Formation mechanism of high quality source rocks in the depression of faulted basin margin: A case study of Huizhou 26 northeast subsag, Pearl River Mouth Basin
-
摘要:
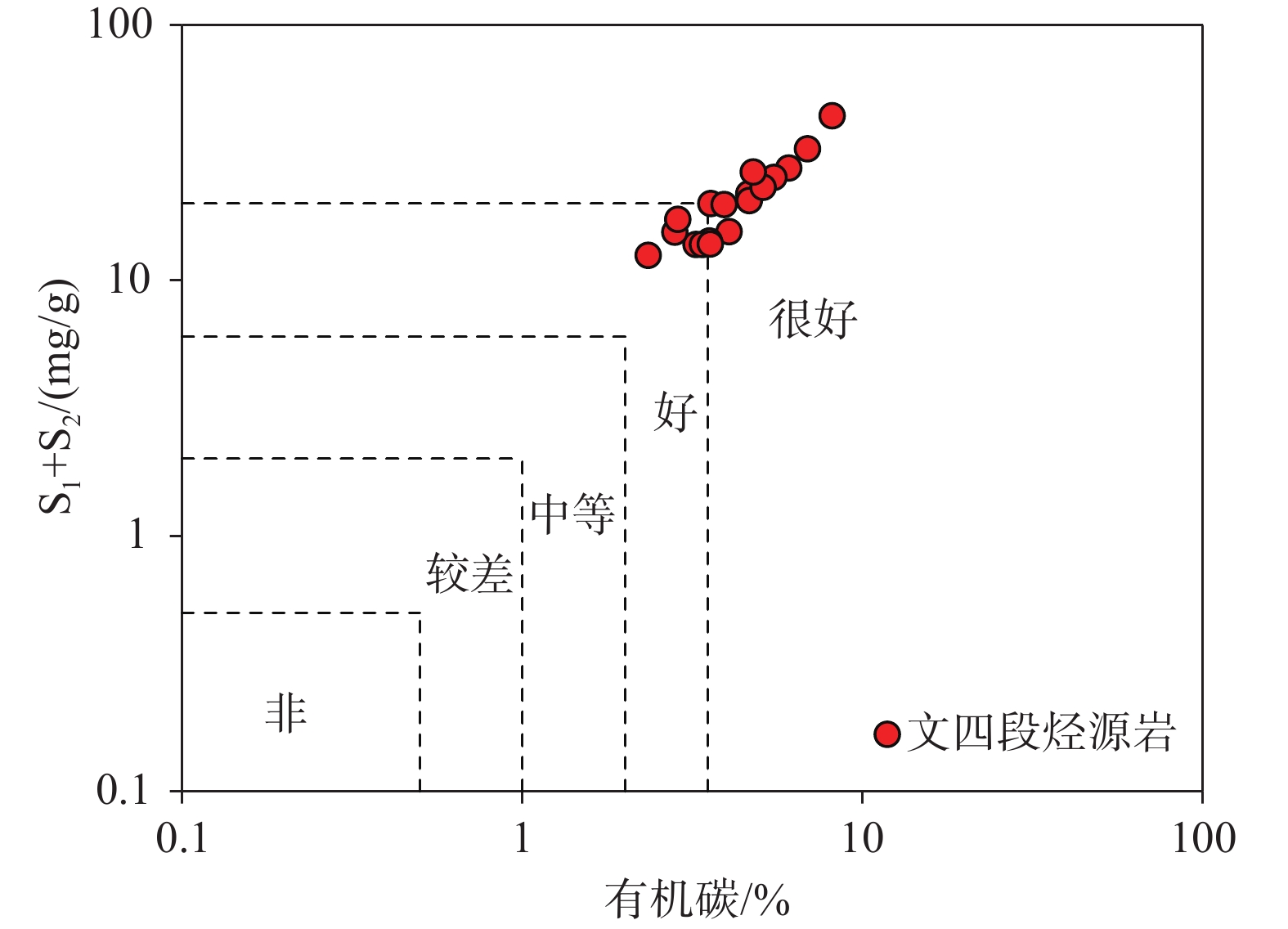
珠江口盆地珠一坳陷惠州26洼为典型的断陷盆地,是已证实的富生烃洼陷。以往对优质烃源岩的研究主要集中在其盆地内部,而对湖盆边缘次洼的烃源岩特征及形成机制鲜有报道。为弥补以往研究的空白,选择惠州26洼东北次洼作为研究区,根据最新的地震、地化和元素分析等资料,对该次洼的烃源岩地化特征和形成机制进行详细研究。结果表明,该次洼文四段发育优质烃源岩,有机质丰度高,含量均值为4.59%,可达“好—很好”烃源岩标准,有机质类型为Ⅰ—Ⅱ1型,以生油为主。文四段沉积时期,惠州26洼东北次洼强烈断陷,形成“洼缘深盆”,且陆源碎屑物质输入量少,为烃源岩发育提供有利的沉积环境,同期火山活动提供了丰富的无机营养物质,形成咸水环境,引起浮游生物勃发,促进有机质的规模形成和保存。综合分析认为,惠州26洼东北次洼文四段优质烃源岩的发现,将优质烃源岩分布范围扩大至湖盆边缘,为该洼陷未来勘探发现奠定生烃基础,对其他地区断陷盆地边缘洼陷评价和勘探潜力分析具有重要的借鉴意义。
Abstract:Huizhou 26 Sag, Zhuyi Depression, Pearl River Mouth Basin, is a typical faulted basin, which is proved to be rich in hydrocarbon generation. The research on high-quality source rocks is mainly concentrated in the interior of the basin, but there is little research on the characteristics and formation mechanism of source rocks in subsag at the margin of sag. Based on the latest data of earthquake, geochemistry and elements analysis, the geochemical characteristics and formation mechanism of source rocks in the Northeast subsag of Huizhou 26 sag are studied in detail. High quality source rocks were developed in WC4 Formation, with high abundance of organic matter, with an average content of 4.59%, which can reach the standard of “good-very good” source rocks, and organic matter type is Ⅰ-Ⅱ1, mainly oil-type source rock. During the sedimentary period of the WC4 Formation, Huizhou 26 northeast subsag was strongly faulted, forming a “Deep basin in sag edge”, Less terrigenous debris input, which provided a favorable sedimentary environment for the development of source rocks. Volcanic activities in the same period provided rich inorganic nutrients, form a salt water environment, cause the plankton bloom, and promote the large-scale formation and preservation of organic matter. The comprehensive analysis shows that the discovery of high-quality source rocks in WC4 Formation, Huizhou 26 northeast subsag, expands the distribution of high-quality source rocks to the edge of the sag, which lays a hydrocarbon generation foundation for the future exploration and discovery of the sag, and has important reference significance for the evaluation and exploration potential analysis of subsag at the edge of fault basin in other areas.
-

-
表 1 惠州26洼东北次洼文昌组文四段烃源岩干酪根显微组分和类型指数
Table 1. Organic microscopic composition and kerogen types in WC4 source rocks of Huizhou 26 northeast subsag
井名 深度/m 层位 岩性 腐泥组/% 壳质组/% 镜质组/% 惰性组/% 类型
指数类型 HZ27-A 3 815~3 819 文四段 泥岩 65 33 2 2 80 Ⅰ 3 860~3 868 41 54 5 5 64 Ⅱ1 3 880~3 890 29 64 7 7 56 Ⅱ1 -
[1] 田立新, 施和生, 刘杰, 等. 珠江口盆地惠州凹陷新领域勘探重大发现及意义[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2020, 25(4):22-30 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2020.04.003
TIAN Lixin, SHI Hesheng, LIU Jie, et al. Great discovery and significance of new frontier exploration in Huizhou sag, Pearl River Mouth Basin [J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2020, 25(4): 22-30. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2020.04.003
[2] 史玉玲, 刘杰, 温华华, 等. 珠江口盆地惠州26-6烃源岩热压模拟实验及生气潜力[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2021, 37(11):53-59
SHI Yuling, LIU Jie, WEN Huahua, et al. Thermo-compression simulation experiment and gas generation potential analysis of Huizhou 26-6 source rocks in the Pearl River Mouth Basin [J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2021, 37(11): 53-59.
[3] 朱俊章, 施和生, 谢泰俊, 等. 惠州26-2油田油藏地球化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2007, 12(2):34-40 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2007.02.006
ZHU Junzhang, SHI Hesheng, XIE Taijun, et al. Geochemical features and geological significance of oil reservoir in Huizhou 26-2 oilfield [J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2007, 12(2): 34-40. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2007.02.006
[4] 李友川, 陶维祥, 孙玉梅, 等. 珠江口盆地惠州凹陷及其邻区原油分类和分布特征[J]. 石油学报, 2009, 30(6):830-834,842 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2697.2009.06.006
LI Youchuan, TAO Weixiang, SUN Yumei, et al. Classification and distribution of oil in Huizhou Depression of Pearl River Mouth Basin [J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2009, 30(6): 830-834,842. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2697.2009.06.006
[5] 李松峰, 徐思煌, 施和生, 等. 珠江口盆地惠州凹陷古近系烃源岩特征及资源预测[J]. 地球科学-中国地质大学学报, 2013, 38(1):112-120 doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2013.011
LI Songfeng, XU Sihuang, SHI Hesheng, et al. Characteristics of paleogene source rocks and prediction of petroleum resources in Huizhou Depression, Pearl River Mouth Basin [J]. Earth Science-Journal of China University of Geoscience, 2013, 38(1): 112-120. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2013.011
[6] 舒誉, 施和生, 杜家元, 等. 珠一坳陷古近系油气成藏特征及勘探方向[J]. 中国海上油气, 2014, 26(3):37-42
SHU Yu, SHI Hesheng, DU Jiayuan, et al. Paleogene characteristics in hydrocarbon accumulation and exploration direction in Zhu I depression [J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2014, 26(3): 37-42.
[7] 施和生, 舒誉, 杜家元, 等. 珠江口盆地古近系石油地质[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2017.
SHI Hesheng, SHU Yu, DU Jiayuan, et al. Petroleum Geology of Paleogene in Pearl River Mouth Basin[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2017.
[8] 米立军, 张向涛, 陈维涛, 等. 珠江口盆地珠一坳陷古近系油气富集规律及下一步勘探策略[J]. 中国海上油气, 2018, 30(6):1-13
MI Lijun, ZHANG Xiangtao, CHEN Weitao, et al. Hydrocarbon enrichment law of Paleogene Zhu1 depression and its next exploration strategy in Pearl River Mouth basin [J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2018, 30(6): 1-13.
[9] 陈长民, 施和生, 许仕策, 等. 珠江口盆地(东部)第三系油气藏形成条件[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2003.
CHEN Changmin, SHI Hesheng, XU Shice, et al. Tertiary Hydrocarbon Accumulation Condition in Pearl River Mouth Basin[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2003.
[10] 杜家元, 施和生, 丁琳, 等. 惠州凹陷油气成藏期次划分及其勘探意义[J]. 中国海上油气, 2009, 21(4):221-226 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1506.2009.04.002
DU Jiayuan, SHI Hesheng, DING Lin, et al. Division of hydrocarbon accumulation stages in Huizhou depression and their exploration significance [J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2009, 21(4): 221-226. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1506.2009.04.002
[11] 陈建渝, 郝芳. 有机岩石学研究有机质类型和成熟度的改进[J]. 石油实验地质, 1990, 12(4):426-431 doi: 10.11781/sysydz199004426
CHEN Jianyu, HAO Fang. Improvement on study of organic types and maturation with organic petrology [J]. Experimental Petroleum Geology, 1990, 12(4): 426-431. doi: 10.11781/sysydz199004426
[12] 梅玲, 张枝焕, 王旭东, 等. 渤海湾盆地南堡凹陷原油地球化学特征及油源对比[J]. 中国石油大学学报:自然科学版, 2008, 32(6):40-46
MEI Ling, ZHANG Zhihuan, WANG Xudong, et al. Geochemical characteristics of crude oil and oil-source correlation in Nanpu sag, Bohai Bay Basin [J]. Journal of China University of Petroleum, 2008, 32(6): 40-46.
[13] 张参, 阳宏, 王飞龙, 等. 渤中凹陷南洼东营组烃源岩有机地球化学特征[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2020, 36(11):35-44
ZHANG Can, YANG Hong, WANG Feilong, et al. Organic geochemistry of the source rocks in the Dongying formation of the South Bozhong subsag [J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2020, 36(11): 35-44.
[14] 贾培蒙, 张向涛, 陈维涛, 等. 珠江口盆地惠州凹陷惠州21古潜山的形成演化及其对深层油气成藏的控制[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2021, 37(12):27-37
JIA Peimeng, ZHANG Xiangtao, CHEN Weitao, et al. Tectonic evolution of Huizhou 21 buried hill and its con-trol over deep oil accumulations in the Huizhou sag of Pearl River Mouth Basin [J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2021, 37(12): 27-37.
[15] 刘池洋, 赵俊峰, 马艳萍, 等. 富烃凹陷特征及其形成研究现状与问题[J]. 地学前缘, 2014, 21(1):75-88
LIU Chiyang, ZHAO Junfeng, MA Yanping, et al. The advances and problems in the study of the characteristics and formation of hydrocarbon-rich sag [J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2014, 21(1): 75-88.
[16] Su W B, He L Q, Wang Y B, et al. K-bentonite beds and high-resolution integrated stratigraphy of the uppermost Ordovician Wufeng and the lowest Silurian Longmaxi Formations in South China [J]. Science in China Series D:Earth Sciences, 2003, 46(11): 1121-1133. doi: 10.1360/01yd0225
[17] 高有峰, 王璞珺, 王成善, 等. 松科1井南孔选址、岩心剖面特征与特殊岩性层的分布[J]. 地质学报, 2008, 82(5):669-675 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2008.05.011
GAO Youfeng, WANG Pujun, WANG Chengshan, et al. Well site selecting, core profile characteristics and distribution of the special lithology in CCSD-SK Ⅱ [J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2008, 82(5): 669-675. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2008.05.011
[18] 邱欣卫, 刘池洋, 李元昊, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地延长组凝灰岩夹层展布特征及其地质意义[J]. 沉积学报, 2009, 27(6):1138-1146
QIU Xinwei, LIU Chiyang, LI Yuanhao, et al. Distribution characteristics and geological significances of tuff interlayers in Yanchang Formation of Ordos Basin [J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2009, 27(6): 1138-1146.
[19] 李光云. 三塘湖盆地马朗凹陷上石炭统火山岩油藏形成条件与主控囚素[D]. 中国地质大学(北京)博士学位论文, 2010
LI Guangyun. The forming condition and the key controlling factor of the upper Carboniferous volcanic oil pool in Malang sag of Santanghu basin[D]. Doctor Dissertation of China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2010.
[20] 单玄龙, 李吉焱, 陈树民, 等. 陆相水下火山喷发作用及其对优质烃源岩形成的影响: 以松辽盆地徐家围子断陷营城组为例[J]. 中国科学:地球科学, 2013, 56(11):1926-1933 doi: 10.1007/s11430-013-4657-7
SHAN Xuanlong, LI Jiyan, CHEN Shumin, et al. Subaquatic volcanic eruptions in continental facies and their influence on high quality source rocks shown by the volcanic rocks of a faulted depression in Northeast China [J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 2013, 56(11): 1926-1933. doi: 10.1007/s11430-013-4657-7
[21] 杜景霞, 石文武, 周贺, 等. 渤海湾盆地南堡凹陷火山岩锆石年代学及形成模式[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2014, 35(5):742-748 doi: 10.11743/ogg20140520
DU Jingxia, SHI Wenwu, ZHOU He, et al. Zircon U-Pb age and formation model of volcanic rocks from Nanpu Sag of Bohai Bay Basin [J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2014, 35(5): 742-748. doi: 10.11743/ogg20140520
[22] 金强, 翟庆龙. 裂谷盆地的火山热液活动和油气生成[J]. 地质科学, 2003, 38(3):342-349 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0563-5020.2003.03.008
JIN Qiang, ZHAI Qinglong. Volcanic and thermal-water activities and hydrocarbon generations in the rift basins, eastern China [J]. Chinese Journal of Geology, 2003, 38(3): 342-349. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0563-5020.2003.03.008
[23] 张文正, 杨华, 彭平安, 等. 晚三叠世火山活动对鄂尔多斯盆地长7优质烃源岩发育的影响[J]. 地球化学, 2009, 38(6):573-582 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0379-1726.2009.06.007
ZHANG Wenzheng, YANG Hua, PENG Pingan, et al. The influence of Late Triassic volcanism on the development of Chang 7 high grade hydrocarbon source rock in Ordos Basin [J]. Geochimica, 2009, 38(6): 573-582. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0379-1726.2009.06.007
[24] 陈小霞, 吴振强, 梁世中. 藻类对微量元素的生物富集及其机理探讨[J]. 食品与发酵工业, 1999, 25(4):56-60 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-990X.1999.04.013
CHEN Xiaoxia, WU Zhenqiang, LIANG Shizhong. Bioenrichment of trace elements by algae and discussion on its mechanisms [J]. Food and Fermentation Industries, 1999, 25(4): 56-60. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-990X.1999.04.013
[25] 谢世文, 王宇辰, 舒誉, 等. 珠一坳陷湖盆古环境恢复与优质烃源岩发育模式[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2022, 42(1):159-169
XIE Shiwen, WANG Yuchen, SHU Yu, et al. Environmental reconstruction for the paleo-lake of Zhu Ⅰ depression and the depositional model for high-quality source rocks [J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2022, 42(1): 159-169.
[26] 郑荣才, 柳梅青. 鄂尔多斯盆地长6油层组古盐度研究[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 1999, 20(1):20-25 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9985.1999.01.005
ZHENG Rongcai, LIU Meiqing. Study on palaeosalinity of Chang 6 oil reservoir set in Ordos Basin [J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 1999, 20(1): 20-25. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9985.1999.01.005
[27] Wignall P B. Large igneous provinces and mass extinctions [J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2001, 53(1-2): 1-33. doi: 10.1016/S0012-8252(00)00037-4
[28] Hartnett H E, Devol A H. Role of a strong oxygen-deficient zone in the preservation and degradation of organic matter: a carbon budget for the continental margins of northwest Mexico and Washington State [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2003, 67(2): 247-264. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(02)01076-1
[29] Jones B, Manning D A C. Comparison of geochemical indices used for the interpretation of palaeoredox conditions in ancient mudstones [J]. Chemical Geology, 1994, 111(1-4): 111-129. doi: 10.1016/0009-2541(94)90085-X
-




 下载:
下载: