Fault characteristics and its significances on hydrocarbon accumulation in northeastern Baiyun Sag, Pearl River Mouth Basin
-
摘要:
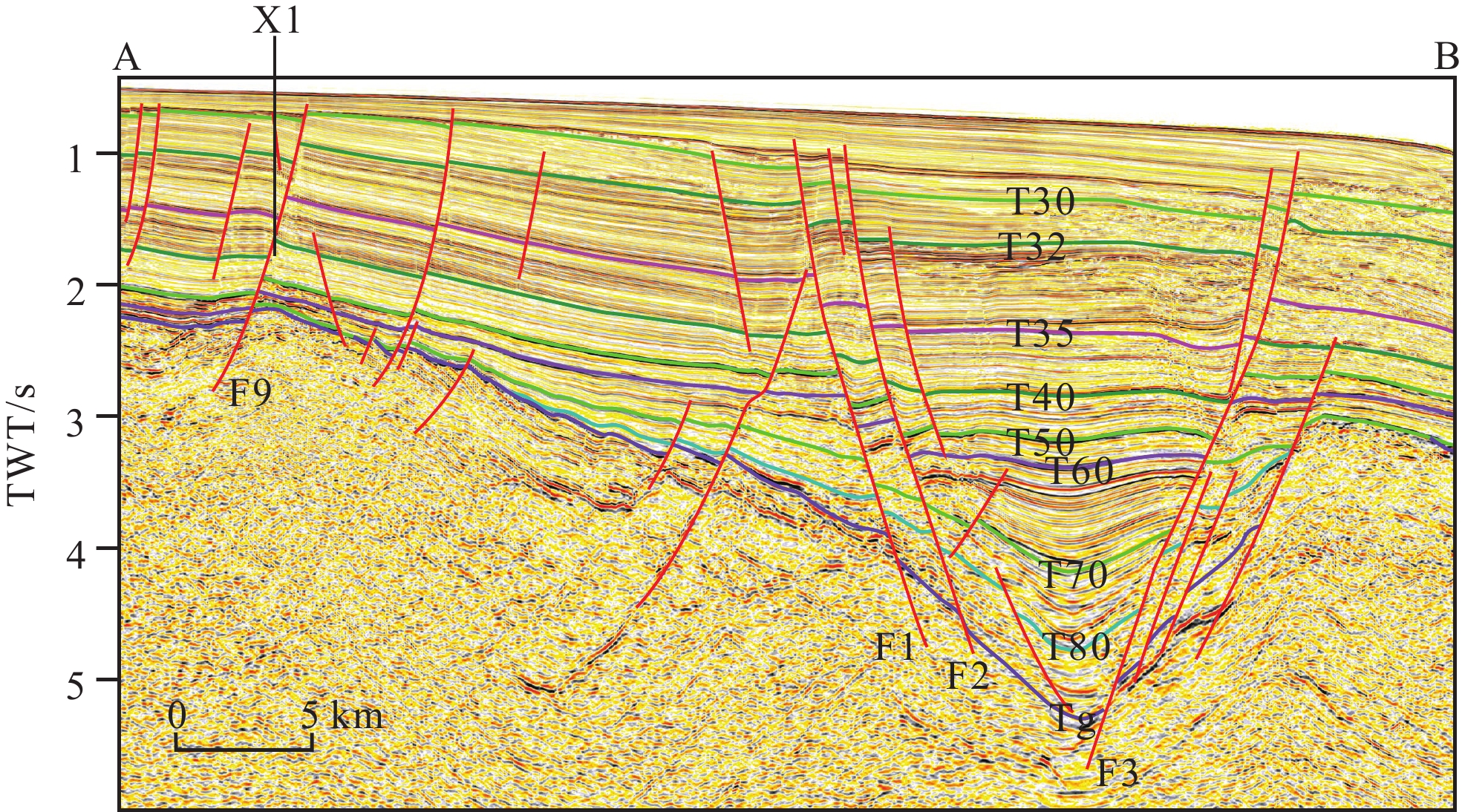
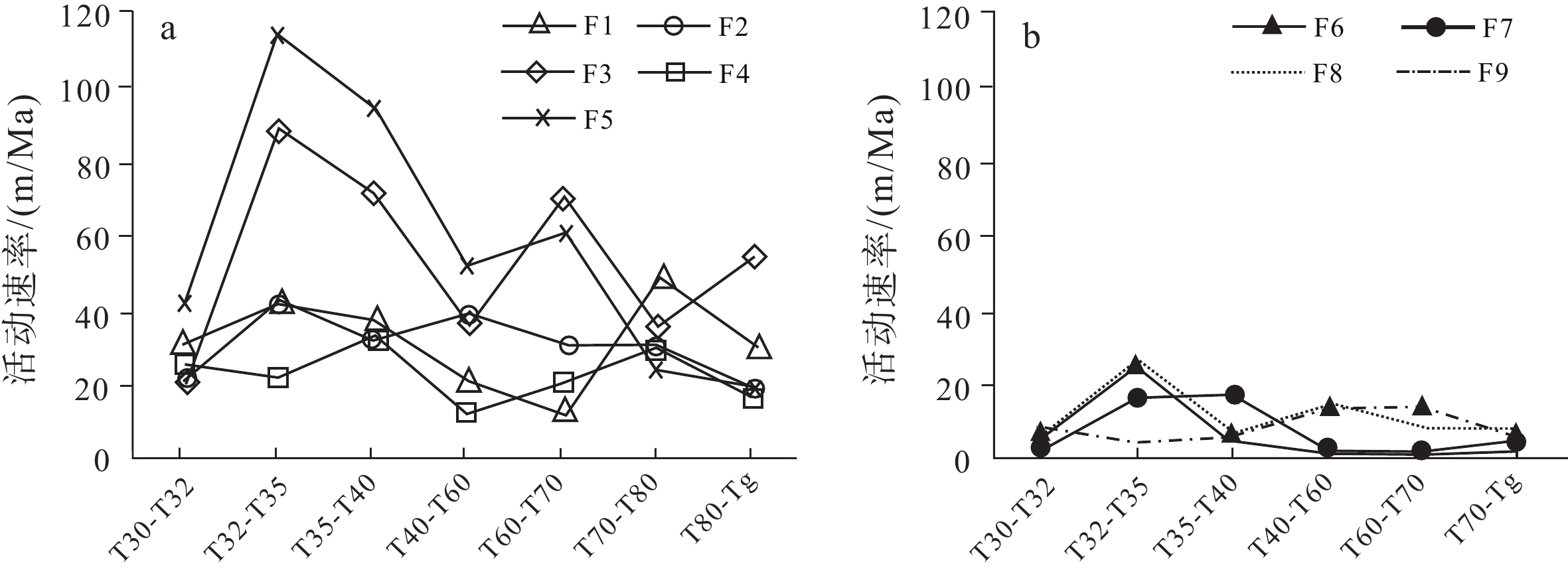
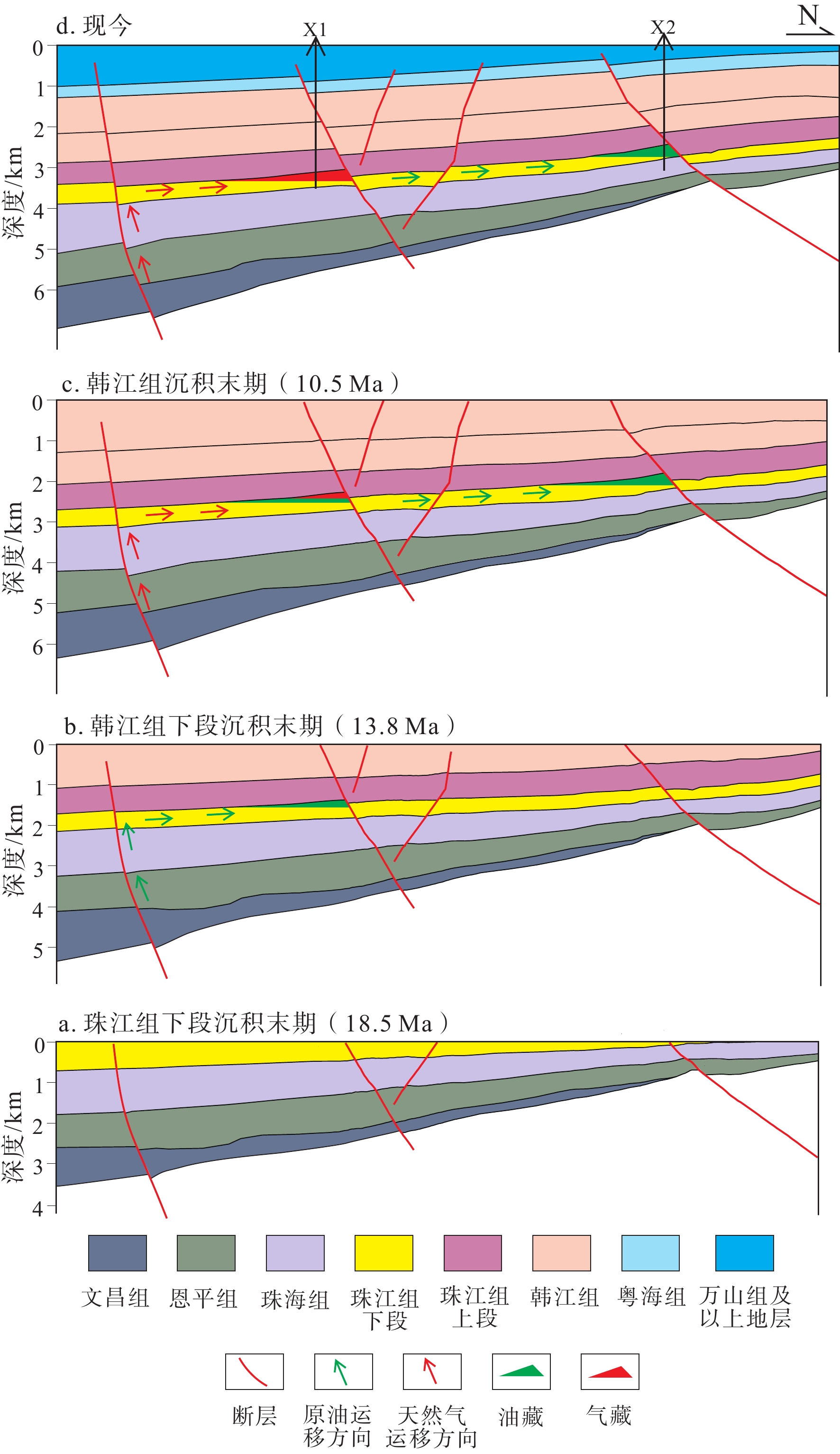
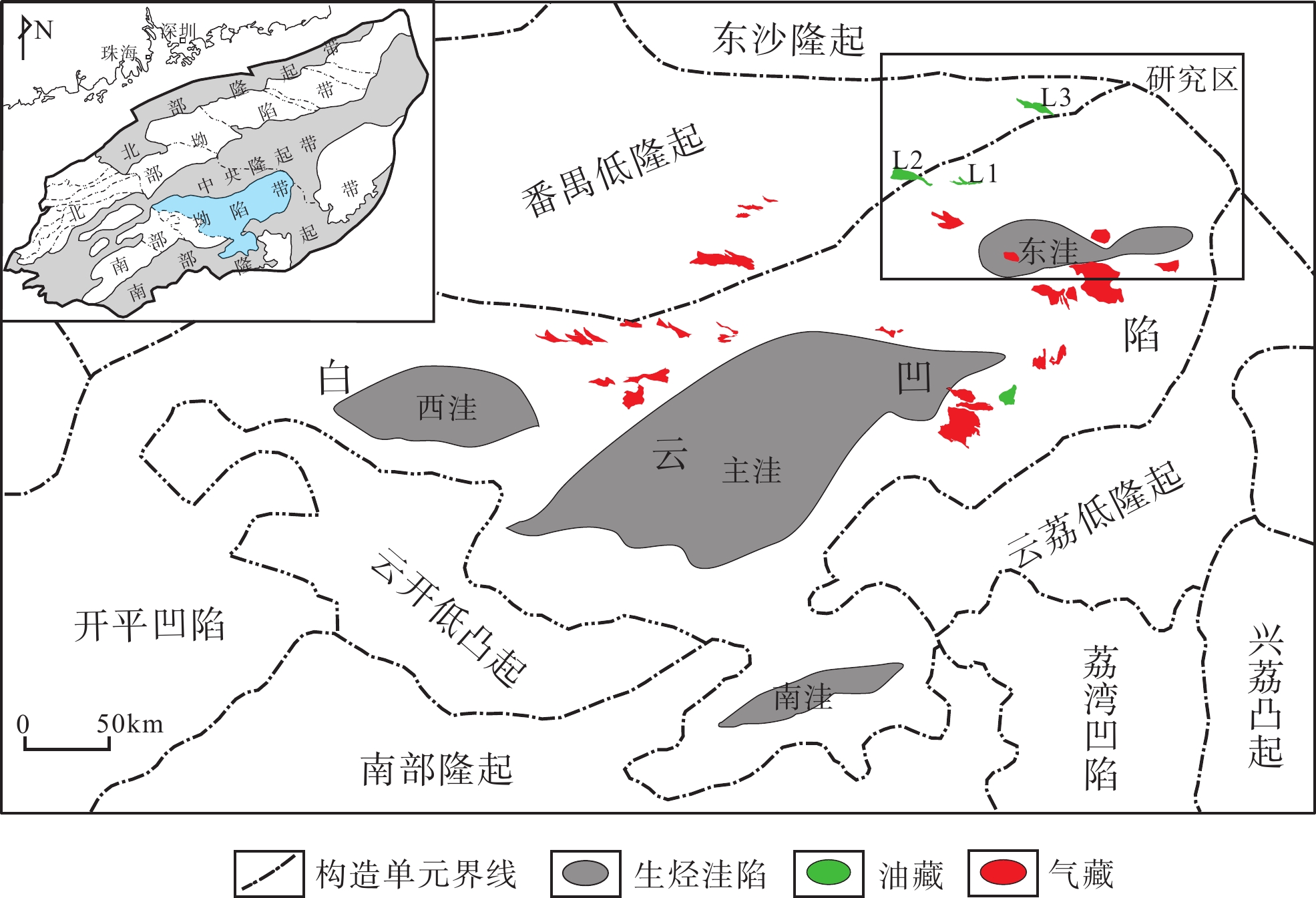
珠江口盆地白云凹陷东北部具有“内气外油”的分布特点,断裂在油气运聚成藏过程中起到了重要作用。本文主要依据地震资料解释成果,分析断裂发育特征,定量评价断裂输导性能,并结合钻探结果探讨断裂对油气运聚成藏的影响。白云凹陷东北部主要发育NWW向和近EW向正断层,在剖面上表现为铲式和板式形态。根据断裂对油气运聚成藏的影响,划分出油源断裂和控圈断裂。油源断裂在成藏期的活动速率达到20~40 m/Ma,在珠江组下段的断层泥比率多大于50%,而且断面正压力超过了泥岩的极限抗压强度,有利于油气沿断裂发生运移。控圈断裂的活动速率一般都小于20 m/Ma,在珠江组下段的断层泥比率都大于95%,而且断面正压力都小于泥岩的极限抗压强度,侧封性能良好。白云凹陷东北部表现出油气差异聚集成藏的特点,远源反向控圈断裂下盘高效封堵聚集原油,而天然气则主要发生近源聚集。
Abstract:The distribution of oil and gas fields in the northeastern Baiyun Sag of the Pearl River Mouth Basin is characterized by the “inner gas, outer oil” pattern, and faults play important roles on hydrocarbon migration and accumulation. Based on seismic interpretation and borehole data, fault characteristics and its significances on hydrocarbon accumulation in the northeastern part of the Baiyun Sag are analyzed in this paper. NWW- and EW-trending faults are predominant in the study area, which are listric and planar shapes in cross section. According to their significances on hydrocarbon accumulation, the faults in the northeastern Baiyun Sag can be divided into oil-source faults and trap-controlled faults. The oil-source faults dipping into source kitchen have an activity rate of 20~40 m/Ma in the key accumulation stage, and a value of shale gouge ratio more than 50% in the lower Zhujiang Formation. Also, the normal stress on oil-source fault surface is larger than the ultimate compressive strength of mudstone. These are helpful for hydrocarbon migration along the oil-source faults. In contrast, the trap-controlled faults have perfect lateral sealing ability, because of activity rate less than 20 m/Ma and value of shale gouge ratio more than 95% in the lower Zhujiang Formation, as well as normal stress on fault surface less than the ultimate compressive strength of mudstone. The feature of differential accumulation of hydrocarbon in the northeastern Baiyun Sag is obvious. Oil is accumulated in the footwall of the far-source antithetic trap- controlled faults, and gas is in the near-source traps.
-

-
图 2 珠江口盆地白云凹陷地层综合柱状图[20]
Figure 2.
表 1 白云凹陷东北部主要断裂珠江组下段SGR和断面正压力计算结果
Table 1. Shale gouge ratio and positive pressure of major faults in the lower Zhujiang Formation in the northeastern Baiyun sag
断裂类型 断裂编号 泥岩厚度/m 断距/m SGR/% 断面正压力/MPa 油源断裂 F1 774 948 82 48.77 F2 627 790 79 66.58 F3 1051 1217 86 48.79 F4 331 483 69 47.93 F5 1967 2152 91 24.58 控圈断裂 F6 233 238 98 23.09 F7 165 175 94 22.68 F8 308 321 96 21.69 F9 116 136 85 19.03 -
[1] Allan U S. Model for hydrocarbon migration and entrapment within faulted structures [J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1989, 73(7): 803-811.
[2] Yielding G, Freeman B, Needham D T. Quantitative fault seal prediction [J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1997, 81(6): 897-917.
[3] 郝芳, 邹华耀, 王敏芳, 等. 油气成藏机理研究进展和前沿研究领域[J]. 地质科技情报, 2002, 21(4):7-14
HAO Fang, ZOU Huayao, WANG Minfang, et al. Research advances and frontier areas of mechanisms of petroleum accumulation [J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2002, 21(4): 7-14.
[4] 陈伟, 吴智平, 侯峰, 等. 断裂带内部结构特征及其与油气运聚关系[J]. 石油学报, 2010, 31(5):774-780 doi: 10.7623/syxb201005012
CHEN Wei, WU Zhiping, HOU Feng, et al. Internal structures of fault zones and their relationship with hydrocarbon migration and accumulation [J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2010, 31(5): 774-780. doi: 10.7623/syxb201005012
[5] 余一欣, 周心怀, 徐长贵, 等. 渤海海域新生代断裂发育特征及形成机制[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2011, 32(2):273-279 doi: 10.11743/ogg20110216
YU Yixin, ZHOU Xinhuai, XU Changgui, et al. Characteristics and formation mechanisms of the Cenozoic faults in the Bohai Sea waters [J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2011, 32(2): 273-279. doi: 10.11743/ogg20110216
[6] 吕延防, 付广, 付晓飞, 等. 断层对油气的输导与封堵作用[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2013.
LV Yanfang, FU Guang, FU Xiaofei, et al. The Transporting and Sealing Roles of Faults on Hydrocarbon[M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 2013.
[7] 庞雄, 施和生, 朱明, 等. 再论白云深水区油气勘探前景[J]. 中国海上油气, 2014, 26(3):23-29
PANG Xiong, SHI Hesheng, ZHU Ming, et al. A further discussion on the hydrocarbon exploration potential in Baiyun deep water area [J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2014, 26(3): 23-29.
[8] 米立军, 张忠涛, 庞雄, 等. 南海北部陆缘白云凹陷油气富集规律及主控因素[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2018, 45(5):902-913 doi: 10.11698/PED.2018.05.17
MI Lijun, ZHANG Zhongtao, PANG Xiong, et al. Main controlling factors of hydrocarbon accumulation in Baiyun Sag at northern continental margin of South China Sea [J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2018, 45(5): 902-913. doi: 10.11698/PED.2018.05.17
[9] 庞雄, 任建业, 郑金云, 等. 陆缘地壳强烈拆离薄化作用下的油气地质特征: 以南海北部陆缘深水区白云凹陷为例[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2018, 45(1):27-39 doi: 10.11698/PED.2018.01.03
PANG Xiong, REN Jianye, ZHENG Jinyun, et al. Petroleum geology controlled by extensive detachment thinning of continental margin crust: a case study of Baiyun Sag in the deep-water area of northern South China Sea [J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2018, 45(1): 27-39. doi: 10.11698/PED.2018.01.03
[10] 侯读杰, 庞雄, 肖建新, 等. 白云凹陷断裂作为天然气运移通道的地质-地球化学证据[J]. 地学前缘, 2008, 15(4):81-87 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2008.04.010
HOU Dujie, PANG Xiong, XIAO Jianxin, et al. The geological and geochemical evidence on the identification of natural gas migration through fault system, Baiyun Sag, Pearl River Mouth Basin, China [J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2008, 15(4): 81-87. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2008.04.010
[11] 施和生, 秦成岗, 张忠涛, 等. 珠江口盆地白云凹陷北坡-番禺低隆起油气复合输导体系探讨[J]. 中国海上油气, 2009, 21(6):361-366 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1506.2009.06.001
SHI Hesheng, QIN Chenggang, ZHANG Zhongtao, et al. A discussion on the complex hydrocarbon transport system in the north slope of Baiyun Sag-Panyu low uplift, Pearl River Mouth Basin [J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2009, 21(6): 361-366. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1506.2009.06.001
[12] 张忠涛, 施和生, 秦成岗, 等. 番禺低隆起-白云凹陷北坡断层封闭性研究[J]. 断块油气田, 2010, 17(1):24-27, 51
ZHANG Zhongtao, SHI Hesheng, QIN Chenggang, et al. Study on fault sealability of Panyu Low Massif and north slope of Baiyun Sag [J]. Fault-block Oil and Gas Field, 2010, 17(1): 24-27, 51.
[13] 邵磊, 孟晓捷, 张功成, 等. 白云凹陷断裂特征对构造与沉积的控制作用[J]. 同济大学学报:自然科学版, 2013, 41(9):1435-1441
SHAO Lei, MENG Xiaojie, ZHANG Gongcheng, et al. Feature of faults system and its influence on tectonic and sedimentary history of Baiyun Sag [J]. Journal of Tongji University:Natural Science, 2013, 41(9): 1435-1441.
[14] Yu Y X, Zhang T L, Zhang Z T, et al. Structural characteristics and its significances on hydrocarbon accumulation in the Yunkai low uplift, Pearl River Mouth Basin [J]. Acta Geologica Sinica:English Edition, 2021, 95(1): 21-29. doi: 10.1111/1755-6724.14622
[15] Zeng J H, Wang C, Guo S, et al. Petroleum migration characteristics in the northeastern part of the Baiyun depression, Pearl River Mouth Basin, South China Sea [J]. Acta Geologica Sinica:English Edition, 2021, 95(1): 208-231. doi: 10.1111/1755-6724.14623
[16] 朱伟林, 张功成, 高乐. 南海北部大陆边缘盆地油气地质特征与勘探方向[J]. 石油学报, 2008, 29(1):1-9 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2697.2008.01.001
ZHU Weilin, ZHANG Gongcheng, GAO Le. Geological characteristics and exploration objectives of hydrocarbons in the northern continental margin basin of South China Sea [J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2008, 29(1): 1-9. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2697.2008.01.001
[17] 何家雄, 颜文, 马文宏, 等. 南海北部准被动陆缘深水区油气地质及与世界深水油气富集区类比[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2010, 21(6):897-908, 995
HE Jiaxiong, YAN Wen, MA Wenhong, et al. Analogy of oil and gas geology between quasi-passive margin of northern South China Sea and global oil and gas enriched areas in deep water [J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2010, 21(6): 897-908, 995.
[18] 张功成, 杨海长, 陈莹, 等. 白云凹陷—珠江口盆地深水区一个巨大的富生气凹陷[J]. 天然气工业, 2014, 34(11):11-25
ZHANG Gongcheng, YANG Haizhang, CHEN Ying, et al. The Baiyun Sag: a giant rich gas-generation sag in the deepwater area of the Pearl River Mouth Basin [J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2014, 34(11): 11-25.
[19] Fu J, Zhang Z T, Chen C, et al. Geochemistry and origins of petroleum in the Neogene reservoirs of the Baiyun Sag, Pearl River Mouth Basin [J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2019, 107: 127-141. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2019.05.015
[20] 庞雄, 陈长民, 彭大钧, 等. 南海北部白云深水区之基础地质[J]. 中国海上油气, 2008, 20(4):215-222 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1506.2008.04.001
PANG Xiong, CHEN Changmin, PENG Dajun, et al. Basic geology of Baiyun deep-water area in the northern South China Sea [J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2008, 20(4): 215-222. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1506.2008.04.001
[21] 周心怀, 牛成民, 滕长宇. 环渤中地区新构造运动期断裂活动与油气成藏关系[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2009, 30(4):469-475, 482 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9985.2009.04.013
ZHOU Xinhuai, NIU Chengmin, TENG Changyu. Relationship between faulting and hydrocarbon pooling during the Neotectonic movement around the central Bohai Bay [J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2009, 30(4): 469-475, 482. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9985.2009.04.013
[22] 彭辉界, 庞雄奇, 李洪博, 等. 珠江口盆地珠一坳陷断裂控藏定量表征与有利勘探区预测[J]. 现代地质, 2016, 30(6):1318-1328 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2016.06.014
PENG Huijie, PANG Xiongqi, LI Hongbo, et al. Quantitative evaluation of control of faults on hydrocarbon accumulation and play fairway prediction in Zhu I depression of Pearl River Mouth Basin [J]. Geoscience, 2016, 30(6): 1318-1328. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2016.06.014
[23] Knipe R J. Juxtaposition and seal diagrams to help analyze fault seals in hydrocarbon reservoirs [J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1997, 81(2): 187-195.
-



 下载:
下载: