Geochemical characteristics of black carbon in surface sediments of the East Siberian Arctic Shelf and their environmental implications
-
摘要:
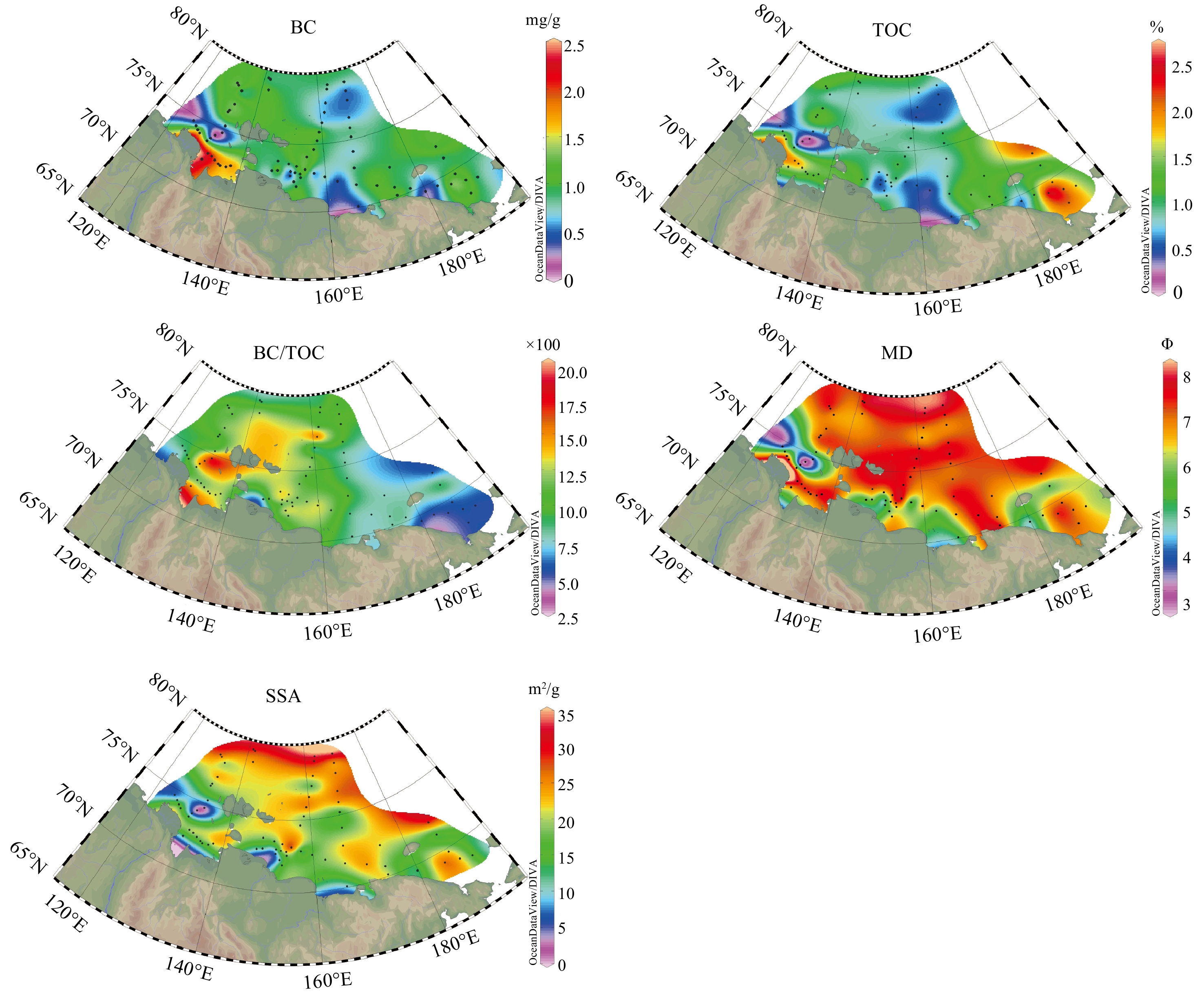
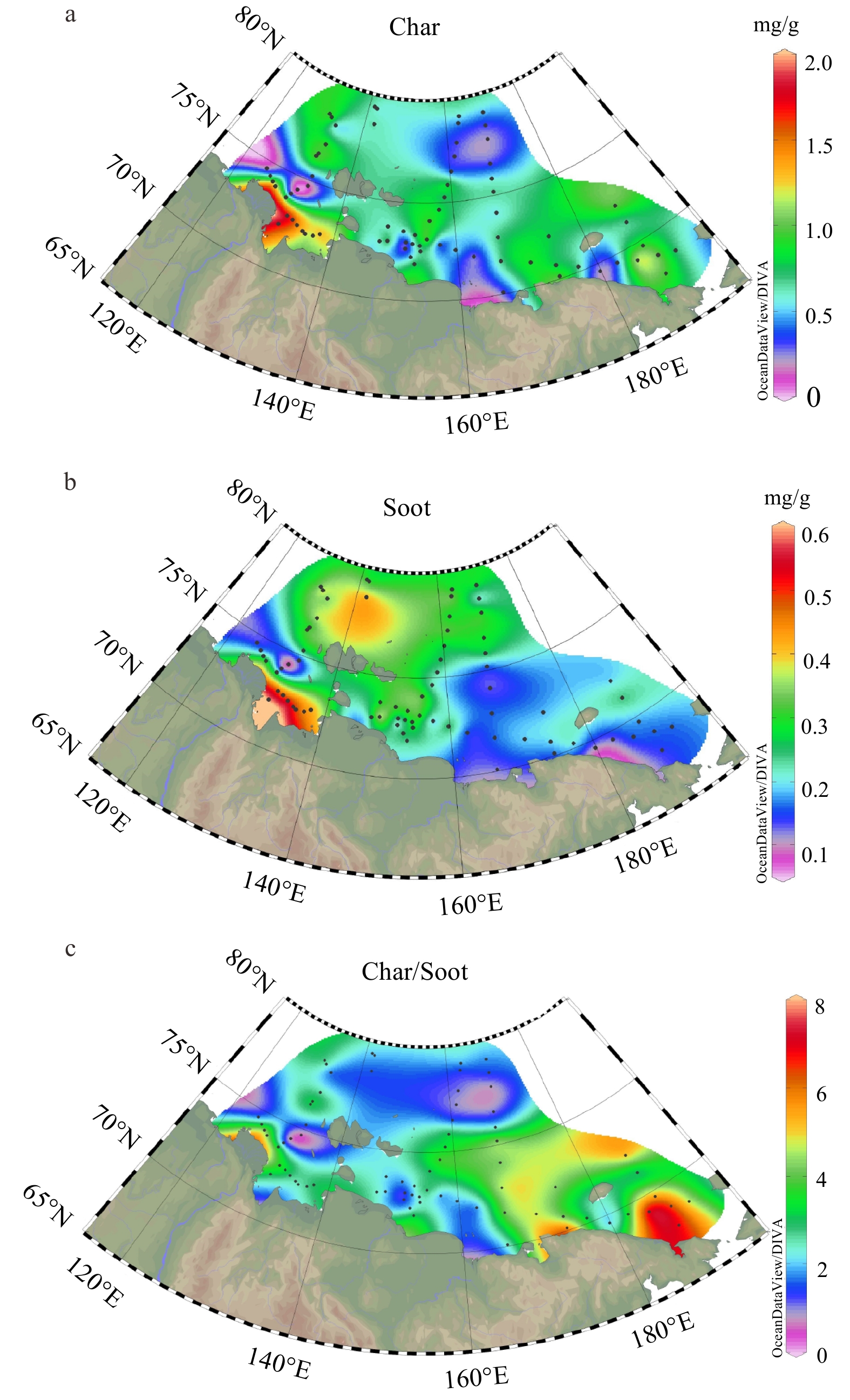
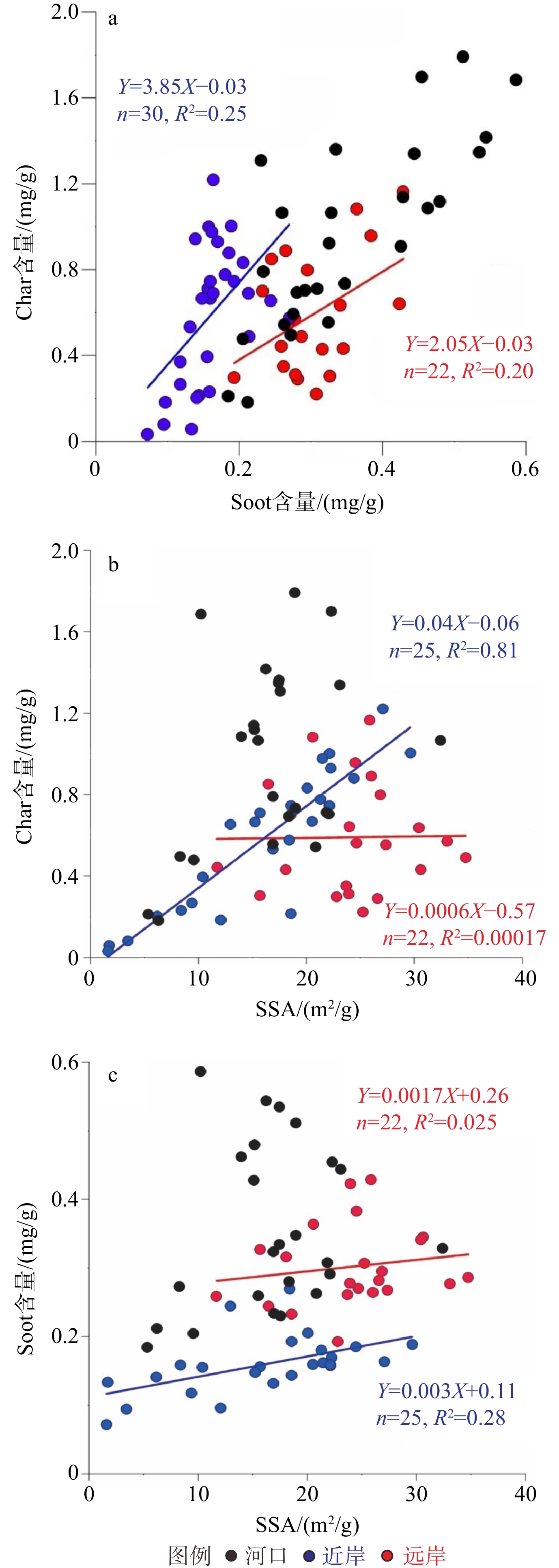
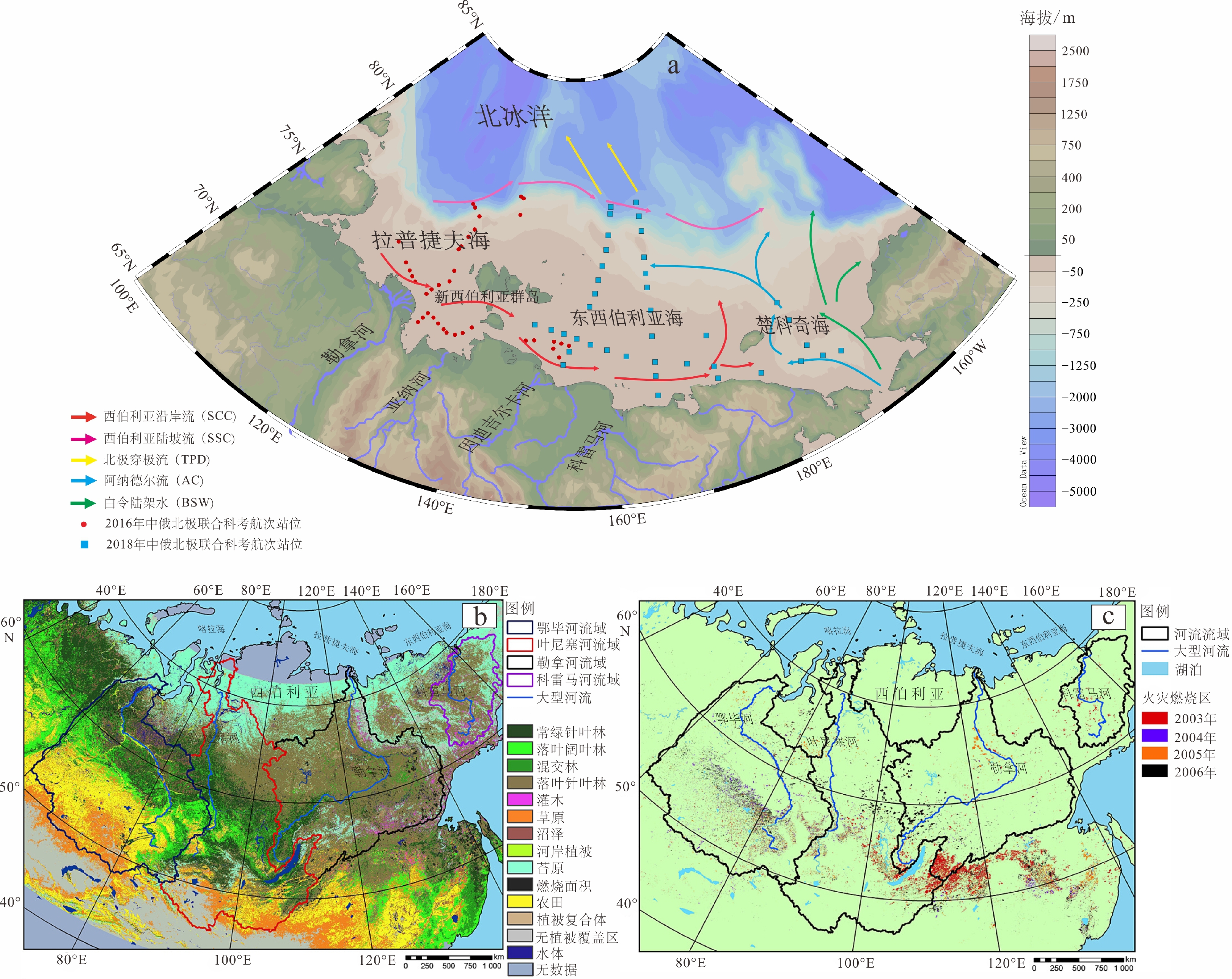
热成因黑碳与气候变化和人类活动关系密切。在全球变暖背景下,这类碳的排放、从陆向海的转移及其环境归宿对于理解北极快速变化下陆源有机碳的源汇过程及其气候环境效应具有重要的科学意义。北极东西伯利亚陆架是全球最为宽浅的陆架,接收了大量来自径流和海岸侵蚀输入的陆源物质,尤其近年来环北极野火的频繁发生,因而成为研究北极沉积黑碳源−汇过程的理想区域。本研究对东西伯利亚陆架表层沉积物中黑碳的含量和组成、空间分布特征及其影响因素等进行了研究,结果表明,黑碳的含量为0.1~2.3 mg/g,平均为0.99 mg/g,其中来自生物质燃烧贡献为主的焦炭平均占70%以上。黑碳总体空间分布具有显著的异质性,拉普捷夫海和东西伯利亚海西部地区黑碳含量较高,与海岸侵蚀和河流输入关系密切;陆架东部(包括楚科奇海)陆源输入相对较少,黑碳含量相对较低。不同类型黑碳的空间分布格局显著不同;对于近岸区,来自径流和海岸侵蚀的输入可能是焦炭从陆向海的主要输入方式。
Abstract:Pyrogenic black carbon (BC) is closely related to climate change and human activities. In the context of global warming, the BC emission and transfer from land to sea and the environmental fate provide important scientific clues for understanding the source-sink course of terrigenous organic carbon and its climate and environmental effects under rapid climate change in the Arctic area. The East Siberian Arctic Shelf is the widest and shallowest shelf in the world, receiving a large amount of terrestrial material input from runoff and coastal erosion. Especially in recent years, frequent occurrence of wildfires around the Arctic makes it an ideal area for studying the course and route of source-sink of BC deposited in the Arctic waters. Based on the data of samples collected from the East Siberian shelf, the content, composition, spatial distribution, and influencing factors of BC in surface sediments were studied. Preliminary results show that the content of BC is 0.1~2.3 mg/g, on average of 0.99 mg/g. Among them, char from biomass combustion contributed more than 70% on average. The spatial distribution of BC is very heterogeneous. BC in the Laptev Sea and the western part of the East Siberian Sea is high, which is closely related to coastal erosion and river input. The eastern part of the shelf (including the Chukchi Sea) has less terrigenous input and relatively low BC content. The spatial variability of different types of BC is obvious. In the nearshore region, runoff and coastal erosion is probably the main input pathway of char.
-
Key words:
- black carbon /
- source and sink /
- surface sediments /
- Arctic rapid change /
- East Siberian Arctic Shelf
-

-
[1] Burdige D J. Preservation of organic matter in marine sediments: controls, mechanisms, and an imbalance in sediment organic carbon budgets? [J]. Chemical Reviews, 2007, 107(2): 467-485. doi: 10.1021/cr050347q
[2] Bianchi T S, Cui X Q, Blair N E, et al. Centers of organic carbon burial and oxidation at the land-ocean interface [J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2018, 115: 138-155. doi: 10.1016/j.orggeochem.2017.09.008
[3] Masiello C A. New directions in black carbon organic geochemistry [J]. Marine Chemistry, 2004, 92(1-4): 201-213. doi: 10.1016/j.marchem.2004.06.043
[4] Schmidt M W I, Noack A G. Black carbon in soils and sediments: analysis, distribution, implications, and current challenges [J]. Global Biogeochemical Cycles, 2000, 14(3): 777-793. doi: 10.1029/1999GB001208
[5] Bird M I, Wynn J G, Saiz G, et al. The pyrogenic carbon cycle [J]. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 2015, 43(1): 273-298. doi: 10.1146/annurev-earth-060614-105038
[6] Bond T C, Doherty S J, Fahey D W, et al. Bounding the role of black carbon in the climate system: a scientific assessment [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Atmospheres, 2013, 118(11): 5380-5552. doi: 10.1002/jgrd.50171
[7] Ramanathan V, Carmichael G. Global and regional climate changes due to black carbon [J]. Nature Geoscience, 2008, 1(4): 221-227. doi: 10.1038/ngeo156
[8] Gustafsson A Ö, Gschwend A P M. The flux of black carbon to surface sediments on the New England continental shelf [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1998, 62(3): 465-472. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(97)00370-0
[9] Kuhlbusch T A J. Black carbon and the carbon cycle [J]. Science, 1998, 280(5371): 1903-1904. doi: 10.1126/science.280.5371.1903
[10] Suman D O, Kuhlbusch T A J, Lim B. Marine sediments: a reservoir for black carbon and their use as spatial and temporal records of combustion[M]//Clark J S, Cachier H, Goldammer J G, et al. Sediment Records of Biomass Burning and Global Change. Berlin: Springer, 1997: 271-293.
[11] Salvadó J A, Bröder L, Andersson A, et al. Release of black carbon from thawing permafrost estimated by sequestration fluxes in the east siberian arctic shelf recipient [J]. Global Biogeochemical Cycles, 2017, 31(10): 1501-1515. doi: 10.1002/2017GB005693
[12] Klinedinst D B, Currie L A. Direct quantification of PM2.5 fossil and biomass carbon within the northern front range air quality study's domain [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 1999, 33(23): 4146-4154.
[13] 王效科, 白艳莹, 欧阳志云, 等. 全球碳循环中的失汇及其形成原因[J]. 生态学报, 2002, 22(1):94-103 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2002.01.013
WANG Xiaoke, BAI Yanying, OUYANG Zhiyun, et al. Missing sink in global carbon cycle and its causes [J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2002, 22(1): 94-103. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2002.01.013
[14] Druffel E R M. Comments on the importance of black carbon in the global carbon cycle [J]. Marine Chemistry, 2004, 92(1-4): 197-200. doi: 10.1016/j.marchem.2004.06.026
[15] Sánchez-García L, Cato I, Gustafsson Ö. The sequestration sink of soot black carbon in the Northern European Shelf sediments [J]. Global Biogeochemical Cycles, 2012, 26(1): GB1001.
[16] Hu L M, Shi X F, Bai Y Z, et al. Distribution, input pathway and mass inventory of black carbon in sediments of the Gulf of Thailand, SE Asia [J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2016, 170: 10-19. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2015.12.019
[17] Fang Y, Chen Y J, Tian C G, et al. Flux and budget of BC in the continental shelf seas adjacent to Chinese high BC emission source regions [J]. Global Biogeochemical Cycles, 2015, 29(7): 957-972. doi: 10.1002/2014GB004985
[18] 方引. 渤黄海黑碳的区域地球化学行为[D]. 中国科学院烟台海岸带研究所博士学位论文, 2016
FANG Yin. Regional geochemical behavior of black carbon in Bohai and Yellow Seas, China[D]. Doctor Dissertation of Yantai Institute of Coastal Zone Research, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2016.
[19] 方引, 陈颖军, 林田, 等. 莱州湾海岸带表层沉积物的黑碳及其与POPs的相关性研究[J]. 地球化学, 2014, 43(4):329-337
FANG Yin, CHEN Yingjun, LIN Tian, et al. Distribution of black carbon and its correlation with persistent organic pollutants (POPs) in the surface sediments of coastal zone, Laizhou Bay [J]. Geochimica, 2014, 43(4): 329-337.
[20] 林田, 方引, 陈颖军, 等. 东海内陆架沉积物中黑碳分布及其与持久性有机污染物的相关性研究[J]. 环境科学, 2012, 33(7):2335-2340
LIN Tian, FANG Yin, CHEN Yingjun, et al. Distribution of black carbon in the surface sediments of the east China sea and their correlations with persistent organic pollutants [J]. Environmental Science, 2012, 33(7): 2335-2340.
[21] 黄亮, 张国森, 吴莹, 等. 东海内陆架表层沉积物中黑碳的分布及来源[J]. 地球与环境, 2012, 40(1):63-69
HUANG Liang, ZHANG Guosen, WU Ying, et al. Distribution and source of black carbon in the surface sediments of the inner continental shelf of the east China sea [J]. Earth and Environment, 2012, 40(1): 63-69.
[22] Flores-Cervantes D X, Plata D L, MacFarlane J K, et al. Black carbon in marine particulate organic carbon: Inputs and cycling of highly recalcitrant organic carbon in the Gulf of Maine [J]. Marine Chemistry, 2009, 113(3-4): 172-181. doi: 10.1016/j.marchem.2009.01.012
[23] Elmquist M, Semiletov I, Guo L D, et al. Pan-Arctic patterns in black carbon sources and fluvial discharges deduced from radiocarbon and PAH source apportionment markers in estuarine surface sediments [J]. Global Biogeochemical Cycles, 2008, 22(2): GB2018.
[24] Guo L D, Semiletov I, Gustafsson Ö, et al. Characterization of Siberian Arctic coastal sediments: implications for terrestrial organic carbon export [J]. Global Biogeochemical Cycles, 2004, 18(1): GB1036.
[25] Running S W. Is global warming causing more, larger wildfires? [J]. Science, 2006, 313(5789): 927-928. doi: 10.1126/science.1130370
[26] Peterson B J, Holmes R M, Mcclelland J W, et al. Increasing river discharge to the arctic ocean [J]. Science, 2002, 298(5601): 2171-2173. doi: 10.1126/science.1077445
[27] Stroeve J, Holland M M, Meier W, et al. Arctic sea ice decline: faster than forecast [J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2007, 34(9): L09501.
[28] Bröder L, Andersson A, Tesi T, et al. Quantifying degradative loss of terrigenous organic carbon in surface sediments across the Laptev and East Siberian Sea [J]. Global Biogeochemical Cycles, 2019, 33(1): 85-99. doi: 10.1029/2018GB005967
[29] Stuecker M F, Bitz C M, Armour K C, et al. Polar amplification dominated by local forcing and feedbacks [J]. Nature Climate Change, 2018, 8(12): 1076-1081. doi: 10.1038/s41558-018-0339-y
[30] Screen J A, Simmonds I. The central role of diminishing sea ice in recent Arctic temperature amplification [J]. Nature, 2010, 464(7293): 1334-1337. doi: 10.1038/nature09051
[31] 张廷军. 全球多年冻土与气候变化研究进展[J]. 第四纪研究, 2012, 32(1):27-38 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7410.2012.01.03
ZHANG Tingjun. Progress in global permafrost and climate change studies [J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2012, 32(1): 27-38. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7410.2012.01.03
[32] Lim S, Lee M, Lee G, et al. Ionic and carbonaceous compositions of PM10, PM2.5 and PM1.0 at Gosan ABC superstation and their ratios as source signature [J]. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 2012, 12(4): 2007-2024. doi: 10.5194/acp-12-2007-2012
[33] Soja A J, Tchebakova N M, N. H. F. French N H F, et al. Climate-induced boreal forest change: Predictions versus current observations [J]. Global Planet. Change, 2007, 56(3-4): 274-296. doi: 10.1016/j.gloplacha.2006.07.028
[34] Myers-Pigg A N, Louchouarn P, Amon R M W, et al. Labile pyrogenic dissolved organic carbon in major Siberian Arctic rivers: implications for wildfire-stream metabolic linkages [J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2015, 42(2): 377-385. doi: 10.1002/2014GL062762
[35] Turetsky M R, Benscoter B, Page S, et al. Global vulnerability of peatlands to fire and carbon loss [J]. Nature Geoscience, 2015, 8(1): 11-14. doi: 10.1038/ngeo2325
[36] Yang W F, Guo L D. Sources and burial fluxes of soot black carbon in sediments on the Mackenzie, Chukchi, and Bering Shelves [J]. Continental Shelf Research, 2018, 155: 1-10. doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2018.01.008
[37] Winiger P, Andersson A, Eckhardt S, et al. Siberian Arctic black carbon sources constrained by model and observation [J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2017, 114(7): E1054-E1061.
[38] Goldberg E D. Black Carbon in the Environment[M]. New York: John Wiley, 1985.
[39] Hammes K, Schmidt M W I, Smernik R J, et al. Comparison of quantification methods to measure fire-derived (black/elemental) carbon in soils and sediments using reference materials from soil, water, sediment and the atmosphere [J]. Global Biogeochemical Cycles, 2007, 21(3): GB3016.
[40] Elmquist M, Cornelissen G, Kukulska Z, et al. Distinct oxidative stabilities of char versus soot black carbon: Implications for quantification and environmental recalcitrance [J]. Global Biogeochemical Cycles, 2006, 20(2): GB2009.
[41] Rein G, Cohen S, Simeoni A. Carbon emissions from smouldering peat in shallow and strong fronts [J]. Proceedings of the Combustion Institute, 2009, 32(2): 2489-2496. doi: 10.1016/j.proci.2008.07.008
[42] Rodionov A, Amelung W, Haumaier L, et al. Black carbon in the zonal steppe soils of Russia [J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Soil Science, 2006, 169(3): 363-369. doi: 10.1002/jpln.200521813
[43] Stein R, Macdonald R W. The Organic Carbon Cycle in the Arctic Ocean[M]. Berlin: Springer, 2004: 315-322.
[44] 胡利民, 石学法, 叶君, 等. 北极东西伯利亚陆架沉积有机碳的源汇过程研究进展[J]. 地球科学进展, 2020, 35(10):1073-1086 doi: 10.11867/j.issn.1001-8166.2020.086
HU Limin, SHI Xuefa, YE Jun, et al. Advances in the sources and sink of sedimentary organic carbon in the East Siberian Arctic Shelf [J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2020, 35(10): 1073-1086. doi: 10.11867/j.issn.1001-8166.2020.086
[45] 陈建芳, 张海生, 金海燕, 等. 北极陆架沉积碳埋藏及其在全球碳循环中的作用[J]. 极地研究, 2004, 16(3):193-201
CHEN Jianfang, ZHANG Haisheng, JIN Haiyan, et al. Accumulation of sedimentary organic carbon in the Arctic shelves and its significance on global carbon budget [J]. Chinese Journal of Polar Research, 2004, 16(3): 193-201.
[46] Günther F, Overduin P P, Sandakov A V, et al. Short- and long-term thermo-erosion of ice-rich permafrost coasts in the Laptev Sea region [J]. Biogeosciences, 2013, 10(6): 4297-4318. doi: 10.5194/bg-10-4297-2013
[47] Schirrmeister L, Kunitsky V, Grosse G, et al. Sedimentary characteristics and origin of the late Pleistocene ice complex on north-east Siberian Arctic coastal lowlands and islands-a review [J]. Quaternary International, 2011, 241(1-2): 3-25. doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2010.04.004
[48] Semiletov I P, Savelieva N I, Weller G E, et al. The dispersion of Siberian River flows into coastal waters: Meteorological, hydrological and hydrochemical aspects[M]//Lewis E L, Jones E P, Lemke P, et al. The Freshwater Budget of the Arctic Ocean. Dordrecht: Springer, 2000: 323-366.
[49] Karlsson E S, Charkin A, Dudarev O, et al. Carbon isotopes and lipid biomarker investigation of sources, transport and degradation of terrestrial organic matter in the Buor-Khaya Bay, SE Laptev Sea [J]. Biogeosciences, 2011, 8(7): 1865-1879. doi: 10.5194/bg-8-1865-2011
[50] Semiletov I, Dudarev O, Luchin V, et al. The east Siberian sea as a transition zone between Pacific-derived waters and Arctic shelf waters [J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2005, 32(10): L10614. doi: 10.1029/2005GL022490
[51] Xu F L, Jin H Y, Ji Z Q, et al. Sources and distribution of sedimentary organic matter along the northern Bering and Chukchi Seas [J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2017, 52: 66-75. doi: 10.1016/j.jes.2016.04.003
[52] Shimada K, Kamoshida T, Itoh M, et al. Pacific Ocean inflow: influence on catastrophic reduction of sea ice cover in the Arctic Ocean [J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2006, 33(8): L08605.
[53] Han Y M, Cao J J, An Z S, et al. Evaluation of the thermal/optical reflectance method for quantification of elemental carbon in sediments [J]. Chemosphere, 2007, 69(4): 526-533. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2007.03.035
[54] Han Y M, Cao J J, Chow J C, et al. Evaluation of the thermal/optical reflectance method for discrimination between char-and soot-EC [J]. Chemosphere, 2007, 69(4): 569-574. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2007.03.024
[55] Han Y M, Bandowe B A M, Wei C, et al. Stronger association of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons with soot than with char in soils and sediments [J]. Chemosphere, 2015, 119: 1335-1345. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2014.02.021
[56] 李秋玲, 乔淑卿, 石学法, 等. 北极东西伯利亚陆架沉积物物源: 来自黏土矿物和化学元素的证据[J]. 海洋学报, 2021, 43(3):76-89
LI Qiuling, QIAO Shuqing, SHI Xuefa, et al. Sediment provenance of the East Siberian Arctic Shelf: evidence from clay minerals and chemical elements [J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2021, 43(3): 76-89.
[57] Hu L M, Shi X F, Guo Z G, et al. Sources, dispersal and preservation of sedimentary organic matter in the Yellow Sea: the importance of depositional hydrodynamic forcing [J]. Marine Geology, 2013, 335: 52-63. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2012.10.008
[58] Yao P, Zhao B, Bianchi T S, et al. Remineralization of sedimentary organic carbon in mud deposits of the Changjiang Estuary and adjacent shelf: Implications for carbon preservation and authigenic mineral formation [J]. Continental Shelf Research, 2014, 91: 1-11. doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2014.08.010
[59] 韩永明, 曹军骥, 金章东, 等. 岱海与太湖沉积物焦碳和烟炱最近200年历史对比研究[J]. 第四纪研究, 2010, 30(3):550-558 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7410.2010.03.13
HAN Yongming, CAO Junji, JIN Zhangdong, et al. Comparison of char and soot variations in sediments from lakes Daihai and Taihu [J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2010, 30(3): 550-558. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7410.2010.03.13
[60] Gustafsson Ö, Haghseta F, Chan C, et al. Quantification of the dilute sedimentary soot phase: implications for PAH speciation and bioavailability [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 1996, 31(1): 203-209.
[61] Karlsson E S, Brüchert V, Tesi T, et al. Contrasting regimes for organic matter degradation in the East Siberian Sea and the Laptev Sea assessed through microbial incubations and molecular markers [J]. Marine Chemistry, 2015, 170: 11-22. doi: 10.1016/j.marchem.2014.12.005
[62] Gordeev V V, Martin J M, Sidorov I S, et al. A reassessment of the Eurasian river input of water, sediment, major elements, and nutrients to the Arctic Ocean [J]. Am. J. Sci, 1996, 296: 664-691,1996. doi: 10.2475/ajs.296.6.664
[63] 李宏亮, 陈建芳, 金海燕, 等. 楚科奇海表层沉积物的生源组分及其对碳埋藏的指示意义[J]. 海洋学报, 2008, 30(1):165-171
LI Hongliang, CHEN Jianfang, JIN Haiyan, et al. Biogenic constituents of surface sediments in the Chukchi Sea: implications for organic carbon burying efficiency [J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2008, 30(1): 165-171.
[64] Lara R J, Rachold V, Kattner G, et al. Dissolved organic matter and nutrients in the Lena River, Siberian Arctic: Characteristics and distribution [J]. Marine Chemistry, 1998, 59(3-4): 301-309. doi: 10.1016/S0304-4203(97)00076-5
[65] Boucsein B, Fahl K, Stein R, et al. Variability of river discharge and Atlantic-water inflow at the Laptev Sea continental margin during the past 15, 000 years: Implications from maceral and biomarker records [J]. International Journal of Earth Sciences, 2000, 89(3): 578-591. doi: 10.1007/s005310000111
[66] Bröder L, Tesi T, Salvadó J A, et al. Fate of terrigenous organic matter across the Laptev Sea from the mouth of the Lena River to the deep sea of the Arctic interior [J]. Biogeosciences, 2016, 13(17): 5003-5019. doi: 10.5194/bg-13-5003-2016
[67] Hedges J I, Keil R G, Benner R. What happens to terrestrial organic matter in the ocean? [J]. Organic Geochemistry, 1997, 27(5-6): 195-212. doi: 10.1016/S0146-6380(97)00066-1
[68] Dethleff D, Kuhlmann G. Fram Strait sea-ice sediment provinces based on silt and clay compositions identify Siberian Kara and Laptev Seas as main source regions [J]. Polar Research, 2010, 29(3): 265-282. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-8369.2010.00149.x
[69] 叶君, 胡利民, 石学法, 等. 基于木质素示踪北极东西伯利亚陆架沉积有机碳的来源、输运与埋藏[J]. 第四纪研究, 2021, 41(3):752-765 doi: 10.11928/j.issn.1001-7410.2021.03.11
YE Jun, HU Limin, SHI Xuefa, et al. Sources, transport and burial of terrestrial organic carbon in the surface sediments across the East Siberian Arctic shelf, insights from lignin [J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2021, 41(3): 752-765. doi: 10.11928/j.issn.1001-7410.2021.03.11
[70] 陈立奇, 高众勇, 杨绪林, 等. 北极地区碳循环研究意义和展望[J]. 极地研究, 2004, 16(3):171-180
CHEN Liqi, GAO Zhongyong, YANG Xulin, et al. Prospects of research on carbon cycle in the arctic [J]. Chinese Journal of Polar Research, 2004, 16(3): 171-180.
[71] Fang Z M, Yang W F, Chen M, et al. Abundance and sinking of particulate black carbon in the western Arctic and Subarctic Oceans [J]. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6(1): 29959. doi: 10.1038/srep29959
[72] Kozlov V S, Panchenko M V, Yausheva E P. Mass fraction of black carbon in submicron aerosol as an indicator of influence of smoke from remote forest fires in Siberia [J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2008, 42(11): 2611-2620. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2007.07.036
[73] Huang X Y, Rein G. Smouldering combustion of peat in wildfires: inverse modelling of the drying and the thermal and oxidative decomposition kinetics [J]. Combustion and Flame, 2014, 161(6): 1633-1644. doi: 10.1016/j.combustflame.2013.12.013
[74] Hugelius G, Loisel J, Chadburn S, et al. Large stocks of peatland carbon and nitrogen are vulnerable to permafrost thaw [J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2020, 117(34): 20438-20446. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1916387117
[75] Kharuk V I, Ranson K J, Dvinskaya M L, et al. Wildfires in northern Siberian larch dominated communities [J]. Environmental Research Letters, 2011, 6(4): 045208. doi: 10.1088/1748-9326/6/4/045208
-



 下载:
下载: