Impact of ash precipitation on marine environments and diatoms: A case of 1991 from the Pinatubo volcano in the South China Sea
-
摘要:
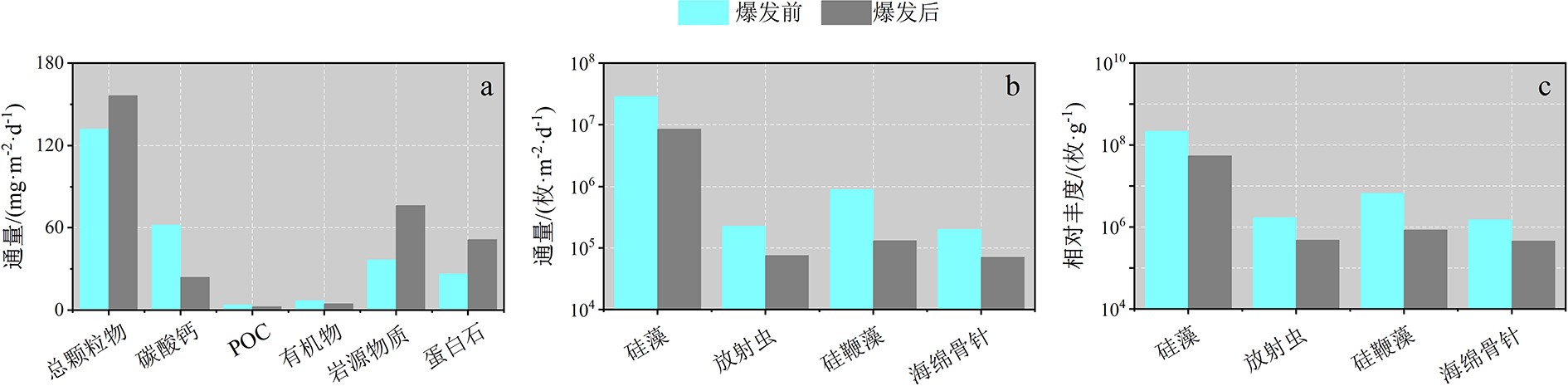
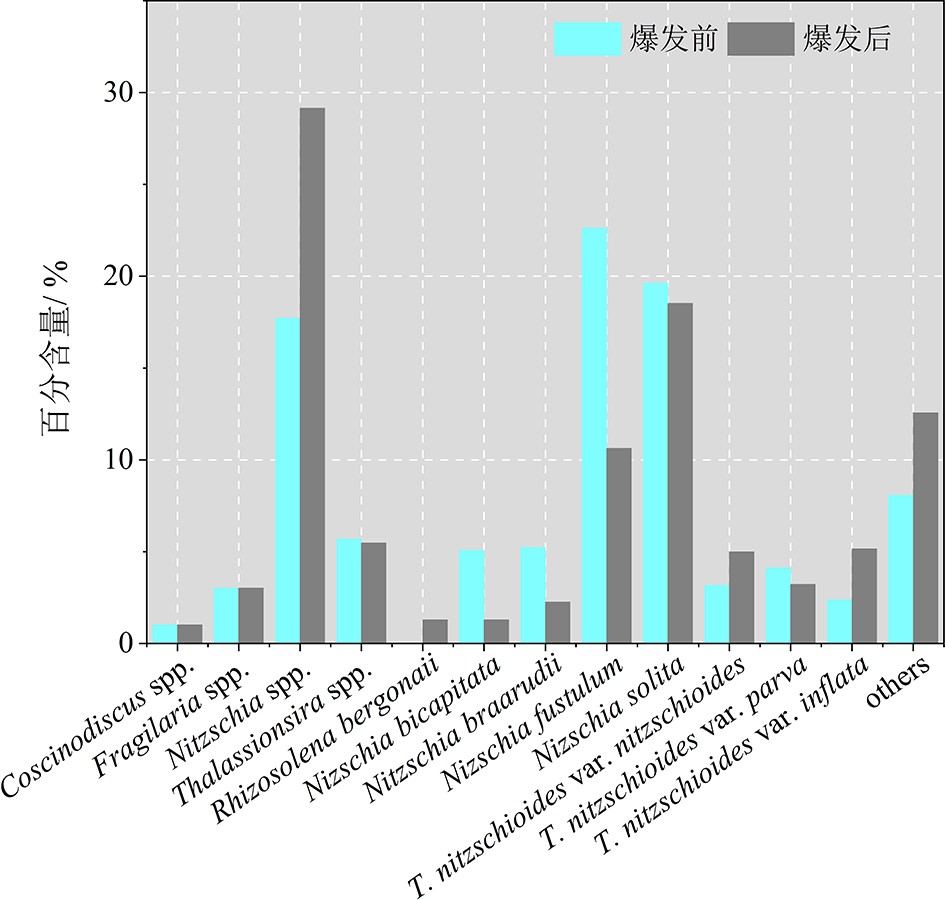
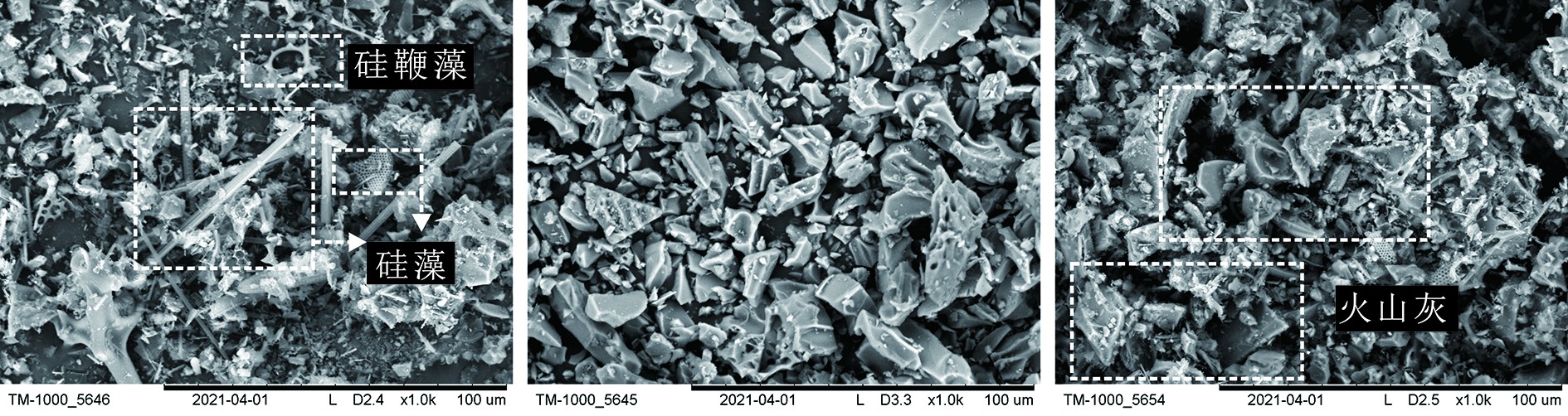
通过对菲律宾皮纳图博(Pinatubo)火山1991年6月爆发前后南海表层沉积物及沉降颗粒物中的硅藻丰度及群落组成进行分析,试图揭示皮纳图博火山爆发对南海硅藻生长的影响。研究发现,火山爆发后南海沉积物中硅藻相对丰度显著减少,原因主要在于皮纳图博火山喷发物大量沉积于南海深海,显著提高了南海沉积速率,同时稀释了沉积物中生源物质的含量。进一步对火山爆发前后同期南海中部深海沉降颗粒物开展研究发现,火山爆发次年同期沉降颗粒物总通量以及生物硅通量明显增加,而硅藻及其他硅质生物相对丰度和通量均显著降低,其中硅藻相对丰度从2.20×108 枚·g−1降到5.48×107 枚·g−1,通量从2.90×107 枚·m−2·d−1降到8.57×106 枚·m−2·d−1。1年后的南海中部深海沉降颗粒物中仍然有大量火山玻璃的存在,可能是导致湿化学法测量生物硅含量明显增加的主要原因,而硅藻乃至所有硅质生物通量及丰度的显著降低可能与火山灰沉降的负面影响有关,也可能与1991年厄尔尼诺对南海海洋环境的影响有关。总之,1991年6月皮纳图博火山爆发后南海的沉积物硅藻及沉降颗粒物硅藻丰度都出现了显著降低,但具体的环境调控机制仍有待进一步深入研究。
Abstract:The abundance and species composition of diatoms and sinking particles in the surface sediments of the South China Sea (SCS) before and after the 1991 eruption of Pinatubo volcano are analyzed in this work, in order to better reveal the impact of ash precipitation on marine diatoms. It is found that the precipitation of volcanic ash apparently increases the sedimentation rate, and dilutes the other components of the surface sediments, as the result, the relative abundance of diatoms in the surface sediments is significantly decreased. The records of sinking particles further suggest that the ash precipitation has a long-term effect to the sea environment. Both the total sinking particle flux and biogenic silica (BSi) flux in the deep water of central SCS increased substantially one year after the eruption, as the relative abundance and flux of diatoms and other siliceous organisms decreased significantly. The relative abundance decreased from 2.20×108 to 5.48×107 individuals g−1, and the flux of diatoms decreased from 2.90×107 to 8.57×106 individuals m−2 d−1. The apparent decrease in siliceous organism fluxes is attributed to the depressed productivity in the central SCS, that might be related to Pinatubo ash falling, or the impact of the El Niño in 1991. On the other hand, the increase in “BSi” flux one year after the eruption is more likely resulted from the dissolution of volcanic glass during measurement of BSi in the lab, but not from the increase of biogenic siliceous organism frustules or skeletons. It is found that there is a large amount of volcanic glass in the sinking particles. Further works are necessary to clarify the change in the BSi flux before and after the Pinatubo eruption, the decrease of siliceous organisms, and the impact of volcanic eruption on biogeochemistry and sedimentation dynamics in the SCS.
-
Key words:
- Pinatubo volcano /
- volcanic ash /
- diatom /
- biogenic silica /
- South China Sea
-

-
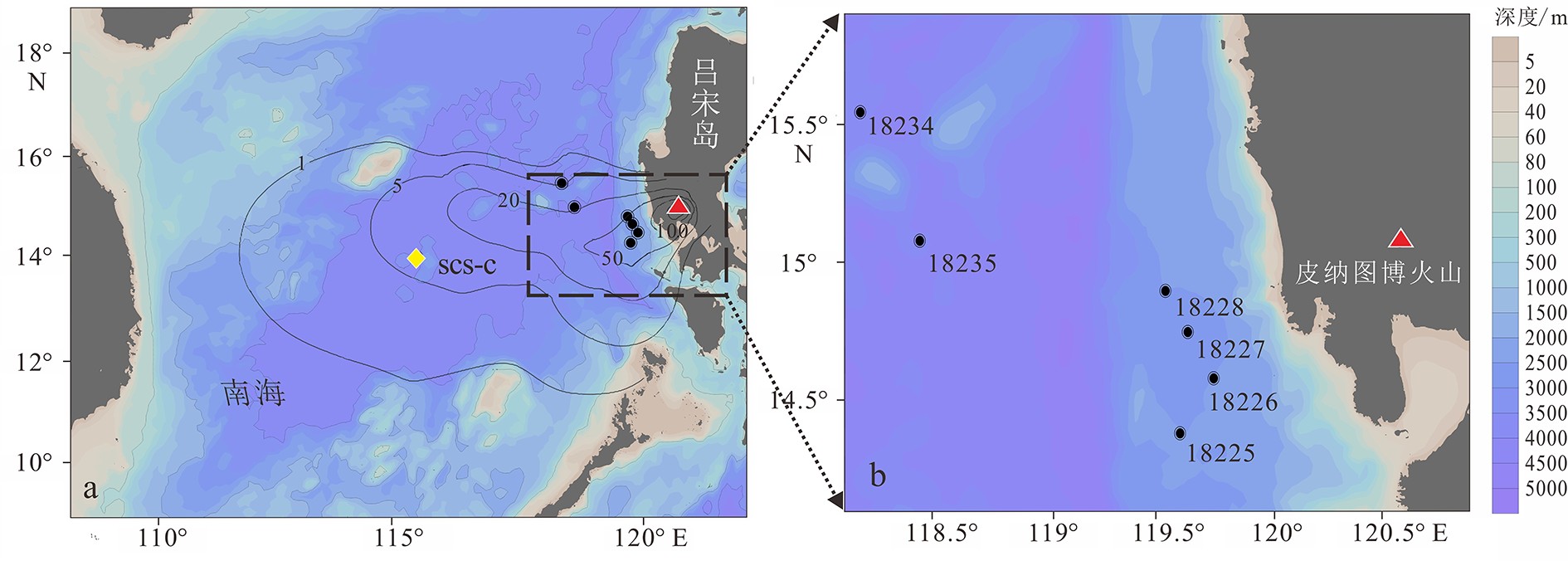
表 1 本研究所采用的箱式沉积物及沉积物捕获器站位信息
Table 1. Basic information of box core and sediment trap mooring stations
站位号 纬度 经度 水深/m 18225 14°23.0′ 119°36.0′ 2 511 18226 14°35.1' 119°45.1' 2 510 18227 14°45.8' 119°38.4' 2 576 18228 14°54.7' 119°32.3' 2 513 18234 15°33.9' 118°10.8' 3 686 18235 15°05.3' 118°26.7' 3 943 SCS-C 14°60.0′ 115°10.0′ 3 730 -
[1] 鄢全树, 石学法, 刘季花, 等. 中沙群岛近海表层沉积物中的火山灰及其对构造环境的响应[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2007, 27(4):9-16
YAN Quanshu, SHI Xuefa, LIU Jihua. Characteristics of volcanic ash in surface sediments around Zhongsha islands: response to tectonic setting in the north margin of the South China Sea [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2007, 27(4): 9-16.
[2] Lowe D J, Alloway B. Tephrochronology[M]//Jack R W, Thompson J W. Encyclopedia of Scientific Dating Methods. Dordrecht: Springer, 2015: 783-799.
[3] Frogner P, Gislason S R, Óskarsson N. Fertilization potential of volcanic ash in ocean surface waters [J]. Journal of Conference Abstracts, 2000, 5(2): 415.
[4] Lin I I, Hu C M, Lu Y H, et al. Fertilization potential of volcanic dust in the low-nutrient low-chlorophyll western North Pacific subtropical gyre: Satellite evidence and laboratory study [J]. Global Biogeochemical Cycles, 2011, 25(1): GB1006.
[5] McKinley G A, Fay A R, Eddebbar Y A, et al. External forcing explains recent decadal variability of the ocean carbon sink [J]. AGU Advances, 2020, 1(2): e2019AV000149.
[6] Song B, Buckner C T, Hembury D J, et al. Impact of volcanic ash on anammox communities in deep sea sediments [J]. Environmental Microbiology Reports, 2014, 6(2): 159-166. doi: 10.1111/1758-2229.12137
[7] Tomas C R. Identifying marine phytoplankton[M]. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 1997.
[8] 王开发, 蒋辉, 冯文科. 南海深海盆地硅藻组合的发现及其地质意义[J]. 海洋学报, 1985, 7(5):590-597
WANG Kaifa, JIANG Hui, FENG Wenke. Discovery of diatom assemblages in deep sea basins of South China Sea and its geological significance [J]. Acta Oceanogica Sinica, 1985, 7(5): 590-597.
[9] 孙美琴, 蓝东兆, 付萍, 等. 南海表层沉积硅藻的分布及其与环境因子的关系[J]. 应用海洋学学报, 2013, 32(1):46-51
SUN Meiqin, LAN Dongzhao, FU Ping, et al. Diatom distribution in surface sediment and its relation with environment factors in the South China Sea [J]. Journal of Applied Oceanography, 2013, 32(1): 46-51.
[10] Wiesner M G, Wang Y B, Zheng L F. Fallout of volcanic ash to the deep South China Sea induced by the 1991 eruption of Mount Pinatubo (Philippines) [J]. Geology, 1995, 23(10): 885-888. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1995)023<0885:FOVATT>2.3.CO;2
[11] Wiesner M G, Wetzel A, Catane S G, et al. Grain size, areal thickness distribution and controls on sedimentation of the 1991 Mount Pinatubo tephra layer in the South China Sea [J]. Bulletin of Volcanology, 2004, 66(3): 226-242. doi: 10.1007/s00445-003-0306-x
[12] Newhall C G, Self S. The volcanic explosivity index (VEI) an estimate of explosive magnitude for historical volcanism [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Oceans, 1982, 87(C2): 1231-1238. doi: 10.1029/JC087iC02p01231
[13] 肖栋, 李建平. 皮纳图博火山爆发对20世纪90年代初平流层年代际变冷突变的影响机理[J]. 科学通报, 2011, 56(8):772-780 doi: 10.1007/s11434-010-4287-9
XIAO Dong, LI Jianping. Mechanism of stratospheric decadal abrupt cooling in the Early 1990s as influenced by the Pinatubo eruption [J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2011, 56(8): 772-780. doi: 10.1007/s11434-010-4287-9
[14] Chu P C, Edmons N L, Fan C W. Dynamical mechanisms for the South China Sea seasonal circulation and thermohaline variabilities [J]. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 1999, 29(11): 2971-2989. doi: 10.1175/1520-0485(1999)029<2971:DMFTSC>2.0.CO;2
[15] Hu J Y, Kawamura H, Hong H S, et al. A review on the currents in the South China Sea: seasonal circulation, South China Sea warm current and Kuroshio intrusion [J]. Journal of Oceanography, 2000, 56(6): 607-624. doi: 10.1023/A:1011117531252
[16] Wyrtki K. Physical oceanography of the Southeast Asian waters[R]. University of California, 1961.
[17] 黄玥, 冉莉华, 蒋辉. 南海北部陆坡晚更新世末期硅藻及其古环境意义[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2006, 26(4):7-13
HUANG Yue, RAN Yihua, JIANG Hui. Diatom from the south china sea during the latest pleistocene and their paleoenvironmental significance [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2006, 26(4): 7-13.
[18] Wong G T F, Ku T L, Mulholland M, et al. The SouthEast Asian time-series study (SEATS) and the biogeochemistry of the South China Sea—an overview [J]. Deep Sea Research Part II:Topical Studies in Oceanography, 2007, 54(14-15): 1434-1447. doi: 10.1016/j.dsr2.2007.05.012
[19] Li H L, Wiesner M G, Chen J F, et al. Long-term variation of mesopelagic biogenic flux in the central South China Sea: Impact of monsoonal seasonality and mesoscale eddy [J]. Deep Sea Research Part I:Oceanographic Research Papers, 2017, 126: 62-72. doi: 10.1016/j.dsr.2017.05.012
[20] Mortlock R A, Froelich P N. A simple method for the rapid determination of biogenic opal in pelagic marine sediments [J]. Deep Sea Research Part A. Oceanographic Research Papers, 1989, 36(9): 1415-1426. doi: 10.1016/0198-0149(89)90092-7
[21] Ran L H, Chen J F, Wiesner M G, et al. Variability in the abundance and species composition of diatoms in sinking particles in the northern South China Sea: Results from time-series moored sediment traps [J]. Deep Sea Research Part II:Topical Studies in Oceanography, 2015, 122: 15-24. doi: 10.1016/j.dsr2.2015.07.004
[22] DeMaster D J. The supply and accumulation of silica in the marine environment [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1981, 45(10): 1715-1732. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(81)90006-5
[23] Shiga K, Koizumi I. Latest Quaternary oceanographic changes in the Okhotsk Sea based on diatom records [J]. Marine Micropaleontology, 1999, 38(2): 91-117. doi: 10.1016/S0377-8398(99)00041-9
[24] Smol J P, Stoermer E F. The Diatoms: Applications for the Environmental and Earth Sciences[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2010.
[25] Kuehl S A, Fuglseth T J, Thunell R C. Sediment mixing and accumulation rates in the Sulu and South China Seas: implications for organic carbon preservation in deep-sea environments [J]. Marine Geology, 1993, 111(1-2): 15-35. doi: 10.1016/0025-3227(93)90186-Y
[26] Li C F, Lin J, Kulhanek D K, et al. Opening of the South China Sea and its implications for Southeast Asian tectonics, climates, and deep mantle processes since the Late Mesozoic[R]. Integrated Ocean Drilling Program: Preliminary Reports, 2014: 1.
[27] Browning T J, Bouman H A, Henderson G M, et al. Strong responses of Southern Ocean phytoplankton communities to volcanic ash [J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2014, 41(8): 2851-2857. doi: 10.1002/2014GL059364
[28] Bryan S E, Cook A G, Evans J P, et al. Rapid, long-distance dispersal by pumice rafting [J]. PLoS One, 2012, 7(7): e40583. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0040583
[29] Hoffmann L J, Breitbarth E, Ardelan M V, et al. Influence of trace metal release from volcanic ash on growth of Thalassiosira pseudonana and Emiliania huxleyi [J]. Marine Chemistry, 2012, 132-133: 28-33. doi: 10.1016/j.marchem.2012.02.003
[30] Mélançon J, Levasseur M, Lizotte M, et al. Early response of the northeast subarctic Pacific plankton assemblage to volcanic ash fertilization [J]. Limnology and Oceanography, 2014, 59(1): 55-67. doi: 10.4319/lo.2014.59.1.0055
[31] 葛祥英. 四川盆地东部奥陶—志留纪交替时期事件沉积与有机质富集[D]. 中国地质大学(北京)博士学位论文, 2020
GE Xiangying. The events across the Ordovician-Silurian transition and the organic enrichment of black shales in the east of Sichuan Basin[D]. Master Dissertation of China University of Geosciences (Beijing).
[32] Flaathen T K, Gislason S R. The effect of volcanic eruptions on the chemistry of surface waters: The 1991 and 2000 eruptions of Mt. Hekla, Iceland [J]. Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, 2007, 164(4): 293-316. doi: 10.1016/j.jvolgeores.2007.05.014
[33] Kockum P C F, Herbert R B, Gislason S R. A diverse ecosystem response to volcanic aerosols [J]. Chemical Geology, 2006, 231(1-2): 57-66. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2005.12.008
[34] Jones M T, Gislason S R. Rapid releases of metal salts and nutrients following the deposition of volcanic ash into aqueous environments [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2008, 72(15): 3661-3680. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2008.05.030
[35] Voskresenskaya E N, Zelenko A A, Polonsky A B. El Niño in 1991-1992 and its manifestations in the tropical Atlantic [J]. Physical Oceanography, 1993, 4(6): 487-495. doi: 10.1007/BF02197410
[36] Wang C Z, Wang W Q, Wang D X, et al. Interannual variability of the South China Sea associated with El Niño [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Oceans, 2006, 111(C3): C03023.
[37] Zhao H, Tang D L. Effect of 1998 El Niño on the distribution of phytoplankton in the South China Sea [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Oceans, 2006, 112(C2): C02017.
-



 下载:
下载: