Geophysical characteristics and migration mechanism of active submarine sand waves off the coast of Dongfang, Hainan
-
摘要:
海南东方近岸海底发育有大量沙波,利用多波束测深、侧扫声呐、浅地层剖面、单道地震资料综合分析了活动沙波的地球物理特征,探讨了沙波的分布特征、迁移机制、活动性及形态演变特征。结果表明,研究区海底沙波分布和规模具有显著空间差异性,大中型沙波主要发育于沙脊上,小型沙波主要发育于沙脊两侧,坑槽区发育近对称沙波,研究区西南部沙波不发育。受潮流和科氏力约束,在海底沙脊西侧沙波迁移方向主要为向北(略偏东),在沙脊东侧主要为向南(略偏西);受地形制约,坑槽区近对称沙波迁移可能停止或方向发生改变。沙波活动性强的标志主要包括:① 形态呈不对称的“脊尖槽缓”,② 叠置小沙波与沙纹发育,③ 浅部有透明层,④ 陡坡面反射模糊,⑤ 内部斜交前积结构。分析认为,沙波活动性与其形态密切相关,包括弱运动、强运动、不运动3个演变阶段。
Abstract:A large numbers of sand waves are developed on the seafloor off the coast of Dongfang, Hainan. This paper is devoted to the study of the geophysical characteristics of active submarine sand waves by means of multi-beam echo-sounding, side-scan sonar, sub-bottom profile, and single-channel seismic, and to the discussion on the distribution pattern, migration mechanism, activity, and morphologic evolution of the sand waves. The results show that there are significant spatial differences in the distribution and scale of submarine sand waves, for examples, large and medium-sized sand waves are mainly developed on the top of sand ridges, small sand waves developed mainly on the two sides of sand ridges, and near-symmetrical sand waves developed in the areas of pits. Submarine sand waves are not developed in the southwest of the study area. Constrained by tidal current and Coriolis force, the migration direction of the sand wave on the west side of the submarine sand ridge is mainly northwards with a few towards east, while those on the east side is mainly southwards with a few slightly towards west. Restricted by topography, the migration of near-symmetric sand waves may stop or change direction. Strongly active submarine sand waves are characterized by the features as follows. (a) Asymmetric shape with "sharp ridge and gentle trough"; (b) Small sand waves and sand ripples superimposed on sand waves; (c)Sub-bottom profile shows transparent layers; (d) Blank reflection on the steep slope; (e) Internal oblique progradation configuration. The analysis shows that the movement of the sand waves is closely related to its morphology, and three stages of evolution from inactive to highly active to motionless are recognized.
-

-
表 1 主要调查设备及数据采集参数
Table 1. Main parameters of the surveying systems
参数 多波束测深 侧扫声呐 浅地层剖面 单道地震 设备型号 EM710S EdgeTech4200 SES2000Medium SIG 2Mille震源Geo-sense 48电缆 中心频率/kHz 120 110 6 0.6~1 量程/m 通常为水深的3~4倍 单侧100 60 海底以下100 声源发射率/Hz 大于5 约为7 约为12 1 观测系统 船底安装 拖曳于船尾后约120 m,近底观测 船底安装 沉放约0.5 m,拖曳于右船尾后约45 m 表 2 海南岛西南近岸海域海底沙波形态参数统计
Table 2. Morphological parameters of submarine sand waves in the southwestern offshore area of Hainan
形态参数 研究区 海南岛西部VI区[7] 东方岸外东区[12] 海南岛西南海域[25] 海南岛东方海域[26] 水深/m 9~46,平均25 19.3~21.3 20~50 30~40 平均15 波长/m 7.1~329,平均93.3 41~148 − 5.8~91.8 41.5~719.7 波高/m 0.3~13.2,平均4.7 1.7~5.9 2~10 0.1~4.3 0.84~9.9 垂直形态参数 5.5~54,平均22 16~29 18~44 − 14.5~196.2 缓坡倾角/(°) 3.2~13,平均5 2.7~5.1 − − 0.34~8.05 陡坡倾角/(°) 3.2~25,平均10.7 10.4~16.8 10~20 − 2.0~13.3 对称指数 1.0~12.8,平均4.5 3.1~4.6 7~12.6 0.32~6.52 0.67~9.63 注:缓坡水平距离(a),陡坡水平距离(b),波长(L=a+b),波高(H),垂直形态参数(L/H),对称指数(a/b)。 表 3 研究区海底活动沙波地球物理特征
Table 3. Geophysical characteristics of active submarine sand waves in the study area
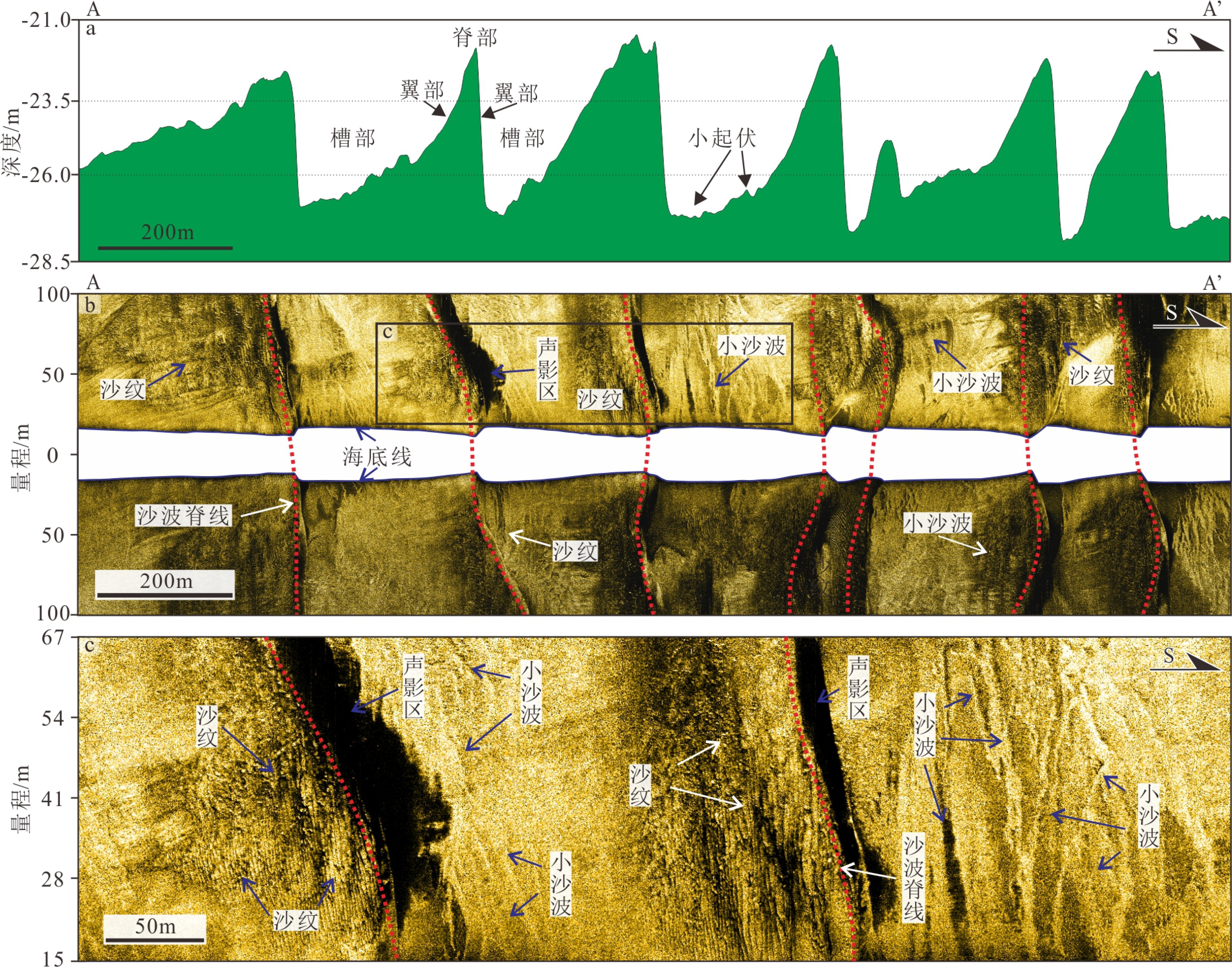
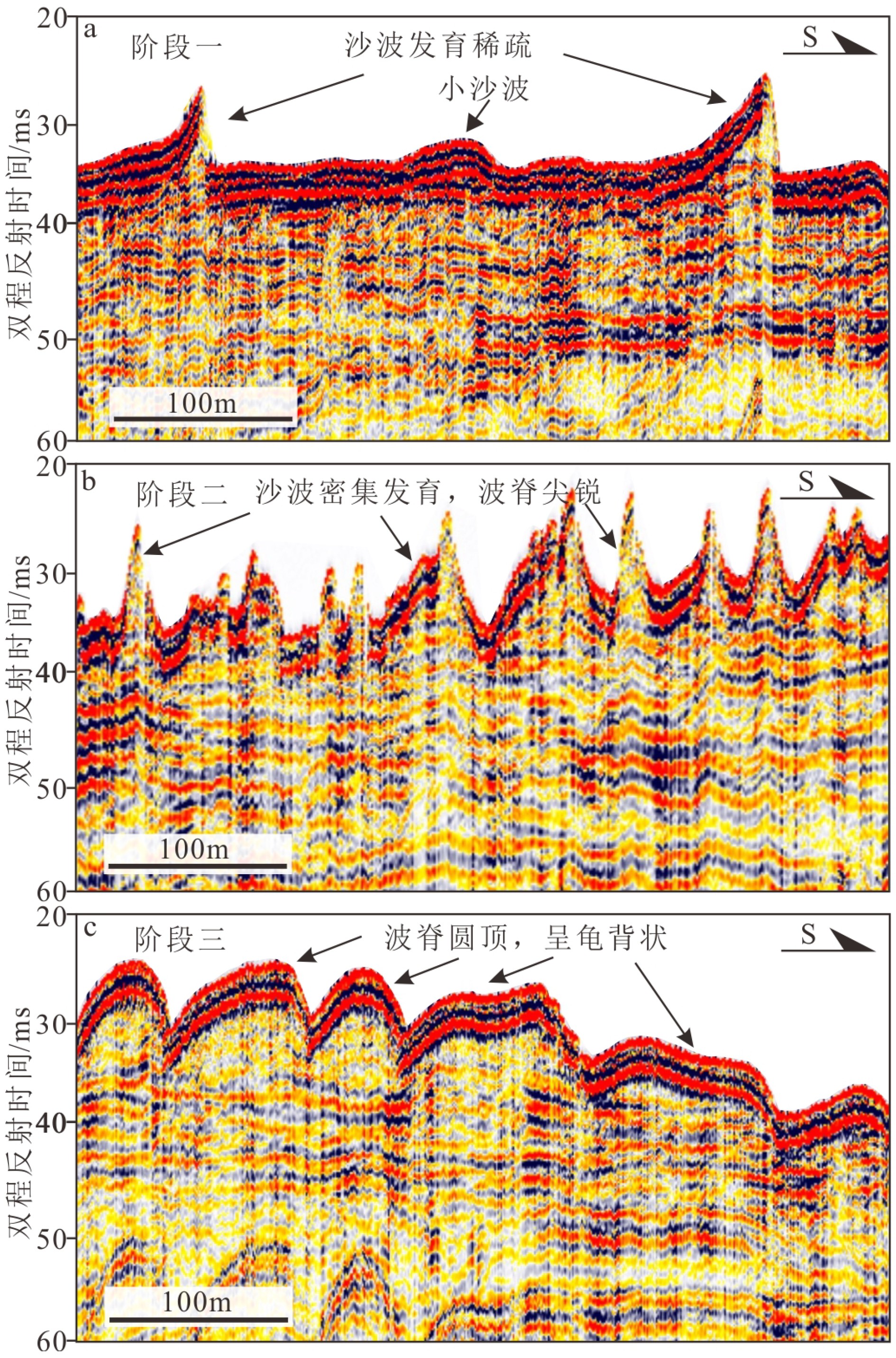
观测方法 地球物理特征 多波束测深 平面上呈韵律的新月形条带状;剖面上呈“脊尖槽缓”的波状排列,成群出现。 侧扫声呐 海底线呈“竹节状”变化,波脊线两侧回波强度变化明显;发育叠置小沙波与沙纹。 浅地层剖面 波状排列,通常波形不对称;浅部有一层透明层;缓坡面反射连续清晰,陡坡面反射模糊;内部可见迁移活动底界面。 单道地震 波状排列,波形陡缓分明;缓坡面表层为连续强振幅反射,陡坡面表层反射模糊。沙波内部为斜交前积反射结构,下伏为亚平行的层状反射。 -
[1] Allen J R L. Developments in Sedimentology[M]. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 1982: 953.
[2] Besio G, Blondeaux P, Vittori G. On the formation of sand waves and sand banks [J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 2006, 557: 1-27. doi: 10.1017/S0022112006009256
[3] 冯文科, 黎维峰, 石要红. 南海北部海底沙波地貌动态研究[J]. 海洋学报, 1994, 16(6):92-99
FENG Wenke, LI Weifeng, SHI Yaohong. Study on seafloor sandwaves dynamics in the northern South China Sea [J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 1994, 16(6): 92-99.
[4] 王尚毅, 李大鸣. 南海珠江口盆地陆架斜坡及大陆坡海底沙波动态分析[J]. 海洋学报, 1994, 16(6):122-132
WANG Shangyi, LI Daming. Analysis on submarine sand waves dynamics of shelf-slope and continental slope in the Pearl River Mouth Basin of the South China Sea [J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 1994, 16(6): 122-132.
[5] 叶银灿, 宋连清, 陈锡土. 东海海底不良工程地质现象分析[J]. 东海海洋, 1984, 2(3):34-39
YE Yincan, SONG Lianqing, CHEN Xitu. An analysis of geotechnical hazards of the East China Sea floor [J]. Donghai Marine Science, 1984, 2(3): 34-39.
[6] 刘振夏, 汤毓祥, 王揆洋, 等. 渤海东部潮流动力地貌特征[J]. 黄渤海海洋, 1996, 14(1):7-21
LIU Zhenxia, TANG Yuxiang, WANG Kuiyang, et al. Tidal dynamic geomorphic system in the east part of the Bohai Sea [J]. Journal of Oceanography of Huanghai & Bohai Seas, 1996, 14(1): 7-21.
[7] 曹立华, 徐继尚, 李广雪, 等. 海南岛西部岸外沙波的高分辨率形态特征[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2006, 26(4):15-22
CAO Lihua, XU Jishang, LI Guangxue, et al. High-resolution morphological characteristics of sand waves off the west Hainan island [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2006, 26(4): 15-22.
[8] 单红仙, 沈泽中, 刘晓磊, 等. 海底沙波分类与演化研究进展[J]. 中国海洋大学学报, 2017, 47(10):73-82
SHAN Hongxian, SHEN Zezhong, LIU Xiaolei, et al. Classification and evolution of submarine sandwave: a review [J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 2017, 47(10): 73-82.
[9] Dalrymple R W. Morphology and internal structure of sandwaves in the Bay of Fundy [J]. Sedimentology, 1984, 31(3): 365-382. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3091.1984.tb00865.x
[10] Doré A, Bonneton P, Marieu V, et al. Numerical modeling of subaqueous sand dune morphodynamics [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Earth Surface, 2016, 121(3): 565-587. doi: 10.1002/2015JF003689
[11] 蔺爱军, 胡毅, 林桂兰, 等. 海底沙波研究进展与展望[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2017, 32(3):1366-1377 doi: 10.6038/pg20170356
LIN Aijun, HU Yi, LIN Guilan, et al. Progress and perspective of submarine sand waves researches [J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2017, 32(3): 1366-1377. doi: 10.6038/pg20170356
[12] 夏东兴, 吴桑云, 刘振夏, 等. 海南东方岸外海底沙波活动性研究[J]. 黄渤海海洋, 2001, 19(1):17-24
XIA Dongxing, WU Shangyun, LIU Zhenxia, et al. Research on the activity of submarine sand waves off Dongfang, Hainan island [J]. Journal of Oceanography of Huanghai & Bohai Seas, 2001, 19(1): 17-24.
[13] 王琳, 吴建政, 石巍. 海南乐东陆架海底沙波形态特征及活动性研究[J]. 海洋湖沼通报, 2007(S1):53-59
WANG Lin, WU Jianzheng, SHI Wei. Research on the shape character and activity of submarine sand waves off Ledong, Hainan island [J]. Transactions of Oceanology and Limnology, 2007(S1): 53-59.
[14] 郭兴杰, 程和琴, 莫若瑜, 等. 长江口沙波统计特征及输移规律[J]. 海洋学报, 2015, 37(5):148-158
GUO Xingjie, CHENG Heqin, MO Ruoyu, et al. Statistical characteristics and transport law of sand waves in the Yangtze Estuary [J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2015, 37(5): 148-158.
[15] 余威, 吴自银, 周洁琼, 等. 台湾浅滩海底沙波精细特征、分类与分布规律[J]. 海洋学报, 2015, 37(10):11-25
YU Wei, WU Ziyin, ZHOU Jieqiong, et al. Meticulous characteristics, classification and distribution of seabed sand wave on the Taiwan bank [J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2015, 37(10): 11-25.
[16] Zheng S W, Cheng H Q, Wu S H, et al. Discovery and implications of catenary-bead subaqueous dunes [J]. Science China: Earth Sciences, 2016, 59(3): 495-502. doi: 10.1007/s11430-015-5194-3
[17] 庄振业, 曹立华, 刘升发, 等. 陆架沙丘(波)活动量级和稳定性标志研究[J]. 中国海洋大学学报, 2008, 38(6):1001-1007
ZHUANG Zhenye, CAO Lihua, LIU Shengfa, et al. Activity level and balance signs of subaqueous dunes (Waves) in the continental shelf [J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 2008, 38(6): 1001-1007.
[18] 林缅, 范奉鑫, 李勇, 等. 南海北部沙波运移的观测与理论分析[J]. 地球物理学报, 2009, 52(3):776-784
LIN Mian, FAN Fengxin, LI Yong, et al. Observation and theoretical analysis for the sand-waves migration in the North Gulf of South China Sea [J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2009, 52(3): 776-784.
[19] Li Y, Lin M, Jiang W B, et al. Process control of the sand wave migration in Beibu Gulf of the South China Sea [J]. Journal of Hydrodynamics, Ser. B, 2011, 23(4): 439-446. doi: 10.1016/S1001-6058(10)60134-5
[20] Jiang W B, Lin M. Research on bilateral reverse migration of one-group seabed sand waves in a small shallow shelf sea [J]. Coastal Engineering, 2016, 111: 70-82. doi: 10.1016/j.coastaleng.2016.01.013
[21] 庄振业, 林振宏, 周江, 等. 陆架沙丘(波)形成发育的环境条件[J]. 海洋地质动态, 2004, 20(4):5-10 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-2722.2004.04.002
ZHUANG Zhenye, LIN Zhenhong, ZHOU Jiang, et al. Environmental conditions for the formation and development of sand dunes (waves) in the continental shelf [J]. Marine Geology Letters, 2004, 20(4): 5-10. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-2722.2004.04.002
[22] 王文介. 南海北部的潮波传播与海底沙脊和沙波发育[J]. 热带海洋, 2000, 19(1):1-7
WANG Wenjie. Propagation of tidal waves and development of sea-bottom sand ridges and sand ripples in Northern South China sea [J]. Tropic Oceanology, 2000, 19(1): 1-7.
[23] 谭文化. 海南岛周边海域底质碎屑矿物分布及其物源分析[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学硕士学位论文(北京), 2007.
TAN Wenhua. Study on the distribution and origin of the seafloor detrital minerals in the offshore water of Hainan Island[D]. Beijing: Master Dissertation of China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2007.
[24] Ashley G M. Classification of large-scale subaqueous bedforms: a new look at an old problem [J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 1990, 60(1): 160-172. doi: 10.2110/jsr.60.160
[25] 张洪运, 栾振东, 李近元. 海南东方岸外风电场海底地形地貌特征[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2016, 32(9):1-6
ZHANG Hongyun, LUAN Zhendong, LI Jinyuan. Research of submarine topgraphy and geomorphology in Dongfang offshore wind farm, Hainan [J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2016, 32(9): 1-6.
[26] 王伟伟, 范奉鑫, 李成钢, 等. 海南岛西南海底沙波活动及底床冲淤变化[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2007, 27(4):23-28
WANG Weiwei, FAN Fengxin, LI Chenggang, et al. Activity of submarine sand waves and seafloor erosion and deposition in the sea area to the southwest of Hainan island [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2007, 27(4): 23-28.
[27] Daniell J J, Hughes M. The morphology of barchan-shaped sand banks from western Torres Strait, northern Australia [J]. Sedimentary Geology, 2007, 202(4): 638-652. doi: 10.1016/j.sedgeo.2007.07.007
-




 下载:
下载: