Facies evolution and its controlling factors of the Pinghu Formation in the Kongqueting area of Xihu Depression, the East China Sea
-
摘要:
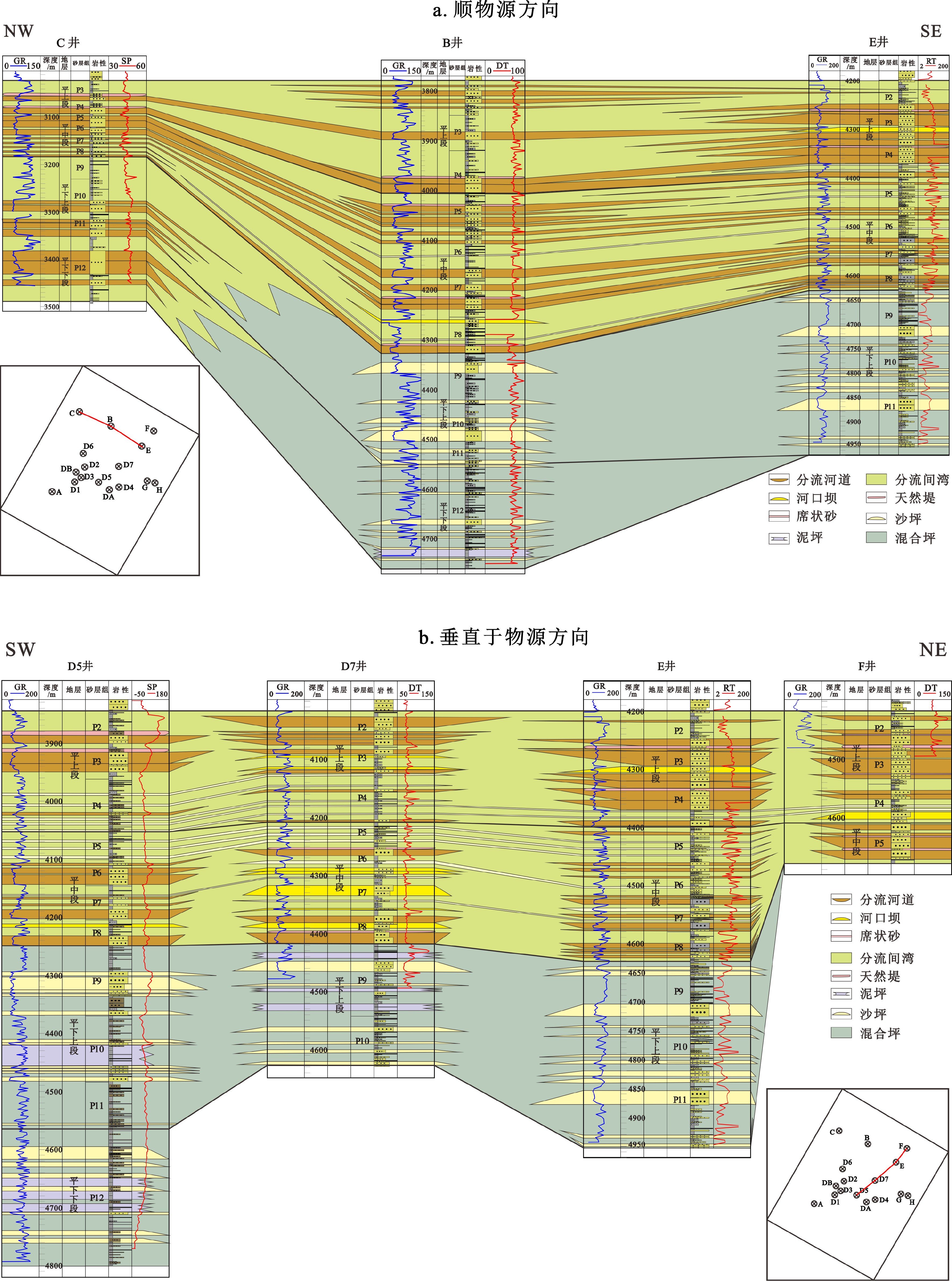
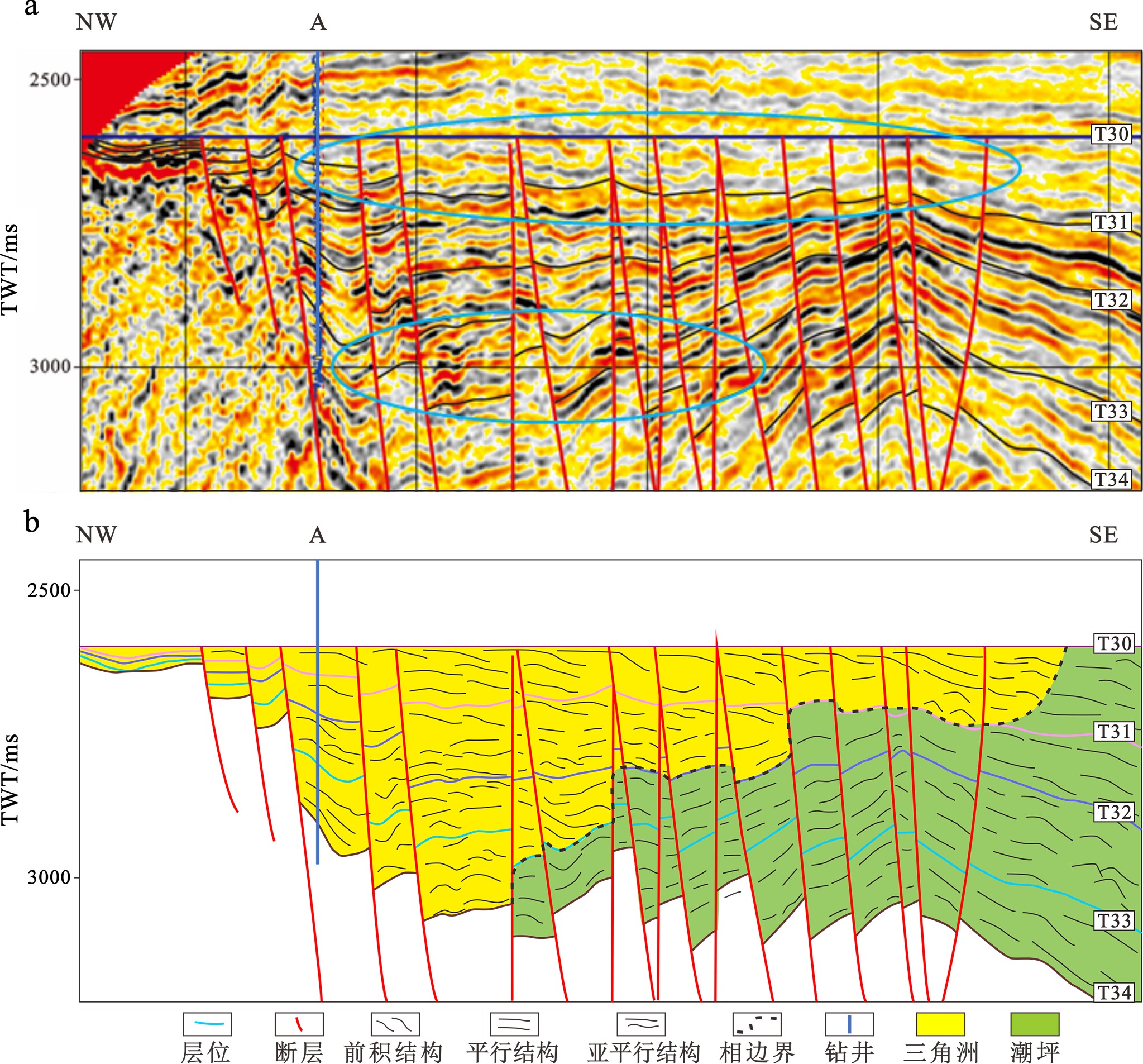
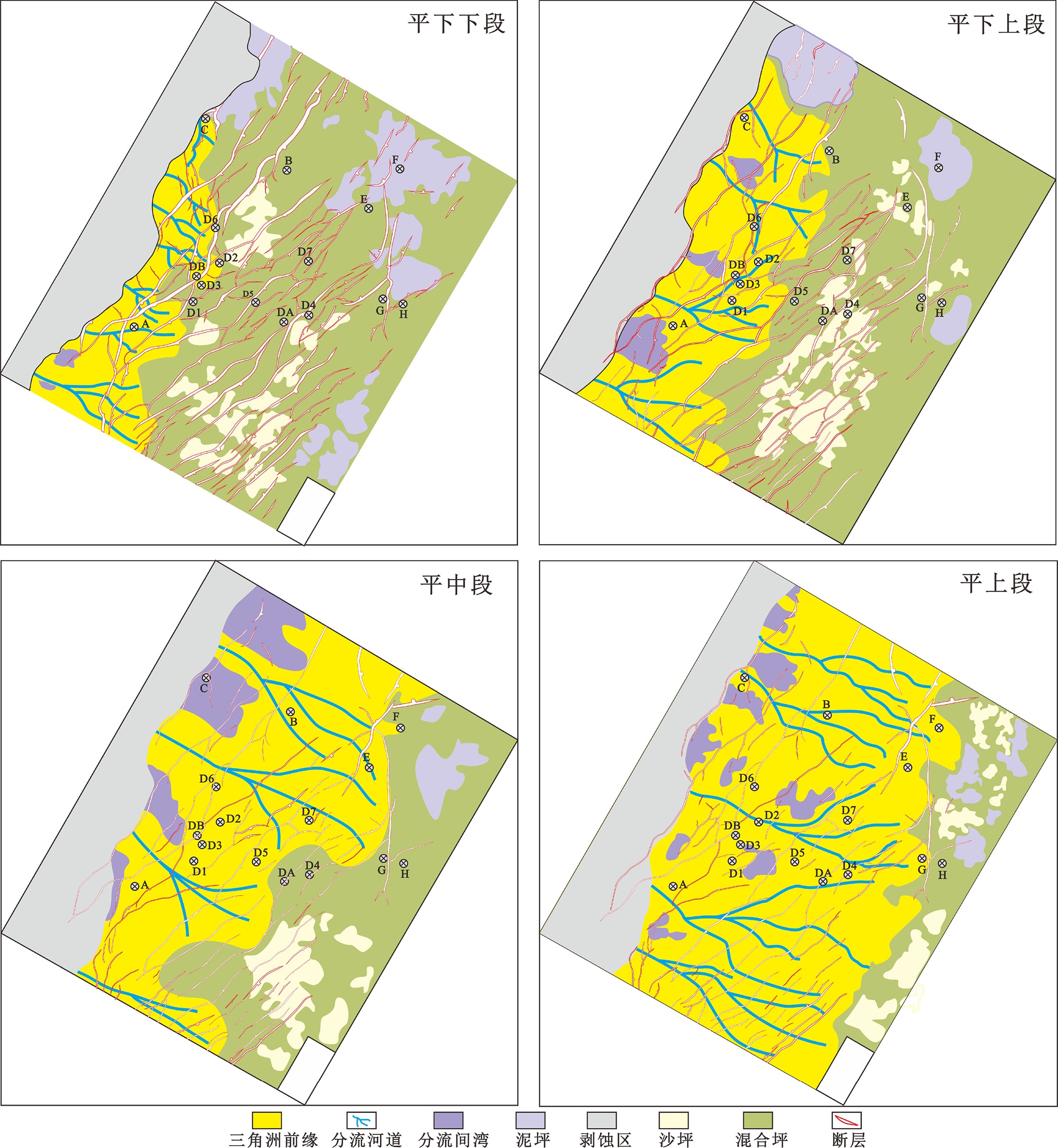
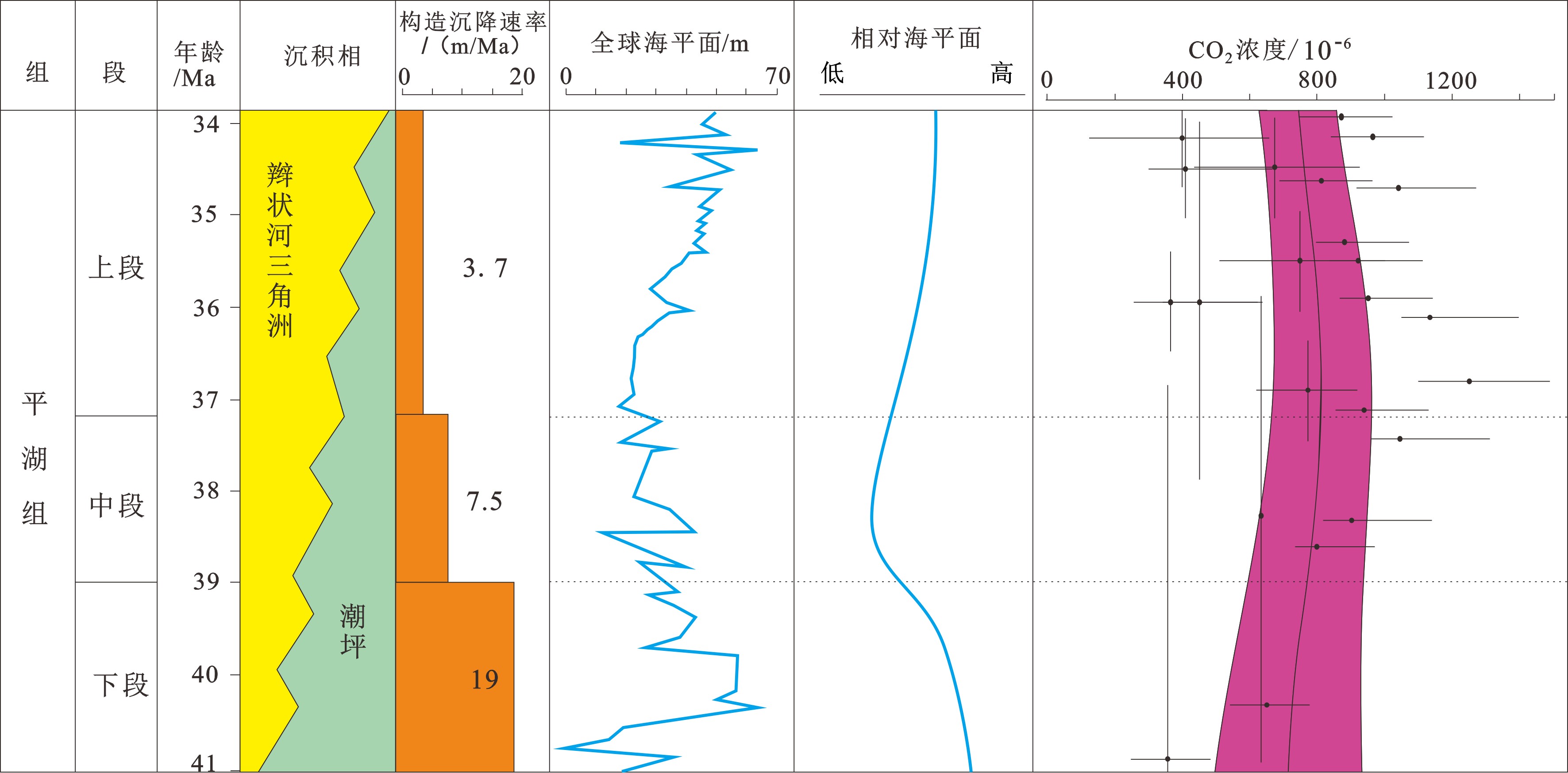
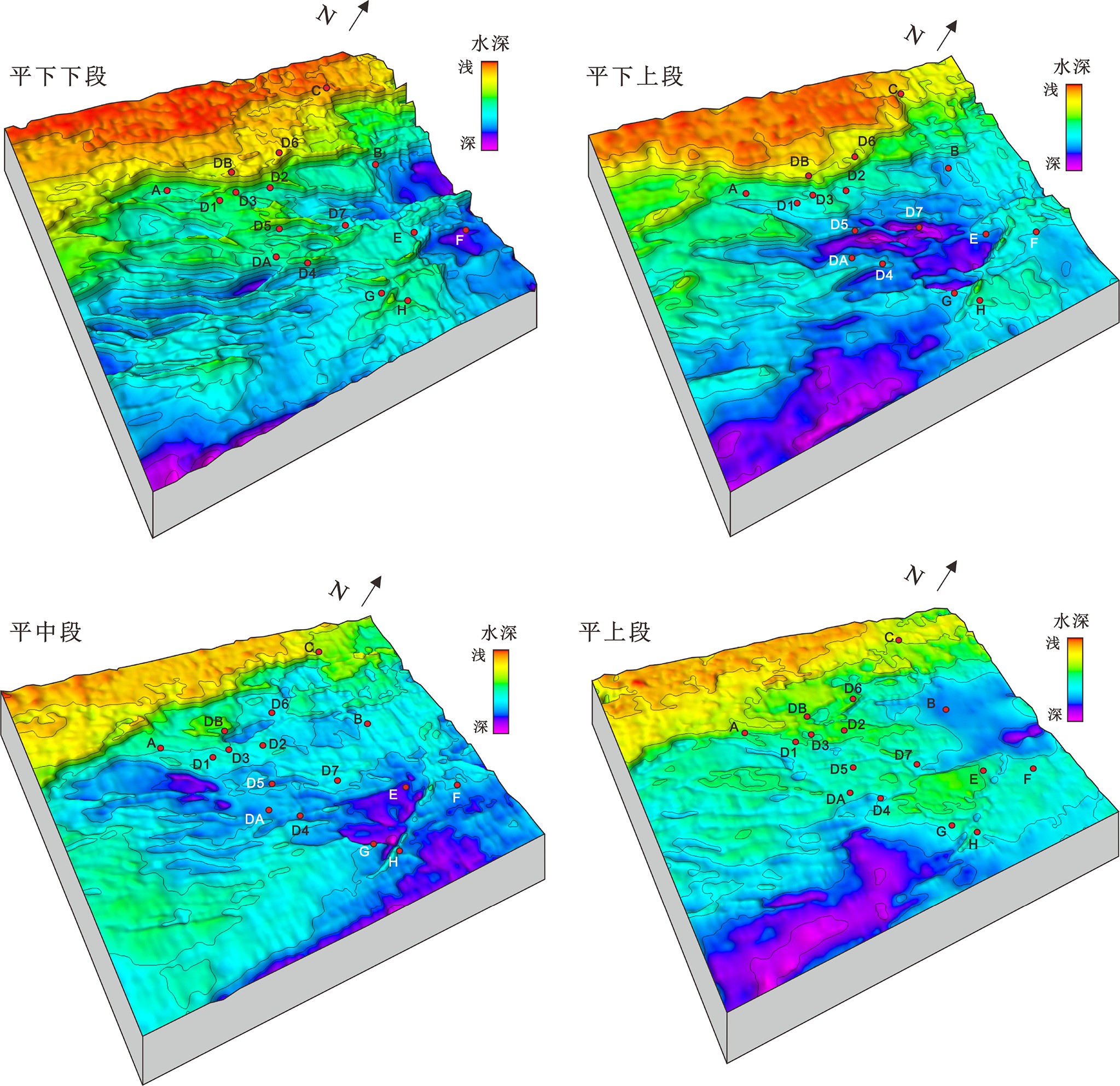
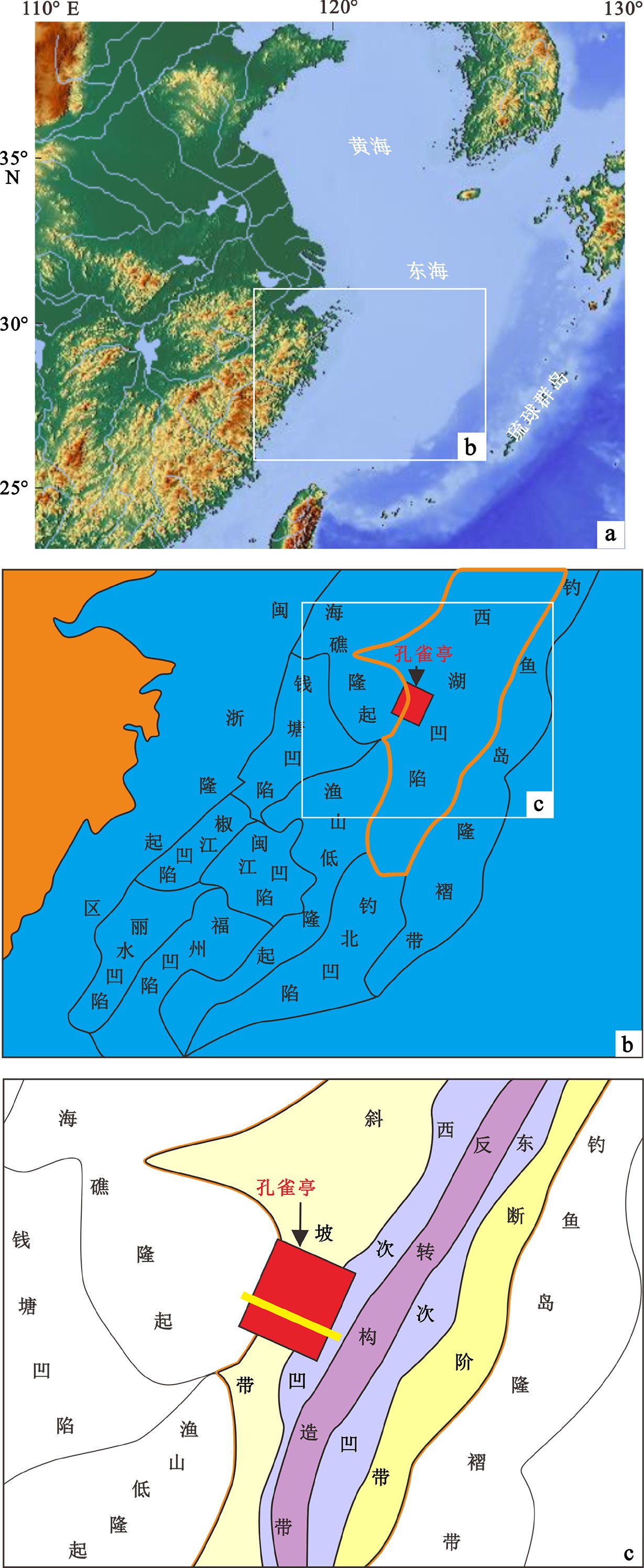
东海陆架盆地西湖凹陷含有巨量的石油天然气资源,具有极佳的勘探潜力,其中平湖组沉积作为重要的含油气层,已成为近期油气勘探的聚焦点。孔雀亭地区为西湖凹陷研究程度较低的区块,对于该区域沉积相及其控制因素方面的研究仍然较少。基于钻井资料与三维地震资料对孔雀亭平湖组沉积微相进行精细刻画,并系统分析了全球海平面、区域构造、古气候、古地貌对研究区沉积微相演变的控制作用。研究表明,平湖组下段(包括平下下段、平下上段)以潮坪沉积为主,辫状河三角洲沉积只发育在源区附近,而平中段与平上段以辫状河三角洲沉积为主,潮坪沉积分布面积迅速降低。由平下段至平中段,随着相对海平面(全球海平面与区域构造综合效应)下降,辫状河三角洲向海方向发生进积。同时,平中段与平上段时期极高的CO2浓度使得大陆源区剥蚀量快速增加,大量沉积物随着河流输入至西湖凹陷,从而进一步加剧了辫状河三角洲的向海推进。平下段与平中段早期的古地貌断陷发育较多,对辫状河三角洲的扩张存在限制作用,而经历了平中段大量沉积物充填之后,早期的洼陷逐渐被填平,从而平上段的辫状河三角洲可以大范围地向海方向发生推进,形成规模庞大的三角洲砂体沉积。
Abstract:The East China Sea Shelf Basin contains a huge amount of petroleum resources and the Pinghu Formation is one of the major exploration targets. However, the Kongqueting area has rarely been researched, and few studies have been made to sedimentary facies evolution and its controlling factors. Based on drilling and 3D seismic data, microfacies of the Pinghu Formation are carefully described in this paper and the controls of global sea level fluctuation, regional tectonics, paleoclimate, and paleogeography over the facies distribution patterns discussed. The Lower Pinghu Formation is dominated by tidal flat facies, and the braided river delta facies only appeared in some places near uplifts. By contrast, the Middle and Upper Pinghu Formations are dominated by deltaic deposits of braided rivers. Relative sea level falling, as a joint result of global sea level change and regional tectonics, resulted in the progradation of braided river delta towards offshore. Meanwhile, the high concentration of CO2 in the atmosphere during the Middle and Later Pinghu periods caused a sharp increase of erosion. Enormous sediments provided by the source areas were transported into the Xihu Depression, which accelerated the progradation of braided river delta into the sea. In addition, the paleogeographic framework during the Middle to Lower Pinghu Periods were characterized by many fault-controlled sags, which limited the expansion of braided river delta. These sags were filled by sediments in Middle Pinghu Period, and turned to tidal flat in Later Pinghu Period, which also helped the expansion of deltaic deposits of the Upper Pinghu Formation.
-
Key words:
- sedimentary facies /
- delta /
- tidal flat /
- paleogeography /
- Xihu Depression
-

-
[1] 张绍亮, 蒋一鸣. 西湖凹陷平湖斜坡带始新统平湖组层序地层[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2013, 29(10):8-13, 64
ZHANG Shaoliang, JIANG Yiming. High resolution sequence stratigraphy of the Eocene Pinghu Formation, Pinghu Slope, Xihu Sag [J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2013, 29(10): 8-13, 64.
[2] 杨彩虹, 高兆红, 蒋一鸣, 等. 西湖凹陷平湖斜坡带始新统平湖组碎屑沉积体系再认识[J]. 石油天然气学报(江汉石油学院院报), 2013, 35(9):11-14
YANG Caihong, GAO Zhaohong, JIANG Yiming, et al. Reunderstanding of Clastic Rock Sedimentary Facies of Eocene Pinghu Formation in Pinghu Slope of Xihu Sag [J]. Journal of Oil and Gas Technology (Journal of Jianghan Petroleum Institute), 2013, 35(9): 11-14.
[3] 李昆, 周兴海, 吴嘉鹏, 等. 西湖凹陷中下始新统宝石组沉积相研究[J]. 海洋石油, 2017, 37(1):16-20, 79 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-2336.2017.01.016
LI Kun, ZHOU Xinghai, Wu Jiapeng, et al. Sedimentary facies of Middle-Lower Eocene Baoshi Formation in Xihu Sag, East China Sea Shelf Basin [J]. Offshore Oil, 2017, 37(1): 16-20, 79. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-2336.2017.01.016
[4] 王果寿, 周卓明, 肖朝辉, 等. 西湖凹陷春晓区带下第三系平湖组、花港组沉积特征[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2002, 23(3):257-261, 265 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9985.2002.03.012
WANG Guoshou, ZHOU Zhuoming, XIAO Chaohui, et al. Sedimentary Characteristics of Eocene Pinghu Formation and Huaguang Formation in Chunxiao zone of Xihu Lake Depression [J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2002, 23(3): 257-261, 265. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9985.2002.03.012
[5] 葛海波. 东海陆架盆地西湖凹陷天外天—黄岩地区平湖—花港组层序地层及沉积相研究[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2014: 1-73.
GE Haibo. The study of Pinghu and Huagang Formation sequence stratigraphy and sedimentation facies feature in Tianwaitian and Huangyan region of Xihu Sag, East China Sea [D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of technology, 2014: 1-73.
[6] 薛丹, 胡明毅, 邓猛. 西湖凹陷Y气田平湖组上段沉积相特征及有利砂体预测[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2014, 14(24):40-47 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2014.24.008
XUE Dan, HU Mingyi, DENG Meng. Sedimentary Facies Characteristics and Sandstone Body Prediction of the Upper Part of Pinghu Formation, Y Gas Field [J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2014, 14(24): 40-47. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2014.24.008
[7] Li S L, Yu X H, Steel R, et al. Change from tide-influenced deltas in a regression-dominated set of sequences to tide-dominated estuaries in a transgression-dominated sequence set, East China Sea Shelf Basin [J]. Sedimentology, 2018, 65(7): 2312-2338. doi: 10.1111/sed.12466
[8] 王超, 唐贤君, 蒋一鸣, 等. 西湖凹陷天台斜坡带北部构造变换带特征及油气地质意义[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2020, 40(6):93-105
WANG Chao, TANG Xianjun, JIANG Yiming, et al. Characteristics of the structural transfer zone of northern Tiantai slope in Xihu Sag of the East China Sea Basin and their petroleum geological significances [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2020, 40(6): 93-105.
[9] 余朝丰, 陈建文, 杜远生, 等. 东海西湖凹陷平湖组层序地层划分[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2007, 27(5):85-90
YU Chaofeng, CHEN Jianwen, DU Yuansheng, et al. Division of sequence stratigraphy of Pinghu Formation in Xihu Sag in East China Sea [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2007, 27(5): 85-90.
[10] 张建培, 徐发, 钟韬, 等. 东海陆架盆地西湖凹陷平湖组-花港组层序地层模式及沉积演化[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2012, 32(1):35-41
ZHANG Jianpei, XU Fa, ZHONG Tao, et al. Sequence stratigraphic models and sedimentary evolution of Pinghu and Huaguang Formations in Xihu Trough [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2012, 32(1): 35-41.
[11] 蔡华, 秦兰芝, 刘英辉. 西湖凹陷平北斜坡带海陆过渡相源-汇系统差异性及其耦合模式[J]. 地球科学, 2019, 44(3):880-897
CAI Hua, QIN Lanzhi, LIU Yinghui. Differentiation and coupling model of source-to-sink systems with transitional facies in Pingbei slope of Xihu Sag [J]. Earth Science, 2019, 44(3): 880-897.
[12] 刘亚茹, 高顺莉, 周平, 等. 西湖凹陷转换断裂发育特征及其油气地质意义[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2020, 36(10):42-49
LIU Yaru, GAO Shunli, ZHOU Ping, et al. Characteristics of transform faults in the Xihu Sag and their significance to hydrocarbon accumulation [J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2020, 36(10): 42-49.
[13] 付振群. 东海陆架盆地西湖凹陷平湖组层序地层及沉积特征研究[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2014: 1-66.
FU Zhenqun. The study of sequence stratigraphy and sedimentary characteristics of Pinghu Formation in Xihu sag of East China Sea Basin [D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of technology, 2014: 1-66.
[14] 于水. 西湖凹陷西斜坡平湖组烃源岩沉积成因分析[J]. 地球科学, 2020, 45(5):1722-1736
YU Shui. Depositional Genesis Analysis of Source Rock in Pinghu Formation of Western Slope, Xihu Depression [J]. Earth Science, 2020, 45(5): 1722-1736.
[15] 赵丽娜, 陈建文, 张银国, 等. 东海西湖凹陷平湖构造带平湖组沉积特征[J]. 世界地质, 2008, 27(1):42-47 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5589.2008.01.008
ZHAO Lina, CHEN Jianwen, ZHANG Yinguo, et al. Sedimentary characteristics of Pinghu Formation in Pinghu structural belt of Xihu depression, East China Sea [J]. Global Geology, 2008, 27(1): 42-47. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5589.2008.01.008
[16] 刘成鑫. 东海平湖油气田平湖组沉积相研究[J]. 海洋石油, 2010, 30(2):9-13 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-2336.2010.02.009
LIU Chengxin. Study on sedimentary facies for Pinghu Formation in Pinghu oil and gas field in East China Sea Basin [J]. Offshore Oil, 2010, 30(2): 9-13. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-2336.2010.02.009
[17] 蒋海军, 胡明毅, 胡忠贵, 等. 西湖凹陷古近系沉积环境分析: 以微体古生物化石为主要依据[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2011, 23(1):74-78 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8926.2011.01.013
JIANG Haijun, HU Mingyi, Hu Zhonggui, et al. Sedimentary environment of Paleogene in Xihu Sag: Microfossil as the main foundation [J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2011, 23(1): 74-78. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8926.2011.01.013
[18] 蒋一鸣, 周倩羽, 李帅, 等. 西湖凹陷西部斜坡带平湖组含煤岩系沉积环境再思考[J]. 中国煤炭地质, 2016, 28(8):18-25 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1803.2016.08.04
JIANG Yiming, ZHOU Qianyu, LI Shuai, et al. Reconsideration of Pinghu Formation coal-bearing rock series sedimentary environment in western slope of Xihu Depression [J]. Coal Geology of China, 2016, 28(8): 18-25. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1803.2016.08.04
[19] 周瑞琦, 傅恒, 徐国盛, 等. 东海陆架盆地西湖凹陷平湖组--花港组沉积层序[J]. 沉积学报, 2018, 36(1):132-141
ZHOU Ruiqi, FU Heng, XU Guosheng, et al. Eocene Pinghu Formation-Oligocene Huagang Formation Sequence Stratigraphy and Depositional Model of Xihu Sag in East China Sea Basin [J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2018, 36(1): 132-141.
[20] Fielding C R, Allen J P, Alexander J, et al. Facies model for fluvial systems in the seasonal tropics and subtropics [J]. Geology, 2009, 37(7): 623-626. doi: 10.1130/G25727A.1
[21] Gould K M, Piper D J W, Pe-Piper G, et al. Facies, provenance and paleoclimate interpretation using spectral gamma logs: Application to the Lower Cretaceous of the Scotian Basin [J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2014, 57: 445-454. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2014.06.008
[22] Mehrabi H, Rahimpour-Bonab H, Hajikazemi E, et al. Controls on depositional facies in Upper Cretaceous carbonate reservoirs in the Zagros area and the Persian Gulf, Iran [J]. Facies, 2015, 61(4): 23. doi: 10.1007/s10347-015-0450-8
[23] Ghandour I M, Haredy R A. Facies Analysis and Sequence Stratigraphy of Al-Kharrar Lagoon Coastal Sediments, Rabigh Area, Saudi Arabia: Impact of Sea-Level and Climate Changes on Coastal Evolution [J]. Arabian Journal for Science and Engineering, 2019, 44(1): 505-520. doi: 10.1007/s13369-018-3662-8
[24] Geyman E C, Maloof A C, Dyer B. How is sea level change encoded in carbonate stratigraphy? [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2021, 560: 116790. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2021.116790
[25] Wu F, Xie X N, Zhu Y H, et al. Sequence stratigraphy of the Late Oligocene carbonate system on the Xisha Islands in the South China Sea [J]. International Journal of Earth Sciences, 2021, 110(5): 1611-1629. doi: 10.1007/s00531-021-02033-9
[26] Assal E M, Abdel-Fattah Z A, El-Asmar H M. Facies architecture and controlling factors induced depositional model of the Quaternary carbonate eolianites in the northwestern Mediterranean coast of Egypt [J]. International Journal of Earth Sciences, 2020, 109(5): 1659-1682. doi: 10.1007/s00531-020-01863-3
[27] 熊萍. 南海西北部陆缘晚更新世以来古地貌重建及沉积响应研究[D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学(武汉), 2019, 1-112.
XIONG Ping. Paleogeographic reconstructions and sedimentary response since Late Pleistocene in the northwestern margin of South China Sea [D]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences (Wuhan), 2019, 1-112.
[28] 张建国, 姜在兴, 刘立安, 等. 渤海湾盆地沾化凹陷沙河街组三段下亚段细粒沉积岩岩相特征与沉积演化[J]. 石油学报, 2021, 42(3):293-306
ZHANG Jianguo, JIANG Zaixing, LIU Li’an, et al. Lithofacies and depositional evolution of fine-grained sedimentary rocks in the lower submember of the Member 3 of Shahejie Formation in Zhanhua sag, Bohai Bay Basin [J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2021, 42(3): 293-306.
[29] 姜衍, 张向涛, 龙祖烈, 等. 南海北部珠江口盆地烃源岩成因: 阳江凹陷的资源潜力[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2021, 45(1):90-107
JIANG Yan, ZHANG Xiangtao, Long Zulie, et al. Formation of Source Rocks in the Pearl River Mouth Basin, Northern South China Sea: Resource Potential of the Yangjiang Sag [J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 2021, 45(1): 90-107.
[30] Bridges R A, Castle J W. Local and regional tectonic control on sedimentology and stratigraphy in a strike-slip basin: Miocene Temblor Formation of the Coalinga area, California, USA [J]. Sedimentary Geology, 2003, 158(3-4): 271-297. doi: 10.1016/S0037-0738(02)00314-7
[31] Tamura T, Masuda F. Inner shelf to shoreface depositional sequence in the Sendai coastal prism, Pacific coast of northeastern Japan: spatial and temporal growth patterns in relation to Holocene relative sea-level change [J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2004, 23(4): 567-576. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2003.09.002
[32] Lin W, Bhattacharya J P. Depositional facies and the sequence stratigraphic control of a mixed-process influenced clastic wedge in the Cretaceous Western Interior Seaway: The Gallup System, New Mexico, USA [J]. Sedimentology, 2020, 67(2): 920-950. doi: 10.1111/sed.12667
[33] Zhu W L, Zhong K, Fu X W, et al. The formation and evolution of the East China Sea Shelf Basin: A new view [J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2019, 190: 89-111. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2018.12.009
[34] Miller G K, Browning V J, Schmelz W J, et al. Cenozoic sea-level and cryospheric evolution from deep-sea geochemical and continental margin records [J]. Science Advances, 2020, 6(20): eaaz 1346. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aaz1346
[35] Clift P D. Controls on the erosion of Cenozoic Asia and the flux of clastic sediment to the ocean [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2006, 241(3-4): 571-580. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2005.11.028
[36] Clift P D, Wan S M, Blusztajn J. Reconstructing chemical weathering, physical erosion and monsoon intensity since 25 Ma in the northern South China Sea: A review of competing proxies [J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2014, 130: 86-102. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2014.01.002
[37] 陈树光, 任建业, 吴峰, 等. 渤中坳陷沙北地区古地貌恢复及其应用[J]. 特种油气藏, 2015, 22(2):52-55 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6535.2015.02.012
CHEN Shuguang, REN Jianye, WU Feng, et al. Palaeogeomorphic Recovery and Its Application in Shabei Area, Central Bohai Depression [J]. Special Oil & Gas Reservoirs, 2015, 22(2): 52-55. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6535.2015.02.012
[38] 林畅松, 夏庆龙, 施和生, 等. 地貌演化、源-汇过程与盆地分析[J]. 地学前缘, 2015, 22(1):9-20
LIN Changsong, XIA Qinglong, SHI Hesheng, et al. Geomorphological evolution, source to sink system and basin analysis [J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2015, 22(1): 9-20.
[39] 金民东, 谭秀成, 童明胜, 等. 四川盆地高石梯—磨溪地区灯四段岩溶古地貌恢复及地质意义[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2017, 44(1):58-68 doi: 10.1016/S1876-3804(17)30008-3
JIN Mindong, TAN Xiucheng, TONG Mingsheng, et al. Karst paleogeomorphology of the fourth Member of Sinian Dengying Formation in Gaoshiti-Moxi area, Sichuan Basin, SW China: Restoration and geological significance [J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2017, 44(1): 58-68. doi: 10.1016/S1876-3804(17)30008-3
-



 下载:
下载: