Sediment grain size characteristics of the Core SH-CL38 in the Shenhu area on the northern continental slope of the South China Sea
-
摘要:
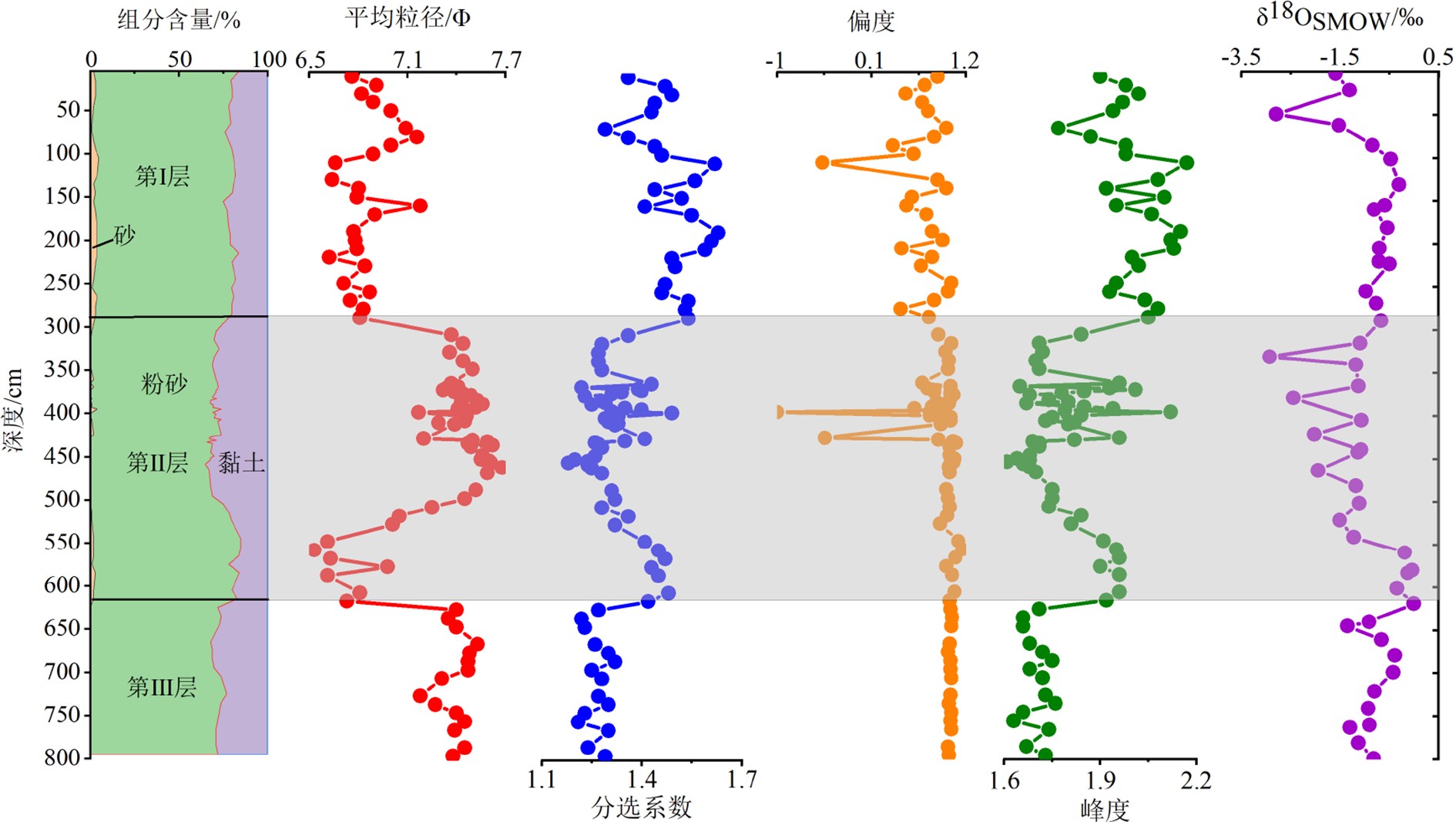
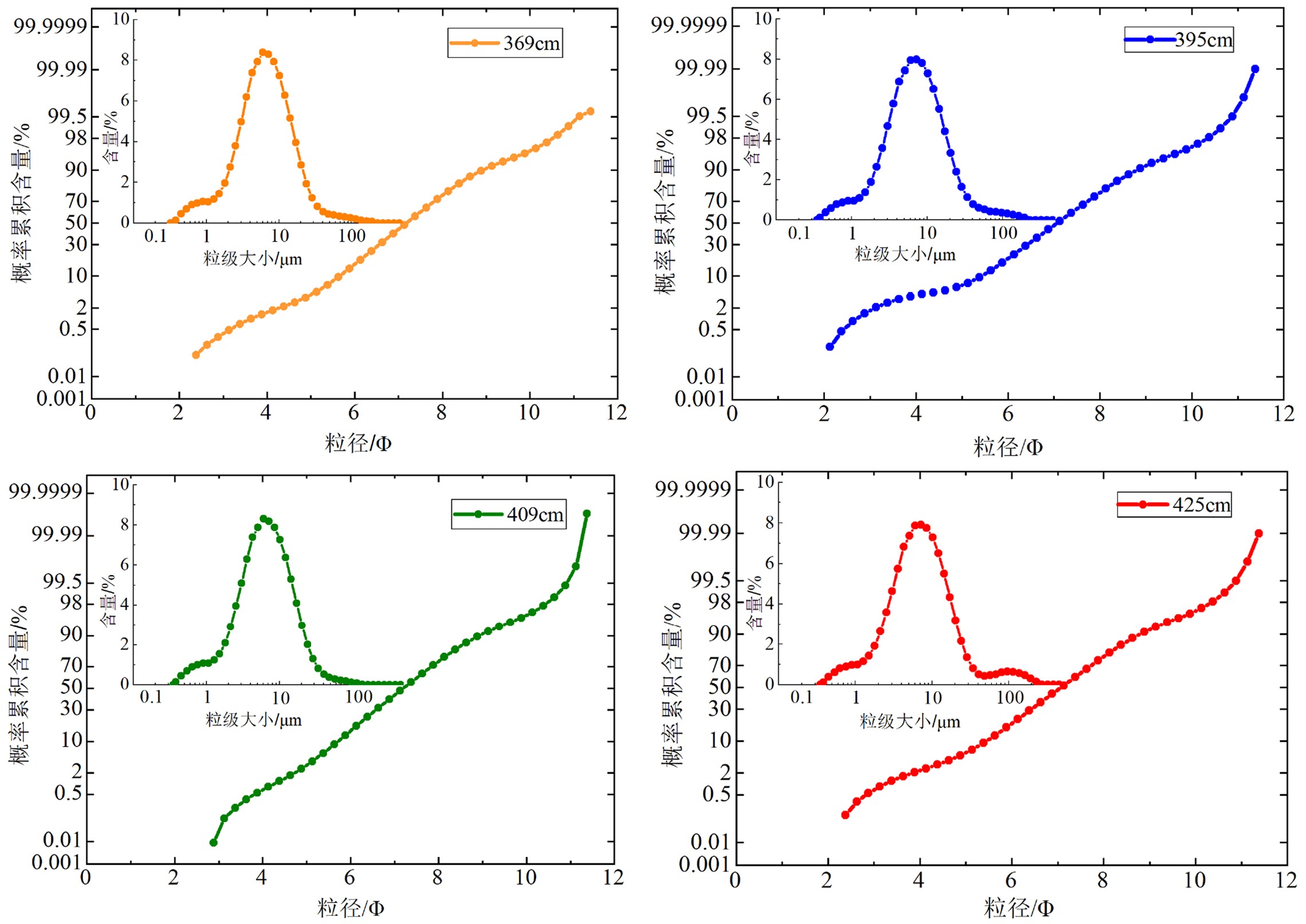
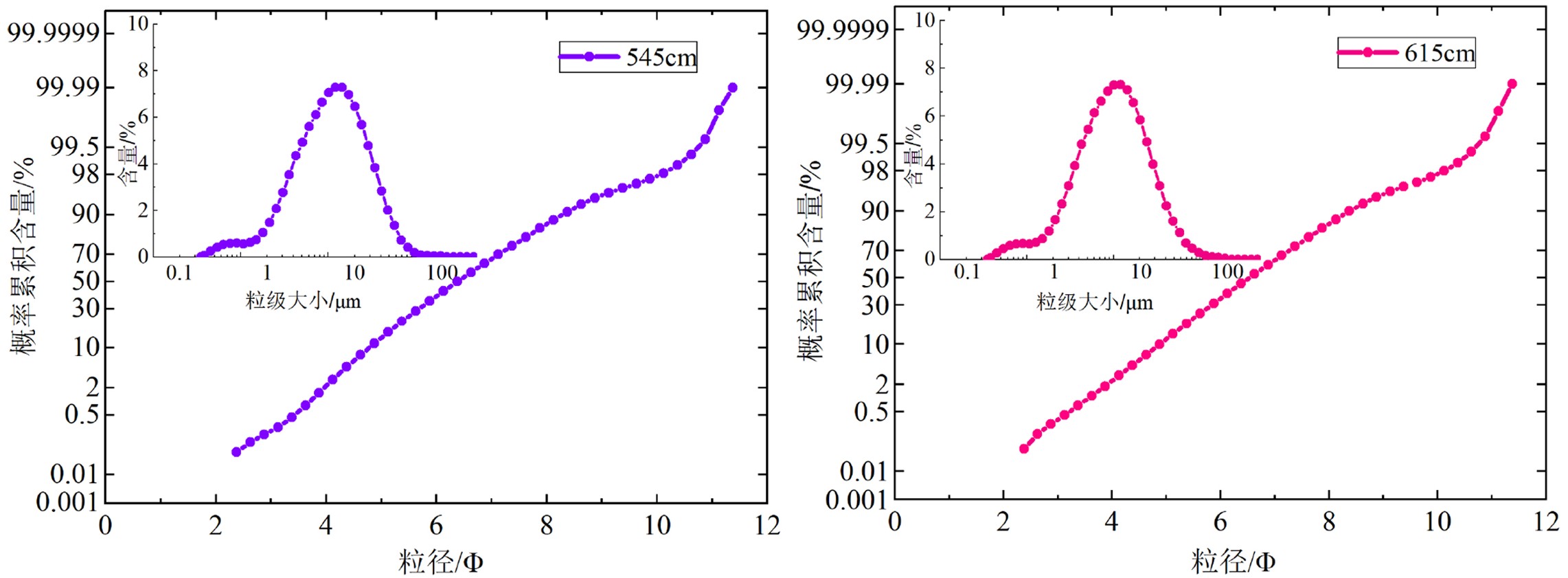
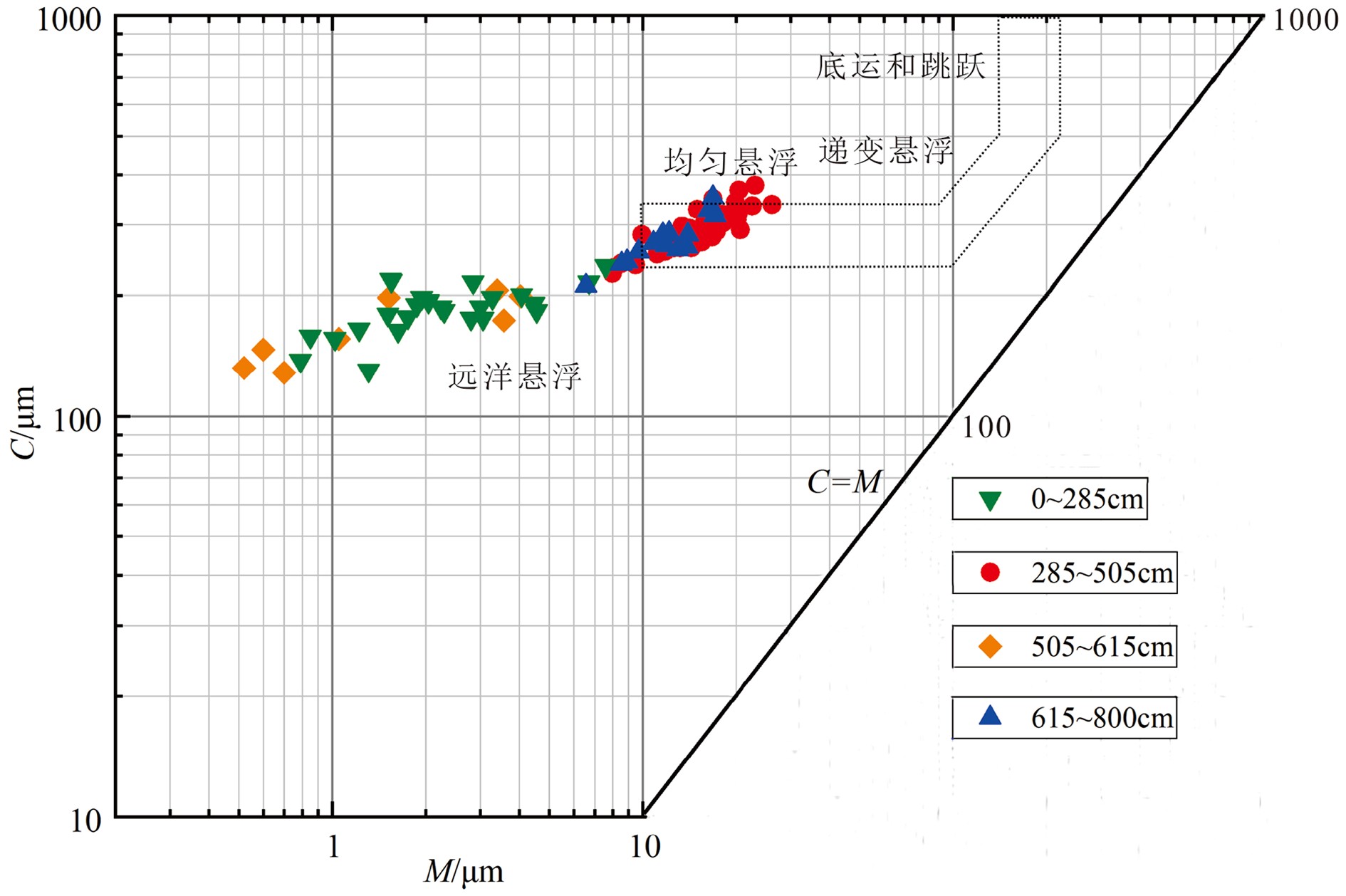
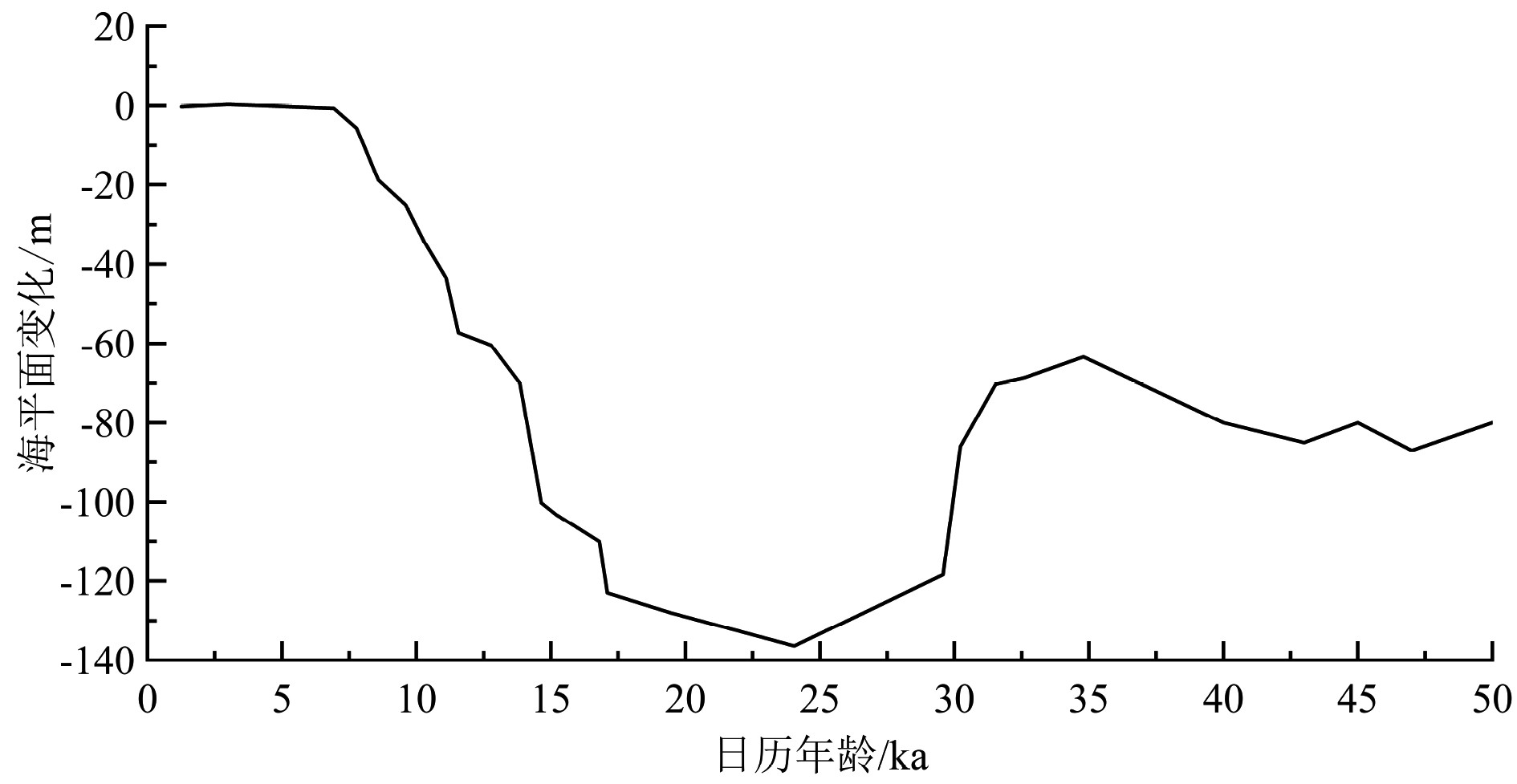
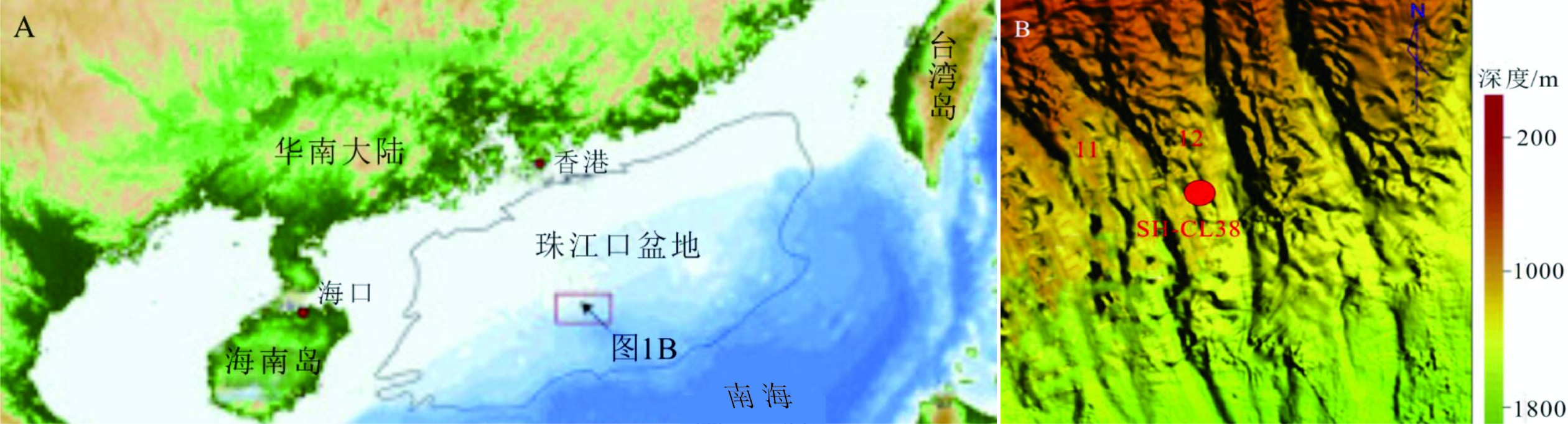
南海北部陆坡神狐海域发育众多海底峡谷,其物质来源、地貌形态、水动力条件、沉积过程复杂,海底滑坡和浊流频发。虽然通过地球物理(多波束和反射地震等)能够识别出数米至百米的滑坡体,但对于浅层海底重力流、浊流和异重流等沉积体系的高分辨率识别还受到很多限制。本研究以南海北部陆坡海底峡谷群12号峡谷脊部下游的SH-CL38站位岩芯沉积物为研究对象,通过粒度测试和浮游有孔虫氧同位素组成分析,将该站位岩芯划分为3个层段:第Ⅰ层段(0~285 cm)、第Ⅱ层段(285~615 cm)以及第Ⅲ层段(615~800 cm)。其中第Ⅱ层段的粒度参数、有孔虫的氧同位素组成明显不同于其他层段,这表明该层段形成时的水动力条件、沉积环境发生了突变。而且第II层段的285~505 cm和505~615 cm具有明显不同的概率累积曲线特征,粒度数据也分布在C-M图上不同的区域。基于此,我们认为该站位的异常沉积层是受深水沉积作用和末次冰期海平面变化的影响,285~505 cm层段发育浊流沉积,而505~615 cm层段可能是浊流或重力流引发的沉积物失稳。
Abstract:A number of submarine canyons has been found in the Shenhu area on the northern continental slope of the South China Sea. Sediment sources, topographic features, hydrodynamic conditions, and depositional processes in these canyons are very complex, owing to the occurrence of submarine landslides and related turbidity currents. Landslides are found, by means of geophysical surveys, such as multi-beam bathymetric survey and high-resolution multi-channel seismic profiles, varying in scale from several to hundred meters. However, the high-resolution identification of the depositional systems, such as gravity flow, turbidity current, and hyperpycnal current on the shallow seafloor remains difficult. In this study, we analyzed the columnar sediments taken from the sampling station of SH-CL38 which is located in the lower reaches of the canyon on the northern slope of the South China Sea. According to the grain size distribution patterns of sediments and the oxygen isotope composition of foraminifera, the core sediments of SH-CL38 can be subdivided into the three units: Unit Ⅰ (0~285 cm), Unit Ⅱ (285~615 cm) and the Unit Ⅲ (615~800 cm). The physical and geochemical features of the Unit II, including grain size and the oxygen isotope composition of foraminifera are obviously different from those of the other two units. This suggests that the hydrodynamic conditions and depositional environment have been sharply changed while the Unit II was deposited. The grain size distribution patterns and the probability cumulative curves at 285~505 cm and 505~615 cm in depth are completely different and located in different areas of the C-M diagram. Based on the data mentioned above, it is concluded that the sediments of SH-CL38 is deposited in a deep-water environment under the influence of sea level change. The sediments of 285~505 cm is related to the turbidity current, while the 505~615 cm is formed in an instable environment under the influence of turbidity current or gravity flow.
-

-
表 1 SH-CL38站位的AMS14C定年结果
Table 1. AMS14C dating results of SH-CL38 station
深度/cm 测试材料 测年结果/aBP 2σ范围/cal.aBP 校正年龄/cal.aBP 0~2 G.ruber 2070±25 1617~1802 1710 48~50 G.ruber 6555±40 7013~7239 7126 100~102 G.ruber 12745±45 14159~14784 14472 130~132 G.ruber 22470±120 26028~26668 26348 155~157 G.ruber 33500±190 36608~38127 37368 255~257 G.ruber >43500 >43500 >43500 365~367 G.ruber 42410±390 >43500 >43500 405~407 G.ruber 34280±230 37733~38946 38340 462~464 G.ruber >43500 >43500 >43500 521~523 G.ruber >43500 >43500 >43500 645~647 G.ruber >43500 >43500 >43500 798~800 G.ruber >43500 >43500 >43500 -
[1] 龚跃华, 张光学, 郭依群, 等. 南海北部神狐西南海域天然气水合物成矿远景[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2013, 33(2):97-104
GONG Yuehua, ZHANG Guangxue, GUO Yiqun, et al. Prospect of gas hydrate resources in the area to southwest Shen-Hu of northern South China Sea [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2013, 33(2): 97-104.
[2] 郭依群, 杨胜雄, 梁金强, 等. 南海北部神狐海域高饱和度天然气水合物分布特征[J]. 地学前缘, 2017, 24(4):24-31
GUO Yiqun, YANG Shengxiong, LIANG Jinqiang, et al. Characteristics of high gas hydrate distribution in the Shenhu area on the northern slope of the South China Sea [J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2017, 24(4): 24-31.
[3] He Y, Zhong G F, Wang L L, et al. Characteristics and occurrence of submarine canyon-associated landslides in the middle of the northern continental slope, South China Sea [J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2014, 57: 546-560. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2014.07.003
[4] 刘杰, 孙美静, 杨睿, 等. 泥底辟输导流体机制及其与天然气水合物成藏的关系[J]. 现代地质, 2016, 30(6):1399-1407 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2016.06.022
LIU Jie, SUN Meijing, YANG Rui, et al. Diapir conduit fluid mechanism and its relationship with gas hydrate accumulations [J]. Geoscience, 2016, 30(6): 1399-1407. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2016.06.022
[5] Zhu M Z, Graham S, Pang X, et al. Characteristics of migrating submarine canyons from the middle Miocene to present: implications for paleoceanographic circulation, northern South China Sea [J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2010, 27(1): 307-319. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2009.05.005
[6] 王珊珊, 王永波, 扶卿华, 等. 珠江口水体组分的吸收特性分析[J]. 环境科学, 2014, 35(12):4511-4521
WANG Shanshan, WANG Yongbo, FU Qinghua, et al. Spectral absorption properties of the water constituents in the estuary of Zhujiang River [J]. Environmental Science, 2014, 35(12): 4511-4521.
[7] 袁圣强, 吴时国, 赵宗举, 等. 南海北部陆坡深水区沉积物输送模式探讨[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2010, 30(4):39-48
YUAN Shengqiang, WU Shiguo, ZHAO Zongju, et al. Deepwater sediment transportation models for northern South China Sea slopes [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2010, 30(4): 39-48.
[8] Doeglas D J. Grain-size indices, classification and environment [J]. Sedimentology, 1968, 10(2): 83-100. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3091.1968.tb01101.x
[9] Xie X N, Müller R D, Ren J Y, et al. Stratigraphic architecture and evolution of the continental slope system in offshore Hainan, northern South China Sea [J]. Marine Geology, 2008, 247(3-4): 129-144. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2007.08.005
[10] 许莎莎, 冯秀丽, 冯利, 等. 南海西北部莺琼陆坡36.6ka以来的浊流沉积[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2020, 40(5):15-24
XU Shasha, FENG Xiuli, FENG Li, et al. Turbidite records since 36.6ka at the Yingqiong continental slope in the northwest of South China Sea [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2020, 40(5): 15-24.
[11] 章伟艳, 张富元, 张霄宇, 等. 南海东部海域柱样沉积物浊流沉积探讨[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2003, 22(3):36-43 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5470.2003.03.006
ZHANG Weiyan, ZHANG Fuyuan, ZHANG Xiaoyu, et al. Characteristics of turbidity deposits from sediment cores in eastern South China Sea [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2003, 22(3): 36-43. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5470.2003.03.006
[12] Zhao Y L, Liu Z F, Colin C, et al. Turbidite deposition in the southern South China Sea during the last glacial: Evidence from grain-size and major elements records [J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2011, 56(33): 3558-3565. doi: 10.1007/s11434-011-4685-7
[13] 周杨锐, 朱友生, 周松望, 等. 南海北部东沙隆起西侧陆坡坡折处浊流沉积[J]. 海洋科学, 2018, 42(2):23-33 doi: 10.11759/hykx20171101003
ZHOU Yangrui, ZHU Yousheng, ZHOU Songwang, et al. Turbidites at the continental slope on the west side of Dongsha uplift in the northern South China Sea [J]. Marine Sciences, 2018, 42(2): 23-33. doi: 10.11759/hykx20171101003
[14] 邵磊, 李学杰, 耿建华, 等. 南海北部深水底流沉积作用[J]. 中国科学 D辑: 地球科学, 2007, 50(7):1060-1066 doi: 10.1007/s11430-007-0015-y
SHAO Lei, LI Xuejie, GENG Jianhua, et al. Deep water bottom current deposition in the northern South China Sea [J]. Science in China Series D: Earth Sciences, 2007, 50(7): 1060-1066. doi: 10.1007/s11430-007-0015-y
[15] 王一凡, 苏正, 苏明, 等. 南海北部陆坡神狐海域沉积物失稳类型探讨[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2017, 37(5):184-194
WANG Yifan, SU Zheng, SU Ming, et al. Sediment failures in the Shenhu area, northern continental slope of the south China Sea [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2017, 37(5): 184-194.
[16] Chen D X, Wang X J, Völker D, et al. Three dimensional seismic studies of deep-water hazard-related features on the northern slope of South China Sea [J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2016, 77: 1125-1139. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2016.08.012
[17] Felix M. Flow structure of turbidity currents [J]. Sedimentology, 2002, 49(3): 397-419. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-3091.2002.00449.x
[18] Su M, Yang R, Wang H B, et al. Gas hydrates distribution in the Shenhu Area, northern South China Sea: comparisons between the eight drilling sites with gashydrate petroleum system [J]. Geologica Acta, 2016, 14(2): 79-100.
[19] Chen H, Xie X N, Mao K N, et al. Depositional characteristics and formation mechanisms of deep-water canyon systems along the northern South China Sea margin [J]. Journal of Earth Science, 2020, 31(4): 808-819. doi: 10.1007/s12583-020-1284-z
[20] 陈芳, 周洋, 苏欣, 等. 南海神狐海域含水合物层粒度变化及与水合物饱和度的关系[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2011, 31(5):95-100
CHEN Fang, ZHOU Yang, SU Xin, et al. Gas hydrate saturation and its relation with grain size of the hydrate-bearing sediments in the Shenhu area of northern South China Sea [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2011, 31(5): 95-100.
[21] 陈芳, 苏新, 周洋. 南海神狐海域水合物钻探区钙质超微化石生物地层与沉积速率[J]. 地球科学—中国地质大学学报, 2013, 38(1):1-9 doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2013.001
CHEN Fang, SU Xin, ZHOU Yang. Late miocene-pleistocene calcareous nannofossil biostratigraphy of Shenhu gas hydrate drilling area in the South China Sea and variations in sedimentation rates [J]. Earth Science—Journal of China University of Geosciences, 2013, 38(1): 1-9. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2013.001
[22] 陈芳, 苏新, 周洋, 等. 南海北部陆坡神狐海域晚中新世以来沉积物中生物组分变化及意义[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2009, 29(2):1-8
CHEN Fang, SU Xin, ZHOU Yang, et al. Variations in biogenic components of late miocene-holocene sediments from Shenhu area in the northern South China Sea and their geological implication [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2009, 29(2): 1-8.
[23] 马俊明, 薛林福, 付少英, 等. 南海神狐海域地震-沉积相分析与沉积环境演化[J]. 世界地质, 2013, 32(2):359-365 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5589.2013.02.021
MA Junming, XUE Linfu, FU Shaoying, et al. Seismic-sedimentary facies analysis and evolution of sedimentary environment in Shenhu area, South China Sea [J]. Global Geology, 2013, 32(2): 359-365. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5589.2013.02.021
[24] Yu X H, Wang J Z, Liang J Q, et al. Depositional characteristics and accumulation model of gas hydrates in northern South China Sea [J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2014, 56: 74-86. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2014.03.011
[25] 刘杰, 苏明, 乔少华, 等. 珠江口盆地白云凹陷陆坡限制型海底峡谷群成因机制探讨[J]. 沉积学报, 2016, 34(5):940-950
LIU Jie, SU Ming, QIAO Shaohua, et al. Forming mechanism of the slope-confined submarine canyons in the Baiyun sag, pearl river mouth basin [J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2016, 34(5): 940-950.
[26] 孙启良, 解习农, 吴时国. 南海北部海底滑坡的特征、灾害评估和研究展望[J]. 地学前缘, 2021, 28(2):258-270
SUN Qiliang, XIE Xinong, WU Shiguo. Submarine landslides in the northern South China Sea: characteristics, geohazard evaluation and perspectives [J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2021, 28(2): 258-270.
[27] Li X S, Zhou Q J, Su T Y, et al. Slope-confined submarine canyons in the Baiyun deep-water area, northern South China sea: variation in their modern morphology [J]. Marine Geophysical Research, 2016, 37(2): 95-112. doi: 10.1007/s11001-016-9269-0
[28] 姜衡, 苏明, 邬黛黛, 等. 南海北部陆坡神狐海域GMGS01区块细粒浊积体的识别特征及意义[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2017, 37(5):131-140
JIANG Heng, SU Ming, WU Daidai, et al. Fine-grained turbidites in GMGS01 of the Shenhu area, northern south China sea and its significance [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2017, 37(5): 131-140.
[29] 吴时国, 秦蕴珊. 南海北部陆坡深水沉积体系研究[J]. 沉积学报, 2009, 27(5):922-930
WU Shiguo, QIN Yunshan. The research of deepwater depositional system in the northern South China Sea [J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2009, 27(5): 922-930.
[30] Ding W W, Li J B, Li J, et al. Morphotectonics and evolutionary controls on the pearl river canyon system, South China Sea [J]. Marine Geophysical Research, 2013, 34(3): 221-238.
[31] 吴嘉鹏, 王英民, 邱燕, 等. 南海北部神狐陆坡限制型滑塌体特征及成因机理[J]. 沉积学报, 2012, 30(4):639-645
WU Jiapeng, WANG Yingmin, QIU Yan, et al. Characteristic and formation mechanism of the frontally confined landslide in Shenhu slope, northern South China Sea [J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2012, 30(4): 639-645.
[32] Su M, Alves T M, Li W, et al. Reassessing two contrasting late miocene-holocene stratigraphic frameworks for the pearl river mouth basin, northern South China sea [J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2019, 102: 899-913. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2018.12.034
[33] Yang J X, Wang X J, Jin J P, et al. The role of fluid migration in the occurrence of shallow gas and gas hydrates in the south of the pearl river mouth basin, South China Sea [J]. Interpretation, 2017, 5(3): SM1-SM11. doi: 10.1190/INT-2016-0197.1
[34] 杨胜雄, 梁金强, 陆敬安, 等. 南海北部神狐海域天然气水合物成藏特征及主控因素新认识[J]. 地学前缘, 2017, 24(4):1-14
Yang Shengxiong, Liang Jinqiang, Lu Jingan, et al. New understandings on the characteristics and controlling factors of gas hydrate reservoirs in the Shenhu area on the northern slope of the South China Sea [J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2017, 24(4): 1-14.
[35] Huang J, Li A C, Wan S M. Sensitive grain-size records of Holocene East Asian summer monsoon in sediments of northern South China Sea slope [J]. Quaternary Research, 2011, 75(3): 734-744. doi: 10.1016/j.yqres.2011.03.002
[36] Lisiecki L E, Raymo M E. A pliocene-pleistocene stack of 57 globally distributed benthic δ18O records [J]. Paleoceanography, 2005, 20(1): PA1003.
[37] 张晋, 李安春, 万世明, 等. 南海南部表层沉积物粒度分布特征及其影响因素[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2016, 36(2):1-10
ZHANG Jin, LI Anchun, WAN Shiming, et al. Grain size distribution of surface sediments in the southern South China Sea and influencing factors [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2016, 36(2): 1-10.
[38] Jan Weltje G, Prins M A. Muddled or mixed? Inferring palaeoclimate from size distributions of deep-sea clastics [J]. Sedimentary Geology, 2003, 162(1-2): 39-62. doi: 10.1016/S0037-0738(03)00235-5
[39] 金秉福. 粒度分析中偏度系数的影响因素及其意义[J]. 海洋科学, 2012, 36(2):129-135
JIN Bingfu. Influencing factors and significance of the skewness coefficient in grain size analysis [J]. Marine Sciences, 2012, 36(2): 129-135.
[40] 王星星. 南海珠江口外峡谷深水沉积作用及响应[D]. 浙江大学博士学位论文, 2019.
WANG Xingxing. Deep-water sedimentary processes and response in the Pearl River Canyon, South China Sea[D]. Doctor Dissertation of Zhejiang University, 2019.
[41] 李军, 高抒, 孙有斌. 冲绳海槽南部A23孔浊流沉积层的粒度特征[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2005, 25(2):11-16
LI Jun, GAO Shu, SUN Youbin. Grain-size characteristics of turbidite sediments in core a23 from the Southern Okinawa Trough [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2005, 25(2): 11-16.
[42] Shanmugam G. The bouma sequence and the turbidite mind set [J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 1997, 42(4): 201-229. doi: 10.1016/S0012-8252(97)81858-2
[43] 曹超, 雷怀彦. 南海北部有孔虫碳氧同位素特征与晚第四纪水合物分解的响应关系[J]. 吉林大学学报: 地球科学版, 2012, 42(S1):162-171
CAO Chao, LEI Huaiyan. The response relationship between carbon and oxygen isotopic characteristics of foraminifera in the northern South China Sea and hydrate decomposition in the late quaternary [J]. Journal of Jilin University: Earth Science Edition, 2012, 42(S1): 162-171.
[44] Lüdmann T, Wong H K, Dinu C, et al. Characterization of gas hydrate and free gas occurrences in the western black sea[C]//Abstracts of the Second International Symposium on Continental Margin Tectonics and Georesources. Qingdao: Chinese Society of Oceanography and Limnology, 2007: 18.
[45] 张一辉. 南海典型沉积区粒度分形特征研究[D]. 合肥工业大学硕士学位论文, 2019.
ZHANG Yihui. A study of fractal characteristic features of typical sediments from the South China Sea[D]. Master Dissertation of Hefei University of Technology, 2019.
[46] 范天来, 范育新. 频率分布曲线和概率累积曲线在沉积物粒度数据分析中应用的对比[J]. 甘肃地质, 2010, 19(2):32-37
FAN Tianlai, FAN Yuxin. A comparison of grain size expression methods: a case study [J]. Acta Geologica Gansu, 2010, 19(2): 32-37.
[47] Passega R. Grain size representation by CM patterns as a geologic tool [J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 1964, 34(4): 830-847. doi: 10.1306/74D711A4-2B21-11D7-8648000102C1865D
[48] 张宝方. 南海北部陆坡区更新世以来沉积物粒度特征及沉积环境演化[D]. 中国海洋大学硕士学位论文, 2015.
ZHANG Baofang. Grain size distribution and sedimentary environment evolution in northern South China Sea slope since pleistocene abstract[D]. Master Dissertation of Ocean University of China, 2015.
[49] 冯轩, 吴永华, 杨宝菊, 等. 冲绳海槽西南端1.3ka以来异重流沉积记录及其古气候响应[J/OL]. 沉积学报, 2020.[2020-03-30]. https://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CJFQ&dbname=CAPJLAST&filename=CJXB20200327002.
FENG Xuan, WU Yonghua, YANG Baoju, et al. Records of hyperpycnal flow deposits in the southwestern Okinawa trough and their paleoclimatic response since 1.3 ka[J/OL]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2020. [2020-03-30]. https://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CJFQ&dbname=CAPJLAST&filename=CJXB2020032700.
[50] 徐尚, 王英民, 彭学超, 等. 台湾峡谷HD133柱状样中重力流、底流交互沉积的证据[J]. 地质学报, 2012, 86(11):1792-1798 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2012.11.008
XU Shang, WANG Yingmin, PENG Xuechao, et al. Evidence for the interactive deposition between gravity and bottom currents revealed by core HD133 from Taiwan canyon [J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2012, 86(11): 1792-1798. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2012.11.008
[51] 苏纪兰. 南海环流动力机制研究综述[J]. 海洋学报, 2005, 27(6):1-8
SU Jilan. Overview of the South China Sea circulation and its dynamics [J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2005, 27(6): 1-8.
[52] 徐景平. 海底浊流研究百年回顾[J]. 中国海洋大学学报, 2014, 44(10):98-105
XU Jingping. Turbidity current research in the past century: an overview [J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 2014, 44(10): 98-105.
[53] 李明坤. 南海西北部36 kyr BP以来的古气候环境演变与驱动机制[D]. 中国科学院大学博士学位论文, 2018.
LI Mingkun. Paleoclimate and paleoenvironment evolutions in the Northwestern South China Sea over the past 36 kyr BP and the forcing mechanisms[D]. Doctor Dissertation of University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2018.
[54] Huang J, Jiang F Q, Wan S M, et al. Terrigenous supplies variability over the past 22, 000 yr in the southern South China Sea slope: Relation to sea level and monsoon rainfall changes [J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2016, 117: 317-327. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2015.12.019
[55] Clarke S, Hubble T, Webster J, et al. Sedimentology, structure and age estimate of five continental slope submarine landslides, eastern Australia [J]. Australian Journal of Earth Sciences, 2016, 63(5): 631-652. doi: 10.1080/08120099.2016.1225600
[56] Pope E L, Talling P J, Urlaub M, et al. Are large submarine landslides temporally random or do uncertainties in available age constraints make it impossible to tell? [J]. Marine Geology, 2015, 369: 19-33. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2015.07.002
[57] Woodroffe C D, McGregor H V, Lambeck K, et al. Mid-Pacific microatolls record sea-level stability over the past 5000 yr [J]. Geology, 2012, 40(10): 951-954. doi: 10.1130/G33344.1
[58] Thom B G, Roy P S. Sea level change in New South Wales over the past 15, 000 years[M]//Hopley D. Australian Sea Levels in the Last 15000 Years: A Review. James Cook: University of North Queensland, 1983: 64-85.
[59] Chappell J, Polach H. Post-glacial sea-level rise from a coral record at Huon Peninsula, Papua New Guinea [J]. Nature, 1991, 349(6305): 147-149. doi: 10.1038/349147a0
[60] Grant K M, Rohling E J, Ramsey C B, et al. Sea-level variability over five glacial cycles [J]. Nature, 2014, 5: 5076.
-



 下载:
下载: