Geochemistry and sources of rare earth elements in cobalt-rich crusts from the Caiwei and Xufu seamounts, West Pacific Ocean
-
摘要:
利用X射线衍射法、等离子体发射光谱法和等离子体质谱法分析了西太平洋采薇海山和徐福海山富钴结壳矿物相组成以及常微量元素含量,探讨稀土元素地球化学特征和物质来源。研究表明,富钴结壳样品主要结晶矿物为水羟锰矿,次要矿物包括石英、斜长石、钾长石和碳氟磷灰石,同时含有大量非晶态铁氧/氢氧化物。富钴结壳的Mn和Fe含量最高,Mn含量为16.20%~26.62%,Fe含量为8.56%~18.19%,老壳层(IV和V)发生了磷酸盐化作用。富钴结壳的稀土元素明显富集,轻稀土元素明显高于重稀土元素,稀土总量为1 842~2 854 µg/g,其中,Ce约占50%。老壳层中稀土元素含量明显高于新壳层,这可能与老壳层发生磷酸盐化作用有关。稀土元素配分模式呈现Ce正异常、Eu无异常,具有明显Ce富集特征。富钴结壳的稀土元素与Ce、Y、CaO、P2O5、Ba和Sr具有正相关性关系,与Fe、Al2O3、Na2O、K2O、MgO、TiO2、Pb和V具有负相关性关系,与Mn、Co、Cu、Ni和Zn相关性不明显。利用聚类分析方法,可以把富钴结壳的元素分成4组:①磷酸盐组:REE、Ce、Y、CaO、P2O5、Ba和Sr; ②亲锰元素组:Mn、Co、Cu、Ni和Zn;③亲铁元素组:Fe、TiO2、Pb和V;④碎屑元素组:Al2O3、Na2O、K2O和MgO。西太平洋采薇海山和徐福海山富钴结壳是水成沉积成因,稀土元素的来源推测为海水中稀土元素随磷酸盐组分共同沉淀而进入富钴结壳,从而导致稀土元素的富集。
Abstract:Using the testing methods of XRD, ICP-OES and ICP-MS, the mineral composition, major and minor elements contents of cobalt-rich crusts collecting from the Caiwei Guyot and Xufu Guyot in the West Pacific Ocean have been determined. Based on the data, we discussed in this paper the geochemical characteristics and material sources of the REE. It is observed that the cobalt-rich crust is dominated by the crystalline mineral of vernadites, accompanied by the auxiliary minerals of quartz, plagioclase, potassium feldspar and carbon fluoride apatite. Amorphous ferric minerals also occur in certain amounts in the crusts. In terms of chemical composition, Mn contents change within 16.20%~26.62%, and Fe contents 8.56%~18.19%, which are the highest among the others. Phosphatization is observed in the old crust layers. REE are enriched in the cobalt-rich crusts. LREE are higher than HREE. REE contents are as high as 1 842~2 854 µg/g, in which Ce accounted for nearly 50%. Moreover, it is found that REE contents in the old layers are higher than that in the new layers, and it is believed that phosphatization in the old layers might play an active role in the REE distribution pattern. And REE diagrams show that there are positive Ce anomalies but no Eu anomalies, so Ce is relatively enriched. Meanwhile, REE show positive correlation with Ce, Y, CaO, P2O5, Ba and Sr, negative correlation with Fe, Al2O3, Na2O, K2O, MgO, TiO2, Pb and V, but no correlation with Mn, Co, Cu, Ni and Zn. By the way, the elements of the cobalt-rich crusts may be classified into four groups by clustering analysis. ①Phosphate group including REE, Ce, Y, CaO, P2O5, Ba and Sr. ② Mn group including Mn, Co, Cu, Ni and Zn. ③ Fe group including Fe, TiO2, Pb and V. ④ Detritus group including Al2O3, Na2O, K2O and MgO. In conclusion, cobalt-rich crusts from the Caiwei Guyot and Xufu Guyot of the West Pacific Ocean are hydrogenetic in origin, and REE are precipitated together with phosphate group in the seawater, that caused the enrichment of REE in the cobalt-rich crusts.
-
Key words:
- cobalt-rich crusts /
- REE /
- geochemical /
- source /
- West Pacific Ocean
-

-
图 4 富钴结壳成因判别三角图[26]
Figure 4.
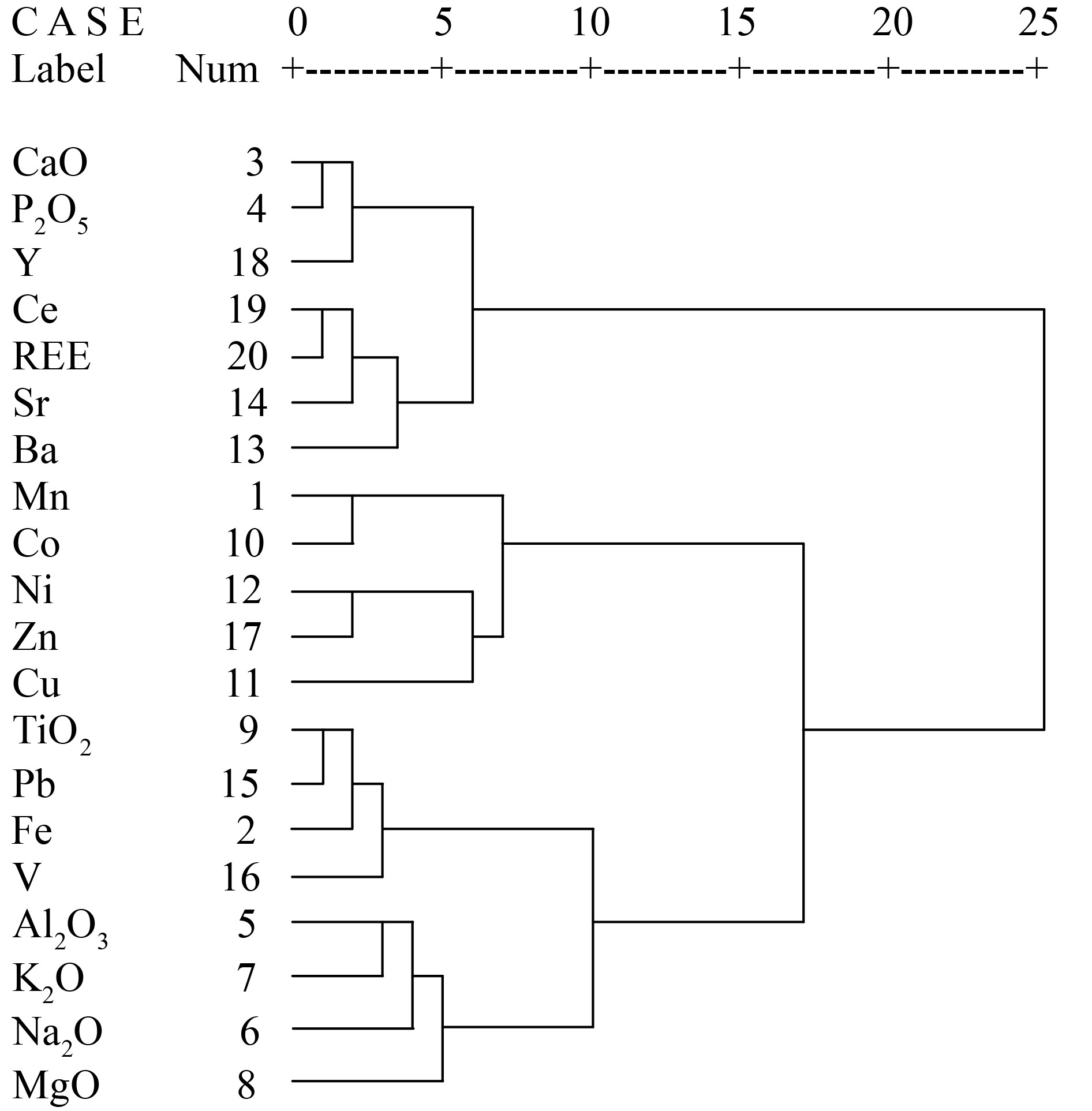
图 6 富钴结壳特征元素相关性图[30]
Figure 6.
表 1 富钴结壳CD16和XD3不同构造层样品描述
Table 1. Description of different structural layer in cobalt-rich crust samples CD16 and XD3
样品编号 构造层 深度/mm 样品描述 CD16(I) 第I构造层 0~16 褐黑色,较致密,表层葡萄体状突起,柱状构造 CD16(II) 第II构造层 16~26 黑色,致密,柱状构造 CD16(III) 第III构造层 26~60 黄褐色,疏松,黏土较多,树丛状构造 CD16(IV) 第IV构造层 60~88 黑色,致密,发育磷酸盐脉,斑杂状构造 CD16(V) 第V构造层 88~98 亮黑色,致密,较多磷酸盐脉,水平层纹状构造 XD3(I) 第I构造层 0~14 褐黑色,较致密,表层鲕粒状突起,柱状构造 XD3(II) 第II构造层 14~24 黑色,致密,柱状构造 XD3(III) 第III构造层 24~56 黄褐色,疏松,黏土较多,树枝状构造 XD3(IV) 第IV构造层 56~82 黑色,致密,磷酸盐化严重,斑杂状构造 XD3(V) 第V构造层 82~120 亮黑色,致密,较多磷酸盐脉,水平纹状构造 表 2 富钴结壳CD16和XD3样品常量元素含量
Table 2. Major elements contents of the cobalt-rich crust samples of CD16 and XD3
元素 CD16(I) CD16(II) CD16(III) CD16(IV) CD16(V) XD3(I) XD3(II) XD3(III) XD3(IV) XD3(V) Mn 16.20 22.78 18.85 18.52 20.26 20.23 24.20 26.62 17.72 21.12 Fe 17.10 16.26 16.62 10.78 8.56 18.19 15.62 11.28 9.71 9.80 CaO 2.65 3.16 3.46 17.12 17.32 2.86 3.37 4.75 17.95 12.39 P2O5 0.80 0.82 1.20 9.45 9.59 0.88 0.78 1.43 10.18 6.49 Al2O3 1.67 1.49 2.81 1.04 0.66 1.52 1.54 1.98 1.23 0.44 Na2O 2.46 2.57 2.61 2.15 1.97 2.20 2.16 2.28 1.92 1.73 MgO 1.70 1.90 1.97 1.64 1.51 1.73 1.80 2.21 1.55 1.34 TiO2 1.89 1.84 1.89 1.38 1.22 1.96 1.75 1.51 1.41 1.62 K2O 0.79 0.60 0.83 0.49 0.47 0.59 0.50 0.72 0.59 0.43 Co 0.43 0.63 0.46 0.40 0.55 0.55 0.62 0.73 0.30 0.58 Ni 0.29 0.44 0.36 0.44 0.42 0.31 0.46 0.78 0.40 0.27 Cu 0.09 0.13 0.12 0.12 0.15 0.15 0.17 0.18 0.13 0.09 Pb 0.18 0.16 0.16 0.12 0.11 0.19 0.17 0.14 0.11 0.15 Ba 0.10 0.14 0.15 0.17 0.19 0.12 0.14 0.17 0.16 0.26 Sr 0.11 0.14 0.13 0.16 0.16 0.14 0.15 0.14 0.14 0.18 V 629 621 561 504 512 621 592 582 452 569 Zn 460 564 597 626 617 502 586 837 545 585 Mn/Fe 0.95 1.40 1.13 1.72 2.37 1.11 1.55 2.36 1.82 2.16 CaO/P2O5 3.31 3.85 2.88 1.81 1.81 3.25 4.32 3.32 1.76 1.91 注:表中元素Mn-Sr单位为%,V-Zn单位为µg/g。 表 3 富钴结壳CD16和XD3样品稀土元素含量
Table 3. REE contents of the cobalt-rich crust sample of CD16 and XD3
元素 CD16(I) CD16(II) CD16(III) CD16(IV) CD16(V) XD3(I) XD3(II) XD3(III) XD3(IV) XD3(V) La 179 220 213 304 323 277 297 286 309 375 Ce 600 752 737 1 078 1 101 820 924 886 1 114 1 459 Pr 33.5 44.2 41.0 47.8 47.9 58.8 65.3 59.7 65.7 76.4 Nd 138 174 162 195 186 235 256 234 261 302 Sm 27.8 35.7 33.3 36.4 35.0 46.8 49.2 47.0 49.6 58.9 Eu 7.18 8.90 8.41 9.48 9.14 11.5 12.1 11.3 12.2 14.6 Gd 34.3 41.8 40.5 50.9 50.8 58.0 58.2 53.1 60.3 68.5 Tb 5.27 6.19 5.89 7.03 6.78 9.31 9.31 8.19 8.71 10.0 Dy 31.3 38.9 37.0 47.3 45.6 54.0 53.5 49.2 50.7 59.3 Ho 6.61 7.78 7.50 10.8 10.2 10.3 11.3 9.6 10.3 11.7 Er 19.4 23.6 21.7 32.6 31.4 32.0 31.6 30.0 29.6 33.7 Tm 2.90 3.53 3.20 4.67 4.73 4.57 4.54 4.22 4.16 4.90 Yb 19.4 23.4 21.0 30.8 31.6 29.7 28.8 26.8 27.1 31.9 Lu 3.02 3.56 3.21 5.00 5.04 4.48 4.35 4.02 4.04 4.76 Y 115 147 131 364 383 191 202 175 306 344 REE 1 223 1 531 1 466 2 223 2 271 1 842 2 007 1 885 2 313 2 854 LREE 986 1 235 1 195 1 670 1 702 1 449 1 604 1 525 1 812 2 286 HREE 237 296 271 553 569 393 404 360 501 569 LREE/HREE 4.15 4.18 4.41 3.02 2.99 3.68 3.97 4.23 3.62 4.02 Y/Ho 17.4 18.9 17.5 33.6 37.6 18.5 17.8 18.2 29.6 29.4 LaN/YbN 0.90 0.91 0.98 0.96 0.99 0.90 1.00 1.04 1.10 1.14 δCe 1.67 1.65 1.70 1.90 1.87 1.40 1.44 1.47 1.70 1.87 δEu 1.02 1.01 1.01 0.97 0.95 0.97 0.99 0.99 0.98 1.01 注:表中元素La-HREE单位为µg/g,轻稀土元素(LREE)=La+Ce+Pr+Nd+Sm+Eu,重稀土元素(HREE)=Gd+Tb+Dy+Ho+Er+Tm+Yb+Lu+Y,δCe=2CeN/(LaN+PrN),δEu=2EuN/(SmN+GdN),LaN、CeN、PrN、SmN、EuN、GdN均为北美页岩标准化后的值。北美页岩数据引自文献[27]。 表 4 富钴结壳元素之间相关系数矩阵
Table 4. Element Correlation matrix of the cobalt-rich crusts
元素 Mn Fe CaO P2O5 Al2O3 Na2O K2O MgO TiO2 Co Cu Ni Ba Sr Pb V Zn Y Ce REE Mn 1 Fe −0.061 1 CaO −0.322 −0.879** 1 P2O5 −0.365 −0.859** 0.999** 1 Al2O3 0.077 0.634* −0.674* −0.668* 1 Na2O 0.003 0.746* −0.719* −0.710* 0.815** 1 K2O −0.169 0.545 −0.592 −0.577 0.876** 0.776** 1 MgO 0.535 0.442 −0.655* −0.673* 0.815** 0.742* 0.665* 1 TiO2 −0.038 0.941** −0.882** −0.862** 0.565 0.621 0.514 0.340 1 Co 0.901** 0.113 −0.493 −0.529 0.051 0.115 −0.093 0.471 0.155 1 Cu 0.727* −0.028 −0.155 −0.184 0.209 0.032 −0.075 0.552 −0.192 0.536 1 Ni 0.735* −0.263 −0.065 −0.105 0.258 0.139 0.141 0.705* −0.355 0.526 0.742* 1 Ba 0.211 −0.761* 0.575 0.554 −0.590 −0.711* −0.591 −0.478 −0.544 0.168 −0.177 0.007 1 Sr 0.288 −0.659* 0.583 0.560 −0.724* −0.756* −0.875** −0.534 −0.539 0.214 0.029 −0.022 0.869** 1 Pb 0.076 0.902** −0.895** −0.882** 0.422 0.491 0.376 0.289 0.945** 0.311 −0.087 −0.307 −0.509 −0.442 1 V 0.301 0.775** −0.899** −0.899** 0.324 0.541 0.332 0.401 0.808** 0.590 −0.003 −0.073 −0.406 −0.369 0.903** 1 Zn 0.720* −0.461 0.091 0.049 0.137 −0.053 0.014 0.532 −0.462 0.551 0.582 0.897** 0.381 0.278 −0.409 −0.174 1 Y −0.141 −0.852** 0.930** 0.921** −0.813** −0.838** −0.806** −0.721* −0.833** −0.255 −0.074 −0.099 0.704* 0.806** −0.758* −0.738* 0.121 1 Ce 0.075 −0.804** 0.740* 0.725* −0.762* −0.912** −0.782** −0.679* −0.630 −0.048 −0.137 −0.101 0.911** 0.906** −0.569 −0.569 0.195 0.863** 1 REE 0.127 −0.790** 0.734* 0.717* −0.767** −0.941** −0.822** −0.652* −0.643* −0.022 −0.015 −0.050 0.857** 0.908** −0.558 −0.573 0.213 0.872** 0.988** 1 注:相关系数为pearson简单系数,n=10;**表示置信度P为99%;*表示置信度P为95%。 表 5 富钴结壳元素因子分析及方差贡献
Table 5. Element factor analysis and variance contribution of the cobalt-rich crusts
元素 成份 F1 F2 F3 Sr 0.93 −0.17 0.16 K2O −0.90 0.13 0.02 REE 0.90 −0.36 0.04 Ce 0.90 −0.37 −0.01 Al2O3 −0.85 0.22 0.22 Na2O −0.85 0.35 0.09 Ba 0.81 −0.26 0.15 Y 0.75 −0.62 −0.10 MgO −0.69 0.22 0.68 V −0.21 0.93 0.09 Pb −0.27 0.93 −0.15 TiO2 −0.42 0.84 −0.24 CaO 0.50 −0.84 −0.19 P2O5 0.48 −0.84 −0.23 Fe −0.58 0.76 −0.20 Ni −0.19 −0.24 0.93 Mn 0.22 0.31 0.91 Zn 0.06 −0.28 0.91 Cu −0.08 −0.02 0.80 Co 0.22 0.56 0.76 特征值 7.67 5.97 4.52 方差贡献/% 38.34 29.84 22.62 累计方差贡献/% 38.34 68.17 90.79 -
[1] Marino E, González F J, Somoza L, et al. Strategic and rare elements in Cretaceous-Cenozoic cobalt-rich ferromanganese crusts from seamounts in the Canary Island Seamount Province (northeastern tropical Atlantic) [J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2017, 87: 41-61. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2016.10.005
[2] Josso P, Rushton J, Lusty P, et al. Late Cretaceous and Cenozoic paleoceanography from north-east Atlantic ferromanganese crust microstratigraphy [J]. Marine Geology, 2020, 422: 106122. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2020.106122
[3] Gueguen B, Rouxel O, Fouquet Y. Nickel isotopes and rare earth elements systematics in marine hydrogenetic and hydrothermal ferromanganese deposits [J]. Chemical Geology, 2021, 560: 119999. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2020.119999
[4] Azami K, Hirano N, Machida S, et al. Rare earth elements and yttrium (REY) variability with water depth in hydrogenetic ferromanganese crusts [J]. Chemical Geology, 2018, 493: 224-233. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2018.05.045
[5] Zawadzki D, Maciąg Ł, Kotliński R A, et al. Geochemistry of cobalt-rich ferromanganese crusts from the Perth Abyssal Plain (E Indian Ocean) [J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2018, 101: 520-531. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2018.08.004
[6] Astakhova N V. Noble metals in ferromanganese crusts from marginal seas of the Northwest Pacific [J]. Marine Geology, 2017, 57(4): 618-627.
[7] Hein J R, Koschinsky A. Deep-ocean ferromanganese crusts and nodules[M]//Holland H D, Turekian K K. Treatise on Geochemistry. 2nd ed. Oxford: Elsevier Ltd. , 2014: 273-291.
[8] Hein J R, Mizell K, Koschinsky A, et al. Deep-ocean mineral deposits as a source of critical metals for high- and green-technology applications: Comparison with land-based resources [J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2013, 51: 1-14. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2012.12.001
[9] Hein J R, Spinardi F, Okamoto N, et al. Critical metals in manganese nodules from the Cook Islands EEZ, abundances and distributions [J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2015, 68: 97-116. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2014.12.011
[10] Konstantinova N, Hein J R, Mizell K, et al. Changes in sediment source areas to the Amerasia Basin, Arctic Ocean, over the past 5.5 million years based on radiogenic isotopes (Sr, Nd, Pb) of detritus from ferromanganese crusts [J]. Marine Geology, 2020, 428: 106280. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2020.106280
[11] Jiang X D, Sun X M, Chou Y M, et al. Geochemistry and origins of carbonate fluorapatite in seamount Fe-Mn crusts from the Pacific Ocean [J]. Marine Geology, 2020, 423: 106135. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2020.106135
[12] Novikov G V, Mel’nikov M E, Bogdanova O Y, et al. Nature of Co-bearing ferromanganese crusts of the Magellan seamounts (Pacific Ocean): communication 1. Geology, mineralogy, and geochem-istry [J]. Lithology and Mineral Resources, 2014, 49(1): 1-22. doi: 10.1134/S0024490213060072
[13] Hein J R, Conrad T, Mizell K, et al. Controls on ferromanganese crust composition and reconnaissance resource potential, Ninetyeast Ridge, Indian Ocean [J]. Deep Sea Research Part I:Oceanographic Research Papers, 2016, 110: 1-19. doi: 10.1016/j.dsr.2015.11.006
[14] Surya P L, Ray D, Nagender N B, et al. Anomalous phase association of REE in ferromanganese crusts from Indian mid-oceanic ridges: Evidence for large scale dispersion of hydrothermal iron [J]. Chemical Geology, 2020, 549: 119679. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2020.119679
[15] Mikhailik P E, Mikhailik E V, Zarubina N V, et al. Distribution of rare-earth elements and yttrium in hydrothermal sedimentary ferromanganese crusts of the Sea of Japan (from phase analysis results) [J]. Russian Geology and Geophysics, 2017, 58(12): 1530-1542. doi: 10.1016/j.rgg.2017.11.013
[16] Khanchuk A I, Mikhailik P E, Mikhailik E V, et al. Peculiarities of the distribution of rare-earth elements and yttrium in mineral phases of the ferromanganese crusts from the Detroit Guyot (Pacific Ocean) [J]. Doklady Earth Sciences, 2015, 465(4): 1243-1247.
[17] Mohwinkel D, Kleint C, Koschinsky A. Phase associations and potential selective extraction methods for selected high-tech metals from ferromanganese nodules and crusts with siderophores [J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2014, 43: 13-21. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2014.01.010
[18] Koschinsky A, Hein J R, Kraemer D, et al. Platinum enrichment and phase associations in marine ferromanganese crusts and nodules based on a multi-method approach [J]. Chemical Geology, 2020, 539: 119426. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2019.119426
[19] Koschinsky A, Hein J R. Uptake of elements from seawater by ferromanganese crusts: Solid-phase associations and seawater speciation [J]. Marine Geology, 2003, 198(3-4): 331-351. doi: 10.1016/S0025-3227(03)00122-1
[20] Koschinsky A, Halbach P. Sequential leaching of marine ferroman-ganese precipitates: Genetic implications [J]. Geochimica et Cosm-ochimica Acta, 1995, 59(24): 5113-5132. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(95)00358-4
[21] Wen X, De Carlo E H, Li Y H. Interelement relationships in ferromanganese crusts from the central Pacific ocean: Their implications for crust genesis [J]. Marine Geology, 1997, 136(3-4): 277-297. doi: 10.1016/S0025-3227(96)00064-3
[22] 任向文, 石学法, 朱爱美, 等. 麦哲伦海山群MK海山富钴结壳稀土元素的赋存相态[J]. 吉林大学学报:地球科学版, 2011, 41(3):707-714
REN Xiangwen, SHI Xuefa, ZHU Aimei, et al. Existing phase of rare earth elements in Co-rich Fe-Mn crusts from seamount MK of Magellan Seamount cluster [J]. Journal of Jilin University:Earth Science Edition, 2011, 41(3): 707-714.
[23] 杨胜雄, 龙晓军, 祁奇, 等. 西太平洋富钴结壳矿物学和地球化学特征: 以麦哲伦海山和马尔库斯-威克海山富钴结壳为例[J]. 中国海洋大学学报, 2016, 46(2):105-116
YANG Shengxiong, LONG Xiaojun, QI Qi, et al. The mineralogical and geochemical characteristics of co-rich crusts from the western Pacific: Taking the co-rich crusts from Magellan and Marcus-wake seamounts as an example [J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 2016, 46(2): 105-116.
[24] 任江波, 何高文, 姚会强, 等. 西太平洋海山富钴结壳的稀土和铂族元素特征及其意义[J]. 地球科学, 2016, 41(10):1745-1757
REN Jiangbo, HE Gaowen, YAO Huiqiang, et al. Geochemistry and significance of REE and PGE of the cobalt-rich crusts from west Pacific Ocean seamounts [J]. Earth Science, 2016, 41(10): 1745-1757.
[25] 潘家华, 刘淑琴, 杨忆, 等. 西太平洋海山磷酸盐的常量、微量和稀土元素地球化学研究[J]. 地质论评, 2002, 48(5):534-541 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.2002.05.012
PAN Jiahua, LIU Shuqin, YANG Yi, et al. Research on geochemical characteristics of major, trace and Rare-Earth Elements in phosphates from the west Pacific Seamounts [J]. Geological Review, 2002, 48(5): 534-541. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.2002.05.012
[26] Bonatti E, kraemer T F, Rydell H. Classification and genesis of submarine iron-manganese deposits[C]//Ferromanganese Deposits on the Ocean Floor. Palisades: Lamont Doherty Geological Observatory of Columbia University, 1972: 149-166.
[27] 王中刚, 于学元, 赵振华, 等. 稀土元素地球化学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1989: 1-535
WANG Zhonggang, YU Xueyuan, ZHAO Zhenhua, et al. Rare earth elements geochemistry[M]. Beijing: Science Publishing House, 1989: 1-535.
[28] 何高文, 孙晓明, 杨胜雄, 等. 太平洋多金属结核和富钴结壳稀土元素地球化学对比及其地质意义[J]. 中国地质, 2011, 38(2):462-472 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2011.02.020
HE Gaowen, SUN Xiaoming, YANG Shengxiong, et al. A comparison of REE geochemistry between polymetallic nodules and cobalt-rich crusts in the Pacific Ocean [J]. Geology in China, 2011, 38(2): 462-472. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2011.02.020
[29] 崔迎春, 刘季花, 任向文, 等. 中太平洋M海山富钴结壳稀土元素地球化学[J]. 中国稀土学报, 2008, 26(6):760-768 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4343.2008.06.018
CUI Yingchun, LIU Jihua, REN Xiangwen, et al. Geochemistry of rare earth elements in cobalt-rich crusts from the Mid-Pacific M Seamount [J]. Journal of the Chinese Rare Earth Society, 2008, 26(6): 760-768. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4343.2008.06.018
[30] Bau M, Schmidt K, Koschinsky A, et al. Discriminating between different genetic types of marine ferromanganese crusts and nodules based on rare earth elements and yttrium [J]. Chemical Geology, 2014, 381: 1-9. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2014.05.004
[31] 何高文, 薛婷, 孙晓明, 等. 西太平洋富钴结壳元素组合特征及其地质意义[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2005, 24(2):125-129 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2005.02.006
HE Gaowen, XUE Ting, SUN Xiaoming, et al. The elemental association characterisitics and the geological significance of cobalt-rich Nodules in the west Pacific Ocean [J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 2005, 24(2): 125-129. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2005.02.006
[32] Halbach P E, Jahn A, Cherkashov G. Marine co-rich ferromanganese crust deposits: description and formation, occurrences and distribution, estimated world-wide resources[M]//Sharma R. Deep-Sea Mining. Cham: Springer, 2017: 65-140.
[33] Bau M, Koschinsky A. Oxidative scavenging of cerium on hydrous Fe oxide: evidence from the distribution of rare earth elements and yttrium between Fe oxides and Mn oxides in hydrogenetic ferromanganese crusts [J]. Geochemical Journal, 2009, 43(1): 37-47. doi: 10.2343/geochemj.1.0005
[34] 高晶晶, 刘季花, 李先国, 等. 富钴结壳中稀土元素化学相态分析方法及其应用[J]. 分析化学, 2015, 43(2):1895-1900
GAO Jingjing, LIU Jihua, LI Xianguo, et al. Chemical phase analysis of rare earth elements in cobalt-rich crusts and its application [J]. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2015, 43(2): 1895-1900.
[35] 高晶晶, 刘季花, 张辉, 等. 太平洋海山富钴结壳中铂族元素赋存状态与富集机理[J]. 海洋学报, 2019, 41(8):115-124
GAO Jingjing, LIU Jihua, Zhang Hui, et al. Occurrence phase and enrichment mechanism of platinum group elements in the Pacific cobalt-rich Crusts [J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2019, 41(8): 115-124.
[36] Hein J R. Cobalt-rich ferromanganese crusts: Global distribution, composition, origin and research activities[C]//Minerals Other than Polymetallic Nodules of the International Seabed Area. Kingston Jamaica: International Seabed Authority, 2004: 188-256.
[37] Hein J R, Koschinsky A, Bau M, et al. Cobalt-rich ferromanganese crusts in the Pacific[M]//Cronan D S. Handbook of Marine Mineral Deposits. Boca Raton: CRC Press, 2000: 239-279.
[38] Koschinsky A, Stascheit A, Bau M, et al. Effects of phosphatization on the geochemical and mineralogical composition of marine ferromanganese crusts [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1997, 61(19): 4079-4094. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(97)00231-7
[39] Pan J H, De Carlo E H, Yang Y, et al. Effect of phosphatization on element concentration of cobalt-rich ferromanganese crusts [J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2005, 79(3): 349-355. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-6724.2005.tb00900.x
[40] 任江波, 何高文, 姚会强, 等. 磷酸盐化作用对富钴结壳中稀土元素的影响[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2017, 37(2):33-43
REN Jiangbo, HE Gaowen, YAO Huiqiang, et al. The effects of phosphatization on the REY of co-rich Fe-Mn crusts [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2017, 37(2): 33-43.
-



 下载:
下载: