Turbidity deposits and their provenance: evidence from core SH37 in Shenhu area of the South China Sea
-
摘要:
为了分析南海北部神狐海域的浊流沉积,对SH37岩心进行了沉积物粒度测试、AMS14C测年和地球化学元素测试等工作。根据粒度特征和C-M图等分析认为,200~300 cm层位属于浊流沉积,该层沉积物粒度较粗,分选较差,敏感粒级端元EM3与Zr/Rb元素比值在该层均含量较高,且有地层年龄倒转现象。推测浊流成因为海平面的变化或重力作用引起的陆坡滑坡。稀土元素含量与(La/Sm)UCC-(Gd/Yb)UCC、(Gd/Yb)UCC-(Gd/Lu)UCC散点图结果显示,SH37岩心沉积物来源较为一致,主要来自于珠江和台湾岛内河流。
Abstract:In order to seek for the origin of the turbidite deposits in the Shenhu area of the northern South China Sea, grain size analysis, AMS14C dating and element geochemical analysis have been carried out for the core of SH37. Grain size distribution and C-M pattern suggest that the core deposits between the interval of 200~300 cm belong to turbidite deposits. The interval is composed of relatively coarse sediments with bad sorting, as EM3 and the ratio of Zr/Rb are rather high. A phenomenon of age reversal is observed. It is speculated that the turbidity current is probably triggered by sea level change or gravity. Rare earth elements and scatter plots of (La/Sm)UCC-(Gd/Yb)UCC and (Gd/Yb)UCC-(Gd/Lu)UCC suggest that the turbidite sediments are mainly sourced from the Pearl River system and the rivers on the Taiwan Island.
-
Key words:
- turbidity deposit /
- strata inversion /
- landslide /
- provenance /
- Shenhu area
-

-
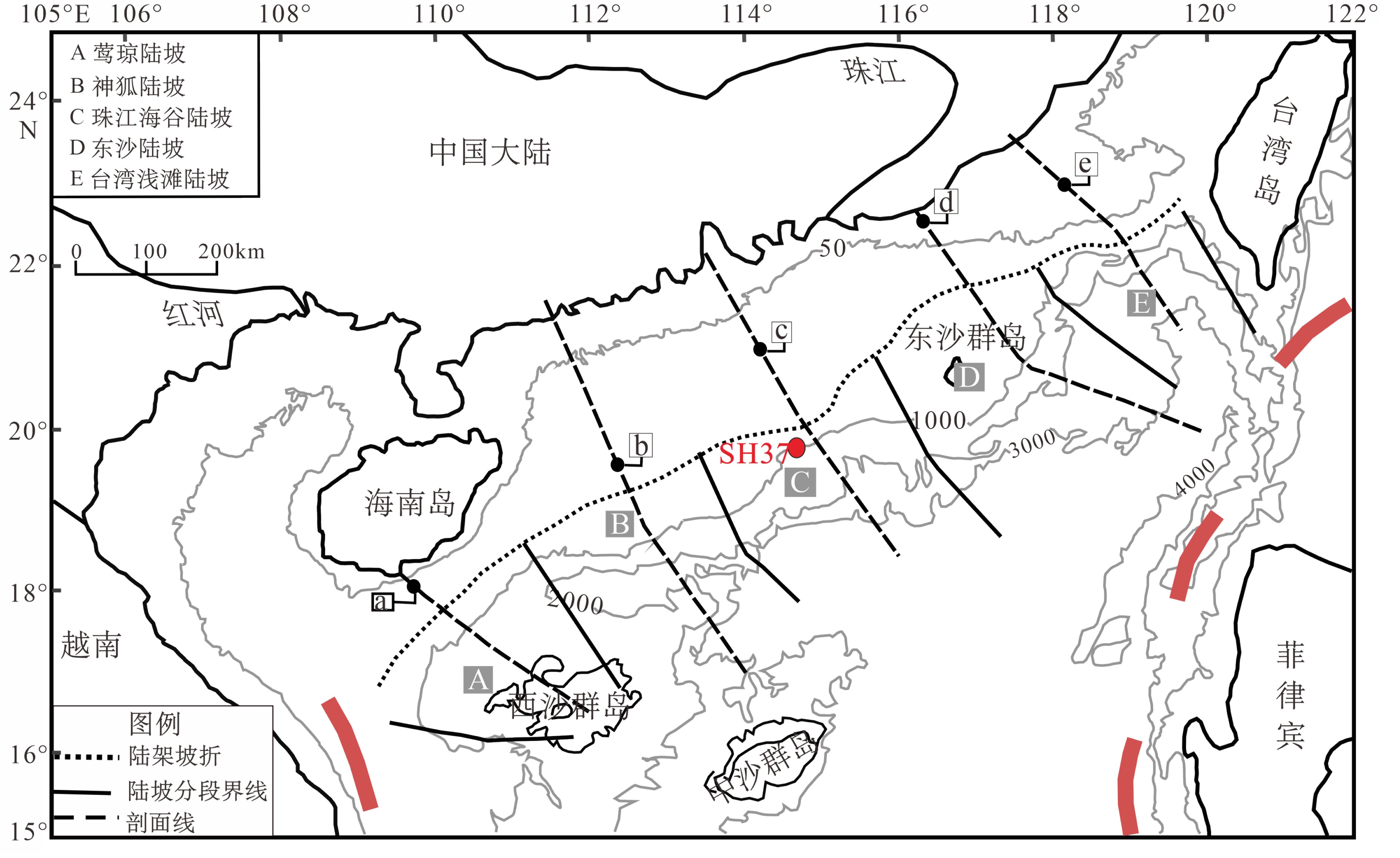
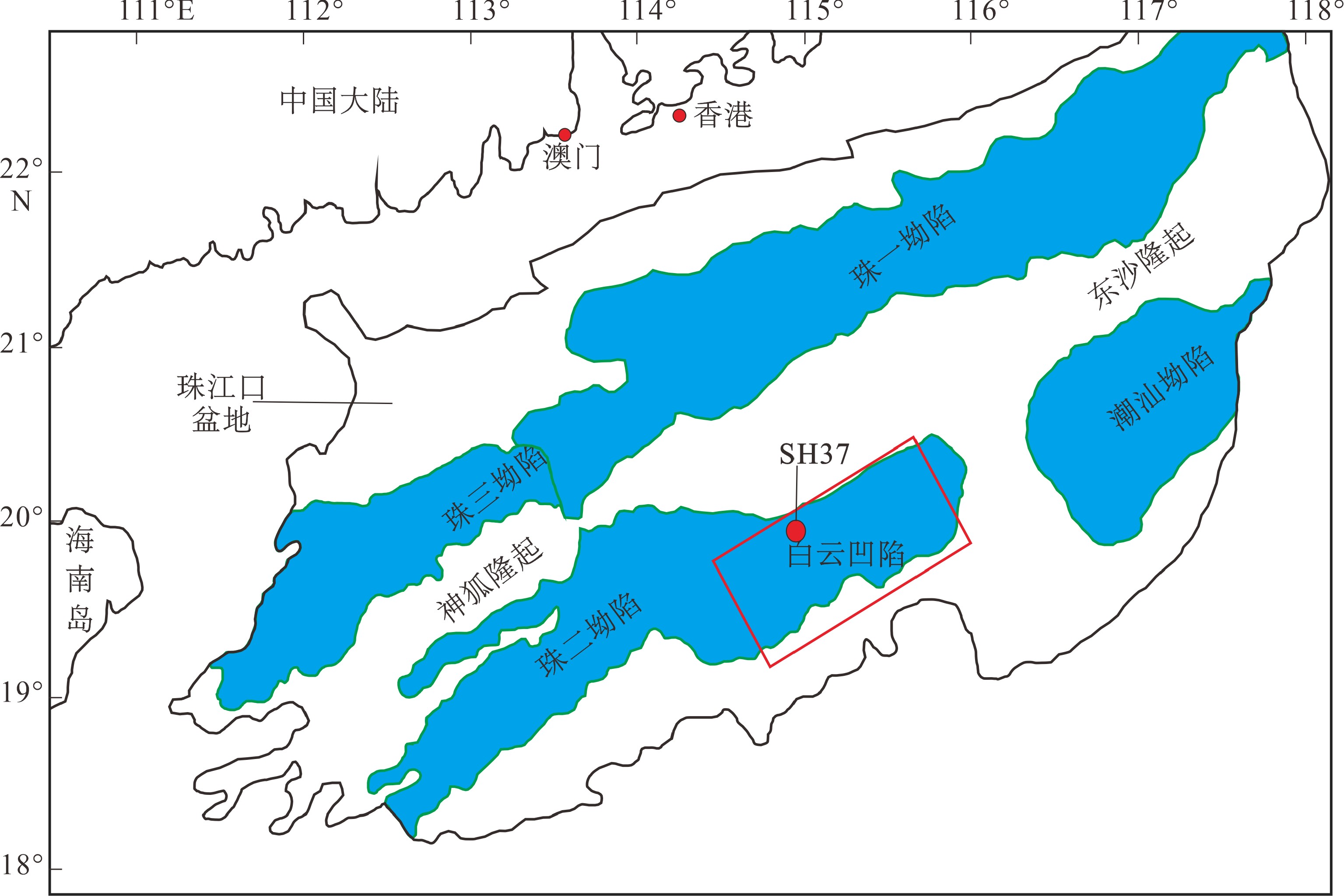
图 1 神狐海域构造图[17]
Figure 1.
图 6 南海北部陆坡分段[[30]]
Figure 6.
表 1 AMS14C测年结果
Table 1. Results of AMS14C dating
取样深度/cm 样品种类 AMS 14C年龄/aBP 校正后日历年龄/cal.aBP 11~12 Globorotalia inflata 680±30 440~225 133~134 Globorotalia inflata 11020±30 12671~12442 218~219 Globorotalia inflata 13120±30 15298~14895 265~266 混合种 12590±40 14206~13889 426~430 混合种 13940±40 16511~16076 表 2 研究区样品各沉积组分含量与粒度参数
Table 2. Contents and grain size parameters of the sediments
粒度参数/组分 砂/% 粉砂/% 黏土/% 平均粒径/μm 中值粒径/μm 分选系数 偏态 峰态 最大值 4.19 78.24 29.24 10.14 11.41 1.76 0.29 1.14 最小值 0.00 69.32 19.65 6.76 7.70 1.48 0.12 0.97 平均值 1.33 73.30 25.37 7.95 9.14 1.59 0.22 1.03 表 3 稀土元素及参数含量
Table 3. Contents of rare earth elements and parameters
元素 La Ce Pr Nd Sm Eu Gd Tb Dy Ho Er Tm Yb Lu 样品最大值 39.10 79.90 9.38 33.20 6.47 1.10 4.58 0.65 4.12 0.70 1.95 0.33 1.99 0.31 样品最小值 27.60 54.90 6.45 23.70 4.50 0.86 3.20 0.45 2.49 0.49 1.32 0.20 1.23 0.20 样品平均值 32.79 66.20 7.75 27.98 5.39 0.97 3.78 0.54 2.98 0.57 1.58 0.24 1.54 0.24 珠江[20] 53.82 103.97 13.08 47.98 9.23 1.92 7.91 1.25 6.53 1.33 3.55 0.62 3.66 0.56 台湾[21] 41.89 82.78 9.35 34.97 6.32 1.34 6.11 0.89 5.09 0.96 2.87 0.43 2.85 0.43 吕宋岛北部[22] 33.34 61.51 6.91 25.11 4.36 1.15 3.61 0.52 3.07 0.68 2.00 / 1.91 0.31 元素参数 ∑REE ∑LREE ∑HREE ∑REE/
HREEδEu δCe (La/Sm)
ucc(Gd/Lu)
ucc(Gd/Yb)
ucc样品最大值 183.02 169.14 13.88 13.90 0.67 1.03 1.03 1.45 1.92 样品最小值 128.97 118.92 9.69 11.18 0.56 0.93 0.83 1.06 1.31 样品平均值 152.55 141.08 11.48 12.32 0.61 0.98 0.92 1.32 1.57 珠江[20] 255.40 229.99 25.41 8.98 0.66 0.92 0.88 1.18 1.48 台湾[21] 196.29 176.66 19.63 8.94 0.64 0.98 0.99 1.21 1.08 吕宋岛北部[22] / 132.38 / / 0.88 0.92 0.71 0.97 1.07 注:元素含量单位为μg /g。 -
[1] 高红灿, 郑荣才, 魏钦廉, 等. 碎屑流与浊流的流体性质及沉积特征研究进展[J]. 地球科学进展, 2012, 27(8):815-827
GAO Hongcan, ZHENG Rongcai, WEI Qinlian, et al. Reviews on fluid properties and sedimentary characteristics of debris flows and turbidity currents [J]. Advances in Earth Sciences, 2012, 27(8): 815-827.
[2] 赵玉龙, 刘志飞, Colin C, 等. 南海南部末次冰期浊流沉积的高分辨率沉积学和地球化学研究[J]. 科学通报, 2011, 56(33):3558-3565 doi: 10.1007/s11434-011-4685-7
ZHAO Yulong, LIU Zhifei, Colin C, et al. Turbidite deposition in the southern South China Sea during the last glacial: evidence from grain-size and major elements records [J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2011, 56(33): 3558-3565. doi: 10.1007/s11434-011-4685-7
[3] Shanmugam G, Moiola R J. Submarine fans: Characteristics, models, classification, and reservoir potential [J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 1988, 24(6): 383-428. doi: 10.1016/0012-8252(88)90064-5
[4] 王存武, 陈红汉, 陈长民, 等. 珠江口盆地深水扇识别和油气成藏关键要素[J]. 西南石油大学学报, 2007, 29(3):12-26
WANG Cunwu, CHEN Honghan, CHEN Changmin, et al. The identification of the Baiyun deep-water fan and the key factors of petroleum accumulation in Pearl river mouth basin [J]. Journal of Southwest Petroleum University, 2007, 29(3): 12-26.
[5] Weber M E, Wiedicke-Hombach M, Kudrass H R, et al. Bengal Fan sediment transport activity and response to climate forcing inferred from sediment physical properties [J]. Sedimentary Geology, 2003, 155(3-4): 361-381. doi: 10.1016/S0037-0738(02)00187-2
[6] Prins M A, Postama G. Effects of climate, sea level, and tectonics unraveled for last deglaciation turbidite records of the Arabian sea [J]. Geology, 2000, 28(4): 375-378. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(2000)28<375:EOCSLA>2.0.CO;2
[7] 苏晶, 钟广法. 南海IODP U1499和U1500站位浊积岩的沉积特征及岩石物理响应[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2020, 40(3):13-24
SU Jing, ZHONG Guangfa. Sedimentary and petrophysical characteristics of various turbidites at IODP Sites U1499 and U1500 in the northern South China Sea [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2020, 40(3): 13-24.
[8] 周杨锐, 朱友生, 周松望, 等. 南海北部东沙隆起西侧陆坡坡折处浊流沉积[J]. 海洋科学, 2018, 42(2):23-33 doi: 10.11759/hykx20171101003
ZHOU Yangrui, ZHU Yousheng, ZHOU Songwang, et al. Turbidites at the continental slope on the west side of Dongsha uplift in the northern South China Sea [J]. Marine Sciences, 2018, 42(2): 23-33. doi: 10.11759/hykx20171101003
[9] 章伟艳, 张富元, 张霄宇. 南海东部海域柱样沉积物浊流沉积探讨[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2003, 22(3):36-43 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5470.2003.03.006
ZHANG Weiyan, ZHANG Fuyuan, ZHANG Xiaoyu. Characteristics of turbidity deposits from sediment cores in eastern South China Sea [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2003, 22(3): 36-43. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5470.2003.03.006
[10] 陈芳, 李学杰, 刘坚, 等. 南海西部深海平原SA14-34岩心浊流沉积特征[J]. 南海地质研究, 2007(1):31-39
CHEN Fang, LI Xuejie, LIU Jian, et al. Characteristics of turbidity current deposits of core SA14-34 in deep Sea Basin of the western South China Sea [J]. Gresearch of Eological South China Sea, 2007(1): 31-39.
[11] 袁圣强, 吴时国, 赵宗举, 等. 南海北部陆坡深水区沉积物输送模式探讨[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2010, 30(4):39-48
YUAN Shengqiang, WU Shiguo, ZHAO Zongju, et al. Deepwater sediment transportation models for northern South China Sea slopes [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2010, 30(4): 39-48.
[12] 姜衡, 苏明, 雷新华, 等. 神狐海域海底峡谷群脊部细粒浊积体分布范围及意义[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2018, 38(5):52-62
JIANG Heng, SU Ming, LEI Xinhua, et al. Distribution of fine-grained turbidites on canyon ridges in the Shenhu area of northern South China sea and its implications [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2018, 38(5): 52-62.
[13] 周航. 南海北部陆坡DLW3101孔沉积物特征及古环境意义[D]. 国家海洋局第一海洋研究所硕士学位论文, 2016.
ZHOU Hang. Sediment characteristics and paleoenvironmental significance of core DLW3101 from northern slope of South China Sea[D]. Master Dissertation of the First Institute of Oceanography, MNR, 2016.
[14] 姜衡, 苏明, 邬黛黛, 等. 南海北部陆坡神狐海域GMGS01区块细粒浊积体的识别特征及意义[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2017, 37(5):131-140
JIANG Heng, SU Ming, WU Daidai, et al. Fine-grained turbidites in GMGS01 of the Shenhu area, northern South China Sea and its significance [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2017, 37(5): 131-140.
[15] 王一凡, 苏正, 苏明, 等. 南海北部陆坡神狐海域沉积物失稳类型探讨[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2017, 37(5):184-194
WANG Yifan, SU Zheng, SU Ming, et al. Sediment failures in the Shenhu area, northern continental slope of the South China Sea [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2017, 37(5): 184-194.
[16] Qiao S H, Su M, Kuang Z G, et al. Canyon-related undulation structures in the Shenhu area, northern South China Sea [J]. Marine Geophysical Research, 2015, 36(2-3): 243-252. doi: 10.1007/s11001-015-9252-1
[17] 姜衡. 神狐海域含水合物浊流沉积体差异性对比研究[D]. 中国地质大学(北京)硕士学位论文, 2018.
JIANG Heng. Comparative study on the difference of hydrate-bearing turbidites in the Shenhu Sea Area[D]. Master Dissertation of China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2018.
[18] 陆敬安, 杨胜雄, 吴能友, 等. 南海神狐海域天然气水合物地球物理测井评价[J]. 现代地质, 2008, 22(3):447-451 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2008.03.015
LU Jing’an, YANG Shengxiong, WU Nengyou, et al. Well logging evaluation of gas hydrates in Shenhu area, South China Sea [J]. Geoscience, 2008, 22(3): 447-451. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2008.03.015
[19] Reimer P J, Bard E, Bayliss A, et al. IntCal13 and Marine13 radiocarbon age calibration curves 0-50,000 years cal BP [J]. Radiocarbon, 2013, 55(4): 1869-1887. doi: 10.2458/azu_js_rc.55.16947
[20] Xu Z F, Han G L. Rare earth elements (REE) of dissolved and suspended loads in the Xijiang River, South China [J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2009, 24(9): 1803-1816. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2009.06.001
[21] Li C S, Shi X F, Kao S J, et al. Rare earth elements in fine-grained sediments of major rivers from the high-standing island of Taiwan [J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2013, 69: 39-47. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2013.03.001
[22] Marini J C, Chauvel C, Maury R C. Hf isotope compositions of northern Luzon arc lavas suggest involvement of pelagic sediments in their source [J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 2005, 149(2): 216-232. doi: 10.1007/s00410-004-0645-4
[23] Bouma A H. Sedimentology of Some Flysch Deposits: A Graphic Approach to Facies Interpretation[M]. New York: Elsevier, 1962.
[24] Shanmugam G. The Bouma Sequence and the turbidite mind set [J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 1997, 42(4): 201-229. doi: 10.1016/S0012-8252(97)81858-2
[25] 袁迎如. 冲绳海槽沉积物的粒度[J]. 东海海洋, 1986, 4(3):42-49
YUAN Yingru. Grain size of the sediments in Okymawa trough [J]. Donghai Marine Science, 1986, 4(3): 42-49.
[26] 许莎莎, 冯秀丽, 冯利, 等. 南海西北部莺琼陆坡36.6 ka以来的浊流沉积[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2020, 40(5):15-24
XU Shasha, FENG Xiuli, FENG Li, et al. Turbidite records since 36.6 Ka at the Yingqiong continental slope in the northwest of South China Sea [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2020, 40(5): 15-24.
[27] Stager J C, Ryves D B, Chase B M, et al. Catastrophic drought in the Afro-Asian monsoon region during heinrich event [J]. Science, 2011, 331(6022): 1299-1302. doi: 10.1126/science.1198322
[28] Arz H W, Lamy F, Ganopolski A, et al. Dominant Northern Hemisphere climate control over millennial-scale glacial sea-level variability [J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2007, 26(3-4): 312-321. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2006.07.016
[29] 张宝方. 南海北部陆坡区更新世以来沉积物粒度特征及沉积环境演化[D]. 中国海洋大学硕士学位论文, 2015.
ZHANG Baofang. Grain size distribution and sedimentary environment evolution in northern South China Sea slope since Pleistocene[D]. Master Dissertation of Ocean University of China, 2015.
[30] 王海荣, 王英民, 邱燕, 等. 南海北部陆坡的地貌形态及其控制因素[J]. 海洋学报, 2008, 30(2):70-79
WANG Hairong, WANG Yingmin, QIU Yan, et al. Geomorphology and its control of deep-water slope of the margin of the South China Sea [J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2008, 30(2): 70-79.
[31] 雷艳, 胡建芳, 向荣, 等. 末次盛冰期以来南海北部神狐海域沉积有机质的组成特征及其古气候/环境意义[J]. 海洋学报, 2017, 39(11):75-84
LEI Yan, HU Jianfang, XIANG Rong, et al. Composition of sedimentary organic matter in Shenhu, northern South China Sea since the Last Glacial Maximum and its implication for paleoclimate [J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2017, 39(11): 75-84.
[32] 黄杰, 李安春, 万世明, 等. 末次盛冰期末期以来南海北部陆坡的陆源物质输入及其控制因素[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2013, 44(4):882-889
HUANG Jie, LI Anchun, WAN Shiming, et al. Terrigenous input to the northern slope of the South China Sea and its controlling factor since the last phase of the last glacial maximum [J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2013, 44(4): 882-889.
[33] 仇晓华, 李铁刚, 常凤鸣, 等. 西菲律宾海15万年以来的浊流沉积及其成因[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2012, 32(4):157-163
QIU Xiaohua, LI Tiegang, CHANG Fengming, et al. Turbidite deposition record and its mechanism since 150 KaBP in Western Philippine Sea [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2012, 32(4): 157-163.
[34] 陈井双, 李前裕. 南海中央海盆更新世以来浊流沉积层的有孔虫记录及古环境意义[J]. 微体古生物学报, 2018, 35(4):348-358
CHEN Jingshuang, LI Qianyu. Foraminiferal paleoceanography of Pleistocene turbidite deposits from the central basin of the South China Sea [J]. Acta Micropalaeontologica Sinica, 2018, 35(4): 348-358.
[35] 秦轲, 孙运宝, 赵铁虎, 等. 南海北部陆坡神狐海域海底滑坡地球物理响应特征及其与流体活动相关性[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2015, 35(5):69-76
QIN Ke, SUN Yunbao, ZHAO Tiehu, et al. Seismic response and genetic mechanism of the submarine landslides in Shenhu area, South China Sea [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2015, 35(5): 69-76.
[36] 邵磊, 李献华, 韦刚健, 等. 南海陆坡高速堆积体的物质来源[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 2001, 31(10):828-833 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1006-9267.2001.10.006
SHAO Lei, LI Xianhua, WEI Gangjian, et al. Material sources of high-speed accumulations on the continental slope of the South China Sea [J]. Science China (Series D: Earth Science), 2001, 31(10): 828-833. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1006-9267.2001.10.006
[37] Milliman J D, Meade R H. World-wide delivery of river sediment to the oceans [J]. The Journal of Geology, 1983, 91(1): 1-21. doi: 10.1086/628741
[38] 汪品先. 十五万年来的南海[M]. 上海: 同济大学出版社, 1995: 10-14.
WANG Pinxian. South China Sea for 150000a[M]. Shanghai: Tongji University Press, 1995: 10-14.
[39] McLennan S M. Rare earth elements in sedimentary rocks: influence of provenance and sedimentary processes[M]//Lipin B R, McKay G A. Geochemistry and Mineralogy of Rare Earth Elements. San Francisco, California: AGU, 1989: 169-200.
[40] 杨文光, 谢昕, 郑洪波, 等. 南海北部陆坡高速堆积体沉积物稀土元素特征及其物源意义[J]. 矿物岩石, 2012, 32(1):74-81 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6872.2012.01.011
YANG Wenguang, XIE Xin, ZHENG Hongbo, et al. Rare earth elements characteristics of sediments from high-deposition-rate sediment in the north slope of South China Sea and its provenance significance [J]. Journal of Mineralogy and Petrology, 2012, 32(1): 74-81. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6872.2012.01.011
[41] Taylor S R, McLennan S M. The geochemical evolution of the continental crust [J]. Reviews of Geophysics, 1995, 33(2): 241-265. doi: 10.1029/95RG00262
[42] Liu C Q, Masuda A, Okada A, et al. A geochemical study of loess and desert sand in northern China: Implications for continental crust weathering and composition [J]. Chemical Geology, 1993, 106(3-4): 359-374. doi: 10.1016/0009-2541(93)90037-J
[43] 沈华悌. 深海沉积物中的稀土元素[J]. 地球化学, 1990(4):340-348 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0379-1726.1990.04.009
SHEN Huati. Rare earth elements in deep-sea sediments [J]. Geochimica, 1990(4): 340-348. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0379-1726.1990.04.009
[44] Sun W, McDonough W. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: Implications for mantle composition and processes[M]//Saunders A D, Norry M J. Magmatism in the Ocean Basins. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 1989, 42(1): 313-345.
-



 下载:
下载: