Radiolarian distribution in surface sediments of the Philippine Sea and adjacent areas and its response to environment
-
摘要:
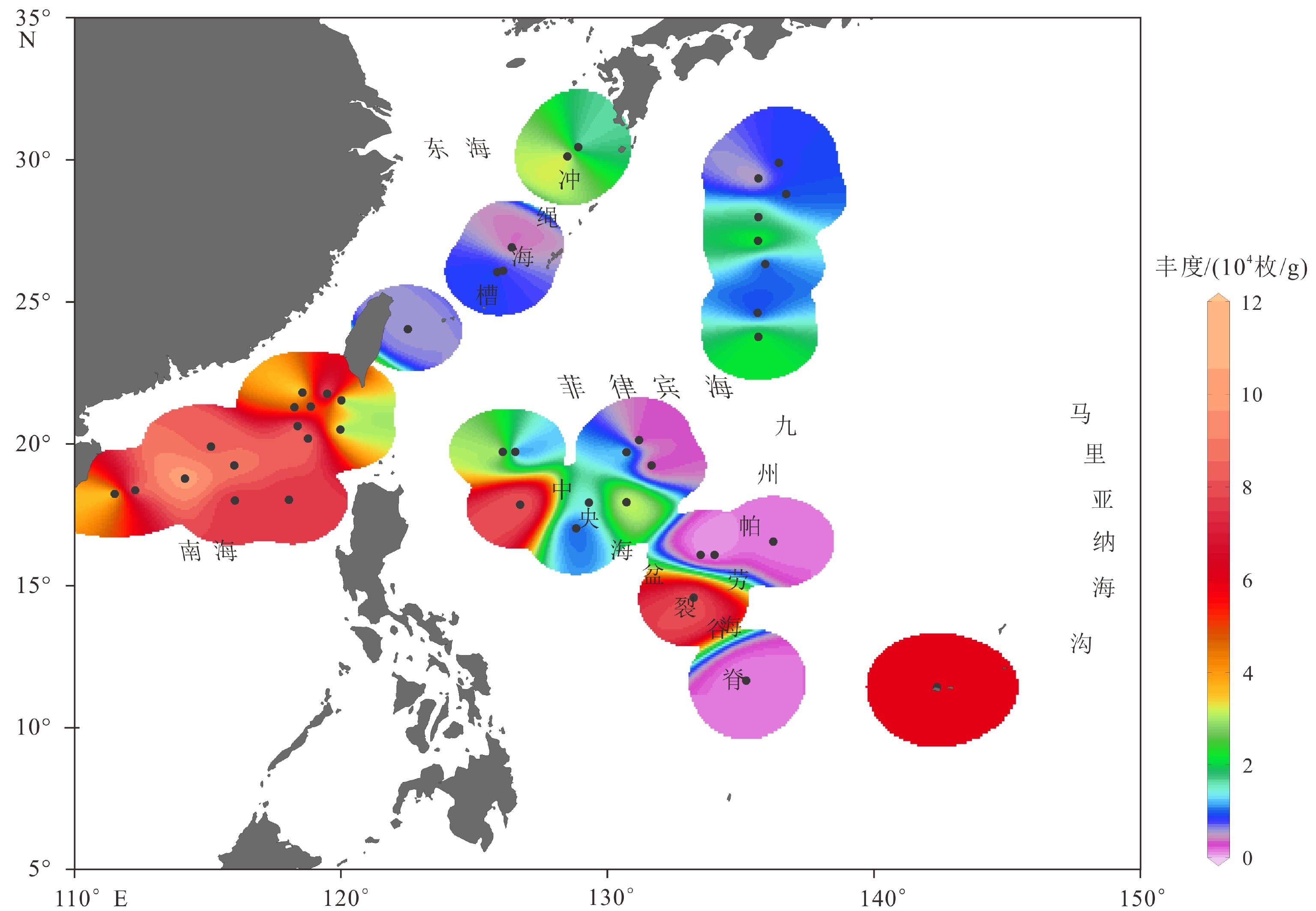
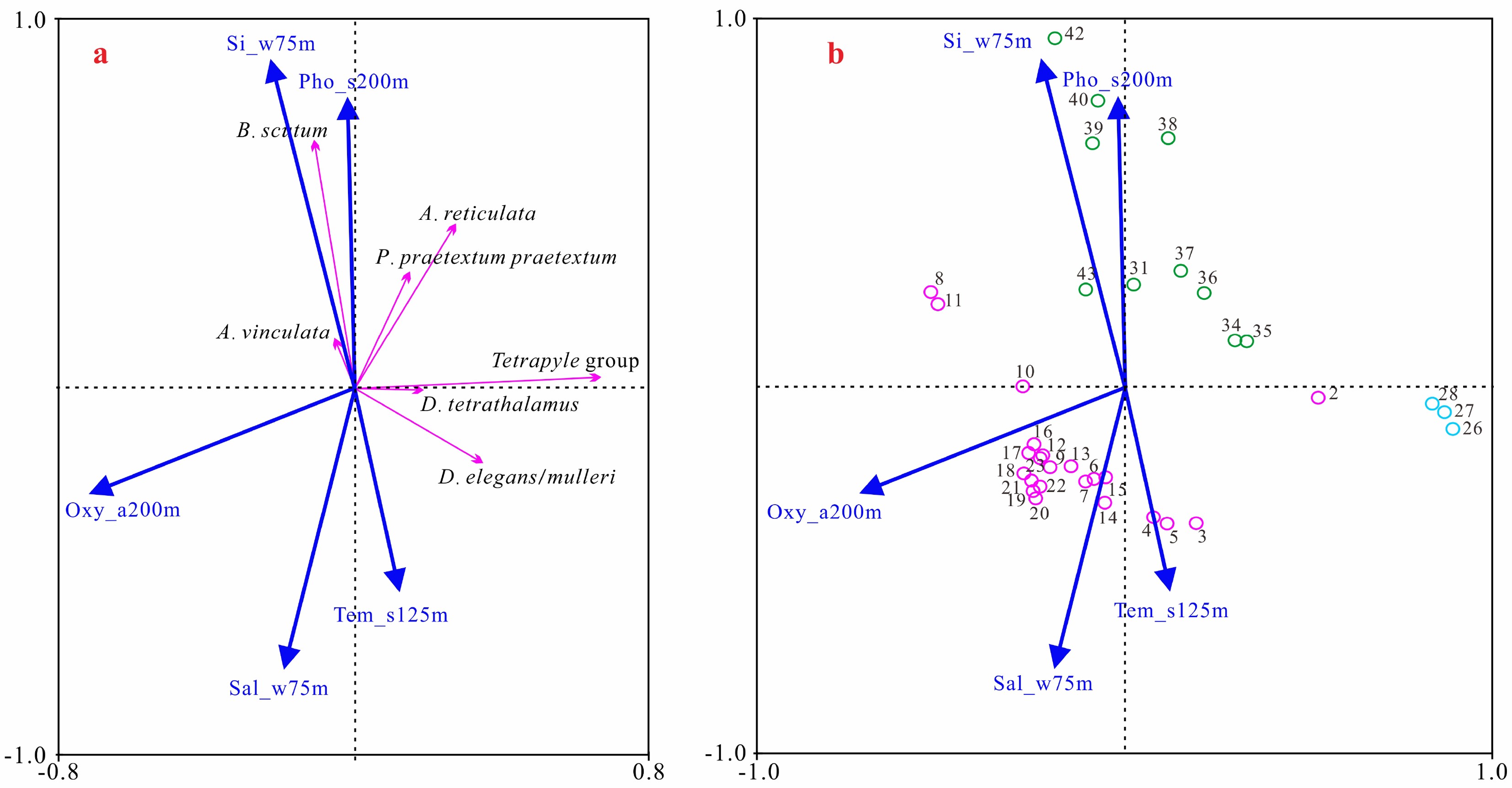
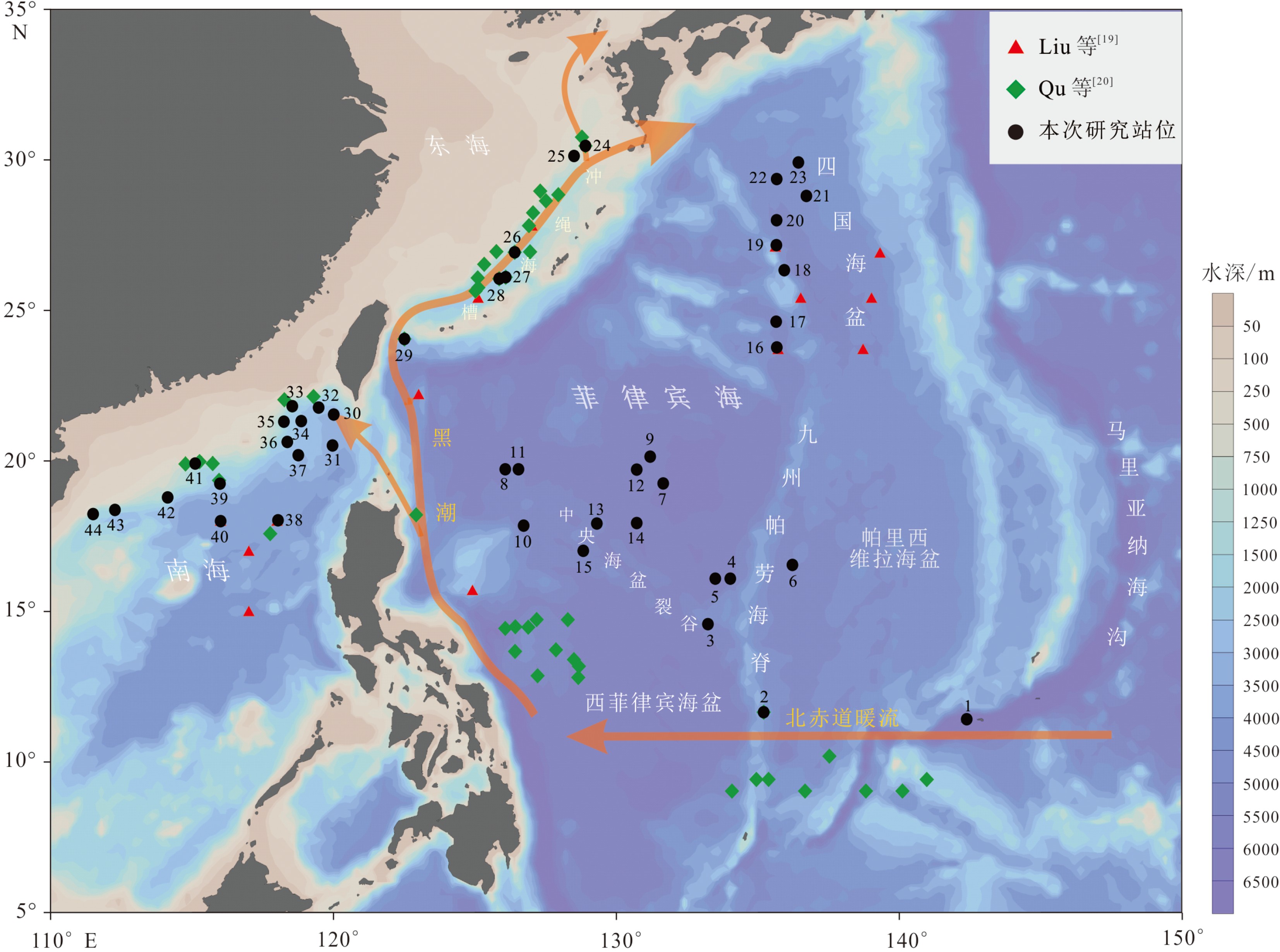
为了解菲律宾海放射虫的区域分布特色,利用同样的样品处理方法,对菲律宾海及其邻近海域的44个表层沉积样中的放射虫进行对比分析,鉴定统计了500个属种,物种多样性较高。菲律宾海表层沉积物中放射虫的群落结构和丰度变化幅度较大,反映了菲律宾海更为复杂的区域生态环境或沉积环境;南海北部放射虫丰度非常高且罩笼虫目占据较大优势,表明南海北部区域营养盐和生物生产力较高;冲绳海槽放射虫丰度相对较低且泡沫虫目占据绝对优势,推测冲绳海槽的海底沉积环境可能不利于放射虫壳体的埋藏富集。RDA分析结果显示暖水种在冲绳海槽的分布与夏季125 m温度呈明显的正相关,可能与夏季黑潮次表层水的影响有关;在南海北部,暖水种的分布主要受冬季75 m硅酸盐和夏季200 m磷酸盐的影响控制,说明高浓度的硅酸盐可能更加有利于罩笼虫目的发育繁殖;菲律宾海主要是次表层水的环境因子影响着放射虫暖水种的分布,比如75 m冬季盐度、200 m年均溶解氧含量和125 m夏季温度。此外,菲律宾海中深层水(1000~3000 m)不同层深66个环境变量和生活于该水体中的5个冷水种的RDA分析结果,显示菲律宾海北部区域主要与1000 m硅酸盐浓度呈显著正相关,可能与富含硅酸盐的北太平洋中深层水南下进入菲律宾有关;而在菲律宾海中南部的分布则主要与1000 m硅酸盐浓度呈显著负相关,与2 000 m溶解氧和2200 m磷酸盐和硝酸盐呈明显正相关,可能与具有高溶解氧低硅酸盐性质的绕极深层水由南端进入菲律宾海后,一部分水体向上进入菲律宾海中层水有关。
-
关键词:
- 放射虫暖水种和冷水种 /
- 环境变量 /
- RDA分析 /
- 表层沉积物 /
- 菲律宾海及其邻近海域
Abstract:In order to understand the distribution pattern of radiolarians in the Philippine Sea, this article, based on a unified method for sample processing and analysis, made analysis and comparison of radiolarians for 44 surface sediment samples taking from the Philippine Sea and its adjacent regions. A total of 500 radiolarians species are identified, suggesting a very high species diversity. The community structure and abundance of radiolarians in the surface sediments of the Philippine Sea vary greatly, suggesting complex regional ecological or sedimentary environments. The abundance of radiolarians dominated by Nassellaria is also very high in the northern South China Sea, indicating that the northern South China Sea is rich in nutrients and high in biological productivity. However, the radiolarian abundance, dominated by Spumellaria, is relatively low in the Okinawa Trough. It is speculated that the submarine environment of the Okinawa Trough is not so conducive to the accumulation and preservation of radiolarian shells. 8 warm water species group living in the euphotic layer and 162 environmental variables at different depths of the 0~200 m water layers are selected for RDA analysis. The results show that the distribution of these warm water species in the Okinawa Trough is significantly positively correlated with the summer temperature in 125 m of water depth, probably owing to the influence of the summer Kuroshio subsurface water. The distribution of warm water species in the northern South China Sea is mainly affected by winter silicate of 75 m and summer phosphate of 200 m. It means that high-concentration silicate is more conducive to the production of Nassellaria. In the Philippine Sea, however, environmental factors mainly in the subsurface water affect the distribution of warm water species, such as winter salinity of 75 m, 200 m annual dissolved oxygen content and summer temperature of 125 m. In addition, the RDA analysis results of 66 environmental variables at different depths of the medium-deep water (1000~3000 m) of the Philippine Sea and 5 cold water species living in this layer show that the northern Philippine Sea is mainly positively correlated with the silicate concentration of 1000 m. This may be related to the fact that the silicate-rich intermediate-deep water mass of the North Pacific moving southward into the Philippine Sea. The distribution in the central and southern part of the Philippine Sea is mainly negatively correlated with the concentration of silicate at 1000 m, and is significantly positively correlated with dissolved oxygen at 2000 m. It may be related to the Circumpolar Deep Water with high dissolved oxygen content and low silicate entering from the southern end of the Philippine Sea, and part of the water upwardly enter the intermediate layer of the Philippine Sea.
-

-
表 1 研究站位位置、水深、放射虫丰度以及放射虫三大类(泡沫虫目、罩笼虫目和胶球虫目)的相对丰度
Table 1. Sampling locations, water depths, total radiolarian abundance, and relative abundance of Spumellaria, Nassellaria, and Collodaria of three order of radiolarian
站位号 位置 水深 /m 放射虫总丰度/(枚/g) 泡沫虫目相对丰度/% 罩笼虫目相对丰度/% 胶球虫目相对丰度/% 1 11.4°N,142.36°E 10853 60051 44.52 54.30 1.18 2 11.64°N,135.19°E 4092 1061 74.90 20.59 4.51 3 14.56°N,133.22°E 5466 80634 52.11 41.48 6.40 4 16.07°N,134.01°E 5472 164 34.78 60.87 4.35 5 16.07°N,133.48°E 5370 9 76.92 23.08 0 6 16.53°N,136.21°E 5060 1181 54.31 40.52 5.17 7 19.23°N,131.64°E 6059 1703 40.70 37.21 22.09 8 19.7°N,126.06°E 5404 38204 43.91 52.88 3.21 9 20.12°N,131.18°E 5801 898 19.32 63.64 17.05 10 17.83°N,126.71°E 5380 81801 50.79 44.94 4.27 11 19.7°N,126.53°E 4882 2325 42.65 35.29 22.06 12 19.69°N,130.7°E 5761 14866 48.82 42.01 9.17 13 17.9°N,129.3°E 5307 13600 53.21 41.44 5.35 14 17.92°N,130.71°E 5708 32243 39.71 52.17 8.12 15 16.99°N,128.82°E 5505 9293 48.04 43.20 8.76 16 23.74°N,135.65°E 5270 21952 60.51 31.94 7.54 17 24.6°N,135.63°E 5370 8269 67.19 25.52 7.29 18 26.31°N,135.92°E 5392 8711 62.21 31.57 6.22 19 27.14°N,135.64°E 5050 23250 62.57 34.67 2.76 20 27.97°N,135.65°E 4865 17102 70.22 25.93 3.86 21 28.77°N,136.7°E 4560 9257 73.62 20.41 5.96 22 29.34°N,135.65°E 4439 3766 86.53 12.03 1.43 23 29.89°N,136.42°E 4725 8901 72.12 24.65 3.23 24 30.44°N,128.89°E 781 10235 85.24 11.99 2.77 25 30.1°N,128.49°E 885 37924 55.23 44.40 0.37 26 26.9°N,126.39°E 1266 3045 78.58 15.83 5.59 27 26.08°N,126.08°E 2044 6414 76.65 16.95 6.40 28 26.03°N,125.85°E 2064 10062 64.74 32.76 2.50 29 24.03°N,122.5°E 1800 5740 73.34 22.96 3.70 30 21.52°N,120°E 3010 7053 40.30 58.96 0.75 31 20.49°N,119.96°E 3347 23908 32.93 65.87 1.20 32 21.75°N,119.47°E 2709 115522 41.09 57.17 1.74 33 21.79°N,118.54°E 2049 18319 47.58 50.97 1.45 34 21.3°N,118.85°E 2620 46887 50.30 48.49 1.21 35 21.28°N,118.24°E 2184 41087 51.43 47.43 1.14 36 20.61°N,118.36°E 2540 90291 54.19 43.01 2.80 37 20.17°N,118.75°E 2893 90042 46.12 51.53 2.35 38 18.01°N,118.03°E 3888 75833 41.76 56.26 1.98 39 19.22°N,115.98°E 2612 86607 50.31 47.84 1.86 40 17.98°N,116°E 3865 75229 35.37 62.44 2.20 41 19.89°N,115.11°E 1182 83800 40.10 55.13 4.77 42 18.77°N,114.13°E 1575 100490 53.66 44.39 1.95 43 18.35°N,112.27°E 1564 101667 44.26 52.82 2.91 44 18.21°N,111.5°E 1808 17314 43.18 55.33 1.50 表 2 菲律宾海放射虫组合和环境变量的RDA分析结果
Table 2. RDA results of radiolarian assemblage and environmental variables in the Philippine Sea(I for warm species-upper environments, II for cold species-intermediate environments)
类型 参数 轴1 轴2 轴3 轴4 总方差 I 特征值 0.325 0.063 0.03 0.006 1 物种-环境相关性 0.676 0.686 0.614 0.489 变量累积百分比 物种数据 32.5 38.8 41.8 42.4 物种-环境关系 76.3 91.1 98.2 99.5 所有特征值总和 1 所有典范特征值总和 0.426 II 特征值 0.268 0.113 0.052 0 1 物种-环境相关性 0.87 0.554 0.455 0.271 变量累积百分比 物种数据 26.8 38.1 43.2 43.3 物种-环境关系 61.9 88 99.9 100 所有特征值总和 1 所有典范特征值总和 0.433 注:I 暖水种-上层水环境因子,II 冷水种-中深层水环境因子。 -
[1] Gallinari M, Ragueneau O, Corrin L, et al. The importance of water column processes on the dissolution properties of biogenic silica in deep-sea sediments I. Solubility [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2002, 66(15): 2701-2717.
[2] Hu W F, Zhang L L, Chen M H, et al. Distribution of living radiolarians in spring in the South China Sea and its responses to environmental factors [J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 2015, 58(2): 270-285.
[3] Itaki T. Depth-related radiolarian assemblage in the water-column and surface sediments of the Japan Sea [J]. Marine Micropaleontology, 2003, 47(3-4): 253-270.
[4] Kamikuri S I, Moore T C. Reconstruction of oceanic circulation patterns in the tropical Pacific across the early/middle Miocene boundary as inferred from radiolarian assemblages [J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2017, 487: 136-148.
[5] Sandoval M I, Boltovskoy D, Baxter A T, et al. Neogene paleoceanography of the eastern equatorial Pacific based on the radiolarian record of IODP drill sites off Costa Rica [J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2017, 18(3): 889-906.
[6] 陈木宏, 张兰兰, 张丽丽, 等. 南海表层沉积物中放射虫多样性与丰度的分布与环境[J]. 地球科学—中国地质大学学报, 2008, 33(4):431-442
CHEN Muhong, ZHANG Lanlan, ZHANG Lili, et al. Distributions of radiolarian diversity and abundance in surface sediments of the South China Sea and their environmental implications [J]. Earth Science—Journal of China University of Geosciences, 2008, 33(4): 431-442.
[7] 张杰, 张兰兰, 陈木宏, 等. 现代放射虫的高阶分类现状及其生态学意义[J]. 微体古生物学报, 2020, 37(1):82-98
ZHANG Jie, ZHANG Lanlan, CHEN Muhong, et al. The higher level classification of modern radiolarians and their ecological significance [J]. Acta Micropalaeontologica Sinica, 2020, 37(1): 82-98.
[8] Hu D X, Wu L X, Cai W J, et al. Pacific western boundary currents and their roles in climate [J]. Nature, 2015, 522(7556): 299-308.
[9] Yan X H, Ho C R, Zheng Q N, et al. Temperature and size variabilities of the Western Pacific Warm Pool [J]. Science, 1992, 258(5088): 1643-1645.
[10] Palmer M R, Pearson P N. A 23, 000-year record of surface water pH and PCO2 in the western equatorial Pacific Ocean [J]. Science, 2003, 300(5618): 480-482.
[11] 张兰兰, 胡邦琦, 邱卓雅, 等. 西菲律宾海硅藻席沉积中的多囊虫类放射虫记录及其环境意义[J]. 地球科学, 2020
ZHANG Lanlan, HU Bangqi, QIU Zhuoya, et al. Records of polycystine Radiolaria in the diatom mats sediments from the West Philippe Sea and their environmental significance [J]. Earth Science, 2020.
[12] 李铁刚, 熊志方, 翟滨. 低纬度西太平洋硅藻席沉积与碳循环[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社. 2015.
LI Tiegang, XIONG Zhifang, ZHAI Bin. Laminated Diatom Mat Deposits from the Low-Latitude Western Pacific Linked to Global Carbon Cycle[M]. Beijing: Ocean Press, 2015.
[13] Chen M H, Tan Z Y. Radiolarian distribution in surface sediments of the northern and central South China Sea [J]. Marine Micropaleontology, 1997, 32(1-2): 173-194.
[14] Matsuzaki K M, Itaki T, Kimoto K. Vertical distribution of polycystine radiolarians in the northern East China Sea [J]. Marine Micropaleontology, 2016, 125: 66-84.
[15] Zhang L L, Chen M H, Xiang R, et al. Distribution of polycystine radiolarians in the northern South China Sea in September 2005 [J]. Marine Micropaleontology, 2009, 70(1-2): 20-38.
[16] Chang F M, Zhuang L H, Li T G, et al. Radiolarian fauna in surface sediments of the northeastern East China Sea [J]. Marine Micropaleontology, 2003, 48(3-4): 169-204.
[17] 董智, 石学法, 邹欣庆, 等. 冲绳海槽表层沉积物放射虫属种空间分布特征及其影响因素[J]. 地学前缘, 2020, 27(6):300-312
DONG Zhi, SHI Xuefa, ZOU Xinqing, et al. Spatial distribution characteristics of radiolarian species in surface sediments from the Okinawa Trough and its influence factors [J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2020, 27(6): 300-312.
[18] Liu L, Zhang Q, Chen M H, et al. Radiolarian biogeography in surface sediments of the Northwest Pacific marginal seas [J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 2017, 60(3): 517-530.
[19] Qu H X, Wang J B, Xu Y, et al. Radiolarian assemblage as an indicator of environmental conditions in the marginal seas of the Western North Pacific [J]. Marine Micropaleontology, 2020, 157: 101859.
[20] Hernández-Almeida I, Cortese G, Yu P S, et al. Environmental determinants of radiolarian assemblages in the western Pacific since the last deglaciation [J]. Paleoceanography and Paleoclimatology, 2017, 32(8): 830-847.
[21] Matsuzaki K M, Itaki T. New northwest Pacific radiolarian data as a tool to estimate past sea surface and intermediate water temperatures [J]. Paleoceanography and Paleoclimatology, 2017, 32(3): 218-245.
[22] Hsueh Y. The Kuroshio in the East China Sea [J]. Journal of Marine Systems, 2000, 24(1-2): 131-139.
[23] Matsuno T, Lee J S, Yanao S. The Kuroshio exchange with the South and East China Seas [J]. Ocean Science, 2009, 5(3): 303-312.
[24] 张弦, 俞慕耕, 江伟, 等. 菲律宾海及其邻近海区的水文特征[J]. 海洋通报, 2004(1):8-14 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6392.2004.01.002
ZHANG Xuan, YU Mugeng, JIANG Wei, et al. Hydrologic characteristic of the Philippine Sea and its nearby areas [J]. Marine Science Bulletin, 2004(1): 8-14. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6392.2004.01.002
[25] 赵一阳, 何丽娟, 张秀莲, 等. 冲绳海槽沉积物地球化学的基本特征[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 1984, 15(4):371-379
ZHAO Yiyang, HE Lijuan, ZHANG Xiulian, et al. Basic characteristics of geochemistry of sediments in Okinawa trough [J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 1984, 15(4): 371-379.
[26] 黄财京. 菲律宾海深层水团与环流特征分析[J]. 中国科学院大学硕士学位论文, 2018.
HUANG Caijing. Analysis of the characteristics of deep water mass and circulation in the Philippine sea[D]. Master Dissertation of University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2018.
[27] Zhang L L, Suzuki N. Taxonomy and species diversity of Holocene pylonioid radiolarians from surface sediments of the northeastern Indian Ocean [J]. Palaeontologia Electronica, 2017, 20(3).
[28] 陈木宏, 谭智源. 南海中、北部沉积物中的放射虫[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1996: 271.
CHEN Muhong, TAN Zhiyuan. Radiolaria from Surface Sediments of the Central and Northern South China Sea[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1996: 271.
[29] 谭智源, 陈木宏. 中国近海的放射虫[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1999: 404.
TAN Zhiyuan, CHEN Muhong. Radiolaria off the Coast of China[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1999: 404.
[30] Boltovskoy D. Classification and distribution of South Atlantic recent polycystine Radiolaria [J]. Palaeontologia Electronica, 1998, 1(2): 116.
[31] Matsuzaki K M, Suzuki N, Nishi H. Middle to Upper Pleistocene polycystine radiolarians from Hole 902-C9001C, northwestern Pacific [J]. Paleontological Research, 2015, 19(1): 1-77.
[32] Zhang L L, Suzuki N, Nakamura Y, et al. Modern shallow water radiolarians with photosynthetic microbiota in the western North Pacific [J]. Marine Micropaleontology, 2018, 139: 1-27.
[33] Müller J. Über die Thalassicollen, Polycystinen und Acanthometren des Mittelmeeres[M]. Abhandlungen: Konigliche Preussische Akademie der Wissenschaften zu Berlin, 1858: 1-62.
[34] Haeckel E. Report on the radiolaria collected by H. M. S. Challenger during the Years 1873-1876[R]. Report on the Scientific Results of the Voyage of H. M. S. Challenger, 1887: 1-1803.
[35] Petrushevskaya M G. Radiolarians of the Ocean [J]. Reports on the Soviet Expeditions. Academy of Sciences of the U.S.S.R., Zoological Institute, Explorations of the Fauna of the Seas, 1971, 9(17): 1-418.
[36] Renz G W. Radiolaria from Leg 27 of the Deep Sea Drilling Poject[R]. Initial Reports of the Deep Dea Drilling Project (U. S. Government Printing Office), 1974, 27: 769-841.
[37] Takahashi K, Honjo S. Vertical flux of Radiolaria: A taxon-quantitative sediment trap study from the western tropical Atlantic [J]. Micropaleontology, 1981, 27(2): 140-190.
[38] Matsuzaki K M, Itaki T, Sugisaki S. Polycystine radiolarians vertical distribution in the subtropical Northwest Pacific during Spring 2015 (KS15-4) [J]. Paleontological Research, 2020, 24(2): 113-133.
[39] Adl S M, Bass D, Lane C E, et al. Revisions to the classification, nomenclature, and diversity of eukaryotes [J]. Journal of Eukaryotic Microbiology, 2019, 66(1): 4-119.
[40] Zhang J, Zhang L L, Xiang R, et al. Radiolarian biogeographic contrast between spring of 2017 and winter of 2017-2018 in the South China sea and Malacca Strait [J]. Continental Shelf Research, 2020, 208: 104245.
[41] 常凤鸣, 庄丽华, 李铁刚, 等. 冲绳海槽北部表层沉积物中的放射虫组合[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2003, 34(2):208-216 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.2003.02.012
CHANG Fengming, ZHUANG Lihua, LI Tiegang, et al. Modern radiolarian assemblages in surficial sediments of northern Okinawa Trough [J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2003, 34(2): 208-216. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.2003.02.012
[42] 程振波, 鞠小华. 冲绳海槽中部表层沉积物中的放射虫[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 1998, 29(6):656-662 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.1998.06.015
CHEN Zhenbo, JU Xiaohua. Radiolaria from the surface sediments in the middle Okinawa Trough [J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 1998, 29(6): 656-662. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.1998.06.015
[43] 王汝建, 陈荣华. 冲绳海槽南部表层沉积物中放射虫的初步研究[J]. 同济大学学报, 1996, 24(6):670-676
WANG Rujian, CHEN Ronghua. Preliminary study on the radiolaria from the surface sediments in southern Okinawa Trough [J]. Journal of Tongji University, 1996, 24(6): 670-676.
[44] 王越奇, 宋金明, 袁华茂, 等. 西北太平洋黑潮源区沉积特征及黑潮输入对东海沉积物的影响[J]. 海洋科学, 2018, 42(9):112-126 doi: 10.11759/hykx20180129001
WANG Yueqi, SONG Jinming, YUAN Huamao, et al. Sedimentary characteristics of the Kuroshio origination area and the influence of the Kuroshio intrusion on sediments of the East China Sea [J]. Marine Sciences, 2018, 42(9): 112-126. doi: 10.11759/hykx20180129001
[45] 宋金明, 袁华茂. 黑潮与邻近东海生源要素的交换及其生态环境效应[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2017, 48(6):1169-1177 doi: 10.11693/hyhz20170900234
SONG Jinming, YUAN Huamao. Exchange and ecological effects of biogenic elements between Kuroshio and adjacent east China sea [J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2017, 48(6): 1169-1177. doi: 10.11693/hyhz20170900234
[46] 冯庆来. 放射虫古生态的初步研究[J]. 地质科技情报, 1992, 11(2):41-46
FENG Qinglai. A preliminary study on the rediolarian palaeoecology [J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 1992, 11(2): 41-46.
[47] 梁文, NILANTHI P, 冉莉华, 等. 南海北部和西菲律宾海颗石藻种群特征及差异[J]. 微体古生物学报, 2017, 34(3):279-290
LIANG Wen, NILANTHI P, RAN Lihua, et al. Community structures of the living coccolithophores in the northern South China Sea and the western Philippines sea [J]. Acta Micropalaeontologica Sinica, 2017, 34(3): 279-290.
[48] Takahashi K. Vertical flux, ecology and dissolution of Radiolaria in tropical oceans: implications for the silica cycle[D]. Doctor Dissertation of Massachusetts Institute of Technology and Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution, 1981: 1-461.
[49] 袁梁英, 戴民汉. 南海北部低浓度磷酸盐的测定与分布[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2008, 39(3):202-208 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.2008.03.002
YUAN Liangying, DAI Minhan. The distribution of low-level phosphate in the northern South China sea [J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2008, 39(3): 202-208. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.2008.03.002
[50] Glud R N, Wenzhöfer F, Middelboe M, et al. High rates of microbial carbon turnover in sediments in the deepest oceanic trench on Earth [J]. Nature Geoscience, 2013, 6(4): 284-288.
[51] 杨海燕, 毛新燕, 郭新宇. 基于WOD数据集的西北太平洋混合层内营养盐浓度初步研究[J]. 中国海洋大学学报, 2018, 48(8):1-9
YANG Haiyan, MAO Xinyan, GUO Xinyu. A preliminary study on nutrients concentration within the mixed layer in the northwest pacific based on WOD data [J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 2018, 48(8): 1-9.
[52] Liu K K, Chao S Y, Shaw P T, et al. Monsoon-forced chlorophyll distribution and primary production in the South China Sea: observations and a numerical study [J]. Deep Sea Research Part I: Oceanographic Research Papers, 2002, 49(8): 1387-1412.
[53] 张金鹏, 邓希光, 杨胜雄, 等. 马里亚纳海沟挑战者深渊南部7000 m水深处发现硅藻化石软泥[J]. 地质通报, 2015, 34(12):2352-2354 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2015.12.021
ZHANG Jinpeng, DENG Xiguang, YANG Shengxiong, et al. Diatom ooze found in 7000 m submarine area of Challenger Depth in Mariana Trench [J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2015, 34(12): 2352-2354. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2015.12.021
[54] 黄财京, 谢强, 陈举, 等. 菲律宾海底层水体在1990s—2010s之间的暖化[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2018, 37(6):26-32
HUANG Caijing, XIE Qiang, CHEN Ju, et al. Bottom-water warming in the Philippine Sea between 1990s and 2010s [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2018, 37(6): 26-32.
[55] Kawabe M, Fujio S. Pacific ocean circulation based on observation [J]. Journal of Oceanography, 2010, 66(3): 389-403.
[56] 张兰兰, 陈木宏, 胡维芬, 等. 现生放射虫的水深分布及其环境指示意义[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2013, 32(6):101-107 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5470.2013.06.015
ZHANG Lanlan, CHEN Muhong, HU Weifen, et al. Vertical distribution of living radiolarians and its environmental implication [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2013, 32(6): 101-107. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5470.2013.06.015
[57] Zhang Q, Chen M H, Zhang L L, et al. Variations in the radiolarian assemblages in the Bering Sea since Pliocene and their implications for paleoceanography [J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2014, 410: 337-350.
[58] Matsuzaki K M, Itaki T, Tada R. Paleoceanographic changes in the Northern East China Sea during the last 400 kyr as inferred from radiolarian assemblages (IODP Site U1429) [J]. Progress in Earth and Planetary Science, 2019, 6: 22.
[59] 畠田 健太朗. 現世放散虫に関する生態情報リスト[J]. 大阪微化石研究会誌, 2009, S1(14):31-41
Hatakeda K. Compiled ecological data on living Polycystine radiolarian [J]. News of Osaka Micropaleontologists (NOM), 2009, S1(14): 31-41.
[60] Boltovskoy D. Vertical distribution patterns of Radiolaria Polycystina (Protista) in the World Ocean: living ranges, isothermal submersion and settling shells [J]. Journal of Plankton Research, 2017, 39(2): 330-349.
[61] Welling L A, Pisias N G. Radiolarian fluxes, stocks, and population residence times in surface waters of the central equatorial Pacific [J]. Deep Sea Research Part I: Oceanographic Research Papers, 1998, 45(4-5): 639-671.
[62] Pisias N G. Vertical water mass circulation and the distribution of radiolaria in surface sediments of the Gulf of California [J]. Marine Micropaleontology, 1986, 10(1-3): 189-205.
[63] Matsuzaki K M, Itaki T, Tada R, et al. Paleoceanographic history of the Japan Sea over the last 9.5 million years inferred from radiolarian assemblages (IODP Expedition 346 Sites U1425 and U1430) [J]. Progress in Earth and Planetary Science, 2018, 5: 54.
[64] Takahashi K. Radiolaria: Flux, Ecology, and Taxonomy in the Pacific and Atlantic[M]. Woods Hole, MA: Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution Ocean, 1991.
-



 下载:
下载: