Characteristics and controlling factors of suspended sediment transportation in summer spring tide in Funing Bay
-
摘要:
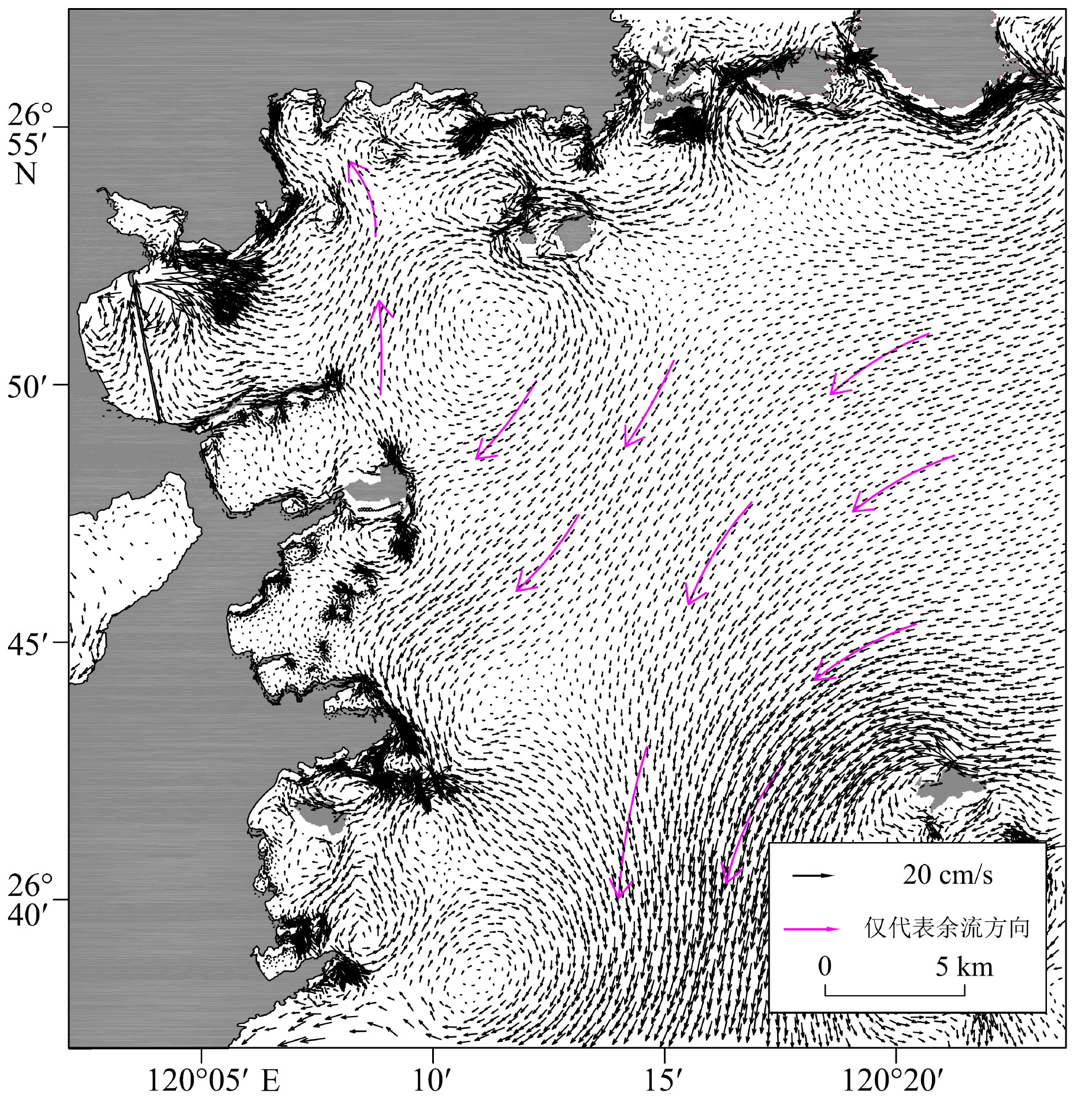
根据福宁湾夏季水文泥沙实测资料,分析了研究区悬浮泥沙浓度变化特征,研究了悬浮泥沙的输运机制,探讨了悬浮泥沙输运的控制因素。结果表明,平面上,悬浮泥沙浓度从湾内到湾外呈现递减的分布趋势;垂向上,各站位平均含沙量由底层向表层逐层递减。悬浮泥沙在湾内表现为向陆方向输运, 在湾口和湾外整体则向西南方向输运,平流输运在悬沙输运中占主导地位。正常天气下,研究区夏季的悬沙净输运方向与余流方向基本一致;西南强风天气下,研究区悬浮泥沙的浓度增大,其输运方向受风向控制指向东北向。闽浙沿岸流(夏季)活动较弱,对研究区悬浮泥沙的输运基本没有影响。
Abstract:Using the measured hydrological and sediment data in the summer Funing Bay, the variation characteristics of suspended sediment concentrations are analyzed, the transport mechanism of suspended sediment studied, and the controlling factors of suspended sediment transportation discussed in this paper. The results show that the suspended sediment concentration decreases from the inside to the outside of the bay in plane view. Vertically, the average sediment concentration of each station decreases from the bottom layer to the surface layer. Suspended sediment is transported landward within the bay, and moves southwestward in the mouth and outside the bay, and advection transport dominates the transport of suspended sediment. Under normal weather, the net transport direction of suspended sediment in the study area in summer is basically consistent with the residual flow direction. Under the southwest strong wind weather, however, the concentration of suspended sediment in the study area increases, and the transport direction turns to northeast. The Min-Zhe coastal current is weak in summer and has little effect on the transportation of suspended sediment in the study area.
-
Key words:
- suspended sediment /
- change in time and space /
- transport mechanism /
- control factors /
- Funing Bay
-

-
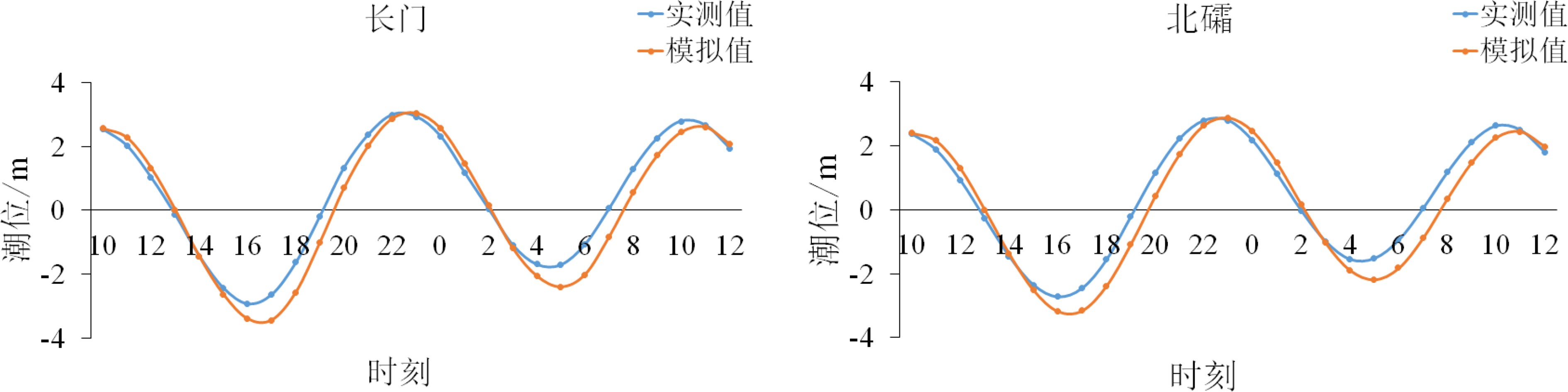
表 1 遥感卫片日期对应的风速风向
Table 1. The wind speed and direction corresponding to the date of the remote sensing image
时间 风速/(m/s) 风向/(°) 时间 风速/(m/s) 风向/(°) 2014.07.28 00:00 2.91 256 2016.08.19 00:00 8.38 228 2014.07.28 06:00 5.55 257 2016.08.19 06:00 8.98 222 2014.07.28 12:00 4.07 259 2016.08.19 12:00 11.46 224 2014.07.28 18:00 3.36 246 2016.08.19 18:00 14.87 232 表 2 各站位余流流速流向统计
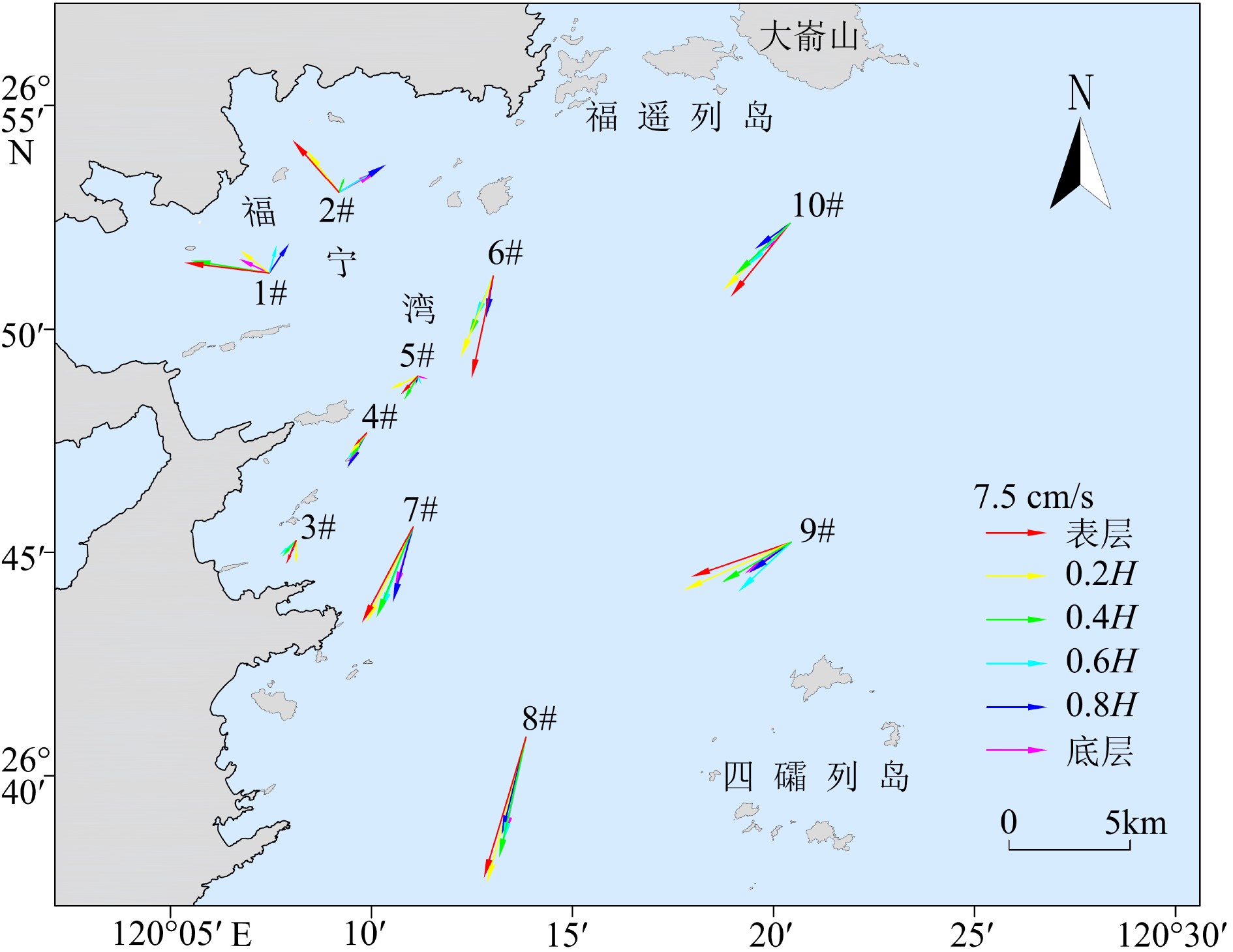
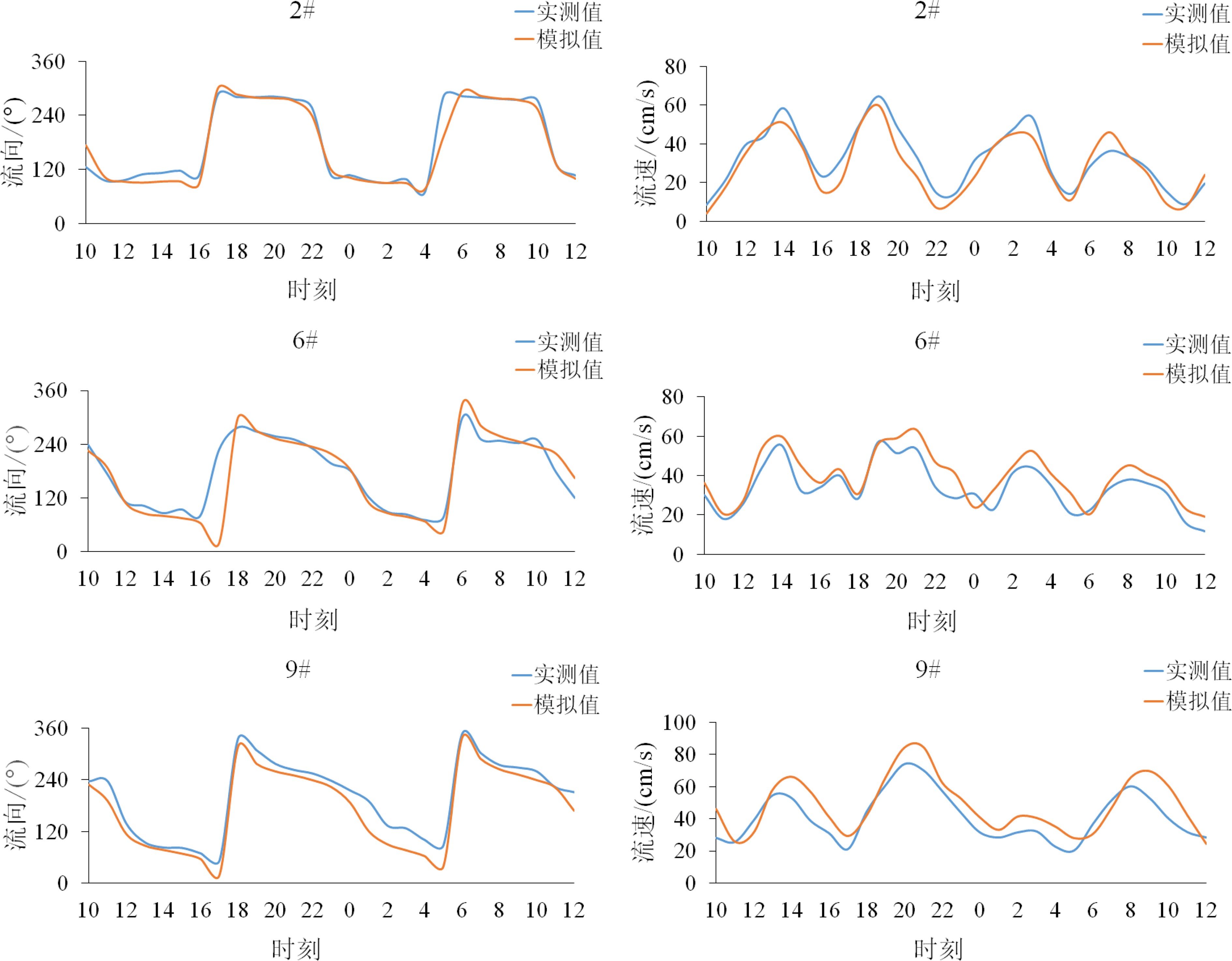
Table 2. Residual flow statistics for each station
站位 表层 0.2H 0.4H 0.6H 0.8H 底层 流速/
(cm/s)流向/
(°)流速/
(cm/s)流向/
(°)流速/
(cm/s)流向/
(°)流速/
(cm/s)流向/
(°)流速/
(cm/s)流向/
(°)流速/
(cm/s)流向/
(°)1# 13.4 277 5.8 308 10.9 279 4.3 359 4.9 18 6.3 292 2# 9.2 322 7.2 327 1.9 35 4.1 52 7.0 55 5.7 57 3# 2.4 215 1.7 168 1.7 230 2.1 238 1.4 206 0.2 173 4# 1.8 305 2.1 276 2.1 267 2.4 258 2.8 231 2.4 247 5# 2.2 263 3.8 276 2.2 239 1.2 26 1.1 347 2.1 28 6# 13.5 190 10.8 200 8.3 199 5.7 204 5.0 194 4.0 194 7# 12.7 213 12.3 211 11.1 206 10.3 206 8.7 198 7.6 200 8# 20.2 197 20.7 195 17.0 193 14.7 192 13.8 194 13.9 192 9# 14.3 256 15.4 251 10.2 247 9.0 237 6.9 247 7.3 248 10# 12.5 219 12.1 226 7.5 230 8.2 225 5.8 242 5.0 230 表 3 各层位平均悬浮泥沙浓度
Table 3. Average suspended sediment concentration in each layer
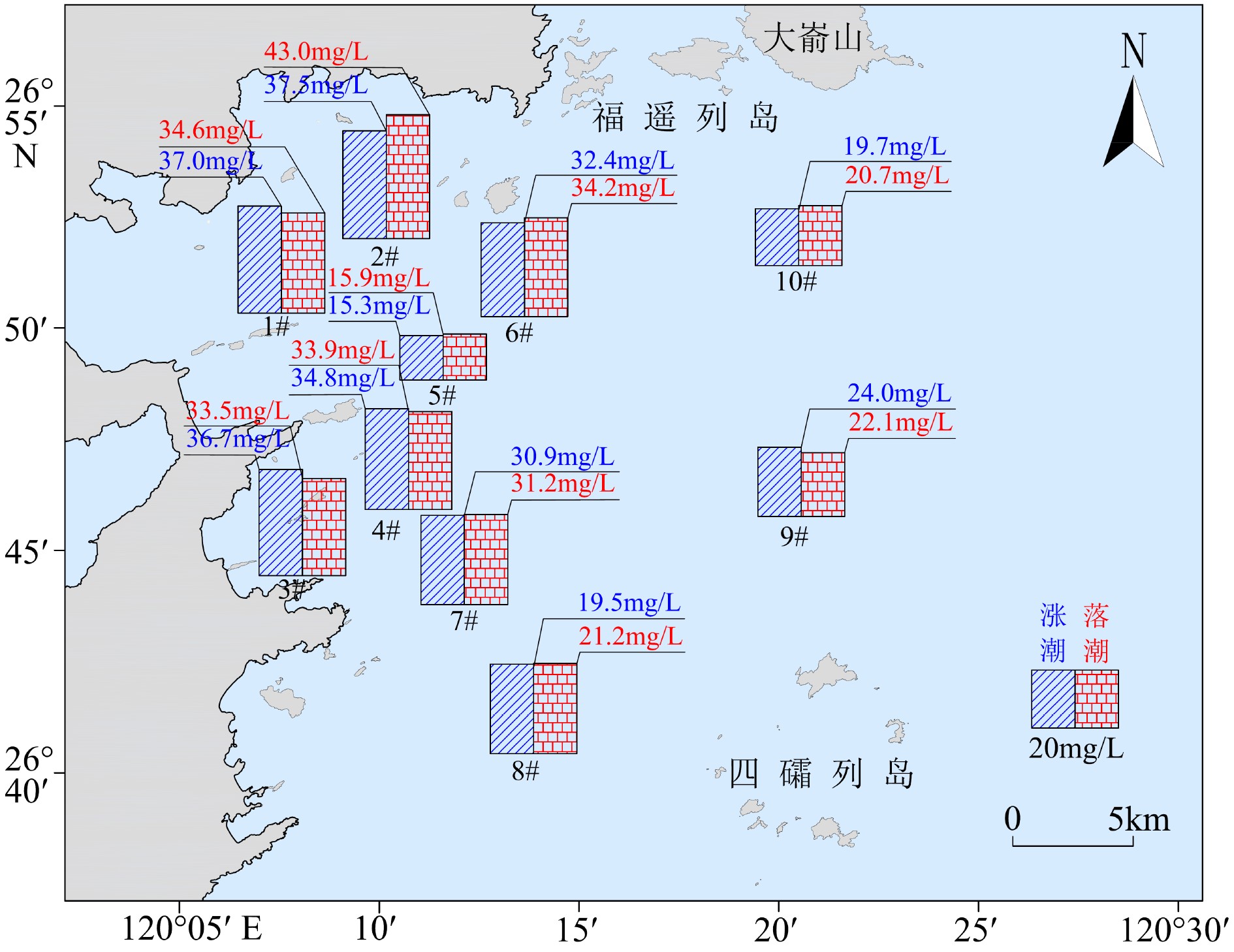
mg/L 站位 表层 0.2H 0.4H 0.6H 0.8H 底层 1# 27.8 32.0 29.8 39.9 52.1 59.1 2# 26.4 26.9 28.4 30.9 44.4 91.6 3# 31.3 31.7 32.3 32.9 34.8 48.9 4# 28.8 29.3 30.1 31.5 33.7 52.0 5# 9.9 10.2 10.9 12.9 17.5 27.5 6# 26.4 26.7 27.0 28.7 31.7 57.9 7# 22.0 22.7 24.0 26.9 33.7 55.8 8# 15.2 15.6 16.5 18.3 22.0 35.2 9# 19.9 20.1 20.7 21.6 23.2 32.3 10# 15.7 15.8 16.3 17.4 19.7 34.9 表 4 正常天气与强风天气悬浮泥沙浓度
Table 4. Suspended sediment concentration in normal and strong wind weather
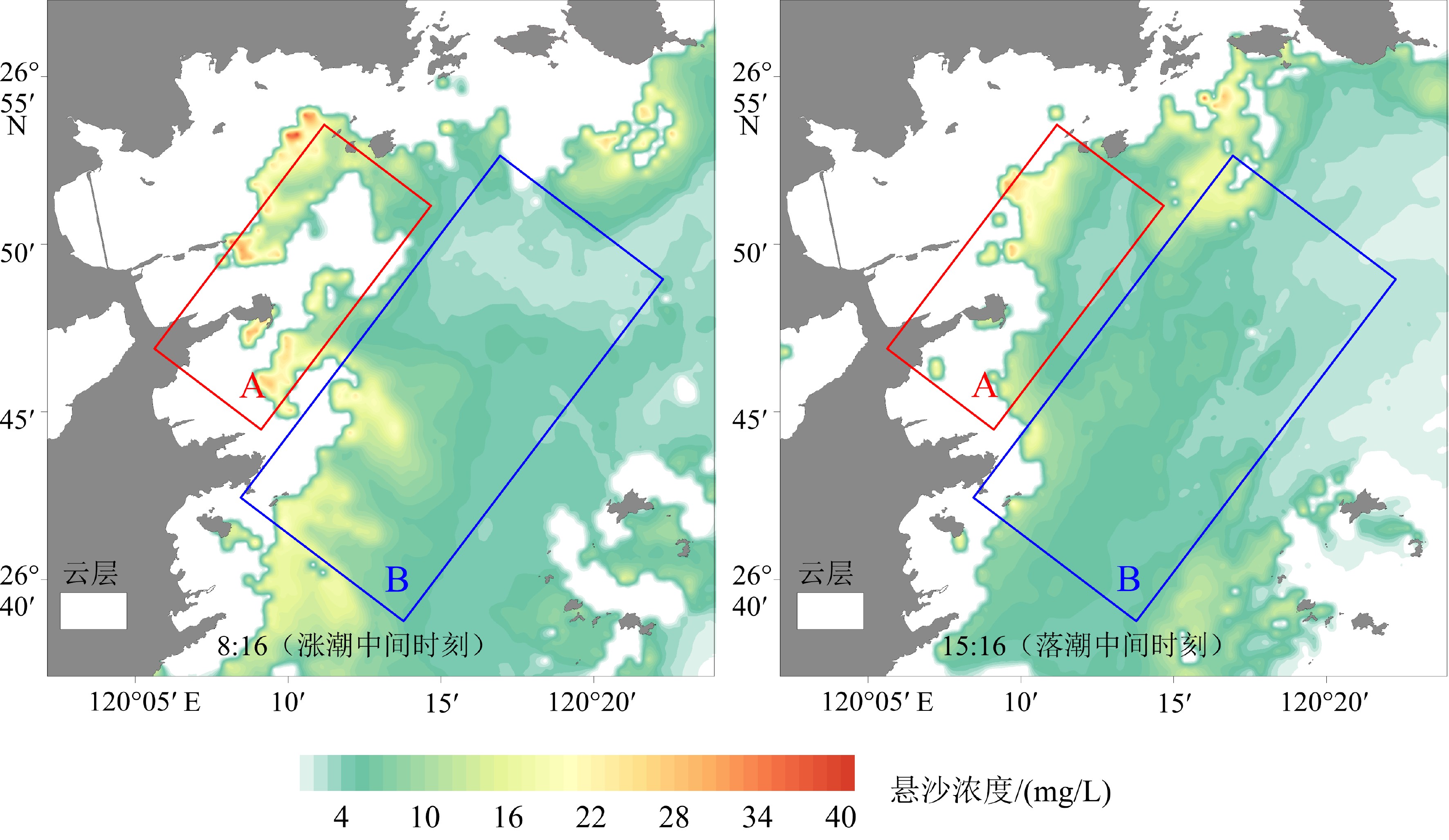
mg/L 区域 正常天气 强风天气 涨潮中间时刻 落潮中间时刻 涨潮中间时刻 落潮中间时刻 最小 最大 平均 最小 最大 平均 最小 最大 平均 最小 最大 平均 A 4.76 30.04 7.95 3.65 27.36 7.10 5.76 36.56 10.23 4.24 22.12 9.71 B 2.87 21.74 5.64 2.55 17.16 5.12 3.56 44.56 9.42 3.57 19.88 7.73 表 5 各站位输沙率
Table 5. Sediment transport rate of each station
g·s−1·m−1 站位 输沙项 T1 T2 T1+T2 T3+T4 T5 T6+T7+T8 T总 1# 输沙率 11.40 3.09 12.24 0.23 2.91 0.33 9.39 方向 301 220 287 185 79 133 293 2# 输沙率 6.69 2.74 4.61 0.25 4.15 0.50 4.75 方向 350 324 329 288 33 142 279 3# 输沙率 3.93 3.02 6.85 0.01 0.18 0.06 6.62 方向 210 184 187 179 256 263 188 4# 输沙率 4.91 7.22 11.37 0.30 0.21 0.07 11.78 方向 248 207 223 226 187 70 222 5# 输沙率 3.14 4.19 6.31 0.19 0.91 0.16 5.44 方向 273 211 237 181 68 102 232 6# 输沙率 30.35 6.32 36.23 0.17 2.19 0.28 34.22 方向 202 226 206 239 23 121 206 7# 输沙率 30.04 12.67 42.68 1.04 1.89 0.62 41.41 方向 206 201 205 192 50 39 203 8# 输沙率 44.82 4.85 49.46 0.43 1.81 0.27 47.93 方向 196 214 198 204 24 74 197 9# 输沙率 30.35 6.32 36.23 0.17 2.19 0.28 34.22 方向 202 226 206 239 23 121 206 10# 输沙率 25.15 5.33 30.35 0.29 1.66 0.29 28.76 方向 233 247 235 268 47 104 236 表 6 各站位输沙项占比
Table 6. Proportion of sediment transport items at each station
% 站位 T1 T2 T1+T2 T3+ T4 T5 T6+T7+T8 1# 121.5 32.9 130.4 2.4 31.0 11.4 2# 140.9 57.6 97.0 5.2 87.4 23.5 3# 59.3 45.6 103.4 0.2 2.7 1.2 4# 41.7 61.2 96.5 2.5 1.8 0.7 5# 57.8 77.0 116.1 3.5 16.7 3.4 6# 88.7 18.5 105.9 0.5 6.4 1.2 7# 72.6 30.6 103.1 2.5 4.6 1.5 8# 93.5 10.1 103.2 0.9 3.8 0.6 9# 88.7 18.5 105.9 0.5 6.4 1.2 10# 87.4 18.5 105.5 1.0 5.8 1.1 -
[1] Xie D F, Gao S, Wang Z B, et al. Numerical modeling of tidal currents, sediment transport and morphological evolution in Hangzhou Bay, China [J]. International Journal of Sediment Research, 2013, 28(3): 316-328. doi: 10.1016/S1001-6279(13)60042-6
[2] 刘潇, 冯秀丽, 刘杰, 等. 山东半岛靖海湾及其附近海域悬沙粒度特征及再悬浮作用研究[J]. 泥沙研究, 2013(4):68-73 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0468-155X.2013.04.011
LIU Xiao, FENG Xiuli, LIU Jie, et al. Characteristics of grain size distribution and resuspension process of suspended sediment in Jinghai Bay and its adjacent waters, Shandong Peninsula [J]. Journal of Sediment Research, 2013(4): 68-73. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0468-155X.2013.04.011
[3] Bian C W, Jiang W S, Quan Q, et al. Distributions of suspended sediment concentration in the Yellow Sea and the East China Sea based on field surveys during the four seasons of 2011 [J]. Journal of Marine Systems, 2013, 121-122: 24-35. doi: 10.1016/j.jmarsys.2013.03.013
[4] 宋泽坤, 张俊彪, 施伟勇, 等. 杭州湾口门中部水沙输运机制初探: 以岱衢洋为例[J]. 海洋通报, 2015, 34(3):267-274 doi: 10.11840/j.issn.1001-6392.2015.03.005
SONG Zekun, ZHANG Junbiao, SHI Weiyong, et al. Mechanism of water and suspended sediment transport in the middle outlet of the Hangzhou Bay: a case study of Daiquyang Sea [J]. Marine Science Bulletin, 2015, 34(3): 267-274. doi: 10.11840/j.issn.1001-6392.2015.03.005
[5] 陈斌, 高飞, 刘健. 夏季浙江沿岸陆架区泥沙输运机制[J]. 海洋学报, 2017, 39(3):96-105
CHEN Bin, GAO Fei, LIU Jian. Sediment transport mechanism in the Zhejiang inner continental shelf in summer [J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2017, 39(3): 96-105.
[6] Hu R J, Ma F, Wu J Z, et al. Sediment transport in the nearshore area of Phoenix Island [J]. Journal of Ocean University of China, 2016, 15(5): 767-782. doi: 10.1007/s11802-016-2967-z
[7] 陈瑞瑞, 蒋雪中. 长江河口悬浮泥沙向浙闽沿岸输运近期变化的遥感分析[J]. 海洋科学, 2017, 41(3):89-101 doi: 10.11759/hykx20160920002
CHEN Ruirui, JIANG Xuezhong. Analysis of suspended sediment variations from the Yangtze Estuary to Zhejiang-Fujian Provincial coastal waters using remotely sensed data [J]. Marine Sciences, 2017, 41(3): 89-101. doi: 10.11759/hykx20160920002
[8] Doxaran D, Froidefond J M, Lavender S, et al. Spectral signature of highly turbid waters: Application with SPOT data to quantify suspended particulate matter concentrations [J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2002, 81(1): 149-161. doi: 10.1016/S0034-4257(01)00341-8
[9] Waghmare S M, Hanamgond P T, Mitra D, et al. Application of remote sensing and GIS techniques to study sediment movement along Harwada Beach, Uttar Kannada, West Coast of India [J]. Journal of Coastal Research, 2020, 36(6): 1121-1129.
[10] Li P, Ke Y H, Wang D W, et al. Human impact on suspended particulate matter in the Yellow River Estuary, China: Evidence from remote sensing data fusion using an improved spatiotemporal fusion method [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2021, 750: 141612. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.141612
[11] Ryu J H, Han H J, Cho S, et al. Overview of geostationary ocean color imager (GOCI) and GOCI data processing system (GDPS) [J]. Ocean Science Journal, 2012, 47(3): 223-233. doi: 10.1007/s12601-012-0024-4
[12] 刘波, 程乾, 曾焕建, 等. 基于GOCI数据的杭州湾跨海大桥两侧水域悬浮泥沙浓度空间分异规律研究[J]. 杭州师范大学学报: 自然科学版, 2016, 15(1):102-107
LIU Bo, CHENG Qian, ZENG Huanjian, et al. On the suspended sediment concentration distribution and diversity of the waters on both sides of Hangzhou Bay sea-crossing bridge based on GOCI data [J]. Journal of Hangzhou Normal University: Natural Science Edition, 2016, 15(1): 102-107.
[13] 周钰, 宣基亮, 黄大吉. 基于GOCI观测数据的长江浅滩悬浮泥沙的潮周期变化特征[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2020, 63(9):1381-1389 doi: 10.1007/s11430-019-9618-7
ZHOU Yu, XUAN Jiliang, HUANG Daji. Tidal variation of total suspended solids over the Yangtze Bank based on the geostationary ocean color imager [J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 2020, 63(9): 1381-1389. doi: 10.1007/s11430-019-9618-7
[14] 杨雪飞. 基于GOCI和数值模拟的东海近岸悬浮泥沙浓度逐时变化研究[D]. 中国科学院研究生院(上海技术物理研究所)博士学位论文, 2016.
YANG Xuefei. Diurnal variation of suspended sediment concentration coupled GOCI and numerical simulation in coastal waters of the East China Sea[D]. Doctor Dissertation of Shanghai Institute of Technical Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2016.
[15] Yin W B, Huang D J. Evolution of submesoscale coastal frontal waves in the East China Sea based on geostationary ocean color imager observational data [J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2016, 43(18): 9801-9809. doi: 10.1002/2016GL070232
[16] 艾乔, 石勇, 高建华, 等. 辽东半岛东岸近海泥区悬沙浓度的时空分布及控制因素分析[J]. 海洋学报, 2019, 41(1):121-133
AI Qiao, SHI Yong, GAO Jianhua, et al. Spatio-temporal distribution and control factors of surface suspended sediment concentration in the mud deposition along eastern coast offshore of the Liaodong Peninsula [J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2019, 41(1): 121-133.
[17] Pang C G, Yuan D L, Jiang M, et al. Observed cross-shelf suspended sediment flux in the southern Yellow Sea in winter [J]. Marine Geology, 2020, 419: 106067. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2019.106067
[18] 杜家笔, 裴艳东, 高建华, 等. 弱动力浅海中的悬沙输运机制: 以天津港附近海域为例[J]. 海洋学报, 2012, 34(1):136-144
DU Jiabi, PEI Yandong, GAO Jianhua, et al. The suspended sediment transport associated with low flow patterns in shallow waters: a case study from the Tianjin subtidal area [J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2012, 34(1): 136-144.
[19] Moskalski S, Floc'h F, Verney R. Suspended sediment fluxes in a shallow macrotidal estuary [J]. Marine Geology, 2020, 419: 106050. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2019.106050
[20] Milliman J D, Meade R H. World-wide delivery of river sediment to the oceans [J]. Journal of Geology, 1983, 91(1): 1-21. doi: 10.1086/628741
[21] Pang C G, Li K, Hu D X. Net accumulation of suspended sediment and its seasonal variability dominated by shelf circulation in the Yellow and East China Seas [J]. Marine Geology, 2016, 371: 33-43. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2015.10.017
[22] Qiao L L, Liu S D, Xue W J, et al. Spatiotemporal variations in suspended sediments over the inner shelf of the East China Sea with the effect of oceanic fronts [J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2020, 234: 106600. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2020.106600
[23] Wang S Q, Mao Y, Zheng L F, et al. Remote sensing of water turbidity in the Eastern China Seas from Geostationary Ocean Colour Imager [J]. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 2020, 41(11): 4080-4101. doi: 10.1080/01431161.2020.1714775
[24] 薛碧颖, 王厚杰, 张勇, 等. 闽北附近海域悬浮体输运及通量的季节变化[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2018, 38(5):30-40
XUE Biying, WANG Houjie, ZHANG Yong, et al. Seasonal variations of suspended sediments in transport and flux in the coastal area of the northern Fujian Province [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2018, 38(5): 30-40.
[25] 孟令鹏, 胡日军, 李毅, 等. 福宁湾海域冬季大潮期悬浮泥沙输运特征[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2020, 40(3):61-73
MENG Lingpeng, HU Rijun, LI Yi, et al. Transport characteristics of suspended sediment in Funing Bay during spring tide in winter [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2020, 40(3): 61-73.
[26] 江甘兴. 福建海区的潮汐和潮流[J]. 台湾海峡, 1992, 11(2):89-94
JIANG Ganxing. Tides and tidal currents in Fujian waters [J]. Journal of Oceanography in Taiwan Strait, 1992, 11(2): 89-94.
[27] Guan B X. Patterns and structures of the currents in Bohai, Huanghai and East China Seas[M]//Zhou D, Liang Y B, Zeng C K. Oceanology of China Seas. Dordrecht: Springer, 1994: 17-26.
[28] Xiao Y, Wu Z, Cai H Y, et al. Suspended sediment dynamics in a well-mixed estuary: The role of high suspended sediment concentration (SSC) from the adjacent sea area [J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2018, 209: 191-204. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2018.05.018
[29] Ingram R G. Characteristics of the Great Whale River plume [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 1981, 86(C3): 2017-2023. doi: 10.1029/JC086iC03p02017
[30] Uncles R J, Elliott R C A, Weston S A. Dispersion of salt and suspended sediment in a partly mixed estuary [J]. Estuaries, 1985, 8(3): 256-269. doi: 10.2307/1351486
[31] 范恩梅, 陈沈良, 张国安. 连云港海域水文泥沙运动特征[J]. 世界科技研究与发展, 2009, 31(4):703-707 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6055.2009.04.040
FAN Enmei, CHEN Shenliang, ZHANG Guoan. The hydrological and sediment characteristics in lianyungang coastal waters [J]. World Sci-Tech R & D, 2009, 31(4): 703-707. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6055.2009.04.040
[32] 史文奇, 邢传玺, 马玉贤, 等. 辽东湾中部西岸浅水海域冬季实测海流分析[J]. 海洋通报, 2018, 37(4):389-395 doi: 10.11840/j.issn.1001-6392.2018.04.004
SHI Wenqi, XING Chuanxi, MA Yuxian, et al. Analysis of current observation in shallow inshore waters along the west coast of central Liaodong Bay in winter [J]. Marine Science Bulletin, 2018, 37(4): 389-395. doi: 10.11840/j.issn.1001-6392.2018.04.004
[33] Bowden K F. The mixing processes in a tidal estuary [J]. International Journal of Air and Water Pollution, 1965, 7: 343-356.
[34] Yu Q, Wang Y W, Gao J H, et al. Turbidity maximum formation in a well-mixed macrotidal estuary: The role of tidal pumping [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 2014, 119(11): 7705-7724. doi: 10.1002/2014JC010228
[35] Man J, Pang C G, Liu Z L, et al. Sediment resuspension in winter in an exceptional low suspended sediment concentration area off Qinhuangdao in the Bohai Sea [J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2020, 245: 106859. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2020.106859
[36] 刘波, 胡日军, 袁晓东, 等. 龙口近岸海域潮流作用下悬浮泥沙时空分布特征及输运机制[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2020, 40(4):55-66
LIU Bo, HU Rijun, YUAN Xiaodong, et al. Spatiotemporal distribution pattern and transport mechanism of suspended sediments in Longkou offshore under the action of tidal current [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2020, 40(4): 55-66.
[37] 边淑华, 胡泽建, 迟万清, 等. 粉砂质海岸大风天泥沙运动研究[J]. 海洋科学, 2007, 31(12):4-8 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3096.2007.12.002
BIAN Shuhua, HU Zejian, CHI Wanqing, et al. Sediment movement on the silty coast during a storm [J]. Marine Sciences, 2007, 31(12): 4-8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3096.2007.12.002
[38] 张火明, 邵力行, 田中仁, 等. 基于MIKE21模型的椒江口台州湾在异常天气下的泥沙输运研究[J]. 中国计量大学学报, 2019, 30(4):441-448
ZHANG Huoming, SHAO Lixing, TIAN Zhongren, et al. Study on sediment transport in Taizhou Bay of Jiaojiang Estuary based on MIKE21 model under abnormal weather [J]. Journal of China University of Metrology, 2019, 30(4): 441-448.
[39] 王华强, 高抒. 杭州湾北岸高潮滩沉积与沿岸物质输运趋势[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2007, 27(6):25-30
WANG Huaqiang GAO Shu. Tidal flat sediment characteristics and transport trends along the northern bank of Hangzhou bay [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2007, 27(6): 25-30.
[40] 乔璐璐. 冬季大风事件下渤黄海环流及泥沙输运过程研究[D]. 中国海洋大学博士学位论文, 2008.
QIAO Lulu. Circulation and sediments transport due winter storms in the Bohai Sea and Yellow Sea[D]. Doctor Dissertation of Ocean University of China, 2008.
[41] 曾定勇, 倪晓波, 黄大吉. 冬季浙闽沿岸流与台湾暖流在浙南海域的时空变化[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2012, 42(7):1123-1134 doi: 10.1360/zd-2012-42-7-1123
ZENG Dingyong, NI Xiaobo, HUANG Daji. Temporal and spatial variability of the ZheMin Coastal Current and the Taiwan Warm Current in winter in the southern Zhejiang coastal sea [J]. Scientia Sinica Terrae, 2012, 42(7): 1123-1134. doi: 10.1360/zd-2012-42-7-1123
[42] 邱云, 许金电, 郭小钢, 等. 东北季风期台湾海峡的逆温现象[J]. 海洋学报, 2012, 34(2):13-22
QIU Yun, XU Jindian, GUO Xiaogang, et al. Temperature inversion in the Taiwan Strait during northeast monsoon [J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2012, 34(2): 13-22.
[43] 万小芳, 潘爱军, 郭小钢, 等. 台湾海峡西侧水动力环境的季节变化特征[J]. 应用海洋学学报, 2013, 32(2):156-163 doi: 10.3969/J.ISSN.2095-4972.2013.02.002
WAN Xiaofang, PAN Aijun, GUO Xiaogang, et al. Seasonal variation features of the hydrodynamic environment in the western Taiwan Strait [J]. Journal of Applied Oceanography, 2013, 32(2): 156-163. doi: 10.3969/J.ISSN.2095-4972.2013.02.002
[44] 张志欣. 中国近海沿岸流及毗邻流系的观测与分析研究[D]. 中国海洋大学博士学位论文, 2014.
ZHANG Zhixin. Observation and analysis of the coastal current and its adjacent current system in the China offshore waters[D]. Doctor Dissertation of Ocean University of China, 2014.
[45] 王颖. 中国海洋地理[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2013.
WANG Ying. Marine Geography of China[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2013.
-




 下载:
下载: