Magnetostratigraphy of core XT06 and Quaternary sedimentary dynamics of the deep-sea deposits in the West Philippian Basin
-
摘要:
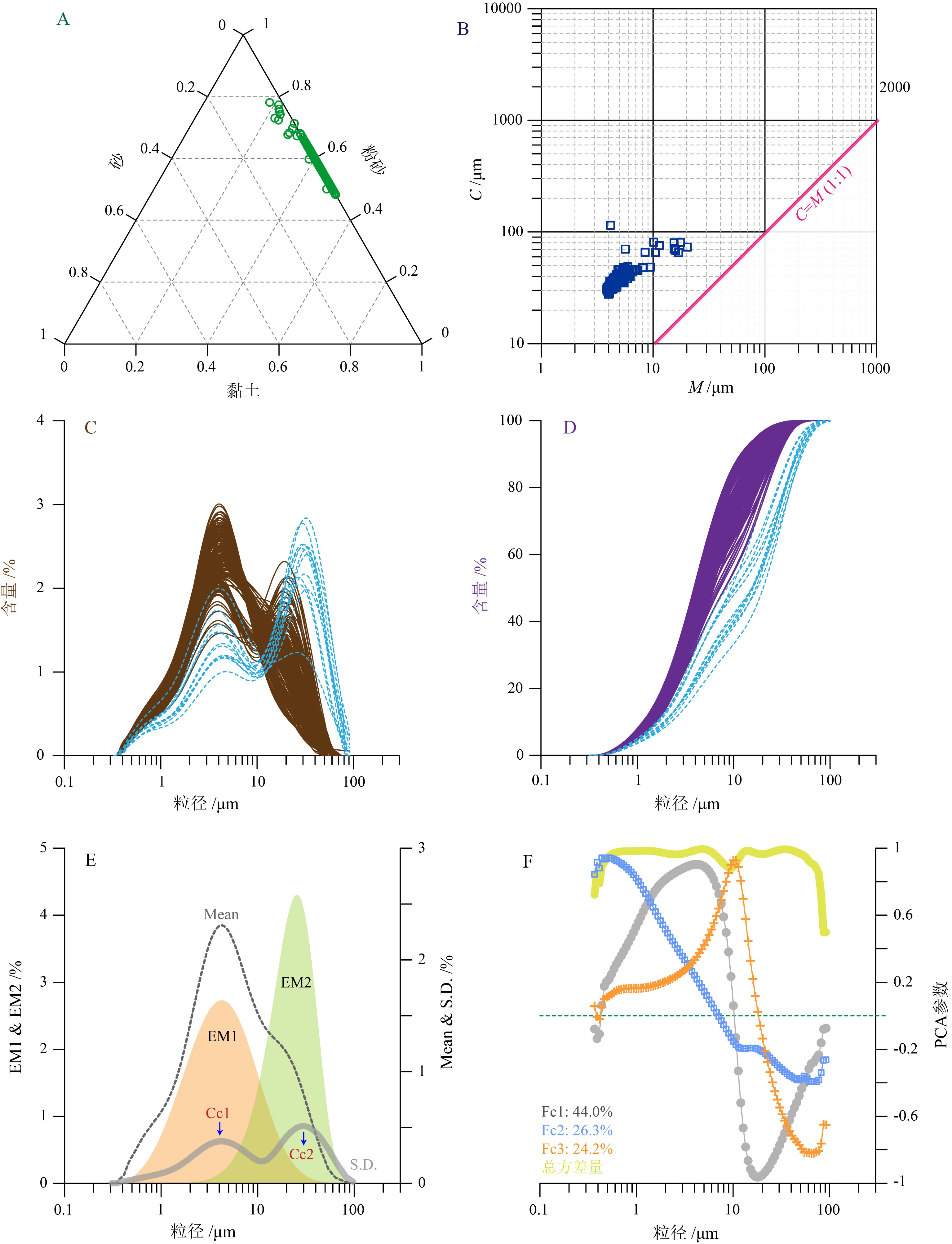
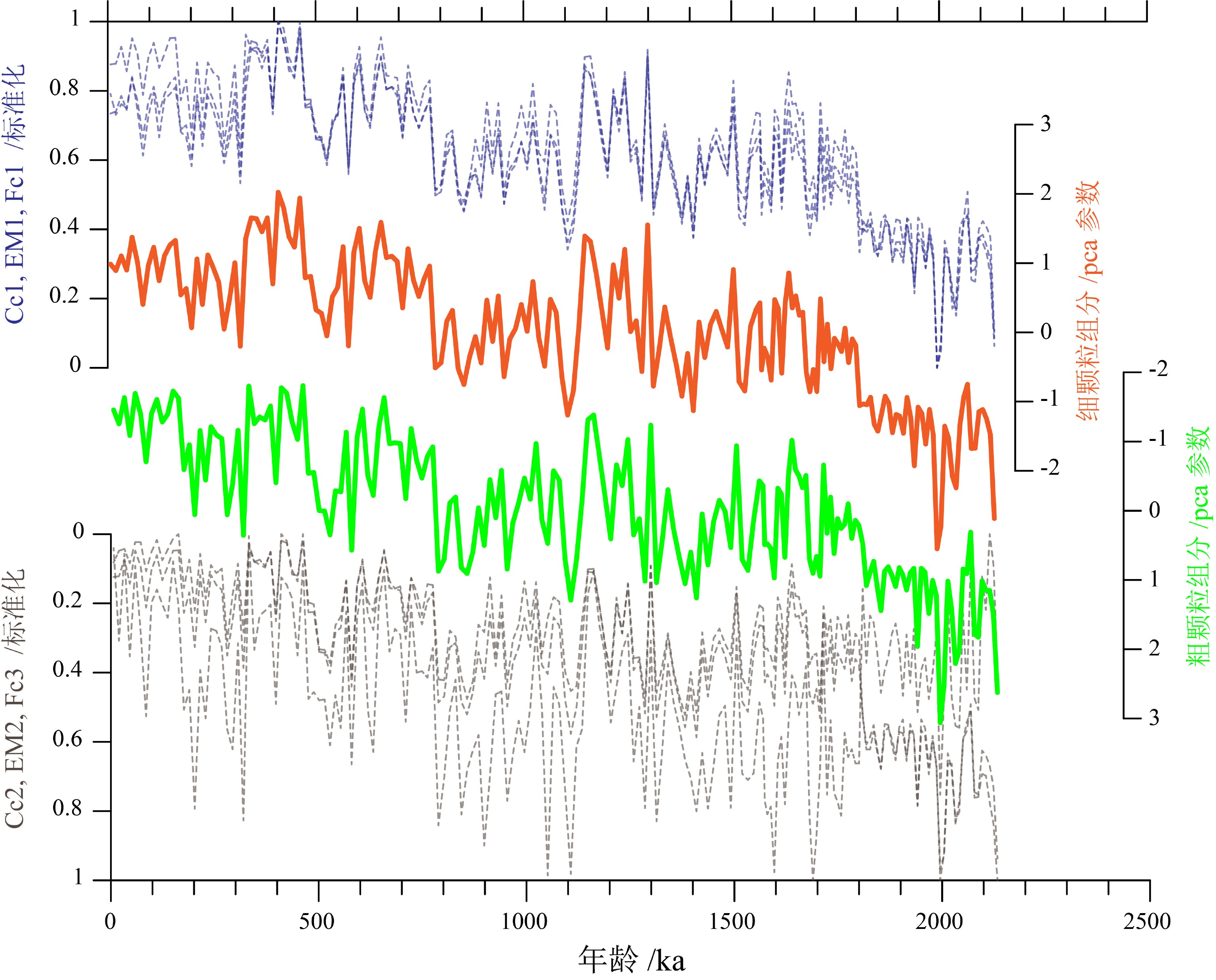
菲律宾海是西太平洋典型的风尘汇集区,也是南极底层水影响的远端地区。由于水深较大等原因,这一热点地区沉积物的古环境研究尚未全面展开。本文对菲律宾海中部XT06孔沉积物开展了磁性地层和粒度测试工作,分析了XT06孔沉积记录的年代学特征和沉积过程,初步探讨了区域沉积演化的控制因素与古环境意义。结果表明:(1)通过系统交变退磁实验,XT06孔沉积物可以辨识出6个磁极性区间,分别对应于布容正极性时、加拉米洛亚极性时、奥杜维尔正极性时和松山负极性时。通过与国际标准磁极性序列对比,发现XT06孔的沉积速率由快转慢,指示了在1.0~1.5 Ma曾发生过一次明显的沉积转折,可能代表了区域深海沉积中心的迁移,与东亚-西太平洋构造活动等密切相关。(2)XT06沉积物属于典型的远洋悬浮体,反映了较弱的沉积动力环境。通过多种粒度分析方法的交叉对比和验证,发现XT06孔沉积物包含粗、细两个互为消长的动力学组分,指示了较为稳定的深海沉积环境。通过对比其他古环境指标,我们推测在构造时间尺度上,亚洲内陆干旱化导致的粉尘输入增加可能是控制XT06孔沉积物粒度逐步变细的主要因素;而在更高时间分辨率上XT06孔沉积物粒度粗细变化可能主要受深海环流强度的控制作用,体现了冰期南极深/底层水团影响减弱、而间冰期增强的区域特征。本文结果展现了菲律宾海中部沉积过程的一些关键特征,揭示了菲律宾海沉积记录在深入研究地球系统多圈层耦合过程中的巨大潜力。
Abstract:The Philippine Sea, as a key area in the Western Pacific Warm Pool, is a characterized by wind-dust deposition. Sedimentary and paleo-environmental researches are relatively rare in the region due to large water depth and other reasons. In this paper, magnetic stratigraphy and sediment grain size data from the gravity core XT06, which is located in the central Philippine Sea, are used as the raw materials to establish the chronological sequence and to reveal the sedimentary processes. Upon the basis, the controlling factors on regional sediment distribution pattern and paleoenvironmental processes are discussed. The results suggest that: (1) After alternative demagnetization, the core XT06 can be subdivided into 6 magnetic polarity intervals, corresponding to the Brunhes (C1n) chron, the Jaramillo (C1r.1n) subchron, the Olduvia (C2n) chron, and the successive polarity-reversed intervals of the Matuyama chron respectively. After calibrated with the geomagnetic polarity timescale (GPTS), it is found that the sedimentation rate of core XT06 had an obvious change from fast to slow at 1.0~1.5 Ma, indicating a regional deep-water environment transition event, probably controlled by the tectonic activities related to the interaction between the Asian continent and the Pacific plate. (2) The core sediments are dominated by pelagic suspended matters, reflecting a weak sedimentary dynamic environment. Grain-size data further suggest that there occur two, coarse and fine, dynamic components in a compensated relationship, indicating a relatively stable dynamic environment. By comparisons with the proxies of global ice volume, deep-sea ventilation, and Inner Asian aridification, we proposed that regional tectonic activities with enhanced aridification and increased flux of aeolian input are the major factors to control the regional sedimentation on tectonic timescales, and the bottom-water circulation is the dominating factor on glacial-interglacial timescales. This paper presented some key sedimentary features for the central part of the Philippine Sea which may contribute much to the in-depth study of the coupling process of some key Earth systems.
-
Key words:
- magnetostratigraphy /
- sediment grain size /
- abyssal environment /
- Quaternary /
- the Philippian Sea
-

-
表 1 XT06站磁极性柱年龄对比
Table 1. Correlation of magnetozones of core XT06 to the geomagnetic polarity time scale
国 际标准磁极性年表 年 龄 1)/Ma XT06深度 /cm J01A2)深度/cm A252)深度 /cm F0901023)深度 /cm 布容C1n(底) 0.781 120 11 25 182 加拉米洛C1r.1n(顶) 0.988 150 43 56 232 加拉米洛C1r.1n(底) 1.072 162 58 72 242 Cobb漂移事件(顶) 1.186 – 89 91 – Bjorn漂移事件(底) 1.253 – 96 101 – Gilsa漂移事件(顶) 1.567 234 – – – Gilsa漂移事件(底) 1.575 238 – – – 奥杜维尔C2n(顶) 1.778 286 138 – 344 奥杜维尔C2n(底) 1.945 324 151 – 354 Reunion漂移事件(顶) 2.128 364 – – – Reunion漂移事件(底) 2.148 368 – – – 高斯C2An.1n(顶) 2.581 – 208 144 – 注:1)年龄数据来自文献[41]和文献[42];2)数据来自文献[40];3)数据来自文献[43]。 表 2 XT06站沉积物粒度主成分分析结果
Table 2. Results of principal component analysis for XT06 sediments
分析数据 主成分 主成分参数 特征根 方差 /% 累计方差 /% 所有样品的粒度分布数据 Fc1 42.2 44.0 44.0 Fc2 25.3 26.3 70.3 Fc3 23.2 24.2 94.5 Fc1、Cc-1、EM1三个序列 1 3.0 98.6 98.6 2 0.038 1.252 99.9 3 0.003 0.108 100 Fc2、Cc-2、EM2三个序列 1 2.1 70.8 70.8 2 0.872 29.1 99.9 3 0.004 0.1 100 -
[1] Sato T, Oda H, Ishizuka O, et al. Detailed bathymetry and magnetic anomaly in the central Ryukyu Arc, Japan: Implications for a westward shift of the volcanic front after approximately 2.1 Ma [J]. Earth, Planets and Space, 2014, 66: 68. doi: 10.1186/1880-5981-66-68
[2] Kawabe M, Fujio S. Pacific ocean circulation based on observation [J]. Journal of Oceanography, 2010, 66(3): 389-403. doi: 10.1007/s10872-010-0034-8
[3] Zhai F G, Gu Y Z. Abyssal circulation in the Philippine Sea [J]. Journal of Ocean University of China, 2020, 19(2): 249-262. doi: 10.1007/s11802-020-4241-7
[4] Nechaev V P. Evolution of the Philippine and Japan Seas from the clastic sediment record [J]. Marine Geology, 1991, 97(1-2): 167-190. doi: 10.1016/0025-3227(91)90025-Y
[5] Xu Z K, Li T G, Clift P D, et al. Quantitative estimates of asian dust input to the western Philippine Sea in the mid-late Quaternary and its potential significance for paleoenvironment [J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2015, 16(9): 3182-3196. doi: 10.1002/2015GC005929
[6] Ming J, Li A C, Huang J, et al. Assemblage characteristics of clay minerals and its implications to evolution of eolian dust input to the Parece Vela basin since 1.95 ma [J]. Chinese Journal of Oceanology and Limnology, 2014, 32(1): 174-186. doi: 10.1007/s00343-014-3066-x
[7] Jiang Z Z, Sun Z L, Liu Z Q, et al. Rare-earth element geochemistry reveals the provenance of sediments on the southwestern margin of the Challenger Deep [J]. Journal of Oceanology and Limnology, 2019, 37(3): 998-1009. doi: 10.1007/s00343-019-8046-8
[8] 王汾连, 何高文, 王海峰, 等. 马里亚纳海沟柱状沉积物稀土地球化学特征及其指示意义[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2016, 36(4):67-75
WANG Fenlian, HE Gaowen, WANG Haifeng, et al. Geochemistry of rare earth elements in a core from Mariana Trench and its significance [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2016, 36(4): 67-75.
[9] Xiao C H, Wang Y H, Tian J W, et al. Mineral composition and geochemical characteristics of sinking particles in the Challenger Deep, Mariana Trench: Implications for provenance and sedimentary environment [J]. Deep Sea Research Part I: Oceanographic Research Papers, 2020, 157: 103211. doi: 10.1016/j.dsr.2019.103211
[10] Rea D K. The paleoclimatic record provided by eolian deposition in the deep sea: The geologic history of wind [J]. Reviews of Geophysics, 1994, 32(2): 159-195. doi: 10.1029/93RG03257
[11] Rea D K, Hovan S A. Grain size distribution and depositional processes of the mineral component of abyssal sediments: Lessons from the north Pacific [J]. Paleoceanography and Paleoclimatology, 1995, 10(2): 251-258.
[12] Hovan S A, Rea D K, Pisias N G, et al. A direct link between the China loess and marine δ18O records: Aeolian flux to the north Pacific [J]. Nature, 1989, 340(6231): 296-298. doi: 10.1038/340296a0
[13] Windom H L. Atmospheric dust records in permanent snowfields: Implications to marine sedimentation [J]. GSA Bulletin, 1969, 80(5): 761-782. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(1969)80[761:ADRIPS]2.0.CO;2
[14] Pettke T, Halliday A N, Hall C M, et al. Dust production and deposition in Asia and the north Pacific Ocean over the past 12 Myr [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2000, 178(3-4): 397-413. doi: 10.1016/S0012-821X(00)00083-2
[15] Xiao C H, Wang Y H, Lin J. Constraints of magnetostratigraphic and mineralogical data on the provenance of sediments in the Parece Vela basin of the western Pacific [J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2020, 196: 104373. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2020.104373
[16] 黄杰, 万世明, 张国良, 等. 海底地形特征对东菲律宾海表层黏土矿物分布的影响[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2017, 37(1):77-85
HUANG Jie, WAN Shiming, ZHANG Guoliang, et al. Impact of seafloor topography on distribution of clay minerals in the east Philippines Sea [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2017, 37(1): 77-85.
[17] Yu Z J, Wan S M, Colin C, et al. Co-evolution of monsoonal precipitation in east Asia and the tropical Pacific ENSO system since 2.36 Ma: New insights from high-resolution clay mineral records in the west Philippine Sea [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2016, 446: 45-55. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2016.04.022
[18] Jiang F Q, Frank M, Li T G, et al. Asian dust input in the western Philippine Sea: Evidence from radiogenic Sr and Nd isotopes [J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2013, 14(5): 1538-1551. doi: 10.1002/ggge.20116
[19] Wan S M, Yu Z J, Clift P D, et al. History of Asian eolian input to the west Philippine Sea over the last one million years [J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2012, 326-328: 152-159. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2012.02.015
[20] Seo I, Lee Y I, Yoo C M, et al. Sr-Nd isotope composition and clay mineral assemblages in eolian dust from the central Philippine Sea over the last 600 kyr: Implications for the transport mechanism of Asian dust [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 2014, 119(19): 11492-11504. doi: 10.1002/2014JD022025
[21] Kirschvink J L. The least-squares line and plane and the analysis of palaeomagnetic data [J]. Geophysical Journal of the Royal Astronomical Society, 1980, 62(3): 699-718. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-246X.1980.tb02601.x
[22] Ashley G M. Interpretation of polymodal sediments [J]. The Journal of Geology, 1978, 86(4): 411-421. doi: 10.1086/649710
[23] Kranck K, Smith P C, Milligan T G. Grain-size characteristics of fine-grained unflocculated sediments I: 'One-round' distributions [J]. Sedimentology, 1996, 43(3): 589-594. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-3091.1996.d01-27.x
[24] Kranck K, Smith P C, Milligan T G. Grain-size characteristics of fine-grained unflocculated sediments II: 'Milti-round' distributions [J]. Sedimentology, 1996, 43(3): 597-606. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-3091.1996.d01-28.x
[25] Sun D H, Bloemendal J, Rea D K, et al. Grain-size distribution function of polymodal sediments in hydraulic and aeolian environments, and numerical partitioning of the sedimentary components [J]. Sedimentary Geology, 2002, 152(3-4): 263-277. doi: 10.1016/S0037-0738(02)00082-9
[26] Qin X G, Cai B G, Liu T S. Loess record of the aerodynamic environment in the east Asia monsoon area since 60, 000 years before present [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 2005, 110(B1): B01204.
[27] 易亮, 于洪军, 徐兴永, 等. 碳酸盐含量对莱州湾南岸钻孔沉积物粒度测试结果的影响[J]. 海洋科学进展, 2010, 28(3):325-331 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2010.03.008
YI Liang, YU Hongjun, XU Xingyong, et al. Influences of carbonate contents on the grain-size measurements of borehole sediments from southern shore of Laizhou Bay [J]. Advances in Marine Science, 2010, 28(3): 325-331. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2010.03.008
[28] Chen G Q, Yi L, Chen S L, et al. Partitioning of grain-size components of estuarine sediments and implications for sediment transport in southwestern Laizhou bay, China [J]. Chinese Journal of Oceanology and Limnology, 2013, 31(4): 895-906. doi: 10.1007/s00343-013-2304-y
[29] Yi L, Deng C L, Xu X Y, et al. Paleo-megalake termination in the Quaternary: Paleomagnetic and water-level evidence from south Bohai Sea, China [J]. Sedimentary Geology, 2015, 319: 1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.sedgeo.2015.01.005
[30] Yi L, Yu H J, Ortiz J D, et al. A reconstruction of late Pleistocene relative sea level in the south Bohai Sea, China, based on sediment grain-size analysis [J]. Sedimentary Geology, 2012, 281: 88-100. doi: 10.1016/j.sedgeo.2012.08.007
[31] Su Q, Peng C S, Yi L, et al. An improved method of sediment grain size trend analysis in the Xiaoqinghe estuary, southwestern Laizhou Bay, China [J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2016, 75: 1185. doi: 10.1007/s12665-016-5924-7
[32] Boulay S, Colin C, Trentesaux A, et al. Sedimentary responses to the Pleistocene climatic variations recorded in the South China Sea [J]. Quaternary Research, 2007, 68(1): 162-172. doi: 10.1016/j.yqres.2007.03.004
[33] Boulay S, Colin C, Trentesaux A, et al. Mineralogy and sedimentology of Pleistocene sediment in the South China Sea (ODP Site 1144)[C]//Prell W L, Wang P, Blum P, et al. Proceedings of the Ocean Drilling Program: Scientific Results. 2003, 184: 1-21.
[34] Darby D A, Ortiz J D, Polyak L, et al. The role of currents and sea ice in both slowly deposited central Arctic and rapidly deposited Chukchi–Alaskan margin sediments [J]. Global and Planetary Change, 2009, 68(1-2): 58-72. doi: 10.1016/j.gloplacha.2009.02.007
[35] Yi L, Yu H J, Ortiz J D, et al. Late quaternary linkage of sedimentary records to three astronomical rhythms and the Asian monsoon, inferred from a coastal borehole in the south Bohai Sea, China [J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2012, 329-330: 101-117. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2012.02.020
[36] Hu B Q, Yang Z S, Zhao M X, et al. Grain size records reveal variability of the east Asian winter monsoon since the middle Holocene in the central Yellow Sea Mud Area, China [J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 2012, 55(10): 1656-1668. doi: 10.1007/s11430-012-4447-7
[37] Zijderveld J D A. A. C. Demagnetization of rocks: Analysis of results [M] //Collinson D W, Creer K M, Runco S K. Methods in paleomagnetism. Amsterdam: Elsevier. 1967: 254-286.
[38] 孟庆勇, 李安春, 蒋富清, 等. 近2 Ma来东菲律宾海地球磁场相对强度变化的沉积记录[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2010, 41(4):606-613 doi: 10.11693/hyhz201004021021
Meng Q Y, Li A C, Jiang F Q, et al. A geomagnetic paleointensity record over the last 2 Ma from the east Philippine Sea [J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2010, 41(4): 606-613. doi: 10.11693/hyhz201004021021
[39] 孟庆勇, 李安春, 靳宁, 等. 东菲律宾海柱样沉积物的磁性特征[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2006, 26(3):57-63
Meng Q Y, Li A C, Jin N, et al. Magnetostratigraphic and magnetic properties of marine sediments from the east Philippine Sea [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2006, 26(3): 57-63.
[40] Yi L, Xu D, Jiang X Y, et al. Magnetostratigraphy and authigenic 10Be/9Be dating of Plio-Pleistocene abyssal surficial sediments on the southern slope of Mariana Trench and sedimentary processes during the mid-Pleistocene transition [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 2020, 125(8): e2020JC016250.
[41] Hilgen F J, Lourens L J, van Dam J A, et al. The Neogene period[M]//Gradstein F M, Ogg J G, Schmitz M D, et al. The Geologic Time Scale 2012. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2012: 923-978.
[42] Channell J E T, Singer B S, Jicha B R. Timing of Quaternary geomagnetic reversals and excursions in volcanic and sedimentary archives [J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2020, 228: 106114. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2019.106114
[43] Jiang F Q, Zhu X, Li T G, et al. Increased dust deposition in the Parece Vela basin since the mid-Pleistocene inferred from radiogenic Sr and Nd isotopes [J]. Global and Planetary Change, 2019, 173: 83-95. doi: 10.1016/j.gloplacha.2018.12.011
[44] Passega R. Grain size representation by CM patterns as a geologic tool [J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 1964, 34(4): 830-847. doi: 10.1306/74D711A4-2B21-11D7-8648000102C1865D
[45] Yao H, Wang F, Wang H, et al. Pleistocene magnetostratigraphy of four cores in the west Philippian basin and regional sedimentary shift during the mid-Pleistocene transition [J]. Geological Journal, 2020. doi: 10.1002/gj.4082
[46] Hays J D, Imbrie J, Shackleton N J. Variations in the Earth's orbit: Pacemaker of the ice ages [J]. Science, 1976, 194(4270): 1121-1132. doi: 10.1126/science.194.4270.1121
[47] Clark P U, Alley R B, Pollard D. Northern hemisphere ice-sheet influences on global climate change [J]. Science, 1999, 286(5442): 1104-1111. doi: 10.1126/science.286.5442.1104
[48] Zachos J, Pagani M, Sloan L, et al. Trends, rhythms, and aberrations in global climate 65 Ma to present [J]. Science, 2001, 292(5517): 686-693. doi: 10.1126/science.1059412
[49] Sun Y B, Yin Q Z, Crucifix M, et al. Diverse manifestations of the mid-Pleistocene climate transition [J]. Nature Communications, 2019, 10: 352. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-08257-9
[50] Sun J M, Liu T S. Stratigraphic evidence for the uplift of the Xizang Plateau between ~1.1 and ~0.9 myr ago [J]. Quaternary Research, 2000, 54(3): 309-320. doi: 10.1006/qres.2000.2170
[51] Sun Y B, An Z S. Late Pliocene-Pleistocene changes in mass accumulation rates of eolian deposits on the central Chinese Loess Plateau [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 2005, 110(D23): D23101. doi: 10.1029/2005JD006064
[52] Ford H L, Raymo M E. Regional and global signals in seawater δ18O records across the mid-Pleistocene transition [J]. Geology, 2020, 48(2): 113-117. doi: 10.1130/G46546.1
[53] Clark P U, Archer D, Pollard D, et al. The middle Pleistocene transition: Characteristics, mechanisms, and implications for long-term changes in atmospheric pCO2 [J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2006, 25(23-24): 3150-3184. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2006.07.008
[54] Yi L, Ye X Y, Chen J B, et al. Magnetostratigraphy and luminescence dating on a sedimentary sequence from northern East China Sea: Constraints on evolutionary history of eastern marginal seas of China since the early Pleistocene [J]. Quaternary International, 2014, 349: 316-326. doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2014.07.038
[55] Jolivet L, Tamaki K, Fournier M. Japan sea, opening history and mechanism: A synthesis [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 1994, 99(B11): 22237-22259. doi: 10.1029/93JB03463
[56] Underwood M B, Fergusson C L. Late Cenozoic evolution of the Nankai trench-slope system: Evidence from sand petrography and clay mineralogy [J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 2005, 244(1): 113-129. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.2005.244.01.07
[57] Zhu R X, Zheng T Y. Destruction geodynamics of the north China Craton and its paleoproterozoic plate tectonics [J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2009, 54(10): 3354-3366.
[58] Lisiecki L E, Raymo M E. A Pliocene-Pleistocene stack of 57 globally distributed benthic δ18O records [J]. Paleoceanography and Paleoclimatology, 2005, 20(1): PA1003.
[59] Hodell D A, Venz-Curtis K A. Late Neogene history of deepwater ventilation in the Southern Ocean [J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2006, 7(9): Q09001.
[60] Elderfield H, Ferretti P, Greaves M, et al. Evolution of ocean temperature and ice volume through the mid-Pleistocene climate transition [J]. Science, 2012, 337(6095): 704-709. doi: 10.1126/science.1221294
[61] Hodell D A, Venz K A, Charles C D, et al. Pleistocene vertical carbon isotope and carbonate gradients in the south Atlantic Sector of the Southern Ocean [J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2003, 4(1): 1-19.
[62] Howe J N W, Piotrowski A M, Noble T L, et al. North Atlantic deep water production during the last glacial maximum [J]. Nature Communications, 2016, 7: 11765. doi: 10.1038/ncomms11765
[63] Jaccard S L, Galbraith E D, Martínez-García A, et al. Covariation of deep Southern Ocean oxygenation and atmospheric CO2 through the last ice age [J]. Nature, 2016, 530(7589): 207-210. doi: 10.1038/nature16514
[64] Sigman D M, Hain M P, Haug G H. The polar ocean and glacial cycles in atmospheric CO2 concentration [J]. Nature, 2010, 466(7302): 47-55. doi: 10.1038/nature09149
[65] Sun Y B, Clemens S C, An Z S, et al. Astronomical timescale and palaeoclimatic implication of stacked 3.6-myr monsoon records from the Chinese Loess Plateau [J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2006, 25(1-2): 33-48. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2005.07.005
[66] Rea D K, Snoeckx H, Joseph L H. Late Cenozoic eolian deposition in the north Pacific: Asian drying, Xizang uplift, and cooling of the northern hemisphere [J]. Paleoceanography and Paleoclimatology, 1998, 13(3): 215-224.
[67] Zhang Q, Liu Q S, Roberts A P, et al. Mechanism for enhanced eolian dust flux recorded in north Pacific Ocean sediments since 4.0 Ma: Aridity or humidity at dust source areas in the Asian interior? [J]. Geology, 2019, 48(1): 77-81.
[68] Serno S, Winckler G, Anderson R F, et al. Eolian dust input to the subarctic north Pacific [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2014, 387: 252-263. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2013.11.008
-




 下载:
下载: