Rare earth element geochemistry characteristics and implications of pore-water from deep sea sediment in Western Pacific Ocean
-
摘要:
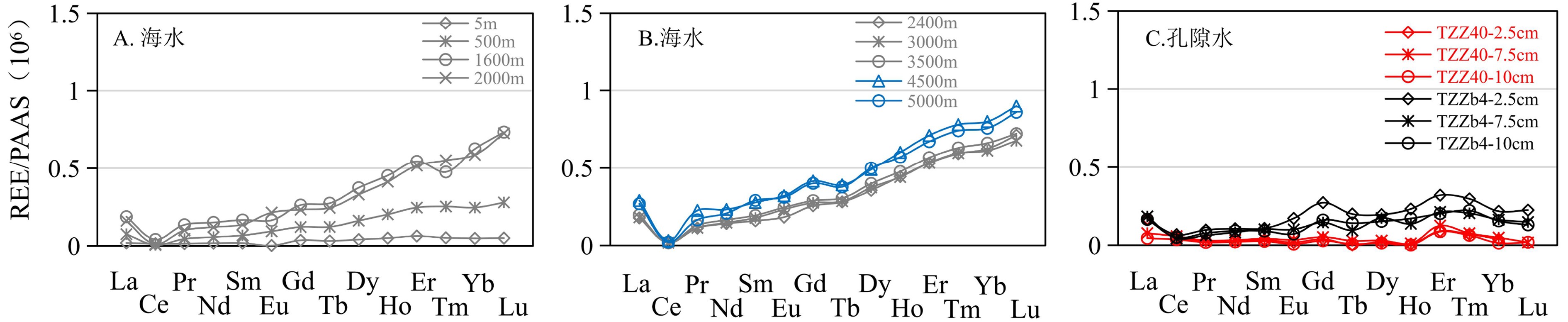
为探索深海孔隙水中稀土元素的生物地球化学循环过程,对太平洋菲律宾海九州-帕劳海脊东、西两侧的两个钻孔沉积物进行了高精度的孔隙水采样工作,分析了主、微量元素和稀土元素的地球化学特征,并对稀土元素的浓度、配分模式以及分馏特征进行了详细的讨论。结果表明:这两个钻孔沉积物均处于氧化环境,表现出海水-沉积物界面和浅层孔隙水(2.5~20 cm)中相对富集轻稀土和中稀土,而中层(25~60 cm)和深层沉积物(>65 cm)孔隙水中则相对富集重稀土元素的特征。初步推断有机质和锰(氢)氧化物的分解和吸附作用是造成孔隙水中稀土元素分馏的主要因素。相比于九州-帕劳海脊的东、西两侧海域,孔隙水中的稀土元素浓度和分馏程度存在一定的差异,周围环境中的矿物组成和锰(氢)氧化物等是其主要的控制因素,但是研究区域深海孔隙流体并不能为海洋贡献稀土元素。
Abstract:In order to explore the biogeochemical process of the rare earth elements in deep sea pore water, high-precision samples were collected from the two stations of the Philippine Sea. Geochemical characteristics of the main elements, trace elements and REE are analyzed and the concentration, distribution and fractionation of the REE discussed in details. It is found that both the two stations are in an oxidizing environment. HREE and MREE are enriched around the water-sediment interface and in the shallow pore water (2.5~20 cm), while MREE and HREE enriched in the middle (25~60 cm) and lower layers of sediments. We believe that the decomposition and adsorption of organic matter and Mn oxide are the main factors for the fractionation of REE in pore water. Concentrations and fractionations of REE in pore water are found different in the East and West sides of the Kyushu Palau Ridge because of the difference in volcanic activities, mineral composition and Mn oxide in the surrounding environment. However, the pore fluid of the study area makes no contribution of REE to the ocean.
-
Key words:
- rare earth element /
- pore water /
- trace elements /
- geochemistry /
- Philippine Sea
-

-
表 1 孔隙水中主量元素和微量元素的分析结果
Table 1. Concentrations of major and trace elements in the pore-water
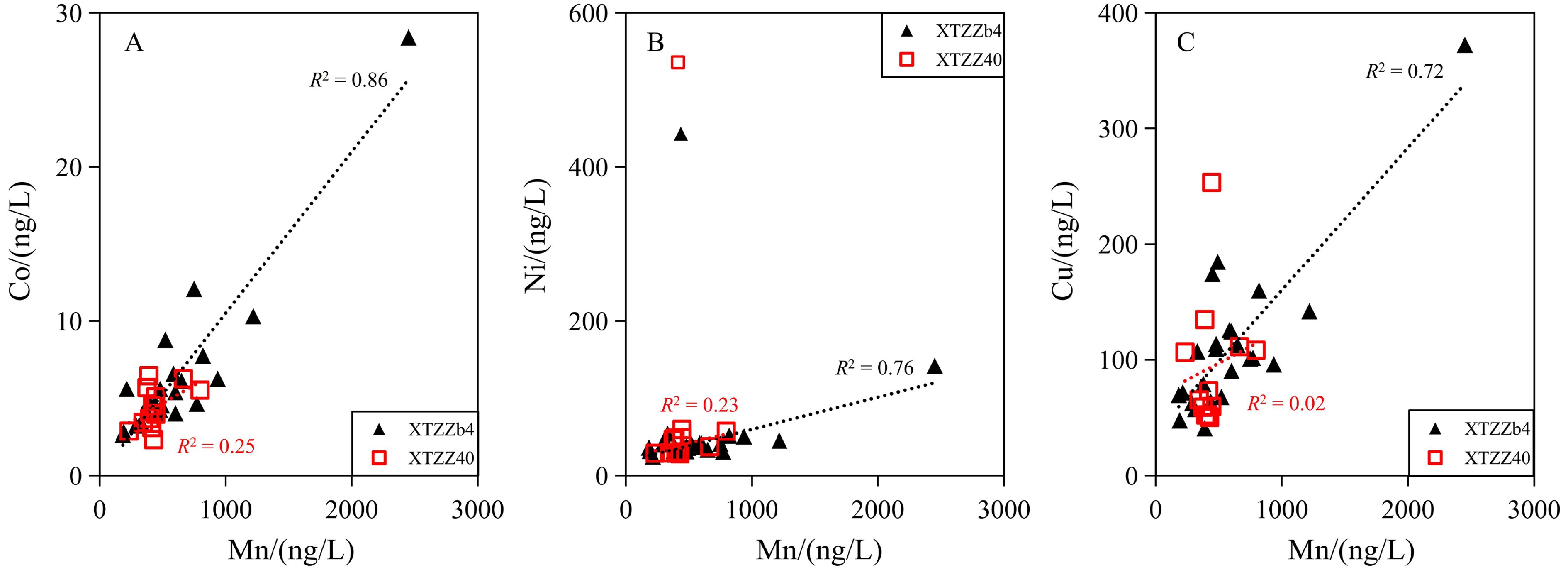
站位 深度/cm Ca/(mg/L) K/(mg/L) Mn/(ng/L) Co/(ng/L) Cu/(ng/L) Zn/(ng/L) Sr/(μg/L) Mo/(μg/L) XTZZ40 2.5 259 367 796 5.5 108 2 574 6 561 9.17 7.5 259 363 428 2.3 50 1 713 6 663 6.78 10 259 392 414 3.1 52 2 137 6 593 10.4 25 258 394 346 3.4 65 1 449 6 432 9.34 42.5 259 425 390 6.5 135 2 984 6 386 11.1 45 259 433 445 5.1 253 3 955 6 465 11.4 55 255 431 445 4.0 60 958 6 409 12.9 60 265 441 421 4.5 73 947 6 929 12.4 65 261 450 664 6.3 111 2 758 6 648 12.3 75 267 433 397 3.7 52 1 634 6 154 11.8 95 263 405 376 5.7 59 927 6 379 13.6 100 305 457 233 2.9 106 1 116 6 510 16.2 XTZZ64 2.5 311 403 184 2.6 70 1 098 6 858 14.7 7.5 315 421 389 4.8 41 1 311 6 845 9.02 10 323 447 2 451 28.4 372 1 983 6 976 8.25 15 267 411 586 6.6 126 2 164 6 238 4.17 17.5 285 439 771 4.7 102 1 748 6 560 9.07 20 288 446 649 6.1 113 2 965 6 584 9.71 22.5 302 454 493 4.5 185 2 573 6 667 9.81 25 305 443 601 4.0 90 1 806 6 564 8.20 27.5 319 453 480 5.6 109 1 477 6 738 9.65 30 282 408 1 219 10.3 142 1 731 6 307 9.38 32.5 301 434 330 3.4 107 1 406 6 074 8.19 35 313 452 215 5.6 72 1 536 6 754 10.1 40 303 444 379 4.0 79 1 067 6 605 7.03 45 300 446 313 3.2 57 1 025 6 588 8.48 47.5 301 441 749 12.1 101 1 215 6 660 9.48 50 300 434 521 8.8 68 1 178 6 570 7.18 60 290 445 290 3.3 63 1 609 6 604 9.59 65 313 465 191 2.8 48 1 044 6 563 7.82 70 303 449 600 5.4 124 2 062 6 481 8.60 75 303 450 480 4.2 114 5 675 6 476 8.85 80 314 461 436 4.7 64 1 873 6 350 9.04 90 303 514 820 7.8 160 1 953 6 425 15.7 95 330 488 451 3.9 174 1 671 6 808 14.7 100 326 483 936 6.3 96 1 590 6 491 13.0 表 2 孔隙水中稀土元素的分析结果
Table 2. Concentration of REEs in the pore-water
pmol/kg 站位 深度/cm La Ce Pr Nd Sm Eu Gd Tb Dy Ho Er Tm Yb Lu XTZZ40 2.5 46.39 27.47 1.85 7.48 1.28 0.13 1.14 0.01 0.61 0.04 1.54 0.17 0.63 7.5 21.11 32.86 1.85 7.69 1.54 0.24 1.55 0.14 0.86 0.07 2.13 0.18 0.79 0.04 10 12.23 20.50 1.13 5.00 0.93 0.05 0.84 0.04 0.40 0.01 1.47 0.15 0.22 0.05 25 69.26 96.41 8.15 31.97 5.57 1.26 5.53 1.02 5.27 1.10 6.96 0.71 3.10 0.50 42.5 49.76 26.83 7.04 30.59 6.06 1.27 6.93 1.00 5.42 1.15 4.66 0.74 3.82 0.48 45 67.64 94.41 6.95 27.25 5.24 0.99 5.49 0.53 3.75 0.89 6.71 0.48 2.97 0.43 55 116.28 90.07 9.16 39.21 7.99 1.03 8.33 1.12 6.90 1.12 6.38 0.86 4.42 0.53 60 47.02 53.73 5.35 22.91 4.12 0.84 5.92 0.72 4.41 1.01 4.93 0.49 3.33 0.47 65 11.24 29.78 1.82 7.55 1.84 0.18 1.38 0.05 1.11 0.05 2.31 0.20 1.07 0.05 75 33.66 50.47 7.27 35.83 6.16 1.66 7.31 1.03 6.08 0.98 4.40 0.65 3.16 0.53 95 29.43 36.14 4.60 20.31 4.59 1.01 3.83 0.51 3.76 0.57 2.31 0.45 1.87 0.22 100 20.63 25.49 3.36 15.52 3.00 0.64 3.01 0.52 3.19 0.60 2.16 0.49 2.45 0.32 XTZZ64 2.5 44.87 38.31 6.10 24.79 3.96 1.22 8.05 0.97 5.62 1.39 5.44 0.71 3.54 0.55 7.5 50.60 24.61 3.92 19.45 3.76 0.72 4.29 0.47 4.99 0.82 3.61 0.49 2.66 0.37 10 45.50 27.82 4.82 21.61 3.33 0.51 4.76 0.69 4.38 1.03 3.43 0.53 2.53 0.32 15 40.60 29.18 4.54 21.50 2.92 0.49 4.37 0.52 3.37 0.66 2.74 0.48 2.14 0.26 17.5 48.26 47.08 4.54 20.05 3.58 0.48 4.53 0.53 4.80 0.80 4.14 0.46 2.36 0.34 20 39.60 49.56 4.60 20.62 3.72 2.17 4.53 0.65 3.86 0.82 4.37 0.54 2.29 0.46 22.5 37.32 47.22 4.31 21.54 4.25 0.68 5.03 0.54 3.96 0.90 4.85 0.38 3.01 0.46 25 36.51 35.31 4.11 18.31 4.74 0.57 4.89 0.56 3.61 1.00 3.53 0.39 2.23 0.32 27.5 35.82 36.06 3.70 17.56 2.94 0.15 3.74 0.57 3.20 0.43 3.48 0.47 2.36 0.23 30 42.04 52.90 4.26 20.66 3.32 0.44 3.88 0.59 3.03 0.72 4.92 0.37 2.47 0.25 32.5 34.90 31.23 4.34 17.10 4.03 0.61 4.11 0.53 3.33 0.83 2.80 0.52 2.07 0.33 35 42.45 48.02 4.09 19.71 3.54 0.74 4.56 0.57 3.64 0.72 4.31 0.53 2.54 0.29 40 42.13 36.63 6.21 29.64 6.45 1.39 7.82 0.96 6.17 1.28 5.14 0.75 3.57 0.72 45 40.92 41.99 4.00 18.25 3.51 0.64 4.37 0.46 3.45 0.77 4.30 0.48 2.55 0.26 47.5 34.90 43.08 4.38 21.82 3.60 0.54 4.51 0.53 3.37 0.96 3.17 0.52 1.99 0.26 50 40.03 42.99 4.88 20.79 4.80 0.80 5.97 0.96 4.31 1.07 4.75 0.71 3.64 0.69 60 34.30 36.40 4.16 20.40 3.10 0.51 3.68 0.56 3.40 0.81 3.57 0.39 2.77 0.34 65 28.47 37.17 3.62 14.79 2.44 0.61 4.36 0.48 3.65 0.86 3.81 0.40 2.25 0.33 70 30.87 37.43 4.11 18.45 2.28 0.53 3.89 0.48 4.07 0.92 3.65 0.48 2.46 0.35 75 33.55 40.68 4.41 19.66 3.25 0.63 4.38 0.56 4.15 0.71 4.21 0.45 2.65 0.36 80 36.05 51.44 4.86 20.51 2.91 0.70 4.72 0.58 4.30 0.93 4.05 0.61 3.31 0.34 90 35.91 34.89 4.70 20.10 3.27 0.81 4.21 0.47 3.56 0.74 2.95 0.47 2.80 0.33 95 33.35 42.42 3.67 17.19 3.63 0.56 3.38 0.45 2.98 0.59 3.74 0.39 2.09 0.27 100 30.61 49.24 4.17 19.18 2.78 0.48 5.27 0.28 2.97 0.78 4.15 0.42 2.65 0.31 -
[1] German C R, Elderfield H. Rare earth elements in the NW Indian Ocean [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1990, 54(7): 1929-1940. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(90)90262-J
[2] Bertram C J, Elderfield H. The geochemical balance of the rare earth elements and neodymium isotopes in the oceans [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1993, 57(9): 1957-1986. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(93)90087-D
[3] Osborne A H, Haley B A, Hathorne E C, et al. Rare earth element distribution in Caribbean seawater: Continental inputs versus lateral transport of distinct REE compositions in subsurface water masses [J]. Marine Chemistry, 2015, 177: 172-183. doi: 10.1016/j.marchem.2015.03.013
[4] Stichel T, Hartman A E, Duggan B, et al. Separating biogeochemical cycling of neodymium from water mass mixing in the Eastern North Atlantic [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2015, 412: 245-260. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2014.12.008
[5] Kynicky J, Smith M P, Xu C. Diversity of rare earth deposits: the key example of China [J]. Elements, 2012, 8(5): 361-367. doi: 10.2113/gselements.8.5.361
[6] Che H, Zhang J. Water mass analysis and end-member mixing contribution using coupled radiogenic Nd isotopes and Nd concentrations: interaction between marginal seas and the northwestern pacific [J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2018, 45(5): 2388-2395. doi: 10.1002/2017GL076978
[7] Zhang J, Liu Q, Bai L L, et al. Water mass analysis and contribution estimation using heavy rare earth elements: Significance of Kuroshio intermediate water to Central East China Sea shelf water [J]. Marine Chemistry, 2018, 204: 172-180. doi: 10.1016/j.marchem.2018.07.011
[8] Murphy K, Dymond J. Rare earth element fluxes and geochemical budget in the eastern equatorial Pacific [J]. Nature, 1984, 307(5950): 444-447. doi: 10.1038/307444a0
[9] Elderfield H, Upstill-Goddard R, Sholkovitz E R. The rare earth elements in rivers, estuaries, and coastal seas and their significance to the composition of ocean waters [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1990, 54(4): 971-991. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(90)90432-K
[10] Nozaki Y, Zhang J, Amakawa H. The fractionation between Y and Ho in the marine environment [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1997, 148(1-2): 329-340. doi: 10.1016/S0012-821X(97)00034-4
[11] Zhang J, Nozaki Y. Rare earth elements and yttrium in seawater: ICP-MS determinations in the East Caroline, Coral Sea, and South Fiji Basins of the Western South Pacific Ocean [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1996, 60(23): 4631-4644. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(96)00276-1
[12] Lacan F, Jeandel C. Tracing Papua New Guinea imprint on the central Equatorial Pacific Ocean using neodymium isotopic compositions and Rare Earth Element patterns [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2001, 186(3-4): 497-512. doi: 10.1016/S0012-821X(01)00263-1
[13] Deng Y N, Ren J B, Guo Q J, et al. Rare earth element geochemistry characteristics of seawater and porewater from deep sea in western pacific [J]. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7: 16539. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-16379-1
[14] Zhao M Y, Zheng Y F. Marine carbonate records of terrigenous input into Paleotethyan seawater: geochemical constraints from Carboniferous limestones [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2014, 141: 508-531. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2014.07.001
[15] Zhao M Y, Zheng Y F. A geochemical framework for retrieving the linked depositional and diagenetic histories of marine carbonates [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2017, 460: 213-221. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2016.11.033
[16] Service R F. Nations move to head off shortages of rare earths [J]. Science, 2010, 327(5973): 1596-1597. doi: 10.1126/science.327.5973.1596
[17] Yasukawa K, Liu H J, Fujinaga K, et al. Geochemistry and mineralogy of REY-rich mud in the eastern Indian Ocean [J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2014, 93: 25-36. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2014.07.005
[18] Emsbo P, McLaughlin P I, Breit G N, et al. Rare earth elements in sedimentary phosphate deposits: Solution to the global REE crisis? [J]. Gondwana Research, 2015, 27(2): 776-785. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2014.10.008
[19] 张霄宇, 石学法, 黄牧, 等. 深海富稀土沉积研究的若干问题[J]. 中国稀土学报, 2019, 37(5):517-529
ZHANG Xiaoyu, SHI Xuefa, HUANG Mu, et al. Some problems in research of deep sea rare earth rich deposit [J]. Journal of the Chinese Society of Rare Earths, 2019, 37(5): 517-529.
[20] Kato Y, Fujinaga K, Nakamura K, et al. Deep-sea mud in the Pacific Ocean as a potential resource for rare-earth elements [J]. Nature Geoscience, 2011, 4(8): 533-539.
[21] Martin J M, Høgdahl O, Philippot J C. Rare earth element supply to the ocean [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 1976, 81(18): 3119-3124. doi: 10.1029/JC081i018p03119
[22] Greaves M J, Statham P J, Elderfield H. Rare earth element mobilization from marine atmospheric dust into seawater [J]. Marine Chemistry, 1994, 46(3): 255-260. doi: 10.1016/0304-4203(94)90081-7
[23] Sholkovitz E R, Elderfield H, Szymczak R, et al. Island weathering: river sources of rare earth elements to the Western Pacific Ocean [J]. Marine Chemistry, 1999, 68(1-2): 39-57. doi: 10.1016/S0304-4203(99)00064-X
[24] Chen J B, Algeo T J, Zhao L S, et al. Diagenetic uptake of rare earth elements by bioapatite, with an example from Lower Triassic conodonts of South China [J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2015, 149: 181-202. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2015.01.013
[25] Haley B A, Klinkhammer G P, McManus J. Rare earth elements in pore waters of marine sediments [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2004, 68(6): 1265-1279. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2003.09.012
[26] Pearce C R, Jones M T, Oelkers E H, et al. The effect of particulate dissolution on the neodymium (Nd) isotope and rare earth element (REE) composition of seawater [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2013, 369-370: 138-147. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2013.03.023
[27] Rousseau T C C, Sonke J E, Chmeleff J, et al. Rapid neodymium release to marine waters from lithogenic sediments in the amazon estuary [J]. Nature Communications, 2015, 6: 7592. doi: 10.1038/ncomms8592
[28] Kim I, Kim G. Submarine groundwater discharge as a main source of rare earth elements in coastal waters [J]. Marine Chemistry, 2014, 160: 11-17. doi: 10.1016/j.marchem.2014.01.003
[29] Abbott A N, Haley B A, McManus J, et al. The sedimentary flux of dissolved rare earth elements to the ocean [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2015, 154: 186-200. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2015.01.010
[30] Gaillard J F, Jeandel C, Michard G, et al. Interstitial water chemistry of villefranche bay sediments: Trace metal diagenesis [J]. Marine Chemistry, 1986, 18(2-4): 233-247. doi: 10.1016/0304-4203(86)90011-3
[31] Graybeal A L, Heath G R. Remobilization of transition metals in surficial pelagic sediments from the eastern pacific [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1984, 48(5): 965-975. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(84)90188-1
[32] Zhang H, Davison W, Miller S, et al. In situ high resolution measurements of fluxes of Ni, Cu, Fe, and Mn and concentrations of Zn and Cd in porewaters by DGT [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1995, 59(20): 4181-4192. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(95)00293-9
[33] Morford J L, Martin W R, Kalnejais L H, et al. Insights on geochemical cycling of U, Re and Mo from seasonal sampling in Boston Harbor, Massachusetts, USA [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2007, 71(4): 895-917. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2006.10.016
[34] 邓义楠, 任江波, 郭庆军, 等. 西太平洋深水盆地海水及孔隙水的微量元素地球化学特征[J]. 地球科学, 2019, 44(9):3101-3114
DENG Yinan, REN Jiangbo, GUO Qingjun, et al. Trace elements geochemistry characteristics of seawater and porewater in Deep-Water Basin, Western Pacific [J]. Earth Science, 2019, 44(9): 3101-3114.
[35] 杨娅敏, 曾志刚, 殷学博, 等. 深海富REY泥中稀土元素赋存载体及其富集机制研究进展[J]. 海洋科学, 2019, 43(8):93-107 doi: 10.11759/hykx20181129002
YANG Yamin, ZENG Zhigang, YIN Xuebo, et al. Advances in research on the host and the enrichment mechanism of REY-rich mud in deep-sea sediments [J]. Marine Sciences, 2019, 43(8): 93-107. doi: 10.11759/hykx20181129002
[36] Klinkhammer G P. Early diagenesis in sediments from the eastern equatorial pacific, II. Pore water metal results [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1980, 49(1): 81-101. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(80)90151-X
[37] Klinkhammer G, Heggie D T, Graham D W. Metal diagenesis in oxic marine sediments [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1982, 61(2): 211-219. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(82)90054-1
[38] 刘季花, 张丽洁, 梁宏峰. 太平洋东部CC48孔沉积物稀土元素地球化学研究[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 1994, 25(1):15-22 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.1994.01.003
LIU Jihua, ZHANG Lijie, LIANG Hongfeng. The REE Geochemistry of sediments in core CC48 from the east pacific ocean [J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 1994, 25(1): 15-22. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.1994.01.003
[39] 王汾连, 何高文, 孙晓明, 等. 太平洋富稀土深海沉积物中稀土元素赋存载体研究[J]. 岩石学报, 2016, 32(7):2057-2068
WANG Fenlian, HE Gaowen, SUN Xiaoming, et al. The host of REE+Y elements in deep-sea sediments from the Pacific Ocean [J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2016, 32(7): 2057-2068.
[40] McLennan S M. Rare earth elements in sedimentary rocks; influence of provenance and sedimentary processes [J]. Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry, 1989, 21(1): 169-200.
[41] Canfield D E, Thamdrup B. Towards a consistent classification scheme for geochemical environments, or, why we wish the term 'Suboxic' would go away [J]. Geobiology, 2010, 7(4): 385-392.
[42] Madison A S, Tebo B M, Mucci A, et al. Abundant porewater Mn (Ⅲ) is a major component of the sedimentary Redox System [J]. Science, 2013, 341(6148): 875-878. doi: 10.1126/science.1241396
[43] Wu Q, Colin C, Liu Z F, et al. New insights into hydrological exchange between the South China Sea and the Western Pacific Ocean based on the Nd isotopic composition of seawater [J]. Deep Sea Research Part II: Topical Studies in Oceanography, 2015, 122: 25-40. doi: 10.1016/j.dsr2.2015.11.005
[44] 张丽洁, 刘季花, 姚德. 海底水-沉积物界面系统中稀土元素的变化及配分特征[J]. 海洋学报, 1995, 17(1):52-58
ZHANG Lijie, LIU Jihua, YAO De. The distribution of Rare earth elements in the water-sediment interface system of the seabed [J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 1995, 17(1): 52-58.
[45] Sholkovitz E R, Piepgras D J, Jacobsen S B. The pore water chemistry of rare earth elements in Buzzards Bay sediments [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1989, 53(11): 2847-2856. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(89)90162-2
[46] Elderfield H, Pagett R. Rare earth elements in ichthyoliths: variations with redox conditions and depositional environment [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 1986, 49: 175-197. doi: 10.1016/0048-9697(86)90239-1
[47] Sholkovitz E R, Landing W M, Lewis B L. Ocean particle chemistry: The fractionation of rare earth elements between suspended particles and seawater [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1994, 58(6): 1567-1579. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(94)90559-2
[48] Tachikawa K, Handel C, Dupré B. Distribution of rare earth elements and neodymium isotopes in settling particulate material of the tropical Atlantic Ocean (EUMELI site) [J]. Deep Sea Research Part I: Oceanographic Research Papers, 1997, 44(11): 1769-1792. doi: 10.1016/S0967-0637(97)00057-5
[49] Arraes-Mescoff R, Roy-Barman M, Coppola L, et al. The behavior of Al, Mn, Ba, Sr, REE and Th isotopes during in vitro degradation of large marine particles [J]. Marine Chemistry, 2001, 73(1): 1-19. doi: 10.1016/S0304-4203(00)00065-7
[50] Bayon G, German C R, Burton K W, et al. Sedimentary Fe-Mn oxyhydroxides as paleoceanographic archives and the role of Aeolian flux in regulating oceanic dissolved REE [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2004, 224(3-4): 477-492. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2004.05.033
[51] 邓义楠, 任江波, 郭庆军, 等. 太平洋西部富稀土深海沉积物的地球化学特征及其指示意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2018, 34(3):733-747
DENG Yinan, REN Jiangbo, GUO Qingjun, et al. Geochemistry characteristics of REY-rich sediment from deep sea in Western Pacific, and their indicative significance [J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2018, 34(3): 733-747.
[52] 朱克超, 任江波, 王海峰, 等. 太平洋中部富REY深海粘土的地球化学特征及REY富集机制[J]. 地球科学—中国地质大学学报, 2015, 40(6):1052-1060 doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2015.087
ZHU Kechao, REN Jiangbo, WANG Haifeng, et al. Enrichment mechanism of REY and geochemical characteristics of REY-Rich pelagic clay from the Central Pacific [J]. Earth Science—Journal of China University of Geosciences, 2015, 40(6): 1052-1060. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2015.087
[53] Goldberg E D, Koide M, Schmitt R A, et al. Rare-earth distributions in the marine environment [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1963, 68(14): 4209-4217. doi: 10.1029/JZ068i014p04209
[54] Bright C A, Cruse A M, Lyons T W, et al. Seawater rare-earth element patterns preserved in apatite of Pennsylvanian conodonts? [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2009, 73(6): 1609-1624. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2008.12.014
[55] Bayon G, Birot D, Ruffine L, et al. Evidence for intense REE scavenging at cold seeps from the Niger Delta margin [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2011, 312(3-4): 443-452. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2011.10.008
[56] Gutjahr M, Frank M, Stirling C H, et al. Reliable extraction of a deepwater trace metal isotope signal from Fe-Mn oxyhydroxide coatings of marine sediments [J]. Chemical Geology, 2007, 242(3-4): 351-370. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2007.03.021
[57] Kashiwabara T, Toda R, Nakamura K, et al. Synchrotron X-ray spectroscopic perspective on the formation mechanism of REY-rich muds in the Pacific Ocean [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2018, 240: 274-292. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2018.08.013
[58] Yasukawa K, Nakamura K, Fujinaga K, et al. Rare-earth, major, and trace element geochemistry of deep-sea sediments in the Indian Ocean: implications for the potential distribution of REY-rich mud in the Indian Ocean [J]. Geochemical Journal, 2015, 49(6): 621-635. doi: 10.2343/geochemj.2.0361
[59] Ohta J, Yasukawa K, Machida S, et al. Geological factors responsible for REY-rich mud in the western North Pacific Ocean: Implications from mineralogy and grain size distributions [J]. Geochemical Journal, 2016, 50(6): 591-603. doi: 10.2343/geochemj.2.0435
[60] Iijima K, Yasukawa K, Fujinaga K, et al. Discovery of extremely REY-rich mud in the western North Pacific Ocean [J]. Geochemical Journal, 2016, 50(6): 557-573. doi: 10.2343/geochemj.2.0431
[61] Fujinaga K, Yasukawa K, Nakamura K, et al. Geochemistry of REY-rich mud in the Japanese exclusive economic zone around Minamitorishima Island [J]. Geochemical Journal, 2016, 50(6): 575-590. doi: 10.2343/geochemj.2.0432
[62] Menendez A, James R H, Roberts S, et al. Controls on the distribution of rare earth elements in deep-sea sediments in the North Atlantic Ocean [J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2017, 87: 100-113. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2016.09.036
-



 下载:
下载: