Environmental evolution and carbon burial assessment of the west coast of Bohai Bay since Late Pleistocene
-
摘要:
对海岸带滨海湿地土壤或沉积物中碳通量的定量评估是国内外碳循环研究的热点,但目前对碳通量评估涉及地面以下的土壤或沉积物深度大多不超过1 m(最多3 m),少有对更深更长时间尺度(如千年尺度)的沉积物中碳通量进行评估研究。对2016年在渤海湾西岸老黄河三角洲沉积区获取的BHZK13钻孔(长32.68 m)开展AMS14C测年和光释光(OSL)测年、粒度、有孔虫、总碳(TC)和有机碳(OC)浓度、主量元素(含营养元素)和原位密度等参数进行分析测试。结果显示,渤海湾西岸老黄河三角洲沉积区自晚更新世晚期以来,沉积环境自下而上可划分出7个沉积单元,分别对应MIS5期的潮坪相(U1)、泛滥平原相(U2)、河道相(U3)、全新世的潮坪—浅海相(U4)、一期黄河三角洲(5500~3600 cal.aBP)(U5)、改造层(3600 cal.aBP~700 BC)(U6)、二期黄河三角洲(700 BC—11 AD)(U7)。沉积速率在U5前缘相中最大(1.99 cm/a),在U1沉积环境中最小(0.014 cm/a)。相应地,有机碳埋藏通量在U5前缘相最大(134.56 g/(m2·a)),而最小值(0.16 g/(m2·a))出现在U3环境中。沉积速率是有机碳埋藏通量的主控因素,TC和OC与各营养元素都呈极显著的相关性。虽然老黄河三角洲沉积物中有机碳含量较低,但由于沉积速率相对较快,使得老黄河三角洲沉积体也是较好的有机碳贮库。
Abstract:The quantitative assessment of carbon flux in soil or sediments of coastal wetlands has recently become a hotspot in carbon cycle research both at home and abroad. However, most of the depth of the sediment samples studied is less than 1 m (or a maximum no more than 3 meters), and there are few studies on carbon fluxes in deeper sediments or longer time scales, such as the millennium scale available. In order to reveal the carbon fluxes in deeper layers, a hole of 32.68 m deep (BHZK13) was drilled in the old Yellow River Delta on the west bank of Bohai Bay in 2016. Core samples are carefully described and tested for AMS14C and OSL dating, grain size analysis, foraminifera identification, and analysis of total carbon(TC), organic carbon (OC), and major elements (including nutrient elements) in addition to in-situ densities. The results show that since Late Pleistocene, the sedimentary environment of the old Yellow River Delta on the west coast of Bohai Bay can be subdivided into seven sub-environments, namely, the tidal flat in MIS5 (U1), floodplain (U2), river channel (U3), Holocene tidal flat (U4), Yellow River Delta phase one (U5, 5500~3600 cal.aBP), reconstruction layer (U6) and Yellow River Delta phase two (U7). The highest sedimentation rate is found in the deltaic front of the delta phase one (1.99 cm/a), while the lowest found in the tidal flat (0.014 cm/a). Correspondingly, the highest burial rate of organic carbon is found in the deltaic front of the Yellow River Delta phase one (134.56 g/(m2·a)), with the lowest found in river channel deposits. Correlation analysis suggests that the sedimentation rate is the main controlling factor on the burial rate of organic carbon in various sedimentary environments. TC and OC has a very significant correlation with each nutrient element. Although the content of organic carbon in the sediments of the Old Yellow River Delta is relatively low due to the high sedimentation rate of the Delta, the modern Yellow River Delta can still be considered as an excellent carbon sink also due to its high sedimentation rate.
-
Key words:
- organic carbon /
- deposition rate /
- buried flux /
- Yellow River Delta
-

-
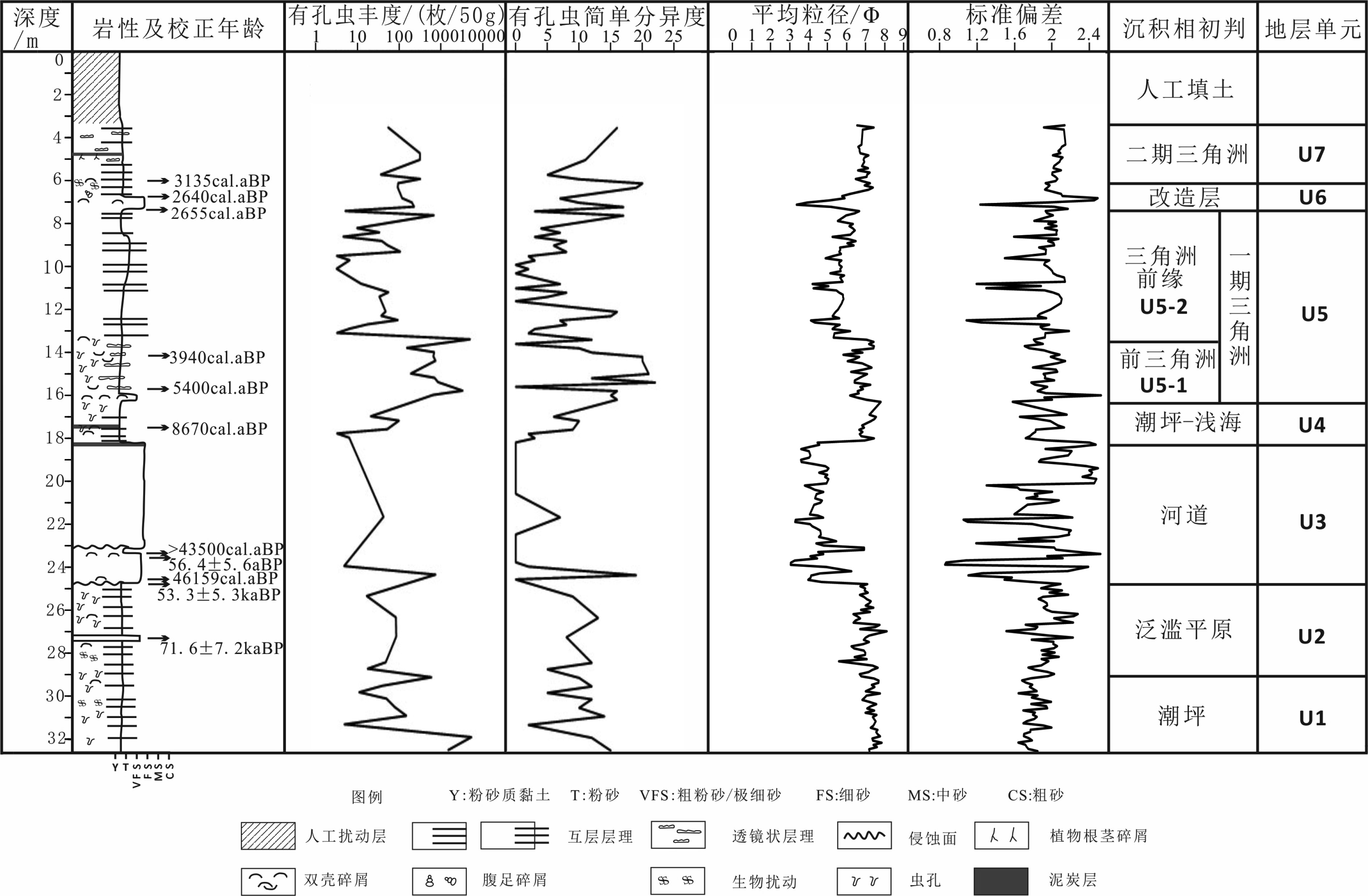
表 1 BXZK13孔AMS14C测年数据
Table 1. AMS14C data of Core BXZK13
样品编号 深度/m 测试材料 校正后年龄/cal.aBP(1σ) 校正后年龄中值/cal.aBP BXZK13S1 6.1 Potamocorbula laevis 3047~3222 3135 BXZK13S7 6.8 Terebra koreana 2568~2730 2640 BXZK13S8 7 Potamocorbula laevis 2595~2738 2655 BXZK13S2 14.07 Venus sp. 3851~4042 3940 BXZK13S3 15.77 Venus sp. 5316~5457 5400 BXZK13S4 17.46 有机质 8602~8704 8670 BXZK13S5 23.25 Potamocorbula laevis >43500 BXZK13S6 24.63 Scapharca kagoshimensis 45494~46816 46195 表 2 BXZK13孔OSL测年数据
Table 2. OSL data of Core BXZK13
样品编号 样品深度/m 实验编号 U/ (μg/g) Th/ (μg/g) K/% 等效剂量/Gy 年龄/aBP 误差/aBP OSL-8 23.4 2017A008 1.22 5.95 1.95 174.8 56400 ±5600 OSL-9 24.7 2017A009 1.46 7.25 2.15 184.7 53300 ±5300 OSL-10 27.33 2017A010 1.34 6.48 1.91 225.6 71600 ±7200 表 4 BHZK13沉积物碳及营养成分浓度的相关系数
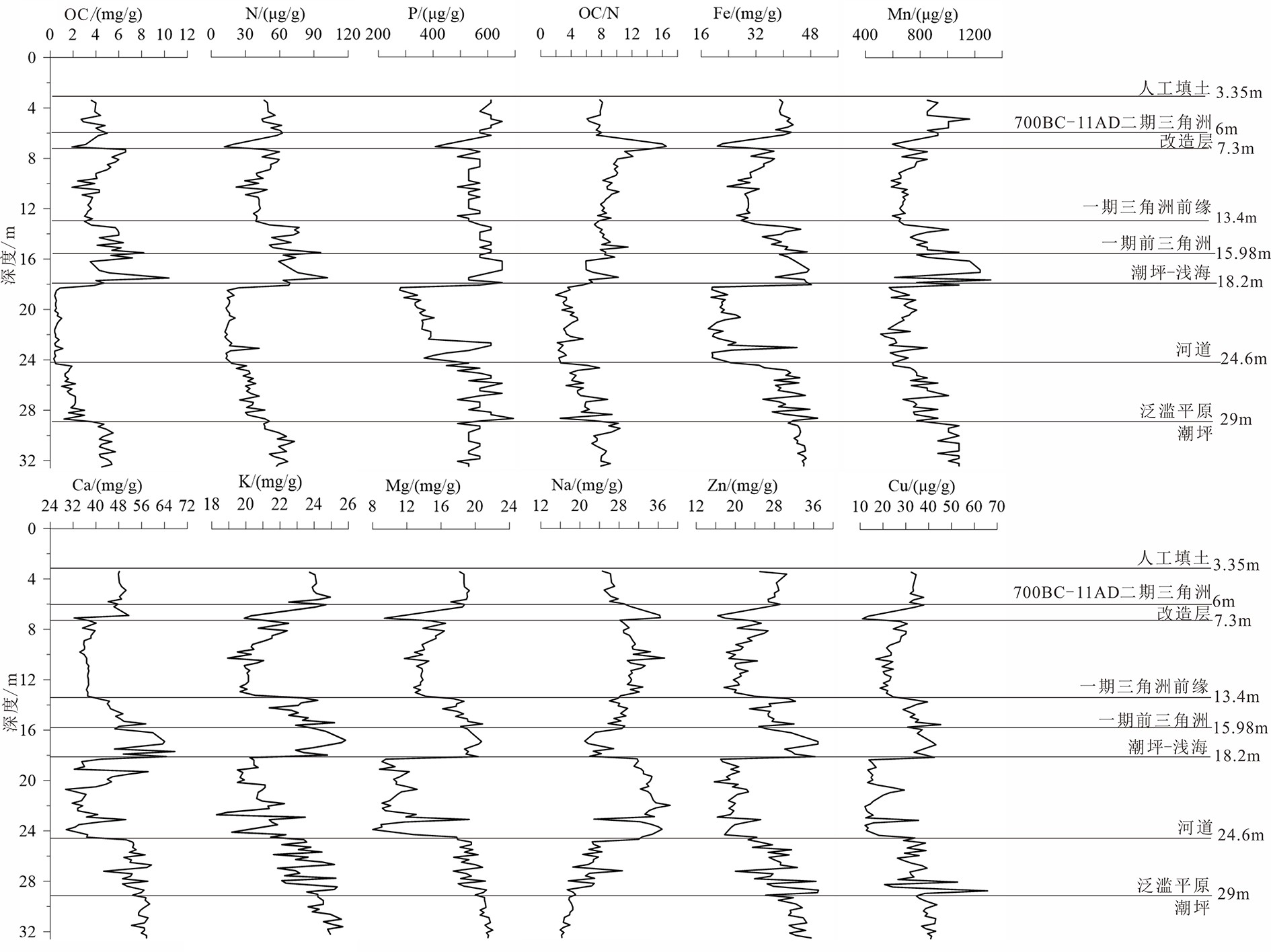
Table 4. Correlations between carbons and nutrients of the sediments
Cu N Mn P Zn Al Fe Mg Ca Na K TC OC Cu 1 0.742 0.764 0.639 0.907 0.879 0.937 0.923 0.734 −0.84 0.875 0.834 0.558 N 1 0.635 0.638 0.721 0.813 0.775 0.731 0.485 −0.57 0.665 0.861 0.912 Mn 1 0.495 0.842 0.728 0.825 0.788 0.815 −0.78 0.818 0.808 0.441 P 1 0.604 0.768 0.76 0.728 0.457 −0.54 0.523 0.613 0.52 Zn 1 0.847 0.919 0.897 0.803 −0.88 0.922 0.858 0.506 Al 1 0.949 0.944 0.686 −0.82 0.823 0.826 0.68 Fe 1 0.979 0.801 −0.89 0.877 0.885 0.592 Mg 1 0.825 −0.9 0.868 0.872 0.561 Ca 1 −0.82 0.766 0.833 0.267 Na 1 −0.823 −0.788 −0.392 K 1 0.781 0.471 TC 1 0.683 OC 1 注:表中所列相关系数显著性均小于0.01。 表 5 沉积物TC、OC埋藏通量的相关系数
Table 5. Correlations between TC、OC accretion rates in the sediments
沉积速率 原为密度 TC浓度 TC堆积速率 OC浓度 OC堆积速率 TIC浓度 TIC堆积速率 沉积速率 1 0.262** −0.161 0.993** 0.337** 0.950** −0.425** 0.987** 原为密度 1 −0.704** 0.258** −0.506** 0.234* −0.580** 0.262** TC浓度 1 −0.13 0.647** −0.116 0.869** −0.132 TC堆积速率 1 0.357** 0.959** −0.399** 0.993** OC浓度 1 0.420** 0.184 0.321** OC堆积速率 1 −0.423** 0.919** TIC浓度 1 −0.379** TIC堆积速率 1 注:**为在0.01水平(双侧)上显著相关;*为在0.05水平(双侧)上显著相关 表 6 沉积速率、BD和OC浓度与碳埋藏通量协方差分析
Table 6. C, DR, and BD contributions to the variance of carbon burial rate.
V(DR) V(BD) V(C) 2COV(DR, BD) 2COV(BD, C) 2COV(DR, C) 0.75 0.00 0.16 0.01 −0.01 0.45 注:V 代表方差,COV 代表协方差,DR 代表沉积速率 表 3 黄河三角洲不同沉积环境垂向沉积速率与碳的埋藏通量
Table 3. Vertical sedimentation rate and accretion rate of carbon of different sediment environments in the Yellow River Delta
沉积层位 沉积速率/
(cm/a)原位密度/
(g/cm3)TC浓度/
(mg/g)OC浓度/
(mg/g)TIC浓度/
(mg/g)TC堆积速率/
(g/ (m2·a)OC堆积速率/
(g/ (m2·a)TIC堆积速率/
(g/ (m2·a)沉积环境 U7 0.1 1.54 16.7 3.9 12.8 25.54 5.88 19.86 二期三角洲沉积 U6 0.14 1.48 13.9 3.6 9 28.18 7.09 73.99 改造层沉积 U5-2 1.99 1.65 14.2 4.1 10.2 467.48 134.56 336.61 一期黄河三角洲前缘沉积 U5-1 0.12 1.41 19.9 5.7 14.2 33.42 9.82 23.95 一期黄河三角洲前三角洲沉积 U4 0.052 1.46 23.8 5.4 19.1 18.41 3.81 14.6 潮坪-浅海相 U3 0.015 1.73 11.2 0.6 10.7 2.92 0.16 2.76 河流相 U2 0.014 1.45 16.9 1.9 15.1 3.45 0.39 3.06 泛滥平原 U1 1.38 21 4.8 16.2 -
[1] 范德江, 杨作升, 郭志刚. 中国陆架210Pb测年应用现状与思考[J]. 地球科学进展, 2000, 15(3):297-302 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.2000.03.011
FAN Dejiang, YANG Zuosheng, GUO Zhigang. Review of 210Pb dating in the continental shelf of China [J]. Advance In Earth Sciences, 2000, 15(3): 297-302. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.2000.03.011
[2] Brevik E C, Homburg J A, 20 04. A 5000 year record of carbon sequestration from a coastal lagoon and wetland complex [J]. Southern California, USA. Catena, 2000, 57(3): 221-232.
[3] Smith P. Carbon sequestration in croplands: the potential in Europe and the global context [J]. Agronomy, 2004, 20(3): 229-236.
[4] Duan X N, Wang X K, Lu F, et al. Primary evaluation of carbon sequestration potential of wetlands in China [J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2008, 28(2): 463-469. doi: 10.1016/S1872-2032(08)60025-6
[5] Zhang S P, Wang L, Hu J J, et al. Organic carbon accumulation capability of two typical tidal wetland soils in Chongming Dongtan, China [J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2011, 23(1): 87-94. doi: 10.1016/S1001-0742(10)60377-4
[6] 赵广明, 叶思源, 丁喜桂, 袁红明, 王锦. 黄河三角洲全新世以来沉积环境的划分及各环境中碳埋藏速率的评价[J]. 地球科学(中国地质大学学报), 2014(4):80-90
ZHAO Guangming, YE Siyuan, DING Xigui, et al. Sedimentary Environmental Partitioning of Holocene Strata and Assessment of Carbon Burial Rate of Various Paleo-Environments in the Yellow River Delta [J]. Earth Science, 2014(4): 80-90.
[7] 欧莉华, 伊海生, 王刚, 等. 桂西地区乐平统合山组底部海绵骨针硅质岩的发现及古环境意义[J]. 中国地质, 2012, 39(5):1280-1289 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2012.05.015
OU Lihua, YI Haisheng, WANG Gang, et al. The discovery of sponge chert on the bottom of the Lopingian Heshan Formation in western Guangxi and its palaeoenvironment [J]. Geology in China, 2012, 39(5): 1280-1289. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2012.05.015
[8] Ye Siyuan, Laws E A, Wu Qiang, Zhong Shaojun, Ding Xigui, Zhao Guangming, Gong Shaojun. Pyritization of trace metals in estuarine sediments and the controlling factors: a case in Jiaojiang Estuary of Zhejiang Province, China [J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2020, 61(5): 973-982.
[9] Ye Siyuan, Laws E A, Zhong Shaojun, Ding Xigui, Pang Shouji. Sequestration of metals through association with pyrite in subtidal sediments of the Nanpaishui Estuary on the Western Bank of the Bohai Sea, China [J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2011, 62(5): 934-941. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2011.02.052
[10] 丁玉蓉, 叶思源, 赵全升. 黄河三角洲新生湿地土壤对营养成分和碳的扣留[J]. 地质论评, 2012, 58(1):183-189 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0371-5736.2012.01.016
DING Yurong, YE Siyuan, ZHAO Quansheng. Nutrient sand carbon sequestration the newly created wetland of Yellow River Delta [J]. Geological Review, 2012, 58(1): 183-189. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0371-5736.2012.01.016
[11] Smith T M, Cramer W P, Dixon R K, et al. The global terrestrial carbon cycle [J]. Water Air and Soil Pollution, 1993, 70(1-4): 19-37. doi: 10.1007/BF01104986
[12] Muller-Karger, Frank E. The importance of continental margins in the global carbon cycle [J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2015, 32(1): L01602.
[13] Zhao Guangming, Ye Siyuan, Li Guangxue, et al. Late Quaternary Strata and Carbon Burial Records in the Yellow River Delta, China [J]. Journal of Ocean University of China, 2015, 03: 446-456.
[14] 丁喜桂, 叶思源, 赵广明, 袁红明, 王锦. 黄河三角洲滨海湿地演化及其对碳与营养成分的扣留[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2014(1):96-104
DING Xigui, YE Siyuan, ZHAO Guangming, et al. Accumulation of Carbon and Nutrients in Coastal Wetland in the Yellow River Delta [J]. Oceanloogia et Limnologia Sinica, 2014(1): 96-104.
[15] 丁喜桂, 王吉松, 赵广明, 袁红明, 王锦, 叶思源. 黄河三角洲滨海湿地演化过程中的碳埋藏效率及其控制因素[J]. 中国地质, 2016(1):319-328 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2016.01.024
DING Xigui, WANG Jisong, ZHAO Guangming, et al. Accretion rate and controlling factors of carbon and nutrients during coastal wetland evolution in Yellow River Delta [J]. China Geology, 2016(1): 319-328. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2016.01.024
[16] 成国栋, 薛春汀. 黄河三角洲沉积地质学[M]. 地质出版社: 1997, 1-8.
CHENG Guodong, XUE Chunting. Sedimentary Geology of Yellow River Delta[M]. Geological Publishing House: 1997, 1-8.
[17] 赵松龄, 杨光复, 苍树溪, 等. 关于渤海湾西岸海相地层与海岸线问题[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 1978, 9:15-25
ZHAO Songling, YANG Guangfu, CANG Shuxi, et al. On the Marine stratigraphy and coastlines of the western coast of the gulf of Bohai [J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 1978, 9: 15-25.
[18] 薛春汀, 成国栋. 渤海西岸贝壳堤及全新世黄河三角洲体系//杨子赓, 林和茂. 中国沿海及近海地区第四纪进程与事件[M]. 海洋出版社: 1989, 117-125.
XUE Chunting, CHENG Guodong. Shelly ridges in west coast of Bohai Sea and Holocene Yellow River delta system//Yang Zigeng, Lin Hemao. Quaternary Processes and Events in China Offshore and Onshore Areas[M]. ChinaOcean Press: 1989, 117-125.
[19] 薛春汀, 周永青, 王桂玲. 古黄河三角洲若干问题的思考[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2003, 23(3):23-29
XUE Chunting, ZHOU Yongqing, WANG Guiling. Reviews of the Yellow River delta superlobes since 700BC [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2003, 23(3): 23-29.
[20] 薛春汀, 周永青, 朱雄华. 晚更新世末至公元前7世纪的黄河流向和黄河三角洲[J]. 海洋学报, 2004, 26(1):48-61
XUE Chunting, ZHOU Yongqing, ZHU Xionghua. The Yellow River course and delta from end of Late Pleistocene to the 7th century BC [J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2004, 26(1): 48-61.
[21] Xue Chunting. Historical changes in the Yellow River delta, China [J]. Marine Geology, 1993, 113: 321-330. doi: 10.1016/0025-3227(93)90025-Q
[22] Xue Chunting, Zhu Xionghua, Lin Hemao. Holocene sedimentary sequence, foraminifera and ostracodain westcoastal lowland of BohaiSea, China [J]. Quaternary Science Review, 1995, 14: 521-530. doi: 10.1016/0277-3791(95)00013-F
[23] He Lei, Xue Chunting, Ye Siyuan, Alessandro Amorosi, Yuan Hongming, Yang Shixiong, Edward A. Laws New evidence on the spatial-temporal distribution of superlobes in the Yellow River Delta Complex [J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2019, 214: 117-138. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2019.05.003
[24] 何磊, 叶思源, 袁红明, 薛春汀. 黄河三角洲利津超级叶瓣时空范围的再认识[J]. 地理学报, 2019, 74(1):146-616 doi: 10.11821/dlxb201901011
HE Lei, YE Siyuan, YUAN Hongming, XUE Chunting. Rethinking the spatio-temporal distribution of Lijin superlobei n the Yellow River Delta [J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2019, 74(1): 146-616. doi: 10.11821/dlxb201901011
[25] 雷雁翔, 何磊, 叶思源, 等. 渤海湾晚更新世晚期以来古河道分布和三角洲发育[J]. 中国地质, 2021待刊.
LEI Yanxiang, HE Lei, YE Siyuan, et al. Paleochannel distribution and delta development since the Late Pleistocene in the Bohai Bay[J]. Geology in China, 2021 to be published.
[26] 中国科学院海洋研究所. 渤海地质[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1985.
Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences. Bohai Sea Geology[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1985.
[27] 董礼先, 苏纪兰, 王康墡. 黄渤海潮流场及其与沉积物搬运的关系[J]. 海洋学报, 1989, 11:102-114
DONG Lixian, SU Jilan, WANG Kangshan. Tide current in the Yellow Sea and its relationship with sediment transport [J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 1989, 11: 102-114.
[28] 赵保仁, 庄国文, 曹德明, 雷方辉. 渤海的环流、潮余流及其对沉积物分布的影响[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 1995, 26(5):466-473 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.1995.05.003
ZHAO Baoren, ZHUANG Guoqiang, CAO Deming, LEI Fanghui. The circulation and tidal residual current of Bohai Sea and their influence on sediment disribution [J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 1995, 26(5): 466-473. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.1995.05.003
[29] Southon John, Kashgarian Michaele, Fontugne Michel, Merivier Bernard, Yim Wyss. Marine reservoir corrections for the Indian Ocean and Southeast Asia [J]. Radiocarbon, 2002, 44: 167-180. doi: 10.1017/S0033822200064778
[30] Reimer Paula J, Bard Edouard, Bayliss Alex, Beck J Warren, Blackwell Paul G, Ramsey Christopher Bronk, Buck Caitlin E, Cheng Hai, Edwards R Lawrence, Friedrich Michael, Grootes Pieter M, Guilderson Thomas P, Haflidason Haflidi, Hajdas Irka, Hatte Christine, Heaton Timothy J, Hoffmann Dirk L, Hogg Alan G, Hughen Konrad A, Kaiser K Felix, Kromer Bernd, Manning Sturt M, Niu Mu, Reimer Ron W, Richards David A, Scott E Marian, Southon John R, Staff Richard A, Turney Christian S M, Plicht Johannes van der. IntCal13 and Marine13 Radiocarbon Age Calibration Curves 0-50000 Years cal BP [J]. Radiocarbon, 2013, 55: 1869-1887. doi: 10.2458/azu_js_rc.55.16947
[31] Wintle Ann G. Luminescence dating: laboratory procedures and protocols [J]. Radiat. Meas, 1997, 27: 769-817. doi: 10.1016/S1350-4487(97)00220-5
[32] Qiu Jiandong, Liu Jian, Saito Yoshiki, Wang Hong, Yang Zigeng, Nakashima Rei. Sedimentary evolution ofthe Holocene subaqueous clinoform off the Southern Shandong Peninsula in theWestern South Yellow Sea [J]. Ocean Univ. China, 2014, 13(5): 747-760. doi: 10.1007/s11802-014-2227-z
[33] Liu Jin, Ye Siyuan, Allen Laws E, Lu Qingyuan. Sedimentary environment evolution and biogenic silica records over 33, 000 years in the Liaohe delta, China [J]. Limnology and Oceanography, 2017, 62(2): 474-489. doi: 10.1002/lno.10435
[34] 王雪飞, 叶思源, 韩宗珠, 等. 近33 ka以来辽河口沉积环境演变与生物硅记录[J]. 中国地质, 2015, 42(4):1092-1102 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2015.04.023
WANG Xuefei, YE Siyuan, HAN Zongzhu, et al. The sedimentary environment evolution and biogenic silica records of the Liaohe Estuary since 33 ka BP [J]. Geology in China, 2015, 42(4): 1092-1102. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2015.04.023
[35] Nair V D, Graetz D A, Reddy K R, Olila O G. Soil development in phosphatemined created wetlands of Florida, USA [J]. Wetlands, 2001, 21(2): 232-239. doi: 10.1672/0277-5212(2001)021[0232:SDIPMC]2.0.CO;2
[36] Azevedo W R, Faquin V, Femandes L A. Boron absorption in lowland soils flux southern of the state of Minas Gerais, Brazil [J]. Pesquisa AgTopecuaria Brasileira, 2001, 36(7): 957-964. doi: 10.1590/S0100-204X2001000700005
[37] Meyers P A. Preservation of elemental and isotopic source identification of sedimentary organic matter [J]. Chemical Geology, 1994, 114(3-4): 289-302. doi: 10.1016/0009-2541(94)90059-0
[38] Meyers P A. Organic geochemical proxies of paleoceanographic, paleolimnologic, and paleoclimatic processe [J]. Organic Geochemistry, 1997, 27(5-6): 213-250. doi: 10.1016/S0146-6380(97)00049-1
[39] Prahl F G, Ertel J R, Goni M A, et al. Terrestrial organic carbon contributions to sediments on the Washington margin [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1994, 58(14): 3035-3048. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(94)90177-5
[40] Thornton S F, McManus J. Application of organic carbon and nitrogen stable isotope and C/N ratios as source indicators of organic matter provenance in estuarine systems: Evidence from the Tay Estuary, Scotland [J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 1994, 38(3): 219-233. doi: 10.1006/ecss.1994.1015
[41] Ruttenberg K C, Goni M A. Phosphorus distribution, C:N:P ratios, and δ13Corg in arctic, temperate, and tropical coastal sediments: Tools for characterizing bulk sedimentary organic matter [J]. Marine Geology, 1997, 139(1): 123-145.
[42] Andrews J E, Greenaway A M, Dennis P F. Combined carbon isotope and C/N ratios as indicators of source and fate of organic matter in a poorly flushed, tropical estuary: Hunts Bay, Kingston Harbour, Jamaica [J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 1998, 46(5): 743-756. doi: 10.1006/ecss.1997.0305
[43] Muller A, Mathesius U. The paleoenvironments of coastal lagoons in the southern Baltic Sea, I. The application of sedimentary Corg/N ratios as source indicators of organic matter [J]. Palaeogeography Palaeoclimatology Palaeoecology, 1999, 145(1): 1-16.
[44] Bordovsky O K. Accumulation and transformation of organic substances in marine sediments [J]. Marine Geology, 1965, 3(1-2): 3-114. doi: 10.1016/0025-3227(65)90002-2
[45] Prahl F G, Bennett J T, Carpenter R. The early diagenesis of aliphatic hydrocarbons and organic matter in sedimentary particulates from Dabob Bay, Washington [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1980, 44(12): 1967-1976. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(80)90196-9
[46] Hatton R S, Patrick W H, DeLaune R D. Sedimentation, nutrient accumulation, and early digenesis in Louisiana Barataria Basin coastal marshes. In: Kennedy V S ed. Estuarine Comparisons. Academic Press, New York, USA: 1982, 255—267.
[47] Jia Jianjun, Gao Jianhua, Liu Yifei, Gao Shu, Yang Yang. Environmental changes in Shamei Lagoon, Hainan Island, China: Interactions between natural processes and human activities [J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2012, 52(30): 158-168.
[48] Chmura G L, Anisfeld S C, Cahoon D R, et al. Global carbon sequestration in tidal, saline wetland soils [J]. Global Biogeochemistry, 2003, 17(4): 1111-1121.
[49] Craft C B. Freshwater input structures soil properties, vertical accretion, and nutrient accumulation of Georgia and U.S. tidal marshes [J]. Limnol Oceanogr, 2007, 52(3): 1220-1230. doi: 10.4319/lo.2007.52.3.1220
-



 下载:
下载: