Reconstruction of terrestrial input changes in sediments in the Western Pacific warm pool using bacterial membrane lipids
-
摘要:
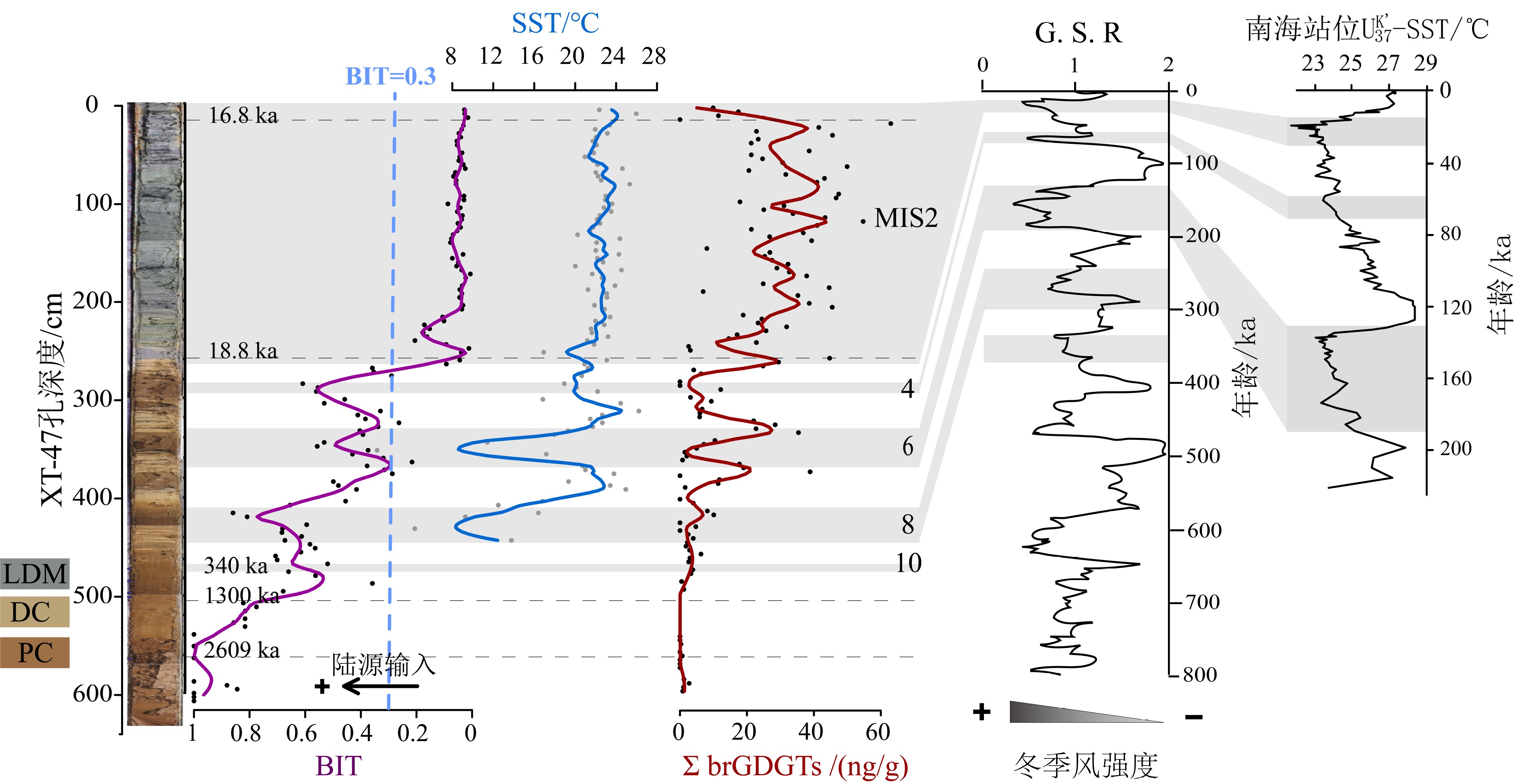
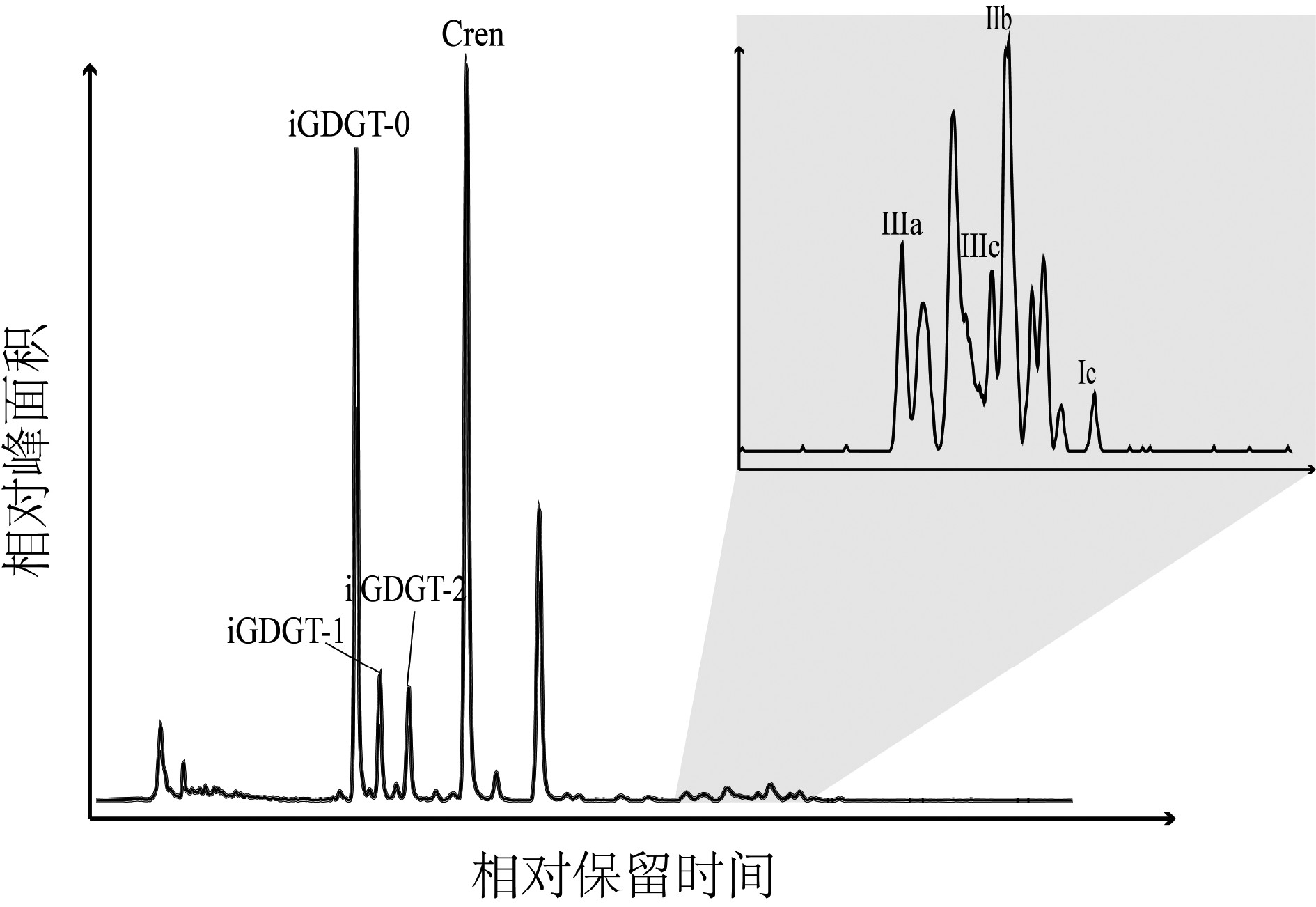
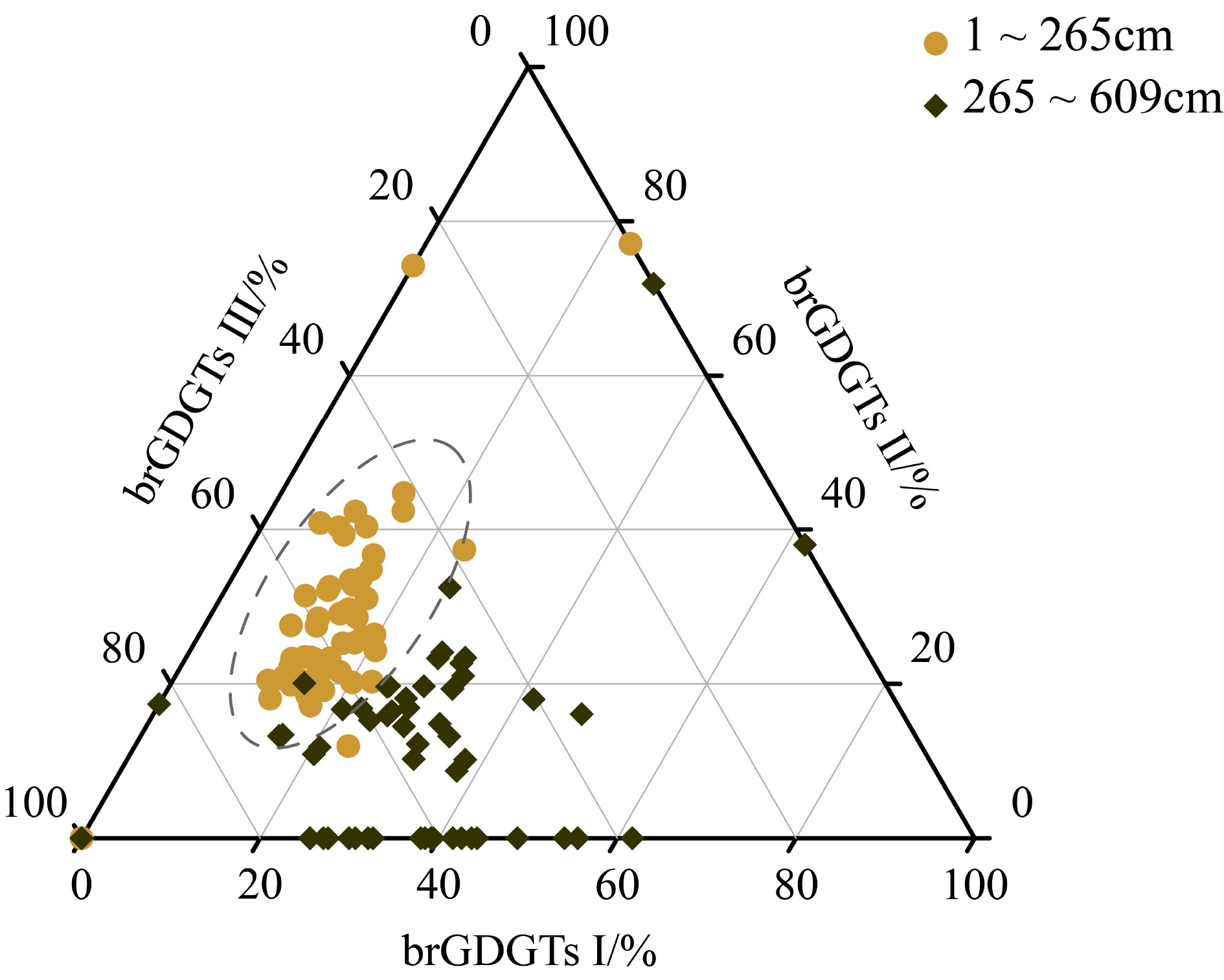
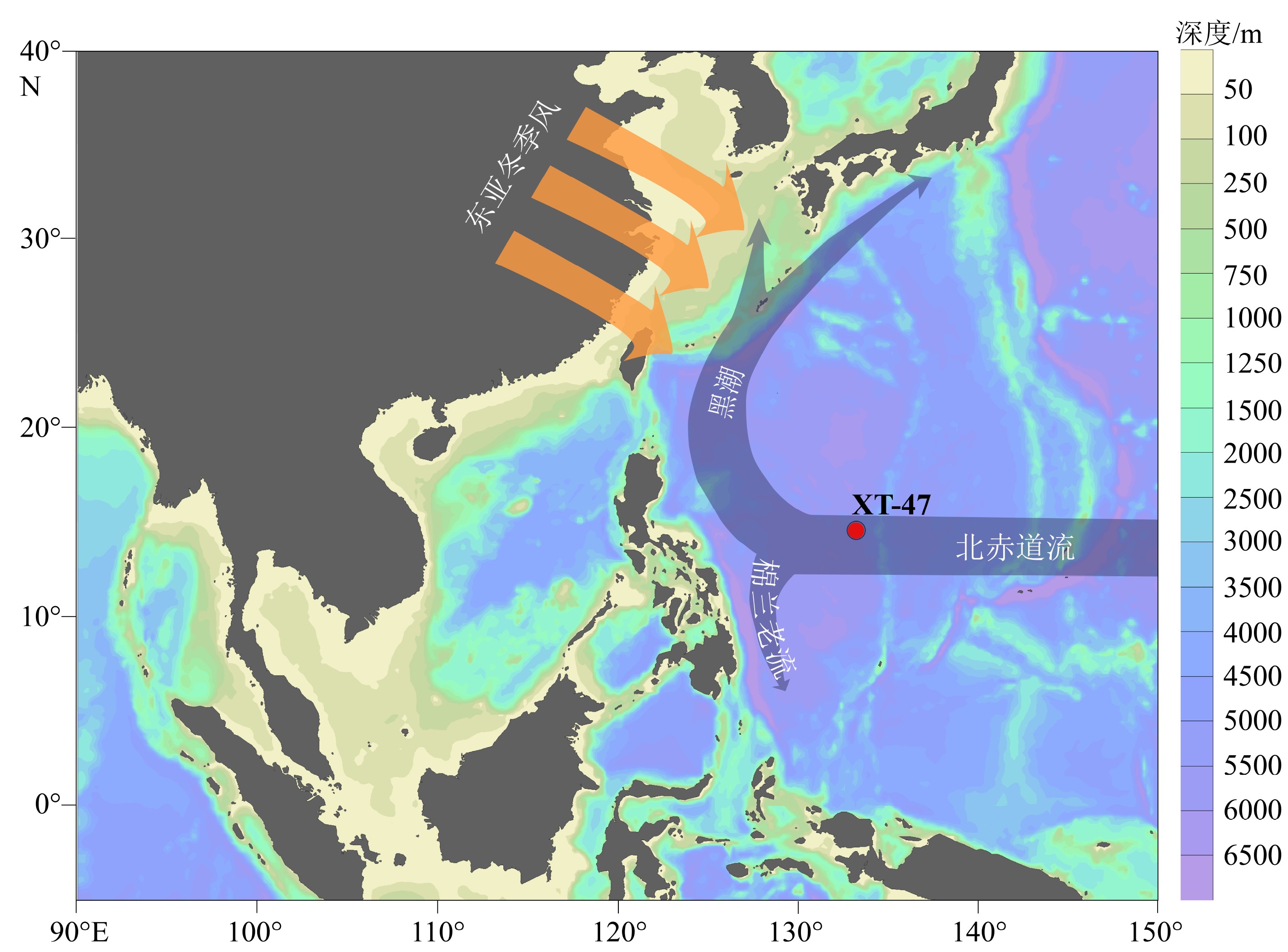
西菲律宾海作为西太平洋暖池的一部分,重建其在地质历史时期的热力学变化、陆源输入变化,对于理解西太平洋暖池在全球地质时间尺度上的作用具有重要意义。利用古菌与细菌的细胞膜质甘油二烷基甘油四醚(glycerol dialkyl glycerol tetraethers, GDGTs)对西菲律宾海XT-47孔沉积物的陆源输入及其上方水体温度的变化进行重建,发现该沉积柱顶部(0~260 cm,约16.6~18.8 ka)BIT指标为0.01~0.2,TEXH86重建的上层海水平均温度为22.5 ℃,而底部(260~632 cm,约18.8~4 000 ka)TEXH86重建得到的上层海水温度绝对值波动剧烈(0.6~26 ℃),在此范围内BIT>0.3,并呈现逐渐增加的趋势, 超过BIT界定的陆源输入对TEXH86重建古温度有效性的阈值,这导致了该深度范围内TEXH86重建古温度变化的严重偏差。以260和470 cm为界,该沉积柱的沉积相出现明显变化,上层为大量纹层硅藻席沉积,中层为远洋黏土和硅藻泥互层,下层为远洋黏土沉积;同时,支链GDGTs(branched GDGTs, br GDGTs)的组成也出现明显差异,说明其来源可能有所不同。基于以上分析,提出260 cm以浅,brGDGTs可能主要为海相原位自生为主;而260 cm深度以下,主要以风尘输送的陆源brGDGTs为主。该结果显示陆源输入的变化可以间接反映东亚冬季风的强弱,本研究为高低纬之间的海陆相互作用研究提供了新的视角。
Abstract:The West Philippine Sea is a part of the Western Pacific Warm Pool. To reconstruct its thermodynamic changes and terrestrial input changes in the geological history is of great significance for understanding the role of the Warm Pool on a global geological time scale. In this paper, the glycerol dialkyl glycerol tetraethers (GDGTs) of archaea and bacteria is used to reconstruct the temperature and terrestrial input proxy changes for the core XT-47 taking from the West Philippine Sea. The BIT index on top layer of 0~260 cm, corresponding to 16.6~18.8 ka, varies between 0.01~0.2, and the average sea surface temperature reconstructed with TEXH86 is 22.5°C. The absolute sea surface temperature at the bottom layer from 260 cm to 632 cm, (18.8~4 000 ka) reconstructed by TEXH86 fluctuates drastically between 0.6°C and 26°C; BIT>0.3 within these depth range, shows a gradual increase trend, exceeding the threshold for the validity of paleotemperature reconstruction of TEXH86 defined by terrestrial input proxy-BIT, which leads to a serious deviation of the TEXH86 reconstructed paleotemperature within this depth range. Taking 260 cm and 400 cm as boundaries, the sedimentary facies of the core has changed significantly. In a descending order, the upper layer is a large number of laminar diatom mats, the middle layer is interbedded pelagic clay and diatom clay, and the lower layer is pelagic clay deposit; simultaneously, obvious differences in the composition of branched GDGTs (brGDGTs) are observed, indicating that their sources may also be different. Based on the above analysis, we propose that brGDGTs below 260 cm are marine in-situ autochthonous deposits; while that below 260 cm, terrigenous brGDGTs dominate, which are mainly transported as aeolian dust. The results suggest that the changes in terrestrial input can indirectly reflect the strength of the East Asian winter monsoon, and the results may provide new insights for the study of sea-land interactions between high and low latitudes.
-
Key words:
- terrestrial input /
- BIT index /
- GDGTs /
- diatom mats /
- TEXH86 /
- West Philippine Sea
-

-
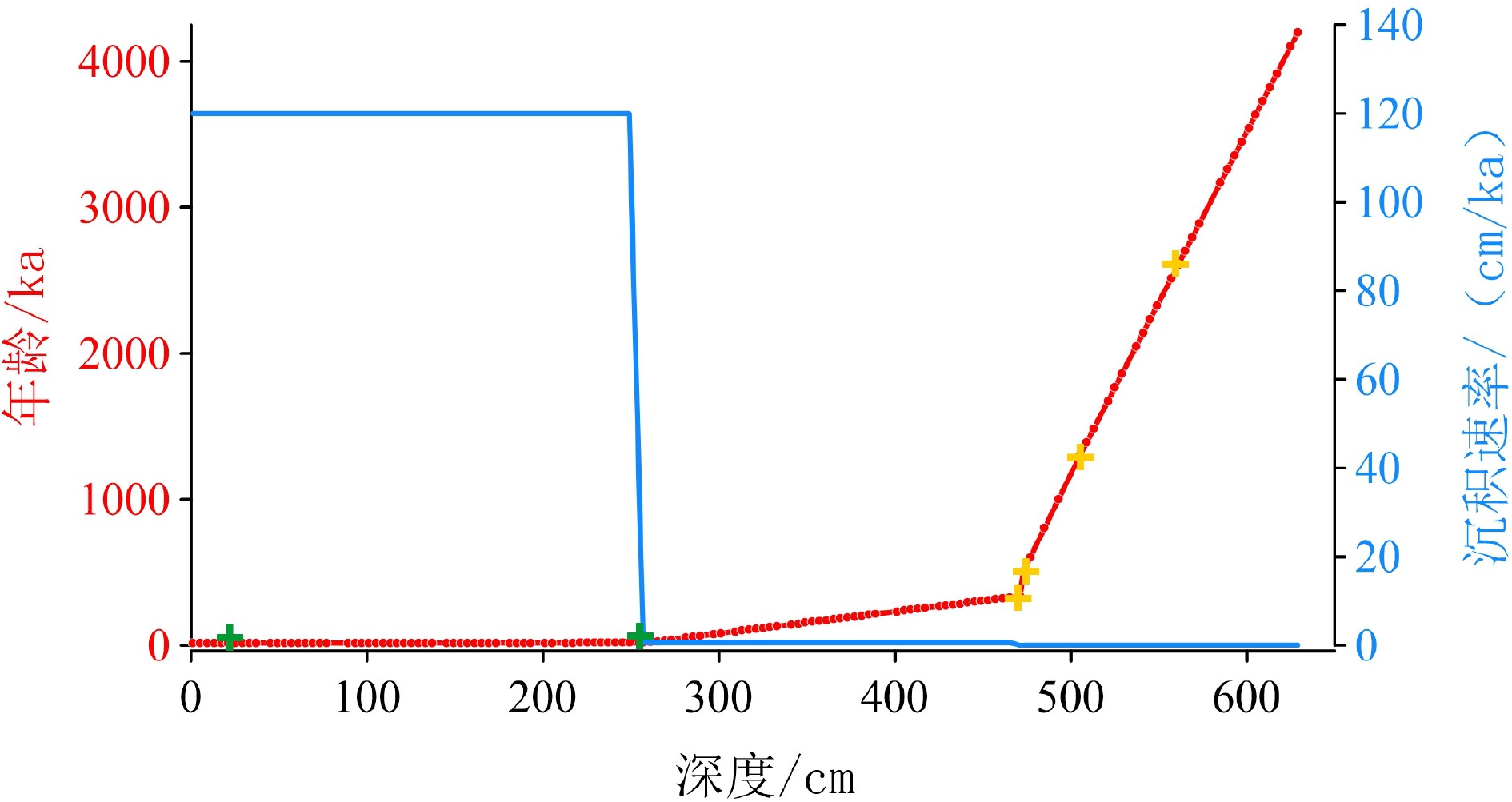
表 1 确定XT-47沉积柱年龄模型的年龄控制点及定年方法
Table 1. Age control points and dating method to determine the core XT-47 age model
深度/cm 年龄/kaBP 定年方法 17 16.8 有机碳AMS 14C 257 18.8 有机碳AMS 14C 471 340 放射虫 473 510 放射虫 505 1300 放射虫 561 2609 放射虫 -
[1] Lea D W. The glacial tropical pacific-not just a west side story [J]. Science, 2002, 297(5579): 202-203. doi: 10.1126/science.1073841
[2] Xu Z K, Li T G, Wan S M, et al. Evolution of East Asian monsoon: Clay mineral evidence in the western Philippine Sea over the past 700 kyr [J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2012, 60: 188-196. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2012.08.018
[3] Xu Z K, Li T G, Clift P D, et al. Quantitative estimates of Asian dust input to the western Philippine Sea in the mid-late Quaternary and its potential significance for paleoenvironment [J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2015, 16(9): 3182-3196. doi: 10.1002/2015GC005929
[4] Hun C A, Peng J L, Chen J C. Late Pleistocene pelagic sedimentation in the West Philippine Basin [J]. Journal of Southeast Asian Earth Sciences, 1992, 7(2-3): 159-164. doi: 10.1016/0743-9547(92)90050-L
[5] Seo I, Lee Y I, Yoo C M, et al. Sr-Nd isotope composition and clay mineral assemblages in eolian dust from the central Philippine Sea over the last 600 kyr: Implications for the transport mechanism of Asian dust: Source and transport agent of Asian dust [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 2014, 119(19): 11492-11504. doi: 10.1002/2014JD022025
[6] 李铁刚, 熊志方, 翟滨. 低纬度西太平洋硅藻席沉积与碳循环[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 2015: 1-158.
LI Tiegang, XIONG Zhifang, ZHAI Bin. Laminated Diatom Mat Deposits from the Low-Latitude Western Pacific Linked to Global Carbon Cycle[M]. Beijing: China Ocean Press, 2015: 1-158.
[7] Xu Z K, Li T G, Wan S M, et al. Geochemistry of rare earth elements in the mid-late Quaternary sediments of the western Philippine Sea and their paleoenvironmental significance [J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 2014, 57(4): 802-812. doi: 10.1007/s11430-013-4786-z
[8] Qiu B. Kuroshio and oyashio currents[M]//Steele J H. Encyclopedia of Ocean Sciences. London: Elsevier Science Ltd., 2001: 1413-1425.
[9] Liu J P, Xu K H, Li A C, et al. Flux and fate of Yangtze River sediment delivered to the East China Sea [J]. Geomorphology, 2007, 85(3-4): 208-224. doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2006.03.023
[10] Wan S M, Yu Z J, Clift P D, et al. History of Asian eolian input to the West Philippine Sea over the last one million years [J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2012, 326-328: 152-159. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2012.02.015
[11] Jiang F Q, Zhou Y, Nan Q Y, et al. Contribution of Asian dust and volcanic material to the western Philippine Sea over the last 220 kyr as inferred from grain size and Sr-Nd isotopes [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 2016, 121(9): 6911-6928. doi: 10.1002/2016JC012000
[12] 万世明, 徐兆凯. 西太平洋风尘沉积记录研究进展[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2017, 48(6):1208-1219
WAN Shiming, XU Zhaokai. Research progress on eolian dust records in the west pacific [J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2017, 48(6): 1208-1219.
[13] Jiang F Q, Frank M, Li T G, et al. Asian dust input in the western Philippine Sea: Evidence from radiogenic Sr and Nd isotopes [J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2013, 14(5): 1538-1551. doi: 10.1002/ggge.20116
[14] Wan S M, Sun Y B, Nagashima K. Asian dust from land to sea: processes, history and effect from modern observation to geological records [J]. Geological Magazine, 2020, 157(5): 701-706. doi: 10.1017/S0016756820000333
[15] Ge H M, Zhang C L. Advances in GDGT research in Chinese marginal seas: A review [J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 2016, 59(6): 1173-1186. doi: 10.1007/s11430-015-5242-z
[16] Schouten S, Hopmans E C, Damsté J S S. The organic geochemistry of glycerol dialkyl glycerol tetraether lipids: A review [J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2013, 54: 19-61. doi: 10.1016/j.orggeochem.2012.09.006
[17] Pearson A, Ingalls A E. Assessing the use of archaeal lipids as marine environmental proxies [J]. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 2013, 41: 359-384. doi: 10.1146/annurev-earth-050212-123947
[18] Schouten S, Hopmans E C, Schefuß E, et al. Distributional variations in marine crenarchaeotal membrane lipids: a new tool for reconstructing ancient sea water temperatures? [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2002, 204(1-2): 265-274. doi: 10.1016/S0012-821X(02)00979-2
[19] Li D W, Zhao M X, Tian J, et al. Comparison and implication of TEX86 and UK’ 37 temperature records over the last 356 kyr of ODP Site 1147 from the northern South China Sea [J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2013, 376: 213-223. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2013.02.031
[20] Hopmans E C, Weijers J W H, Schefuß E, et al. A novel proxy for terrestrial organic matter in sediments based on branched and isoprenoid tetraether lipids [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2004, 224(1-2): 107-116. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2004.05.012
[21] Pelejero C, Grimalt J O, Heilig S, et al. High-resolution UK37 temperature reconstructions in the South China Sea over the past 220 kyr [J]. Paleoceanography and Paleoclimatology, 1999, 14(2): 224-231.
[22] Ding Z L, Liu T S, Rutter N W, et al. Ice-volume forcing of East Asian winter monsoon variations in the past 800, 000 years [J]. Quaternary Research, 1995, 44(2): 149-159. doi: 10.1006/qres.1995.1059
[23] Kim J H, Van Der Meer J, Schouten S, et al. New indices and calibrations derived from the distribution of crenarchaeal isoprenoid tetraether lipids: Implications for past sea surface temperature reconstructions [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2010, 74(16): 4639-4654. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2010.05.027
[24] Yamamoto M, Shimamoto A, Fukuhara T, et al. Source, settling and degradation of branched glycerol dialkyl glycerol tetraethers in the marine water column [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2016, 191: 239-254. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2016.07.014
[25] Winckler G, Anderson R F, Fleisher M Q, et al. Covariant glacial-interglacial dust fluxes in the equatorial Pacific and Antarctica [J]. Science, 2008, 320(5872): 93-96. doi: 10.1126/science.1150595
[26] Xu Z K, Li T G, Yu X K, et al. Sediment provenance and evolution of the East Asian winter monsoon since 700 ka recorded by major elements in the West Philippine Sea [J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2012, 58(9): 1044-1052.
[27] De Jonge C, Stadnitskaia A, Hopmans E C, et al. Drastic changes in the distribution of branched tetraether lipids in suspended matter and sediments from the Yenisei River and Kara Sea (Siberia): Implications for the use of brGDGT-based proxies in coastal marine sediments [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2015, 165: 200-225. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2015.05.044
[28] Xiao W J, Wang Y H, Zhou S Z, et al. Ubiquitous production of branched glycerol dialkyl glycerol tetraethers (brGDGTs) in global marine environments: a new source indicator for brGDGTs [J]. Biogeosciences, 2016, 13(20): 5883-5894. doi: 10.5194/bg-13-5883-2016
[29] Liu XL, Zhu C, Wakeham SG, et al. In situ production of branched glycerol dialkyl glycerol tetraethers in anoxic marine water columns [J]. Marine Chemistry, 2014, 166: 1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.marchem.2014.08.008
[30] Zhu C, Weijers J W H, Wagner T, et al. Sources and distributions of tetraether lipids in surface sediments across a large river-dominated continental margin [J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2011, 42(4): 376-386. doi: 10.1016/j.orggeochem.2011.02.002
[31] Damsté J S S. Spatial heterogeneity of sources of branched tetraethers in shelf systems: The geochemistry of tetraethers in the Berau River delta (Kalimantan, Indonesia) [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2016, 186: 13-31. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2016.04.033
[32] Weijers J W H, Schouten S, Van Den Donker J C, et al. Environmental controls on bacterial tetraether membrane lipid distribution in soils [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2007, 71(3): 703-713. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2006.10.003
[33] Peterse F, Schouten S, Van Der Meer J, et al. Distribution of branched tetraether lipids in geothermally heated soils: Implications for the MBT/CBT temperature proxy [J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2009, 40(2): 201-205. doi: 10.1016/j.orggeochem.2008.10.010
[34] Weijers J W H, Schouten S, Spaargaren O C, et al. Occurrence and distribution of tetraether membrane lipids in soils: Implications for the use of the TEX86 proxy and the BIT index [J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2006, 37(12): 1680-1693. doi: 10.1016/j.orggeochem.2006.07.018
[35] 陈敏, 兰彬斌, 沈林南, 等. 西菲律宾海盆表层沉积硅藻分布特征[J]. 微体古生物学报, 2014, 31(4):321-334
CHEN Min, LAN Binbin, SHEN Linnan, et al. Characteristics of diatom distribution in the surface sediments of the Western Philippine Basin [J]. Acta Micropalaeontologica Sinica, 2014, 31(4): 321-334.
[36] De Deckker P, Gingele F X. On the occurrence of the giant diatom Ethmodiscus rex in an 80-ka record from a deep-sea core, southeast of Sumatra, Indonesia: implications for tropical palaeoceanography [J]. Marine Geology, 2002, 183(1-4): 31-43. doi: 10.1016/S0025-3227(01)00252-3
[37] Harrison K G. Role of increased marine silica input on paleo-pCO2 levels [J]. Paleoceanography and Paleoclimatology, 2000, 15(3): 292-298.
[38] Nozaki Y, Yamamoto Y. Radium 228 based nitrate fluxes in the eastern Indian Ocean and the South China Sea and a silicon-induced “alkalinity pump” hypothesis [J]. Global Biogeochemical Cycles, 2001, 15(3): 555-567. doi: 10.1029/2000GB001309
-



 下载:
下载: