Surface sediment resuspension and suspended sediment transportation mechanism in the waters around Miaodao Strait
-
摘要:
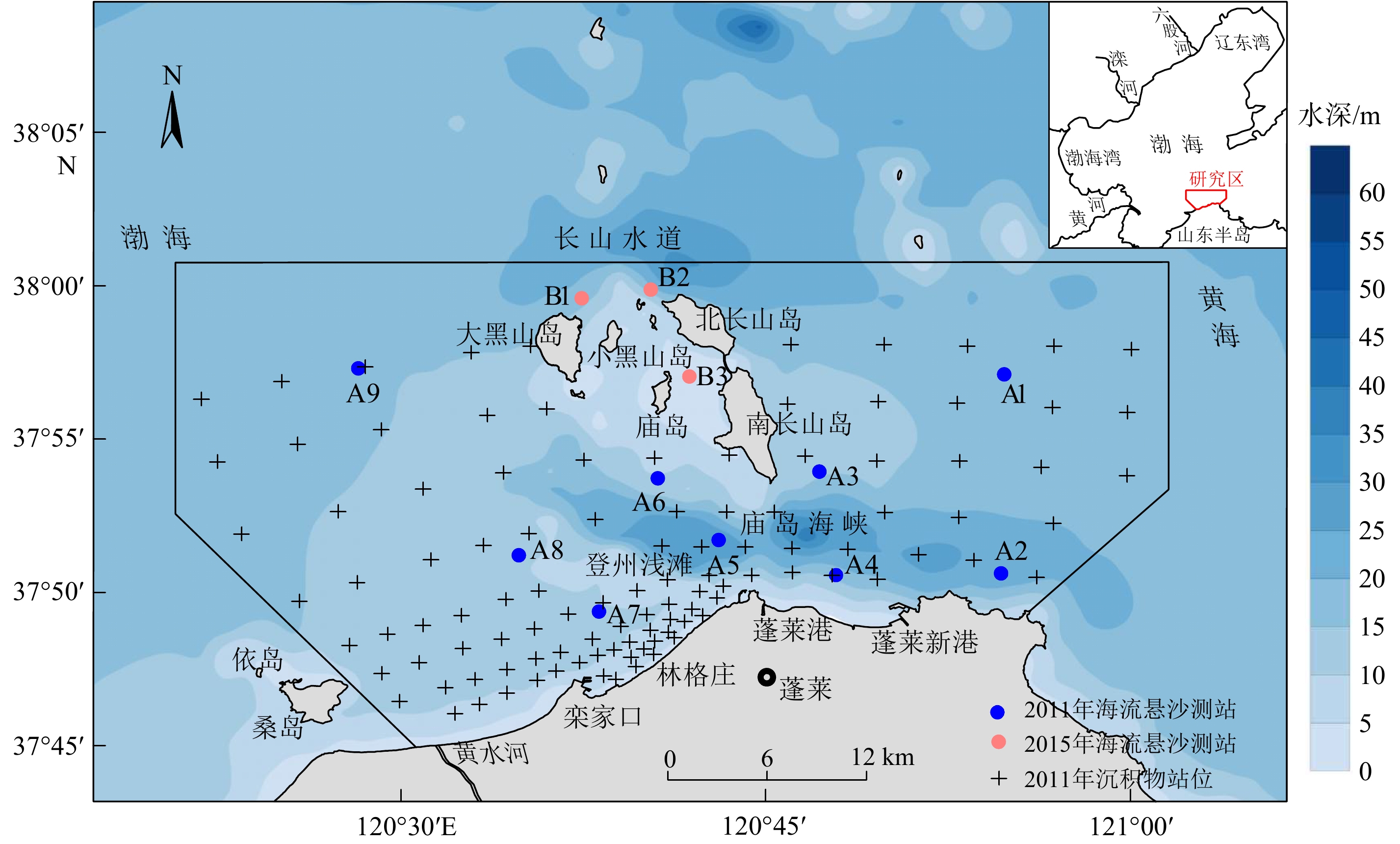
根据实测水文泥沙资料,利用悬浮泥沙沉降公式、泥沙起动流速公式、再悬浮通量与沉降通量公式以及通量机制分解方法,分析了庙岛海峡周边海域的悬浮泥沙时空分布和变化特征,计算了再悬浮通量、沉降通量、单宽悬浮泥沙输运量,探讨了表层沉积物再悬浮和悬浮泥沙运移特征及动力机制。结果表明,悬浮泥沙浓度周期变化与潮流流速周期变化具有较好的相关性,底层悬沙浓度变化对高流速的响应比较明显,表层悬沙浓度变化对低流速响应比较明显;悬浮泥沙单颗粒沉降现象不明显,除庙岛海峡外其他海域较适合悬浮泥沙絮凝沉降,并以中、底层絮凝沉降为主,且表现出自表层至底层絮凝沉降作用逐渐加强趋势;表层沉积物再悬浮对近岸浅水区、庙岛群岛周边海域水体悬浮泥沙浓度的影响显著于其他海域;悬浮泥沙输运整体以平流输运为主,垂向净环流为辅,庙岛海峡南侧向黄海输沙、北侧向渤海输沙,二者同时进行,悬浮泥沙净输运主要由水道向两侧浅滩。
Abstract:Based on the hydrological and sediment measurement data, characteristics of spatiotemporal distributions and variations of suspended sediment concentration and particle size around Miaodao Strait in Bohai Sea were analyzed. By using formulas of suspended sediment settlement, sediment incipient velocity, resuspension flux, and settlement flux, and the flux mechanism decomposition method, the resuspension flux, sedimentation flux, and suspended sediment transport capacity in the study area were calculated. The characteristics and dynamic mechanism of surface sediment resuspension and suspended sediment transport were analyzed. Results reveal a strong relationship between the periodic changes in the suspended sediment concentration and the tidal current velocity. The bottom layer responds obviously to high velocity while the surface layer responds obviously to low velocity. The phenomenon of single particle sedimentation of suspended sediment is not obvious. The hydrodynamic conditions in the sea areas are suitable for flocculation and sedimentation of suspended sediments except for the Miaodao Strait, and are mainly dominated by middle and bottom flocculation and sedimentation. The effect of surface sediment resuspension on the concentration of suspended sediment in the nearshore shallow water area and the sea area around the Miaodao Strait is significantly higher than that in other sea areas. The transport of suspended sediment is mainly advection transport and supplemented by vertical net circulation. In the southern side of Miaodao Strait, sediments are transported to the Yellow Sea, while those on the northern side to the Bohai Sea. The net transport of suspended sediment is mainly from the waterway to the shoals on both sides.
-
Key words:
- suspended sediment /
- settlement and resuspension /
- dynamic mechanism /
- Miaodao Strait
-

-
图 2 各站位垂向平均潮流矢量[22]
Figure 2.
图 4 研究区余流场数值模拟结果[21]
Figure 4.
图 7 悬浮泥沙涨落潮段(左图)与表中底各层(右图)平均浓度分布[22]
Figure 7.
表 1 A1—A9各站悬浮泥沙沉降速度
Table 1. The settling velocity of suspended sediment at stations A1-A9
站位 A1 A2 A3 A4 A5 A6 A7 A8 A9 D50/µm 11 10.7 10.9 10.8 11.1 10.4 11.5 11.4 11.6 沉降速度/(mm/s) 0.0275 0.0260 0.0270 0.0265 0.0280 0.0246 0.0300 0.0295 0.0306 表 2 各站位表层沉积物起动流速
Table 2. The critical motion velocity of surface sediment at each station
站位 A1 A2 A3 A4 A5 A6 A7 A8 A9 B1 B2 B3 水深/m 19.2 30.0 14.9 19.1 29.7 10.2 12.0 11.8 17.0 13.6 14.6 5.0 中值粒径/µm 30.8 21.4 41.6 5000.0 1824.8 415.9 124.1 29.1 42.9 35.3 35.8 26.1 起动流速/(cm/s) 46.0 72.0 34.0 119.0 70.0 28.0 22.0 39.0 35.0 37.0 37.0 32.0 表 3 A1—A9各站位再悬浮通量与沉降通量
Table 3. Resuspension and sedimentation fluxes of stations A1-A9
站位 再悬浮通量/(kg·m−2·s−1) 沉降通量/(kg·m−2·s−1) 悬浮时间/h 沉降时间/h 再悬浮量/(kg/m2) 沉降量/(kg/m2) A1 2.91×10−6~1.45×10−3 5.04×10−8~5.41×10−7 16 8 21.40 7.68×10−3 A2 8.57×10−6~3.24×10−3 1.50×10−7~1.03×10−6 19 5 43.47 6.89×10−3 A3 5.33×10−7~1.44×10−3 3.32×10−8~3.63×10−7 15 9 15.36 5.13×10−3 A5 7.40×10−6~3.78×10−4 1.54×10−8~1.27×10−7 5 19 2.30 4.06×10−3 A6 2.37×10−5~3.40×10−4 4.56×10−8~3.61×10−7 10 14 4.61 7.92×10−3 A7 9.50×10−6~6.37×10−4 3.74×10−8~6.39×10−7 15 9 16.53 7.68×10−3 A8 1.04×10−5~2.05×10−3 1.12×10−8~6.54×10−7 16 8 29.28 6.75×10−3 A9 1.03×10−5~1.72×10−3 7.31×10−10~7.07×10−7 13 11 19.47 6.36×10−3 表 4 A1—A9各站悬沙输运项及单宽悬沙净输运率(大潮)
Table 4. Items of suspended sediment transport and the net transport rate of single-width suspended sediment at stations A1-A9 (spring tide)
站位 输沙项 T1 T2 T5 T1+T2 T3+T4 T6+T7+T8 T A1 输沙率/(g·m−1·s−1) 3.89 0.45 2.81 3.62 0.03 0.05 4.29 方向/(°) 154 285 256 160 273 16 200 A2 输沙率/(g·m−1·s−1) 18.68 0.91 9.42 17.93 0.27 0.12 18.00 方向/(°) 142 289 249 144 105 13 173 A3 输沙率/(g·m−1·s−1) 35.94 1.77 3.81 37.50 0.53 0.18 35.16 方向/(°) 265 236 128 264 288 56 260 A4 输沙率/(g·m−1·s−1) 89.97 2.21 4.43 89.38 1.37 0.32 86.12 方向/(°) 62 316 279 61 128 266 60 A5 输沙率/(g·m−1·s−1) 21.33 1.72 12.27 22.83 0.32 0.05 35.38 方向/(°) 261 291 257 263 271 175 261 A6 输沙率/(g·m−1·s−1) 15.74 1.17 1.03 14.77 0.22 0.09 13.67 方向/(°) 87 301 260 85 317 130 85 A7 输沙率/(g·m−1·s−1) 14.71 0.74 2.70 14.01 0.17 0.13 11.44 方向/(°) 67 265 265 66 258 87 62 A8 输沙率/(g·m−1·s−1) 26.04 1.34 2.93 24.77 0.16 0.08 22.73 方向/(°) 42 240 261 41 328 51 36 A9 输沙率/(g·m−1·s−1) 3.21 0.26 2.75 3.19 0.07 0.07 0.43 方向/(°) 164 262 344 169 57 76 186 表 6 B1—B3各站悬沙输运项及单宽悬沙净输运率(大潮)
Table 6. Items of suspended sediment transport and the net transport rate of single-width suspended sediment at stations B1-B3 (spring tide)
站位 输沙项 T1 T2 T3 T4 T5 T6+T7+T8 T1+T2 T B1 输沙率/(g·m−1·s−1) 1.15 0.34 0.00 0.02 0.02 0.01 1.12 1.13 方向/(°) 156 260 336 69 192 92 174 172 B2 输沙率/(g·m−1·s−1) 4.68 0.10 0.01 0.04 0.01 0.00 4.74 4.75 方向/(°) 201 256 21 240 326 99 202 203 B3 输沙率/(g·m−1·s−1) 0.23 0.04 0.00 0.01 0.02 0.01 0.21 0.20 方向/(°) 187 312 187 251 45 325 195 195 表 5 A1—A9各站悬沙输运项及单宽悬沙净输运率(小潮)
Table 5. Items of suspended sediment transport and the net transport rate of single-width suspended sediment at stations A1-A9 (neap tide)
站位 输沙项 T1 T2 T5 T1+T2 T3+T4 T6+T7+T8 T A1 输沙率/(g·m−1·s−1) 7.96 0.48 4.55 7.49 0.03 0.09 3.27 方向/(°) 90 259 259 91 98 47 107 A2 输沙率/(g·m−1·s−1) 10.82 0.09 4.36 10.87 0.11 0.24 7.83 方向/(°) 118 172 260 119 119 296 139 A3 输沙率/(g·m−1·s−1) 18.61 1.30 1.89 19.86 0.11 0.12 19.81 方向/(°) 249 234 161 248 57 80 243 A4 输沙率/(g·m−1·s−1) 30.53 0.25 2.92 30.53 0.24 0.01 28.26 方向/(°) 61 332 273 60 107 327 57 A5 输沙率/(g·m−1·s−1) 16.26 0.98 3.90 17.23 0.02 0.01 19.64 方向/(°) 273 281 216 273 312 279 263 A6 输沙率/(g·m−1·s−1) 10.06 0.54 1.19 9.61 0.05 0.04 8.55 方向/(°) 72 286 275 70 295 81 67 A7 输沙率/(g·m−1·s−1) 4.44 0.57 0.71 3.89 0.00 0.06 3.33 方向/(°) 67 263 273 65 276 71 60 A8 输沙率/(g·m−1·s−1) 12.87 0.48 0.93 12.64 0.12 0.02 12.04 方向/(°) 142 261 278 144 76 13 146 A9 输沙率/(g·m−1·s−1) 3.31 0.28 1.26 3.07 0.03 0.02 2.14 方向/(°) 95 244 242 98 279 357 117 -
[1] 江文胜, 苏健, 杨华, 等. 渤海悬浮物浓度分布和水动力特征的关系[J]. 海洋学报, 2002, 24(S1):212-217
JIANG Wensheng, SU Jian, YANG Hua, et al. The relationship between SPM concentration and hydrodynamic condition in the Bohai sea [J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2002, 24(S1): 212-217.
[2] 陈斌, 刘健, 高飞. 莱州湾悬沙输运机制研究[J]. 水科学进展, 2015, 26(6):857-866
CHEN Bin, LIU Jian, GAO Fei. Suspended sediment transport mechanism in Laizhou Bay [J]. Advances in Water Science, 2015, 26(6): 857-866.
[3] 江文胜, 王厚杰. 莱州湾悬浮泥沙分布形态及其与底质分布的关系[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2005, 36(2):97-103 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.2005.02.001
JIANG Wensheng, WANG Houjie. Distribution of suspended matter and its relationship with sediment particle size in Laizhou bay [J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2005, 36(2): 97-103. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.2005.02.001
[4] 王庆, 仲少云, 刘建华, 等. 山东庙岛海峡的峡道动力地貌[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2006, 26(2):17-24
WANG Qing, ZHONG Shaoyun, LIU Jianhua, et al. The channel dynamic geomorphology of Miaodao strait, Shandong, China [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2006, 26(2): 17-24.
[5] 刘成, 胡日军, 朱龙海, 等. 庙岛群岛海域沉积动力环境分区及沉积物输运趋势[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2018, 34(8):24-33
LIU Cheng, HU Rijun, ZHU Longhai, et al. Dynamic environment division and sediment transport trend in the area off Miaodao islands [J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2018, 34(8): 24-33.
[6] 李爱超, 乔璐璐, 万修全, 等. 渤海海峡悬浮体分布、通量及其季节变化[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2016, 47(2):310-318
LI Aichao, QIAO Lulu, WAN Xiuquan, et al. Distribution, flux and seasonal variation of suspended particulate matters in the Bohai strait [J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2016, 47(2): 310-318.
[7] 肖合辉, 王厚杰, 毕乃双, 等. 渤黄海海域悬浮体季节性分布及主要运移路径[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2015, 35(2):11-21
XIAO Hehui, WANG Houjie, BI Naishuang, et al. Seasonal variation of suspended sediment in the Bohai and Yellow Sea and the pathway of sediment transport [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2015, 35(2): 11-21.
[8] Yang Z S, Ji Y J, Bi N S, et al. Sediment transport off the Huanghe (Yellow River) delta and in the adjacent Bohai Sea in winter and seasonal comparison [J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2011, 93(3): 173-181. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2010.06.005
[9] 董超. 登州浅滩表层沉积物输运特征的研究[D]. 中国海洋大学硕士学位论文, 2011
DONG Chao. Study on the characters of surface sediment transport in Dengzhou shoal area[D]. Master Dissertation of Ocean University of China, 2011.
[10] 姜胜辉, 王楠, 成海燕, 等. 渤海海峡水动力分布特征研究[J]. 中国海洋大学学报:自然科学版, 2019, 49(S1):66-73
JIANG Shenghui, WANG Nan, CHENG Haiyan, et al. The study on hydrodynamic distribution characteristics of the Bohai strait [J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 2019, 49(S1): 66-73.
[11] 李福林, 夏东兴, 王文海, 等. 登州浅滩的形成、动态演化及其可恢复性研究[J]. 海洋学报, 2004, 26(6):65-73
LI Fulin, XIA Dongxing, WANG Wenhai, et al. Discussion on the evolution cause and its recovery for the Dengzhou Shoal, China [J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2004, 26(6): 65-73.
[12] 陈雪英, 胡泽建. 山东蓬莱西庄附近海域波浪与海岸侵蚀[J]. 黄渤海海洋, 1992, 10(2):19-26
CHEN Xueying, HU Zejian. On waves and coastal erosion in the sea area near west village, Penglai County, Shandong Province [J]. Journal of Oceanography of Huanghai & Bohai Seas, 1992, 10(2): 19-26.
[13] Camenen B. Simple and general formula for the settling velocity of particles [J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 2007, 133(2): 229-233. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9429(2007)133:2(229)
[14] 窦国仁. 再论泥沙起动流速[J]. 泥沙研究, 1999(6):1-9 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0468-155X.1999.06.001
DOU Guoren. Incipient motion of coarse and fine sediment [J]. Journal of Sediment Research, 1999(6): 1-9. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0468-155X.1999.06.001
[15] Partheniades E. Erosion and deposition of cohesive soils [J]. Journal of the Hydraulics Division, 1965, 91(1): 105-139. doi: 10.1061/JYCEAJ.0001165
[16] Krone R B. Flume Studies of the Transport of Sediment in Estuarial Shoaling Processes: Final Report[R]. Berkeley: Hydraulic Engineering Laboratory and Sanitary Engineering Research Laboratory, University of California, 1962.
[17] Clark S, Elliott A J. Modelling suspended sediment concentrations in the firth of forth [J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 1998, 47(3): 235-250. doi: 10.1006/ecss.1998.0359
[18] Ingram R G. Characteristics of the great whale river plume [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1981, 86(C3): 2017-2023. doi: 10.1029/JC086iC03p02017
[19] Uncles R J, Elliott R C A, Weston S A. Dispersion of salt and suspended sediment in a partly mixed estuary [J]. Estuaries, 1985, 8(3): 256-269. doi: 10.2307/1351486
[20] 黄才安, 梅小文. 垂线平均含沙量两种表述方法之比较[J]. 泥沙研究, 1999(1):70-73 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0468-155X.1999.01.013
HUANG Caian, MEI Xiaowen. Comparison on two formulae of mean suspended sediment concentration in vertical [J]. Journal of Sediment Research, 1999(1): 70-73. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0468-155X.1999.01.013
[21] 林纪江. 蓬莱近岸海域悬浮泥沙分布及运移机制研究[D]. 中国海洋大学硕士学位论文, 2017.
LIN Jijiang. The distribution and migration mechanism of suspended sediment in the Penglai coastal waters[D]. Master Dissertation of Ocean University of China, 2017.
[22] 林纪江, 胡日军, 朱龙海, 等. 潮流作用下蓬莱近岸海域悬浮泥沙的时空分布及变化特征[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2017, 33(12):13-23
LIN Jijiang, HU Rijun, ZHU Longhai, et al. Spatio-temporal distribution and variation of suspended sediment by the action of tide in Penglai coastal area [J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2017, 33(12): 13-23.
[23] 陈沈良, 谷国传, 张国安. 长江口南汇近岸水域悬沙沉降速度估算[J]. 泥沙研究, 2003(6):45-51 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0468-155X.2003.06.008
CHEN Shenliang, GU Guochuan, ZHANG Guoan. Settling velocity of suspended sediment in the Nanhui nearshore waters of Changjiang estuary [J]. Journal of Sediment Research, 2003(6): 45-51. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0468-155X.2003.06.008
[24] 程江, 何青, 王元叶. 利用LISST观测絮凝体粒径、有效密度和沉速的垂线分布[J]. 泥沙研究, 2005(1):33-39 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0468-155X.2005.01.006
CHENG Jiang, HE Qing, WANG Yuanye. Using LISST-100 for in-situ estimates of floc size, density and settling velocity, Changjiang Estuary, China [J]. Journal of Sediment Research, 2005(1): 33-39. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0468-155X.2005.01.006
[25] 时钟, 朱文蔚, 周洪强. 长江口北槽口外细颗粒悬沙沉降速度[J]. 上海交通大学学报, 2000, 34(1):18-22 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1006-2467.2000.01.005
SHI Zhong, ZHU Wenwei, ZHOU Hongqiang. Settling velocity of fine suspended sediment in the Changjiang estuary [J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiaotong University, 2000, 34(1): 18-22. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1006-2467.2000.01.005
[26] 唐建华. 长江口及其邻近海域粘性细颗粒泥沙絮凝特性研究[D]. 华东师范大学硕士学位论文, 2007.
TANG Jianhua. Characteristics of fine cohesive sediment’s flocculation in the Changjiang estuary and its adjacent sea area[D]. Master Dissertation of East China Normal University, 2007.
[27] 蒋国俊, 陈吉余, 姚炎明. 舟山群岛峡道潮滩动力沉积特性[J]. 海洋学报, 1998, 20(2):139-147
JIANG Guojun, CHEN Jiyu, YAO Yanming. Characteristics of dynamic sedimentation on tidal flat in channels of Zhoushan islands [J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 1998, 20(2): 139-147.
[28] 徐志刚. 长江口细颗粒泥沙的絮凝特性试验[J]. 东海海洋, 1984(3):45-50
XU Zhigang. Experiment on flocculation characteristics of fine sediments from the Changjiang estuary [J]. Donghai Marine Science, 1984(3): 45-50.
[29] 蒋国俊, 张志忠. 长江口阳离子浓度与细颗粒泥沙絮凝沉积[J]. 海洋学报, 1995, 17(1):76-82
JIANG Guojun, ZHANG Zhizhong. Cation concentration and fine-grained sediment flocculation deposition in the Yangtze Estuary [J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 1995, 17(1): 76-82.
[30] 关许为, 陈英祖. 长江口泥沙絮凝静水沉降动力学模式的试验研究[J]. 海洋工程, 1995, 13(1):46-50
GUAN Xuwei, CHEN Yingzu. Experimental study on dynamic formula of sand coagulation sinking in stationary water in Changjiang estuary [J]. The Ocean Engineering, 1995, 13(1): 46-50.
[31] Li J F, Zhang C. Sediment resuspension and implications for turbidity maximum in the Changjiang Estuary [J]. Marine Geology, 1998, 148(3-4): 117-124. doi: 10.1016/S0025-3227(98)00003-6
[32] 张伟. 渤海海峡南部海域地貌特征及控制因素研究[D]. 中国海洋大学博士学位论文, 2014.
ZHANG Wei. Study on the geomorphological characteristic and controlling factors in the southern Bohai strait[D]. Doctor Dissertation of Ocean University of China, 2014.
[33] 陆建忠. 遥感反演与数值模拟耦合的渤海悬浮泥沙输移研究[D]. 武汉大学博士学位论文, 2010.
LU Jianzhong. Study on suspended sediment transport coupling remote sensing retrieval and numerical simulation in the Bohai Sea, China[D]. Doctor Dissertation of Wuhan University, 2010.
[34] 赵奎寰. 登州浅滩物质来源及运移趋势[J]. 海岸工程, 1992, 11(1):32-40
ZHAO Kuihuan. The sediment source of Dengzhou shallows and its transport tendency [J]. Coastal Engineering, 1992, 11(1): 32-40.
-



 下载:
下载:











