Rare earth element composition of the surface sediments from the Ninetyeast Ridge and its implications for provenance
-
摘要:
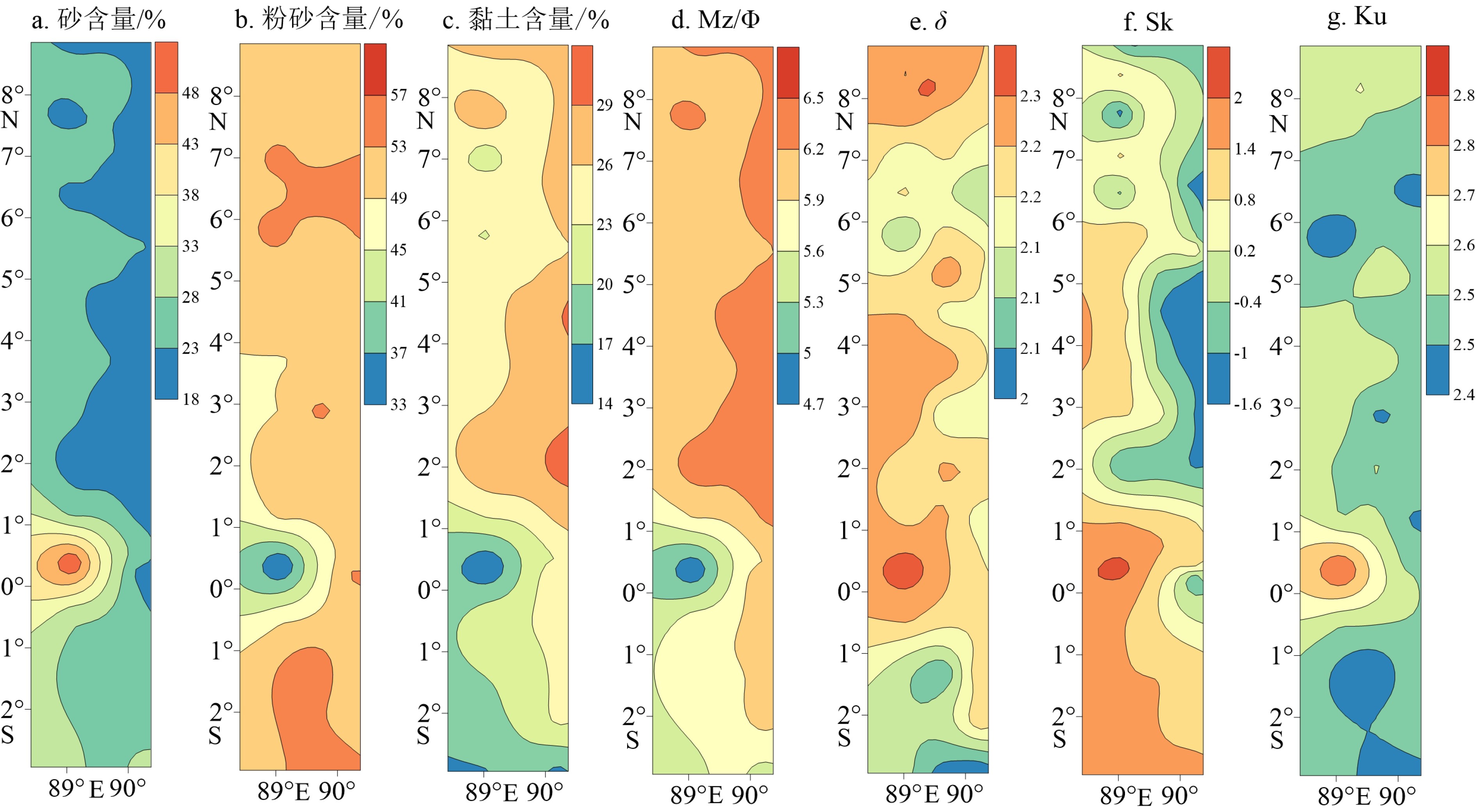
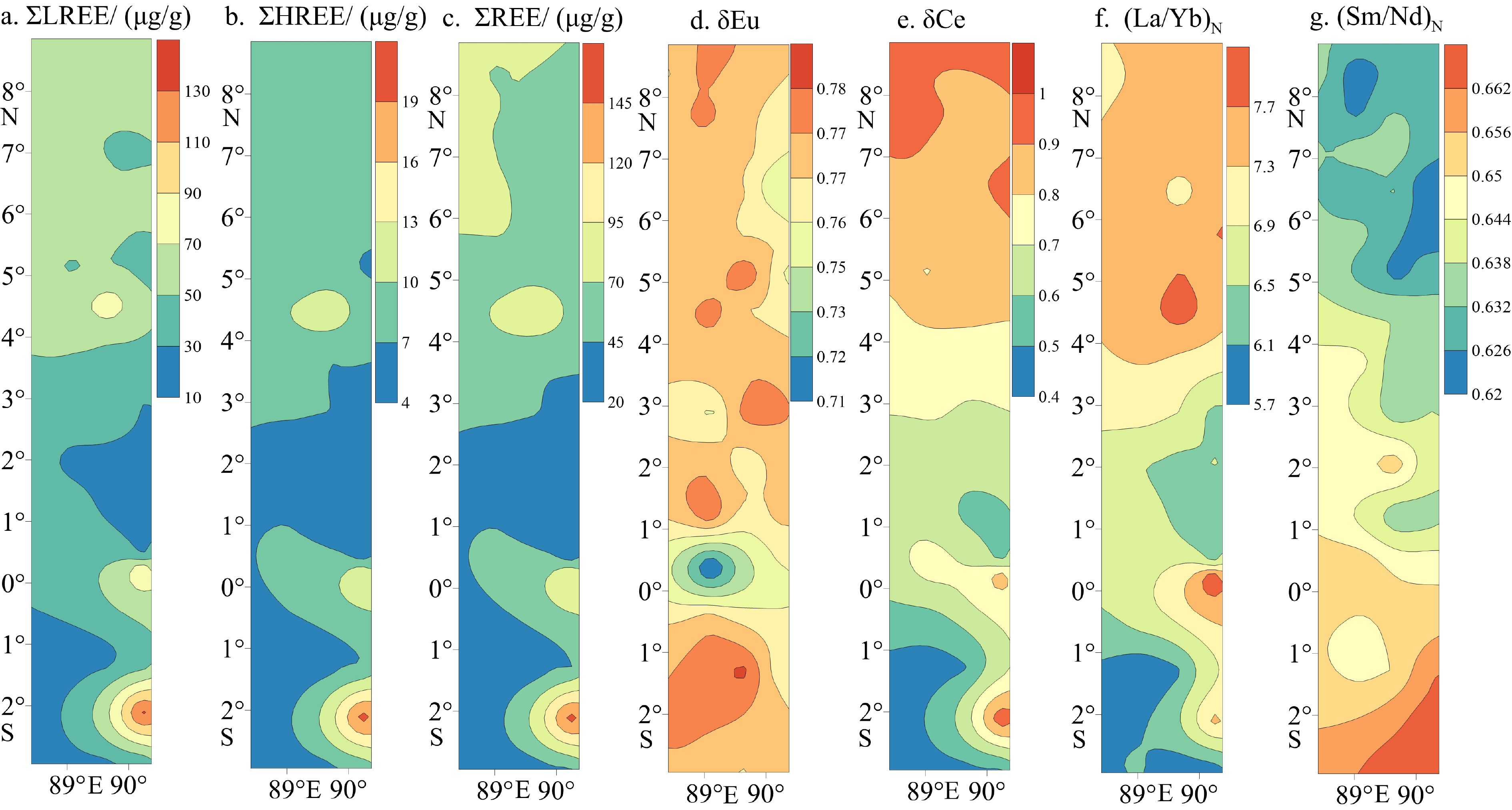
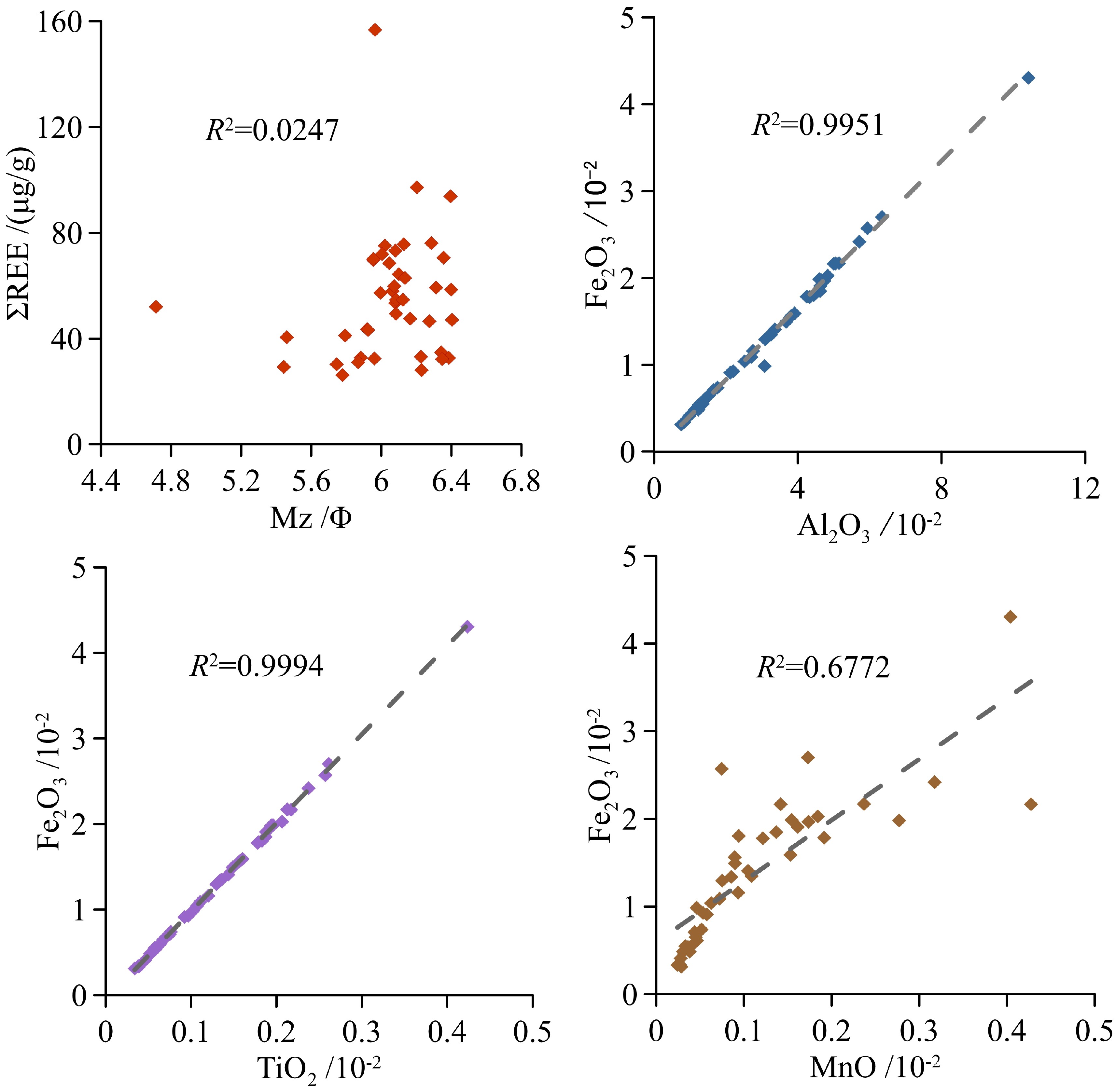
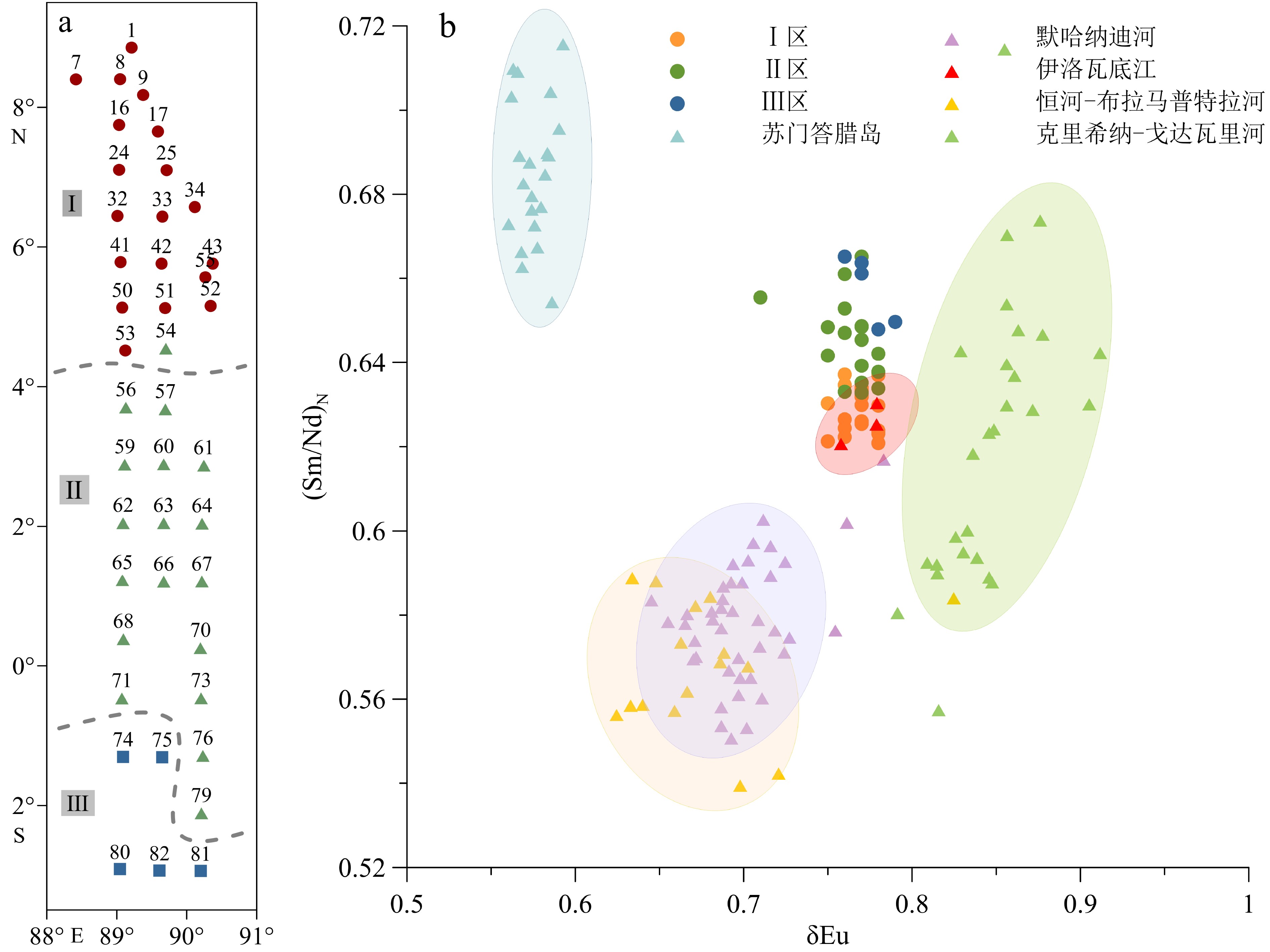
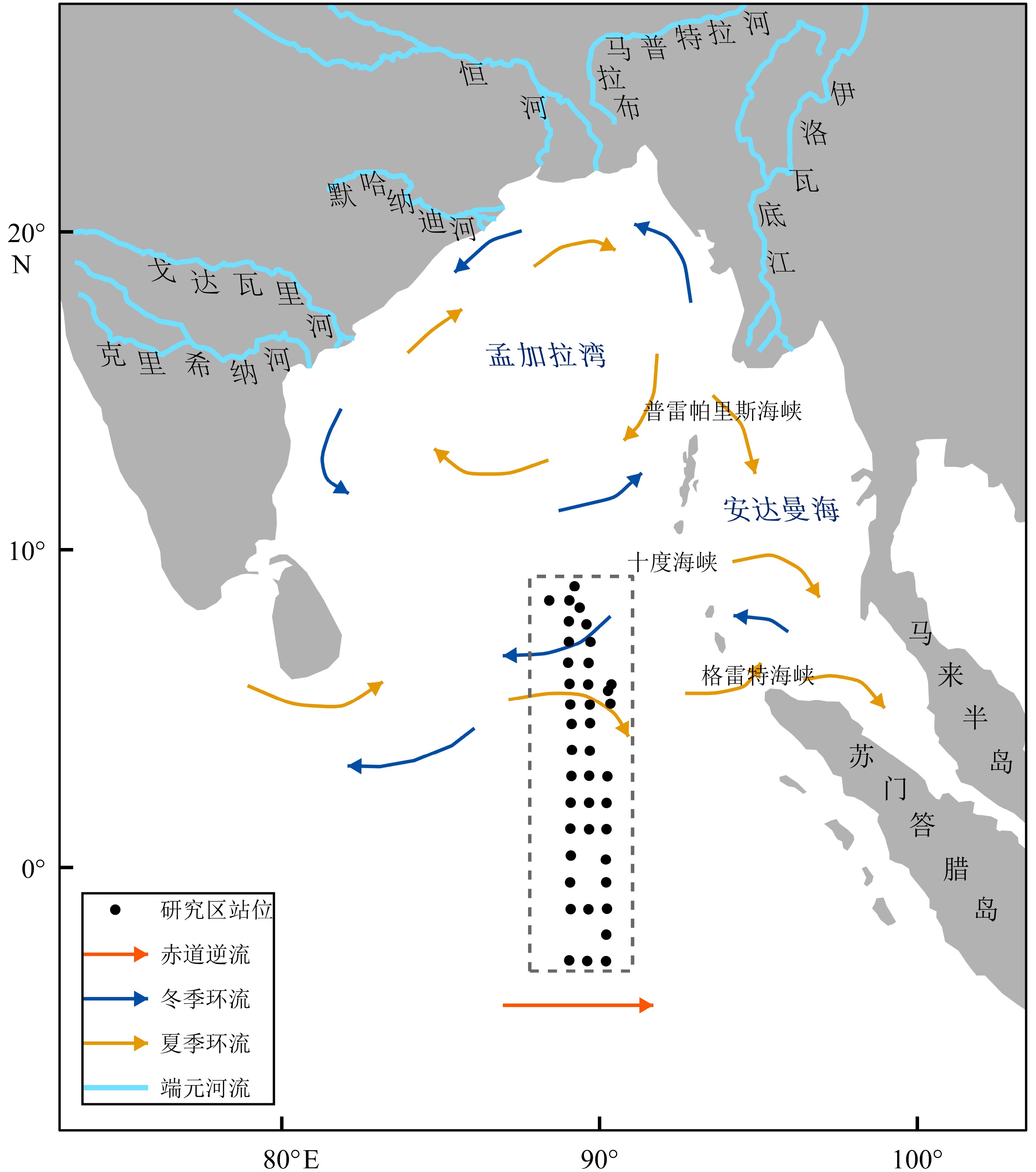
基于印度洋东经90°海岭42个表层沉积物的粒度和稀土元素(REE)组成及其空间分布特征,判别了研究区现代沉积物的主要来源,并结合水动力格局等要素探讨了东经90°海岭北部区域沉积物输运方式。结果显示,研究区42个表层沉积物总稀土含量(∑REE)为26.37~156.8 μg/g,平均值为57.35 μg/g,特点是轻稀土含量(∑LREE)高,重稀土含量(∑HREE)低且均一、存在明显的Ce和Eu异常。REE组成和空间分布受沉积物来源控制显著,球粒陨石标准化后的Sm/Nd-δEu物源判别图以及判别函数(FD)结果显示,研究区北部表层沉积物的最主要来源是伊洛瓦底江陆源物质,次要来源是戈达瓦里-克里希纳河输入的印度半岛物质,而南部区域则受苏门答腊岛陆源物质影响显著。不同源区沉积物在研究区的输运过程主要受控于热带季风系统驱动下的季节性表层环流以及浊流和风。
Abstract:Spatial distribution patterns of grain size and rare earth elements (REE) are studied in this paper for the 42 surface sediment samples collected from the Ninetyeast Ridge of the Indian Ocean. The main sources of sediments are identified and the sediment transport modes are discussed on the hydrodynamic environment features. The results suggest that the total concentrations of rare earth elements in the 42 surface sediments of the study area vary between 26.37 μg/g and 156.8 μg/g, with an average at 57.35 μg/g. The samples are rich in light REE and uniform in heavy REE with obvious negative anomalies of Eu and Ce. The composition and spatial distribution of REE are significantly controlled by the source of sediments. According to the chondrite-normalized Sm/Nd-δEu diagram for provenance identification and the discriminant function (FD), the sediments in the northern study area are mainly coming from the Irrawaddy River, and the subordinate is sourced from the Indian Peninsula by the Godavari River-Krishna River. The sediments in the southern study area are significantly affected by the Sumatra. The transportation process of sediments from different sources in the study area is mainly controlled by seasonal surface circulation driven by the tropical monsoon system, turbidity currents and wind.
-
Key words:
- sediment /
- rare earth elements /
- provenance /
- Ninetyeast ridge /
- Indian Ocean
-

-
表 1 东经90°海岭及周边区域沉积物REE组成
Table 1. REE composition of sediments of the Ninetyeast Ridge and adjacent areas
La Ce Pr Nd Sm Eu Gd Tb Dy Ho Er Tm Yb Lu ∑REE ∑LREE ∑HREE δEu δCe (La/Yb) N (Sm/Nd) N 平均值 12.06 19.05 2.79 11.02 2.29 0.57 2.30 0.37 2.18 0.42 1.18 0.18 1.14 0.18 57.35 47.77 7.94 0.77 0.75 7.03 0.64 最小值 6.54 5.88 1.42 5.89 1.23 0.32 1.35 0.22 1.33 0.27 0.77 0.12 0.74 0.12 26.37 21.30 4.91 0.71 0.46 5.74 0.62 最大值 29.61 60.87 7.65 30.12 6.52 1.61 6.29 0.99 5.71 1.04 2.86 0.44 2.69 0.41 156.80 136.37 20.43 0.79 0.97 8.03 0.67 标准差 4.39 10.34 1.12 4.32 0.92 0.22 0.84 0.13 0.75 0.13 0.36 0.06 0.35 0.05 23.80 21.19 2.67 0.01 0.15 0.62 0.01 上陆壳 31.00 63.00 7.10 27.00 4.70 1.00 4.00 0.70 3.90 0.83 2.30 0.30 2.00 0.31 148.14 133.80 14.34 0.71 1.02 10.45 0.54 I 37.10 85.60 7.85 32.45 6.50 1.60 5.25 0.95 5.20 1.05 2.95 0.45 2.35 0.37 189.67 192.66 22.37 0.84 1.21 10.64 0.62 M 46.30 94.90 8.70 35.60 6.70 1.40 5.70 0.89 4.20 0.88 2.70 0.45 2.30 0.34 211.06 193.60 17.46 0.69 1.14 13.57 0.58 K-G 44.67 89.17 9.53 39.47 8.03 1.80 6.34 1.11 6.19 1.22 3.54 0.50 3.00 0.47 215.03 171.10 18.57 0.77 1.04 10.04 0.63 G-B 29.79 58.96 6.68 24.64 4.72 0.95 4.45 0.96 3.96 0.79 2.27 0.35 2.26 0.32 140.84 125.75 15.09 0.63 1.01 8.89 0.59 S 19.60 38.11 4.37 17.29 3.46 0.82 3.16 0.52 2.94 0.57 1.64 0.25 1.52 0.24 94.49 83.66 10.84 0.75 0.99 8.71 0.62 注:表中各元素含量、∑REE、∑LREE、∑HREE单位为µg/g;δEu、δCe、La/Yb和Sm/Nd均经过球粒陨石标准化;球粒陨石数据引自文献[23];上陆壳数据引自文献[24];伊洛瓦底江(I)数据引自文献[25];默哈纳迪河(M)和克里希纳-戈达瓦里河(K-G)数据引自文献[26];恒河-布拉马普特拉河(G-B)数据引自文献[27];苏门答腊岛(S)数据为“全球变化与海气相互作用”专项“东印度洋IND-CJ01区块调查区块海底底质和底栖生物调查(GASI-02-IND-CJ01)”项目获取的苏门答腊岛西南部近岸海域BS24钻孔样品数据。 表 2 东经90°海岭表层沉积物REE判别函数(FD)计算结果
Table 2. The REE discrimination values for 42 surface sediments of the Ninetyeast Ridge
判别端元 沉积物分区 Ⅰ区 Ⅱ区 Ⅲ区 伊洛瓦底江 0.005 0.032 0.051 克里希纳-戈达瓦里河 0.011 0.037 0.057 苏门答腊岛 0.082 0.058 0.040 -
[1] McLennan S M. Rare earth elements in sedimentary rocks: Influence of provenance and sedimentary processes [J]. Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry, 1989, 21(1): 169-200.
[2] 毛光周, 刘池洋. 地球化学在物源及沉积背景分析中的应用[J]. 地球科学与环境学报, 2011, 33(4):337-348 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6561.2011.04.002
MAO Guangzhou, LIU Chiyang. Application of geochemistry in provenance and depositional setting analysis [J]. Journal of Earth Sciences and Environment, 2011, 33(4): 337-348. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6561.2011.04.002
[3] Cullers R L. The controls on the major and trace element variation of shales, siltstones, and sandstones of Pennsylvanian-Permian age from uplifted continental blocks in Colorado to platform sediment in Kansas, USA [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1994, 58(22): 4955-4972. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(94)90224-0
[4] Lim D, Jung H S, Choi J Y. REE partitioning in riverine sediments around the Yellow Sea and its importance in shelf sediment provenance [J]. Marine Geology, 2014, 357: 12-24. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2014.07.002
[5] Um I K, Choi M S, Bahk J J, et al. Discrimination of sediment provenance using rare earth elements in the Ulleung Basin, East/Japan Sea [J]. Marine Geology, 2013, 346: 208-219. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2013.09.007
[6] Liu S F, Zhang H, Zhu A M, et al. Distribution of rare earth elements in surface sediments of the western Gulf of Thailand: Constraints from sedimentology and mineralogy [J]. Quaternary International, 2019, 527: 52-63. doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2018.08.010
[7] Mi B B, Liu S F, Shi X F, et al. A high resolution record of rare earth element compositional changes from the mud deposit on the inner shelf of the East China Sea: Implications for paleoenvironmental changes [J]. Quaternary International, 2017, 447: 35-45. doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2016.09.056
[8] Curray J R, Emmel F J, Moore D G. The Bengal Fan: morphology, geometry, stratigraphy, history and processes [J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2002, 19(10): 1191-1223. doi: 10.1016/S0264-8172(03)00035-7
[9] Curray J R. The Bengal depositional system: from rift to orogeny [J]. Marine Geology, 2014, 352: 59-69. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2014.02.001
[10] 方念乔, 丁旋, 刘勇勤, 等. 东经90°海岭的远洋沉积记录与晚新生代重大构造-环境事件[J]. 地学前缘, 2002, 9(1):103-111 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2002.01.013
FANG Nianqiao, DING Xuan, LIU Yongqin, et al. Pelagic sedimentary records of the Ninetyeast Ridge and the Late Cenozoic important tectono-environmental events [J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2002, 9(1): 103-111. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2002.01.013
[11] 方念乔, 陈学方, 丁旋, 等. 孟加拉湾和东经90°海岭260 ka以来的古海洋学记录与印度季风的影响[J]. 中国科学 (D辑), 2001, 44(1):351-359
FANG Nianqiao, CHEN Xuefang, DING Xuan, et al. Paleoceanographical records under impact of the Indian monsoon from the Bengal Deep Sea Fan and Ninetyeast Ridge during the last 260 ka [J]. Science in China Series D: Earth Sciences, 2001, 44(1): 351-359.
[12] 张振芳, 方念乔, 吴琳, 等. 孟加拉湾东经90°海岭中上新世以来沉积记录及亚洲季风[J]. 地球科学—中国地质大学学报, 2004, 29(2):157-162
ZHANG Zhenfang, FANG Nianqiao, WU Lin, et al. Sedimentary records and Asian monsoon in ninetyeast ridge of bay of Bengal since Pliocene time [J]. Earth Science—Journal of China University of Geosciences, 2004, 29(2): 157-162.
[13] 魏华玲, 方念乔, 丁旋, 等. 赤道东经90°海岭3.5Ma以来远洋记录反映的重大环境事件[J]. 地质通报, 2007, 26(12):1627-1632 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2007.12.016
WEI Hualing, FANG Nianqiao, DING Xuan, et al. Major environmental events reflected by pelagic records since 3.5 Ma BP in the Ninetyeast Ridge at the equator [J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2007, 26(12): 1627-1632. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2007.12.016
[14] 尚鲁宁, 胡刚, 袁忠鹏, 等. 东北印度洋85°E海脊的性质和起源: 综述和新认识[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2020, 40(4):1-16
SHANG Luning, HU Gang, YUAN Zhongpeng, et al. Tectonic structure and origin of the 85°E ridge, Northeastern Indian Ocean: A review and new observations [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2020, 40(4): 1-16.
[15] 张振国, 方念乔, 李文宝, 等. 东经90°海岭远洋沉积物非碳酸盐组分的粒度特征及环境指示意义[J]. 太原理工大学学报, 2007, 38(1):85-87 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-9432.2007.01.025
ZHANG Zhenguo, FANG Nianqiao, LI Wenbao, et al. The characteristics of the non-CaCO3 grain size of pelagic sediment from the Ninetyeast Ridge and its indicated significance of environment [J]. Journal of Taiyuan University of Technology, 2007, 38(1): 85-87. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-9432.2007.01.025
[16] Kolla V, Moore D G, Curray J. Recent bottom-current activity in the deep western Bay of Bengal [J]. Marine Geology, 1976, 21(4): 255-270. doi: 10.1016/0025-3227(76)90010-4
[17] 李景瑞, 刘升发, 冯秀丽, 等. 孟加拉湾中部表层沉积物稀土元素特征及其物源指示意义[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2016, 36(4):41-50
LI Jingrui, LIU Shengfa, FENG Xiuli, et al. Rare earth element geochemistry of surface sediments in mid-Bengal Bay and implications for provenance [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2016, 36(4): 41-50.
[18] Klootwijk C T, Gee J S, Peirce J W, et al. Neogene evolution of the Himalayan-Xizang region: Constraints from ODP site 758, northern Ninetyeast ridge; bearing on climatic change [J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 1992, 95(1-2): 95-110. doi: 10.1016/0031-0182(92)90167-4
[19] 乔彬, 刘子洲, 张书颖, 等. 季风转换期东印度洋的赤道流系结构和水文特征[J]. 海洋科学进展, 2014, 32(3):301-305 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2014.03.001
QIAO Bin, LIU Zizhou, ZHANG Shuying, et al. Equatorial current system structure and hydrologic characteristics in monsoonal wind transition period [J]. Advances in Marine Science, 2014, 32(3): 301-305. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2014.03.001
[20] 宣莉莉. 热带东印度洋上层海洋环流及其与孟加拉湾水交换的季节变化研究[D]. 国家海洋局第三海洋研究所硕士学位论文, 2013.
XUAN Lili. Seasonal variation of the upper ocean circulation in the eastern tropical Indian Ocean and its water exchange with the Bay of Benga[D]. Master Dissertation of Third Institute of Oceanography, State Oceanic Administration, 2013.
[21] Song Z H, Wan S M, Colin C, et al. Paleoenvironmental evolution of South Asia and its link to Himalayan uplift and climatic change since the late Eocene [J]. Global and Planetary Change, 2021, 200: 103459. doi: 10.1016/j.gloplacha.2021.103459
[22] McManus J. Grain size determination and interpretation[M]//Tucker M. Techniques in Sedimentology. Oxford, UK: Blackwell Scientific Publications, 1988: 63-85.
[23] Evensen N M, Hamilton P J, O'Nions R K. Rare-earth abundances in chondritic meteorites [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1978, 42(8): 1199-1212. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(78)90114-X
[24] Taylor S R, McLennan S M. The geochemical evolution of the continental crust [J]. Reviews of Geophysics, 1995, 33(2): 241-265. doi: 10.1029/95RG00262
[25] Garzanti E, Wang J G, Vezzoli G, et al. Tracing provenance and sediment fluxes in the Irrawaddy River basin (Myanmar) [J]. Chemical Geology, 2016, 440: 73-90. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2016.06.010
[26] Mazumdar A, Kocherla M, Carvalho M A, et al. Geochemical characterization of the Krishna-Godavari and Mahanadi offshore basin (Bay of Bengal) sediments: A comparative study of provenance [J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2015, 60: 18-33. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2014.09.005
[27] Garzanti E, Andó S, France-Lanord C, et al. Mineralogical and chemical variability of fluvial sediments 2. Suspended-load silt (Ganga-Brahmaputra, Bangladesh) [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2011, 302(1-2): 107-120. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2010.11.043
[28] 孔祥淮, 刘健, 李巍然, 等. 山东半岛东北部滨浅海区表层沉积物的稀土元素及其物源判别[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2007, 27(3):51-59
KONG Xianghuai, LIU Jian, LI Weiran, et al. Geochemistry of REE and provenance of surface sediments in the littoral area of the northeastern Shandong peninsula [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2007, 27(3): 51-59.
[29] 杨守业, 李从先. REE示踪沉积物物源研究进展[J]. 地球科学进展, 1999, 14(2):164-167 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.1999.02.010
YANG Shouye, LI Congxian. Research progress in REE tracer for sediment source [J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 1999, 14(2): 164-167. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.1999.02.010
[30] 孙兴全, 刘升发, 李景瑞, 等. 孟加拉湾南部表层沉积物稀土元素组成及其物源指示意义[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2020, 40(2):80-89
SUN Xingquan, LIU Shengfa, LI Jingrui, et al. Rare earth element composition of the surface sediments from the south Bay of Bengal and its implications for provenance [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2020, 40(2): 80-89.
[31] Cullers R L, Barrett T, Carlson R, et al. Rare-earth element and mineralogic changes in Holocene soil and stream sediment: A case study in the Wet Mountains, Colorado, U. S. A. [J]. Chemical Geology, 1987, 63(3-4): 275-297. doi: 10.1016/0009-2541(87)90167-7
[32] 曹鹏, 石学法, 李巍然, 等. 安达曼海东南部海域表层沉积物稀土元素特征及其物源指示意义[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2015, 35(5):57-67
CAO Peng, SHI Xuefa, LI Weiran, et al. Rare earth element geochemistry of surface sediments in southeastern Andaman Sea and implications for provenance [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2015, 35(5): 57-67.
[33] 刘建国, 陈忠, 颜文, 等. 南海表层沉积物中细粒组分的稀土元素地球化学特征[J]. 地球科学—中国地质大学学报, 2010, 35(4):563-571 doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2010.072
LIU Jianguo, CHEN Zhong, YAN Wen, et al. Geochemical characteristics of rare earth elements in the fine-grained fraction of surface sediment from South China Sea [J]. Earth Science—Journal of China University of Geosciences, 2010, 35(4): 563-571. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2010.072
[34] Holser W T. Evaluation of the application of rare-earth elements to paleoceanography [J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 1997, 132(1-4): 309-323. doi: 10.1016/S0031-0182(97)00069-2
[35] 王爱萍, 杨守业, 李从先. 南京地区下蜀土元素地球化学特征及物源判别[J]. 同济大学学报, 2001, 29(6):657-661
WANG Aiping, YANG Shouye, LI Congxian. Elemental geochemistry of the Nanjing Xiashu loess and the provenance study [J]. Journal of Tongji University, 2001, 29(6): 657-661.
[36] Venkatarathnam K, Biscaye P E. Clay mineralogy and sedimentation in the eastern Indian Ocean [J]. Deep Sea Research and Oceanographic Abstracts, 1973, 20(8): 727-738. doi: 10.1016/0011-7471(73)90088-0
-



 下载:
下载: