Environmental reconstruction for the paleo-lake of ZhuⅠdepression and the depositional model for high-quality source rocks
-
摘要:
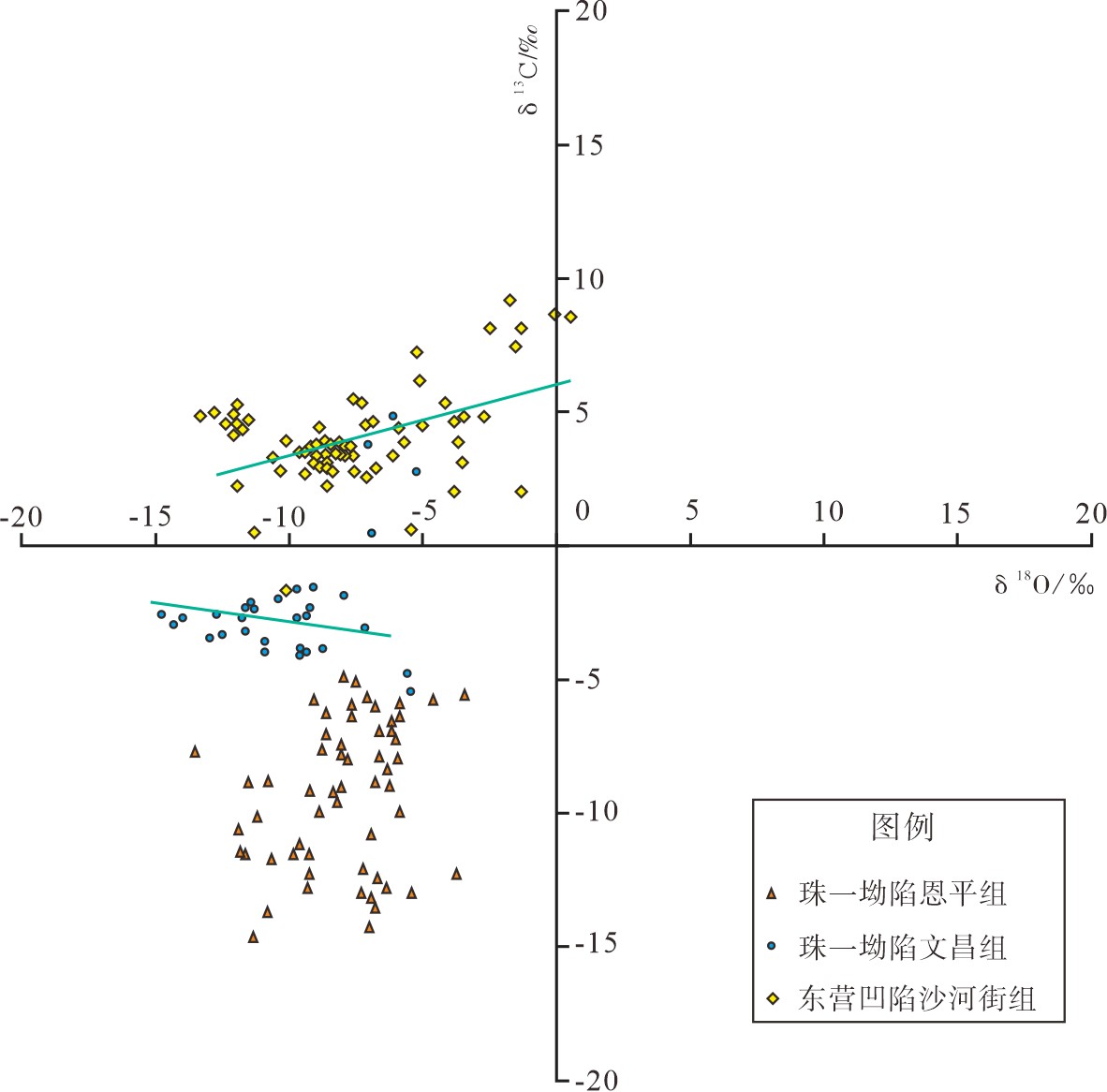
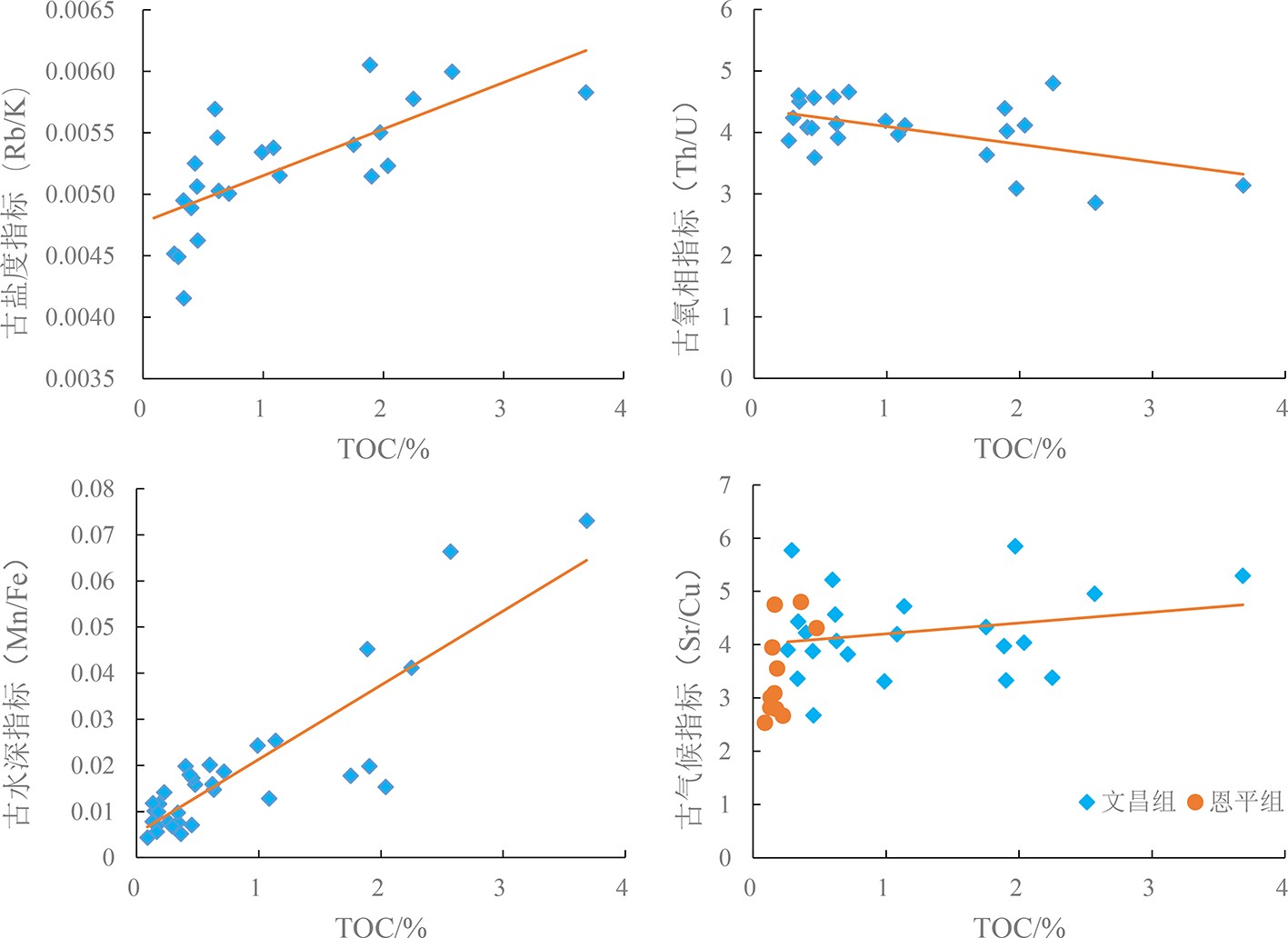
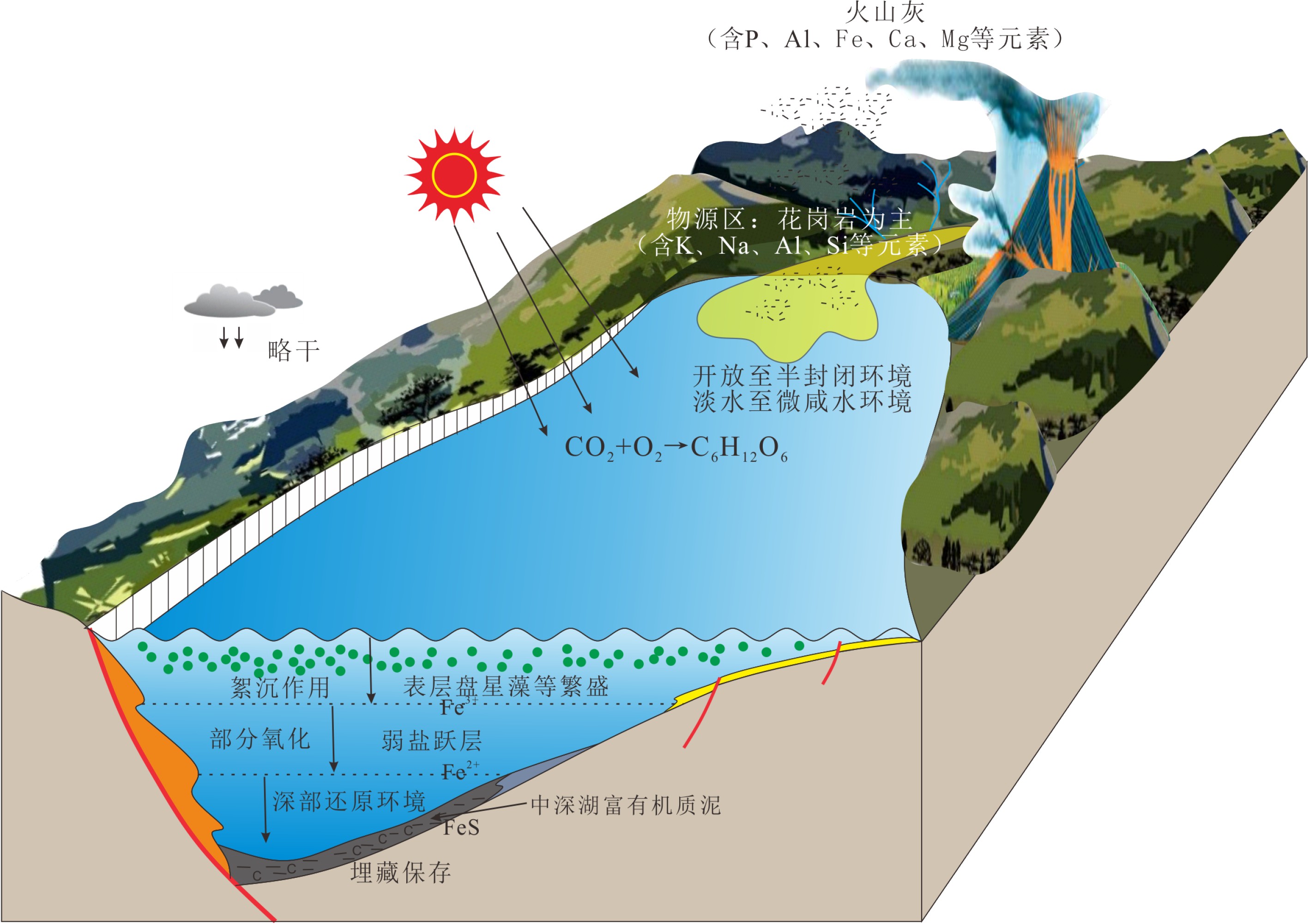
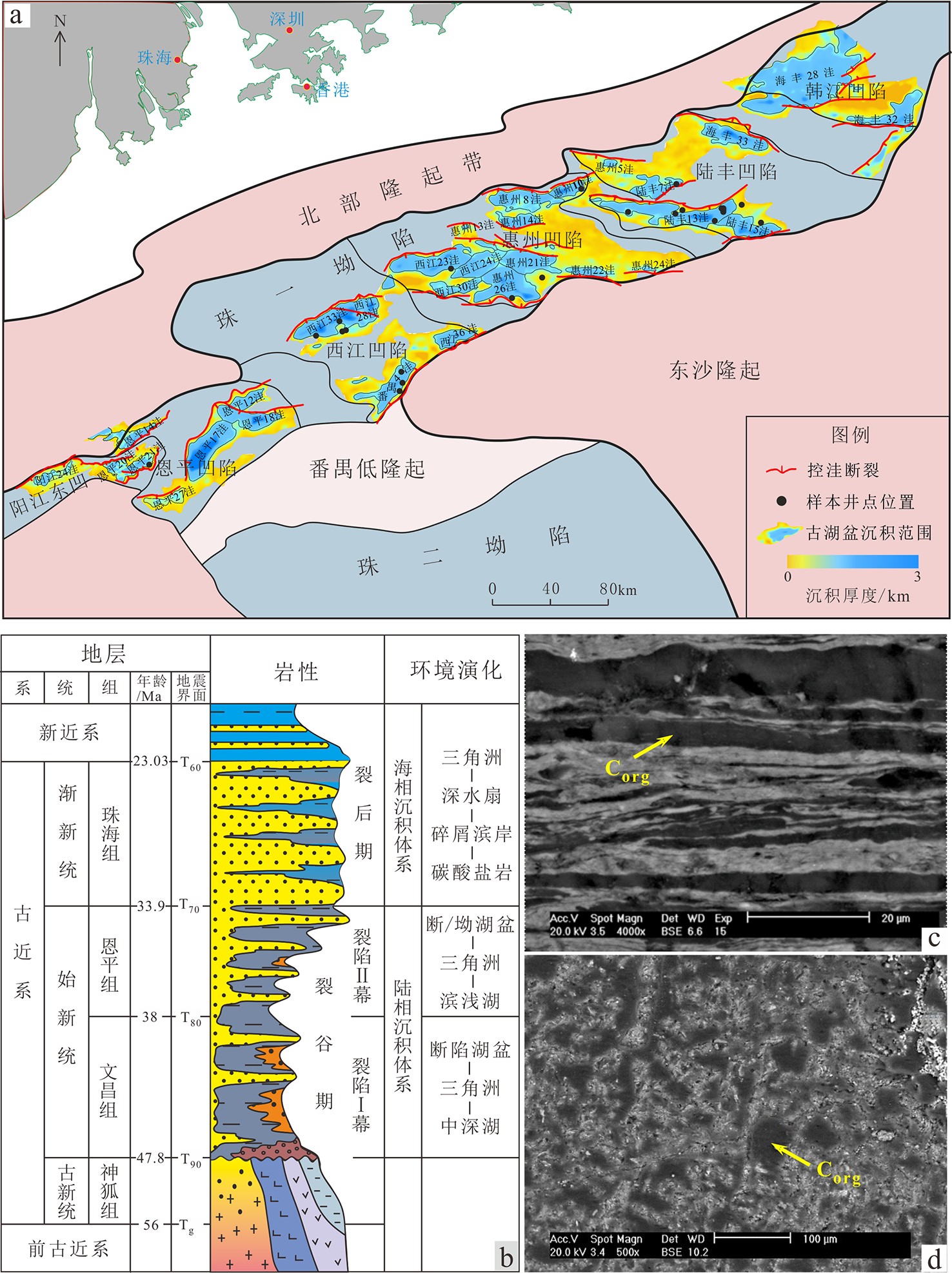
珠一坳陷古近纪陆相湖盆发育优质烃源岩,通过对文昌组、恩平组泥岩系统取样,进行常量、微量元素、同位素含量等分析,优选出对环境敏感的元素与元素比值,系统分析了珠一坳陷烃源岩形成时的古环境,包括古盐度、古水深、氧化还原条件、古气候及古水体的封闭性,并建立了有机碳与环境敏感元素比值的定量关系。开展优质烃源岩发育的水化学性质研究,明确研究区优质烃源岩形成演化所具有的古环境特征,最终探讨了文昌组优质烃源岩的发育模式。研究结果表明,珠一坳陷(除韩江凹陷无样本点)文昌期温暖略干气候条件下,湖盆水体主要为淡水—微咸水,发育中—深湖相,整体表现为开放—半封闭、还原—强还原的环境,极利于有机质的保存和优质烃源岩的发育,各凹陷古环境差异不大。烃源岩质量与咸度、水深、还原条件呈正相关,共同影响了优质烃源岩的发育。总之,温暖略干、微咸、深水及强还原、开放—半封闭环境共同控制了珠一坳陷优质烃源岩的发育。
Abstract:High-quality source rocks are well occurred in the Paleogene lacustrine deposits of the ZhuⅠdepression. Element geochemistry and isotope analysis for mudstone cuttings from the Wenchang Formation and Enping Formation is carried out by this paper in order to optimize the study of element content and elements ratio which are sensitive to paleoenvironment reconstruction. Paleoenvironmental parameters for the source rocks in ZhuⅠdepression are systematically analyzed, which include paleosalinity, paleowater depth, redox conditions, paleoclimate, degree of environmental closure and so on. Upon the basis, we revealed the quantitative relationship between the organic matter content and the ratio of environmental sensitive elements, and established the depositional model for the high-quality source rocks in the Wenchang Formation. The results show that under the warm and slightly dry climate conditions during the Wenchang period, the ZhuⅠdepression was a medium to deep and open to semiclosed lake dominated by fresh water and brackish water under a reductive or strongly reductive environment, which was conducive to the preservation of organic matter and the formation of high-quality source rocks. The quality of source rocks is positively related to salinity, water depth and reduction conditions. In conclusion, in a warm and slightly dry lake with slightly salty deep water as the ZhuⅠdepression, the strong reduction and open-semiclosed environment jointly control the development of high-quality source rocks in ZhuⅠdepression.
-
Key words:
- high-quality source rocks /
- development model /
- paleoenvironment /
- paleo-lake /
- inorganic geochemistry /
- ZhuⅠdepression
-

-
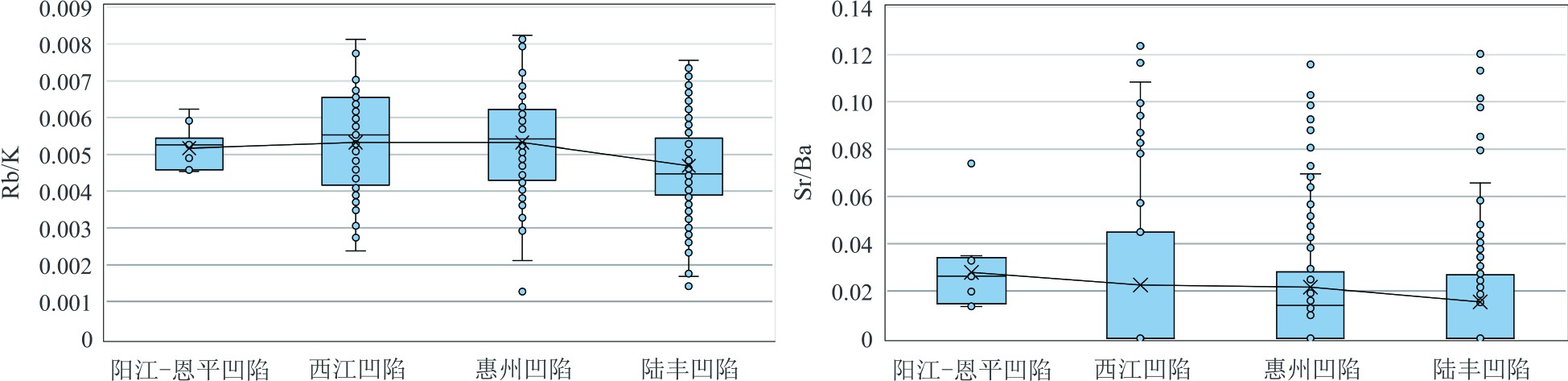
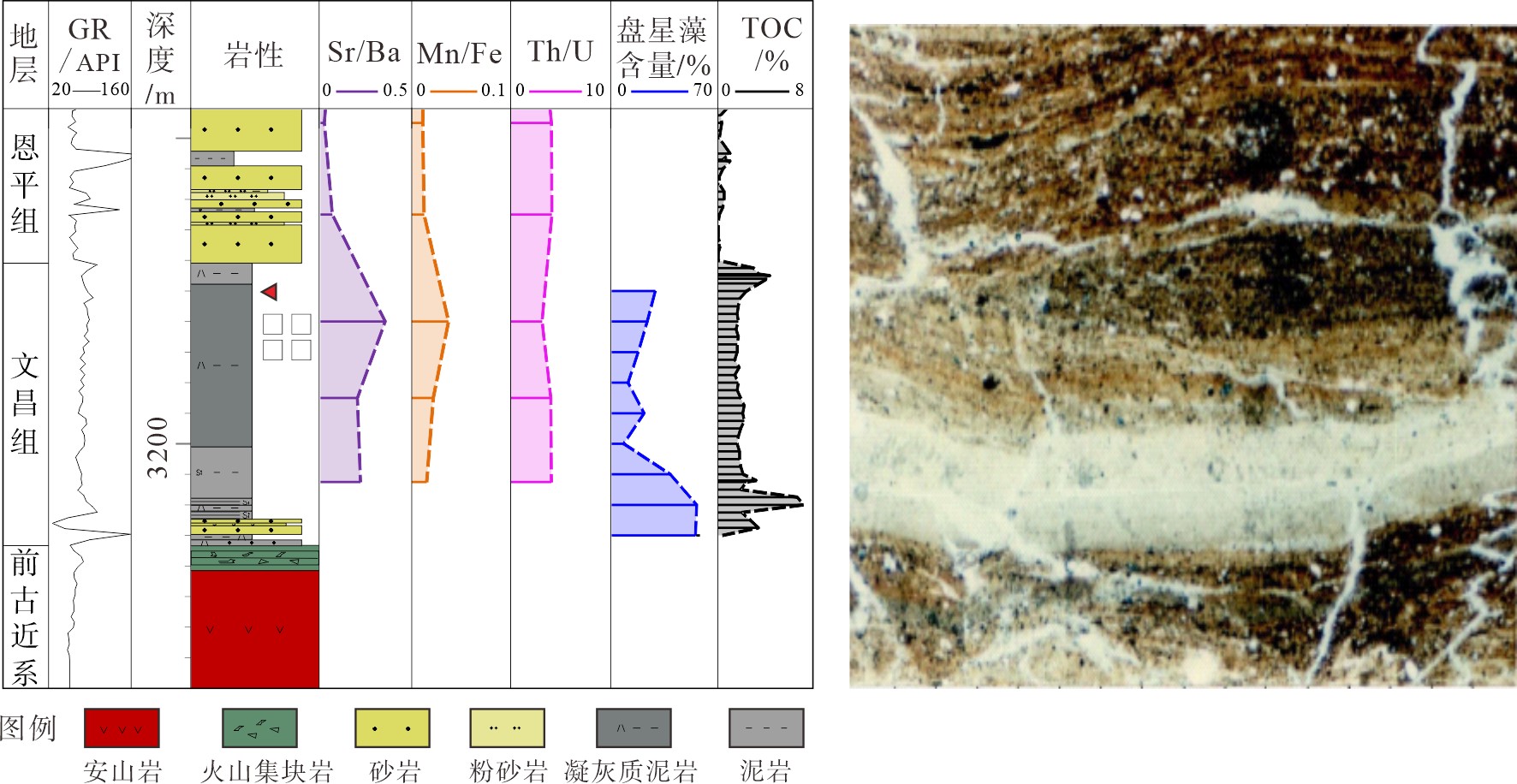
表 1 珠一坳陷文昌期湖盆古盐度重建指标及其指示意义
Table 1. Reconstruction index of paleosalinity for Wenchang Formation in ZhuⅠdepression and its implications
判别指标 淡水 微—半咸水 咸水 B/Ga <1.5 5~6 >7 Rb/K <0.004 0.004~0.006 >0.006 Sr/Ba <0.6为陆相,>1为海相 Z值 <120 − >120 表 2 珠一坳陷文昌期湖盆古氧相重建指标及其指示意义
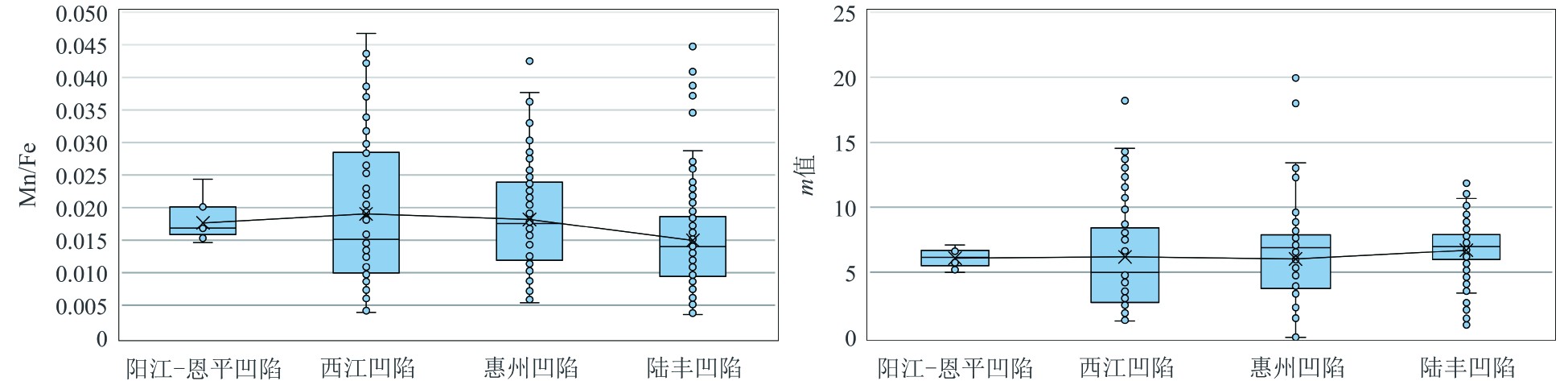
Table 2. Reconstruction index of paleooxygen facies for Wenchang Formation in ZhuⅠdepression and its indicative significance
判别指标 氧化环境 弱还原—氧化 还原环境 强还原环境 Th/U >30 10~30 4~10 <4 V/(V+Ni) <0.46 0.46~0.60 >0.60 − Cu/Zn >0.63 0.38~0.63 0.21~0.38 <0.21 表 3 珠一坳陷文昌期湖盆古气候重建指标及其指示意义
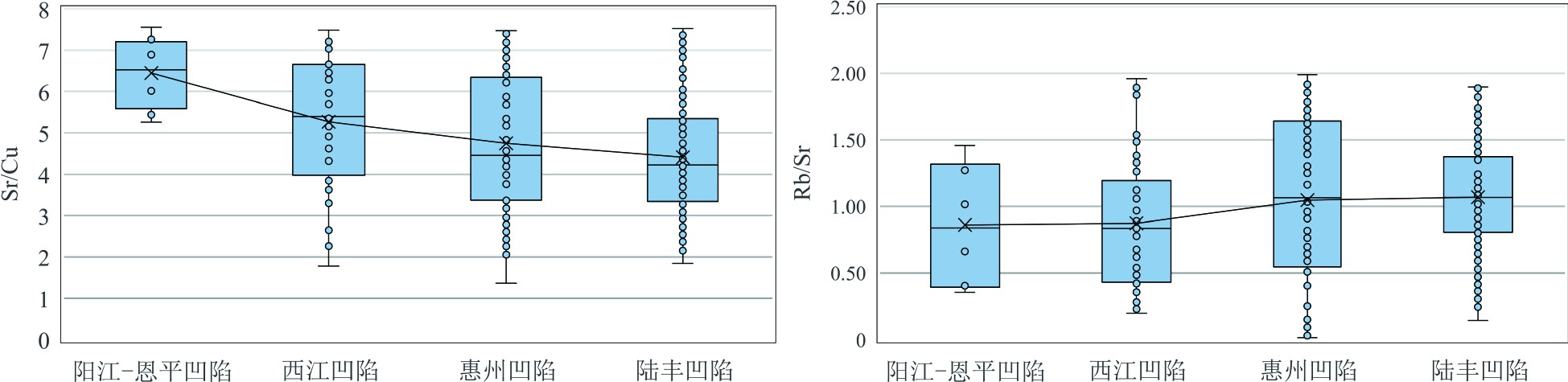
Table 3. Reconstruction index of paleoclimate in ZhuⅠdepression for Wenchang Formation and its indicative significance
判别指标 低值 高值 Sr/Cu 1.3~5.0,温湿 >5,干热 Sr/Ca 温湿 干热 Mg/Ca 潮湿 干旱 Rb/Sr 干燥 湿润 Al2O3/MgO 干旱 湿润 -
[1] 朱伟林. 中国近海新生代含油气盆地古湖泊学与烃源条件[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2009.
ZHU Weilin. Paleolimnology and Source Rock Studies of Cenozoic Hydrocarbon-bearing Offshore Basins in China[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2009.
[2] Mello M R, Maxwell J R. Organic geochemical and biological marker characterization of source rocks and oils derived from lacustrine environments in the Brazilian continental margin[C]//Lacustrine Basin Exploration: Case Studies and Modern Analogs. Tulsa: AAPG, 1999, 50: 77-97.
[3] Rosendahl B R, Reynolds D J, Lorber P M, et al. Structural expressions of rifting: lessons from Lake Tanganyika, Africa [J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 1986, 25(1): 29-43. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.1986.025.01.04
[4] 孟庆涛, 刘招君, 胡菲, 等. 桦甸盆地始新世古湖泊生产力与有机质富集机制[J]. 中国石油大学学报:自然科学版, 2012, 36(5):38-44
MENG Qingtao, LIU Zhaojun, HU Fei, et al. Productivity of Eocene ancient lake and enrichment mechanism of organic matter in Huadian Basin [J]. Journal of China University of Petroleum, 2012, 36(5): 38-44.
[5] 吴克强, 姜雪. 孙和风. 近海富生油凹陷湖相烃源岩发育模式: 以黄河口凹陷古近系为例[J]. 地质科技情报, 2015, 34(2):63-70
WU Keqiang, JIANG Xue, SUN Hefeng. Model of lacustrine source rocks in offshore oil kitchen sag: a case study of Paleogene in Huanghekou sag [J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2015, 34(2): 63-70.
[6] 马小祥, 姚素平, 张柏林, 等. 渤海湾盆地东濮凹陷古近系古湖盆氧化还原条件及其优质烃源岩的发育模式[J]. 高校地质学报, 2019, 25(6):801-812
MA Xiaxiang, YAO Suping, ZHANG Bolin, et al. Redox conditions of Paleogene paleolake and development models of high-quality source rocks in the Dongpu sag, Bohai Bay Basin [J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 2019, 25(6): 801-812.
[7] 王书荣, 宋到福. 何登发. 三塘湖盆地火山灰对沉积有机质的富集效应及凝灰质烃源岩发育模式[J]. 石油学报, 2013, 34(6):1077-1087
WANG Shurong, SONG Daofu, HE Dengfa. The enrichment effect of organic materials by volcanic ash in sediments of the Santanghu Basin and the evolutionary pattern of tuffaceous source rocks [J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2013, 34(6): 1077-1087.
[8] 施和生, 舒誉, 杜家元, 等. 珠江口盆地古近系石油地质[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2017
SHI Hesheng, SHU Yu, DU Jiayuan, et al. Petroleum Geology of Paleogene in Pearl River Mouth Basin[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2017.
[9] 刘海伦. 珠江口盆地珠一坳陷裂陷结构: 基底属性与区域应力联合制约[D]. 中国地质大学博士学位论文, 2018
LIU Hailun. Rift style controlled by basement attribute and regional stress in ZhuⅠ depression, Pearl River Mouth basin[D]. Doctor Dissertation of China University of Geosciences, 2018.
[10] 吴克强, 刘志峰, 王升兰, 等. 珠一坳陷北部洼陷带始新统半深—深湖相烃源岩综合判识[J]. 中国海上油气, 2015, 27(3):10-15, 24
WU Keqiang, LIU Zhifeng, WANG Shenglan, et al. Composite recognition of eocene semi-deep and deep lacustrine facies source rocks in northern subsags belt of ZhuⅠ depression, Pearl River Mouth basin [J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2015, 27(3): 10-15, 24.
[11] 高阳东, 林鹤鸣, 汪旭东, 等. 幕式裂陷控洼背景下的烃源岩分布及岩浆改造——以珠一坳陷番禺4洼为例[J]. 2021, 41(4): 151-160.
GAO Yangdong, LIN Heming, WANG Xudong, et al. Source rock distribution pattern in an episodic rifting sag and later stage magmatiic reformation: A case from Panyu 4 sag, ZhuⅠDepression[J]. 2021, 41(4): 151-160.
[12] 朱明, 张向涛, 黄玉平, 等. 珠江口盆地烃源岩特征及资源潜力[J]. 石油学报, 2019, 40(S1):53-68
ZHU Ming, ZHANG Xiangtao, HUANG Yuping, et al. Source rock characteristics and resource potential in Pearl River Mouth Basin [J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2019, 40(S1): 53-68.
[13] 毛光周, 刘晓通, 安鹏瑞, 等. 无机地球化学指标在古盐度恢复中的应用及展望[J]. 山东科技大学学报:自然科学版, 2018, 37(1):92-102, 118
MAO Guangzhou, LIU Xiaotong, AN Pengrui, et al. Application and outlook of inorganic geochemical indexes in reconstruction of palaeosalinity [J]. Journal of Shandong University of Science and Technology:Natural Science, 2018, 37(1): 92-102, 118.
[14] 王益友, 郭文莹, 张国栋. 几种地球化学标志在金湖凹陷阜宁群沉积环境中的应用[J]. 同济大学学报:自然科学版, 1979(2):51-60
WANG Yiyou, GUO Wenyin, ZHANG Guodong. Application of some geochemical indications in determining of sedimentary environment of the Funing Group (Paleogene), Jin-Hu Depression, Kiangsu Province [J]. Journal of Tongji University:Natural Science, 1979(2): 51-60.
[15] 李进龙, 陈东敬. 古盐度定量研究方法综述[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2003, 10(5):1-3
LI Jinlong, CHEN Dongjing. Summary of quantified research method on paleosalinity [J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2003, 10(5): 1-3.
[16] 张金亮, 张鑫. 塔里木盆地志留系古海洋沉积环境的元素地球化学特征[J]. 中国海洋大学学报, 2006, 36(2):200-208
ZHANG Jinliang, ZHANG Xin. The element geochemical features of ancient oceanic sedimentary environments in the Silurian period in the Tarim Basin [J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 2006, 36(2): 200-208.
[17] Keith M L, Weber J N. Carbon and oxygen isotopic composition of selected limestones and fossils [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1964, 28(10-11): 1787-1816. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(64)90022-5
[18] 庞军刚, 杨友运, 郝磊. 湖盆古水深恢复研究现状综述[J]. 长江大学学报:自然科学版 理工, 2012, 9(9):42-45
PANG Jungang, YANG Youyun, HAO Lei. Review on the research status of ancient water depth restoration in the lake basin [J]. Journal of Yangtze University:Natural Science Edition, Science and Engineering, 2012, 9(9): 42-45.
[19] 逄淑伊, 操应长, 梁超. 渤海湾盆地东营凹陷沙四上亚段—沙三下亚段岩相特征及沉积环境——以樊页1井为例[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2019, 40(4):799-809
PANG Shuyi, CAO Yingchang, LIANG Chao. Lithofacies characteristics and sedimentary environment of Es4U and Es3L: A case study of Well FY1 in Dongying sag, Bohai Bay Basin [J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2019, 40(4): 799-809.
[20] 许中杰, 程日辉, 张莉, 等. 华南陆缘晚三叠-早、中侏罗世海平面相对升降与古气候演化的地球化学记录[J]. 地球科学:中国地质大学学报, 2012, 37(1):113-124
XU Zhongjie, CHENG Rihui, ZHANG Li, et al. The geochemistry records of sea-level relative movement and paleoclimatic evolution of the South China continental margin in Late Triassic-Early-Middle Jurassic [J]. Earth Science:Journal of China University of Geosciences, 2012, 37(1): 113-124.
[21] 李明龙, 陈林, 田景春, 等. 鄂西走马地区南华纪古城期-南沱早期古气候和古氧相演化: 来自细碎屑岩元素地球化学的证据[J]. 地质学报, 2019, 93(9):2158-2170 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2019.09.004
LI Minglong, CHEN Lin, TIAN Jingchun, et al. Paleoclimate and paleo-oxygen evolution during the Gucheng Period-early Nantuo Period of Nanhua system in the Zouma area, West Hubei: Evidence from elemental geochemistry of fine Clastic rocks [J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2019, 93(9): 2158-2170. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2019.09.004
[22] Jones G E. An ecological survey of open ocean and estuarine microbial populations. 1. The importance of trace metal ions to microorganisms in the sea[M]//Stevenson L H, Colwell R R. Estuarine Microbial Ecology. Columbia: University of South Carolina Press, 1973: 233-241.
[23] Emerson S R, Huested S S. Ocean anoxia and the concentrations of molybdenum and vanadium in seawater [J]. Marine Chemistry, 1991, 34(3-4): 177-196. doi: 10.1016/0304-4203(91)90002-E
[24] 梅水泉. 岩石化学在湖南前震旦系沉积环境及铀来源研究中的应用[J]. 湖南地质, 1988, 7(3):25-31, 49
MEI Shuiquan. Application of rock chemistry in the study of presinian sedimentary environment and the source of uranium mineralization in Hunan province [J]. Hunan Geology, 1988, 7(3): 25-31, 49.
[25] 田涛, 付德亮, 周世新, 等. 米仓山-汉南隆起区牛蹄塘组页岩古氧相及其与有机质富集的关系[J]. 兰州大学学报:自然科学版, 2020, 56(1):37-47,55
TIAN Tao, FU Deliang, ZHOU Shixin, et al. The paleo-redox conditions of the shale in Niutitang formation and its effects on organic matter enrichment of the Micangshan-Hannan Uplift [J]. Journal of Lanzhou University:Natural Sciences, 2020, 56(1): 37-47,55.
[26] 刘莹, 展翅飞. 探究影响Pr/Ph值的地质因素及其生烃演化[J]. 中国石油和化工标准与质量, 2014(5):203-203
LIU Ying, ZHAN Chifei. Explore the geological gactors affecting Pr/Ph and its hydrocarbon generation evolution [J]. China Petroleum and Chemical Standard and Quality, 2014(5): 203-203.
[27] Lerman A, Imboden D M, Gat J R. Physics and Chemistry of Lakes[M]. 2nd ed. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer, 1995.
[28] 石军, 邹艳荣, 余江, 等. 准噶尔盆地阜康凹陷芦草沟组高有机碳页岩发育的古环境[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2018, 29(8):1138-1150 doi: 10.11764/j.issn.1672-1926.2018.06.016
SHI Jun, ZOU Yanrong, YU Jiang, et al. Paleoenvironment of organic-rich shale from the Lucaogou Fromation in the Fukang Sag, Junggar Basin, China [J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2018, 29(8): 1138-1150. doi: 10.11764/j.issn.1672-1926.2018.06.016
[29] 戴贤铎, 杜远生, 马千里, 等. 秭归盆地峡口剖面中侏罗统千佛崖组古气候演化的地球化学记录[J]. 地质科技情报, 2018, 37(2):50-58
DAI Xianduo, DU Yuansheng, MA Qianli, et al. Palaeoclimate change of the Middle Jurassic Qianfoya formation revealed by geochemical records of Xiakou section in Zigui Basin [J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2018, 37(2): 50-58.
[30] 余素华, 文启忠, 张士三, 等. 中国西北地区晚第四纪黄土中镁铝地球化学与古气候意义[J]. 沉积学报, 1994, 3(12):112-116
YU Shuhua, WEN Qizhong, ZHANG Shisan, et al. The geochemistry and paleoclimate significance of magnesium and aluminium in loess of late Quaternary in Northwestern China [J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 1994, 3(12): 112-116.
[31] 吴国瑄. 珠江口盆地东部古近系沉积环境及烃源研究[R]. 同济大学内部科技报告, 2007.
WU Guoxuan. Study on Paleogene Sedimentary Environment and Hydrocarbon Sources in the Eastern Pearl River Basin[R]. Tongji University, Internal technology report, 2007.
[32] Talbot M R. A review of the palaeohydrological interpretation of carbon and oxygen isotopic ratios in primary lacustrine carbonates [J]. Chemical Geology:Isotope Geoscience Section, 1990, 80(4): 261-279. doi: 10.1016/0168-9622(90)90009-2
[33] 刘庆. 渤海湾盆地东营凹陷烃源岩碳氧同位素组成及地质意义[J]. 石油实验地质, 2017, 39(2):247-252 doi: 10.11781/sysydz201702247
LIU Qing. Composition and geologic significance of carbon and oxygen isotopes in hydrocarbon source rocks, Dongying Sag, Bohai Bay Basin [J]. Petroleum Geology and Experiment, 2017, 39(2): 247-252. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201702247
[34] 刘传联. 东营凹陷沙河街组湖相碳酸盐岩碳氧同位素组分及其古湖泊学意义[J]. 沉积学报, 1998, 16(3):109-114
LIU Chuanlian. Carbon and oxygen isotopic compositions of lacustrine carbonates of the Shahejie formation in the Dongying depression and their paleolimnological significance [J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 1998, 16(3): 109-114.
[35] 孙莎莎, 姚艳斌, 吝文. 鄂尔多斯盆地南缘铜川地区油页岩元素地球化学特征及古湖泊水体环境[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2015, 34(3):642-645
SUN Shasha, YAO Yanbin, LIN Wen. Elemental geochemical characteristics of the oil shale and the paleo-lake environment of the Tongchuan Area, Southern Ordos Basin [J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 2015, 34(3): 642-645.
[36] 金强, 朱光有, 王娟. 咸化湖盆优质烃源岩的形成与分布[J]. 中国石油大学学报:自然科学版, 2008, 32(4):19-23
JIN Qiang, ZHU Guangyou, WANG Juan. Deposition and distribution of high-potential source rocks in saline lacustrine environments [J]. Journal of China University of Petroleum, 2008, 32(4): 19-23.
[37] Katz B J. Factors controlling the development of lacustrine petroleum source rocks-An update [J]. AAPG Studies in Geology, 1995, 40: 61-79.
[38] 秦建中. 中国烃源岩[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2005.
QIN Jianzhong. Source Rocks in China[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2005.
[39] 王建, 王权, 钟雪梅, 等. 二连盆地优质烃源岩发育特征及成藏贡献[J]. 石油实验地质, 2015, 37(5):641-647 doi: 10.11781/sysydz201505641
WANG Jian, WANG Quan, ZHONG Xuemei, et al. Characteristics of high-quality hydrocarbon source rocks and their contributions to reservoirs in the Erlian Basin [J]. Petroleum Geology and Experiment, 2015, 37(5): 641-647. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201505641
-



 下载:
下载: