Geochemical characteristics and their geological implication in sediments from Laizhou Bay since late Quaternary
-
摘要:
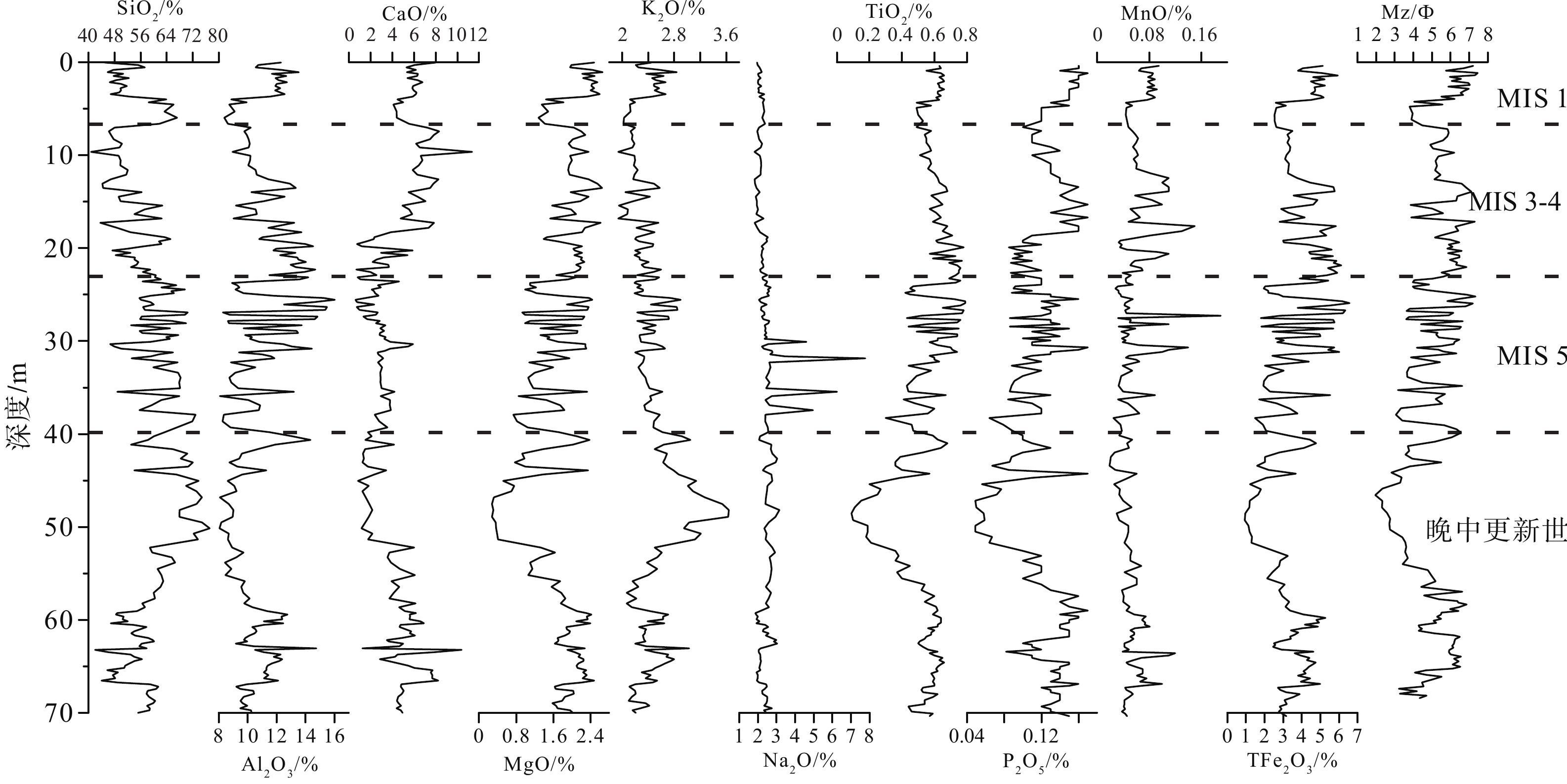
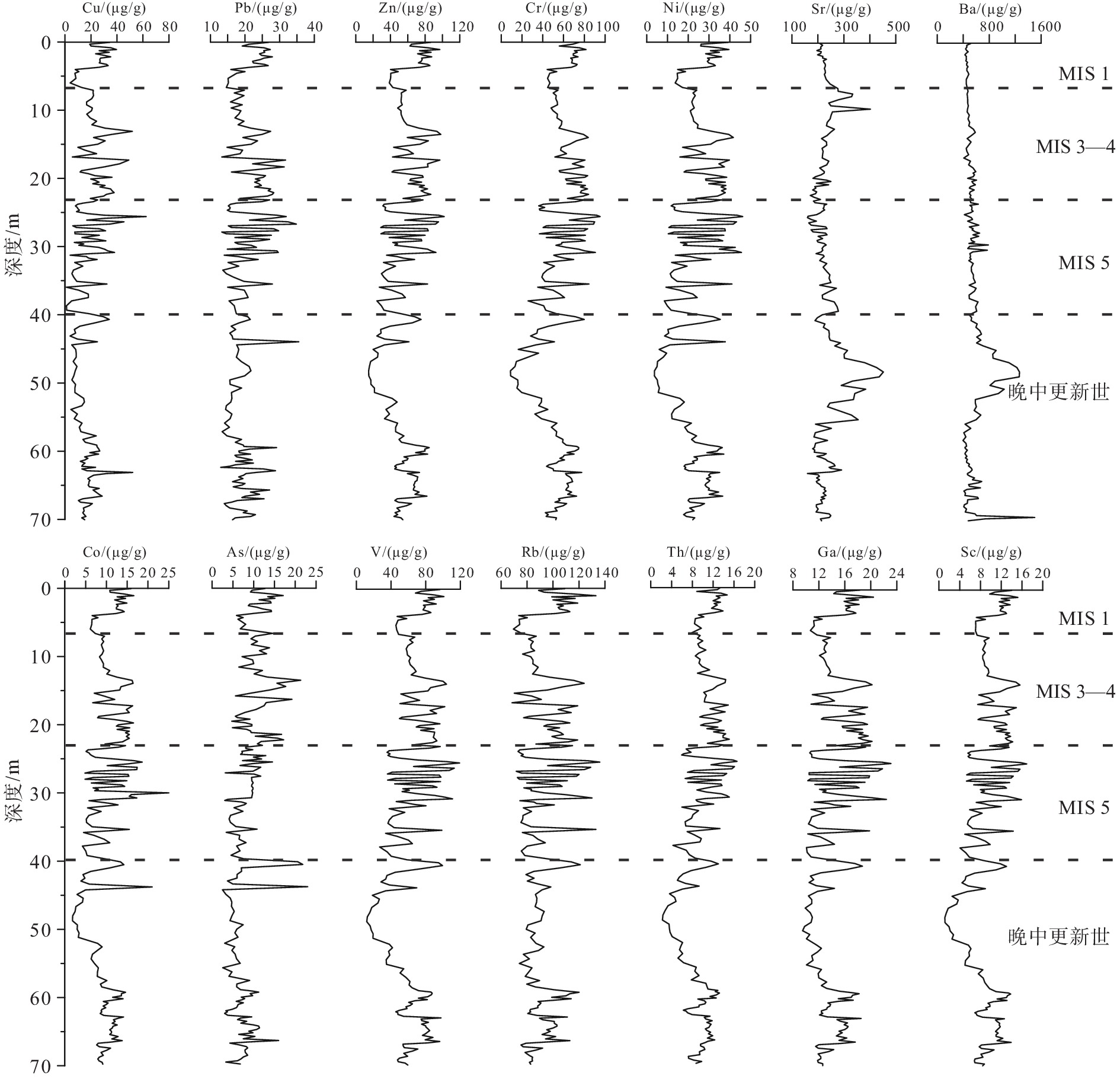
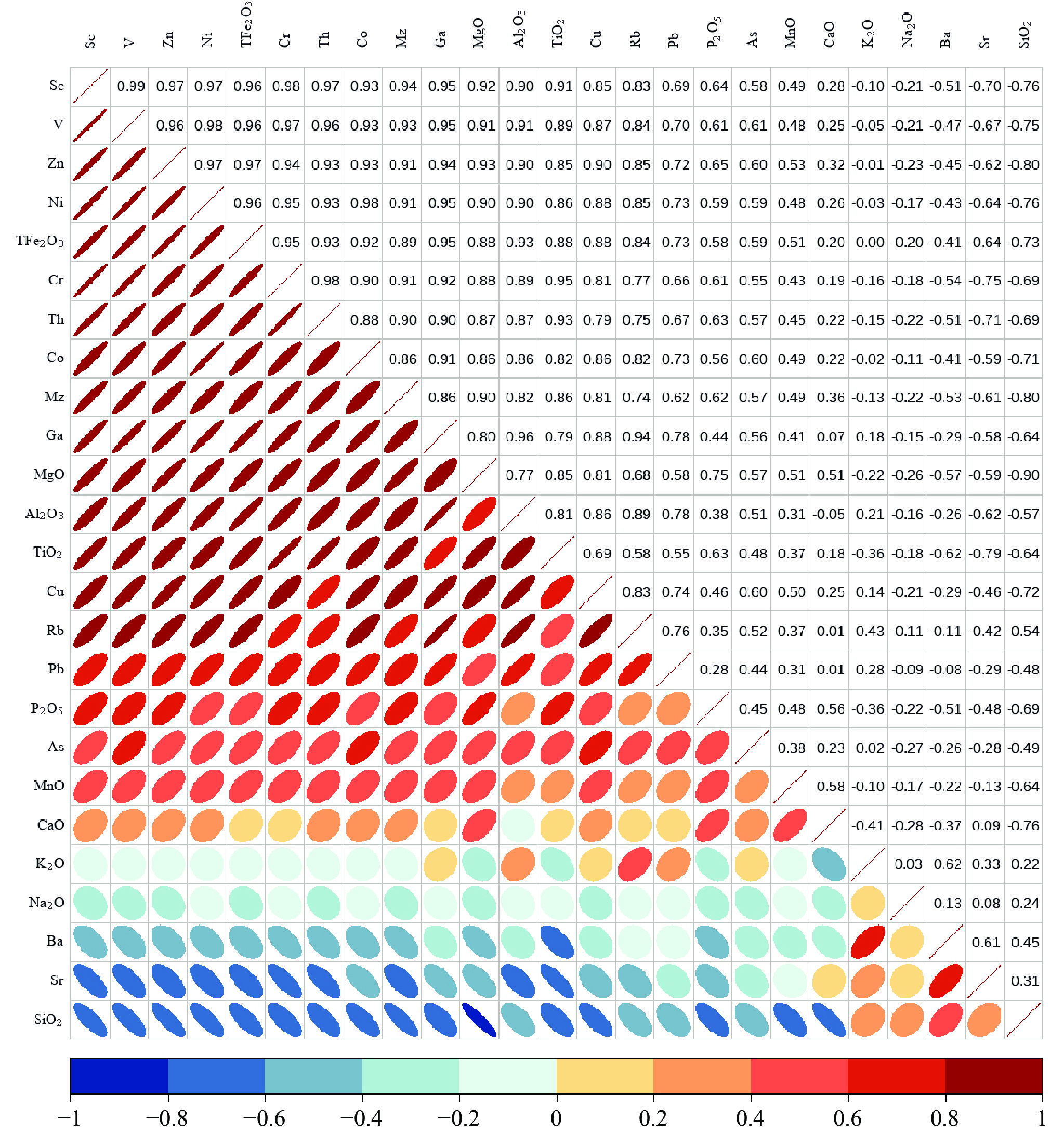
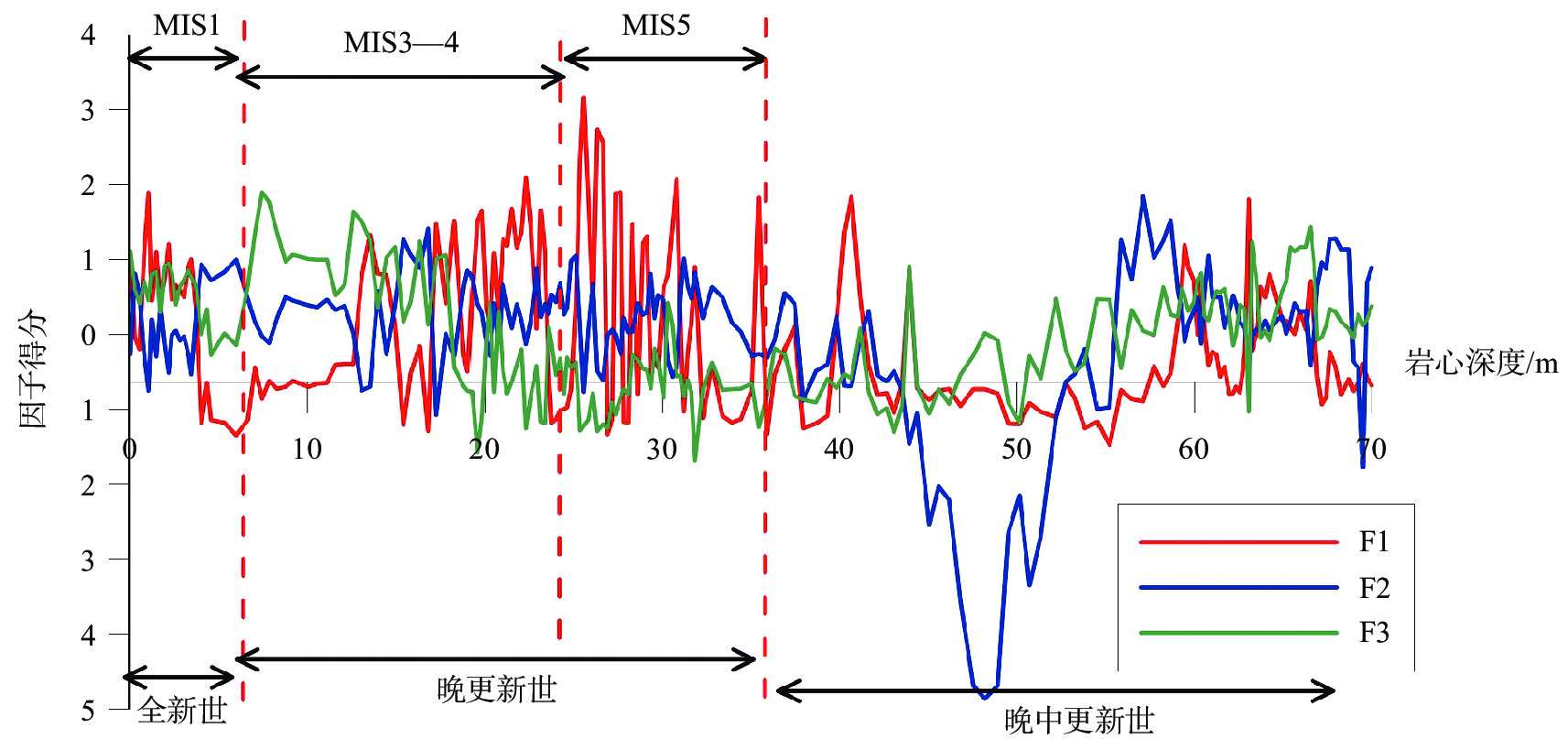
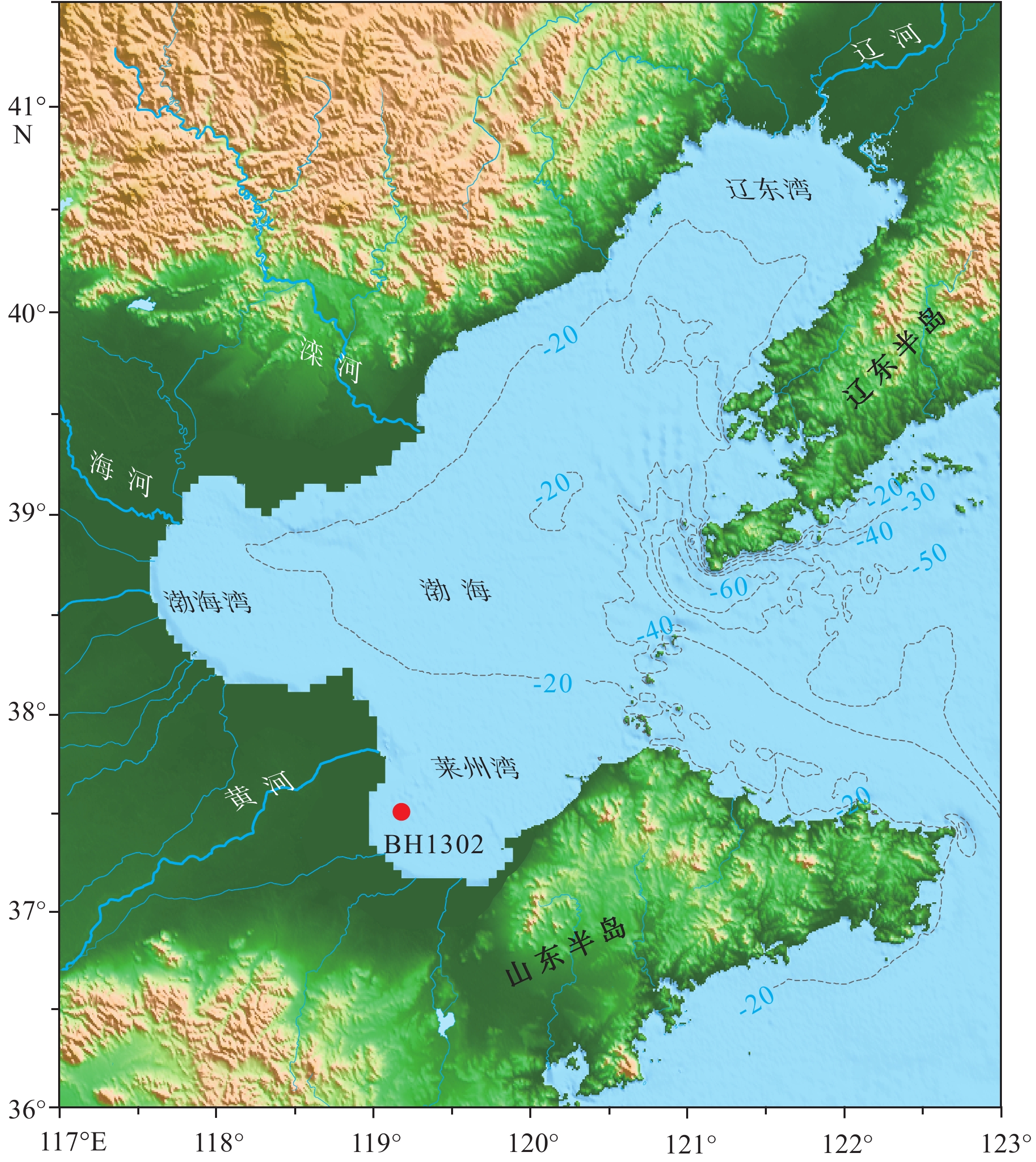
元素地球化学信息对于地层划分和物源分析具有重要的指示意义。通过分析莱州湾BH1302孔岩芯沉积物常微量元素特征发现,元素含量在地层分界处发生明显变化,可以作为晚第四纪地层划分的重要指标。结合钻孔岩性相、粒度特征和测年数据,将研究区晚第四纪以来的沉积划分为4段,分别对应于晚中更新世、MIS 5期、MIS 4—3期和MIS 1期。钻孔岩芯沉积物常微量元素在垂向上变化存在着共生的关系,除Na2O、Ba和Sr外,大部分常微量元素变化与粒径强相关。R型因子分析揭示陆源细颗粒碎屑沉积、陆源粗颗粒碎屑沉积和海洋自生元素供应对BH1302孔沉积物的地球化学组成具有重要作用,但不同时期影响作用有所差异,陆源细颗粒碎屑沉积占主导地位,但短时期内陆源粗颗粒碎屑沉积或海洋自生元素供应也可能成为主导因素。
Abstract:Element geochemical information is important for stratigraphic division and provenance analysis. The characteristics of major and trace elements in the sediments of core BH1302 in Laizhou Bay are analyzed, whose concentrations change obviously at the stratigraphic boundary and can be used as an important index for the classification of late Quaternary strata. Combined with the lithologic facies, grain size and dates of core BH1302, the sediments in the study area since the late Quaternary can be divided into four phases, which corresponding to late Middle Pleistocene, MIS 5, MIS 4—3 and MIS 1, respectively. In vertical, the changes of major and trace elements of the core are characterized by a symbiotic relationship. Except for Na2O、Ba and Sr, most of the major and trace elements are strongly correlated with the mean particle size in the vertical distribution. R-type factor analysis revealed that the supply of terrigenous fine and coarse particulate and marine authigenic elements had important effects on the geochemical composition, but the effects are different in different periods. Terrigenous fine particulate supply is the dominant factor, but terrigenous coarse particulate supply or marine authigenic elements supply may also be the dominant factor in a short period.
-
Key words:
- geochemical /
- R-type factor analysis /
- late Quaternary /
- Laizhou Bay
-

-
表 1 BH-1302孔AMS14C测年结果
Table 1. AMS14C dating results of core BH1302
深度/m 材料 δ13C
/‰14C年龄/a 日历年龄(cal.aBP) 中值 范围(2σ) 4.38 螺 −3.2 6 530 ± 40 7 233 7 166~7 299 14.38 螺 −8.3 >43 500 — — 18.23 螺 −6.1 >43 500 — — 47.46 螺 +1.1 >43 500 — — 表 2 BH1302孔沉积物样品光释光测年结果
Table 2. Optically stimulated luminescence dating results for sediment samples of core BH1302
样品编号 深度/m 含水率ω /% U/10-6 Th/10-6 K/% 等效剂量/Gy 年龄/ka OSL-1 9.22 10.22 2.25 9.14 1.98 91.46 33.1±2.3 OSL-2 11.15 17.22 2.55 10.43 2.02 126.05 43.0±1.9 OSL-3 13.45 12.52 2.15 7.36 1.56 133.43 59.0±3.9 OSL-4 19.90 14.76 2.21 6.05 1.75 138.29 66.7±3.2 OSL-5 22.46 11.19 1.85 6.11 2.20 185.70 68.5±5.5 OSL-6 25.22 12.26 1.99 6.22 2.19 190.48 71.3±3.4 OSL-7 30.25 14.47 1.84 7.35 2.10 201.66 76.4±3.5 OSL-8 33.05 25.65 2.22 8.85 2.28 222.76 80.1±7.3 OSL-9 36.00 10.51 1.98 7.31 1.99 259.86 102.3±5.0 表 3 BH1302孔沉积物常微量元素统计表
Table 3. Statistics of major and trace elements in the sediments of core BH1302
平均值 最大值 最小值 标准偏差 变异系数 主量元素
/%SiO2 57.65 77.26 40.76 7.91 0.14 Al2O3 10.96 16.03 8.06 1.82 0.17 CaO 4.27 11.37 0.62 2.07 0.48 MgO 1.79 2.66 0.28 0.56 0.31 K2O 2.44 3.64 1.94 0.29 0.12 Na2O 2.41 7.78 1.82 0.61 0.25 TiO2 0.56 0.79 0.09 0.14 0.24 P2O5 0.12 0.17 0.05 0.03 0.23 MnO 0.06 0.19 0.02 0.02 0.43 TFe2O3 3.68 6.58 0.94 1.32 0.36 微量元素/(μg/g) Ba 549.11 1 499.00 396.00 155.54 0.28 Sr 232.24 452.00 160.00 47.69 0.21 Rb 93.40 136.00 68.50 15.07 0.16 V 64.66 119.00 11.90 23.20 0.36 Cr 57.52 95.20 8.90 17.32 0.30 Zn 57.32 102.00 14.80 20.36 0.36 Ni 24.43 46.20 3.70 10.07 0.41 Pb 20.38 35.50 13.00 4.78 0.23 Cu 19.48 62.50 1.00 10.62 0.55 Ga 14.40 23.10 9.50 3.15 0.22 Co 10.24 25.00 1.83 4.00 0.39 Th 10.01 16.60 2.23 3.01 0.30 Sc 9.51 16.90 1.14 3.37 0.35 As 8.78 23.00 2.49 3.81 0.43 表 4 BH1302孔沉积物主微量元素方差极大旋转因子载荷表
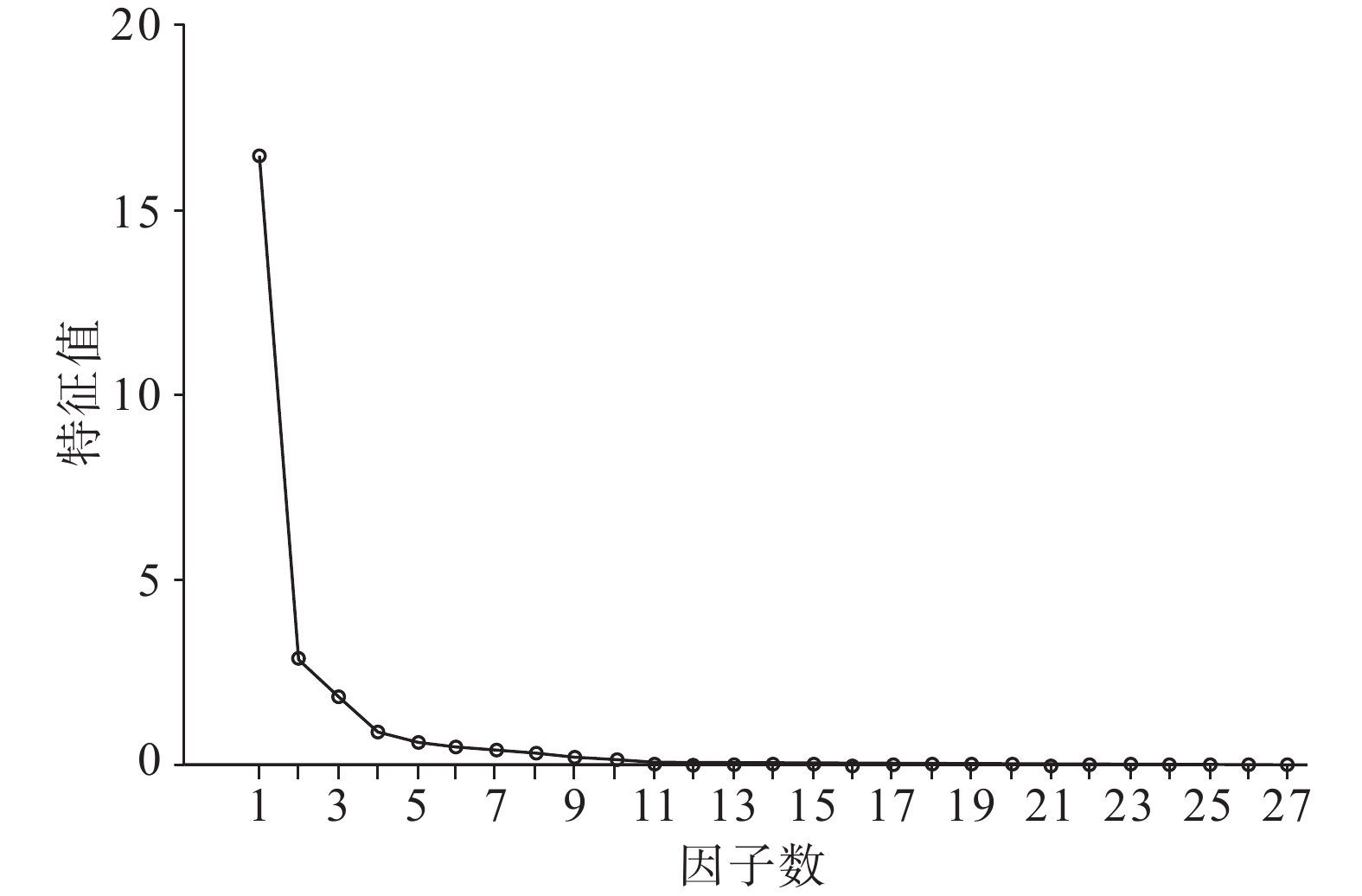
Table 4. Load table of maximum variance rotation factor of major and trace elements in the sediments of core BH1302
元素 因子1 因子2 因子3 元素 因子1 因子2 因子3 砂 −0.736 −0.479 −0.349 Co 0.882 0.23 0.248 粉砂 0.645 0.574 0.31 Sc 0.887 0.356 0.267 黏土 0.812 0.148 0.374 Ga 0.977 0.092 0.125 Al2O3 0.975 0.105 0.005 Th 0.852 0.403 0.209 MgO 0.728 0.415 0.486 Mz 0.807 0.37 0.359 TiO2 0.741 0.612 0.126 As 0.551 0.042 0.366 Fe2O3 0.915 0.247 0.24 K2O 0.299 −0.847 −0.208 Rb 0.945 −0.156 0.108 Sr −0.565 −0.692 0.203 V 0.903 0.305 0.259 Ba −0.191 −0.818 −0.203 Cu 0.866 0.03 0.327 CaO −0.076 0.229 0.934 Pb 0.825 −0.164 0.103 MnO 0.317 0.02 0.713 Zn 0.89 0.248 0.344 P2O5 0.356 0.495 0.546 Cr 0.87 0.43 0.168 SiO2 −0.531 −0.265 −0.746 Ni 0.907 0.262 0.267 方差贡献率/% 67.017 10.602 6.665 -
[1] 中国科学院海洋研究所海洋地质研究室. 渤海地质[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1985
Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences. Bohai Sea Geology[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1985].
[2] Yao Z Q, Shi X F, Liu Q S, et al. Paleomagnetic and astronomical dating of sediment core BH08 from the Bohai Sea, China: Implications for glacial-interglacial sedimentation [J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2014, 393: 90-101. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2013.11.012
[3] Yang S Y, Li C X, Cai J G. Geochemical compositions of core sediments in eastern China: Implication for Late Cenozoic palaeoenvironmental changes [J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2006, 229(4): 287-302. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2005.06.026
[4] Yi L, Yu H J, Ortiz J D, et al. Late Quaternary linkage of sedimentary records to three astronomical rhythms and the Asian monsoon, inferred from a coastal borehole in the south Bohai Sea, China [J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2012, 329-330: 101-117. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2012.02.020
[5] Yi L, Deng C L, Tian L Z, et al. Plio-Pleistocene evolution of Bohai Basin (East Asia): demise of Bohai Paleolake and transition to marine environment [J]. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6: 29403. doi: 10.1038/srep29403
[6] 高茂生, 郭飞, 侯国华, 等. 渤海南部莱州湾晚更新世以来沉积演化特征[J]. 中国地质, 2018, 45(1):59-68 doi: 10.12029/gc20180106
GAO Maosheng, GUO Fei, HOU Guohua, et al. The evolution of sedimentary environment since late Pleistocene in Laizhou Bay, Bohai Sea [J]. Geology in China, 2018, 45(1): 59-68. doi: 10.12029/gc20180106
[7] Yi L, Lai Z P, Yu H J, et al. Chronologies of sedimentary changes in the south Bohai Sea, China: constraints from luminescence and radiocarbon dating [J]. Boreas, 2013, 42(2): 267-284. doi: 10.1111/j.1502-3885.2012.00271.x
[8] 雷雁翔. 渤海湾晚更新世以来的地层序列及沉积地球化学特征[D]. 山东科技大学硕士论文, 2020
LEI Yanxiang. Stratigraphic sequences and characteristics of sedimentary geochemistry since the late Pleistocene in the Bohai Bay[D]. Master Dissertation of Shandong University of Science and Technology, 2020.
[9] 蓝先洪, 秦亚超, 王中波, 等. 渤海东部晚更新世以来的沉积物地球化学特征[J]. 沉积学报, 2016, 34(5):892-901
LAN Xianhong, QIN Yachao, WANG Zhongbo, et al. Geochemical characteristics of sediments in the eastern Bohai Sea since late Pleistocene [J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2016, 34(5): 892-901.
[10] 张现荣, 李军, 窦衍光, 等. 辽东湾东南部海域柱状沉积物稀土元素地球化学特征及物源识别[J]. 沉积学报, 2014, 32(4):684-691
ZHANG Xianrong, LI Jun, DOU Yanguang, et al. REE geochemical characteristics and provenance discrimination of core LDC30 in the southeastern part of Liaodong Bay [J]. Acta Oceanological Sinica, 2014, 32(4): 684-691.
[11] 刘建国, 李安春, 陈木宏, 等. 全新世渤海泥质沉积物地球化学特征[J]. 地球化学, 2007, 36(6):559-568 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0379-1726.2007.06.004
LIU Jianguo, LI Anchun, CHEN Muhong, et al. Geochemical characteristics of sediments in the Bohai Sea mud area during Holocene [J]. Geochimica, 2007, 36(6): 559-568. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0379-1726.2007.06.004
[12] 李淑媛, 苗丰民, 赵全民, 等. 辽东半岛西南及渤海中部海域表层沉积物的地球化学[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2010, 30(4):123-130
LI Shuyuan, MIAO Fengmin, ZHAO Quanmin, et al. Geodchemistry of surface sediments off southwest Liaodong Peninsula and in Mid-Bohai Sea [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2010, 30(4): 123-130.
[13] 蓝先洪, 李日辉, 陈晓辉, 等. 渤海西部晚更新世以来沉积地球化学研究[J]. 海洋科学进展, 2018, 36(1):67-78 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2018.01.006
LAN Xianhong, LI Rihui, CHEN Xiaohui, et al. Study of sedimentary geochemistry in the western Bohai Sea since late Pleistocene [J]. Advances in Marine Science, 2018, 36(1): 67-78. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2018.01.006
[14] 韩德亮. 莱州湾E孔中更新世末期以来的地球化学特征[J]. 海洋学报, 2001, 23(2):79-85
HAN Deliang. Geochemistry of core E in the Laizhou Bay since late stage of Middle Pleistocene [J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2001, 23(2): 79-85.
[15] 郭飞, 高茂生, 侯国华, 等. 莱州湾07钻孔沉积物晚更新世以来的元素地球化学特征[J]. 海洋学报, 2016, 38(3):145-155
GUO Fei, GAO Maosheng, HOU Guohua, et al. Geochemical characteristics of sediment in core 07 since the late Pleistocene in Laizhou Bay [J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2016, 38(3): 145-155.
[16] Guo F, Gao M S, Hou G H, et al. Source tracing of rare earth elements: A case study of core 07 on the southern coast of Laizhou Bay [J]. Continental Shelf Research, 2017, 136: 29-38. doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2017.01.002
[17] Gong C Z, Li G X, Liu Y, et al. Source evolution and its relationship to climate change since the Middle-late Pleistocene in Laizhou Bay, China [J]. Journal of Ocean University of China, 2020, 19(1): 113-123. doi: 10.1007/s11802-020-3937-z
[18] 庄振业, 李建华, 仇士华, 等. 莱州湾东岸的全新世海侵和地层[J]. 海洋湖沼通报, 1987(2):31-39
ZHUANG Zhenye, LI Jianhua, QIU Shihua, et al. Holocene transgression and its layers in the east coast of Laizhou Gulf, Bohai [J]. Transactions of Oceanology & Limnology, 1987(2): 31-39.
[19] 宫少军, 秦志亮, 叶思源, 等. 黄河三角洲ZK5钻孔沉积物地球化学特征及其沉积环境[J]. 沉积学报, 2014, 32(5):855-862
GONG Shaojun, QIN Zhiliang, YE Siyuan, et al. Geochemical characteristics and sedimentary environment of ZK5 core sediments in Yellow River Delta [J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2014, 32(5): 855-862.
[20] Stuiver M, Reimer P. 1986-2014. Calib Radiocarbon Calibration Program.
[21] Yuan X, Feng X, Hu R, et al. Late Quaternary sedimentary records and implications for sea level changes and the East Asian monsoon inferred from BH1302 in the Bohai Sea, China[J]. Marine Geology (under review), 2022.
[22] Taylor S R, McLennan S M. The geochemical evolution of the continental crust [J]. Reviews of Geophysics, 1995, 33(2): 241-265. doi: 10.1029/95RG00262
[23] Martin J M, Zhang J, Shi M C, et al. Actual flux of the Huanghe (Yellow River) sediment to the Western Pacific Ocean [J]. Netherlands Journal of Sea Research, 1993, 31(3): 243-254. doi: 10.1016/0077-7579(93)90025-N
[24] Chappell J, Omura A, Esat T, et al. Reconciliation of late Quaternary sea levels derived from coral terraces at Huon Peninsula with deep sea oxygen isotope records [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1996, 141(1-4): 227-236. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(96)00062-3
[25] Shi X F, Yao Z Q, Liu Q S, et al. Sedimentary architecture of the Bohai Sea China over the last 1 Ma and implications for sea-level changes [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2016, 451: 10-21. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2016.07.002
[26] 易亮, 姜兴钰, 田立柱, 等. 渤海盆地演化的年代学研究[J]. 第四纪研究, 2016, 36(5):1075-1087 doi: 10.11928/j.issn.1001-7410.2016.05.05
YI Liang, JIANG Xingyu, TIAN Lizhu, et al. Geochronological study on Plio-Pleistocene evolution of Bohai Basin [J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2016, 36(5): 1075-1087. doi: 10.11928/j.issn.1001-7410.2016.05.05
[27] 岳保静, 刘金庆, 刘健, 等. 渤海西缘YRD-1101孔晚更新世以来沉积物粒度特征及其环境变迁[J]. 中国地质, 2020, 47(3):853-867 doi: 10.12029/gc20200321
YUE Baojing, LIU Jinqing, LIU Jian, et al. Grain size distribution of sediment of core YRD-1101 in the western margin of the modern Bohai Sea since the latest Pleistocene and its environmental change [J]. Geology in China, 2020, 47(3): 853-867. doi: 10.12029/gc20200321
[28] Bi N S, Yang Z S, Wang H J, et al. Seasonal variation of suspended-sediment transport through the southern Bohai Strait [J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2011, 93(3): 239-247. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2011.03.007
[29] Zhou L Y, Liu J, Saito Y, et al. Fluvial system development and subsequent marine transgression in Yellow River (Huanghe) delta and its adjacent sea regions during last glacial maximum to early Holocene [J]. Continental Shelf Research, 2014, 90: 117-132. doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2014.06.012
[30] 阎玉忠, 王宏, 李凤林, 等. 渤海湾西岸BQ1孔揭示的沉积环境与海面波动[J]. 地质通报, 2006, 25(3):357-382 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2006.03.006
YAN Yuzhong, WANG Hong, LI Fenglin, et al. Sedimentary environment and sea-level fluctuations revealed by Borehole BQ1 on the west coast of the Bohai Bay, China [J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2006, 25(3): 357-382. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2006.03.006
[31] 汪品先, 闵秋宝, 卞云华, 等. 我国东部第四纪海侵地层的初步研究[J]. 地质学报, 1981, 55(1):1-13
WANG Pinxian, MIN Qiubao, BIAN Yunhua, et al. Strata of quaternary transgressions in east China: a preliminary study [J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 1981, 55(1): 1-13.
[32] Liu J, Wang H, Wang F F, et al. Sedimentary evolution during the last ~1.9 Ma near the western margin of the modern Bohai Sea [J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2016, 451: 84-96. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2016.03.012
[33] Li G X, Li P, Liu Y, et al. Sedimentary system response to the global sea level change in the East China Seas since the last glacial maximum [J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2014, 139: 390-405. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2014.09.007
[34] 庄振业, 许卫东, 刘东生, 等. 渤海南部S3孔及晚第四纪海相地层的划分及环境演变[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 1999, 19(2):27-35
ZHUANG Zhenye, XU Weidong, LIU Dongsheng, et al. Division and environmental evolution of late Quaternary marine beds of S3 hole in the Bohai Sea [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 1999, 19(2): 27-35.
[35] 刘健, 段宗奇, 梅西, 等. 南黄海中部隆起晚新近纪-第四纪沉积序列的地层划分与沉积演化[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2021, 41(5):25-43
LIU Jian, DUAN Zongqi, MEI Xi, et al. Stratigraphic classification and sedimentary evolution of the late Neogene to Quaternary sequence on the Central Uplift of the South Yellow Sea [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2021, 41(5): 25-43.
-



 下载:
下载: