Study on sequence stratigraphy and sedimentary systems of the Wenchang Formation in the southern Xijiang depression of the Pearl River Mouth Basin
-
摘要:
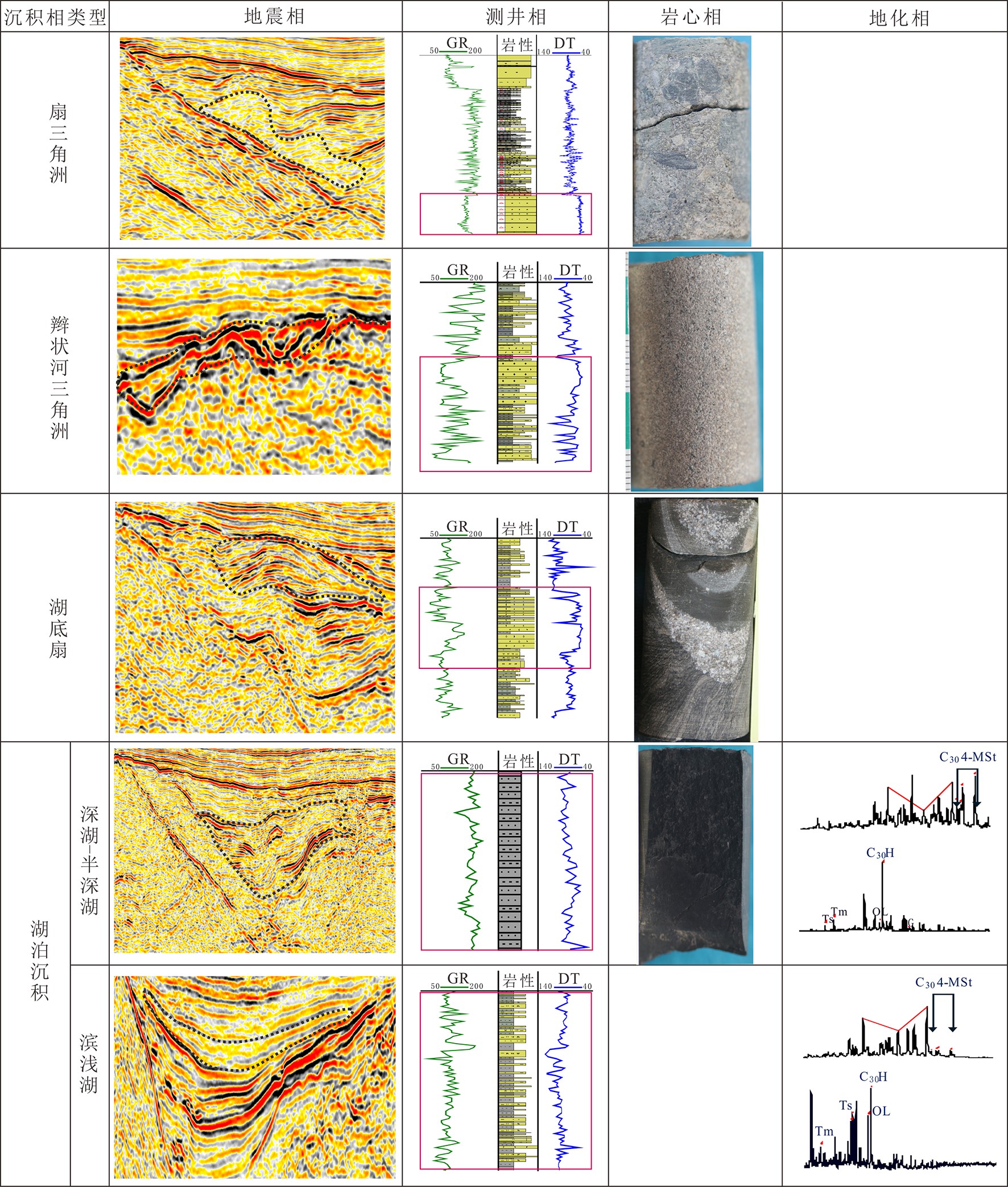
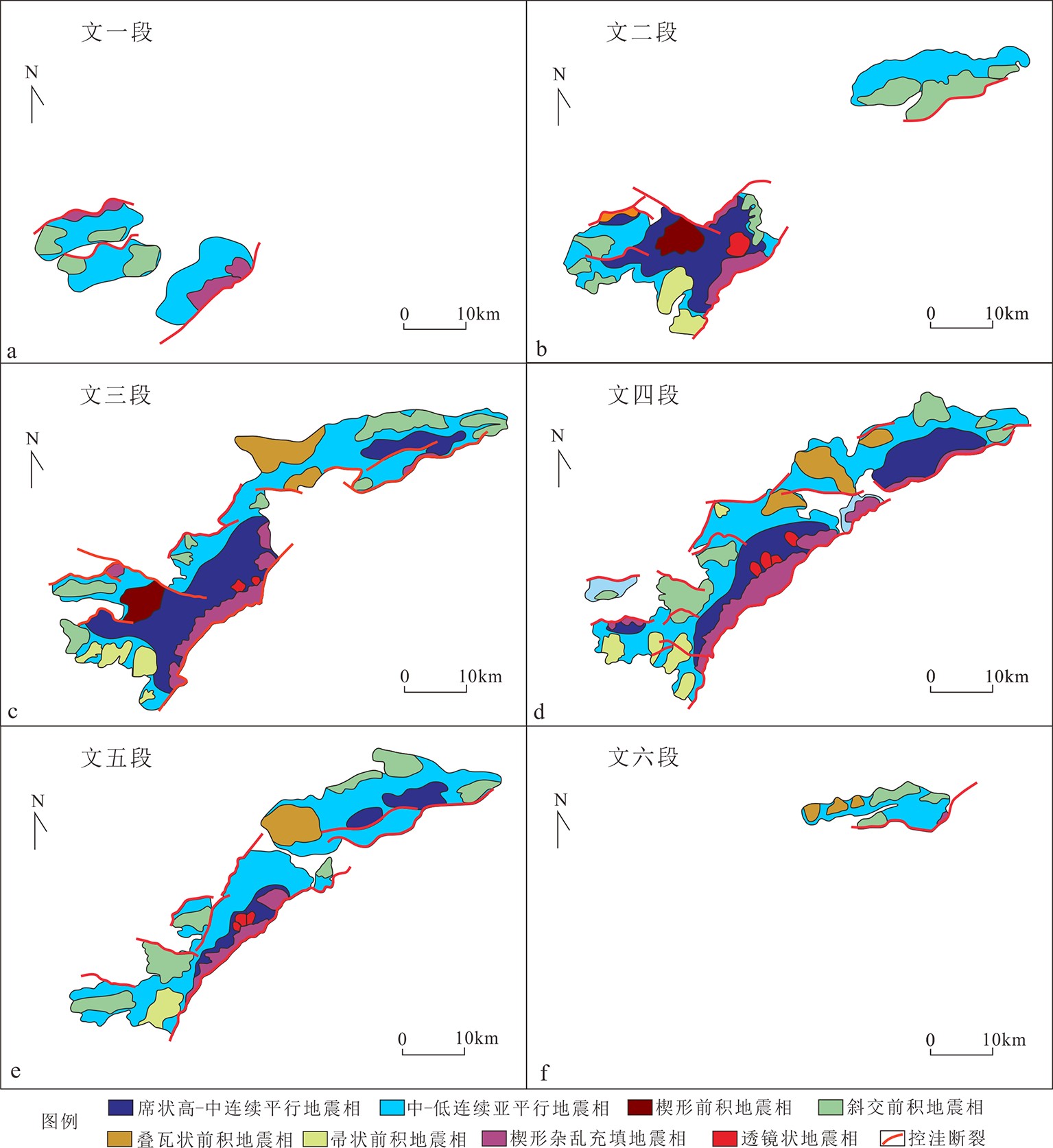
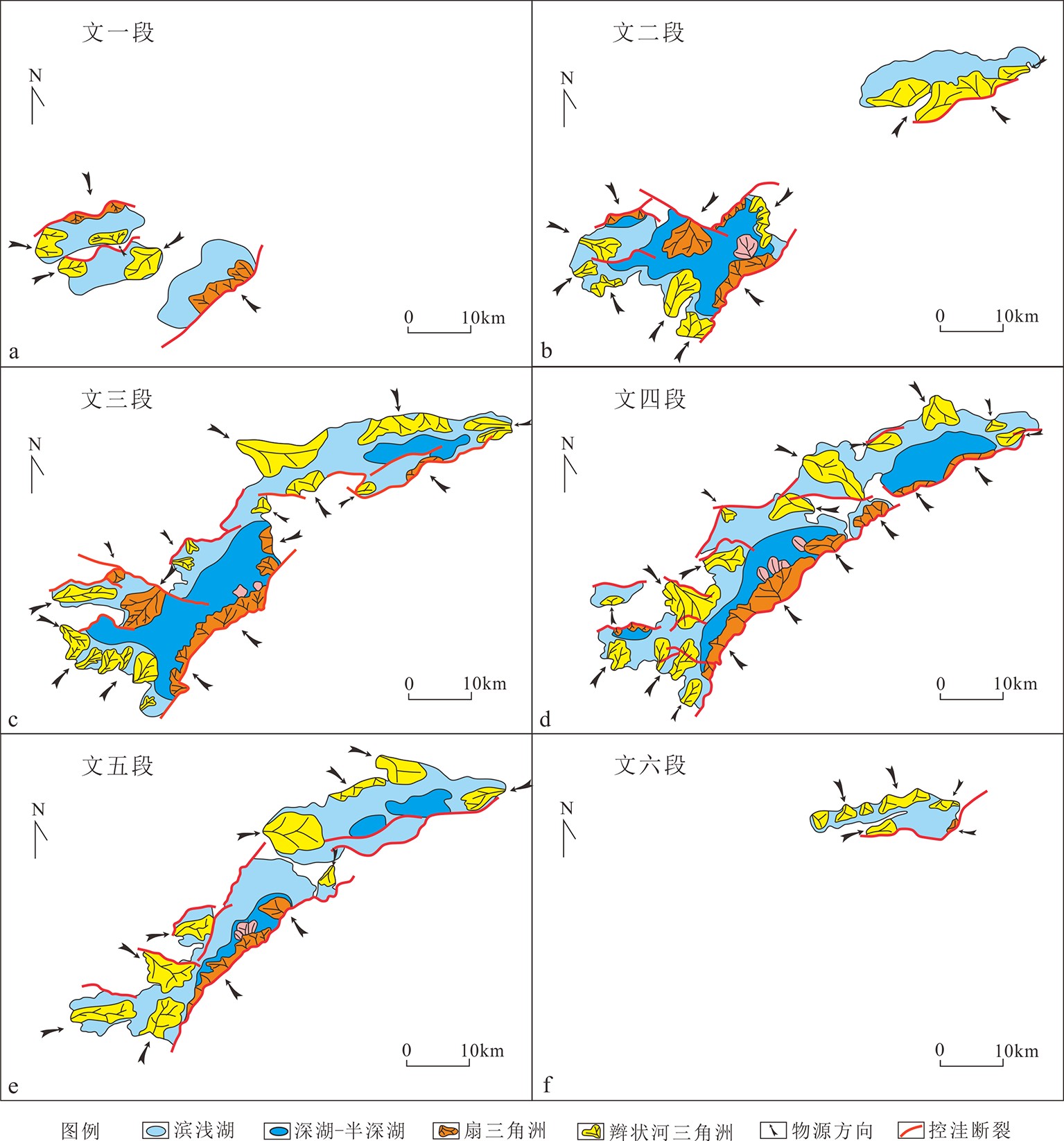
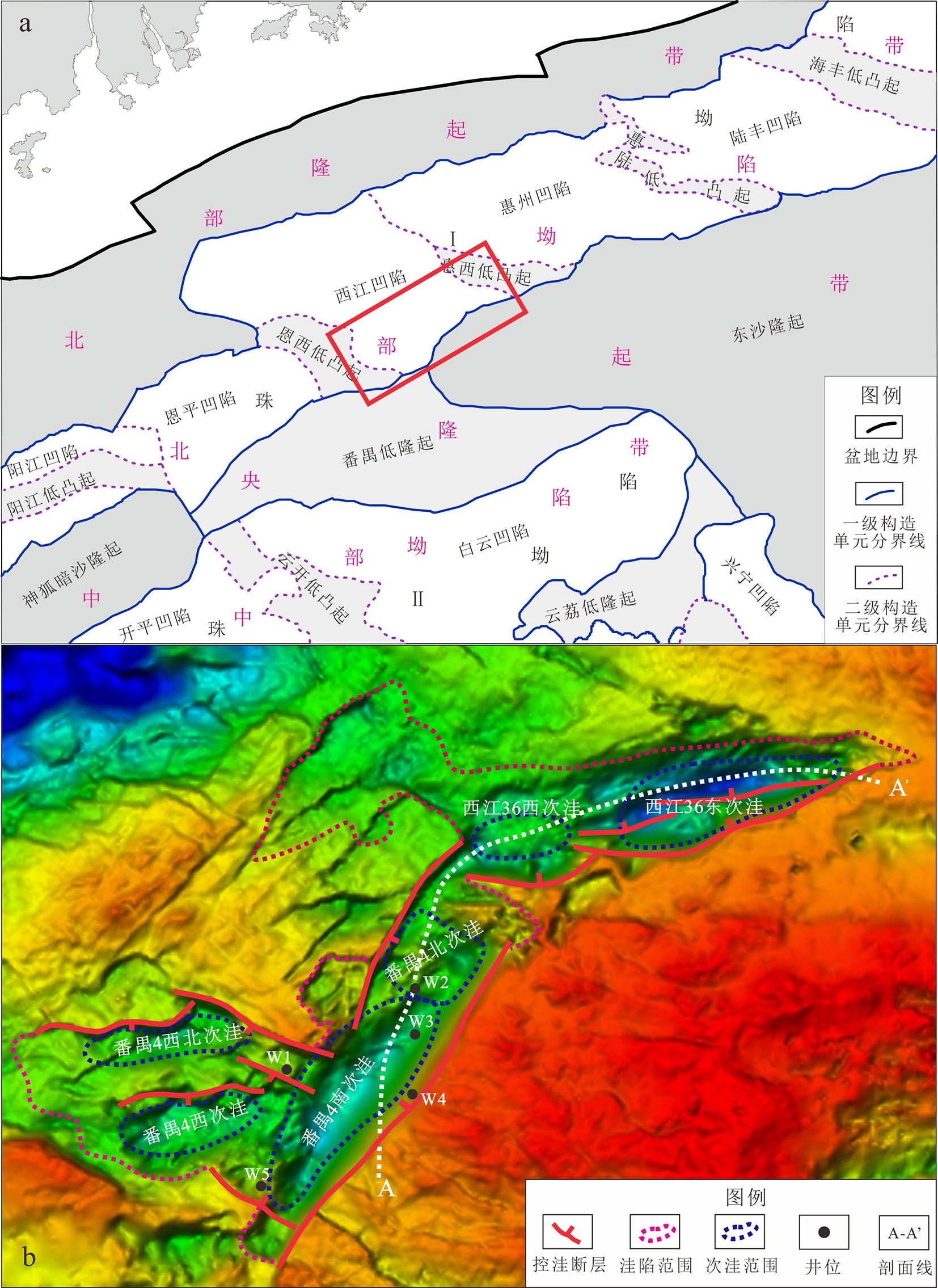
珠江口盆地西江凹陷南部包括两个相邻洼陷:西江36洼和番禺4洼,钻探结果却揭示了截然不同的油气勘探前景,其中,番禺4洼探明储量已过亿吨,而西江36洼却未有商业发现,导致勘探上对西江36洼烃源潜力有所顾虑。为了揭示这种差异油气地质条件产生的原因,亟待开展两个洼陷的对比研究。以主要烃源层系文昌组为切入点,通过开展精细的层序-沉积研究,进一步系统评估西江36洼烃源潜力。依据地震、钻井及分析化验等资料,在西江36洼与番禺4洼文昌组共识别了6个三级层序。西江36洼和番禺4洼文昌组发育扇三角洲、辫状河三角洲、湖底扇及湖泊沉积等沉积相类型,垂向上沉积相带具有旋回特征。伴随裂陷不同阶段和边界断层活动差异,陡坡带和缓坡带三角洲沉积体系规模呈现差异演化特征,而湖盆和半深湖-深湖相规模总体呈现出先增大后减小的规律。沉积相带在横向上也具有明显的迁移特征,表现为文六段时期先在西江36洼开始沉积,文五段开始再扩展到番禺4洼,同时文一段时期西江36洼湖盆已经消失,只在番禺4洼沉积充填。进一步对比两个洼陷各三级层序反映优质烃源岩条件的半深湖-深湖规模及物源供给量,结果显示在文六段至文四段时期两个洼陷烃源条件基本一致。鉴于该层段作为番禺4洼的主力源岩,其巨大的生烃潜力已经被勘探所证实,因此认为不能低估具有相似烃源条件的西江36洼生烃潜力。
Abstract:The Xijiang depression in the Pearl River Mouth Basin consists of two adjacent sags, the Panyu 4 sag and the Xijiang 36 sag, in which quite different oil and gas exploration prospects have been revealed by drilling. The proved reserves of Panyu 4 sag have exceeded 100 million tons, while no commercial discoveries been found in the Xijiang 36 sag so far. In order to reveal the causes of such a difference in oil and gas geological conditions, it is necessary to carry out a comparative studies of the two sags. In this paper, the Wenchang Formation, the main source series, is selected as the key point for breakthrough, and the hydrocarbon source potential of Xijiang 36 sag is systematically evaluated through detailed sequence stratigraphic studies. Based on the data of seismic, drilling and laboratory analysis, six third-order sequences have been identified in the Wenchang Formation in both of the Xijiang 36 and Panyu 4 sags. There are fan delta, braided river delta, sublacustrine fan and lacustrine sedimentary facies in the Wenchang Formation of Xijiang 36 and Panyu 4 sags, and the sedimentary facies belts also show a cyclic patterns vertically. In the different stages of rifting and/or boundary fault activities, the scale of delta depositional system in steep slope zone and gentle slope zone shows different evolutionary features, whereas the scales of Lake Basin and its deep part in the middle lake expanded in the beginning and shrank later on. The sedimentary facies belt also has obvious migration in lateral direction. In the Wen-6 Period, the deposition was initiated in the Xijiang 36 sag, and then extended to Panyu 4 sag with time. In the period of Wen-1, the lake basin occurred only in the Panyu 4 sag and disappeared in the Xijiang 36 sag. The distribution pattern of semi deep and deep lake deposits and study of sediment sources suggest that the high-quality hydrocarbon source potential values of each third-order sequence in the two sags are comparable and the source rock conditions are basically the same in the two sags in the wen-6 and wen-4 periods. As the main source rock of the Panyu 4 sag has been confirmed by exploration, therefore, it is considered that the exploration potential of Xijiang 36 sag with similar hydrocarbon source conditions should not be underestimated too early.
-

-
图 1 珠江口盆地[6](a)和西江凹陷南部(b)构造单元划分
Figure 1.
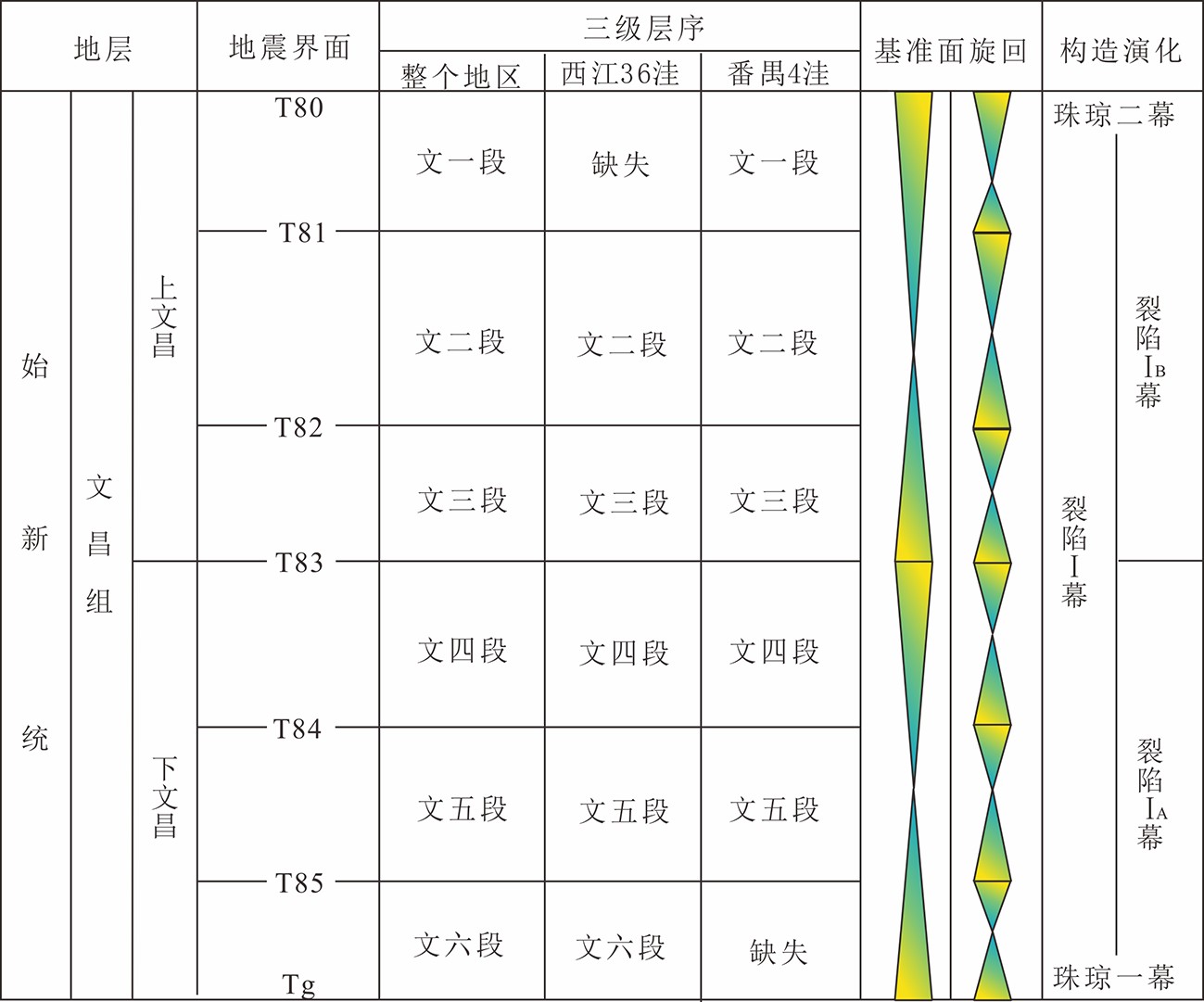
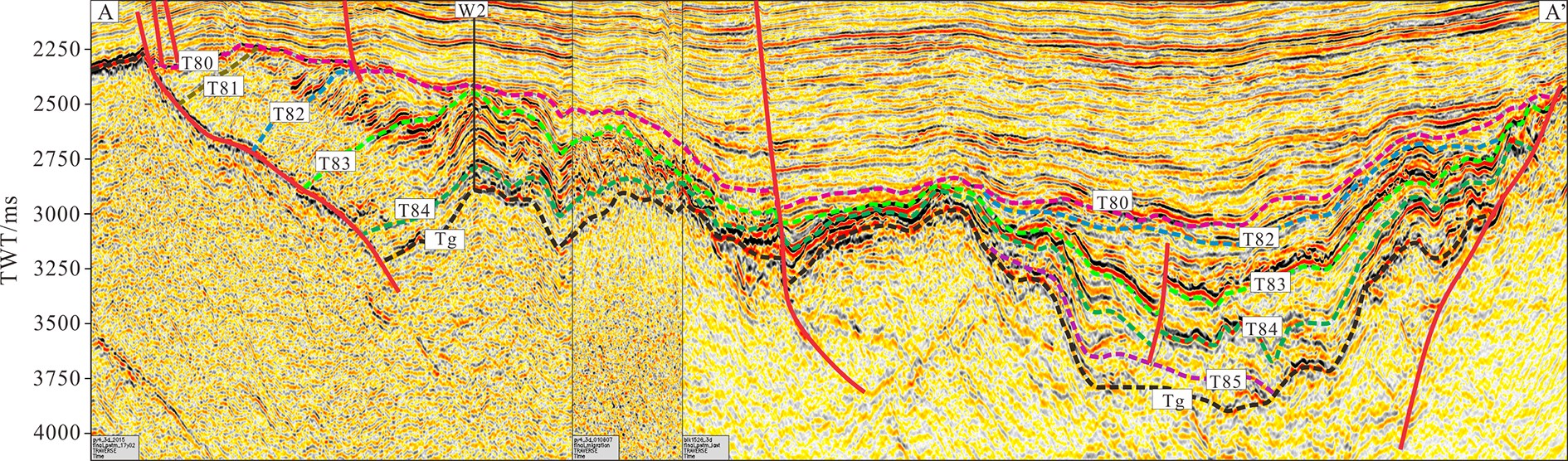
图 2 西江36洼与番禺4洼文昌组层序地层格架[11]
Figure 2.
表 1 西江36洼与番禺4洼烃源岩条件对比
Table 1. Comparison of source rock conditions between Xijiang 36 sag and Panyu 4 sag
西江36洼 番禺4洼 层序 中深湖规模 物源供给量 生烃
潜力值中深湖规模 物源供给量 生烃
潜力值面积
/km2平均
厚度/m面积
/km2平均
厚度/m面积
/km2平均
厚度/m面积
/km2平均
厚度/m上文昌 文一段 0 0 − − 0 0 0 − − 0 文二段 0 0 − − 0 180 400 150 250 1.92 文三段 42 450 60 125 2.52 300 600 147 200 6.12 下文昌 文四段 83 650 80 110 6.13 132 600 110 100 7.2 文五段 45 500 70 120 2.68 50 350 80 120 1.82 文六段 0 0 − − 0 0 0 − − 0 注:生烃潜力值=(中深湖面积×中深湖平均厚度)/(物源面积×物源平均厚度)。 -
[1] 朱筱敏, 黄捍东, 代一丁, 等. 珠江口盆地番禺4洼文昌组层序格架与沉积体系研究[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2014, 26(4):1-8 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8926.2014.04.001
ZHU Xiaomin, HUANG Handong, DAI Yiding, et al. Study on depositional system and sequence framework of Wenchang Formation in Panyu 4 sag of the Pearl River Mouth Basin [J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2014, 26(4): 1-8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8926.2014.04.001
[2] 张向涛, 朱俊章, 熊万林, 等. 番禺4洼文昌组烃源岩生物标志化合物特征与油源判识[J]. 中国海上油气, 2020, 32(4):12-23
ZHANG Xiangtao, ZHU Junzhang, XIONG Wanlin, et al. Biomarker characteristics and oil-source discrimination of source rocks in Wenchang Formation of Panyu 4 sag [J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2020, 32(4): 12-23.
[3] 代一丁. 珠江口盆地西江南洼古近系构造演化与沉积特征[J]. 中国海上油气, 2013, 25(3):1-7
DAI Yiding. Paleogene tectonic evolution and sedimentation in South Xijiang Sag, Pearl River Mouth Basin [J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2013, 25(3): 1-7.
[4] 江宁, 全志臻, 张向涛, 等. 珠江口盆地番禺4洼古近系层序地层及储层分布预测[J]. 天然气勘探与开发, 2015, 38(4):23-27 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-3177.2015.04.006
JIANG Ning, QUAN Zhizhen, ZHANG Xiangtao, et al. Paleogene sequence stratigraphy and reservoir distribution, Panyu 4 Sag, Pearl River Mouth Basin [J]. Natural Gas Exploration and Development, 2015, 38(4): 23-27. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-3177.2015.04.006
[5] 吴宇翔, 舒誉, 丁琳, 等. 珠江口盆地番禺4洼文昌组基于层序地层格架约束下的优质烃源岩预测[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2021, 37(3):41-49
WU Yuxiang, SHU Yu, DING Lin, et al. Prediction of high quality source rocks based on sequence stratigraphic framework of Wenchang Formation, Panyu 4 sag, the Pearl River Mouth Basin [J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2021, 37(3): 41-49.
[6] 张丽丽, 舒誉, 蔡国富, 等. 珠江口盆地东部始新世渐新世沉积环境演变及对烃源条件的影响[J]. 石油学报, 2019, 40(S1):153-165 doi: 10.7623/syxb2019S1013
ZHANG Lili, SHU Yu, CAI Guofu, et al. Eocene-Oligocene sedimentary environment evolution and its impact on hydrocarbon source conditions in eastern Pearl River Mouth basin [J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2019, 40(S1): 153-165. doi: 10.7623/syxb2019S1013
[7] 施和生, 何敏, 张丽丽, 等. 珠江口盆地(东部)油气地质特征、成藏规律及下一步勘探策略[J]. 中国海上油气, 2014, 26(3):11-22
SHI Hesheng, HE Min, ZHANG Lili, et al. Hydrocarbon Geology, accumulation pattern and the next exploration Stratagy in there eastern Pearl River Mouth basin [J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2014, 26(3): 11-22.
[8] 舒誉, 施和生, 杜家元, 等. 珠一坳陷古近系油气成藏特征及勘探方向[J]. 中国海上油气, 2014, 26(3):37-42
SHU Yu, SHI Hesheng, DU Jiayuan, et al. Paleogene characteristics in hydrocarbon accumulation and exploration direction in Zhu I depression [J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2014, 26(3): 37-42.
[9] 施和生, 舒誉, 杜家元, 等. 珠江口盆地古近系石油地质[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2017: 1-4
SHI Hesheng, SHU Yu, DU Jiayuan, et al. Petroleum Geology of the Paleogene in the Pearl River Mouth Basin[M]. Beijing: China Geology Press, 2017: 1-4.
[10] 陈长民. 珠江口盆地东部石油地质及油气藏形成条件初探[J]. 中国海上油气(地质), 2000, 14(2):73-83
CHEN Changmin. Petroleum geology and conditions for hydrocarbon accumulation in the eastern Pearl River mouth basin [J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas (Geology), 2000, 14(2): 73-83.
[11] 米立军, 张向涛, 陈维涛, 等. 珠江口盆地珠一坳陷古近系油气富集规律及下一步勘探策略[J]. 中国海上油气, 2018, 30(6):1-13
MI Lijun, ZHANG Xiangtao, CHEN Weitao, et al. Hydrocarbon enrichment law of Paleogene Zhu 1 depression and its next exploration strategy in Pearl River Mouth basin [J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2018, 30(6): 1-13.
[12] 施和生, 杜家元, 梅廉夫, 等. 珠江口盆地惠州运动及其意义[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2020, 47(3):447-461
SHI Hesheng, DU Jiayuan, MEI Lianfu, et al. Huizhou Movement and its significance in Pearl River Mouth Basin, China [J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2020, 47(3): 447-461.
[13] Vail P R, Mitchum P M. Seismic stratigraphic and global changes in sea leavel. Parts Ⅰ-Ⅱ [J]. AAPG Memoir, 1977, 26: 51-212.
[14] Mitchum P M, Sangree J B, Vail P R, et al. Recognizing sequences and systems tracts from well logs, seismic data, and biostratigraphy: Examples from the late Cenozoic of the Gulf of Mexico[M]//Weimer P, Posamentier H. Siliciclastic Sequence Stratigraphy: Recent Developments and Applications. California: American Association of Petroleum Geologists, 1993: 163-199.
[15] Mitchum R M, Van Wagoner J C. High-frequency sequences and their stacking patterns: sequence-stratigraphic evidence of high-frequency eustatic cycles [J]. Sedimentary Geology, 1991, 70(2-4): 131-160. doi: 10.1016/0037-0738(91)90139-5
[16] 王英民. 对层序地层学工业化应用中层序分级混乱问题的探讨[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2007, 19(1):9-15 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8926.2007.01.002
WANG Yingmin. Analysis of the mess in sequence hierarchy applied in the industrialized application of the sequence stratigraphy [J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2007, 19(1): 9-15. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8926.2007.01.002
[17] 卓海腾, 王英民, 徐强, 等. 南海北部陆坡分类及成因分析[J]. 地质学报, 2014, 88(3):327-336
ZHUO Haiteng, WANG Yingmin, XU Qiang, et al. Classification and genesis of continental slopes on the northern South CHINA Sea [J]. Actav Geologica Sinica, 2014, 88(3): 327-336.
[18] 于兴河, 姜辉, 李胜利, 等. 中国东部中、新生代陆相断陷盆地沉积充填模式及其控制因素: 以济阳坳陷东营凹陷为例[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2007, 19(1):39-45 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8926.2007.01.007
YU Xinghe, JIANG Hui, LI Shengli, et al. Depositional filling models and controlling factors on Mesozoic and Cenozoic fault basins of terrestrial facies in eastern China: A case study of Dongying Sag of Jiyang Depression [J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2007, 19(1): 39-45. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8926.2007.01.007
[19] 冯有良. 大民屯凹陷沙四段—沙三段层序地层格架及岩性油气藏预测[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2008, 20(4):14-19 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8926.2008.04.003
FENG Youliang. Sequence stratigraphy framework and lithologic reservoirs prediction of the third and fourth members of Shahejie Formation, Damintun Depression [J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2008, 20(4): 14-19. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8926.2008.04.003
[20] 吴嘉鹏, 王英民, 马贵明, 等. 孟加拉扇某区块地层层序划分及典型地震相识别[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2010, 22(2):69-73 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8926.2010.02.012
WU Jiapeng, WANG Yingmin, MA Guiming, et al. Sequence stratigraphy and typical seismic facies in one exploration block of Bengal Fan [J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2010, 22(2): 69-73. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8926.2010.02.012
[21] 张功成, 梁建设, 徐建永, 等. 中国近海潜在富烃凹陷评价方法与烃源岩识别[J]. 中国海上油气, 2013, 25(1):13-19
ZHANG Gongcheng, LIANG Jianshe, XU Jianyong, et al. An evaluation method of potential hydrocarbon-rich sags and their source rock identification offshore China [J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2013, 25(1): 13-19.
[22] 郭来源. 陆相断陷湖盆富有机质页岩非均质性及其控制因素分析: 以泌阳和沾化凹陷为例[D]. 中国地质大学博士学位论文, 2017
GUO Laiyuan. Heterogeneity and controlling factors of organic-rich shale in continental rift basin: a case study of Biyang and Zhanhua depressions[D]. Doctor Dissertation of China University of Geosciences, 2017.
-



 下载:
下载: