东经 水深/m 1-3-1 17.393° 153.125° 1 327 1-3-2 17.393° 153.125° 1 327 2-5 17.472° 153.168° 1 318 3-1 17.493° 153.237° 1 370 3-2 17.493° 153.237° 1 368 4-3 17.332° 153.214° 1 652 4-5 17.336° 153.207° 1 314 6-2 17.346° 153.138° 1 382 7-1 17.341° 152.698° 1 570 7-4 17.346° 152.697° 1 572 7-5 17.346° 152.697° 1 572 表 2 Kocebu海山与附近其他海山(区)铁锰结壳表层稀土元素含量
Table 2. Mean concentrations of rare earth elements and yttrium(REY) in surface layer of crusts from Kocebu Guyot and other areas nearby
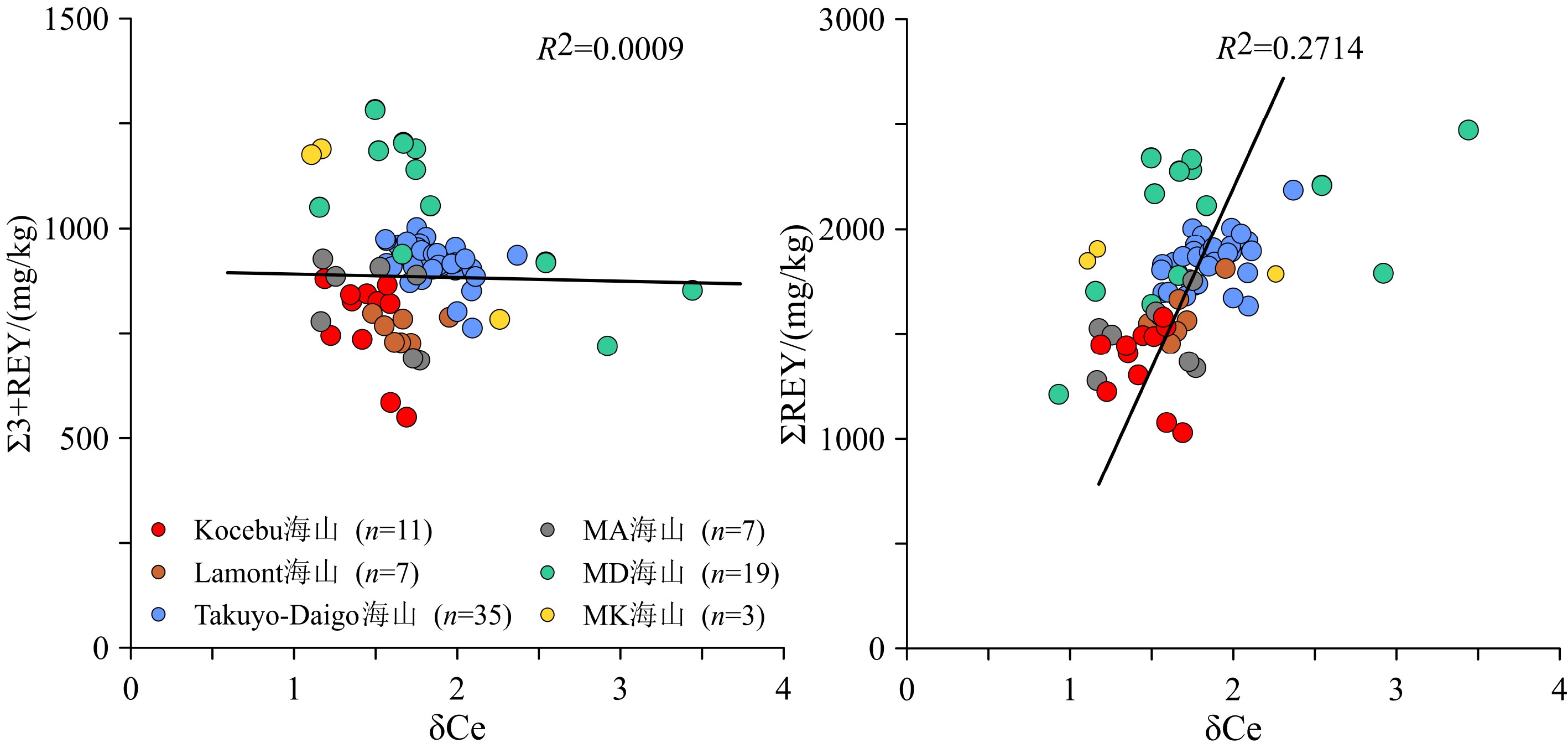
样品编号 La Ce Pr Nd Sm Eu Gd Tb Dy Y Ho Er Tm Yb Lu ΣREY Σ3+REY ΣLREE ΣHREE δCe 1-3-1 204 479 39.9 167 34.7 8.57 41.0 6.32 36.8 154 7.87 20.9 3.08 19.1 2.80 1 224 745 933 292 1.22 1-3-2 223 582 43.9 185 38.3 9.52 45.7 7.01 41.5 172 8.79 23.3 3.51 21.8 3.16 1 409 827 1 082 326 1.36 2-5 230 649 46.6 192 41.2 10.0 46.7 7.22 41.9 170 8.72 22.8 3.39 20.9 2.99 1 493 844 1 168 324 1.45 3-1 221 662 46.4 192 41.1 9.83 47.0 7.23 41.5 162 8.60 22.6 3.31 20.6 2.93 1 488 826 1 172 316 1.51 3-2 230 601 46.3 194 40.3 9.77 47.3 7.21 41.9 166 8.78 23.1 3.39 21.0 3.06 1 444 842 1 122 321 1.34 4-3 232 714 46.4 192 40.6 9.86 46.3 7.14 40.4 151 8.28 21.8 3.19 20.1 2.88 1 535 821 1 234 301 1.59 4-5 238 715 46.2 193 41.0 9.98 48.1 7.45 43.0 177 9.02 23.8 3.55 22.1 3.27 1 580 865 1 243 337 1.57 6-2 148 479 28.9 123 26.3 6.52 31.4 4.79 28.1 112 5.95 15.7 2.33 15.1 2.22 1 029 550 812 218 1.69 7-1 167 492 30.0 125 25.9 6.28 31.2 4.79 28.7 120 6.27 17.0 2.59 17.0 2.56 1 078 585 847 230 1.59 7-4 245 568 49.9 207 43.6 10.4 49.4 7.59 43.5 163 8.94 23.5 3.45 21.6 3.07 1 448 880 1 124 324 1.19 7-5 209 567 40.6 169 35.1 8.44 40.6 6.27 36.3 139 7.58 20.0 2.96 18.7 2.77 1 304 736 1 029 274 1.42 平均 213 592 42.3 176 37.1 9.02 43.1 6.64 38.5 153 8.07 21.3 3.16 19.8 2.88 1 366 775 1 070 297 1.45 MA(Pallada) 海山[24] 220 651 47.8 197 39.3 10.1 46.7 6.66 39.5 159 8.18 22.2 3.11 20.4 3.06 1 474 823 1 165 309 1.48 MD(Govorov) 海山[12, 25-26] 305 1 061 61.1 263 54.1 13.6 62.3 9.21 53.4 188 11.1 29.5 4.26 28.0 4.11 2 059 1072 1 748 385 1.81 ME(Il'ichev) 海山[12, 25] 365 1 198 70.8 301 60.9 15.2 71.5 10.1 58.2 222 12.5 33.4 4.66 31.0 4.59 2 164 1163 1 927 434 1.77 MK(Skornyakov) 海山[15-16, 25] 275 737 49.4 222 46.2 11.6 56.0 7.96 47.8 158 10.0 27.7 3.94 25.4 3.93 1 704 967 1 340 364 1.50 麦哲伦其他海山[13, 17] 316 961 59.6 261 54.4 13.3 62.9 9.29 53.2 − 11.3 30.4 4.43 27.6 4.32 1 866 907 1 665 203 1.84 Lamont 海山[14] 264 832 50.2 216 46.0 11.0 50.2 8.02 46.1 − 9.40 25.9 3.92 25.6 3.76 1 592 760 1 419 173 1.66 Takuyo-Daigo Smt.[27] 249 933 55.2 234 51.4 12.4 53.3 7.99 47.1 145 9.15 25.2 3.58 22.2 3.29 1 853 919 1 535 317 1.85 西北太平洋[28-29] 213 1 179 47.5 218 48.5 11.5 53.5 7.51 43.8 143 7.69 22.9 3.01 20.2 2.87 1 894 843 1 717 304 2.77 中国南海[30] 191 1 149 39.2 160 36.3 9.23 38.2 5.79 33.4 127 6.20 17.9 2.55 14.9 2.41 1 831 682 1 585 506 3.16 注:Σ3+REY为不包含Ce的ΣREY含量,ΣLREE为La—Eu,ΣHREE为Gd—Lu,δCe=2×CeSN/(LaSN+PrSN),La—ΣHREE的单位为mg/kg;−表示无数据。 -
[1] Hein J R, Mizell K, Koschinsky A, et al. Deep-ocean mineral deposits as a source of critical metals for high-and green-technology applications: Comparison with land-based resources [J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2013, 51: 1-14. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2012.12.001
[2] Lusty P A J, Hein J R, Josso P. Formation and occurrence of ferromanganese crusts: earth's storehouse for critical metals [J]. Elements, 2018, 14(5): 313-318. doi: 10.2138/gselements.14.5.313
[3] Hein J R, Spinardi F, Okamoto N, et al. Critical metals in manganese nodules from the Cook Islands EEZ, abundances and distributions [J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2015, 68: 97-116. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2014.12.011
[4] Hein J R, Koschinsky A. Deep-ocean ferromanganese crusts and nodules[M]//Holland H D, Turekian K K. Treatise on Geochemistry. 2nd ed. Oxford: Elsevier Ltd., 2014.
[5] Pak S J, Seo I, Lee K Y, et al. Rare earth elements and other critical metals in deep seabed mineral deposits: Composition and implications for resource potential [J]. Minerals, 2019, 9(1): 3.
[6] Li D F, Fu Y, Sun X M, et al. Critical metal enrichment mechanism of deep-sea hydrogenetic nodules: Insights from mineralogy and element mobility [J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2020, 118: 103371. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2020.103371
[7] Guan Y, Sun X M, Shi G Y, et al. Rare earth elements composition and constraint on the genesis of the polymetallic crusts and nodules in the South China Sea [J]. Acta Geologica Sinica-English Edition, 2017, 91(5): 1751-1766. doi: 10.1111/1755-6724.13409
[8] Ren Y Z, Sun X M, Guan Y, et al. Distribution of rare earth elements plus yttrium among major mineral phases of marine Fe–Mn crusts from the South China Sea and Western Pacific Ocean: A comparative study [J]. Minerals, 2019, 9(1): 8.
[9] Smith W H F, Staudigel H, Watts A B, et al. The Magellan seamounts: early cretaceous record of the South Pacific isotopic and thermal anomaly [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 1989, 94(B8): 10501-10523. doi: 10.1029/JB094iB08p10501
[10] Koppers A A P, Staudigel H, Wijbrans J R, et al. The Magellan seamount trail: implications for Cretaceous hotspot volcanism and absolute Pacific plate motion [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1998, 163(1-4): 53-68. doi: 10.1016/S0012-821X(98)00175-7
[11] Hein J R, Conrad T A, Dunham R E. Seamount characteristics and mine-site model applied to exploration-and mining-lease-block selection for cobalt-rich ferromanganese crusts [J]. Marine Georesources & Geotechnology, 2009, 27(2): 160-176.
[12] 朱克超, 赵祖斌, 李扬. 麦哲伦海山区MD、ME、MF海山富钴结壳特征[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2001, 21(1):33-38
ZHU Kechao, ZHAO Zubin, LI Yang. Cobalt-rich ferromanganese crusts from the MA, ME and MF seamounts of the Magellan seamounts [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2001, 21(1): 33-38.
[13] 卜文瑞. 太平洋富钴结壳稀有气体地球化学特征及其成矿指示意义[D]. 中国科学院研究生院(海洋研究所)博士学位论文, 2008.
BU Wenrui. Noble Gas geochemistry of ferromanganese crusts form pacific ocean and their significations for the formation of crusts[D]. Doctor Dissertation of Graduate University of Chinese Academy of Sciences (The Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences), 2008.
[14] 李江山, 石学法, 刘季花, 等. 古海洋环境演化对富钴结壳稀土元素富集的制约[J]. 中国稀土学报, 2011, 29(5):622-629
LI Jiangshan, SHI Xuefa, LIU Jihua, et al. Constraints of paleoceanographic environmental evolution on REEs enrichment in co-rich crust [J]. Journal of the Chinese Society of Rare Earths, 2011, 29(5): 622-629.
[15] 任向文, 石学法, 朱爱美, 等. 麦哲伦海山群MK海山富钴结壳稀土元素的赋存相态[J]. 吉林大学学报: 地球科学版, 2011, 41(3):707-714
REN Xiangwen, SHI Xuefa, ZHU Aimei, et al. Existing phase of rare earth elements in Co-Rich Fe-Mn crusts from seamount MK of magellan seamount cluster [J]. Journal of Jilin University: Earth Science Edition, 2011, 41(3): 707-714.
[16] 杨胜雄, 龙晓军, 祁奇, 等. 西太平洋富钴结壳矿物学和地球化学特征: 以麦哲伦海山和马尔库斯-威克海山富钴结壳为例[J]. 中国海洋大学学报, 2016, 46(2):105-116
YANG Shengxiong, LONG Xiaojun, QI Qi, et al. The mineralogical and geochemical characteristics of co-rich crusts from the western pacific: Taking the co-rich crusts from Magellan and Marcus-wake seamounts as an example [J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 2016, 46(2): 105-116.
[17] 薛婷, 孙晓明, 张美, 等. 西太平洋海山富钴结壳稀土元素(REE)组成原位LA-ICPMS测定[J]. 岩石学报, 2008, 24(10):2423-2432
XUE Ting, SUN Xiaoming, ZHANG Mei, et al. In-situ LA-ICPMS analysis of rare earth elements of ferromanganese crusts from west Pacific Ocean seamounts [J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2008, 24(10): 2423-2432.
[18] 王晓红, 周力平, 王毅民, 等. 太平洋富钴结壳高密度环境记录解读[J]. 中国科学 D辑: 地球科学, 2008, 51(10):1460-1469 doi: 10.1007/s11430-008-0092-6
WANG Xiaohong, ZHOU Limin, WANG Yimin, et al. Paleoenvironmental implications of high-density records in Co-rich seamount crusts from the Pacific Ocean [J]. Science in China Series D: Earth Sciences, 2008, 51(10): 1460-1469. doi: 10.1007/s11430-008-0092-6
[19] Lee T G, Hein J R, Lee K, et al. Sub-seafloor acoustic characterization of seamounts near the Ogasawara Fracture Zone in the western Pacific using chirp (3-7 kHz) subbottom profiles [J]. Deep Sea Research Part I: Oceanographic Research Papers, 2005, 52(10): 1932-1956. doi: 10.1016/j.dsr.2005.04.009
[20] Clouard V, Bonneville A. Ages of seamounts, islands, and plateaus on the Pacific plate[M]//Foulger G R, Natland J H, Presnall D C, et al. Plates, plumes and paradigms. Geological Society of America, 2005, 388: 71.
[21] Rashidov V A. Geologic-geophysical investigations of Magellan Seamount Guyots, Pacific Ocean. Vestnik KRAUNC (Bulletin of Kamchanka Regional Association "Educational-Scientific Center") [J]. Earth Sciences, 2003(1): 103-126.
[22] Pringle M S. Radiometric ages of basaltic basement recovered at Sites 800, 801, and 802, Leg 129, western Pacific Ocean [J]. Proceedings of the Ocean Drilling Program, Scientific Results, 1992, 129: 389-404.
[23] 赵俐红, 金翔龙, 高金耀, 等. 麦哲伦海山链漂移史及可能的来源[J]. 海洋学报, 2010, 32(3):60-66
ZHAO Lihong, JIN Xianglong, GAO Jinyao, et al. The research on the drifting history and possible origin of the Magellan seamount trail [J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2010, 32(3): 60-66.
[24] 王嘹亮, 钟和贤, 曾繁彩, 等. 麦哲伦海山区MA、MC海山富钴结壳元素间关系及成因意义[J]. 南海地质研究, 1999, 11:26-46
WANG Liaoliang, ZHONG Hexian, ZENG Fancai, et al. Interelement relationships and their implications for crust genesis in cobalt-rich ferromanganese crusts from the MA and MC seamounts of the Magellan seamounts [J]. Gresearch of Eological South China Sea, 1999, 11: 26-46.
[25] 任向文. 西太平洋富钴结壳成矿系统[D]. 中国科学院海洋研究所博士学位论文, 2005.
REN Xiangwen. The Metallogenic system of co-rich manganese crusts in western pacific[D]. Doctor Dissertation of Institute of oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2005.
[26] 任向文, 刘季花, 石学法, 等. 麦哲伦海山群M海山富钴结壳成因与成矿时代: 来自地球化学和Co地层学的证据[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2011, 31(6):65-74
REN Xiangwen, LIU Jihua, SHI Xuefa, et al. Genesis and Ore-forming stages of Co-rich ferromanganese crusts from seamount M of magellan seamounts: evidence from geochemistry and Co Chronology [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2011, 31(6): 65-74.
[27] Usui A, Nishi K, Sato H, et al. Continuous growth of hydrogenetic ferromanganese crusts since 17 Myr ago on Takuyo-Daigo Seamount, NW Pacific, at water depths of 800-5500 m [J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2017, 87: 71-87. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2016.09.032
[28] Hein J R, Conrad T A, Frank M, et al. Copper‐nickel‐rich, amalgamated ferromanganese crust‐nodule deposits from Shatsky Rise, NW Pacific [J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2012, 13(10): Q10022.
[29] Azami K, Hirano N, Machida S, et al. Rare earth elements and yttrium (REY) variability with water depth in hydrogenetic ferromanganese crusts [J]. Chemical Geology, 2018, 493: 224-233. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2018.05.045
[30] Guan Y, Sun X M, Ren Y Z, et al. Mineralogy, geochemistry and genesis of the polymetallic crusts and nodules from the South China Sea [J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2017, 89: 206-227. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2017.06.020
[31] Gromet L P, Haskin L A, Korotev R L, et al. The “North American shale composite”: its compilation, major and trace element characteristics [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1984, 48(12): 2469-2482. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(84)90298-9
[32] Bau M, Koschinsky A, Dulski P, et al. Comparison of the partitioning behaviours of yttrium, rare earth elements, and titanium between hydrogenetic marine ferromanganese crusts and seawater [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1996, 60(10): 1709-1725. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(96)00063-4
[33] Menendez A, James R H, Roberts S, et al. Controls on the distribution of rare earth elements in deep-sea sediments in the North Atlantic Ocean [J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2017, 87: 100-113. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2016.09.036
[34] Bau M, Schmidt K, Koschinsky A, et al. Discriminating between different genetic types of marine ferro-manganese crusts and nodules based on rare earth elements and yttrium [J]. Chemical Geology, 2014, 381: 1-9. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2014.05.004
[35] 赵广涛, 何雨旸, 陈淳, 等. 太平洋铁锰结核与富Co结壳的矿物地球化学比较研究[J]. 中国海洋大学学报, 2011, 41(5):85-93
ZHAO Guangtao, HE Yuyang, CHEN Chun, et al. Comparison of the mineral and geochemistry characteristics between co-rich crusts and ferromanganese nodules from the Pacific ocean [J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 2011, 41(5): 85-93.
[36] Marino E, González F J, Kuhn T, et al. Hydrogenetic, diagenetic and hydrothermal processes forming ferromanganese crusts in the Canary Island Seamounts and their influence in the metal recovery rate with hydrometallurgical methods [J]. Minerals, 2019, 9(7): 439. doi: 10.3390/min9070439
[37] Fitzgerald C E, Gillis K M. Hydrothermal manganese oxide deposits from Baby Bare seamount in the Northeast Pacific Ocean [J]. Marine Geology, 2006, 225(1-4): 145-156. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2005.09.005
[38] Pelleter E, Fouquet Y, Etoubleau J, et al. Ni-Cu-Co-rich hydrothermal manganese mineralization in the Wallis and Futuna back-arc environment (SW Pacific) [J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2017, 87: 126-146. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2016.09.014
[39] Josso P, Pelleter E, Pourret O, et al. A new discrimination scheme for oceanic ferromanganese deposits using high field strength and rare earth elements [J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2017, 87: 3-15. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2016.09.003
[40] De Carlo E H, McMurtry G M. Rare-earth element geochemistry of ferromanganese crusts from the Hawaiian Archipelago, central Pacific [J]. Chemical Geology, 1992, 95(3-4): 235-250. doi: 10.1016/0009-2541(92)90014-V
[41] Lécuyer C. Seawater residence times of some elements of geochemical interest and the salinity of the oceans [J]. Bulletin de la Société Géologique de France, 2016, 187(6): 245-260.
[42] 任江波, 邓希光, 邓义楠, 等. 中国富钴结壳合同区海水的稀土元素特征及其意义[J]. 地球科学, 2019, 44(10):3529-3540
REN Jiangbo, DENG Xiguang, DENG Yi’nan, et al. Rare earth element characteristics and its geological implications for seawater from cobalt-rich ferromanganese crust exploration contract area of China [J]. Earth Science, 2019, 44(10): 3529-3540.
[43] Bau M, Koschinsky A. Hafnium and neodymium isotopes in seawater and in ferromanganese crusts: the “element perspective” [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2006, 241(3-4): 952-961. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2005.09.067
[44] Ohta A, Kawabe I. Rare earth element partitioning between Fe oxyhydroxide precipitates and aqueous NaCl solutions doped with NaHCO3: Determinations of rare earth element complexation constants with carbonate ions [J]. Geochemical Journal, 2000, 34(6): 439-454. doi: 10.2343/geochemj.34.439
[45] Patten J T, Byrne R H. Assessment of Fe (III) and Eu (III) complexation by silicate in aqueous solutions [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2017, 202: 361-373. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2016.12.004
[46] Ohta A, Kawabe I. REE (III) adsorption onto Mn dioxide (δ-MnO2) and Fe oxyhydroxide: Ce (III) oxidation by δ-MnO2 [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2001, 65(5): 695-703. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(00)00578-0
[47] Luo Y R, Byrne R H. Carbonate complexation of yttrium and the rare earth elements in natural waters [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2004, 68(4): 691-699. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(03)00495-2
[48] Koschinsky A, Hein J R. Uptake of elements from seawater by ferromanganese crusts: solid-phase associations and seawater speciation [J]. Marine Geology, 2003, 198(3-4): 331-351. doi: 10.1016/S0025-3227(03)00122-1
[49] Kuhn T, Wegorzewski A, Rühlemann C, et al. Composition, formation, and occurrence of polymetallic nodules[M]//Sharma R, ed. Deep-sea Mining. Cham: Springer, 2017: 23-63.
[50] Langmuir D. Aqueous environmental geochemistry[M]. Englewood Cliffs: Prentice-Hall, Inc., 1997.
[51] Bau M, Koschinsky A. Oxidative scavenging of cerium on hydrous Fe oxide: evidence from the distribution of rare earth elements and yttrium between Fe oxides and Mn oxides in hydrogenetic ferromanganese crusts [J]. Geochemical Journal, 2009, 43(1): 37-47. doi: 10.2343/geochemj.1.0005
[52] Byrne R H, Kim K H. Rare earth element scavenging in seawater [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1990, 54(10): 2645-2656. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(90)90002-3
[53] Cantrell K J, Byrne R H. Rare earth element complexation by carbonate and oxalate ions [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1987, 51(3): 597-605. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(87)90072-X
[54] Alibo D S, Nozaki Y. Dissolved rare earth elements in the eastern Indian Ocean: chemical tracers of the water masses [J]. Deep Sea Research Part I: Oceanographic Research Papers, 2004, 51(4): 559-576. doi: 10.1016/j.dsr.2003.11.004
[55] Mizell K, Hein J R, Lam P J, et al. Geographic and oceanographic influences on ferromanganese crust composition along a pacific ocean meridional transect, 14 N to 14S [J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2020, 21(2): e2019GC008716.
[56] Mizell K, Hein J R. Ferromanganese crusts and nodules, rocks that grow[M]. Springer International Publishing, 2016.
[57] Liu Z F, Zhao Y L, Colin C, et al. Source-to-sink transport processes of fluvial sediments in the South China Sea [J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2016, 153: 238-273. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2015.08.005
[58] Prakash L S, Ray D, Paropkari A L, et al. Distribution of REEs and yttrium among major geochemical phases of marine Fe–Mn-oxides: Comparative study between hydrogenous and hydrothermal deposits [J]. Chemical Geology, 2012, 312-313: 127-137. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2012.03.024
[59] Zhang J, Nozaki Y. Rare earth elements and yttrium in seawater: ICP-MS determinations in the East Caroline, Coral Sea, and South Fiji basins of the western South Pacific Ocean [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1996, 60(23): 4631-4644. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(96)00276-1
[60] Deng Y N, Ren J B, Guo Q J, et al. Rare earth element geochemistry characteristics of seawater and porewater from deep sea in western Pacific [J]. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7: 16539. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-16379-1
[61] Conrad T, Hein J R, Paytan A, et al. Formation of Fe-Mn crusts within a continental margin environment [J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2017, 87: 25-40. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2016.09.010
[62] Kawabe M, Fujio S, Yanagimoto D, et al. Water masses and currents of deep circulation southwest of the Shatsky Rise in the western North Pacific [J]. Deep Sea Research Part I: Oceanographic Research Papers, 2009, 56(10): 1675-1687. doi: 10.1016/j.dsr.2009.06.003
[63] Marcus M A, Toner B M, Takahashi Y. Forms and distribution of Ce in a ferromanganese nodule [J]. Marine Chemistry, 2018, 202: 58-66. doi: 10.1016/j.marchem.2018.03.005
[64] 韩杰, 武光海, 叶瑛, 等. 铁锰结壳中底层洋流活动的地球化学研究[J]. 矿床地质, 2006, 25(5):620-628 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2006.05.009
HAN Jie, WU Guanghai, YE Ying, et al. Geochemical record of bottom water in ferromanganese crusts [J]. Mineral Deposits, 2006, 25(5): 620-628. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2006.05.009
[65] De Carlo E H. Paleoceanographic implications of rare earth element variability within a Fe-Mn crust from the central Pacific Ocean [J]. Marine Geology, 1991, 98(2-4): 449-467. doi: 10.1016/0025-3227(91)90116-L
[66] 姜学钧, 林学辉, 姚德, 等. 稀土元素在水成型海洋铁锰结壳中的富集特征及机制[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2011, 54(2):197-203 doi: 10.1007/s11430-010-4070-4
JIANG Xuejun, LIN Xuehui, YAO De, et al. Enrichment mechanisms of rare earth elements in marine hydrogenic ferromanganese crusts [J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 2011, 54(2): 197-203. doi: 10.1007/s11430-010-4070-4
-



 下载:
下载: