Evolution of clay minerals assemblages since Late Pliocene and its paleoenvironmental implications: Evidence from Core XT4 of the Philippine Sea Basin
-
摘要:
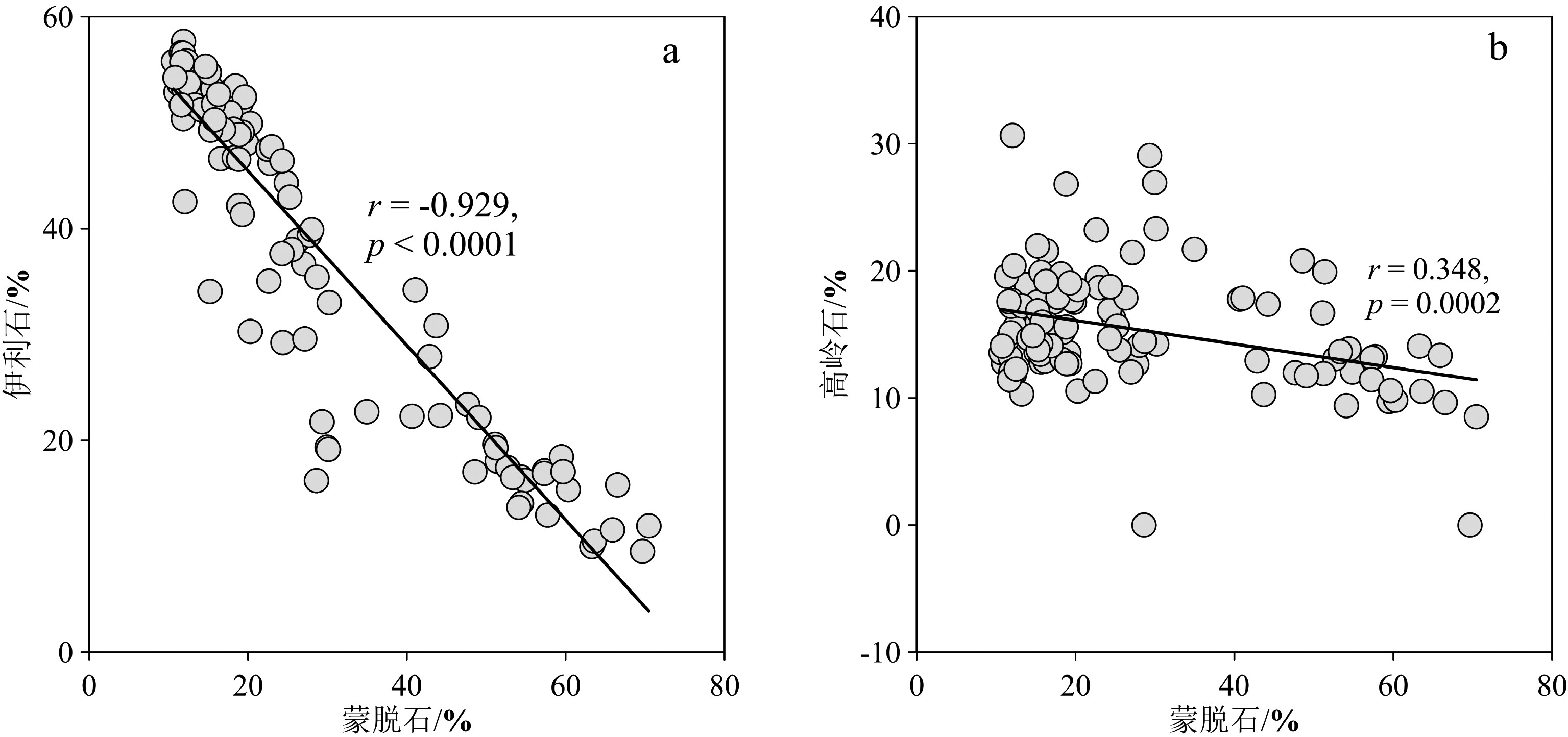
菲律宾海是典型风尘汇聚区,菲律宾海远离吕宋岛的深海沉积物是重建构造尺度亚洲风尘演化历史的良好载体。选取菲律宾海盆XT4孔沉积物开展了黏土矿物研究,并结合前人研究成果,在明确该孔黏土矿物来源的基础上,探讨了晚上新世以来亚洲风尘的演化历史及其可能的影响机制。菲律宾海盆XT4孔黏土矿物以伊利石为主,平均含量为39%,蒙脱石含量次之,平均为28%,绿泥石平均含量为18%,高岭石平均含量为15%。XT4孔黏土矿物组成符合亚洲大陆风尘与周边火山岛弧的二端元混合模型特征,其中蒙脱石主要为周边火山岛弧物质贡献,而伊利石、绿泥石和高岭石主要是亚洲风尘贡献。晚上新世以来XT4孔的伊利石/蒙脱石比值表现为阶段性变化,主要反映了北半球高纬冰川的扩张导致亚洲中纬度地区干旱化加剧。此外,东亚夏季风降雨强弱和空间分布的变化也是源区风尘释放的重要环境因子之一。本文结果初步揭示了晚上新世以来中国干旱-半干旱地区的环境演化历程,有助于深入理解多圈层相互作用下的风尘循环及其生物地球化学效应。
Abstract:Clay mineral assemblage data of Core XT4 from the Philippine Sea Basin in the western Philippine Sea is used by this paper as proxies to trace sediment provenance and transporting mechanisms so as to constrain past changes in Asian eolian input to the basin since 3.7 Ma. The clay minerals consist of illite (39%) and smectite (28%), with minor chlorite (18%) and kaolinite (15%). Provenance analysis suggests that smectite are sourced predominantly from the alteration of local volcanic rocks, while illite, chlorite, and kaolinite primarily derived from the central Asia continent by eolian origin. Thus, the illite/smectite ratio can be used as a proxy to seek for Asian dust input to the Philippine Sea Basin since 3.7 Ma, and to reconstruct the aridification history of the source region. On the whole, the illite/smectite ratio from Core XT4 shows three stages variation pattern, reflecting the glaciers expansion in the high latitudes of the Northern Hemisphere. This led to the intensification of drought in the middle latitudes of Asia. Within the three stages, the illite/smectite ratio is inversely related to the change in East Asian Summer Monsoon (EASM). The eolian dust flux carried by EAWM on tectonic timescales may be also controlled by the underlying surface conditions, which is in turn influenced by EASM rainfall. Our results preliminarily reveal the environmental evolution of arid and semi-arid areas in China since Late Pliocene, which is helpful to understand the dust cycle under the multisphere interaction and its biogeochemical effect.
-
Key words:
- clay minerals /
- eolian dust /
- monsoon /
- Pliocene /
- Philippine Sea
-

-
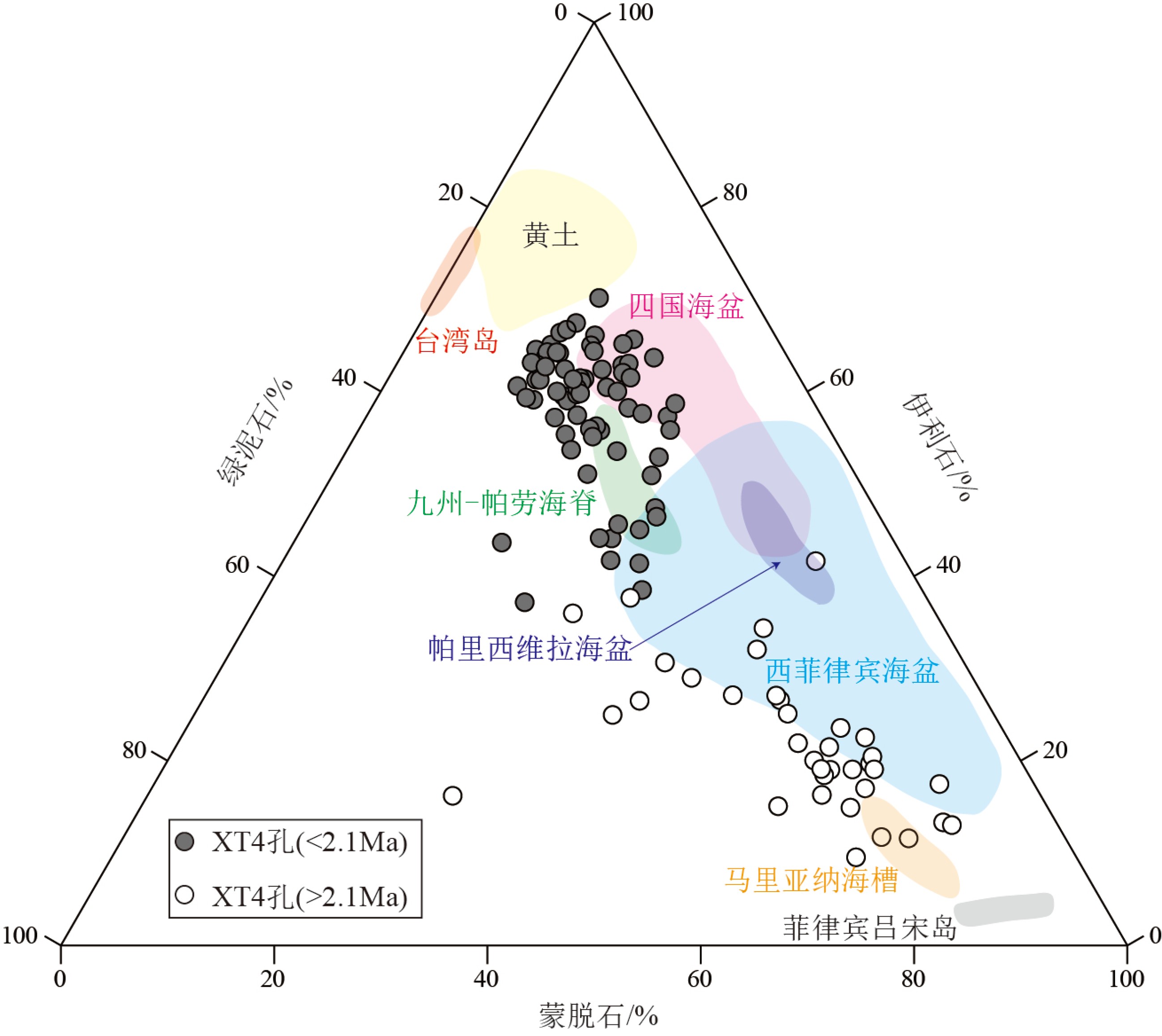
图 4 XT4孔与潜在物源区的蒙脱石-伊利石-绿泥石三角图解[29]
Figure 4.
-
[1] Marx S K, Kamber B S, McGowan H A, et al. Palaeo-dust records: A window to understanding past environments [J]. Global and Planetary Change, 2018, 165: 13-43. doi: 10.1016/j.gloplacha.2018.03.001
[2] Shao Y P, Wyrwoll K H, Chappell A, et al. Dust cycle: An emerging core theme in Earth system science [J]. Aeolian Research, 2011, 2(4): 181-204. doi: 10.1016/j.aeolia.2011.02.001
[3] Muhs D R. The geologic records of dust in the Quaternary [J]. Aeolian Research, 2013, 9: 3-48. doi: 10.1016/j.aeolia.2012.08.001
[4] 万世明, 徐兆凯. 西太平洋风尘沉积记录研究进展[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2017, 48(6):1208-1219
WAN Shiming, XU Zhaokai. Research progress on eolian dust records in the west Pacific [J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2017, 48(6): 1208-1219.
[5] Wan S M, Yu Z J, Clift P D, et al. History of Asian eolian input to the West Philippine Sea over the last one million years [J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2012, 326-328: 152-159. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2012.02.015
[6] Xu Z K, Li T G, Clift P D, et al. Quantitative estimates of Asian dust input to the western Philippine Sea in the mid-late Quaternary and its potential significance for paleoenvironment [J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2015, 16(9): 3182-3196. doi: 10.1002/2015GC005929
[7] Xu Z K, Li T G, Wan S M, et al. Evolution of East Asian monsoon: Clay mineral evidence in the western Philippine Sea over the past 700 kyr [J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2012, 60: 188-196. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2012.08.018
[8] Seo I, Lee Y I, Yoo C M, et al. Sr-Nd isotope composition and clay mineral assemblages in eolian dust from the central Philippine Sea over the last 600 kyr: Implications for the transport mechanism of Asian dust: source and transport agent of Asian dust [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 2014, 119(19): 11492-11504. doi: 10.1002/2014JD022025
[9] Jiang F Q, Zhou Y, Nan Q Y, et al. Contribution of Asian dust and volcanic material to the western Philippine Sea over the last 220 kyr as inferred from grain size and Sr-Nd isotopes [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 2016, 121(9): 6911-6928. doi: 10.1002/2016JC012000
[10] Seo I, Lee Y I, Yoo C M, et al. Reply to Comment by Xu et al. on “Sr‐Nd isotope composition and clay mineral assemblages in eolian dust from the central Philippine Sea over the last 600 kyr: Implications for the transport mechanism of Asian dust” by Seo et al [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 2016, 121(23): 14298-14303. doi: 10.1002/2016JD025444
[11] Xu Z K, Li T G, Clift P D, et al. Comment on “Sr-Nd isotope composition and clay mineral assemblages in Eolian dust from the central Philippine Sea over the last 600 kyr: Implications for the transport mechanism of Asian dust” by Seo et al [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 2016, 121(23): 14137-14141. doi: 10.1002/2016JD024946
[12] Xu Z K, Li T G, Colin C, et al. Seasonal variations in the siliciclastic fluxes to the Western Philippine sea and their impacts on seawater εNd values inferred from 1 year of in situ observations above Benham rise [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 2018, 123(9): 6688-6702. doi: 10.1029/2018JC014274
[13] 王薇, 徐兆凯, 冯旭光, 等. 西菲律宾海现代风尘物质组成特征及其物源指示意义[J]. 地球科学, 2020, 45(2):559-568
WANG Wei, XU Zhaokai, FENG Xuguang, et al. Composition characteristics and provenance implication of modern dust in the West Philippine sea [J]. Earth Science, 2020, 45(2): 559-568.
[14] Yu Z J, Wang S M, Colin C, et al. ENSO-like modulated tropical pacific climate changes since 2.36 myr and its implication for the middle pleistocene transition [J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2018, 19(2): 415-426. doi: 10.1002/2017GC007247
[15] Yu Z J, Wan S M, Colin C, et al. Co-evolution of monsoonal precipitation in East Asia and the tropical Pacific ENSO system since 2.36 Ma: New insights from high-resolution clay mineral records in the West Philippine Sea [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2016, 446: 45-55. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2016.04.022
[16] Xiong Z F, Li T G, Chang F M, et al. Rapid precipitation changes in the tropical West Pacific linked to North Atlantic climate forcing during the last deglaciation [J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2018, 197: 288-306. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2018.07.040
[17] Xiong Z F, Li T G, Jiang F Q, et al. Millennial-scale evolution of elemental ratios in bulk sediments from the western Philippine Sea and implications for chemical weathering in Luzon since the Last Glacial Maximum [J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2019, 179: 127-137. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2019.04.021
[18] Xu Z K, Wan S M, Colin C, et al. Enhanced terrigenous organic matter input and productivity on the western margin of the Western Pacific Warm Pool during the Quaternary sea-level lowstands: Forcing mechanisms and implications for the global carbon cycle [J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2020, 232: 106211. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2020.106211
[19] Jiang F Q, Zhu X, Li T G, et al. Increased dust deposition in the Parece Vela Basin since the mid- Pleistocene inferred from radiogenic Sr and Nd isotopes [J]. Global and Planetary Change, 2019, 173: 83-95. doi: 10.1016/j.gloplacha.2018.12.011
[20] 周宇, 蒋富清, 徐兆凯, 等. 近2 Ma帕里西-维拉海盆沉积物中碎屑组分粒度特征及其物源和古气候意义[J]. 海洋科学, 2015, 39(9):86-93 doi: 10.11759/hykx20140314001
ZHOU Yu, JIANG Fuqing, XU Zhaokai, et al. Grain-size distribution of detrital sediment in the Parece Vela Basin and its implication of provenance and palaeoclimate over the last 2 Ma [J]. Marine Sciences, 2015, 39(9): 86-93. doi: 10.11759/hykx20140314001
[21] 陈骏, 李高军. 亚洲风尘系统地球化学示踪研究[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2011, 54(9):1279-1301 doi: 10.1007/s11430-011-4269-z
CHEN Jun, LI Gaojun. Geochemical studies on the source region of Asian dust [J]. Science China Earth Science, 2011, 54(9): 1279-1301. doi: 10.1007/s11430-011-4269-z
[22] Sun Y B, Yan Y, Nie J S, et al. Source-to-sink fluctuations of Asian aeolian deposits since the late Oligocene [J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2020, 200: 102963. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2019.102963
[23] Chen J, Li G J, Yang J D, et al. Nd and Sr isotopic characteristics of Chinese deserts: Implications for the provenances of Asian dust [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2007, 71(15): 3904-3914. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2007.04.033
[24] Li D W, Zhao M X, Chen M T. East Asian winter monsoon controlling phytoplankton productivity and community structure changes in the southeastern South China Sea over the last 185 kyr [J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2014, 414: 233-242. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2014.09.003
[25] Liu Z F, Zhao Y L, Colin C, et al. Source-to-sink transport processes of fluvial sediments in the South China Sea [J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2016, 153: 238-273. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2015.08.005
[26] Shen X Y, Wan S M, France-Lanord C, et al. History of Asian eolian input to the Sea of Japan since 15 Ma: Links to Xizang uplift or global cooling? [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2017, 474: 296-308. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2017.06.053
[27] 王晨, 徐方建, 胡邦琦, 等. 3.7 Ma以来西菲律宾海XT-4孔沉积物元素特征及其古环境指示意义[J]. 海洋科学, 2020, 44(8):205-214
WANG Chen, XU Fangjian, HU Bangqi, et al. Elemental geochemistry of Core XT-4 sediments from the western Philippines Sea since 3.7 Ma and its paleoenvironmental implications [J]. Marine Sciences, 2020, 44(8): 205-214.
[28] 明洁, 李安春, 孟庆勇, 等. 东菲律宾海帕里西维拉海盆第四纪黏土矿物组合特征及物源分析[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2012, 32(4):139-148
MING Jie, LI Anchun, MENG Qingyong, et al. Quaternary assemblage characteristic and provenance of clay minerals in the Parecevela Basin of the East Philippine Sea [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2012, 32(4): 139-148.
[29] 刘华华, 蒋富清, 周烨, 等. 晚更新世以来奄美三角盆地黏土矿物的来源及其对古气候的指示[J]. 地球科学进展, 2016, 31(3):286-297 doi: 10.11867/j.issn.1001-8166.2016.03.0286.
LIU Huahua, JIANG Fuqing, ZHOU Ye, et al. Provenance of clay minerals in the Amami Sankaku Basin and their paleoclimate implications since late Pleistocene [J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2016, 31(3): 286-297. doi: 10.11867/j.issn.1001-8166.2016.03.0286.
[30] 靳宁, 李安春, 刘海志, 等. 帕里西维拉海盆西北部表层沉积物中粘土矿物的分布特征及物源分析[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2007, 38(6):504-511 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814x.2007.06.004
JIN Ning, LI Anchun, LIU Haizhi, et al. Clay minerals in surface sediment of the northwest Parece Vela Basin: distribution and provenace [J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2007, 38(6): 504-511. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814x.2007.06.004
[31] 黄杰, 万世明, 张国良, 等. 海底地形特征对东菲律宾海表层黏土矿物分布的影响[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2017, 37(1):77-85
HUANG Jie, WAN Shiming, ZHANG Guoliang, et al. Impact of seafloor topography on distribution of clay minerals in the East Philippines Sea [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2017, 37(1): 77-85.
[32] Li C S, Shi X F, Kao S J, et al. Clay mineral composition and their sources for the fluvial sediments of Taiwanese rivers [J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2012, 57(6): 673-681. doi: 10.1007/s11434-011-4824-1
[33] Liu Z F, Zhao Y L, Colin C, et al. Chemical weathering in Luzon, Philippines from clay mineralogy and major-element geochemistry of river sediments [J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2009, 24(11): 2195-2205. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2009.09.025
[34] 石学法, 陈丽蓉, 李坤业, 等. 西菲律宾海西部海域粘土沉积物的成因矿物学研究[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 1995, 15(2):61-72
SHI Xuefa, CHEN Lirong, LI Kunye, et al. Study on minerageny of the clay sediment in the West of Philippine Sea [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 1995, 15(2): 61-72.
[35] Ji J F, Chen J, Lu H Y. Origin of illite in the loess from the Luochuan area, Loess Plateau, Central China [J]. Clay Minerals, 1999, 34(4): 525-532. doi: 10.1180/000985599546398
[36] Windom H L. Lithogenous material in marine sediments[M]//Riley J P, Chester R. Chemical Oceanography. London: Academic Press, 1976, 5: 103-135.
[37] Chamley H. Clay sedimentation in Shikoku Basin since the Middle Miocene (North Philippine Sea, Leg 58) [J]. Initial Report of Deep Sea Drilling Project, 1981, 58: 669-678.
[38] Nagel U, Muller G, Schumann D. Mineralogy of sediments cored during Deep Sea Project Leg 58-60 Clay sedimentation in Shikoku Basin since the Middle Miocene (North Philippine Sea, Leg 58) in the North and South Philippine Sea: Results of X-ray diffraction analyses. Hussong D M, Uyeda S, Blanchet R, et al. eds. Initial Reports of the Deep Sea Drilling Project, USA: National Science Famdation, 1981. 60: 415-435.
[39] Biscaye P E. Mineralogy and sedimentation of recent deep-sea clay in the Atlantic Ocean and adjacent seas and oceans [J]. GSA Bulletin, 1965, 76(7): 803-832. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(1965)76[803:MASORD]2.0.CO;2
[40] Rea D K, Snoeckx H, Josep L H. Late Cenozoic eolian deposition in the North Pacific: Asian drying, Xizang uplift, and cooling of the northern hemisphere [J]. Paleoceanography and Paleoclimatology, 1998, 13(3): 215-224.
[41] Zhang W F, De Vleeschouwer D, Shen J, et al. Orbital time scale records of Asian eolian dust from the Sea of Japan since the early Pliocene [J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2018, 187: 157-167. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2018.03.004
[42] Guo Z T, Ruddiman W F, Hao Q Z, et al. Onset of Asian desertification by 22 Myr ago inferred from loess deposits in China [J]. Nature, 2002, 416(6877): 159-163. doi: 10.1038/416159a
[43] An Z S, Kutzbach J, Prell W L, et al. Evolution of Asian monsoons and phased uplift of the Himalaya–Xizang plateau since Late Miocene times [J]. Nature, 2001, 411(6833): 62-66. doi: 10.1038/35075035
[44] Sun Y B, An Z S, Clemens S C, et al. Seven million years of wind and precipitation variability on the Chinese Loess Plateau [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2010, 297(3-4): 525-535. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2010.07.004
[45] Sun Y B, An Z S. Late Pliocene‐Pleistocene changes in mass accumulation rates of eolian deposits on the central Chinese Loess Plateau [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 2005, 110(D23): D23101. doi: 10.1029/2005JD006064
[46] Yu Y, Kalashnikova O V, Garay M J, et al. Climatology of Asian dust activation and transport potential based on MISR satellite observations and trajectory analysis [J]. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 2019, 19(1): 363-378. doi: 10.5194/acp-19-363-2019
[47] Serno S, Winckler G, Anderson R F, et al. Change in dust seasonality as the primary driver for orbital‐scale dust storm variability in East Asia [J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2017, 44(8): 3796-3805. doi: 10.1002/2016GL072345
[48] Fedorov A V, Burls N J, Lawrence K T, et al. Tightly linked zonal and meridional sea surface temperature gradients over the past five million years [J]. Nature Geoscience, 2015, 8(12): 975-980. doi: 10.1038/ngeo2577
[49] Lisiecki L E, Raymo M E. A pliocene-pleistocene stack of 57 globally distributed benthic δ18o records [J]. Paleoceanography and Paleoclimatology, 2005, 20(1): PA1003.
[50] Lu H Y, Yi S W, Liu Z Y, et al. Variation of East Asian monsoon precipitation during the past 21 k.y. and potential CO2 forcing [J]. Geology, 2013, 41(9): 1023-1026. doi: 10.1130/G34488.1
[51] Jin R, Wu Z W, Zhang P. Xizang Plateau capacitor effect during the summer preceding ENSO: from the Yellow River climate perspective [J]. Climate Dynamics, 2017, 51(24): 57-71.
[52] Broecker W S, Putnam A E. Hydrologic impacts of past shifts of Earth’s thermal equator offer insight into those to be produced by fossil fuel CO2 [J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2013, 110(42): 16710-16715. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1301855110
[53] Yang F L, Lau K M. Trend and variability of China precipitation in spring and summer: linkage to sea-surface temperatures [J]. International Journal of Climatology, 2004, 24(13): 1625-1644. doi: 10.1002/joc.1094
[54] Chang C P, Zhang Y S, Li T. Interannual and interdecadal variations of the East Asian Summer Monsoon and Tropical Pacific SSTs. Part Ⅱ: meridional structure of the monsoon [J]. Journal of Climate, 2000, 13(24): 4326-4340. doi: 10.1175/1520-0442(2000)013<4326:IAIVOT>2.0.CO;2
[55] Rao Z G, Jia G D, Li Y X, et al. Asynchronous evolution of the isotopic composition and amount of precipitation in north China during the Holocene revealed by a record of compound-specific carbon and hydrogen isotopes of long-chain n-alkanes from an alpine lake [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2016, 446: 68-76. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2016.04.027
[56] Wara M W, Ravelo A C, Delaney M L. Permanent El Niño-like conditions during the Pliocene warm period [J]. Science, 2005, 309(5735): 758-761. doi: 10.1126/science.1112596
-




 下载:
下载: