Element geochemistry and genesis of cobalt-rich crust on the Line Seamount of the Central Pacific
-
摘要:
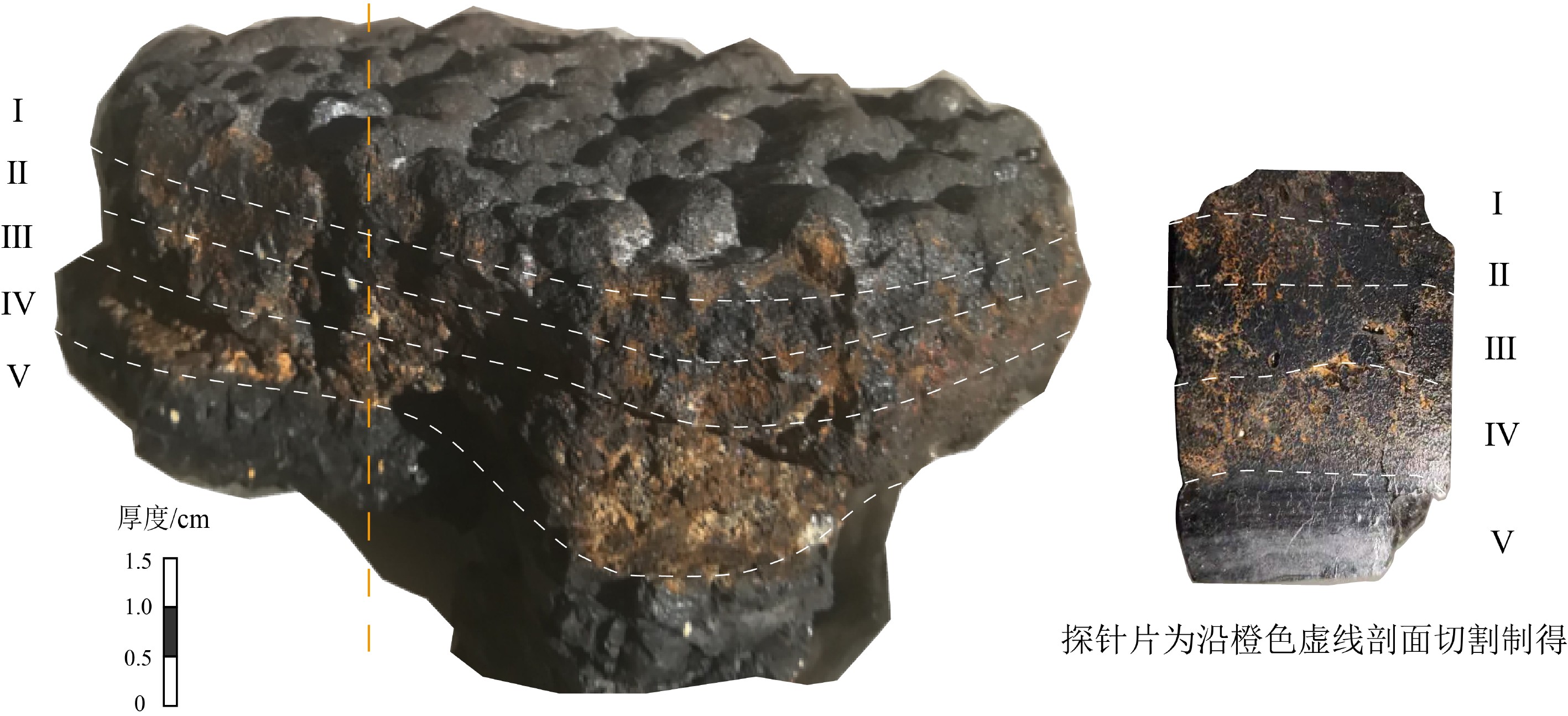
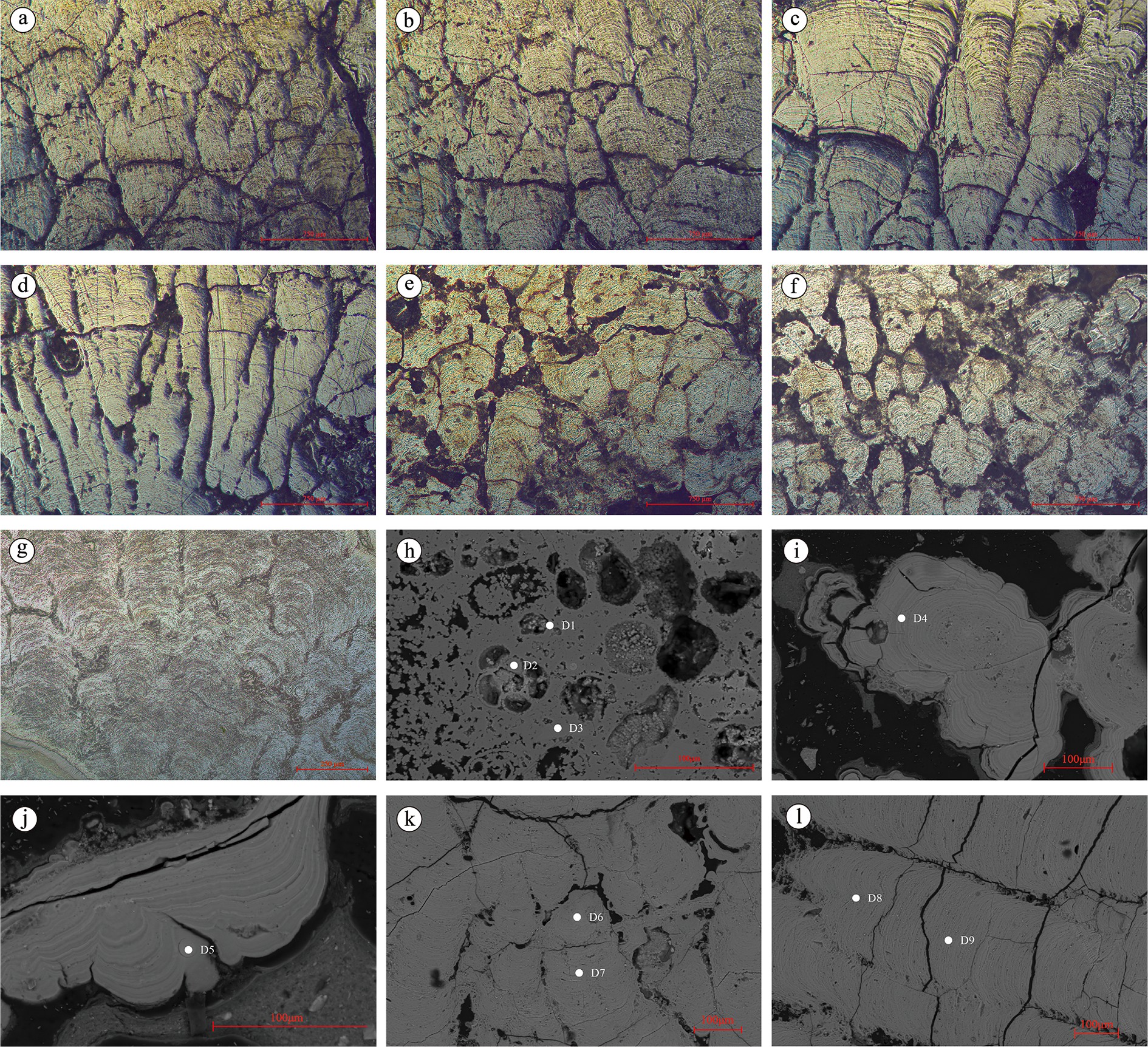
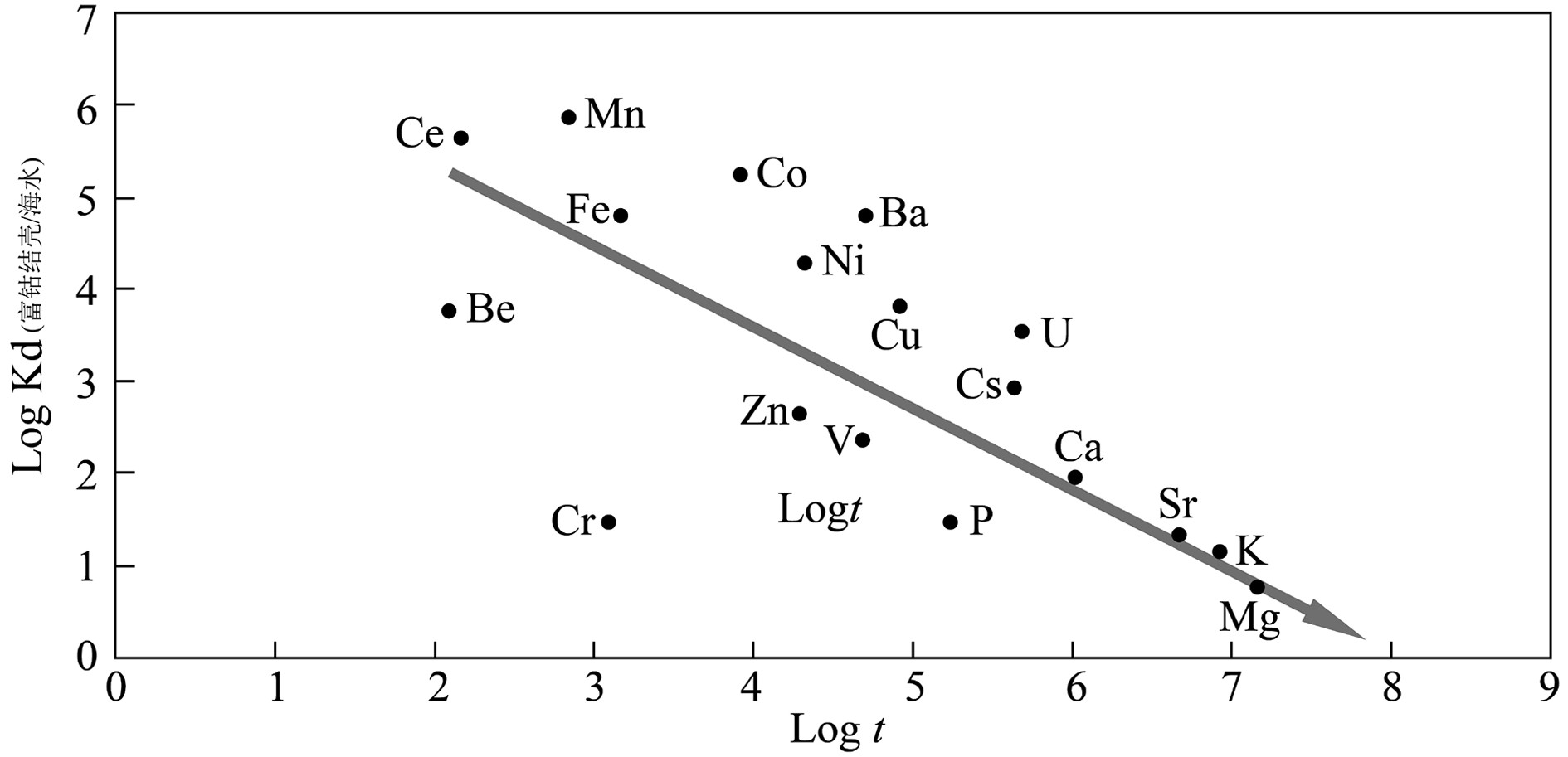
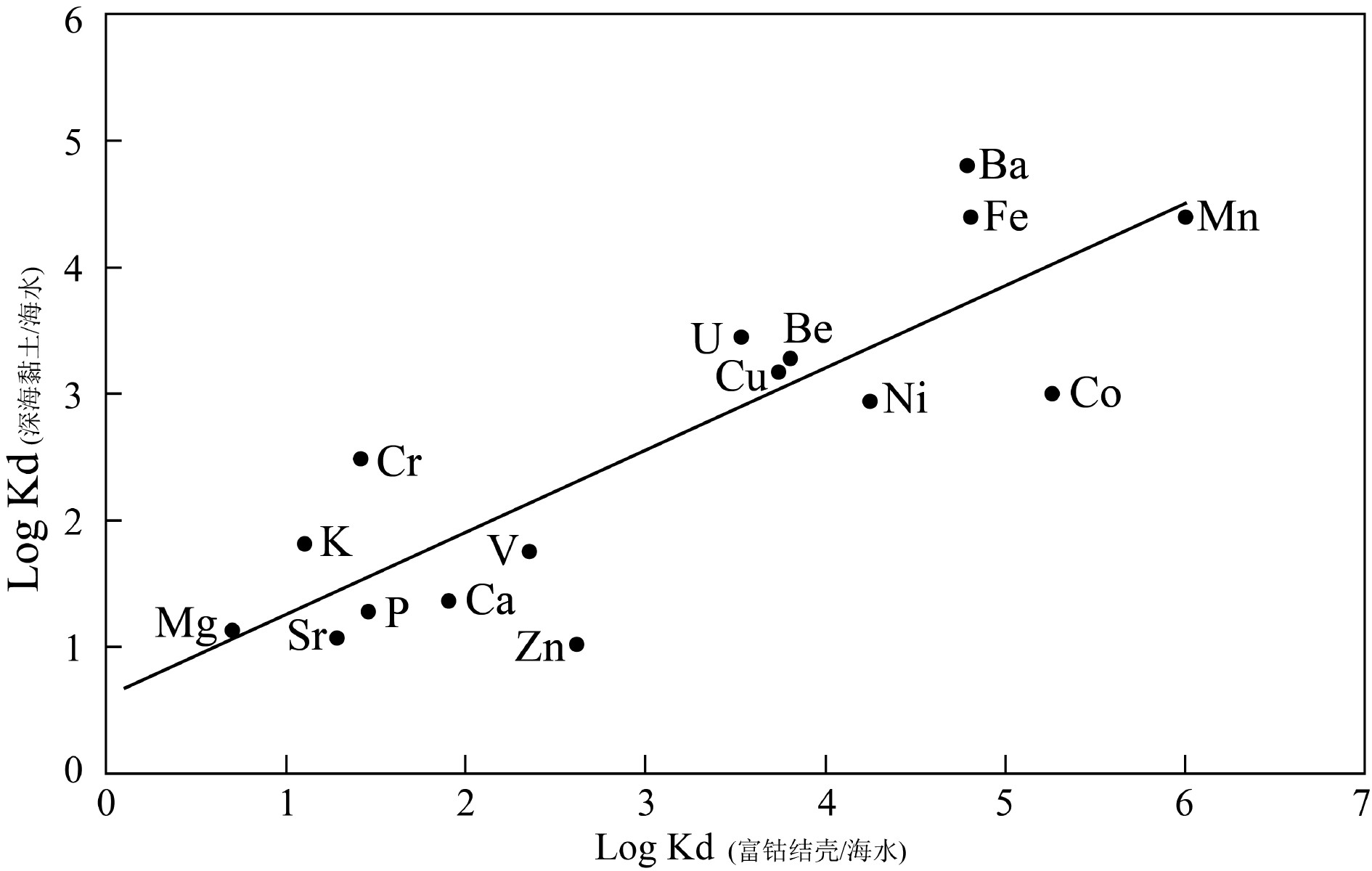
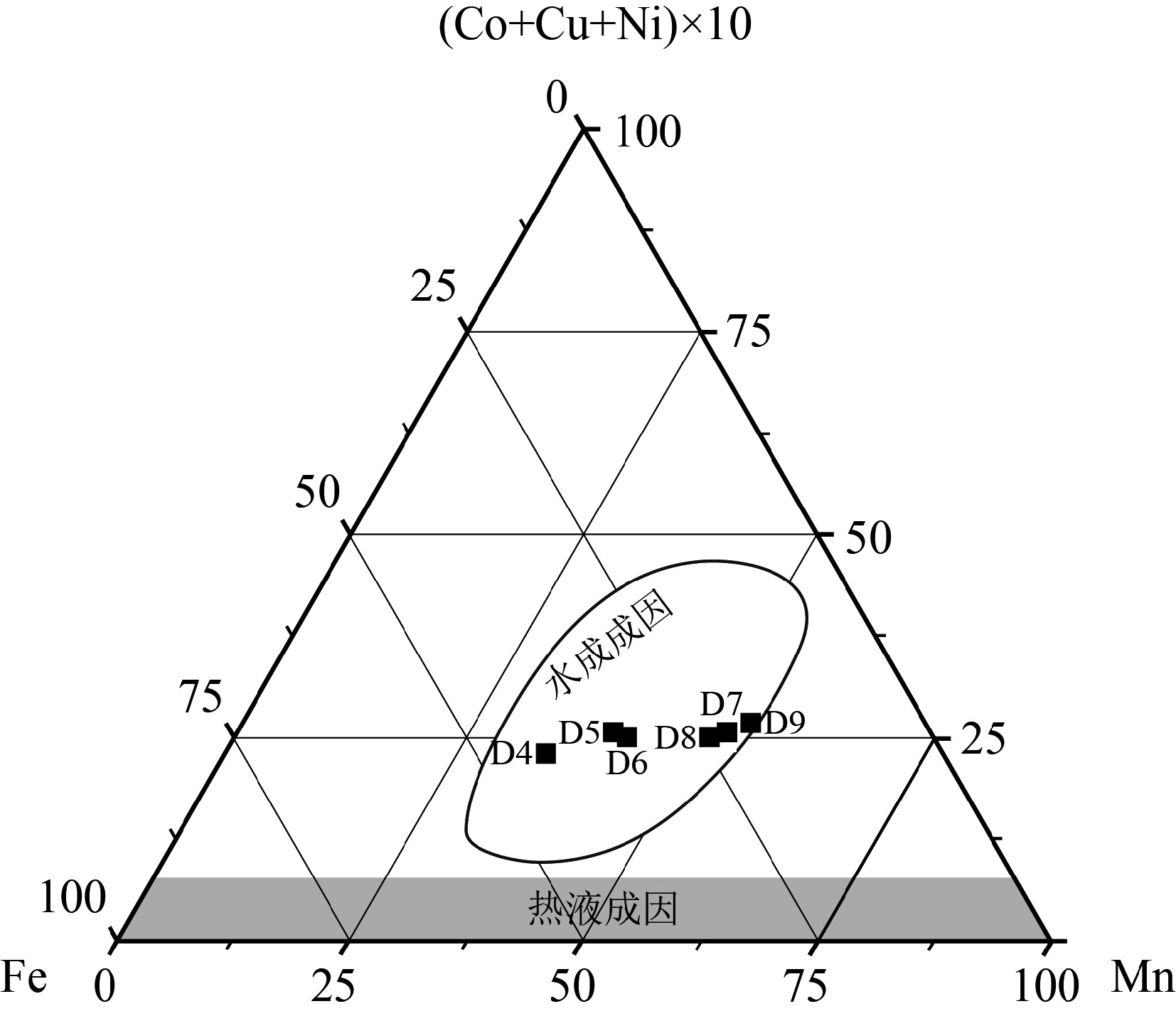
富钴结壳是一种经济价值高、开发前景好的海洋矿产资源,其外部形态、内部构造和地球化学特征记录了古海洋环境的演变信息。本次研究借助富钴结壳细致分层的显微构造及元素地球化学的差异分析,探讨中太平洋莱恩海山富钴结壳成因及形成过程。富钴结壳样品由上至下可分为5层,顶部较致密Ⅰ层黑褐色,表面光滑,杂质较少,具有雪松状叠层石构造,反映了沉积水动力较强;较致密Ⅱ层与Ⅰ层宏观特征类似,具有柱状和胡萝卜状叠层石构造,沉积水动力最强;疏松Ⅲ层和疏松Ⅳ层黄褐色,内含沉积物杂质,多见斑杂状构造,沉积水动力比较弱;致密Ⅴ层为磷酸盐层,具有亮黑色的沥青光泽,富含有孔虫化石,底部Ⅴ层Sr、P、Ca等元素明显富集,表明了海洋生物的明显参与,沉积水动力最弱。莱恩海山Ce异常及高钴高锰低铁特征,表明结壳长期处于氧化环境;而Mn、Fe、Co等元素地球化学特征综合表明,海洋水动力及氧化性总体表现为由底部Ⅴ层至Ⅱ层氧化性逐渐增强,至顶部Ⅰ层有所减弱的趋势;依据元素分配系数、Ce正异常、Ho正异常、Y负异常及成因三角图,判定结壳为南极底流影响下的海水成因。综合结壳年代学数据,在元素剖面中记录了三期磷酸盐化事件,恢复了莱恩海山富钴结壳的生长过程。
Abstract:Cobalt rich crust is a kind of marine mineral resource with high economic value and significant development prospect. The external morphology, internal structure and geochemical characteristics of the crust recorded the evolution of paleoceanographic environment. In this paper, the genesis or forming process of the cobalt rich crusts on the Line Seamount of the Central Pacific Ocean is studied upon the basis of microstructure and element geochemistry. The cobalt rich crust sample is composed of five layers from top to bottom. The top layer is relatively dense, dark brown in color with smooth surface and little impurities. It has a cedar-like stromatolite structure, indicating a strong hydrodynamic environment; The second layer has similar macroscopic characteristics with the first, characterized by columnar and carrot shaped stromatolite structure, which indicates the strongest hydrodynamic deposition; The third and fourth layers are yellowish brown in color, with patchy structures containing certain amount of sediment impurities suggesting weak hydrodynamics; The fifth is a phosphatic layer with bright black asphalt luster, and rich in foraminifera fossils. Meanwhile, the fifth layer is rich in Sr, P, Ca and other elements, indicating obvious involvement of marine organisms and the weakest hydrodynamics. The geochemical characteristics of Ce anomaly and high Co, high Mn and low Fe indicate that the cobalt rich crust was formed in an oxidizing environment for a long time. The geochemical characteristics of Mn, Fe, Co and other elements reveal that the marine hydrodynamic and oxidizability of the environment gradually increases starting from the fifth on bottom layer up to the second layer, but decreases at the first or top layer. According to the distribution coefficients of the elements, positive anomaly of Ce, positive anomaly of Ho, negative anomaly of Y and the triangle genesis diagram, it is inferred that the cobalt-rich crust of the Line Seamount is formed in seawater environment under the influence of the Antarctic bottom current. Based on the geochronological data of the cobalt rich crusts, the growth process of the cobalt rich crusts is recovered in the paper, and three phosphorylation events are recognized on the element profile.
-
Key words:
- cobalt-rich crusts /
- paleoceanography /
- geochemistry /
- Line Seamount
-

-
图 7 莱恩海山富钴结壳的三角成因判别图[30]
Figure 7.
表 1 莱恩海山电子探针元素分析
Table 1. Electron probe element analysis of the Line Seamount
% 测点 层位 Na2O FeO P2O5 MgO MnO CaO CoO K2O ZnO SO3 CuO 总量 D1 Ⅴ 1.05 0.07 30.95 0.27 — 51.67 — 0.03 0.09 1.19 — 89.07 D2 1.15 0.04 31.14 0.34 — 47.36 — 0.03 0.04 1.21 — 85.11 D3 1.02 0.06 31.18 0.27 — 47.55 — 0.04 — 1.43 — 84.99 D4 Ⅳ 1.41 24.81 1.05 2.31 20.79 2.09 0.45 0.79 0.09 0.38 0.04 54.21 D5 Ⅲ 2.32 20.86 0.83 1.79 29.91 3.10 0.63 0.47 0.03 0.75 0.11 60.80 D6 Ⅱ 1.26 20.53 0.85 2.11 31.47 3.59 0.84 0.90 — 0.50 0.12 62.17 D7 2.74 11.44 0.48 2.56 39.09 3.32 1.06 0.78 0.04 0.51 0.19 62.21 D8 Ⅰ 2.29 15.09 0.56 1.94 38.63 3.58 1.13 0.53 0.09 0.79 0.09 64.72 D9 2.95 12.87 0.59 2.27 36.20 3.41 1.30 0.61 0.11 0.59 0.09 60.99 注:测点D1 —D9见图3h-l,D4—D9见图7投点。 表 2 莱恩海山结壳样品分层微量元素含量
Table 2. Trace elements of layered cobalt rich crusts on the Line Seamount
μg/g 样品编号 分层 Co Ni Cu Zn V Cr Sr Mo Ba W Pb Th U Th/U Ni/Co Q1 Ⅰ 较
致
密
层10 444 3 038 392 497 612 7.77 1 560 492 1 012 93.2 1 717 15.8 12.0 1.32 0.29 Q2 Ⅱ 10 311 3 120 500 520 563 9.16 1 626 449 1 115 99.8 1 545 8.8 11.9 0.74 0.24 Q3 Ⅲ 疏
松
层9 924 3 561 618 502 536 8.86 1 432 464 1 198 99.9 1 554 7.84 11.2 0.70 0.36 Q4 Ⅳ 6 673 3 373 790 559 521 13.4 1 558 366 1 315 79.2 1 333 9.78 10.2 0.96 0.51 Q5 Ⅴ 致
密
层10 425 6 003 965 714 599 1.19 1 662 624 1 723 127.0 1 349 2.51 11.9 0.21 0.58 平均值 9 555 3 819 653 588 566 8.08 1 568 479 1 273 99.8 1 500 8.95 11.4 0.79 0.39 表 3 莱恩海山富钴结壳样品稀土元素
Table 3. Analysis table of rare earth elements of cobalt rich crust samples from the Line Seamount
样品
编号分层 La Ce Pr Nd Sm Eu Gd Tb Dy Ho Er Tm Yb Lu Y LREE/
HREE(La/Sm)N (Gd/Yb)N Y/Ho δCe δEu δGd δY Q1 Ⅰ 233 682 43.6 189 38.4 9.88 40.3 7.12 41.8 9.27 27.9 4.48 27.1 4.17 185 7.38 0.83 0.89 19.96 1.46 1.10 0.95 0.85 Q2 Ⅱ 202 657 29.7 149 28.8 7.49 33.2 6 32.9 8.31 23.4 4.06 26.7 4.01 159 7.75 0.73 0.74 19.13 1.79 1.06 0.97 0.86 Q3 Ⅲ 171 786 28.9 130 26.4 6.81 28.7 5.16 27.5 6.54 19.6 3.56 22 3.53 133 9.86 0.75 0.78 20.34 2.39 1.08 0.96 0.89 Q4 Ⅳ 213 761 39.3 182 35.7 8.99 39.1 6.85 36.2 8.52 25.5 3.95 24.7 3.96 190 8.33 0.84 0.94 22.30 1.79 1.05 0.98 0.98 Q5 Ⅴ 232 775 38.3 167 32.2 7.12 33.0 6.17 33.2 8.13 24.8 3.94 25.5 4.00 218 9.02 0.88 0.77 26.81 1.76 0.96 0.98 1.19 注:稀土元素单位为μg/g,δCe=2*CeN/(LaN+PrN),δY=2*YN/(DyN+HoN),δEu、δGd的计算方法类似,N为经北美页岩标准化后的数据,北美页岩数据取自文献[31]。 -
[1] 武光海, 周怀阳, 陈汉林. 大洋富钴结壳研究现状与进展[J]. 高校地质学报, 2001, 7(4):379-389 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7493.2001.04.002
WU Guanghai, ZHOU Huaiyang, CHEN Hanlin. Progress in the research of cobalt-rich crusts [J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 2001, 7(4): 379-389. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7493.2001.04.002
[2] 张富元, 章伟艳, 朱克超, 等. 太平洋海山钴结壳资源评价[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 2011: 2-10
ZHANG Fuyuan, ZHANG Weiyan, ZHU Kechao, et al. Evaluation of Ferromanganese Crust Resources on Seamounts in the Pacific Ocean[M]. Beijing: China Ocean Press, 2011: 2-10.
[3] 崔迎春, 刘季花, 任向文, 等. 中太平洋M海山富钴结壳稀土元素地球化学[J]. 中国稀土学报, 2008, 26(6):760-768 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4343.2008.06.018
CUI Yingchun, LIU Jihua, REN Xiangwen, et al. Geochemistry of rare earth elements in cobalt-rich crusts from the mid-pacific mseamount [J]. Journal of the Chinese Rare Earth Society, 2008, 26(6): 760-768. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4343.2008.06.018
[4] 陈守余, 张海生, 赵鹏大. 中太平洋和中国南海富钴结壳稀土元素地球化学[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2006, 26(4):45-50
CHEN Shouyu, ZHANG Haisheng, ZHAO Pengda. Rare earth element geochemistry of Co-rich crust in the Mid-Pacific and South China Sea [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2006, 26(4): 45-50.
[5] 龙晓军, 赵广涛, 杨胜雄, 等. 西太平洋麦哲伦海山富钴结壳成分特征及古环境记录[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2015, 35(5):47-55
LONG Xiaojun, ZHAO Guangtao, YANG Shengxiong, et al. Chemical composition and paleoenvironmental record of the co-rich crust from magellan seamount in western pacific [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2015, 35(5): 47-55.
[6] Halbach P, Puteanus D. The influence of the carbonate dissolution rate on the growth and composition of Co-rich ferromanganese crusts from Central Pacific seamount areas [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1984, 68(1): 73-87. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(84)90141-9
[7] Halbach P. Processes controlling the heavy metal distribution in pacific ferromanganese nodules and crusts [J]. Geologische Rundschau, 1986, 75(1): 235-247. doi: 10.1007/BF01770191
[8] 蔡毅华, 黄奕普, 邢娜. 基于连续沥取的富钴结壳成因机制的探讨[J]. 台湾海峡, 2011, 30(1):1-9
CAI Yihua, HUANG Yipu, XING Na. Genesis of Co-rich crust from sequential leaching [J]. Journal of Oceanography in Taiwan Strait, 2011, 30(1): 1-9.
[9] 武光海, 刘捷红. 海山当地物源和南极底层水对富钴结壳成矿作用的影响: 来自海山周围水柱化学分析的证据[J]. 海洋学报, 2012, 34(3):92-98
WU Guanghai, LIU Jiehong. A local metal sources and the influence of the Antarctic Bottom Water on the cobalt-rich crust formatim: New evidence from the data of seawater column chemistry around a seamount [J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2012, 34(3): 92-98.
[10] 任向文, 闫仕娟, 刘季花, 等. 富钴结壳结构成因初探: 来自DLA模拟的证据[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2015, 34(5):931-937 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2015.05.006
REN Xiangwen, YAN Shijuan, LIU Jihua, et al. Origin of texture of co-rich ferromanganese crust: evidences from the simulation based on diffusion-limited aggregation [J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 2015, 34(5): 931-937. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2015.05.006
[11] 崔迎春. 中太平洋海区富钴结壳地球化学特征及成因机制[D]. 中国科学院海洋研究所博士学位论文, 2008
CUI Yingchun. Geochemical characteristics and origin of cobalt-rich crusts from central pacific ocean[D]. Doctoral Dissertation of Institute of Oceanography, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2008.
[12] 潘家华, 刘淑琴, DeCarlo E. 大洋磷酸盐化作用对富钴结壳元素富集的影响[J]. 地球学报, 2002, 23(5):403-407 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1006-3021.2002.05.003
PAN Jiahua, LIU Shuqin, DeCarlo E. The effects of marine phospharization on element concentration of cobalt-rich crusts [J]. Acta Geoscientia Sinica, 2002, 23(5): 403-407. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1006-3021.2002.05.003
[13] 武光海, 周怀阳, 凌洪飞, 等. 富钴结壳中的磷酸盐岩及其古环境指示意义[J]. 矿物学报, 2005, 25(1):39-44 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4734.2005.01.007
WU Guanghai, ZHOU Huaiyang, LING Hongfei, et al. Phosphorites in Co-rich crusts and their palaeooceanographic singificance [J]. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 2005, 25(1): 39-44. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4734.2005.01.007
[14] Hein J R, Yeh H W, Gunn S H, et al. Two major Cenozoic episodes of phosphogenesis recorded in equatorial Pacific seamount deposits [J]. Paleoceanography, 1993, 8(2): 293-311. doi: 10.1029/93PA00320
[15] 佟景贵. 太平洋富钴结壳矿物地球化学及古海洋与古环境重建[D]. 中国地质大学(北京)博士学位论文, 2007
TONG Jinggui. Geochemical and mineralogical study on the co-rich ferromanganese crust from the pacific ocean and the palaeoocean and palaeoenvironment reconstruction[D]. Doctoral Dissertation of China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2007.
[16] 丁旋, 高莲凤, 方念乔, 等. 太平洋海山富钴结壳生长过程与新生代海洋演化关系[J]. 中国科学 D辑:地球科学, 2009, 52(8):1091-1103 doi: 10.1007/s11430-009-0106-z
DING Xuan, GAO Lianfeng, FANG Nianqiao, et al. The relationship between the growth process of the ferromanganese crusts in the pacific seamount and Cenozoic ocean evolvement [J]. Science in China Series D:Earth Sciences, 2009, 52(8): 1091-1103. doi: 10.1007/s11430-009-0106-z
[17] 许东禹, 姚德, 陈宗团. 锰结核生长的古海洋环境与事件[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 1993, 13(2):1-11
XU Dongyu, YAO De, CHEN Zongtuan. Ancient marine environment for manganese nonules and related events [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 1993, 13(2): 1-11.
[18] 李江山, 石学法, 刘季花, 等. 古海洋环境演化对富钴结壳稀土元素富集的制约[J]. 中国稀土学报, 2011, 29(5):622-629
LI Jiangshan, SHI Xuefa, LIU Jihua, et al. Constraints of paleoceanographic environmental evolution on rees enrichment in co-rich crust [J]. Journal of the Chinese Rare Earth Society, 2011, 29(5): 622-629.
[19] 符亚洲. 中太平洋莱恩海山富钴结壳的地球化学及Os同位素地层年代学研究[D]. 中国科学院地球化学研究所博士毕业论文, 2006
FU Yazhou. Geochemical and Os isotopic geochronology of cobalt-rich crusts in the Line Seamount of Central Pacific[D]. Doctoral Dissertation of Institute of geochemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2006.
[20] 李江山, 方念乔, 石学法, 等. 中太平洋富钴结壳不同壳层He, Ar同位素组成[J]. 地球科学—中国地质大学学报, 2012, 37(S1):93-100
LI Jiangshan, FANG Nianqiao, SHI Xuefa, et al. Helium and argon isotopic compositions of various crustal layers of a Co-Rich Fe-Mn crust from Central Pacific [J]. Earth Science—Journal of China University of Geosciences, 2012, 37(S1): 93-100.
[21] Clouard V, Bonneville A. How many Pacific hotspots are fed by deep-mantle plumes? [J]. Geology, 2001, 29(8): 695-698. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(2001)029<0695:HMPHAF>2.0.CO;2
[22] Davis A S, Gray L B, Clague D A, et al. The Line Islands revisited: new 40Ar/39Ar geochronologic evidence for episodes of volcanism due to lithospheric extension [J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2002, 3(3): 1-28.
[23] Parés J M, Moore T C. New evidence for the Hawaiian hotspot plume motion since the Eocene [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2005, 237(3-4): 951-959. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2005.06.012
[24] 章伟艳, 张富元, 朱克超, 等. 西太平洋海域海山地形分形特征研究[J]. 现代地质, 2009, 23(6):1138-1146 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2009.06.020
ZHANG Weiyan, ZHANG Fuyuan, ZHU Kechao, et al. Fractal research on seamount topography in the West Pacific Ocean [J]. Geoscience, 2009, 23(6): 1138-1146. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2009.06.020
[25] 章伟艳, 张富元, 胡光道, 等. 中西太平洋海山形态类型与钴结壳资源分布关系[J]. 海洋学报, 2008, 30(6):76-84
ZHANG Weiyan, ZHANG Fuyuan, HU Guangdao, et al. Relationship between shape classification of Pacific seamount morphology and distribution of cobalt-rich crust resources [J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2008, 30(6): 76-84.
[26] Kawabe M, Fujio S. Pacific Ocean circulation based on observation [J]. Journal of Oceanography, 2010, 66(3): 389-403. doi: 10.1007/s10872-010-0034-8
[27] 任向文, 刘季花, 石学法, 等. 莱恩海山链富钴结壳新壳层标志物的成分特征[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2011, 31(3):41-46
REN Xiangwen, LIU Jihua, SHI Xuefa, et al. Geochemistry of a maker of younger deposit of co-rich ferromanganese crust from Line Islands [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2011, 31(3): 41-46.
[28] 何高文. 太平洋多金属结核和富钴结壳地质地球化学特征与成矿机制对比研究[D]. 中山大学博士学位论文, 2006
HE Gaowen. A comparative study of the geology, geochemistry and metallogenetic mechanism of polymetallic nodules mad cobalt-rich crusts from the Pacific Ocean[D]. Doctoral Dissertation of Sun Yat-Sen University, 2006.
[29] Koschinsky A, Stascheit A, Bau M, et al. Effects of phosphatization on the geochemical and mineralogical composition of marine ferromanganese crusts [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1997, 61(19): 4079-4094. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(97)00231-7
[30] 任向文. 西太平洋富钴结壳成矿系统[D]. 中国科学院海洋研究所博士学位论文, 2005
REN Xiangwen. The Metallogenic system of co-rich manganese crusts in western pacific[D]. Doctor Dissertation of Institute of oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2005.
[31] Gromet L P, Haskin L A, Korotev R L, et al. The "North American shale composite": Its compilation, major and trace element characteristics [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1984, 48(12): 2469-2482. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(84)90298-9
[32] Li Y H. Distribution patterns of the elements in the ocean: A synthesis [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1991, 55(11): 3223-3240. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(91)90485-N
[33] 张正斌, 刘莲生, 陈念贻. 海洋中化学过程的Ф (
$\frac{z}{l}$ ZHANG Zhengbin, LIU Liansheng, CHEN Nianyi. A Ф (
$\frac{z}{l}$ [34] 朱克超, 任江波, 王海峰, 等. 太平洋中部富REY深海粘土的地球化学特征及REY富集机制[J]. 地球科学——中国地质大学学报, 2015, 40(6):1052-1060 doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2015.087
ZHU Kechao, REN Jiangbo, WANG Haifeng, et al. Enrichment mechanism of REY and geochemical characteristics of REY-rich pelagic clay from the Central Pacific [J]. Earth Science—Journal of China University of Geosciences, 2015, 40(6): 1052-1060. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2015.087
[35] 任江波, 何高文, 姚会强, 等. 西太平洋海山富钴结壳的稀土和铂族元素特征及其意义[J]. 地球科学, 2016, 41(10):1745-1757
REN Jiangbo, HE Gaowen, YAO Huiqiang, et al. Geochemistry and significance of REE and PGE of the cobalt-rich crusts from west pacific ocean seamounts [J]. Earth Science, 2016, 41(10): 1745-1757.
[36] Bonatti E, Kraemer T, Rydell H. Classification and genesis of submarine iron-manganese deposits[M]//Horn D R. Ferromanganese Deposits on the Ocean Floor. Harriman, NY, USA: Arden House, 1972: 149-165.
[37] Klemm V, Levasseur S, Frank M, et al. Osmium isotope stratigraphy of a marine ferromanganese crust [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2005, 238(1-2): 42-48. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2005.07.016
[38] Prakash S L, Ray D, Nath N B, et al. Anomalous phase association of REE in ferromanganese crusts from Indian mid-oceanic ridges: Evidence for large scale dispersion of hydrothermal iron [J]. Chemical Geology, 2020, 549: 119679. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2020.119679
[39] Halbach P, Segl M, Puteanus D, et al. Co-fluxes and growth rates in ferromanganese deposits from Central Pacific Seamount areas [J]. Nature, 1983, 304(5928): 716-719. doi: 10.1038/304716a0
[40] Puteanus D, Halbach P. Correlation of Co concentration and growth rate: a method for age determination of ferromanganese crusts [J]. Chemical Geology, 1988, 69(1-2): 73-85. doi: 10.1016/0009-2541(88)90159-3
[41] McMurtry G M, Vonderhaar D L, Eisenhauer A, et al. Cenozoic accumulation history of a Pacific ferromanganese crust [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1994, 125(1-4): 105-118. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(94)90209-7
[42] Halbach P E, Sattler C D, Teichmann F, et al. Cobalt-rich and platinum-bearing manganese crust deposits on seamounts: Nature, formation, and metal potential [J]. Marine Mineral, 1989, 8(1): 23-29.
[43] 任向文, 刘季花, 崔迎春, 等. 磷酸盐化对莱恩海山链MP2海山结壳Co富集的影响[J]. 海洋科学进展, 2011, 29(3):323-329 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2011.03.008
REN Xiangwen, LIU Jihua, CUI Yingchun, et al. Effects of phosphatization on enrichment of cobalt in the Co-rich Fe-Mn crusts from seamount MP2 of the line islands in the Central Pacific [J]. Advances in Marine Science, 2011, 29(3): 323-329. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2011.03.008
-



 下载:
下载: