The sea-level highstand of the Changjiang River estuary in the Holocene revealed from tidal bore deposits
-
摘要:
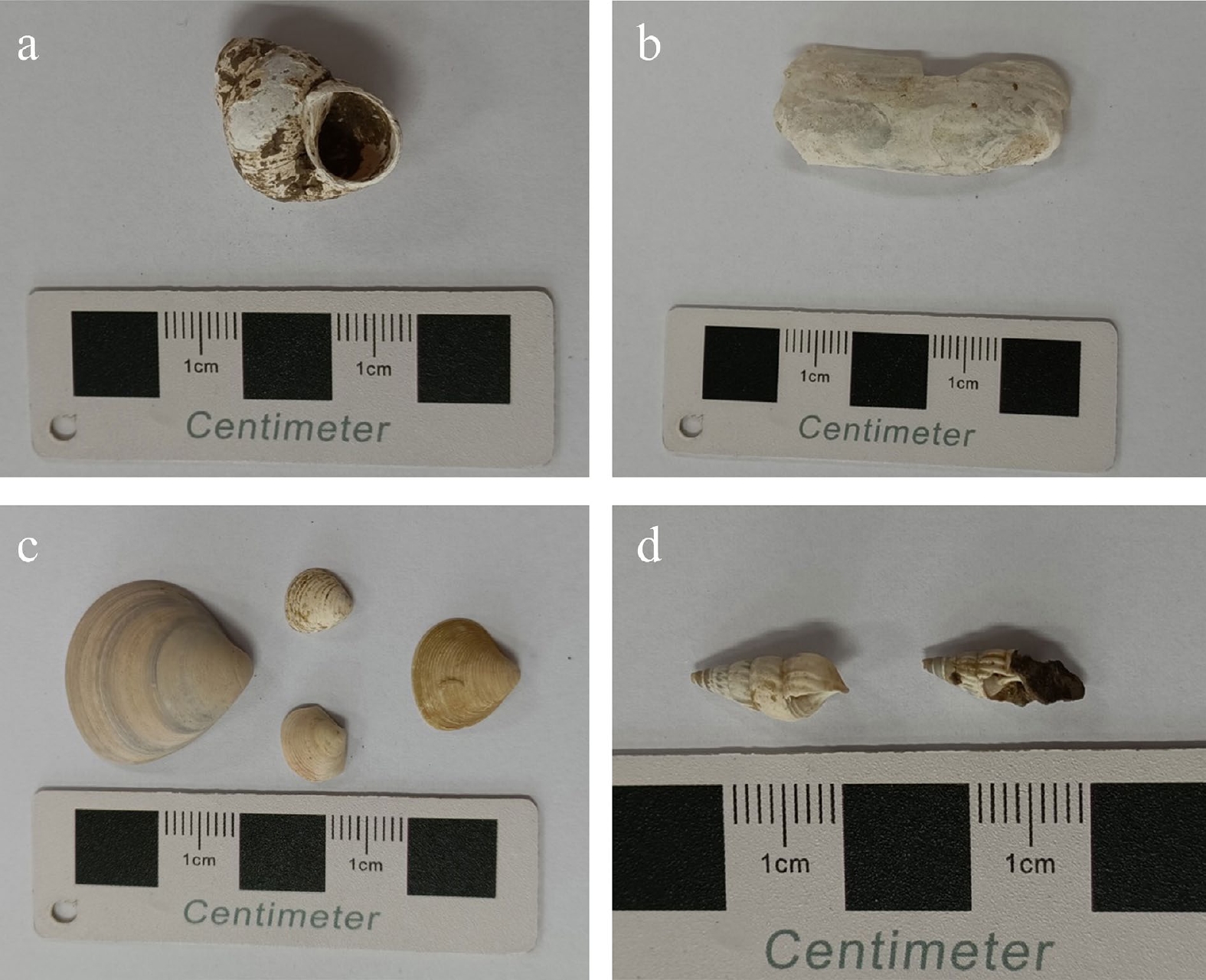
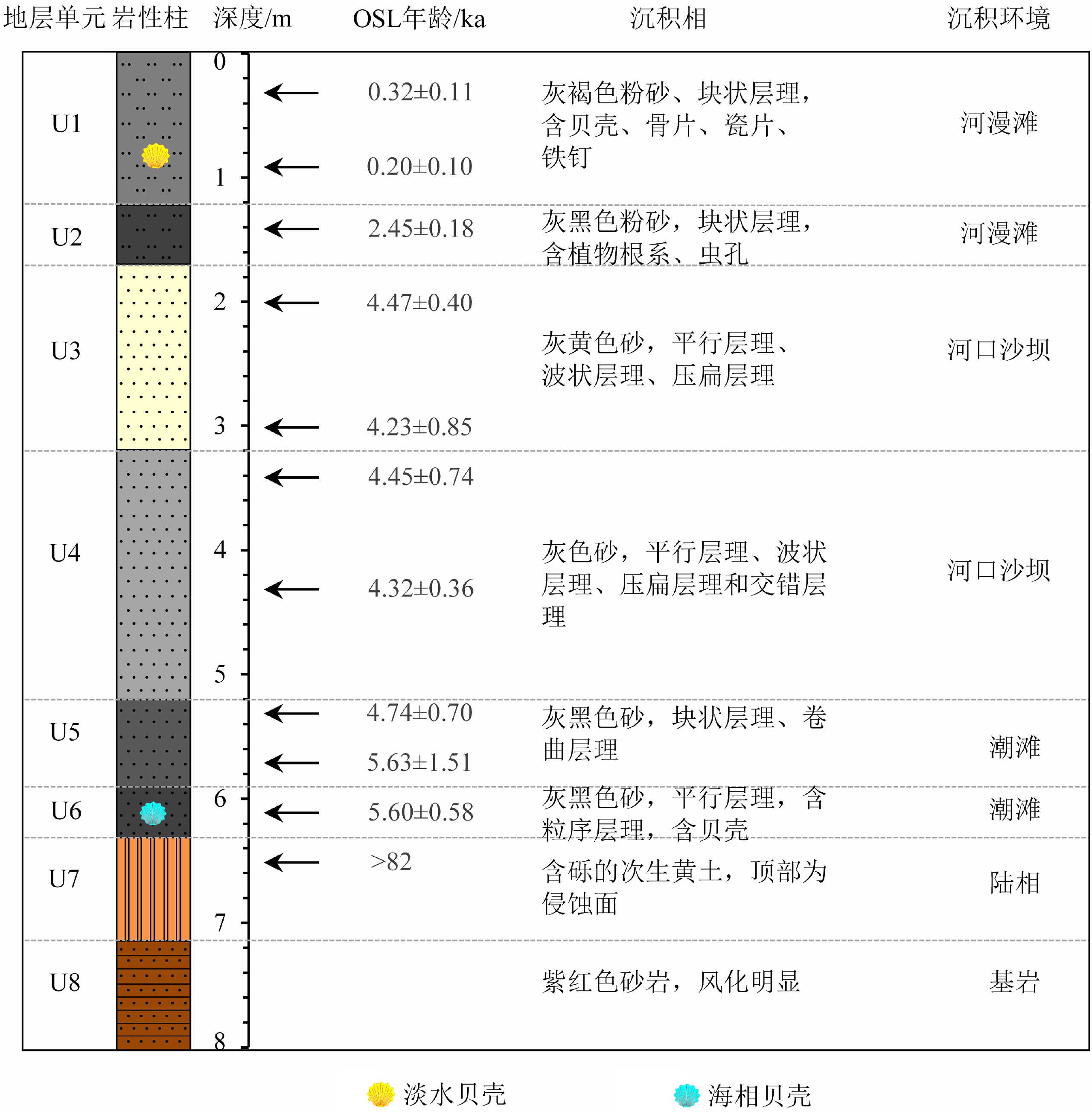
海面变化对沿海地区的自然环境和社会经济有着重要影响,了解过去海面变化规律可以为预测未来海面上升情景提供参考依据。以长江古河口湾湾顶附近的扬州市昌建广场建筑工地所揭示的自然沉积剖面(CJGC剖面)为研究对象,通过详细调研,在剖面下部发现了保存有海相贝壳的涌潮沉积,为研究全新世最高海面和最大海侵提供了绝佳的地质材料。通过系统的沉积相与光释光(OSL)年代学研究,重建了古河口湾中全新世以来沉积环境的变化过程。结果表明,该地点中全新世以来经历了从陆相→潮滩→河口沙坝→河漫滩的沉积环境变迁,清晰显示了由海侵到海退的变化过程。OSL测年数据表明长江河口全新世最高海面和河口湾湾顶最大海侵出现的年代约为5.6 ka,当时对应的海面高度不低于海拔1.3 m,这一时期的高海面在世界多地均有记录。
Abstract:Sea level changes have an important impact on the natural environment and community economy of coastal areas. Understanding the evolution of sea level in the past could help predict the future sea level rising. In this study, a natural Holocene soil outcrop (CJGC profile) was scrutinized. The profile was located in a construction site of Changjian Square in Yangzhou City, east Jiangsu Province in ancient estuary of the Yangtze River. The tidal bore deposits contain euryhaline mollusc shells in the lower part of the profile, which provides excellent geological materials for studying the sea-level highstand and the maximum transgression in the Holocene. In addition, we studied the sedimentary facies and conducted optically stimulated luminescence (OSL) dating, from which the evolution of sedimentary environment in the study area since the middle Holocene was reconstructed. Results show that this site has undergone sedimentary environmental changes of land →tidal beach→river mouth bar→floodplain, which clearly shows a change from transgression to regression. The OSL ages show that the sea-level highstand and the maximum transgression of ancient Changjiang River estuary in the Holocene appeared at ~5.6 ka in elevation no less than 1.3 m above sea level, which is consistent with the sea-level highstand of the same period found elsewhere in many places of the world.
-
Key words:
- estuary /
- sea level change /
- OSL /
- tidal bore deposit /
- Yangtze River Delta
-

-
表 1 CJGC剖面光释光样品测年结果
Table 1. OSL dating results of the samples from CJGC profile
样品号 埋深/cm U/10-6 Th/10-6 K/% 总剂量/Gy 剂量率/(Gy/ka) 年龄/ka CJGC-0.3m 30 2.56 15.28 1.90 1.19 ± 0.39 3.69 ± 0.11 0.32 ± 0.11 CJGC-0.9m 90 2.17 13.21 1.83 0.69 ± 0.33 3.49 ± 0.09 0.20 ± 0.10 CJGC-1.4m 140 2.30 13.29 1.86 7.97 ± 0.50 3.26 ± 0.12 2.45 ± 0.18 CJGC-2.0m 200 2.13 11.53 1.60 13.18 ± 1.11 2.95 ± 0.09 4.47 ± 0.40 CJGC-3.0m 300 1.81 11.04 1.66 12.48 ± 2.50 2.95 ± 0.08 4.23 ± 0.85 CJGC-3.4m 340 1.73 9.29 1.62 12.11 ± 2.00 2.72 ± 0.08 4.45 ± 0.74 CJGC-4.3m 430 1.80 10.89 1.61 12.31 ± 0.98 2.85 ± 0.08 4.32 ± 0.36 CJGC-5.3m 530 2.15 12.23 1.60 13.47 ± 1.93 2.84 ± 0.10 4.74 ± 0.70 CJGC-5.7m 570 2.21 13.18 1.61 16.53 ± 4.39 2.94 ± 0.10 5.63 ± 1.51 CJGC-6.1m 610 2.61 14.83 1.53 17.26 ± 1.69 3.08 ± 0.10 5.60 ± 0.58 CJGC-6.5m 650 1.84 12.50 1.10 >191.94 2.34 ± 0.08 >82 -
[1] Chen Z Y, Stanley D J. Sea-level rise on Eastern China's Yangtze delta [J]. Journal of Coastal Research, 1998, 14(1): 360-366.
[2] 赵希涛. 海面变化研究的回顾与展望[J]. 地球科学信息, 1988(1):36-40
ZHAO Xitao. Review and prospect of sea level change research [J]. Advances in Earth Science, 1988(1): 36-40.
[3] 陈梦熊. 关于海平面上升及其环境效应[J]. 地学前缘, 1996(2):133-140 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.1996.02.002
CHEN Mengxiong. The rise of sea level and its environmental effects [J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 1996(2): 133-140. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.1996.02.002
[4] 谢志仁, 袁林旺. 略论全新世海面变化的波动性及其环境意义[J]. 第四纪研究, 2012, 32(6):1065-1077 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7410.2012.06.02
XIE Zhiren, YUAN Linwang. Fluctuation Characteristics of Holocene sea-level change and its environmental implications [J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2012, 32(6): 1065-1077. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7410.2012.06.02
[5] 任美锷. 第四纪海面变化及其在海岸地貌上的反映[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 1965(3):295-305
REN Meie. Quaternary changes in sea-level and their effects on coastal morphology [J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 1965(3): 295-305.
[6] Scott D B, Medioli F S. Foraminifera as sea-level indicators[M]//Van De Plassche O. Sea-Level Research. Dordrecht: Springer, 1986: 435-456.
[7] Zhao X T. Cheniers in China: An overview [J]. Marine Geology, 1989, 90(4): 311-320. doi: 10.1016/0025-3227(89)90133-3
[8] 施雅风. 中国气候与海面变化及其趋势和影响2: 中国海面变化[M]. 济南: 山东科技出版社, 1996.
SHI Yafeng. Climate and Sea-Level Change and Its Trends and Impacts in China 2: Sea-Level Change in China[M]. Ji’nan: Shandong Science and Technology Press, 1996.
[9] 李恒鹏, 杨桂山. 海平面上升的海岸形态响应研究方法与进展[J]. 地球科学进展, 2000, 15(5):598-603 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.2000.05.019
LI Hengpeng, YANG Guishan. Response of coast to sea-level rise: A review of study methods [J]. Advances in Earth Sciences, 2000, 15(5): 598-603. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.2000.05.019
[10] 朱诚, 张强, 张芸, 等. 长江三角洲长江以北地区全新世以来人地关系的环境考古研究[J]. 地理科学, 2003, 23(6):705-712 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0690.2003.06.011
ZHU Cheng, ZHANG Qiang, ZHANG Yun et al. Relationship between human and nature in the north part of the Yangtze delta since the Holocene [J]. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 2003, 23(6): 705-712. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0690.2003.06.011
[11] 李从先, 许世远. 河流三角洲沉积的基本特征[J]. 自然杂志, 1978(3):45-49
LI Congxian, XU Shiyuan. Basic characteristics of river delta deposition [J]. Chinese Journal of Nature, 1978(3): 45-49.
[12] 同济大学海洋地质系三角洲科研组. 全新世长江三角洲的形成和发育[J]. 科学通报, 1978, 23(5):310-313 doi: 10.1360/csb1978-23-5-310
Delta Scientific Research Group, Department of Marine Geology, Tongji University. The formation and development of the Holocene Yangtze River delta [J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 1978, 23(5): 310-313. doi: 10.1360/csb1978-23-5-310
[13] 王靖泰, 汪品先. 中国东部晚更新世以来海面升降与气候变化的关系[J]. 地理学报, 1980, 35(4):299-312 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0375-5444.1980.04.003
WANG Jingtai, WANG Pinxian. Relationship between sea-level changes and climatic fluctuations in East Chinasince late Pleistocene [J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 1980, 35(4): 299-312. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0375-5444.1980.04.003
[14] 严钦尚, 洪雪晴. 长江三角洲南部平原全新世海侵问题[J]. 海洋学报, 1987, 9(6):744-752
YAN Qinshang, HONG Xueqing. The Holocene transgression problem in the southern plain of the Yangtze River Delta [J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 1987, 9(6): 744-752.
[15] Hori K, Saito Y. An early Holocene sea-level jump and delta initiation [J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2007, 34(18): L18401. doi: 10.1029/2007GL031029
[16] 李从先, 闵秋宝. 全新世长江三角洲顶部的海进时间和海面位置[J]. 同济大学学报, 1981(3):104-108
LI Congxian, MIN Qiubao. The time of Holocene transgression and sea level changes in apical area of Yangtze delta [J]. Journal of Tongji University, 1981(3): 104-108.
[17] 勾韵娴, 唐领余, 孙息春, 等. 江苏建湖地区全新世生物群和古环境[J]. 第四纪研究, 1992, 12(3):203-215 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.1992.03.002
GOU Yunxian, TANG Lingyu, SUN Xichun et al. Holocene biota and palaeoenvironment in Jianhu, Jiangsu [J]. Quaternary Sciences, 1992, 12(3): 203-215. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.1992.03.002
[18] Shu Q, Zhao Y F, Hu Z et al. Multi-proxy reconstruction of the Holocene transition from a transgressive to regressive coastal evolution in the northern Jiangsu Plain, East China [J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2021, 572: 110405. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2021.110405
[19] 夏东兴. 全新世高海面何在[J]. 海洋学报, 1981, 3(4):601-609
XIA Dongxing. Whence comes the high sea-level during the Holocene? [J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 1981, 3(4): 601-609.
[20] 薛春汀. 对我国沿海全新世海面变化研究的讨论[J]. 海洋学报, 2002, 24(4):58-67
XUE Chunting. Holocene sea-level change along China coast [J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2002, 24(4): 58-67.
[21] 徐映深, 季幼庭, 高中和, 等. 下扬子地区全新世海平面变化特征的初步研究[J]. 地震学刊, 1989(3):41-47
XU Yingshen, JI Youting, GAO Zhonghe et al. Preliminary study on the characteristics of the changing Holocene Sea level in lower Yangtze region [J]. Journal of Disaster Prevention and Mitigation Engineering, 1989(3): 41-47.
[22] 郑洪波, 周友胜, 杨青, 等. 中国东部滨海平原新石器遗址的时空分布格局: 海平面变化控制下的地貌演化与人地关系[J]. 中国科学:地球科学, 2018, 61(2):123-133 doi: 10.1007/s11430-017-9121-y
ZHENG Hongbo, ZHOU Yousheng, YANG Qing et al. Spatial and temporal distribution of Neolithic sites in coastal China: Sea level changes, geomorphic evolution and human adaption [J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 2018, 61(2): 123-133. doi: 10.1007/s11430-017-9121-y
[23] 李保华, 李从先, 沈焕庭. 冰后期长江三角洲沉积通量的初步研究[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 2003, 46(7):743-752 doi: 10.1360/03yd9065
LI Baohua, LI Congxian, SHEN Huanting. A preliminary study on sediment flux in the Changjiang Delta during the postglacial period [J]. Science in China Series D:Earth Sciences, 2003, 46(7): 743-752. doi: 10.1360/03yd9065
[24] 李从先, 王靖泰, 许世远, 等. 全新世长江三角洲地区的海进海退层序[J]. 地质科学, 1980, 15(4):322-330
LI Congxian, WANG Jingtai, XU Shiyuan et al. Holocene transgressive-regressive sequence in Yangtze delta area [J]. Chinese Journal of Geology, 1980, 15(4): 322-330.
[25] 黄竞争, 张先毅, 吴峥, 等. 长江感潮河段潮波传播变化特征及影响因素分析[J]. 海洋学报, 2020, 42(3):25-35
HUANG Jingzheng, ZHANG Xianyi, WU Zheng et al. Investigation into the spatial and temporal tide-river dynamics and the underlying controlled factors along the tidal reach of the Changjiang River [J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2020, 42(3): 25-35.
[26] 吴标云, 李从先. 长江三角洲第四纪地质[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 1987
WU Biaoyun, LI Congxian. Quaternary Geology of the Yangtze River Delta[M]. Beijing: China Ocean Press, 1987.
[27] 陈吉余. 长江河口动力过程和地貌演变[M]. 上海: 上海科学技术出版社, 1988
CHEN Jiyu. Dynamic Process and Geomorphological Evolution of the Yangtze River Estuary[M]. Shanghai: Shanghai Scientific & Technical Publishers, 1988.
[28] 曹光杰, 王建, 屈贵贤. 全新世以来长江河口段河道的演变[J]. 人民长江, 2006, 37(2):25-27,36 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4179.2006.02.010
CAO Guangjie, WANG Jian, QU Guixian. River channel evolution of the Yangtze river estuary since Holocene epoch [J]. Yangtze River, 2006, 37(2): 25-27,36. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4179.2006.02.010
[29] 王靖泰, 郭蓄民, 许世远, 等. 全新世长江三角洲的发育[J]. 地质学报, 1981(1):67-81
WANG Jingtai, GUO Xumin, XU Shiyuan et al. Evolution of the Holocene Changjiang delta [J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 1981(1): 67-81.
[30] 陈吉余, 沈焕庭. 我国河口基本水文特征分析[J]. 水文, 1987(3):1-8
CHEN Jiyu, SHEN Huanting. Analysis of basic hydrological characteristics of estuaries in China [J]. Journal of China Hydrology, 1987(3): 1-8.
[31] 朱玉荣. 冰后期最大海侵以来长江口潮波特性的变化[J]. 海洋科学, 2000, 24(5):34-36 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3096.2000.05.012
ZHU Yurong. The change of characteristics of tidal wave in the Changjiang River mouth area since the post-Glacial transgression Maximum [J]. Marine Sciences, 2000, 24(5): 34-36. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3096.2000.05.012
[32] 李从先, 范代读. 全新世长江三角洲的发育及其对相邻海岸沉积体系的影响[J]. 古地理学报, 2009, 11(1):115-122
LI Congxian, FAN Daidu. Development of the Holocene Changjiang delta and its influence on adjacent coastal sedimentary systems [J]. Journal of Palaeogeography, 2009, 11(1): 115-122.
[33] 朱诚, 程鹏, 卢春成, 等. 长江三角洲及苏北沿海地区7000年以来海岸线演变规律分析[J]. 地理科学, 1996, 16(3): 207-213
ZHU Cheng, CHENG Peng, LU Chuncheng et al. Analysis on the evolution law of coastline in the Yangtze River Delta and the coastal area of Northern Jiangsu since 7000 a B. P. [J]. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 1996, 16(3): 207-213.
[34] 虞志英, 陈德昌, 唐寅德. 关于苏北中部平原海岸古砂堤形成年代的认识[J]. 海洋科学, 1982, 6(4):11-14
YU Zhiying, CHEN Dechang, TANG Yinde. On the formation of fossil barriers in the middle flat of Jiangsu northern part [J]. Ocean Science, 1982, 6(4): 11-14.
[35] 刘苍字, 吴立成, 曹敏. 长江三角洲南部古沙堤(冈身)的沉积特征、成因及年代[J]. 海洋学报, 1985, 7(1):55-66
LIU Cangzi, WU Licheng, CAO Min. Features, formation and age of the shell beach ridges in the south Yangtze Delta [J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 1985, 7(1): 55-66.
[36] Jiang M Y, Han Z Y, Li X S et al. Beach ridges of Dali Lake in Inner Mongolia reveal precipitation variation during the Holocene [J]. Journal of Quaternary Science, 2020, 35(5): 716-725. doi: 10.1002/jqs.3195
[37] Duller G A T. Distinguishing quartz and feldspar in single grain luminescence measurements [J]. Radiation Measurements, 2003, 37(2): 161-165. doi: 10.1016/S1350-4487(02)00170-1
[38] Wintle A G, Murray A S. A review of quartz optically stimulated luminescence characteristics and their relevance in single-aliquot regeneration dating protocols [J]. Radiation Measurements, 2006, 41(4): 369-391. doi: 10.1016/j.radmeas.2005.11.001
[39] 范代读, 蔡国富, 尚帅, 等. 钱塘江河口北边滩涌潮沉积作用与特征[J]. 科学通报, 2012, 57(13):1578-1589 doi: 10.1007/s11434-012-4993-6
FAN Daidu, CAI Guofu, SHANG Shuai et al. Sedimentation processes and sedimentary characteristics of tidal bores along the north bank of the Qiantang Estuary [J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2012, 57(13): 1578-1589. doi: 10.1007/s11434-012-4993-6
[40] 刘江艳, 张昌民, 尹太举, 等. 涌潮沉积研究现状及进展[J]. 地球科学进展, 2018, 33(1):66-74 doi: 10.11867/j.issn.1001-8166.2018.01.0066
LIU Jiangyan, ZHANG Changmin, YIN Taiju et al. Current status and advance of tidal-bore deposit study [J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2018, 33(1): 66-74. doi: 10.11867/j.issn.1001-8166.2018.01.0066
[41] Fan D D, Tu J B, Shang S et al. Characteristics of tidal-bore deposits and facies associations in the Qiantang Estuary, China [J]. Marine Geology, 2014, 348: 1-14. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2013.11.012
[42] 李保华, 王强, 李从先. 长江三角洲亚三角洲地层结构对比[J]. 古地理学报, 2010, 12(6):685-698 doi: 10.7605/gdlxb.2010.06.005
LI Baohua, WANG Qiang, LI Congxian. Correlation of stratigraphic architecture of sub-deltas of Changjiang River delta [J]. Journal of Palaeogeography, 2010, 12(6): 685-698. doi: 10.7605/gdlxb.2010.06.005
[43] Tam C Y, Zong Y Q, Bin Hassan K et al. A below-the-present late Holocene relative sea level and the glacial isostatic adjustment during the Holocene in the Malay Peninsula [J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2018, 201: 206-222. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2018.10.009
[44] Bradley S L, Milne G A, Horton B P et al. Modelling sea level data from China and Malay-Thailand to estimate Holocene ice-volume equivalent sea level change [J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2016, 137: 54-68. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2016.02.002
[45] 田立柱, 陶有兵, 姜兴钰, 等. 莱州湾南岸全新世相对海平面变化重建[J]. 地质通报, 2016, 35(10):1679-1691 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2016.10.016
TIAN Lizhu, TAO Youbing, JIANG Xingyu et al. Reconstruction of the Holocene relative sea level change for the south coast of Laizhou Bay [J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2016, 35(10): 1679-1691. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2016.10.016
[46] Yan S, Zhao J X, Lau A Y A et al. Episodic reef growth in the Northern South China Sea linked to warm climate during the past 7, 000 years: potential for future coral refugia [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Biogeosciences, 2019, 124(4): 1032-1043. doi: 10.1029/2018JG004939
[47] Zong Y Q. Mid-Holocene sea-level highstand along the Southeast Coast of China [J]. Quaternary International, 2004, 117(1): 55-67. doi: 10.1016/S1040-6182(03)00116-2
[48] Wang F, Zong Y Q, Mauz B et al. Holocene sea-level change on the central coast of Bohai Bay, China [J]. Earth Surface Dynamics, 2020, 8(3): 679-693. doi: 10.5194/esurf-8-679-2020
[49] 朱诚, 吴立, 李兰, 等. 对江苏新石器时代海面变化问题的再认识[J]. 科学通报, 2016, 61(3):374-387 doi: 10.1360/N972015-00713
ZHU Cheng, WU Li, LI Lan et al. Recognition of sea-level change during the Neolithic period in the Jiangsu Area, East China [J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2016, 61(3): 374-387. doi: 10.1360/N972015-00713
[50] Fleming K, Johnston P, Zwartz D et al. Refining the eustatic sea-level curve since the Last Glacial Maximum using far-and intermediate-field sites [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1998, 163(1-4): 327-342. doi: 10.1016/S0012-821X(98)00198-8
[51] 朱诚, 郑朝贵, 马春梅, 等. 对长江三角洲和宁绍平原一万年来高海面问题的新认识[J]. 科学通报, 2003, 48(24):2672-2683 doi: 10.1007/BF02901755
ZHU Cheng, ZHENG Chaogui, MA Chunmei et al. On the Holocene sea-level highstand along the Yangtze Delta and Ningshao Plain, East China [J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2003, 48(24): 2672-2683. doi: 10.1007/BF02901755
-




 下载:
下载: