Spatio-temporal variation and influencing factors of seafloor sediment grain size off the mouth of Dingzi Bay of Southern Shandong Peninsula
-
摘要:
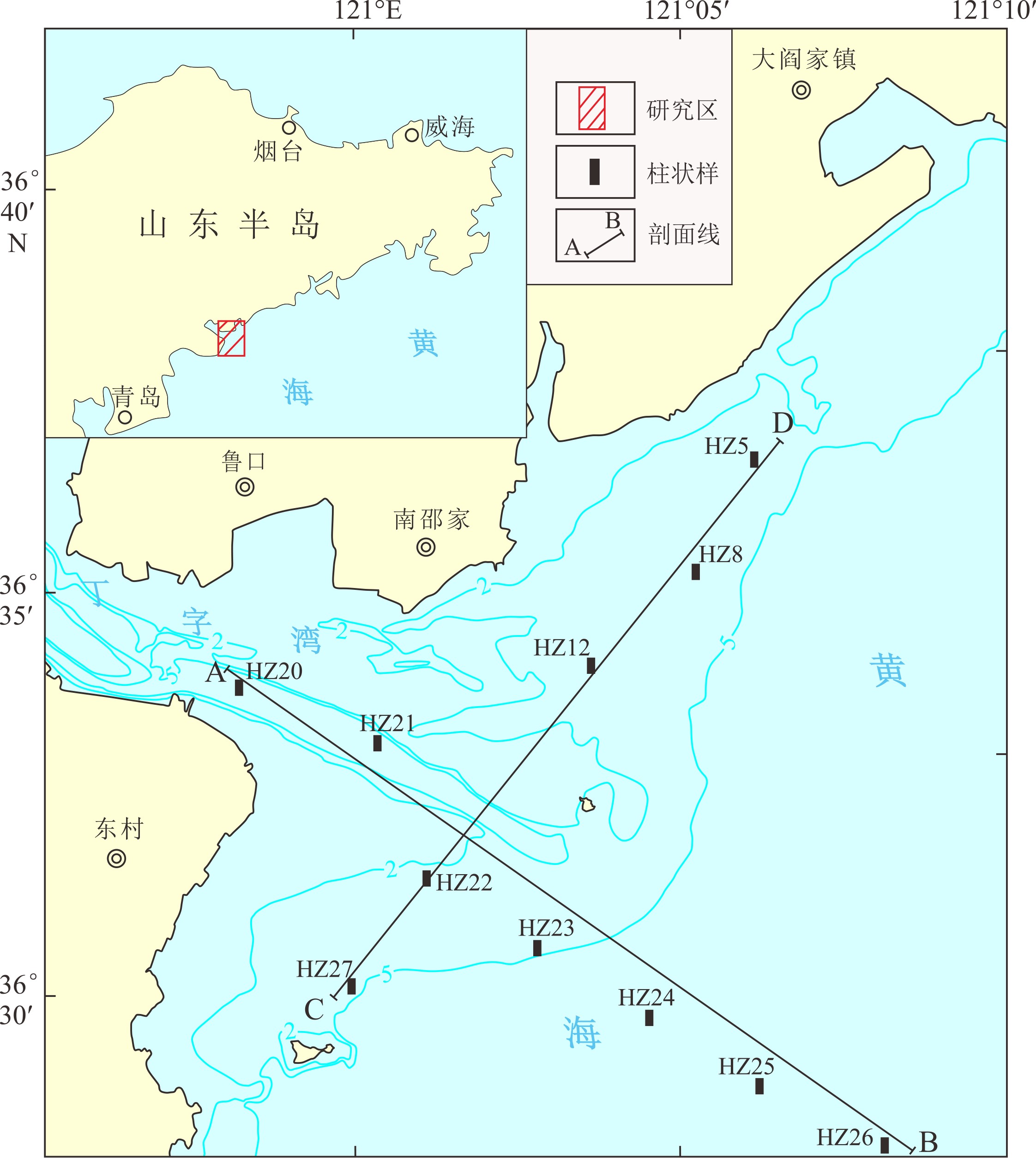
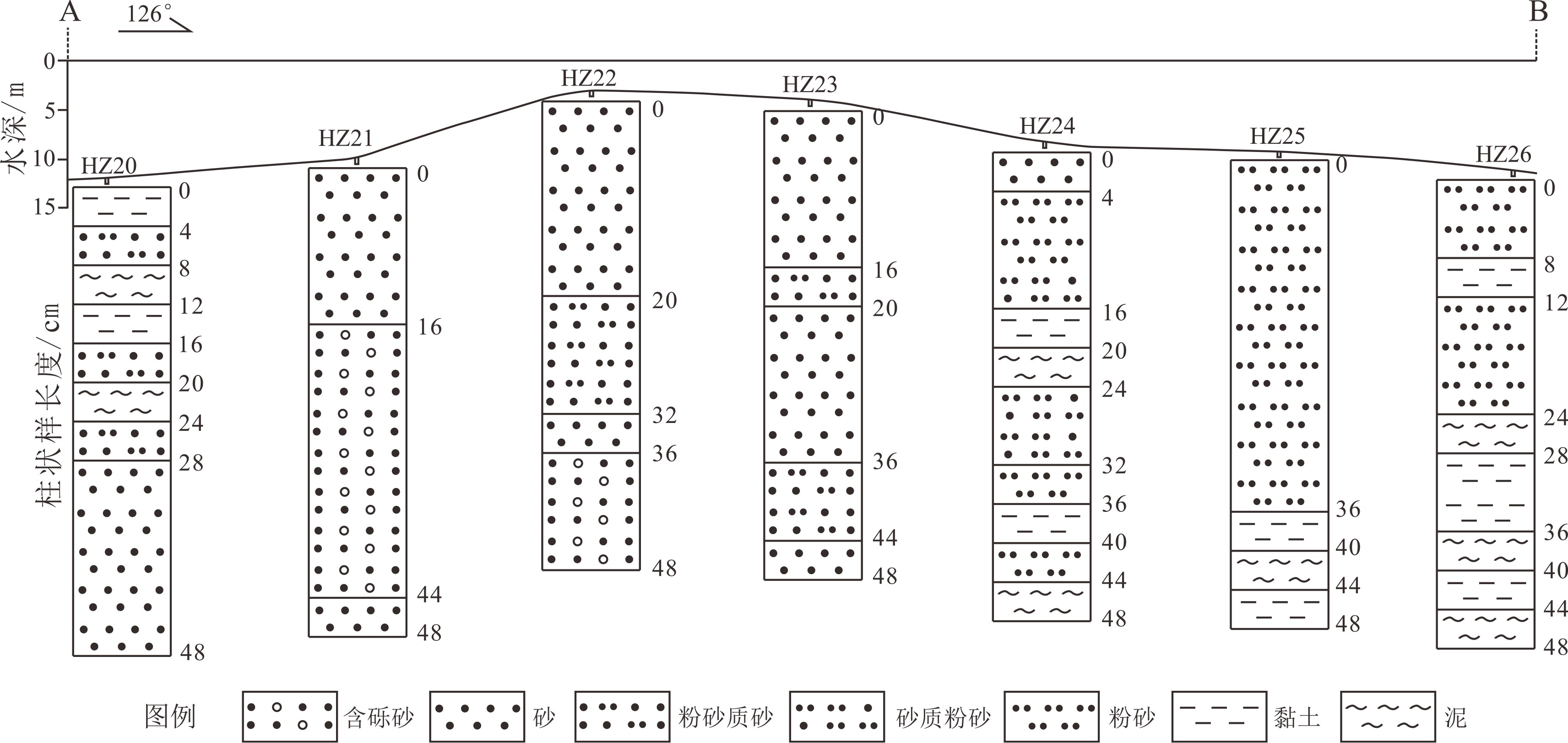
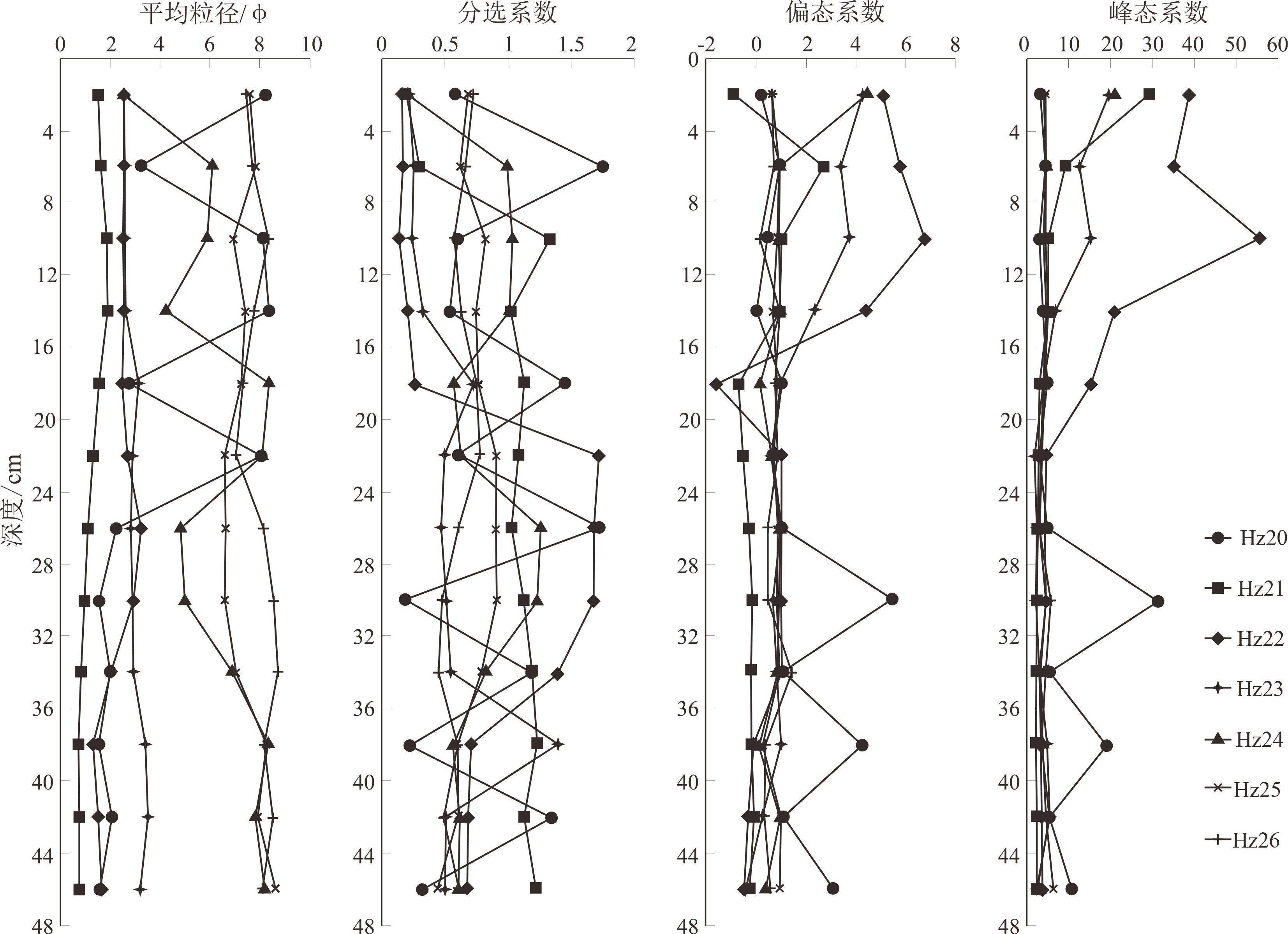
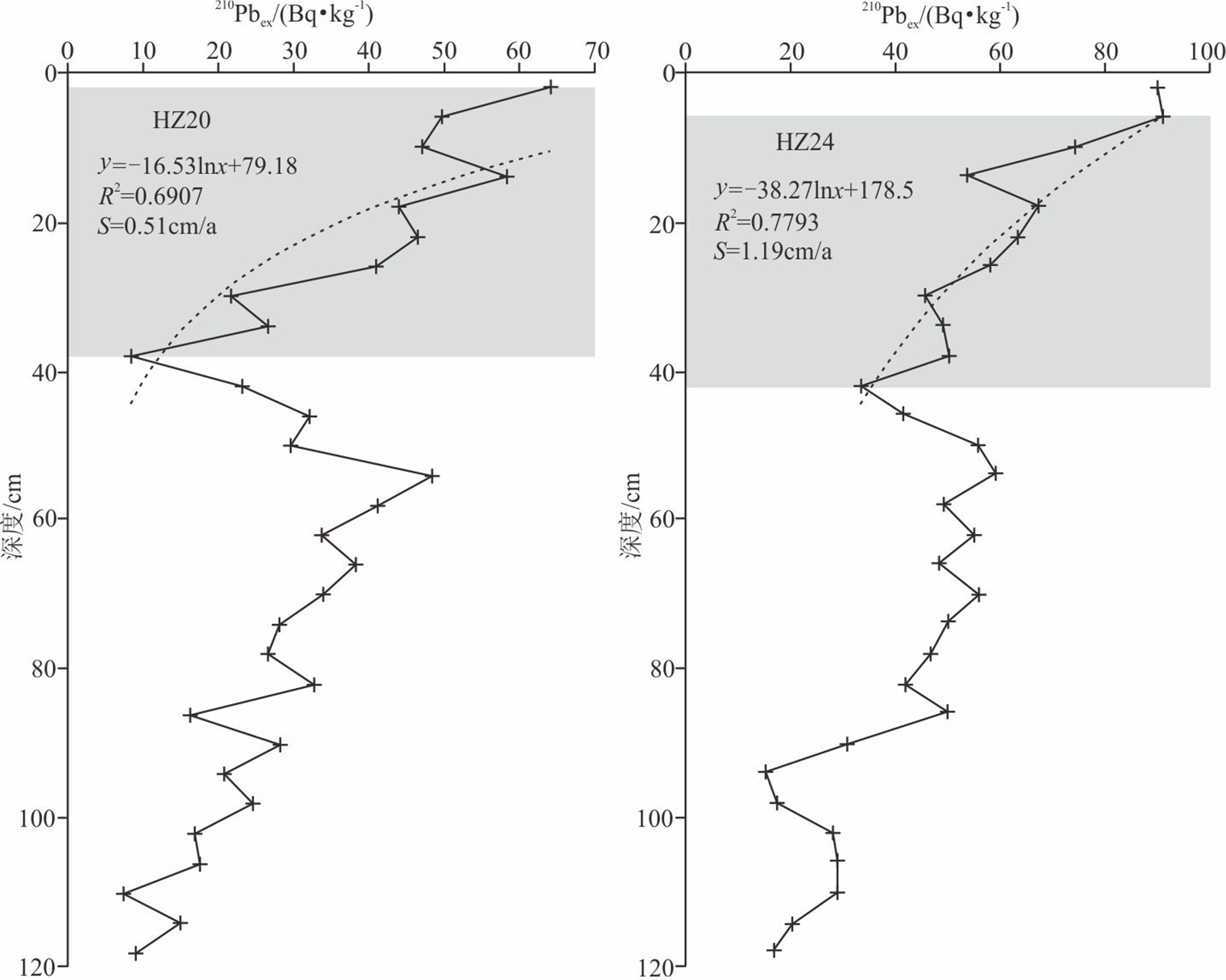
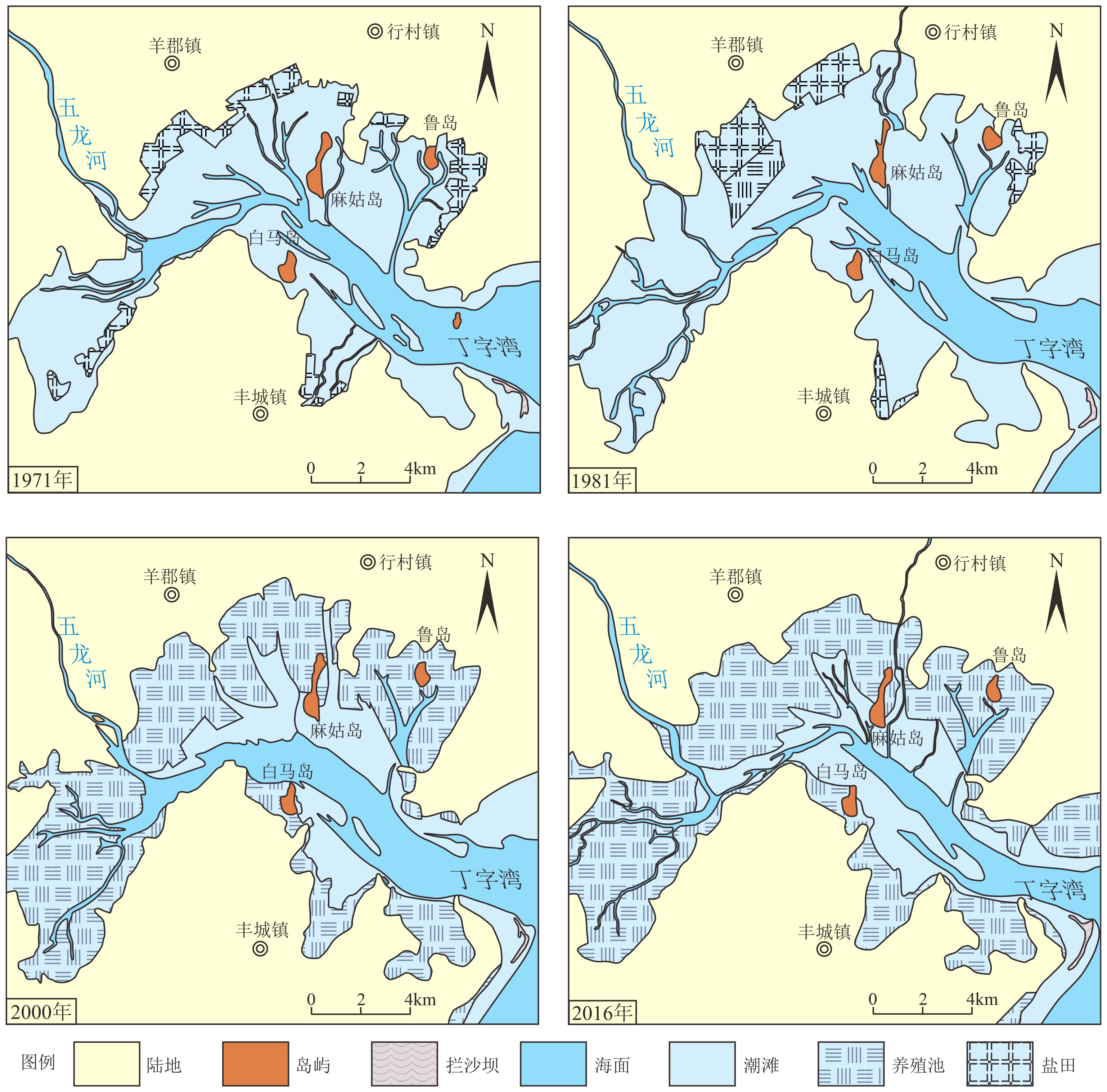
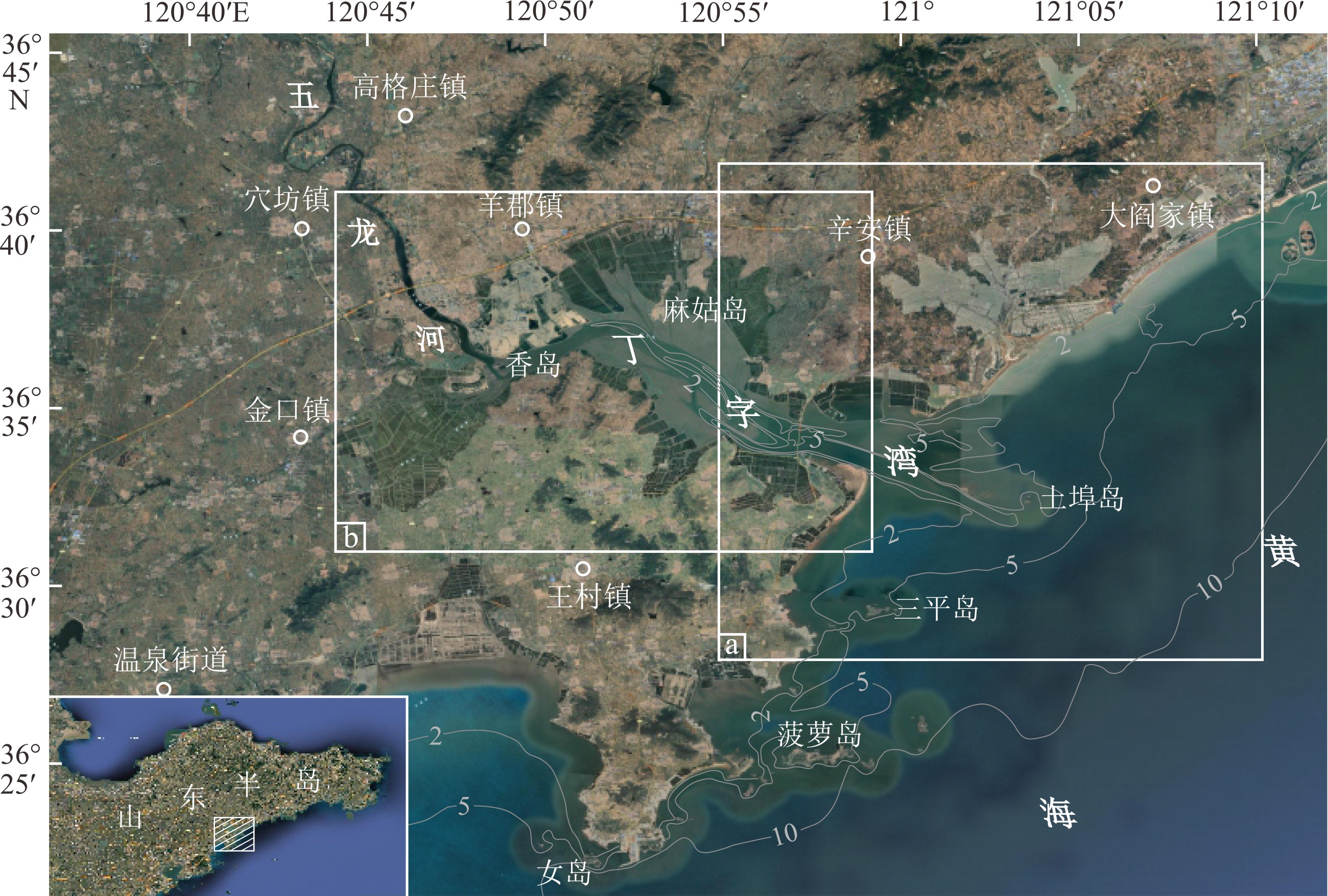
对丁字湾口外浅海区平行海岸线及垂直海岸线方向上的11个柱状沉积物进行了粒度和210Pb放射性活度测试,分析了沉积物类型和粒度参数变化特征并计算了沉积速率,结合丁字湾地貌演变、流域人类活动变化,分析了人类活动对丁字湾口外滨海段沉积物粒度演变的影响。海底柱状沉积物可划分7种类型,水平方向上平均粒径Φ值从三角洲中心向四周整体呈现逐渐增大的趋势,垂直方向上平均粒径Φ值呈现不规则变化特征。沉积物分选性属于较好—中等,偏态为近对称—正偏,峰态为尖锐。不同沉积物类型及特征参数揭示沉积时期相应的水动力环境,砂、含砾砂和粉砂质砂及其较小的平均粒径Φ值揭示相对较强的水动力环境,砂质粉砂、粉砂、黏土和泥及其较大的平均粒径Φ值揭示了相对较弱的水动力环境。受不同水动力环境影响,三角洲顶端和前缘平均沉积速率分别为0.51和1.19 cm/a。与1980年前相比,1980年以后人类对滩涂围垦等活动影响强度加大,海湾纳潮空间、入海泥沙流量和流速均减小,在人类影响范围区域内的沉积物颗粒具有总体向上变细的趋势。
Abstract:11 columnar sediment samples are collected off the mouth of Dingzi Bay for grain size analysis and 210Pb radioactivity measurement. With the results, the sediments are classified and grain size parameters and sedimentation rate calculated. Combined with the geomorphologic evolution of Dingzi Bay and the change in human activities in the Wulong River Basin, the influence of human activities on the evolution of sediment grain size in the coastal section out the Wulong River estuary is discussed. The results suggested that the columnar sediments may be divided into seven types, and the mean grain size (Φ) in the horizontal direction shows a trend of increase from the deltaic center to all directions as well as an irregular pattern in vertical direction. The sediment sorting changes from good to medium, with a near-symmetric-positive skewness and sharp kurtosis. Sediment types and their diagnostic parameters may be used as tools to reveal depositional environments. Sand, gravelly and silty sand and their small Φ-values suggest relatively strong hydrodynamic environments, while sandy silt, silt, clay and mud and their large Φ-values indicate relatively weak hydrodynamic environments. The average sedimentation rate at the top and front of the delta was 0.51 cm·a−1 and 1.19 cm·a−1, respectively. Human activities in beach reclamation and others increased since 1980, which have caused the decrease in tidal space, sediment discharge and velocity into the sea. As the results, the overall trend of sediment particles in the human-influenced area becomes finer.
-
Key words:
- ebb tide delta /
- grain size parameters /
- sedimentation rate /
- human activity /
- Dingzi Bay /
- southern Shandong Peninsula
-

-
表 1 沉积物粒度参数分级[27]
Table 1. Classification of grain size parameters
分选系数 定性描述 偏态系数 定性描述 峰态系数 定性描述 <0.35 分选极好 0.35~0.50 分选好 >1.30 极正偏 <1.70 很平坦 0.50~0.71 分选较好 0.43~1.30 正偏 1.70~2.55 平坦 0.71~1.00 分选中等 −0.43~0.43 近对称 2.55~3.70 中等(正态) 1.00~2.00 分选较差 −0.43~−1.30 负偏 3.70~7.40 尖锐 2.00~4.00 分选差 <−1.30 极负偏 >7.40 很尖锐 >4.00 分选极差 -
[1] 夏东兴, 刘振夏. 中国海湾的成因类型[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 1990, 21(2):185-191
XIA Dongxing, LIU Zhenxia. Classification of bays in China [J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 1990, 21(2): 185-191.
[2] 张忍顺, 李坤平. 黄渤海沿岸海湾-溺谷型潮汐汊道的地貌结构[J]. 黄渤海海洋, 1994, 12(4):1-10
ZHANG Renshun, LI Kunping. Geomorphological structure of Bay and Drowned-Valley type tidal inlet along coasts of the Huanghai and Bohai seas [J]. Journal of Oceanography of Huanghai & Bohai Seas, 1994, 12(4): 1-10.
[3] 田清, 王庆, 战超, 等. 最近60年来气候变化和人类活动对山地河流入海径流、泥沙的影响: 以胶东半岛南部五龙河为例[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2012, 43(5):891-899 doi: 10.11693/hyhz201205003003
TIAN Qing, WANG Qing, ZHAN Chao, et al. Impact of climate change and human activities on the runoff and sediment load discharged into the sea from mountainous rivers during the last 60 years: a case study of Wulong river in southern Jiaodong Peninsula [J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2012, 43(5): 891-899. doi: 10.11693/hyhz201205003003
[4] 陈聚法, 周诗赉, 马绍赛. 丁字湾水文环境特征[J]. 黄渤海海洋, 1997, 15(1):58-63
CHEN Jufa, ZHOU Shilai, MA Shaosai. The hydrological conditions of Dingzi Bay [J]. Journal of Oceanography of Huanghai & Bohai Seas, 1997, 15(1): 58-63.
[5] 战超, 王庆, 夏艳玲, 等. 胶东半岛南部典型海湾地貌过程对滩涂养殖的响应[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2013, 44(2):283-291 doi: 10.11693/hyhz201302003003
ZHAN Chao, WANG Qing, XIA Yanling, et al. The response of geomorphic process to aquaculture on tidal flat in typical tidal inlet bays along the southern Jiaodong Peninsula [J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2013, 44(2): 283-291. doi: 10.11693/hyhz201302003003
[6] 孙英兰, 张越美. 丁字湾物质输运及水交换能力研究[J]. 青岛海洋大学学报, 2003, 33(1):1-6
SUN Yinglan, ZHANG Yuemei. A numerical model of pollutant transport and seawater exhange in Dingzi Bay [J]. Journal of Ocean University of Qingdao, 2003, 33(1): 1-6.
[7] 杨世伦. 长江口沉积物粒度参数的统计规律及其沉积动力学解释[J]. 泥沙研究, 1994(3):23-31
YANG Shilun. Statistic features for grain-size parameters of the Yangtze River estuary and their hydrodynamic explanation [J]. Journal of Sediment Research, 1994(3): 23-31.
[8] 赵建春, 戴志军, 李九发, 等. 强潮海湾近岸表层沉积物时空分布特征及水动力响应: 以杭州湾北岸为例[J]. 沉积学报, 2008, 26(6):1043-1051
ZHAO Jianchun, DAI Zhijun, LI Jiufa, et al. Study on the characteristics of temporal and spatial changes in properties of surface sediment on near-shore seabed of strong-tide bay: a case from the north bank of Hangzhou Bay in Shanghai [J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2008, 26(6): 1043-1051.
[9] 高抒, Collins M. 沉积物粒径趋势与海洋沉积动力学[J]. 中国科学基金, 1998, 12(4):241-246 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8217.1998.04.002
GAO Shu, Collins M. The use of grain size trends in marine sediment dynamics [J]. Bulletin of National Natural Science Foundation of China, 1998, 12(4): 241-246. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8217.1998.04.002
[10] 汤世凯, 于剑峰, 李金鹏, 等. 丁字湾近岸海域表层沉积物粒度特征及沉积动力环境[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2019, 39(2):70-78
TANG Shikai, YU Jianfeng, LI Jinpeng, et al. Grain size characteristics and dynamic environment of surface sediments on the near shore seabed of Dingzi Bay [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2019, 39(2): 70-78.
[11] 程知欣, 刘月, 李富祥, 等. 近百年来人类活动对鸭绿江口河床演变影响的粒度沉积记录[J]. 辽东学院学报:自然科学版, 2012, 19(2):89-93
CHENG Zhixin, LIU Yue, LI Fuxiang, et al. Grain size sedimentary records representing influence of human activities on riverbed evolution in Yalu River Estuary during recent 100 years [J]. Journal of Eastern Liaoning University:Natural Science, 2012, 19(2): 89-93.
[12] 赵华云, 戴仕宝, 杨世伦, 等. 流域人类活动对三角洲演变影响研究进展[J]. 海洋科学, 2007, 31(12):83-87 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3096.2007.12.018
ZHAO Huayun, DAI Shibao, YANG Shilun, et al. Progress in studying on the delta evolution influenced by the human activity [J]. Marine Sciences, 2007, 31(12): 83-87. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3096.2007.12.018
[13] Hao X M, Chen Y N, Xu C C, et al. Impacts of climate change and human activities on the surface runoff in the Tarim river basin over the last fifty years [J]. Water Resources Management, 2008, 22(9): 1159-1171. doi: 10.1007/s11269-007-9218-4
[14] 许炯心. 流域降水和人类活动对黄河入海泥沙通量的影响[J]. 海洋学报, 2003, 25(5):125-135
XU Jiongxin. Sediment flux into the sea as influenced by the changing human activities and precipitation: example of the Huanghe River, China [J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2003, 25(5): 125-135.
[15] 王兆印, 程东升, 刘成. 人类活动对典型三角洲演变的影响: Ⅱ黄河和海河三角洲[J]. 泥沙研究, 2006(1):76-81 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0468-155X.2006.01.012
WANG Zhaoyin, CHENG Dongsheng, LIU Cheng. Delta processes and management strategies in China: Ⅱ The Yellow and Haihe River deltas [J]. Journal of Sediment Research, 2006(1): 76-81. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0468-155X.2006.01.012
[16] 王庆, 杨华, 仲少云, 等. 山东莱州浅滩的沉积动态与地貌演变[J]. 地理学报, 2003, 58(5):749-756 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0375-5444.2003.05.014
WANG Qing, YANG Hua, ZHONG Shaoyun, et al. Sedimentary dynamics and geomorphic evolution of the Laizhou Shoal [J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2003, 58(5): 749-756. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0375-5444.2003.05.014
[17] 王文海. 中国海湾志: 第四分册(山东半岛南部和江苏省海湾)[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 1993: 73-94
WANG Wenhai. Bays in the South Shandong Peninsula and Jiangsu Province[M]. Beijing: China Ocean Press, 1993: 73-94. ]
[18] 李凤业, 高抒, 贾建军, 等. 黄、渤海泥质沉积区现代沉积速率[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2002, 33(4):364-369 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.2002.04.004
LI Fengye, GAO Shu, JIA Jianjun, et al. Contemporary deposition rates of fine-grained sediment in the Bohai and Yellow Seas [J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2002, 33(4): 364-369. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.2002.04.004
[19] 胡邦琦, 李国刚, 李军, 等. 黄海、渤海铅-210沉积速率的分布特征及其影响因素[J]. 海洋学报, 2011, 33(6):125-133
HU Bangqi, LI Guogang, LI Jun, et al. Spatial variability of the 210Pb sedimentation rates in the Bohai and Huanghai Seas and its influencing factors [J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2011, 33(6): 125-133.
[20] 李凤业, 宋金明, 李学刚, 等. 胶州湾现代沉积速率和沉积通量研究[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2003, 23(4):29-33
LI Fengye, SONG Jinming, LI Xuegang, et al. Modern sedimentation rate and flux in the Jiaozhou Bay [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2003, 23(4): 29-33.
[21] 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局. GB/T 12763.8-2007 海洋调查规范 第8部分: 海洋地质地球物理调查[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2008: 1-94
General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China. GB/T 12763.8-2007 Specifications for oceanographic survey-Part 8: Marine geology and geophysics survey[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2008: 1-94.
[22] 何起祥, 李绍全, 刘健. 海洋碎屑沉积物的分类[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2002, 22(1):115-121
HE Qixiang, LI Shaoquan, LIU Jian. Classification of marine clastic sediments [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2002, 22(1): 115-121.
[23] Folk R L, Andrews P B, Lewis D W. Detrital sedimentary rock classification and nomenclature for use in New Zealand [J]. New Zealand Journal of Geology and Geophysics, 1970, 13(4): 937-968. doi: 10.1080/00288306.1970.10418211
[24] 卢连战, 史正涛. 沉积物粒度参数内涵及计算方法的解析[J]. 环境科学与管理, 2010, 35(6):54-60 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1212.2010.06.013
LU Lianzhan, SHI Zhengtao. Analysis for sediment grain size parameters of connotations and calculation method [J]. Environmental Science and Management, 2010, 35(6): 54-60. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1212.2010.06.013
[25] Collias E E, Rona M R, McManus D A, et al. Machine Processing of Geological Data[R]. Washington, USA: Department of Oceanalgraphy, University of Washington, 1963: 119-120.
[26] 刘志杰, 公衍芬, 周松望, 等. 海洋沉积物粒度参数3种计算方法的对比研究[J]. 海洋学报, 2013, 35(3):179-188
LIU Zhijie, GONG Yanfen, ZHOU Songwang, et al. A comparative study on the grain-size parameters of marine sediments derived from three different computing methods [J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2013, 35(3): 179-188.
[27] Blott S J, Pye K. GRADISTAT: a grain size distribution and statistics package for the analysis of unconsolidated sediments [J]. Earth Surface Processes & Landforms, 2001, 26(11): 1237-1248.
[28] 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会. GB/T 11743-2013 土壤中放射性核素的γ能谱分析方法[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2014: 1-6
General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China, Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China. GB/T 11743-2013 Determination of radionuclides in soil by gamma spectrometry[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2014: 1-6.
[29] 许冬, 初凤友, 杨海丽, 等. 北部湾现代沉积速率[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2012, 32(6):17-26
XU Dong, CHU Fengyou, YANG Haili, et al. Modern sedimentation rates in the Beibu Gulf [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2012, 32(6): 17-26.
[30] 肖志建, 李团结, 廖世智. 伶仃洋表层沉积物特征及其泥沙运移趋势[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2011, 30(4):58-65 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5470.2011.04.009
XIAO Zhijian, LI Tuanjie, LIAO Shizhi. Surface sediment characteristics and transport trend in Lingdingyang Bay of the Pearl River Estuary [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2011, 30(4): 58-65. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5470.2011.04.009
[31] 宫少军, 赵卫, 乔吉果, 等. 渤海湾西部海域底质特征及其沉积环境分析[J]. 天津科技大学学报, 2017, 32(3):50-57
GONG Shaojun, ZHAO Wei, QIAO Jiguo, et al. Characteristics of western Bohai Bay Sea bottom sediment: Sedimentary environment analysis [J]. Journal of Tianjin University of Science & Technology, 2017, 32(3): 50-57.
[32] 田清. 最近60年来胶东半岛气候变化和人类活动对五龙河口(丁字湾)动力地貌演变的影响[D]. 鲁东大学硕士学位论文, 2012
TIAN Qing. Impact of climate change and human activity on the dynamic geomorphcial evolution of the estuary of Wulong River (Dingzi Bay) in Jiaodong Peninsula[D]. Master Dissertation of LudongUniversity, 2012.
-



 下载:
下载: