Geochemistry of the water profiles at the slope of East China Sea and Okinawa Trough and its implications
-
摘要:
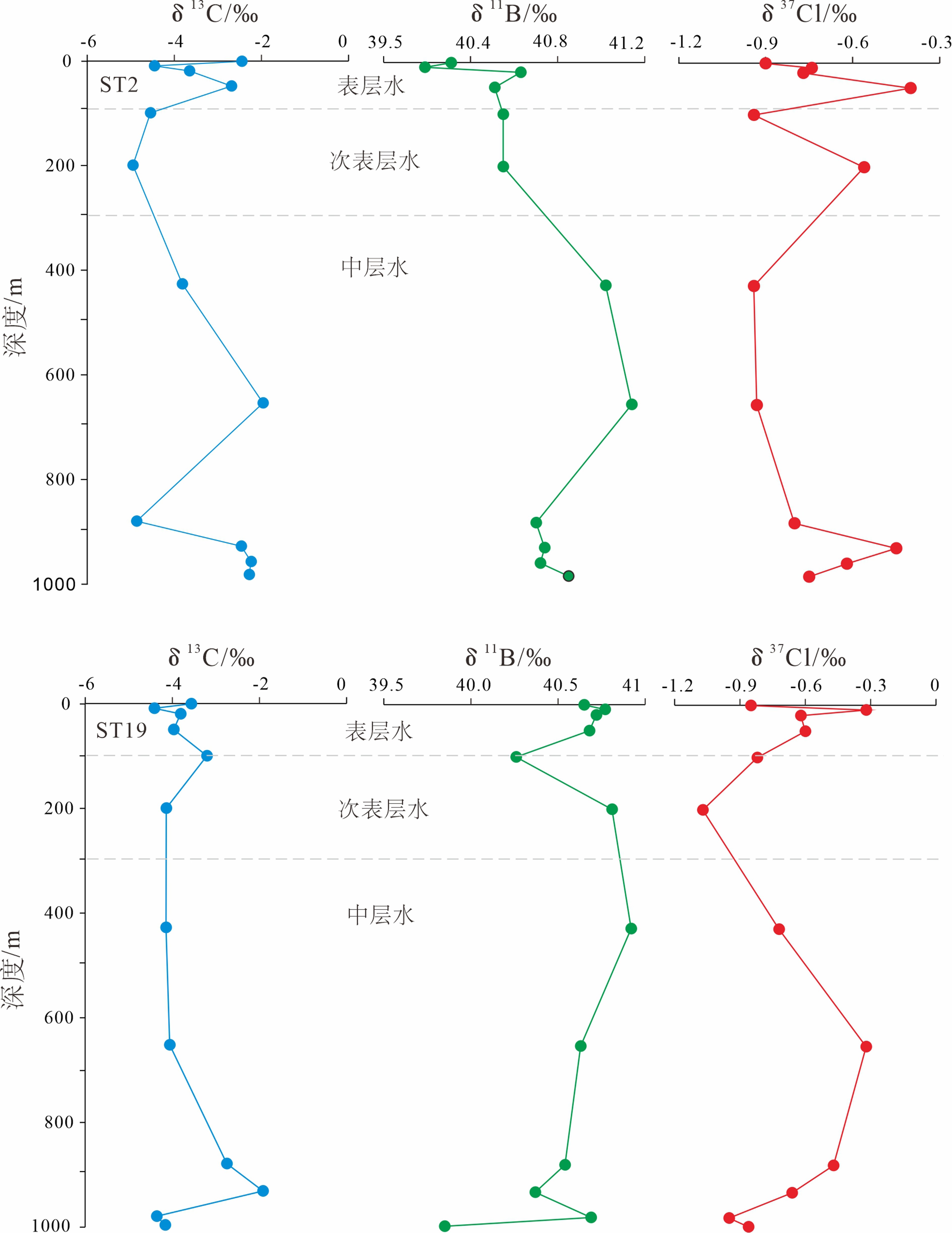
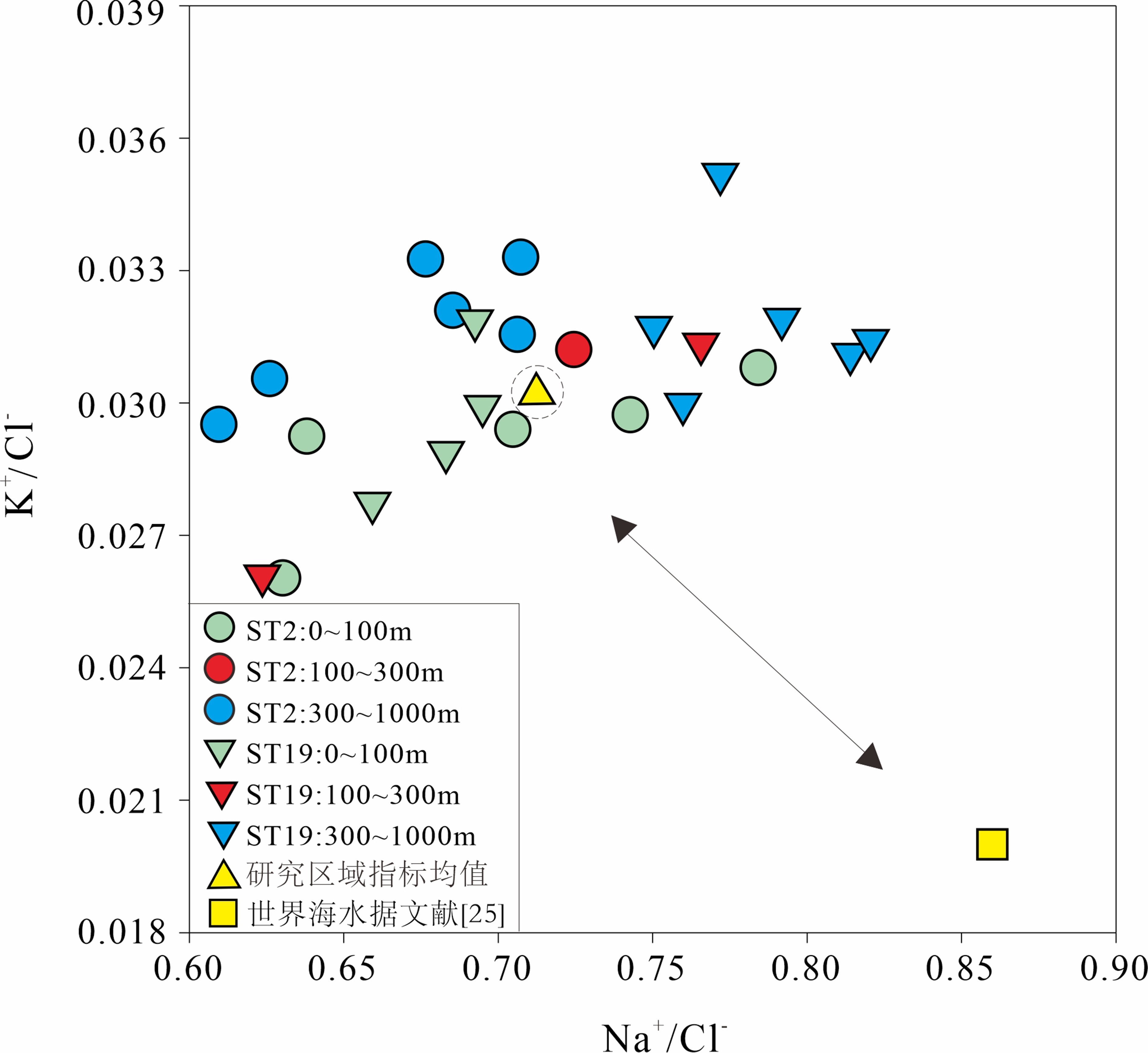
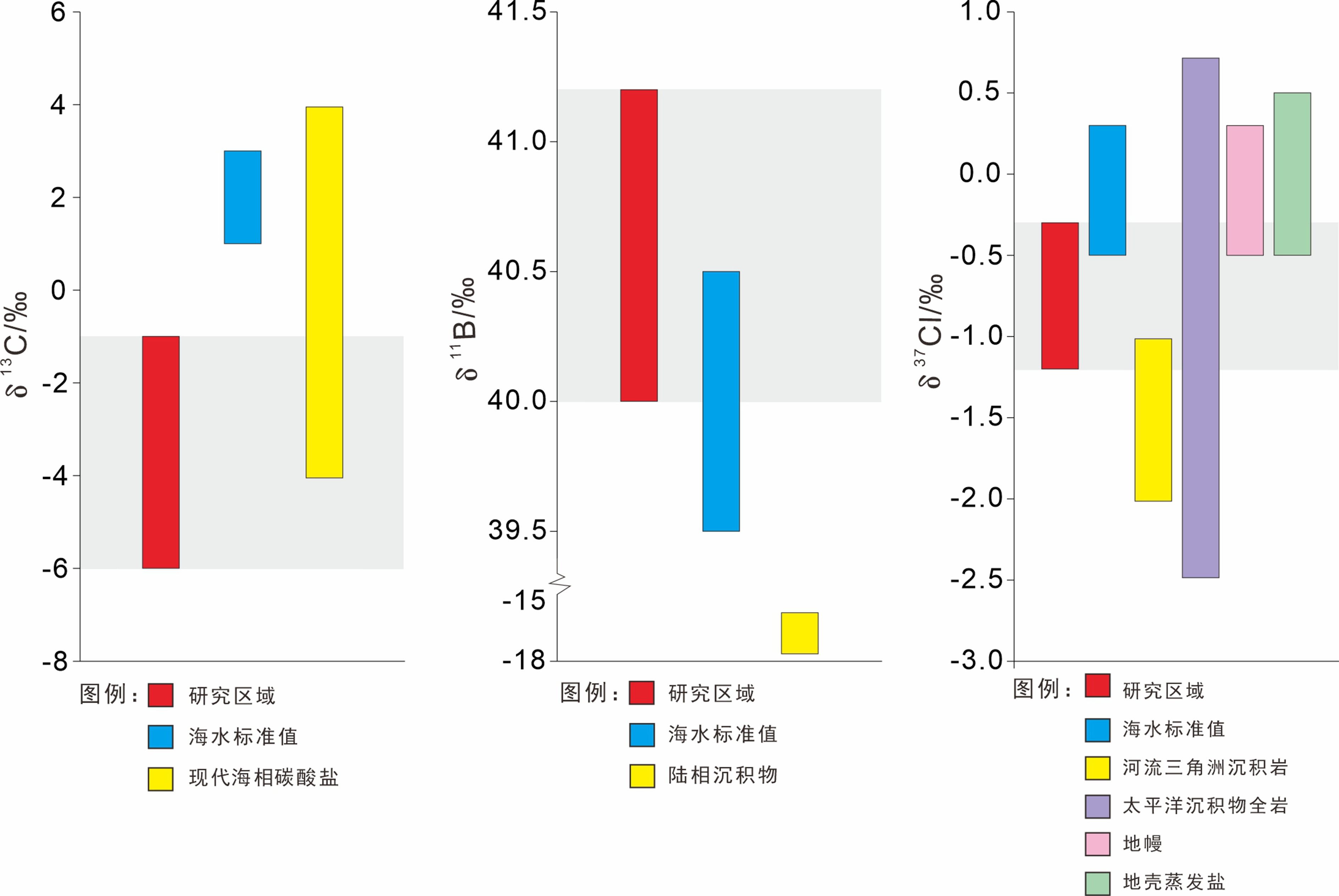
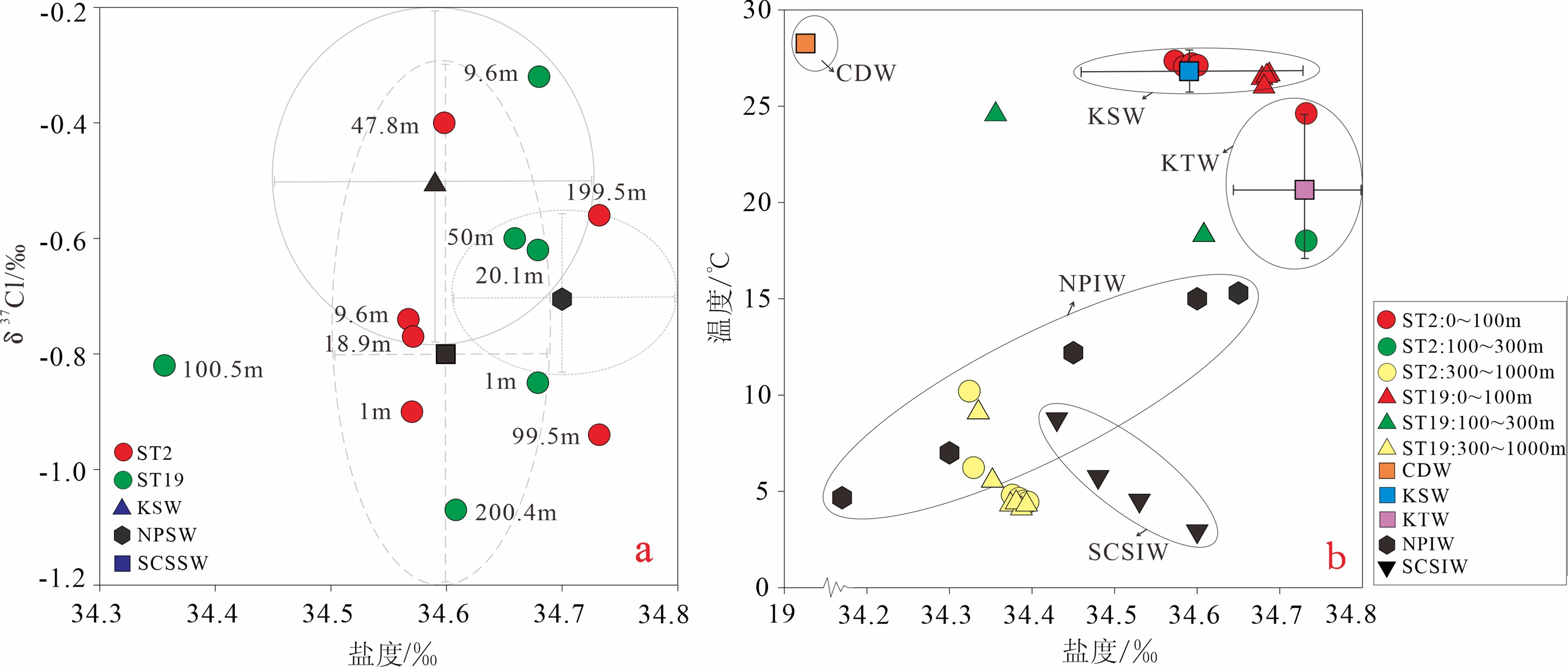
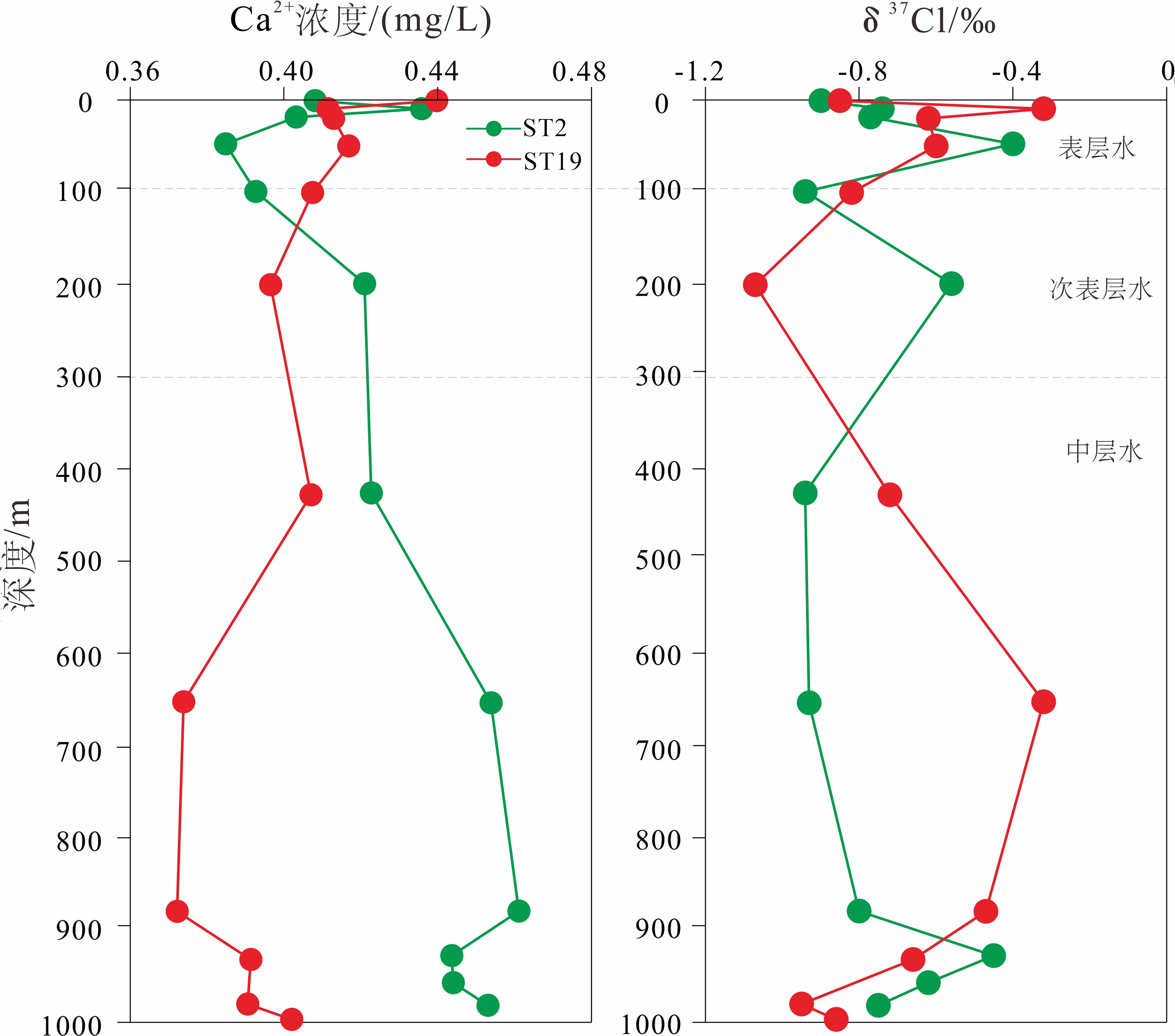
通过对东海陆坡—冲绳海槽中北部两个水体剖面的碳、氯、硼同位素和离子浓度的分析,探讨了水体剖面的离子和同位素组成的控制因素、水体来源以及现代水体交换过程。结果表明,水体剖面中表层水、次表层水、中层水体的性质明显不同,ST2水体剖面K+、Ca2+、SO42−等离子浓度整体随深度增加而升高,δ13C、δ11B、δ37Cl垂向变化波动较大,ST19剖面离子浓度、同位素垂向变化趋势与ST2剖面相反。ST2、ST19水体剖面表层水(0~100 m)和次表层水(100~300 m)主要来源于黑潮表层水(Kuroshio Surface Water,KSW)和黑潮热带水(Kuroshio Tropical Water,KTW),同时受长江冲淡水(Changjiang Diluted Water,CDW)/陆架水影响;中层水体(300~1 000 m)组成与北太平洋中层水(North Pacific Intermediate Water,NPIW)和南海中层水(South China Sea Intermediate Water,SCSIW)相似。两水体剖面水体组成存在较为明显的南北差异,可能与所处海区地理位置、CDW/陆架水传输路径、区域性地形导致局部上升流、水体剖面中NPIW与SCSIW占比不同有关。
Abstract:Two water profiles are selected from the northern part of the Okinawa Trough and the elements, such as carbon, chlorine, and boron isotopes and ion concentrations analyzed for investigation of the control factors of the ion and isotope compositions, water source, and modern water exchange process of the water profiles. It is seen that the properties of surface water, subsurface water, and intermediate water in the water profiles are obviously different. The ion concentrations of K+, Ca2+, and SO42− in the ST2 profile increase with water depth, and the vertical changes of δ13C, δ11B, and δ37Cl fluctuate substantially. The vertical changing pattern of ion concentrations, and isotopes along the profile ST19 is opposite to the profile ST2. The surface water (0~100 m) and subsurface water (100~300 m) of the profiles ST2 and ST19 are mainly coming from KSW(Kuroshio Surface Water)and KTW(Kuroshio Tropical Water), affected by CDW(Changjiang Diluted Water)/shelf water, whereas the composition of the intermediate water (300~1000 m) is similar to that of NPIW(North Pacific Intermediate Water) and SCSIW(South China Sea Intermediate Water). There are obvious north-south differences in water composition between the two profiles, owing to the differences in locality, CDW/shelf water transmission path, local upwelling caused by regional topography and the proportions of NPIW and SCSIW in the water profiles.
-

-
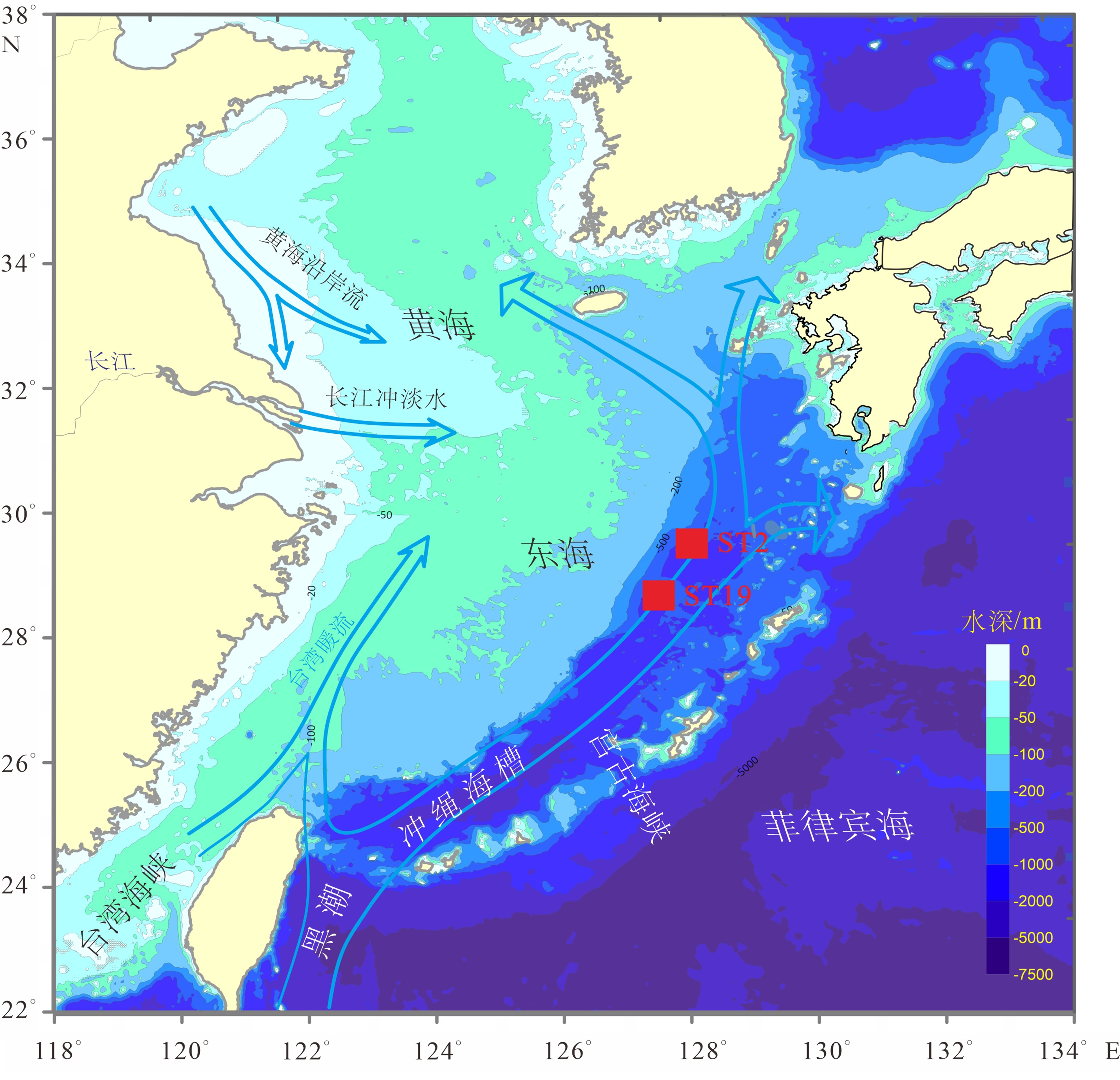
图 1 东海陆架—冲绳海槽环流格局与水体剖面位置[15]
Figure 1.
表 1 研究剖面样品碳、氯、硼同位素和离子含量
Table 1. Contents of carbon, chlorine, boron isotopes and ion of the water profiles
水体剖面 深度/m 盐度/‰ 温度/℃ δ13C/‰ δ11B/‰ 误差/(±‰) δ37Cl/‰ 误差/(±‰) Na+/(mg/L) K+/(mg/L) Ca2+/(mg/L) Mg2+/(mg/L) SO42−/(mg/L) Cl−/(mg/L) ST2 1 34.57 26.40 −2.45 40.31 0.22 −0.90 0 10.82 0.45 0.41 1.27 2.54 17.16 9.6 34.57 26.39 −4.45 40.19 0.20 −0.74 0.10 10.61 0.49 0.44 1.36 2.55 16.63 18.9 34.57 26.34 −3.65 40.63 0.10 −0.77 0.03 10.76 0.45 0.40 1.26 2.36 15.26 47.8 34.60 26.34 −2.69 40.51 0.15 −0.40 0.05 10.88 0.43 0.38 1.21 2.33 13.88 99.5 34.73 24.62 −4.55 40.55 0.04 −0.94 0.01 11.01 0.44 0.39 1.23 2.47 14.83 199.5 34.73 18.00 −4.95 40.55 0.09 −0.56 0.05 10.84 0.47 0.42 1.30 2.50 14.96 426.4 34.32 10.20 −3.81 41.02 0.10 −0.94 0.03 10.64 0.48 0.42 1.32 2.61 15.07 653.7 34.33 6.23 −1.96 41.14 0.09 −0.93 0.03 10.43 0.51 0.45 1.41 2.65 15.42 879.7 34.38 4.80 −486 40.70 0.17 −0.80 0.12 10.48 0.51 0.46 1.43 2.72 16.74 927.8 34.38 4.63 −2.46 40.74 0.13 −0.45 0.01 10.62 0.50 0.44 1.38 2.73 15.50 957.2 34.39 4.50 −2.24 40.72 0.25 −0.62 0.09 10.51 0.49 0.44 1.38 2.63 14.86 981.9 34.40 4.44 −2.28 40.85 0.26 −0.75 0.05 10.49 0.51 0.45 1.40 2.71 17.21 ST19 1 34.68 26.32 −3.57 40.65 0.03 −0.85 0.08 10.69 0.49 0.44 1.37 2.67 15.44 9.6 34.68 26.32 −4.41 40.77 0.08 −0.32 0.02 10.85 0.46 0.41 1.28 2.50 16.45 20.1 34.68 26.31 −3.81 40.72 0.07 −0.62 0.15 10.81 0.46 0.41 1.29 2.54 15.83 50 34.66 26.18 −3.97 40.68 0.18 −0.60 0.03 10.82 0.47 0.42 1.30 2.63 15.57 100.5 34.36 24.57 −3.21 40.26 0.06 −0.82 0.15 10.83 0.45 0.41 1.27 2.59 17.37 200.4 34.61 18.30 −4.14 40.81 0.04 −1.07 0.17 10.95 0.45 0.40 1.24 2.49 14.30 428.3 34.34 9.10 −4.14 40.92 0.04 −0.72 0.19 10.78 0.46 0.41 1.26 2.51 14.36 652.7 34.35 5.55 −4.06 40.63 0.10 −0.32 0.01 11.00 0.42 0.37 1.16 2.39 13.51 879.9 34.38 4.70 −2.75 40.54 0.15 −0.47 0.13 10..97 0.42 0.37 1.15 2.35 13.36 932 34.39 4.53 −1.92 40.37 0.07 −0.66 0.26 10.90 0.44 0.39 1.21 2.44 13.77 980.3 34.40 4.36 −4.36 40.69 0.04 −0.95 0.11 10.89 0.43 0.39 1.21 2.42 14.33 ST19 997.1 34.40 4.35 −4.16 39.85 0.16 −0.86 0.27 10.81 0.50 0.40 1.24 2.52 14.10 CDW 0 28.30 19.10 − − − − − − − − − − − KSW 0~100 34.59±0.14 26.81±1.11 − − − −0.5±0.3 − − − − − − − KTW 100~200 34.73±0.09 20.66±3.40 − − − − − − − − − − − NPSW 0~200 34.70±0.10 18−26 − − − −0.7±0.15 − − − − − − − NPIW 398 34.65 15.30 − − − − − − − − − − − 455 34.60 15.00 − − − − − − − − − − − 505 34.45 12.20 − − − − − − − − − − − 651 34.30 7.00 − − − − − − − − − − − 794 34.17 4.67 − − − − − − − − − − − SCSSW 0~200 34.60±0.10 18.60−26.80 − − − −0.8±0.50 − − − − − − − SCSIW 495 34.43 8.75 − − − − − − − − − − − 795 34.48 5.75 − − − − − − − − − − − 997 34.53 4.53 − − − − − − − − − − − 1 488 34.60 2.93 − − − − − − − − − − − 注:黑潮表层水(KSW)与黑潮热带水(KTW)分层数据参考文献[6]和[18],北太平洋中层水(NPIW)和南海中层水(SCSIW)分层数据参考文献[19−20]。长江冲淡水(CDW)盐度数据和温度数据参考文献[5],黑潮表层水与黑潮热带水盐度数据和温度数据参考文献[21]。北太平洋中层水(NPIW)盐度数据和温度数据参考文献[22],南海中层水(SCSIW)盐度数据和温度数据参考文献[23]。黑潮表层水和北太平洋表层水(NPSW)盐度数据和δ37Cl数据参考文献[24],南海表层水(SCSS)盐度数据和δ37Cl数据参考文献[16]。“−”表示研究区域来源水体没有碳、氯、硼同位素参数和离子含量参数。 -
[1] 林红梅, 林奇, 徐国杰, 等. 离子色谱法测定海水中的阳离子[J]. 化学分析计量, 2011, 20(2):27-29 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-6145.2011.02.007
LIN Hongmei, LIN Qi, XU Guojie, et al. Determination of cation in seawater by ion chromatography [J]. Chemical Analysis and Meterage, 2011, 20(2): 27-29. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-6145.2011.02.007
[2] Southon J, Noronha A L, Cheng H, et al. A high-resolution record of atmospheric 14C based on Hulu Cave speleothem H82 [J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2012, 33: 32-41. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2011.11.022
[3] Nakamura H, Nishina A, Liu Z J, et al. Intermediate and deep water formation in the Okinawa Trough [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Oceans, 2013, 118(12): 6881-6893. doi: 10.1002/2013JC009326
[4] Chen C T A, Kandasamy S, Chang Y P, et al. Geochemical evidence of the indirect pathway of terrestrial particulate material transport to the Okinawa Trough [J]. Quaternary International, 2017, 441: 51-61. doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2016.08.006
[5] Zhang L, Liu Z, Zhang J, et al. Reevaluation of mixing among multiple water masses in the shelf: An example from the East China Sea [J]. Continental Shelf Research, 2007, 27(15): 1969-1979. doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2007.04.002
[6] Bai L L, Zhang J. Clarifying the structure of water masses in East China Sea using low-volume seawater measurement with rare earth elements [J]. Advances in Geosciences, 2008, 18: 169-180.
[7] Lee H, Kim G, Kim J, et al. Tracing the flow rate and mixing ratio of the Changjiang Diluted Water in the northwestern Pacific marginal seas using radium isotopes [J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2014, 41(13): 4637-4645. doi: 10.1002/2014GL060230
[8] Nishina A, Nakamura H, Park J H, et al. Deep ventilation in the Okinawa Trough induced by Kerama Gap overflow [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Oceans, 2016, 121(8): 6092-6102. doi: 10.1002/2016JC011822
[9] Kubota Y, Suzuki N, Kimoto K, et al. Variation in subsurface water temperature and its link to the Kuroshio Current in the Okinawa Trough during the last 38.5 kyr [J]. Quaternary International, 2017, 452: 1-11. doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2017.06.021
[10] Minakawa M, Watanabe Y. Aluminum in the East China Sea and Okinawa Trough, marginal sea areas of the western North Pacific [J]. Journal of Oceanography, 1998, 54(6): 629-640. doi: 10.1007/BF02823283
[11] Amakawa H, Sasaki K, Ebihara M. Nd isotopic composition in the central North Pacific [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2009, 73(16): 4705-4719. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2009.05.058
[12] 秦蕴珊, 赵一阳, 陈丽蓉, 等. 东海地质[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1987: 1-263.
QIN Yunshan, ZHAO Yiyang, CHEN Lirong, et al. East China Sea Geology[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1987: 1-263.
[13] 窦衍光, 陈晓辉, 李军, 等. 东海外陆架-陆坡-冲绳海槽不同沉积单元底质沉积物成因及物源分析[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2018, 38(4):21-31
DOU Yanguang, CHEN Xiaohui, LI Jun, et al. Origin and provenance of the surficial sediments in the subenvironments of the East China Sea [J]. Marine Geology and Quaternary Geology, 2018, 38(4): 21-31.
[14] 高金满, 李国胜, 孙家淞, 等. 冲绳海槽的地形地貌特征[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 1987, 7(1):51-60
GAO Jinman, LI Guosheng, SUN Jiasong, et al. Geomorphic characteristics of Okinawa Trough [J]. Marine Geology and Quaternary Geology, 1987, 7(1): 51-60.
[15] Dou Y G, Yang S Y, Liu Z X, et al. Provenance discrimination of siliciclastic sediments in the middle Okinawa Trough since 30 ka: constraints from rare earth element compositions [J]. Marine Geology, 2010, 275(1-4): 212-220. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2010.06.002
[16] Yu H T, Ma T, Du Y, et al. Genesis of formation water in the northern sedimentary basin of South China Sea: Clues from hydrochemistry and stable isotopes (D, 18O, 37Cl and 81Br) [J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2019, 196: 57-65. doi: 10.1016/j.gexplo.2018.08.005
[17] Xiao Y K, Beary E S, Fassett J D. An improved method for the high-precision isotopic measurement of boron by thermal ionization mass spectrometry [J]. International Journal of Mass Spectrometry and Ion Processes, 1988, 85(2): 203-213. doi: 10.1016/0168-1176(88)83016-7
[18] Chen C T A, Ruo R, Paid S C, et al. Exchange of water masses between the East China Sea and the Kuroshio off northeastern Taiwan [J]. Continental Shelf Research, 1995, 15(1): 19-39. doi: 10.1016/0278-4343(93)E0001-O
[19] Talley L D, Nagata Y, Fujimura M, et al. North Pacific Intermediate Water in the Kuroshio/Oyashio mixed water region [J]. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 1995, 25(4): 475-501. doi: 10.1175/1520-0485(1995)025<0475:NPIWIT>2.0.CO;2
[20] Li G, Rashid H, Zhong L F, et al. Changes in deep water oxygenation of the South China Sea since the last glacial period [J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2018, 45(17): 9058-9066. doi: 10.1029/2018GL078568
[21] 卢汐, 宋金明, 袁华茂, 等. 黑潮主流径海域海水中的无机碳及其对东海陆架区的影响[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2016, 47(1):16-28
LU Xi, SONG Jinming, YUAN Huamao, et al. Distribution of inorganic carbon parameters in Kuroshio and its impact on adjacent East China Sea shelf [J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2016, 47(1): 16-28.
[22] Amakawa H, Nozaki Y, Alibo D S, et al. Neodymium isotopic variations in Northwest Pacific waters [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2004, 68(4): 715-727. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(03)00501-5
[23] Alibo D S, Nozaki Y. Dissolved rare earth elements in the eastern Indian Ocean: chemical tracers of the water masses [J]. Deep Sea Research Part I:Oceanographic Research Papers, 2004, 51(4): 559-576. doi: 10.1016/j.dsr.2003.11.004
[24] Shirodkar P V, Xiao Y K, Sarkar A, et al. Influence of air–sea fluxes on chlorine isotopic composition of ocean water: Implications for constancy in δ37Cl—A statistical inference [J]. Environment International, 2006, 32(2): 235-239. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2005.08.017
[25] Jung J, Furutani H, Uematsu M, et al. Atmospheric inorganic nitrogen input via dry, wet, and sea fog deposition to the subarctic western North Pacific Ocean [J]. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 2013, 13: 411-428. doi: 10.5194/acp-13-411-2013
[26] Magaritz M, Nadler A, Koyumdjisky H, et al. The use of Na/Cl ratios to trace solute sources in a semiarid zone [J]. Water Resources Research, 1981, 17(3): 602-608. doi: 10.1029/WR017i003p00602
[27] 蒋保刚, 闫正, 宋献方, 等. 汉江上游金水河流域河水的化学特征[J]. 环境化学, 2013, 32(6):980-986 doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2013.06.010
JIANG Baogang, YAN Zheng, SONG Xianfang, et al. Water chemistry of the Jinshui River Basin in the Upper Han River [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2013, 32(6): 980-986. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2013.06.010
[28] Cui B L, Li X Y, Wei X H. Isotope and hydrochemistry reveal evolutionary processes of lake water in Qinghai Lake [J]. Journal of Great Lakes Research, 2016, 42(3): 580-587. doi: 10.1016/j.jglr.2016.02.007
[29] Kim Y, Lee K S, Koh D C, et al. Hydrogeochemical and Isotopic evidence of groundwater salinization in a coastal aquifer: a case study in Jeju volcanic island, Korea [J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2003, 270(3-4): 282-294. doi: 10.1016/S0022-1694(02)00307-4
[30] 周胜杰, 张洪海, 杨桂朋. 东海PM2.5和PM10中水溶性离子的组成与化学特性[J]. 中国环境科学, 2018, 38(3):900-909 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2018.03.012
ZHOU Shengjie, ZHANG Honghai, YANG Guipeng. Distributions and chemical characteristics of water soluble ions in PM2.5 and PM10 over the East China Sea [J]. China Environmental Science, 2018, 38(3): 900-909. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2018.03.012
[31] 江峰, 李强, 吉勤克补子, 等. 贵州省岩溶地区饮用天然矿泉水化学特征及其宏量组分来源分析[J]. 贵州地质, 2019, 36(2):173-179 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5943.2019.02.010
JIANG Feng, LI Qiang, JI Qinkebuzi, et al. The chemical characteristics of the potable natural mineral water and its major components source analysis of the karst area in Guizhou province [J]. Guizhou Geology, 2019, 36(2): 173-179. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5943.2019.02.010
[32] Wang H B, Shooter D. Water soluble ions of atmospheric aerosols in three New Zealand cities: seasonal changes and sources [J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2001, 35(34): 6031-6040. doi: 10.1016/S1352-2310(01)00437-X
[33] 殷美雪. 中国中东部地区大气湿沉降中的离子化学特征[D]. 上海师范大学硕士学位论文, 2015: 1-67. ]
YIN Meixue. Ion chemical characteristics and elements of morphological characteristics in China’s central[D]. Master Dissertation of Shanghai Normal University, 2015: 1-67
[34] Wong G T F, Chao S Y, Li Y H, et al. The Kuroshio edge exchange processes (KEEP) study: an introduction to hypotheses and highlights [J]. Continental Shelf Research, 2000, 20(4-5): 335-347. doi: 10.1016/S0278-4343(99)00075-8
[35] Hung J J, Chen C H, Gong G C, et al. Distributions, stoichiometric patterns and cross-shelf exports of dissolved organic matter in the East China Sea [J]. Deep Sea Research Part II:Topical Studies in Oceanography, 2003, 50(6-7): 1127-1145. doi: 10.1016/S0967-0645(03)00014-6
[36] 林久人, 祁建华, 谢丹丹, 等. 海洋降水中无机离子浓度及湿沉降通量: 中国海及西北太平洋降水的研究[J]. 中国环境科学, 2017, 37(5):1706-1715 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2017.05.013
LIN Jiuren, QI Jianhua, XIE Dandan, et al. The concentrations and wet depositions fluxes of inorganic ions in oceanic precipitation-Study on precipitation over the China Sea and Northwest Pacific Ocean [J]. China Environmental Science, 2017, 37(5): 1706-1715. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2017.05.013
[37] 余伟, 杨海全, 郭建阳, 等. 贵州草海水化学特征及离子来源分析[J]. 地球与环境, 2021, 49(1):32-41
YU Wei, YANG Haiquan, GUO Jianyang, et al. Hydrochemical characteristics and major ion sources of Lake Caohai in Guizhou province [J]. Earth and Environment, 2021, 49(1): 32-41.
[38] Sibuet J C, Letouzey J, Barbier F, et al. Back arc extension in the Okinawa Trough [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Solid Earth, 1987, 92(B13): 14041-14063. doi: 10.1029/JB092iB13p14041
[39] 吴自银, 李家彪, 金翔龙, 等. 冲绳海槽海底地形地貌界限特征及影响因素[J]. 中国科学:地球科学, 2014, 57(8):1185-1896
WU Ziyin, LI Jiabiao, JIN Xianglong, et al. Distribution, features, and influence factors of the submarine topographic boundaries of the Okinawa Trough [J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 2014, 57(8): 1185-1896.
[40] Hatta M, Zhang J. Possible source of advected water mass and residence times in the multi-structured Sea of Japan using rare earth elements [J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2006, 33(16): L16606. doi: 10.1029/2006GL026537
[41] 杜金秋, 陈敏, 曹建平, 等. 南黄海和东海海水18O的组成及其意义[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2012, 43(6):1057-1066 doi: 10.11693/hyhz201206005005
DU Jinqiu, CHEN Min, CAO Jianping, et al. Oxygen isotope in seawater and its hydrological implication in the southern Yellow Sea and the East China Sea [J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2012, 43(6): 1057-1066. doi: 10.11693/hyhz201206005005
[42] 杨会, 王华, 吴夏, 等. 样品采集和保存方法对水中溶解无机碳同位素分馏的影响[J]. 中国岩溶, 2015, 34(6):642-647 doi: 10.11932/karst20150614
YANG Hui, WANG Hua, WU Xia, et al. The influence of different pretreatment methods on the δ13C value of dissolved inorganic carbon in water [J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2015, 34(6): 642-647. doi: 10.11932/karst20150614
[43] Chen X Y, Tung K K. Varying planetary heat sink led to global-warming slowdown and acceleration [J]. Science, 2014, 345(6199): 897-903.
[44] 杨杰东, 徐士进. 同位素与全球环境变化[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2007: 28-30.
YANG Jiedong, XU Shijin. Isotopes and Global Environmental Changes[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2007: 28-30.
[45] Anderson T F, Arthur M A. Stable isotopes of oxygen and carbon and their application to sedimentologic and paleoenvironmental problems[M].Stable Isotopes in Sedimentary Geology. SEPM, 1983: 1.1-1.151.
[46] Hoffman P F, Kaufman A J, Halverson G P, et al. A neoproterozoic snowball earth [J]. Science, 1998, 281(5381): 1342-1346. doi: 10.1126/science.281.5381.1342
[47] Mcnichol A P, Druffel E R M. Variability of the δ13C of dissolved inorganic carbon at a site in the north Pacific Ocean [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1992, 56(9): 3589-3592. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(92)90402-5
[48] 曹敏, 蒋勇军, 蒲俊兵, 等. 重庆南山老龙洞地下河流域岩溶地下水DIC和δ13CDIC及其流域碳汇变化特征[J]. 中国岩溶, 2012, 31(2):145-153 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4810.2012.02.006
CAO Min, JIANG Yongjun, PU Junbing, et al. Variations in DIC and δ13CDIC of the karst groundwater and in carbon sink of Laolongdong subterranean stream basin at Nanshan, Chongqing [J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2012, 31(2): 145-153. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4810.2012.02.006
[49] 李银川, 董戈, 雷昉, 等. 硼同位素分馏的实验理论认识和矿床地球化学研究进展[J]. 地学前缘, 2020, 27(3):14-28
LI Yinchuan, DONG Ge, LEI Fang, et al. Experimental and theoretical understanding of boron isotope fractionation and advances in ore deposit geochemistry study [J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2020, 27(3): 14-28.
[50] Nomura M, Okamoto M, Kakihana H. Determination of boron content and boron isotopic ratio of seawater samples [J]. Bulletin of the Society of Sea Water Science, Japan, 1984, 38(1): 28-33.
[51] Marschall H R, Foster G L. Boron isotopes in the Earth and planetary sciences: a short history and introduction[M]. Advances in Isotope Geochemistry. Switzerland: Springer, 2018: 1-11.
[52] Rustad J R, Bylaska E J, Jackson V E, et al. Calculation of boron-isotope fractionation between B(OH)3 and B(OH)4- [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2010, 74(10): 2843-2850. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2010.02.032
[53] Nir O, Vengosh A, Harkness J S, et al. Direct measurement of the boron isotope fractionation factor: reducing the uncertainty in reconstructing ocean paleo-pH [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2015, 414: 1-5. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2015.01.006
[54] 刘茜, 王奕菁, 魏海珍. 稳定氯同位素地球化学研究进展[J]. 地学前缘, 2020, 27(3):29-41
LIU Xi, WANG Yijing, WEI Haizhen. Advances in stable chlorine isotope geochemistry [J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2020, 27(3): 29-41.
[55] Barnes J D, Paulick H, Sharp Z D, et al. Stable isotope (δ18O, δD, δ37Cl) evidence for multiple fluid histories in mid-Atlantic abyssal peridotites (ODP Leg 209) [J]. Lithos, 2009, 110(1-4): 83-94. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2008.12.004
[56] Selverstone J, Sharp Z D. Chlorine isotope behavior during prograde metamorphism of sedimentary rocks [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2015, 417: 120-131. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2015.02.030
[57] Bonifacie M, Jendrzejewski N, Agrinier P, et al. The chlorine isotope composition of Earth’s mantle [J]. Science, 2008, 319(5869): 1518-1520. doi: 10.1126/science.1150988
[58] Bolin B, Degens E T, Kempe S, et al. The Global Carbon Cycle[M]. NY: John Wiley Sons, 1978: 35-38.
[59] Ishikawa T, Nakamura E. Boron isotope systematics of marine sediments [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1993, 117(3-4): 567-580. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(93)90103-G
[60] Eastoe C J, Peryt T M, Petrychenko O Y, et al. Stable chlorine isotopes in Phanerozoic evaporites [J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2007, 22(3): 575-588. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2006.12.012
[61] Sharp Z. Principles of Stable Isotope Geochemistry[M]. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Pearson Education, 2007: 1-334.
[62] Jian Z M, Wang P X, Saito Y, et al. Holocene variability of the Kuroshio Current in the Okinawa Trough, northwestern Pacific Ocean [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2000, 184(1): 305-319. doi: 10.1016/S0012-821X(00)00321-6
[63] Yang D Z, Yin B S, Liu Z L, et al. Numerical study of the ocean circulation on the East China Sea shelf and a Kuroshio bottom branch northeast of Taiwan in summer [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Oceans, 2011, 116(C5): C05015.
[64] Behrens M K, Pahnke K, Paffrath R, et al. Rare earth element distributions in the West Pacific: Trace element sources and conservative vs. non-conservative behavior [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2018, 486: 166-177. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2018.01.016
[65] Talley L D, Reid J L, Robbins P E. Data-based meridional overturning streamfunctions for the global ocean [J]. Journal of Climate, 2003, 16(19): 3213-3226. doi: 10.1175/1520-0442(2003)016<3213:DMOSFT>2.0.CO;2
[66] Niwa Y, Hibiya T. Estimation of baroclinic tide energy available for deep ocean mixing based on three-dimensional global numerical simulations [J]. Journal of Oceanography, 2011, 67(4): 493-502. doi: 10.1007/s10872-011-0052-1
[67] Shinjo R. Geochemistry of high Mg andesites and the tectonic evolution of the Okinawa Trough–Ryukyu arc system [J]. Chemical Geology, 1999, 157(1-2): 69-88. doi: 10.1016/S0009-2541(98)00199-5
-



 下载:
下载: